The Skillsoft Learning Growth Model
|
|
|
- Maude Hill
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WHITE PAPER The Skillsoft Growth Model A Blueprint for Integrating into the Life of the Enterprise in Five Manageable Stages Dorman Woodall, Director of April 2013 Executive Summary During times of turbulent economic and demographic changes learning professionals must tackle both what is important and what is urgent. programs should closely align with your organization s strategic goals and skills need to be quickly used in the workplace. As the demand for increased talent will intensify in the coming years you need to be ready to maintain your organization s agility. This rising sea of change will require global organizations to increasingly employ technology-based learning resources. The Skillsoft Growth Model will assist you in charting a realistic direction for your organization through these important changes. This essential five-stage model will guide you to implement the right learning resources, at the right time. The three essential phases outlined in this model will empower you to better articulate the organizational value of learning and gain the necessary support from other leaders to successfully deliver cost-effective learning programs.
2 Table of Contents Transforming training into learning 3 The Skillsoft Growth Model 3 Increasing organizational agility 4 Dealing with change requires leadership 4 Classrooms won t be enough 5 A shift in mindset is needed 6 Exploiting learning technologies 7 Moving beyond workplace skills 7 Three Growth Model Phases 8 Implementation Phase (Stages 1 and 2) 8 The Transformation Phase (Stage 3) 10 The Expansion Phase (Stages 4 and 5) 13 Stage 5 and Beyond 14 Applying the key success factors 16 Profile for Stage 1 Supplement 17 Profile for Stage 2 Targeted 18 Profile for Stage 3 Strategic 19 Profile for Stage 4 Integrated 20 Profile for Stage 5 Optimized 21 Skillsoft Strategic Planning Resources 21 2
3 Transforming training into learning Over twenty-five years ago, the shift from mainframe computers to personal computers decentralized the way in which users collected and used information. This revolution in computing power along with the democratization of the Internet forever changed the role of the user in every organization. Now global commerce has been completely transformed and younger workers are technologysavvy like no generation before them. Nothing is as powerful as an idea whose time has come Victor Hugo French romantic writer All organizations, regardless of size or sector, have a pressing need to chart out a plan to use learning technology to develop and continuously increase the talent of their employees. Responding to this directive will require the application of a multi-stage blended learning framework to provide a wide-range of formal, informal and social learning opportunities to your organization. The fundamental question is Are you ready to use technology to transform training into learning? The Skillsoft Growth Model The Skillsoft Growth Model was developed by Skillsoft in conjunction with our customers to assist them in successfully integrating technology-based learning (elearning) into their organization. We found this model works best when both our customer and Skillsoft are in a close partnership. Now that you have had a look at a graphical view of the phases and stages, the rest of this paper is constructed to give you a closer look at how this framework can benefit your organization. This THE SKILLSOFT LEARNING GROWTH MODEL 3
4 first section covers some of the reasons which will assist you in understanding how learning can be used as the fuel to increased organizational agility. The second part walks you through an overview of the phases and how each stage moves your organization closer to becoming the type of learning organization to which you aspire. The final segment defines and examines the key success factors and how these factors evolve from one stage to the next. We find when customers use this framework they are much better prepared to utilize our content, service and expertise to quickly ramp up to Stage 3. If you have a solid foothold in Stage 3, the implementation of the remaining two stages becomes more apparent and is easily endorsed by your leadership. Increasing organizational agility In order to deal with the onslaught of never-ending economic and social changes, an organization must remain agile. The degree to which an organization can adapt to rapid changes in demographics, along with emerging technologies, shifting market conditions and abrupt competitor appearances is a measure of their capability to deal with changing priorities. Since 2008, the economy has created uncertainty and risk and this volatility has caused organizations to become less agile. 1 This shrinkage in competence can seriously hamper the agility and future success of your organization. While most organizations can quickly grasp the apparent value of adopting technology for their economic advantage, it is ironic how many are slow to understand that this approach can significantly increase the value of their human capital. 2 The advent of the Internet combined with the changing demographics of the learner has added a whole new dimension to learning design, development and delivery, just waiting to be more fully exploited by alert, business-savvy leadership. It has always been a good idea to link strategic business goals and the learning function. Recent research studies from ASTD, Bersin and McBassi 3 show a direct correlation between investments in learning and a subsequent improvement in market performance, profitability and employee retention. This alignment of learning to performance has made the value for business alignment crystal clear. It s very simple to understand, but somewhat harder to achieve. When this alignment is made, organizations reap both short and long-term benefits in increased cost-savings, productivity, performance, leadership, and competitive advantage. Dealing with change requires leadership Major changes are currently at work that includes the retirement of the baby-boomer workforce and the demands of the growing talent crisis to replace the exodus of workers who are now occupying key roles. 1 Sources: Economist Intelligence Unit, Organisational Agility: How business can survive and thrive in turbulent times, sponsored by EMC, 2009 and PMI Pulse of the Profession In-Depth Report: Organizational Agility, Service Masters, W. Scott Gould, Deputy Secretary of Veterans Affairs, Training and Development magazine, November 2012, ASTD 3 Sources: ASTD State of Industry Report 2012, Bersin & Associates The High-Impact Organization Maturity Model 2012, The New Economics of People & Profits McBassi & Company 2010 & Measuring For Success: How Executives View Metrics, by Patti and Jack Phillips of the ROI Institute, Inc., Chief Officer Magazine, December
5 The Silver Tsunami The impending repercussions from a large aging workforce entering retirement are called The Silver Tsunami or Boomsday. This phenomenon can have a profound effect on many areas of life and potentially change society as a whole. A wave of retirements means babyboomers will leave work in droves. Most organizations are remarkably unprepared to handle the consequences of this debilitating loss of talent and leadership. 4 The Talent Crisis Having the right talent is priceless. Attracting, developing and retaining talent requires active engagement on the part of the organization. Methods which suited the baby-boomers won t work as well for younger workers. Classrooms are not as easily scalable as online learning. As baby-boomers retire over the next few years, the need to supply online learning resources to a younger workforce increases dramatically. Generations X, Y and Z, mostly comprised of learners under 40 years old, lack patience for the traditional approach to learning. This new workforce was raised expecting to have quick access to technology, anywhere and anytime. 5 Classrooms won t be enough Faced with this huge change in workforce demographics, classrooms alone won t be able to deliver sufficient training to accommodate all of an organization s growing demands. The Transfer Problem Ask yourself What happens once a class is over? Will all of the learners quickly transfer their new knowledge and skills in the workplace within the next 4 to 6 weeks? Unfortunately, the answer is no. Old habits kick in and the learning fades over time if learning is not reinforced before and after the training event. If this happens, the classroom event can incur a scrap learning rate of between 55% and 80%, meaning that as little as In a time of drastic change it is the learners who inherit the future. The learned usually find themselves equipped to live in a world that no longer exists. Eric Hoffer philosopher I am always ready to learn, but I do not always like being taught. Winston Churchill British Prime Minister 45% of the cost of an event actually pays off. Research shows that when learning is reinforced, the positive effects are greater and last longer. For transfer of learning into the workplace, the application of knowledge and skills must continue on the job. 6 The Model In 1998, the US Department of Labor Statistics reported that people learned about 70% of what they know about their jobs informally and only 30% formally such as in classrooms. 7 Subsequently, the Center for Creative Leadership (CCL) developed their model which estimates: 4 U.S. Department of Labor, Bureau of Labor Statistics. (1996). The 1995 Survey of Employer-Provided Training. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Labor. 5 The Silver Tsunami, The Economist, February Generations at Work: Managing the Clash of Veterans, Boomers, Xers, and Nexters in Your Workplace. Zemke, Ron, Claire Raines, and Bob Filipczak. AMACOM Manager Engagement: Reducing Scrap by John R. Mattox, II, Ph.D., Training Industry Quarterly, Fall 2010, & The Six Disciplines of Breakthrough : How to Turn Training and Development into Business Results, Second Edition. Pfeiffer. Wick, Calhoun, and Roy Pollock. 2010, Manager Engagement: Reducing Scrap by John R. Mattox, II, Ph.D. Training Industry Quarterly, Fall
6 70% of learning is provided through assignments and on-the-job experiences (informal). 20% of learning is developed through relationships, networks, and feedback (social). 10% of the learning is delivered via formal training processes (formal). 8 This model shows the great majority (90%) of learning is non-formal and only a small amount (10%) is formal. While both are important to building a strong learning culture, the problem is that most funding and attention is paid to the smaller formal component leaving little or no funding for the remaining 90%. In a real sense, this is a classic example of the Pareto Principle and proves that the value actually received is in reverse proportion to the investment made. Blended Using the CCL as a model will require pre-work (before) being followed by the learning event (during) and followed up with subsequent support (after). The best form of blending is the productive mixing of formal, informal and social learning along with a mix of modalities. One study 9 shows once again the value and funding are still reversed in many cases. Here is a summary of the value of a blended leadership program versus the typical investment in these three components as follows: Typical Value: Pre-work = 26%, Formal learning event = 24% and Follow-up = 50%, meaning over 75% of the value was derived from the non-formal methods, not the formal event. Typical Investment: Pre-work = 10%, event = 85% and Follow-up = 5%, showing actual training dollars are spent on the event while very little goes toward pre-work and follow-up. A shift in mindset is needed Research continues to show us why classroom and online learning shouldn t be thought of as competitive rivals. Instead we should think of them as alternative forms of delivery. What we know is each domain performs well when they work together proving that using well-designed blend of delivery methods, the sum of the parts is much greater than the whole. The advantage of blending is having the right resources at the right time and in the right mix. The actual problem is really in how we think of learning. Most of our thinking is based on our academic/ cultural background which engendered the belief unless you went away from work, you couldn t become educated. And in some cases, going away for training was a reward for good performance. Baby-boomers generally think classroom because of their previous academic experience and young workers think technology because using technology is just as natural to them as using their TV or toaster. We need to re-program our thinking. When executives ask for a classroom, this question gives us an opportunity to re-think and instead ask ourselves What blended learning design will work best for this business problem? We need both formal training and non-formal learning. Together these are the yin and yang of learning. Formal training provides what you must learn (albeit it provides very little wiggle room) while non-formal provides the freedom of choice I will prepare for some day my chance will come. Abraham Lincoln US President 8 The Rule, Center of Creative Leadership, Leading Effectively e-newsletter, November The Promise of Phase 3 by Jack Zenger, Joe Folkman and Robert Sherwin, T+D Magazine, January
