BioSciences. Peripheral Blood Smear Preparation. Blood Smear Preparation Materials
|
|
|
- Marilyn Melton
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PolyFacts Vol. 5 No. 1 BioSciences Use the Wright Stain High Quality StainRITE Ready-to-Use Stains for Hematology Peripheral blood smear (peripheral blood film) is a glass microscope slide coated with a thin layer of venous blood on one side that has been air dried and fixed with methanol. A Romanowsky stain variant such as StainRITE Wright Stain (Cat. #24986) is used primarily to stain peripheral blood smears and bone marrow aspirates and examined under a microscope. Microscope examination of the peripheral blood smear is only one consideration, the second and third are peripheral blood counts and red blood cell (RBC) indices, respectively. These three tools evaluate hematological disorders as well. Peripheral blood smears are stained with StainRITE Wright Giemsa (Cat. #24985), StainRITE Wright Stain (Cat. #24986) and StainRITE MGG (Cat. #24981). These stains are utilized to identify different blood disorders in RBC, white blood cells (WBC) and platelet population of cells. Morphologic abnormalities of peripheral blood cells are discovered by microscopic examination with the oil immersion lens of well-prepared peripheral blood smear films stained with Wright s stain. In the interpretation of the morphology of RBCs, an examiner concentrates on areas of red cells that are singly spread out. The peripheral blood smear is very important because it validates and supplements information provided by automated hematology analyzers ( blood cell counters ). Blood StainRITE Wright Stain, 100x (Cat. #24986) cell counters are precise with the classification of abnormal cells, however, it is required that a trained microscopist, peripheral blood smear and light microscope be used when a specimen is flagged by the hematology analyzer in order to obtain an accurate conclusion. News Views Insights INSIDE THIS ISSUE Featured Product 1 Use the Wright Stain: High Quality StainRITE Ready-to-Use Stains for Hematology Science Solutions 4 Fix Lymphoreticular Myeloid, Lymph Nodes and Bone Marrow Tissues Product Spotlight 5 Gold Standard Series: Gill s Hematoxylins #1, 2 & 3 Additional Lab Products for Hematology Staining 5 Flash Dip FNA / H. Pylori Kit Sudan Black B, C.I Terry s Polychrome Methylene Blue Periodic Acid Schiff s (PAS) Stain Leishman Stain In addition to providing cell counts and graphical displays of the information recovered, these instruments also provide a warning that atypical cells were found and provide a presumptive identification of the abnormality. The instrument operator reviews the information from each specimen, to determine if a smear preparation and light microscopy will be necessary. If a specimen is not flagged by the blood cell count analyzer and does not require a microscopic evaluation the information is immediately released to the clinician. StainRITE Wright Giemsa, Stain, 100x (Cat. #24985) The wedge slide, ( push slide ) technique developed by Maxwell Wintrobe remains the standard method for the preparation of peripheral blood smears (films). The following procedure is used to prepare a peripheral smear. Peripheral Blood Smear Preparation Blood Smear Preparation Materials StainRITE May-Grünwald Giemsa Stain, 100x (Cat. #24981) Sterilized lancet or needle 20 clean microscope slides and coverslips Canada balsam 95% ethyl or methyl alcohol Distilled water Giemsa stain with buffer and protocol Microscope 200x or greater Immersion Oil.... Continued on page 2
2 .... Use the Wright Stain, continued Taking the blood Cleanse finger with a sterile lancet and puncture fingertip. Keep all the materials needed ready and protected from dust, particularly the clean microscope slides. APPROACHING ADHESION ADVANCEMENT drop of blood Bring edge of another slide in contact with the drop and allow the drop to bank evenly behind the spreader. The angle between the two slides has to be 30º - 40º. Push to the left in a smooth quick motion. The smear should cover about half the slide. It is important that the quantity of blood is not excessive otherwise the red cells could hide the leukocytes. If you succeed in making a gradual transition from thick to thin in your smear, you should get a zone with a satisfactory distribution of cells. With a single drop of blood, you can make several smears. Perform multiple smears. They are not always successful but with multiple attempts one well prepared smear should be achieved. To avoid producing clots, you must make each smear with fresh blood straight after having deposited it. It is useful to be helped by another person where one deposits the blood and the other makes the smears. With a microscope, observe to check if smears are properly made. Red cells must not overlap each other, nor be so scarce that they are too spread out. Place a 1 x 3 glass