7 when employees can t wait for someone else to solve a problem. With vision, strength of conviction, and leadership, this freedom to have employees pull learning into the workplace can change any organization for the better. Exploiting learning technologies Over the last decade, the use of learning technologies has become much more commonplace and this trend is transforming learning as we know it. According to the recent ASTD State of the Industry report, 10 investments in online content have tripled while instructor-led classrooms have been reduced by a third. The use of online and self-paced tools has increased significantly, along with virtual classes, mobile delivery and social networking. Elearning is no longer an emerging technology. It is generating results. Leaders always have more to learn. Technology integration is among the more difficult issues facing organizations. L&D managers, once centered on coordinating and delivering classroom content, must now manage more complex technology issues and learn how to design better blends of formal/non-formal learning. Both tasks demand increased expertise and vision. To address the interface of business and technical requirements, L&D needs supportive leadership to guide their acquisition of learning resources. Moving beyond workplace skills Basic skills-focused training is essential for any organization. In fact, most learning initiatives center on building repeatable workplace skills, such as customer service, technical skills such as IT-related or desktop, management and supervisory, various industry certifications, communication, teamwork, and many other basic skills. This strategy places an emphasis on obtaining efficiency and lowest cost not necessarily on increasing learning across the organization. Implementing a good skills-based program using elearning does provide significant cost savings versus traditional classroom-only delivery. However, efforts focused solely on building tactical workplace skills may have limited impact on any desired strategic initiatives. Well-defined competencies and job roles are required in order for employees to make significant performance gains and drive bottom-line business results. Enlightened organizations also provide business-focused learning to address a wider range of key job skills which best align to their strategic business goals. These business skills can include improved customer contacts, services and sales, enhanced quality processes along with sound metrics. At this point, there is a pressing need to measure learning results and place more emphasis on providing greater business value. 10 ASTD Research State of the Industry, 2012: ASTD s Annual Review of Workplace and Development Data 7
8 At the highest level, enlightened organizations actively seek to include individual performers into the ongoing strategic thought and performance. The concept of performer-focused learning requires the leadership to change the push of learning into a pull by empowering the individual performer. This approach is quite common among leading management consulting firms. To achieve the ultimate business impact all learning organizations must focus on learners and the organizational skills, motivation, competencies and knowledge they will need to meet their business goals. Three Growth Model Phases Each of the five LGM stages are grouped into three important phases; Implementation, Transformation and Expansion. Your immediate goal should be to reach to the Transformation Phase (Stage 3) as quickly as possible. Doing so will better position you to begin harvesting both the cost benefits and an increased return in value from your investment. The following two stages are your pathway to arriving there. Implementation Phase (Stages 1 and 2) The first two stages (Supplement and Targeted) focus on building overall access, awareness, functionality, responsiveness and cost effectiveness of elearning. The L&D group, along with key executive support, provides the leadership to move through these important first, tactical steps. The key to success for this period is the implementation of sufficient libraries of learning content to address a backlog of training demands not previously supported by more traditional methods (classroom). During this implementation period traditional and new methods begin to merge. This period provides the fundamental deployment of elearning and allows each learner enough time to adapt to using new learning methods. Concurrently, the L&D group learns how to market, manage and measure the use of the alternative learning content. Local management begins observing the immediate application of skills within the workplace. 8
9 During the first stage, it is common to see significant cost savings result from the introduction of elearning as it boosts an employee s career and provides more formal training to the organization. In the second stage, further cost benefits can be achieved by replacing redundant instructor-led topics with equivalent elearning content. Doing so gives blended learning an excellent start. This period proves the value of elearning to executive leadership so they continue to fund and support the movement forward to the next stage. To encourage elearning adoption, L&D professionals must provide adequate targeting and promotion. Connect with the business A learning strategy must align with your organization s strategy. Brush up on your business acumen and proactively seek to understand the business issues learning initiatives should support. Build relationships on the front line of your organization so you are perceived as a credible business partner. Evangelize how learning can impact business results when properly aligned and supported. Buy more and build less It isn t necessary to build everything; you can source most of the content you need then customize it. Use your funding for learning content which is specific to your organization. According to an industry rule-of-thumb, at least half of the learning topics are the same across any organization. Independent of industry, every organization has an ongoing need for learning content for a wide range of topics, such as; desktop, IT, communications, management, leadership, customer services and so forth. Seek out Software as a Service (SaaS) partners, cloud services and off-the-shelf content providers. Leverage technology that automates existing programs and procedures so you can increase learning s reach and frequency. For example, identify which classroom courses could be delivered as effectively via virtual classroom technologies. Identify classroom offerings that can blend with elearning components to reduce time in the classroom, provide reinforcement and make informal resources more readily available. Establish consistent business-like evaluation methods Measures of learning efficiency and effectiveness are much more important to business managers than learner feedback and test scores. The traditional measures of learning success (such as Kirkpatrick) should be expanded to focus on the observation and evaluation of business impact. Here are some suggestions: Stop using smile sheets as your only measure of success. Focus less on Kirkpatrick s Level 1 (reaction) and Level 2 (learning) reporting, and report more on Level 3 (behavior) and Level 4 (results). These metrics should focus on the actual impact of the learning--not how much the students liked the instructor. 9
10 Additional business measures (efficiency) are required to show how much time and money is saved by using technology versus expenses for travel along with time away from the workplace to attend a classroom event. Look at how the learning is actually transferred into the workplace (effectiveness). Getting reports or anecdotal stories from the workplace is easy. The learner and their supervisors will let you know if your training efforts are beneficial or not. Some are actually eager to share their results. Expand new team roles A blended learning program will deliver on expectations if it is well-designed and delivered. Since rolling out a new program is only the beginning, here are some suggestions that can be used to increase the overall skills of the L&D team. Identify the learning professionals who will have ongoing responsibility for each aspect of program management strategy, alignment, marketing, evaluation, results reporting, deployment and other important components. Conduct some training for each role and encourage the application of new skills wherever and whenever needed. Follow up with acknowledgements, awards, bonuses or other intrinsic and extrinsic rewards. Introduce leadership resources to your executives early Every working adult learns by doing. If you introduce your executive team to leadership resources via elearning, this decision-making group will become better informed of the value of this approach. Involving them will allow them to support you as you move forward through these stages. Having your leadership participate in the change will increase their understanding of the value of this approach as you move closer to Stage 3 where you will need their ongoing support. Blend elearning resources (portals, videos, articles, assessment, etc.) with any existing leadership efforts. The Transformation Phase (Stage 3) The third stage (Strategic) seeks to obtain overall organizational acceptance for using learning as a strategic resource and move forward to complete the transformation begun in the two earlier stages. This middle stage takes the proof of concept created in the earlier stages and focuses on key business competencies that are critical to the organization s transformation from training to learning. This provides the organization with the foundation for a more business-oriented return on investment. Led by executive and training leadership teams, this period establishes and completes the breakthrough point for the organization. The key objective is to shift from training-only objectives in order to realize the full potential of business-focused learning. In this stage executive leadership moves from the more familiar training paradigm to a new one focused on building strategic learning paths centered on key 10
11 job competencies for those in critical roles. This stage requires a great deal of leadership, talent, resources and increased communications backed by a clearly stated and motivating vision. Increase your stakeholder relationships and alignment efforts Use the early efforts of business partnerships to cast a wider net for impact. With the experience and credibility gained during the first two stages, communicate successes to new stakeholders and expand into additional areas of the business. The business value of your success will provide a required proof of concept to those who need to see practical business outcomes. By this stage, you should be able to expand the leadership programs you started in the earlier stages. Continue to provide more management and leadership topics to this audience. Encourage more participation and feedback. Show your executives the value of expanding learning within the overall organization at all levels of employees. With their support, the organization will see quicker gains in overall job performance, more engagement, decreases in turnover, increases in revenue, budget reductions and increased customer satisfaction. Since this stage requires creative transformational thought and effort, the likelihood of your efforts being thwarted will be much greater. Your vision for change will create natural, predictable barriers. Having strong stakeholder support to assist you in overcoming these obstacles is essential. Focus on competency and start small With a solid understanding of the performance needs required to achieve business aims, you can initiate learning efforts with a specific job family or roles such as sales, customer service or leadership. While some organizations do elect to apply certain software to support this process, it is certainly not an absolute requirement. Competency management practices include: Defining the competencies, identifying the required levels of proficiency, Measuring the existence of those competencies within the target populations, Implementing steps to close skill gaps. Manager s role in creating competency The basic principle for management is to ensure the organization has the right people at the right time for accomplishing business objectives. The manager s ultimate goal is to ensure their employees are competent, productive and can safely, effectively and efficiently perform their jobs. The manager must ensure: Employees are taught skills to deal with day-today demands. Without continual growth and progress, such words as improvement, achievement, and success have no meaning. Benjamin Franklin US Statesman The learning environment is supportive and positive. 11
12 Employees are active participants in the learning process. New employees must be encouraged to use their newly acquired skills right away. Activities include learner participation in order to increase retention and build new skills. Focus the on the-job-training (OJT) efforts so these can be successfully completed as a normal part of day-to-day operations. Barriers or conflicts to learning activities are either removed or minimized. Create well-designed blended learning programs During stage 2, you began building basic blends using a core and spoke model (e.g. elearning prior to or elearning within a classroom event). Now it is time to design more complex blended learning programs. Using The Blended Book by Josh Bersin and Skillsoft s Eight Phases of Workplace for guidance, here are suggestions: Provide a design principle that keeps moving the learning into the workplace. Have the learner participate as a team member and hold them accountable. Include more learner interaction, feedback and assessments. Increase the use of multiple assets that elicit learner interaction The breakthrough point in this stage is marked by an increase in the application and complexity of blended learning approaches. This will demand more talent within your team to design and deliver the best programs possible. Advance the evaluation strategy With a well-established foundation of efficiency and effectiveness, metrics should already be in place. Here are some suggestions for furthering your evaluation strategy: Institute regular evaluations at Level 3 (application of skills and knowledge to the job). Report upward on how the learning programs are influencing and improving job performance. Communicate testimonials within the organization to encourage interest and awareness among populations you have yet to reach. Without the application of the learning in the workplace the desired business results can t occur. Once you have evidence of business impact, it is time to provide more proof in the form of a formal ROI (Return on Investment) report. Report results such as performance gains, decreases in turnover, increases in revenue, budget reductions, customer satisfaction and other meaningful measures. Establish a formal governance group Shared leadership within an organization makes everything about this transformation work more smoothly. Begin a three-tiered governance group (e.g. Council). Successful IT departments have used this approach quite often over the last few years. It will pay off for you in increased budget funding and larger spotlight on your contributions. 12
13 The first tier is L&D because this is a working group that creates and manages learning. This includes roles such as learning infrastructure, vendor selections, management of programs and learning functions. The second tier is a learning council that reviews strategy, budget development, and program prioritization along with business impact measurement. The third tier is composed of executives who review program requests and provide the necessary funding. Later on, the L&D group and the Council will work together to create Communities of Practice, which may include instructional design and learning measurement committees or best practices. The Expansion Phase (Stages 4 and 5) The stages four and five (Integrated and Optimized) are more complex in both structure and design. Success depends heavily on executive sponsorship of programs that address strategic business demands. Organizations that achieve this level are considered best in class and referred to as having a strong learning culture. The fourth stage leverages the key practices applied within stage three more consistently and systematically. It focuses on smoothing the balance between formal and informal learning; stage four introduces a broader set of sophisticated learning tools, resource types, and practices as well. Also, the L&D group addresses a wider range of business objectives. in stage four is liberated from the learning management system (LMS). resources are still maintained and tracked through the LMS, but the LMS becomes a back office system to the organization s intranet and portals. Organizations at this level embed learning directly into the traffic patterns of their target audiences, alleviating the need to go to the front door of the LMS. Instead, deep linking directly to relevant resources is common practice. Organizations that propagate this approach see much higher levels of elearning adoption. Finally, the fifth stage is when every employee has faster and more personalized access to learning resources whenever and wherever they are required. Some refer to this stage as the point of learning ubiquity. Here, the line between work and learning blurs because learning is such a natural part of accomplishing work tasks. Like stage four, learning is also accessible from the learning management system, embedded into intranet portals and retrievable via mobile devices. is also considered a key lever to organizational advantage. Integrate learning into human capital management functions Organizations at these advanced stages have often integrated learning with functions such as performance management, on-boarding, succession planning, compensation and talent management. In stage 4, L&D will pay particular attention to how this group can play a key role in this integration. 13
14 Leverage enabling technologies Organizations should take advantage of a wide variety of tools to communicate back to the business in relevant terms. These tools often expand the reach of learning programs and make the integration with human capital functions easier. Authoring environments, analytics tools, Web 2.0 capabilities, virtual mediums, advanced blended learning structures, learning management systems, content management systems, customization, social collaboration and personalization tools are frequently a part of the learning infrastructure. While the number of tools may increase dramatically, avoid introducing tools for their own sake, incorporate only those that are woven into the business process and contribute to results. Expand your reach to partners and customers Continue to look within your organization to address the needs of new learners. Also consider developing learning services for your supplier partners and customers. Frequently, organizations implement the internal learning practices with the extended enterprise to further accelerate business outcomes. Stage 5 and Beyond What does Stage 5 really look like? With one of the largest customer bases in the global learning industry, Skillsoft is well positioned to observe how the most advanced organizations use learning to achieve their business goals. Several of our customers are regularly awarded industry accolades, such as ASTD s BEST award. A majority of Skillsoft s customers also attend the annual Perspectives user event. Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop Ancient Fabulist Since Skillsoft was founded, we have actively sought out the opinions of our customers; they have proven a bellwether of the overall learning market and its trends. Here are some of the learning moments we have taken away from some of the highperforming organizations with which we partner as they continue their Stage 5 journey to maintain organizational advantage. benefits continue to accrue All of our Stage 5 customers experienced the positive impact that learning provided within their organizations. The quantitative (hard) savings occurred during Stage 1 and continued throughout their learning maturity efforts. In many ways, these savings more than offset the initial costs involved in bringing elearning into their business units. The qualitative (soft) results provide an increased focus on process and customers and overall productivity. Finally the difficult to measure (fuzzy) benefits from meeting expectations are either well-known or assumed. As a general rule of thumb, most organizations desire proof of hard savings first and foremost. Once these benefits begin to accumulate, then the softer measures begin to signal the arrival of the envisioned business impact. 14
15 Governance on key learning decisions The transformation of training into learning defined during Stage 3 will require leadership at all levels, executives, management, L&D and a critical mass of engaged learners. There is no question about it. Using learning to integrate into talent management and improve business performance and support overall business goals requires forward-thinking leadership. Determining direction and providing top-down support is crucial on the journey to obtaining the full Stage 5 results. Usually some form of focused hierarchy meets this need. An executive steering committee must answer questions along the lines of; How much should we spend on formal, informal and social learning programs? It takes executive leadership to define the strategic role learning will play in the organization, then determine funding needed to achieve that objective. The consequences of not deciding means the organization fails to develop an overall learning structure that furthers its strategy, despite increased spending for human capital. Another question could be, Which business groups should receive the most learning dollars? Making a clear decision about which learning initiatives will and will not be funded based upon strategic advantage is essential. A lack of focus here overwhelms L&D, which tries to deliver many projects that may have little organization-wide impact or can t be implemented well simultaneously. A general model is for L&D to bring together key stakeholders and form a Council which defines and evaluates learning efforts. Following closely is the executive leadership s need to steer both groups, provide funding and seek accountability for results. A well-organized structure will lead to better practices and increased learning and performance results. A stronger market position and stock value are natural outcomes of good leadership working together. Common strategies for all organizations Abundance of content - All organizations represented at this level provide learning across the spectrum from formal classroom training to informal performance support tools and from available learning content to custom-developed content. These learning resources are well-aligned with specific business initiatives and organizational needs. These Stage 5 organizations have an abundance of content types at their fingertips and well-developed delivery systems. In most cases learning systems are integrated with competency management capabilities, human resources and other human capital management software. Balanced blend of formal, informal and social learning L&D leaders are challenged to create the most effective mix of learning delivery possible. Having these options allows them to maximize business impact in the shortest time and at the lowest cost for large populations of diverse learners. A typical learning mix may include about 10% classroom training, 30% technology-based training (online courses, books, videos, podcasts, etc.) and 60% of training delivered as on-the-job performance support via social media. This approach reduces the time it takes to train employees in key job skills by tuning the mix of learning types to match the skill and the need. portals Well-designed portals deliver a rich set of learning resources tailored to the needs of specific audiences. Several of Skillsoft s clients have implemented portals focused on key strategic topics which provide links to formal and informal assets, learning paths, collaboration and social networking, interactive learning tools and more. As the director of global learning for a consulting organization stated, The value isn t in the pieces; it s putting them into a meaningful business context. 15
16 Applying the key success factors There are eight key success factors which must be addressed in order to bring strategic learning into your organization. Apply these factors consistently across all five stages as follows. Stage Goal Business Case Culture s Role Blended Design Marketing & Promotion Learner Adoption Each stage has an overarching objective for each stage (milestone) as it relates to the construction of a learning organization. These goals include efforts to initiate, manage, align, and integrate and then to expand enterprise-wide learning. Developing a business case helps to create a wider framework that is essential for the desired benefits to actually materialize. These benefits include; better market performance, competitive advantage, and employee retention. The business case focuses primarily on cost benefits/offsets during the first two stages to ensure ongoing savings are secure as work moves forward into stage 3 where outcomes are measured using return on investment. A learning culture seeks to build increased engagement and job satisfaction. This effort results in greater motivation to transfer learning and reduced turnover. It s an essential task in order to become an innovative, agile organization that builds and sustains a performer-focused learning environment. Adaptation to rapid change isn t a one-time event for an organization, it s a continuous process. It is the role of L&D to create a continuous environment for learning and show how this culture links to overall organizational success. This task includes working with management, learning and other groups to exploit the value of this infrastructure. The role is to balance ongoing demands for running a business with the agility to quickly shift emphasis with changes. Blended design is more than combining classroom with elearning. Well-designed learning blends are the fuel that powers the transformation; beginning with simple blends and moving forward to complex learning design in order to accommodate and ensure a great transfer of learning into the workplace. The old adage Build it and they will come. doesn t work. Consistent and trustworthy communication about the value of learning will continuously motivate the individual, their manager and the organization. Communicating the value on a regular basis empowers the entire organization. Individuals model the behavior of their leaders and their peers. You can t create a transformation solely by pushing content out to employees. It only works when the individual is led to begin pulling learning to them. As adoption grows beyond critical mass, this pull will empower the entire organization. Evaluation Without metrics, you simply don t know if you are making progress or the magnitude of intended change. In a word, you become lost. The adoption rate proves the magnitude of efficiency and how effective the transfer of learning can be. We will examine the profile of each of the five stages within the Skillsoft Growth Model in the following pages. 16
17 Profile for Stage 1 Supplement Business case for elearning culture role Blended design Elearning promotion Learner adoption evaluation Elearning is introduced to address scalability challenges and reduce costs; adoption is ad-hoc - The Supplement stage begins the process of moving from the traditional trainer-centered paradigm to a learner-centered one. Introducing new elearning resources will quickly address a backlog of pent-up demand for skillsfocused learning. This includes scalable learning assets that could not be delivered via traditional methods due to high costs. Reduced travel costs (for both instructors and participants), design and development costs, instructor time, and learners time away from work create significant cost-saving benefits for the organization. These savings are routinely greater than the initial investment. is operationally focused - The successful initiation of the new elearning assets and a smooth transition into the organization is imperative in this stage. Key players, which include IT, managers for the targeted population, stakeholders, instructors, and L&D, focus on driving adoption of elearning resources. Key executives are asked to give their support and become engaged in this initiative. Learners quickly see the nascent value of these new resources and, after completing their desired learning, will share their experiences with co-workers. Their word of mouth promotion shapes and supports an ongoing awareness campaign. Contractor At this stage, the L&D group is generally considered a contractor or a facilitator within the organization. The primary focus is to simply provide learning content to fulfill specific skill gaps or backlogged requests. The introduction of elearning allows L&D to increase their skill levels to ensure the success of the subsequent stages for both L&D and for the learners. Key support for this stage usually consists of establishing program goals, marketing and promotion, demonstrating the design and navigation of learning assets to learners, adding new users to a LMS, managing administrative tasks and tracking learner progress. Very little blending, mostly formal This stage is characterized by little blended design other than existing functions present within elearning resources: most instructor-led classrooms continue as before with no link to the new elearning assets. New assets include libraries of elearning content that deliver formal training in a wide range of technical and business skills along with elearning assets to support instant learning needs. A learning management system (LMS) is used to deliver and track the instructor led and elearning content but those resources are rarely merged into blends. Traditional awareness marketing Since elearning is being introduced to some learners for the first time, elearning promotion focuses on showing learners how to access, view, select, and use these new elearning assets. Regular promotional communications via websites, open houses and other communications are common methods for creating learner awareness and the active use of elearning content. 20%+ mostly push - Expect 20% or more of the learner usage within the targeted population. Uptake is driven by the effectiveness of the push marketing and its focus is on creating learner awareness and describing the benefits. Ensuring learners have an easy experience accessing the resource is essential to make a good first impression. Managers or L&D staff may assign specific resources to help learners gain a comfort level with the elearning resources. Efficiency of elearning Measuring typically focuses on utilization, completions, and overall counting at this stage. content evaluations generally focus on learner reaction (Kirkpatrick level one) or on skills gained as measured through test scores (level two). Managers may request the inclusion of specific learning assets into a few professional development plans. 17
18 Profile for Stage 2 Targeted Business case for elearning culture role Blended design Elearning promotion Learner adoption Evaluation Targeted learning begins to support specific initiatives and job roles to enhance savings & remove redundancy -The Targeted stage seeks to fully exploit the assets in place and continue the expansion of elearning in other workplace areas. As more needs are identified, more elearning content for specific initiatives or job roles will be required. The next task is to maximize the investment in elearning resources and enhance savings from the continued delivery of skills-focused learning. As elearning resources replace redundant classroom, the organization will realize more savings. This stage expands earlier results and provides more resources to more learners for less cost. The cost-savings and renewed focus on specific initiatives and job roles reaffirms the original decision for choosing elearning. Executive support increases & learning strategies emerge - The organization begins to transform and realizes that future maturity can be only achieved with visible executive leadership and more coordination across the organization. An initial Council is often formed to identify enterprise opportunities for learning and to leverage elearning s benefits more fully. Development of formal learning strategies begins. Managers request more content to address specific requirements and other members of HR (i.e. the HR business partners) begin to identify more opportunities to align elearning to internal customer needs. The learner population will begin expanding as marketing and management efforts continue to bear fruit. Consultant - As partnership with the management team increases, L&D becomes more consultative, advising how to leverage elearning to build talent. Support for setting up a blended learning program, measuring marketing results tracking learner uptake, and conducting regular program reviews increase. These changes require some adjustments in the roles, responsibilities, staffing and talent within L&D. Simple blends, social & mobile use begin- Simple blended learning programs begin during this stage. These may include elearning content as a pre-requisite, during or after a classroom event, use of social media to discuss elearning content and access of assets via mobile devices and virtual meeting tools. There is an increased use of informal learning - job aids, videos, simulations, mentoring, online books and other elearning assets. In this stage, the organization also begins to blend elearning resources into management and leadership programs. Highlights & success stories - Marketing and promotional programs continue to build learner awareness, as in Stage 1, while beginning to highlight learner success stories and elearning s positive results. The organization begins promoting elearning features that were not fully exploited during the first stage, such as mentoring, social learning, mobile access and the new blends. 30%+ pull Increases - Expect 30% or more usage from the targeted population. As long as management and L&D actively support the expanded use of elearning features, social media and blended programs, usage will continue to increase. More learners will begin to access content (pull) on their own volition as well as recommend content to their peers. Effectiveness of elearning While the primary focus continues to be measuring adoption, evaluation efforts center more on increasing effectiveness. The routine study of skill improvement and greater application in the workplace (Kirkpatrick levels two and three) takes place. Completions are only a concern for specific (e.g., compliance) related programs because informal learning behaviors are beginning to take root and grow. 18
19 Profile for Stage 3 Strategic Business case for elearning culture role Blended design Elearning promotion Learner adoption Evaluation is aligned to strategic business objectives and begins to connect to talent management to increase the value and impact of learning While previous stages emphasized cost reduction and targeted needs, this pivotal stage is characterized by learning s alignment to the strategic agenda. The job roles or functions that need strategic attention often include leadership and customer-facing functions (e.g. sales and customer service). is also aligned to support enterprise imperatives such as fostering an innovation culture or implementing Six Sigma. The business case centers on increasing learning s business impact while finding more opportunities to expand cost savings and productivity. Success in this stage leads to a breakthrough for the organization, its leadership, L&D and the overall learner population. Governance & talent management begins - Along with the Council started in the previous stage, an Executive Steering Committee is established to ensure that learning is strongly aligned to the strategic goals. In this stage, it is common for organizations to consolidate funding across disparate parts of the organization and form shared services. Communities of practice also emerge to hone L&D expertise. Talent management processes become more integrated and consistent across the organization. content becomes a key component of talent management s success. Key player - This stage is a major point of change into a new learning paradigm: L&D is a key player in making this breakthrough stage a reality. Common learning services include performance consulting, competency model design, custom content creation, business cases, and measuring business outcomes. During this stage, L&D becomes an integral part of organizational success, elevating the function s status. The need for leadership, budgeting, roles, responsibilities, staffing and talent within L&D continues to increase. Blending scales to balance multiple modalities Blended programs become more prevalent in this stage. Since resources become more plentiful, more attention is paid to providing a broader mix of learning modalities. With the inherent growth and complexity in learning s scope, organizations often selectively outsource areas such as custom development, program design and aspects of program management. Portal deep linking begins - Marketing showcases the strategic outcomes achieved from learning. It also continues to highlight success stories that recognize individual learner testimonials and career progression. Visibility begins to take place by deeplinking specific resources into targeted portals so that access is not solely available through the LMS front door. An example of this would be directly linking project management references into an internal project management portal or webpage. 50%+ Pull = Push - Use of elearning exceeds 50% since technology-enabled learning is generally accepted. Greater leadership advocacy, deep-linking and more habitual use of elearning for performance support reinforce this. Most functions have prescriptive learning programs aligned to their job roles. Adoption is balanced between push and pull. Business impact of elearning - With the executive focus on strategic goals, learning evaluation emphasizes more business impact measurements (Kirkpatrick s level 4). scorecards or dashboards may be drafted to communicate learning s contributions to business results. Interest conducting formal ROI studies also emerges, so the organization typically starts building learning measurement expertise. 19
20 Profile for Stage 4 Integrated Business case for elearning culture role Blended design Elearning promotion Learner adoption evaluation Increasing talent and accelerating organizational agility - At this stage, the organization recognizes the correlation between nimble talent and business agility. is well-rooted within the architecture of talent systems, supporting multiple aspects of the talent lifecycle. The overall goal is to establish an ecosystem that supports a performer-focused enterprise. The business case now centers on increasing the value of talent within the organization. The organization will experience a closer connection to learning within the normal work flow of the organization, all of which is focused on accelerating business results, deepening the talent pool, and creating an agile, empowering, productive and creative organization. Recognized as a Organization - is now woven into the fabric of the organization. The line between learning and work blurs because learning is fully integrated into workflows. Governance by the Council and Executive Steering Committee has matured while they continue to encourage and reward communities of practice. Organizations at this stage often receive awards industry leadership. The vision of a performer-focused environment is now up and working. Architect Comprehensive learning business plans illustrate how learning is a critical fulcrum for achieving the strategic agenda. L&D is given increased enterprise responsibilities for workforce planning and has a regular seat at the table. Business process outsourcing of some operations is also typical at this stage. Once again, we see a similar but significant increase in L&D infrastructure. Balanced blends become routine - The organization continues to expand and refine blended learning models. At this stage, many existing programs have been redesigned to blends and most new programs begin as blended models. The organization also has established guidelines for blending that it provides to its program developers. Learner program completions and the transfer of skills increase along with daily interaction with informal, self-directed access to elearning. Active manager level evangelism begins - The unique characteristic of this stage is that the managers become marketers. Managers regularly encourage ongoing progression of development plans, expect to see new skills demonstrated on the job, and recognize results achieved through learning. Managers are often profiled as good role models for continual development. 80%+ increased pull - Utilization is very high because the late adopters of technology are effectively engaged. At least 80% of the target population uses the learning resources. More and more of the adoption represent learner pull. Because access to relevant learning is woven into workflows, adoption is constantly growing as learners take advantage of the learning available at their fingertips. Targeted ROI studies - Formal ROI (return on investment) evaluations are conducted for the most strategic programs. These studies quantify the business results and validate those programs which produce strong returns. scorecards and executive dashboards evolve and mature. Organizations at this stage are readily profiled in case studies and other firms refer to them for benchmarking. 20
Strategic Employee Onboarding: First Impressions Are Everything
 ONBOARDING Strategic Employee Onboarding: First Impressions Are Everything Cornerstone OnDemand Whitepaper Series 2007 Cornerstone OnDemand, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Table of Contents Onboarding: More
ONBOARDING Strategic Employee Onboarding: First Impressions Are Everything Cornerstone OnDemand Whitepaper Series 2007 Cornerstone OnDemand, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Table of Contents Onboarding: More
Five Fallacies About the Role of Learning Content in Talent Management. White Paper. Executive Summary
 White Paper Five Fallacies About the Role of Learning Content in Talent Management John Ambrose Senior Vice President, Strategy, Corporate Development & Emerging Business SkillSoft Executive Summary A
White Paper Five Fallacies About the Role of Learning Content in Talent Management John Ambrose Senior Vice President, Strategy, Corporate Development & Emerging Business SkillSoft Executive Summary A
Skillsoft New Hire Training Program:
 WHITE PAPER Skillsoft New Hire Training Program: Onboarding of New Sales Talent Dorman Woodall, Director, Skillsoft Learning March 2013 Executive Summary The Skillsoft New Hire Training Program has provided
WHITE PAPER Skillsoft New Hire Training Program: Onboarding of New Sales Talent Dorman Woodall, Director, Skillsoft Learning March 2013 Executive Summary The Skillsoft New Hire Training Program has provided
An Executive Primer To Customer Success Management
 A Forrester Consulting Thought Leadership Paper Commissioned By Gainsight April 2014 An Executive Primer To Customer Success Management Table Of Contents We Live In A Subscription Economy Learn To Manage
A Forrester Consulting Thought Leadership Paper Commissioned By Gainsight April 2014 An Executive Primer To Customer Success Management Table Of Contents We Live In A Subscription Economy Learn To Manage
Executive Checklist to Transitioning Processes
 Digital Innovation Series Executive Checklist to Transitioning Processes Building a Flexible Model The Digital Innovation Series traces the trends that are driving the digital-innovation imperative that
Digital Innovation Series Executive Checklist to Transitioning Processes Building a Flexible Model The Digital Innovation Series traces the trends that are driving the digital-innovation imperative that
Developing leaders in challenging times for competitive advantage tomorrow.
 Developing leaders in challenging times for competitive advantage tomorrow. Leadership development is a dynamic process, which means that organizations like Deloitte have a distinct advantage. It s in
Developing leaders in challenging times for competitive advantage tomorrow. Leadership development is a dynamic process, which means that organizations like Deloitte have a distinct advantage. It s in
A Set of Best Practices for Targeting, Aligning and Measuring Learning
 WHITE PAPER A Set of Best Practices for Targeting, Aligning and Measuring Learning KIERAN KING, Global Director, Loyalty Strategy, Skillsoft Executive Summary Learning expectations have never been higher.
WHITE PAPER A Set of Best Practices for Targeting, Aligning and Measuring Learning KIERAN KING, Global Director, Loyalty Strategy, Skillsoft Executive Summary Learning expectations have never been higher.
10 Tips to Education Assistance Program Excellence
 10 Tips to Education Assistance Program Excellence White Paper by Heidi Milberg Director of Business Development General Physics Corporation www.gpworldwide.com General Physics Corporation 2011 As with
10 Tips to Education Assistance Program Excellence White Paper by Heidi Milberg Director of Business Development General Physics Corporation www.gpworldwide.com General Physics Corporation 2011 As with
Adopting a Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery Model to Improve Software Delivery
 Customer Success Stories TEKsystems Global Services Adopting a Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery Model to Improve Software Delivery COMMUNICATIONS AGILE TRANSFORMATION SERVICES Executive Summary
Customer Success Stories TEKsystems Global Services Adopting a Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery Model to Improve Software Delivery COMMUNICATIONS AGILE TRANSFORMATION SERVICES Executive Summary
Successful elearning Business
 10 Critical Components for a Successful elearning Business presented by elearning is a Critical Business Strategy What Nonprofits and Associations Need to Know You have the content. You have the membership.
10 Critical Components for a Successful elearning Business presented by elearning is a Critical Business Strategy What Nonprofits and Associations Need to Know You have the content. You have the membership.
Human Capital Management: Leveraging Your Human Assets
 Human Capital Management: Leveraging Your Human Assets Executive Summary Managers have always intuitively believed that their employees generate value for the organization but today, intuition is no longer
Human Capital Management: Leveraging Your Human Assets Executive Summary Managers have always intuitively believed that their employees generate value for the organization but today, intuition is no longer
White Paper Build A Change Management Office
 Building Change Capability We make it happen. Better. White Paper Build A Change Management Office 9 Steps to Make Your Change Efforts Stick May 2014 Better Change Management Developing a Change Management
Building Change Capability We make it happen. Better. White Paper Build A Change Management Office 9 Steps to Make Your Change Efforts Stick May 2014 Better Change Management Developing a Change Management
Author: Lydia Cillie-Schmidt Page 1
 Talent Management: An integrated framework for implementation L Cillie-Schmidt: Talent Management: An integrated framework for implementation, Management Today, February 2009 Companies like to promote
Talent Management: An integrated framework for implementation L Cillie-Schmidt: Talent Management: An integrated framework for implementation, Management Today, February 2009 Companies like to promote
Global Account Management for Sales Organization in Multinational Companies *
 Global Account Management for Sales Organization in Multinational Companies * Tino Canegrati ** Abstract A Global Company is not just a Multinational Company, but on top it has developed an organizational
Global Account Management for Sales Organization in Multinational Companies * Tino Canegrati ** Abstract A Global Company is not just a Multinational Company, but on top it has developed an organizational
THE EVOLUTION of Talent Management Consulting
 Talent management consulting is the giving of professional, expert advice to executives who are put in charge of handling, directing, or managing those who have a capacity for achievement or success. THE
Talent management consulting is the giving of professional, expert advice to executives who are put in charge of handling, directing, or managing those who have a capacity for achievement or success. THE
WHITE PAPER OCTOBER 2014. Unified Monitoring. A Business Perspective
 WHITE PAPER OCTOBER 2014 Unified Monitoring A Business Perspective 2 WHITE PAPER: UNIFIED MONITORING ca.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Section 1: Today s Emerging Computing Environments 4 Section
WHITE PAPER OCTOBER 2014 Unified Monitoring A Business Perspective 2 WHITE PAPER: UNIFIED MONITORING ca.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Section 1: Today s Emerging Computing Environments 4 Section
The New Value of Change Management: Success at Microsoft
 The New Value of Change Management: Success at Microsoft by Molly Cooper, Microsoft IT Page 1 of 8 Summary Microsoft recently completed a significant IT transformation effort by replacing the existing
The New Value of Change Management: Success at Microsoft by Molly Cooper, Microsoft IT Page 1 of 8 Summary Microsoft recently completed a significant IT transformation effort by replacing the existing
How To Get Started With Customer Success Management
 A Forrester Consulting Thought Leadership Paper Commissioned By Gainsight April 2014 How To Get Started With Customer Success Management Table Of Contents Four Actionable Steps To Setting Up Your Customer
A Forrester Consulting Thought Leadership Paper Commissioned By Gainsight April 2014 How To Get Started With Customer Success Management Table Of Contents Four Actionable Steps To Setting Up Your Customer
Integrating Compliance with Business Strategy: The Skillsoft Compliance Maturity Model
 WHITE PAPER Integrating Compliance with Business Strategy: The Skillsoft Compliance Maturity Model THE SKILLSOFT GLOBAL COMPLIANCE SOLUTIONS TEAM Executive Summary Compliance training is a necessity to
WHITE PAPER Integrating Compliance with Business Strategy: The Skillsoft Compliance Maturity Model THE SKILLSOFT GLOBAL COMPLIANCE SOLUTIONS TEAM Executive Summary Compliance training is a necessity to
Enabling HR service delivery
 Enabling HR service delivery Cloud HR 9 10 HR shared services and Outsourcing Global privacy and Security 11 12 Social media 10 HR Shared Services and Outsourcing Has your organization implemented service
Enabling HR service delivery Cloud HR 9 10 HR shared services and Outsourcing Global privacy and Security 11 12 Social media 10 HR Shared Services and Outsourcing Has your organization implemented service
Understanding Learning and Certification Management Vendors
 Learning Management Systems (LMS) Help Improve Channel Performance The LMS industry is large and crowded. While there has been consolidation recently, there are still many different large and small vendors
Learning Management Systems (LMS) Help Improve Channel Performance The LMS industry is large and crowded. While there has been consolidation recently, there are still many different large and small vendors
ORGANIZED FOR BUSINESS: BUILDING A CONTEMPORARY IT OPERATING MODEL
 ORGANIZED FOR BUSINESS: BUILDING A CONTEMPORARY IT OPERATING MODEL Time is running out for the traditional, monopolistic IT model now that users have so many alternatives readily available. Today s enterprises
ORGANIZED FOR BUSINESS: BUILDING A CONTEMPORARY IT OPERATING MODEL Time is running out for the traditional, monopolistic IT model now that users have so many alternatives readily available. Today s enterprises
The Talent Management Framework
 The Talent Framework Executive Summary Josh Bersin Stacey Harris Kim Lamoureux Madeline Laurano David Mallon May 2010 BERSIN & ASSOCIATES RESEARCH REPORT V.1.0 The Talent Framework Executive Summary The
The Talent Framework Executive Summary Josh Bersin Stacey Harris Kim Lamoureux Madeline Laurano David Mallon May 2010 BERSIN & ASSOCIATES RESEARCH REPORT V.1.0 The Talent Framework Executive Summary The
Corporate Learning Watch
 Quantifying the Organizational Benefits of Training August 2010 The Majority of CEOs Want Return on Investment Data for Training Programs, But Few Receive It Watch List A recent survey of CEOs found that
Quantifying the Organizational Benefits of Training August 2010 The Majority of CEOs Want Return on Investment Data for Training Programs, But Few Receive It Watch List A recent survey of CEOs found that
OPTIMUS SBR. Optimizing Results with Business Intelligence Governance CHOICE TOOLS. PRECISION AIM. BOLD ATTITUDE.
 OPTIMUS SBR CHOICE TOOLS. PRECISION AIM. BOLD ATTITUDE. Optimizing Results with Business Intelligence Governance This paper investigates the importance of establishing a robust Business Intelligence (BI)
OPTIMUS SBR CHOICE TOOLS. PRECISION AIM. BOLD ATTITUDE. Optimizing Results with Business Intelligence Governance This paper investigates the importance of establishing a robust Business Intelligence (BI)
2015 Richardson and Training Industry, Inc. All rights reserved.
 2015 Richardson and Training Industry, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 2015 Richardson and Training Industry, Inc. All rights reserved. Contents Overview...3 Key Findings...3 Best Practices in Design and Delivery
2015 Richardson and Training Industry, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 2015 Richardson and Training Industry, Inc. All rights reserved. Contents Overview...3 Key Findings...3 Best Practices in Design and Delivery
Developing the Best. A Corporate Learning Strategy for the BC Public Service. BC Public Service Agency Bringing out the best
 Developing the Best A Corporate Learning Strategy for the BC Public Service BC Public Service Agency Bringing out the best Overview 3 Introduction Context Overview - A New Vision for Corporate Learning
Developing the Best A Corporate Learning Strategy for the BC Public Service BC Public Service Agency Bringing out the best Overview 3 Introduction Context Overview - A New Vision for Corporate Learning
Sales & Marketing Services & Strategy
 Sales & Marketing Services & Strategy Planning Development Implementation Our Approach We have a passion for helping companies make sales and marketing easier. We want you to receive first class solutions
Sales & Marketing Services & Strategy Planning Development Implementation Our Approach We have a passion for helping companies make sales and marketing easier. We want you to receive first class solutions
Building the Digital HR Organization. Accenture and SuccessFactors on the changing nature of HR
 Building the Digital HR Organization Accenture and SuccessFactors on the changing nature of HR More than ever, HR has to contend with changing business demands and an evolving workforce. At the same time,
Building the Digital HR Organization Accenture and SuccessFactors on the changing nature of HR More than ever, HR has to contend with changing business demands and an evolving workforce. At the same time,
Competency Management at Its Most Competent
 Competency Management at Its Most Competent Competencies That Work for Business A recent survey by Human Resource Executive found that two of the top five challenges facing organizations today are aligning
Competency Management at Its Most Competent Competencies That Work for Business A recent survey by Human Resource Executive found that two of the top five challenges facing organizations today are aligning
Vision. Support. Sun Microsystems Workforce Solutions Initiative. iwork at Sun
 Vision Workplaces Technology Choice Best Practices Support Sun Microsystems Workforce Solutions Initiative iwork at Sun The following is a high level overview of Sun Microsystem's iwork at Sun initiative,
Vision Workplaces Technology Choice Best Practices Support Sun Microsystems Workforce Solutions Initiative iwork at Sun The following is a high level overview of Sun Microsystem's iwork at Sun initiative,
REVAMP YOUR TRAINING 7 STEPS TO A SUCCESSFUL BLENDED LEARNING PROGRAM
 REVAMP YOUR 7 STEPS TO A SUCCESSFUL BLENDED LEARNING PROGRAM BY STEVE O BRIAN, VICE PRESIDENT, CHRONUS CORPORATION WITH KAREN DU FOUR DES CHAMPS, & DEVELOPMENT EXPERT, AUTHOR, SPEAKER, AND CONSULTANT PROGRAM
REVAMP YOUR 7 STEPS TO A SUCCESSFUL BLENDED LEARNING PROGRAM BY STEVE O BRIAN, VICE PRESIDENT, CHRONUS CORPORATION WITH KAREN DU FOUR DES CHAMPS, & DEVELOPMENT EXPERT, AUTHOR, SPEAKER, AND CONSULTANT PROGRAM
Change Management. This resource guide answers eight of the questions most frequently asked of LCE subject matter experts in change management.
 Frequently asked questions SERIES: This resource guide answers eight of the questions most frequently asked of LCE subject matter experts in change management. Life Cycle Engineering 2013 www.lce.com QUESTION
Frequently asked questions SERIES: This resource guide answers eight of the questions most frequently asked of LCE subject matter experts in change management. Life Cycle Engineering 2013 www.lce.com QUESTION
How To Listen To Social Media
 WHITE PAPER Turning Insight Into Action The Journey to Social Media Intelligence Turning Insight Into Action The Journey to Social Media Intelligence From Data to Decisions Social media generates an enormous
WHITE PAPER Turning Insight Into Action The Journey to Social Media Intelligence Turning Insight Into Action The Journey to Social Media Intelligence From Data to Decisions Social media generates an enormous
Corporate Social Responsibility: Implications for Human Resources and Talent Engagement
 Corporate Social Responsibility: Implications for Human Resources and Talent Engagement Winnie Kwan and Emily Tuuk Center for Advanced Human Resource Studies May 2012 I. Introduction Over the past few
Corporate Social Responsibility: Implications for Human Resources and Talent Engagement Winnie Kwan and Emily Tuuk Center for Advanced Human Resource Studies May 2012 I. Introduction Over the past few
UNC Leadership Survey 2014: How to Accelerate Leadership Development
 UNC Leadership Survey 2014: How to Accelerate Leadership Development By: UNC Executive Development & Human Capital Institute Website: www.execdev.unc.edu Phone: 1.800.862.3932 Email: unc_exec@unc.edu Executive
UNC Leadership Survey 2014: How to Accelerate Leadership Development By: UNC Executive Development & Human Capital Institute Website: www.execdev.unc.edu Phone: 1.800.862.3932 Email: unc_exec@unc.edu Executive
Approaches for Survey Feedback and Action Planning
 Introduction Survey feedback and action planning are two of the most important components of an organization s survey process, but they are also the most difficult to do well. Although survey design and
Introduction Survey feedback and action planning are two of the most important components of an organization s survey process, but they are also the most difficult to do well. Although survey design and
BUILDING A SUCCESSFUL BUSINESS CASE FOR TALENT MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGY By Kelly McCombs and Tim Welsh, AON Hewitt
 BUILDING A SUCCESSFUL BUSINESS CASE FOR TALENT MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGY By Kelly McCombs and Tim Welsh, AON Hewitt Introduction Human Resources today sits smack-dab in the middle of the most compelling and
BUILDING A SUCCESSFUL BUSINESS CASE FOR TALENT MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGY By Kelly McCombs and Tim Welsh, AON Hewitt Introduction Human Resources today sits smack-dab in the middle of the most compelling and
Seven Things Employees Want Most From Their Training
 RESEARCH REPORT Seven Things Employees Want Most From Their Training Executive Summary In 2013 we set out to discover what 1,001 office workers really think about training. Commissioning Opinion Matters,
RESEARCH REPORT Seven Things Employees Want Most From Their Training Executive Summary In 2013 we set out to discover what 1,001 office workers really think about training. Commissioning Opinion Matters,
4.5% 2014 Digital Marketing Optimization Survey results > 4.5% Top lessons learned from the leaders
 2014 Digital Marketing Optimization Survey results Top lessons learned from the leaders Table of contents 1: Introduction 2: Five lessons from the top 20% #1: They test to make decisions 3: #2: They put
2014 Digital Marketing Optimization Survey results Top lessons learned from the leaders Table of contents 1: Introduction 2: Five lessons from the top 20% #1: They test to make decisions 3: #2: They put
IT Workforce. Your onboarding program has the potential to increase retention, productivity and revenue
 IT Workforce Planning Perspectives TEKsystems, a leading provider of IT staffing solutions, IT talent management expertise and IT services, recently surveyed more than 2,400 IT professionals for its quarterly
IT Workforce Planning Perspectives TEKsystems, a leading provider of IT staffing solutions, IT talent management expertise and IT services, recently surveyed more than 2,400 IT professionals for its quarterly
Course Descriptions for the Business Management Program
 Course Descriptions for the Business Management Program Upon completion of two quarters, students will earn a Professional Certificate in Business Management with a specialization in a chosen area: HR,
Course Descriptions for the Business Management Program Upon completion of two quarters, students will earn a Professional Certificate in Business Management with a specialization in a chosen area: HR,
Strategic Plan 2013 2017
 Plan 0 07 Mapping the Library for the Global Network University NYU DIVISION OF LIBRARIES Our Mission New York University Libraries is a global organization that advances learning, research, and scholarly
Plan 0 07 Mapping the Library for the Global Network University NYU DIVISION OF LIBRARIES Our Mission New York University Libraries is a global organization that advances learning, research, and scholarly
TALENT OPTIMIZATION. Transforming HR and Human Capital Management for Business Growth
 TALENT OPTIMIZATION Transforming HR and Human Capital Management for Business Growth TALENT OPTIMIZATION Transforming HR and Human Capital Management for Business Growth THE TALENT OPTIMIZATION OBJECTIVE
TALENT OPTIMIZATION Transforming HR and Human Capital Management for Business Growth TALENT OPTIMIZATION Transforming HR and Human Capital Management for Business Growth THE TALENT OPTIMIZATION OBJECTIVE
Get the Facts. Learning and Development Budgets, Staffing, and Trends for 2009. Josh Bersin. May, 2009
 Get the Facts Learning and Development Budgets, Staffing, and Trends for 2009 Josh Bersin May, 2009 Copyright 2009 Bersin & Associates. All rights reserved. About Us Who We Are Industry s primary research
Get the Facts Learning and Development Budgets, Staffing, and Trends for 2009 Josh Bersin May, 2009 Copyright 2009 Bersin & Associates. All rights reserved. About Us Who We Are Industry s primary research
Blanchard Coaching - A Strategic Approach
 The Blanchard Approach to Blended Solutions The Ken Blanchard Companies understands that it takes more than just a quick fix to address organizational renewal. Lasting change requires a systematic approach
The Blanchard Approach to Blended Solutions The Ken Blanchard Companies understands that it takes more than just a quick fix to address organizational renewal. Lasting change requires a systematic approach
Customer Success Programs: Tools to Close Deals
 Customer Success Programs: Tools to Close Deals Integratedcreativecommunications Integratedcreativecommunications contents: CUSTOMER SUCCESS LEADS TO MORE SUCCESS...4 SUCCESS PROGRAM BENEFITS...4 CENTRALIZED
Customer Success Programs: Tools to Close Deals Integratedcreativecommunications Integratedcreativecommunications contents: CUSTOMER SUCCESS LEADS TO MORE SUCCESS...4 SUCCESS PROGRAM BENEFITS...4 CENTRALIZED
Solutions overview. Inspiring talent management. Solutions insight. Inspiring talent management
 Solutions overview Inspiring talent management Solutions insight Inspiring talent management Inspiring talent management Intuitive technology that people love to use Lumesse is the only global company
Solutions overview Inspiring talent management Solutions insight Inspiring talent management Inspiring talent management Intuitive technology that people love to use Lumesse is the only global company
Transforming Training Execution:
 Learning Services : Reducing Cost and Improving Performance Sam Herring, CEO and Co-Founder, Intrepid Learning, Inc. March 2009 : Reducing Cost and Improving Performance Do you know how much your company
Learning Services : Reducing Cost and Improving Performance Sam Herring, CEO and Co-Founder, Intrepid Learning, Inc. March 2009 : Reducing Cost and Improving Performance Do you know how much your company
Talent & Organization. Change Management. Driving successful change and creating a more agile organization
 Talent & Organization Change Management Driving successful change and creating a more agile organization 2 Organizations in both the private and public sectors face unprecedented challenges in today s
Talent & Organization Change Management Driving successful change and creating a more agile organization 2 Organizations in both the private and public sectors face unprecedented challenges in today s
Powering Performance with Customer Intelligence. Are you ready to make Customer Intelligence your performance advantage to outpace the competition?
 Powering Performance with Customer Intelligence Are you ready to make Customer Intelligence your performance advantage to outpace the competition? Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) PNT Marketing Services
Powering Performance with Customer Intelligence Are you ready to make Customer Intelligence your performance advantage to outpace the competition? Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) PNT Marketing Services
SAP Thought Leadership Business Intelligence IMPLEMENTING BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE STANDARDS SAVE MONEY AND IMPROVE BUSINESS INSIGHT
 SAP Thought Leadership Business Intelligence IMPLEMENTING BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE STANDARDS SAVE MONEY AND IMPROVE BUSINESS INSIGHT Your business intelligence strategy should take into account all sources
SAP Thought Leadership Business Intelligence IMPLEMENTING BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE STANDARDS SAVE MONEY AND IMPROVE BUSINESS INSIGHT Your business intelligence strategy should take into account all sources
The Future of Census Bureau Operations
 The Future of Census Bureau Operations Version 1.0 April 25, 2013 The Future of Census Bureau Operations Page ii [This page intentionally left blank] The Future of Census Bureau Operations Page iii Document
The Future of Census Bureau Operations Version 1.0 April 25, 2013 The Future of Census Bureau Operations Page ii [This page intentionally left blank] The Future of Census Bureau Operations Page iii Document
Current learning trends in Europe and the United States
 Current learning trends in Europe and the United States Addressing the challenges of the economic downturn and the development needs of today s learners A whitepaper by: Jeremy Blain Director of the Cegos
Current learning trends in Europe and the United States Addressing the challenges of the economic downturn and the development needs of today s learners A whitepaper by: Jeremy Blain Director of the Cegos
best practices How to engage business leaders in succession Three essentials for the talent review and beyond
 best practices How to engage business leaders in succession Three essentials for the talent review and beyond As an HR professional, you know that effective succession management is critical if you re
best practices How to engage business leaders in succession Three essentials for the talent review and beyond As an HR professional, you know that effective succession management is critical if you re
Touch Points Touch Points Step 1 Spend Areas Step 2 Creating and Developing a Sourcing Team Executive Sponsorship
 Strategic Sourcing: A Step-By-Step Practical Model Robert J. Engel, Vice President-Project Services The Procurement Centre 713-623-0111 Ext. 224; bengel@tpc-usa.com 89 th Annual International Supply Management
Strategic Sourcing: A Step-By-Step Practical Model Robert J. Engel, Vice President-Project Services The Procurement Centre 713-623-0111 Ext. 224; bengel@tpc-usa.com 89 th Annual International Supply Management
Twelve Initiatives of World-Class Sales Organizations
 Twelve Initiatives of World-Class Sales Organizations If the economy were a season, we are looking at an early spring after a long, hard winter. There is still uncertainty that it is here to stay, but
Twelve Initiatives of World-Class Sales Organizations If the economy were a season, we are looking at an early spring after a long, hard winter. There is still uncertainty that it is here to stay, but
The attraction, retention and advancement of women leaders:
 The attraction, retention and advancement of women leaders: Strategies for organizational sustainability BUSINESS CASE 1 Table of Contents Introduction Business Case 1 Barriers and Success Factors Overview
The attraction, retention and advancement of women leaders: Strategies for organizational sustainability BUSINESS CASE 1 Table of Contents Introduction Business Case 1 Barriers and Success Factors Overview
Customer Activation. Marketing with a Measurable Purpose
 Customer Activation Marketing with a Measurable Purpose INTRODUCTION As a marketing leader, you need to think about the lifecycle that each of your customers progresses through from potential customer
Customer Activation Marketing with a Measurable Purpose INTRODUCTION As a marketing leader, you need to think about the lifecycle that each of your customers progresses through from potential customer
QUICK FACTS. Managing a Service Operations Team for a Leading Software Developer. TEKsystems Global Services Customer Success Stories.
 Providing an IT Education Business Processing [ Information Technology, Applications Management ] TEKsystems Global Services Customer Success Stories Client Profile Industry: Software Revenue: $74.3 billion
Providing an IT Education Business Processing [ Information Technology, Applications Management ] TEKsystems Global Services Customer Success Stories Client Profile Industry: Software Revenue: $74.3 billion
planning for success.
 planning for success. how a succession plan can help your business retain knowledge & grow leaders. move up in the world. planning for success: how a succession plan can help your business retain knowledge
planning for success. how a succession plan can help your business retain knowledge & grow leaders. move up in the world. planning for success: how a succession plan can help your business retain knowledge
Improving Sales Performance: New Rules for Leaders
 Improving Sales Performance: New Rules for Leaders by Ron D Andrea and Paul Hennessey BayGroup International Improving sales performance has never been more important for major global corporations. After
Improving Sales Performance: New Rules for Leaders by Ron D Andrea and Paul Hennessey BayGroup International Improving sales performance has never been more important for major global corporations. After
W204 - LMS Consolidation, Underlying Design More Important Than Platform
 W204 - LMS Consolidation, Underlying Design More Important Than Platform Assess the scalability of your organization s LMS platform Evaluate an LMS based upon the size and character of different learner
W204 - LMS Consolidation, Underlying Design More Important Than Platform Assess the scalability of your organization s LMS platform Evaluate an LMS based upon the size and character of different learner
Keys to Effective Knowledge Transfer: Build a Training Program that Really Works
 Keys to Effective Knowledge Transfer: Build a Training Program that Really Works Executive Summary Effective training is an investment. Businesses spend more than $62 billion [per year] on training in
Keys to Effective Knowledge Transfer: Build a Training Program that Really Works Executive Summary Effective training is an investment. Businesses spend more than $62 billion [per year] on training in
COPYRIGHT 2012 VERTICURL WHITEPAPER: TOP MISTAKES TO AVOID WHEN BUILDING A DEMAND CENTER
 COPYRIGHT 2012 VERTICURL WHITEPAPER: TOP MISTAKES TO AVOID WHEN BUILDING A DEMAND CENTER For many B2B organizations, building a demand center is a no-brainer. Learn how to ensure you re successful by avoiding
COPYRIGHT 2012 VERTICURL WHITEPAPER: TOP MISTAKES TO AVOID WHEN BUILDING A DEMAND CENTER For many B2B organizations, building a demand center is a no-brainer. Learn how to ensure you re successful by avoiding
Improving Employee Satisfaction in Healthcare through Effective Employee Performance Management
 Improving Employee Satisfaction in Healthcare through Effective Employee Performance Management Introduction The following quotes are comments made by HR professionals from U.S. healthcare providers who
Improving Employee Satisfaction in Healthcare through Effective Employee Performance Management Introduction The following quotes are comments made by HR professionals from U.S. healthcare providers who
THE VALUE OF VIDEO COLLABORATION TOOLS. 1471 Route 9, Suite 202 Clifton Park, NJ 12065 Phone: (518) 371-2295 www.oneconnectinc.com
 THE VALUE OF VIDEO COLLABORATION TOOLS In the past decade the economic climate and therefore the business climate has changed drastically. Markets have become tougher all around, and competition is fierce.
THE VALUE OF VIDEO COLLABORATION TOOLS In the past decade the economic climate and therefore the business climate has changed drastically. Markets have become tougher all around, and competition is fierce.
Three Strategies for Implementing HR in the Cloud
 Three Strategies for Implementing HR in the Cloud Adoption of cloud-based, software-as-a-service (SaaS) human resource management systems (HRMS) has become one of the hottest trends in HR. According to
Three Strategies for Implementing HR in the Cloud Adoption of cloud-based, software-as-a-service (SaaS) human resource management systems (HRMS) has become one of the hottest trends in HR. According to
White Paper. Executing Organizational. Strategy: Achieving. Success through Talent. Management
 White Paper Executing Organizational Strategy: Achieving Success through Talent Management April 2007 Table of Contents Factors Impacting Business Value and Execution 4 The Solution: Business Execution
White Paper Executing Organizational Strategy: Achieving Success through Talent Management April 2007 Table of Contents Factors Impacting Business Value and Execution 4 The Solution: Business Execution
Business Analytics and Data Warehousing in Higher Education
 WHITE PAPER Business Analytics and Data Warehousing in Higher Education by Jim Gallo Table of Contents Introduction...3 Business Analytics and Data Warehousing...4 The Role of the Data Warehouse...4 Big
WHITE PAPER Business Analytics and Data Warehousing in Higher Education by Jim Gallo Table of Contents Introduction...3 Business Analytics and Data Warehousing...4 The Role of the Data Warehouse...4 Big
PMI s Pulse of the Profession The High Cost of Low Performance
 PMI s Pulse of the Profession The High Cost of Low Performance Pulse Perspective As I travel around the world advocating for the value of project, program and portfolio management with organization leaders
PMI s Pulse of the Profession The High Cost of Low Performance Pulse Perspective As I travel around the world advocating for the value of project, program and portfolio management with organization leaders
Helping Enterprises Succeed: Responsible Corporate Strategy and Intelligent Business Insights
 I D C E X E C U T I V E I N S I G H T S Helping Enterprises Succeed: Responsible Corporate Strategy and Intelligent Business Insights May 2009 By Albert Pang, Research Director, Enterprise Applications
I D C E X E C U T I V E I N S I G H T S Helping Enterprises Succeed: Responsible Corporate Strategy and Intelligent Business Insights May 2009 By Albert Pang, Research Director, Enterprise Applications
Digital Customer Experience
 Digital Customer Experience Digital. Two steps ahead Digital. Two steps ahead Organizations are challenged to deliver a digital promise to their customers. The move to digital is led by customers who are
Digital Customer Experience Digital. Two steps ahead Digital. Two steps ahead Organizations are challenged to deliver a digital promise to their customers. The move to digital is led by customers who are
Organisational Change Management
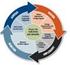 Organisational Change Management The only thing that is constant is change in your business, your market, your competitors, and your technology. Remaining competitive and responsive to your customers and
Organisational Change Management The only thing that is constant is change in your business, your market, your competitors, and your technology. Remaining competitive and responsive to your customers and
Ten Workforce Planning Practices That Leading Companies Use to Their Competitive Advantage
 RESEARCH Ten Workforce Planning Practices That Leading Companies Use to Their Competitive Advantage By Aaron Sorensen, Ph.D., Partner and Juan Pablo Gonzalez, Partner The evidence is clear: Strategic workforce
RESEARCH Ten Workforce Planning Practices That Leading Companies Use to Their Competitive Advantage By Aaron Sorensen, Ph.D., Partner and Juan Pablo Gonzalez, Partner The evidence is clear: Strategic workforce
THE CHANGING ROLE OF THE CHRO
 A HARVARD BUSINESS REVIEW ANALYTIC SERVICES REPORT THE CHANGING ROLE OF THE CHRO Copyright 2015 Harvard Business School Publishing. sponsored by SPONSOR PERSPECTIVE The datafication of HR is a leading
A HARVARD BUSINESS REVIEW ANALYTIC SERVICES REPORT THE CHANGING ROLE OF THE CHRO Copyright 2015 Harvard Business School Publishing. sponsored by SPONSOR PERSPECTIVE The datafication of HR is a leading
ENTERPRISE COMPUTING ENVIRONMENT. Creating connections THROUGH SERVICE & WORKFORCE EXCELLENCE
 ITA Strategic Plan FY 2011 - FY 2016 U.S. Army Information Technology Agency REALIZING The DoD ENTERPRISE COMPUTING ENVIRONMENT Creating connections THROUGH SERVICE & WORKFORCE EXCELLENCE Provide Quality
ITA Strategic Plan FY 2011 - FY 2016 U.S. Army Information Technology Agency REALIZING The DoD ENTERPRISE COMPUTING ENVIRONMENT Creating connections THROUGH SERVICE & WORKFORCE EXCELLENCE Provide Quality
Peirce College. Summary of 2015-2018 Strategic Plan
 Peirce College Summary of 2015-2018 Strategic Plan Contents Strategic Planning Process Vision and Mission Target Market Value Proposition Summary of Strategic Initiatives Timeline and Implementation Strategic
Peirce College Summary of 2015-2018 Strategic Plan Contents Strategic Planning Process Vision and Mission Target Market Value Proposition Summary of Strategic Initiatives Timeline and Implementation Strategic
For Incentive Pay (International Public Management Association for Human Resources)
 For Incentive Pay (International Public Management Association for Human Resources) Getting Incentive Pay Just Right for the Public Sector By Patrick J. Cole, SPHR Faced with challenges to do more with
For Incentive Pay (International Public Management Association for Human Resources) Getting Incentive Pay Just Right for the Public Sector By Patrick J. Cole, SPHR Faced with challenges to do more with
BY KARI VAN DYKE VICE PRESIDENT & SALES LEADER RICHARDSON
 BY KARI VAN DYKE VICE PRESIDENT & SALES LEADER All the time, money, and effort that go into hiring sales employees can be wasted if the right program isn t in place to bring them on board quickly and effectively.
BY KARI VAN DYKE VICE PRESIDENT & SALES LEADER All the time, money, and effort that go into hiring sales employees can be wasted if the right program isn t in place to bring them on board quickly and effectively.
Final. North Carolina Procurement Transformation. Governance Model March 11, 2011
 North Carolina Procurement Transformation Governance Model March 11, 2011 Executive Summary Design Approach Process Governance Model Overview Recommended Governance Structure Recommended Governance Processes
North Carolina Procurement Transformation Governance Model March 11, 2011 Executive Summary Design Approach Process Governance Model Overview Recommended Governance Structure Recommended Governance Processes
Collaboration Tools: Innovation Management and Solution Infusion Benefits
 2007 NASCIO Recognition Awards Information Communications Technology Innovations Collaboration Tools: Innovation Management and Solution Infusion Benefits Michigan Department of Information Technology
2007 NASCIO Recognition Awards Information Communications Technology Innovations Collaboration Tools: Innovation Management and Solution Infusion Benefits Michigan Department of Information Technology
Defining the Modern Marketer From Real to Ideal Flourishes in The Digital Age
 Defining the Modern Marketer From Real to Ideal Flourishes in The Digital Age In partnership with CONTENTS 1. Who is the modern marketer? 2. The ideal : An honest assessment 3. Coping with a changing world
Defining the Modern Marketer From Real to Ideal Flourishes in The Digital Age In partnership with CONTENTS 1. Who is the modern marketer? 2. The ideal : An honest assessment 3. Coping with a changing world
The what, why, when and how of Strategic Workforce Planning
 Future-proof your workforce The what, why, when and how of Strategic Workforce Planning Susan DeFazio Table of contents 3 Introduction 5 What does good SWP look like? 7 Why SWP matters to risk & operational
Future-proof your workforce The what, why, when and how of Strategic Workforce Planning Susan DeFazio Table of contents 3 Introduction 5 What does good SWP look like? 7 Why SWP matters to risk & operational
The Role of Feedback Management in Becoming Customer Centric
 A Customer Centricity White Paper 5 Old Coach Road Hudson, NH 03051 603-491-7948 www.customercentricity.biz The Role of Feedback Management in Becoming Customer Centric By Stewart Nash QuestBack Boston
A Customer Centricity White Paper 5 Old Coach Road Hudson, NH 03051 603-491-7948 www.customercentricity.biz The Role of Feedback Management in Becoming Customer Centric By Stewart Nash QuestBack Boston
THE ORGANIZER S ROLE IN DRIVING EXHIBITOR ROI A Consultative Approach
 7 Hendrickson Avenue, Red Bank, NJ 07701 800.224.3170 732.741.5704 Fax www.exhibitsurveys.com White Paper THE ORGANIZER S ROLE IN DRIVING EXHIBITOR ROI A Consultative Approach Prepared for the 2014 Exhibition
7 Hendrickson Avenue, Red Bank, NJ 07701 800.224.3170 732.741.5704 Fax www.exhibitsurveys.com White Paper THE ORGANIZER S ROLE IN DRIVING EXHIBITOR ROI A Consultative Approach Prepared for the 2014 Exhibition
Compensation accounts for nearly 70 percent
 THE BUSINESS CASE FOR COMPENSATION TECHNOLOGY Compensation accounts for nearly 70 percent of operating expenses for most organizations, 1 and is one of the main reasons employees join and leave organizations.
THE BUSINESS CASE FOR COMPENSATION TECHNOLOGY Compensation accounts for nearly 70 percent of operating expenses for most organizations, 1 and is one of the main reasons employees join and leave organizations.
Business Intelligence
 Transforming Information into Business Intelligence Solutions Business Intelligence Client Challenges The ability to make fast, reliable decisions based on accurate and usable information is essential
Transforming Information into Business Intelligence Solutions Business Intelligence Client Challenges The ability to make fast, reliable decisions based on accurate and usable information is essential
e-training Transition Project
 e-training Transition Project Phase II e-training Communications Guide August 24, 2005 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Communications Guide for the Phase II e-training Transition August 24,
e-training Transition Project Phase II e-training Communications Guide August 24, 2005 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Communications Guide for the Phase II e-training Transition August 24,
Envisioning a Future for Public Health Knowledge Management
 Envisioning a Future for Public Health Knowledge Management By Cadence Group Public health today faces challenges and opportunities of a degree that it has never seen before. Never before have methods
Envisioning a Future for Public Health Knowledge Management By Cadence Group Public health today faces challenges and opportunities of a degree that it has never seen before. Never before have methods
Strategic Human Resource Management Catherine Truss, David Mankin & Clare Kelliher
 Catherine Truss, David Mankin & Clare Kelliher Oxford University Press (2012) ISBN: 978-0199583065 Theme of the Book What makes a good HR strategy and how does one develop it? These are just two of the
Catherine Truss, David Mankin & Clare Kelliher Oxford University Press (2012) ISBN: 978-0199583065 Theme of the Book What makes a good HR strategy and how does one develop it? These are just two of the
Career Management. Making It Work for Employees and Employers
 Career Management Making It Work for Employees and Employers Stuck in neutral. That s how many employees around the world would describe their career. In fact, according to the 2014 Global Workforce Study,
Career Management Making It Work for Employees and Employers Stuck in neutral. That s how many employees around the world would describe their career. In fact, according to the 2014 Global Workforce Study,
Creating Customized Training for a Leading Insurance Company
 Customer Success Stories TEKsystems Global Services Creating Customized Training for a Leading Insurance Company FINANCIAL SERVICES TRAINING AND EDUCATION SERVICES Executive Summary A Fortune 50 insurance
Customer Success Stories TEKsystems Global Services Creating Customized Training for a Leading Insurance Company FINANCIAL SERVICES TRAINING AND EDUCATION SERVICES Executive Summary A Fortune 50 insurance
A guide to strategic human resource planning
 A guide to strategic human resource planning By Workinfo.com, www.workinfo.com 1. Introduction A comprehensive Human Resource Strategy plays a vital role in the achievement of an organisation's overall
A guide to strategic human resource planning By Workinfo.com, www.workinfo.com 1. Introduction A comprehensive Human Resource Strategy plays a vital role in the achievement of an organisation's overall
Pharmaceutical Sales Certificate
 Pharmaceutical Sales Certificate Target Audience Medical representatives Objective The objective of this program is to provide the necessary skills and knowledge needed to succeed as medical representatives.
Pharmaceutical Sales Certificate Target Audience Medical representatives Objective The objective of this program is to provide the necessary skills and knowledge needed to succeed as medical representatives.
2015 South African Cloud Based Solutions to the Contact Centre Product Leadership Award
 2015 2015 South African Cloud Based Solutions to the Contact Centre Product Leadership Award Contents Background and Company Performance... 3 Industry Challenges... 3 Implementation Excellence... 4 Product
2015 2015 South African Cloud Based Solutions to the Contact Centre Product Leadership Award Contents Background and Company Performance... 3 Industry Challenges... 3 Implementation Excellence... 4 Product
The Leader s Edge. How Best Practices Programs Can Be Used Most Effectively to Support the Growth of Women Leaders
 The Leader s Edge How Best Practices Programs Can Be Used Most Effectively to Support the Growth of Women Leaders The Leaders Edge research study completed in February, 2004 demonstrates the need for companies
The Leader s Edge How Best Practices Programs Can Be Used Most Effectively to Support the Growth of Women Leaders The Leaders Edge research study completed in February, 2004 demonstrates the need for companies
Talent Management: A Critical Review
 IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM) e-issn: 2278-487X, p-issn: 2319-7668. Volume 16, Issue 9.Ver. I (Sep. 2014), PP 50-54 Talent Management: A Critical Review Prathigadapa Sireesha, Leela
IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM) e-issn: 2278-487X, p-issn: 2319-7668. Volume 16, Issue 9.Ver. I (Sep. 2014), PP 50-54 Talent Management: A Critical Review Prathigadapa Sireesha, Leela
Business Process Outsourcing Considerations with a Focus on the Customer Experience
 Educational Whitepaper Business Process Outsourcing Considerations with a Focus on the Customer Experience www.vertek.com Business Process Outsourcing Considerations with a Focus on the Customer Experience
Educational Whitepaper Business Process Outsourcing Considerations with a Focus on the Customer Experience www.vertek.com Business Process Outsourcing Considerations with a Focus on the Customer Experience
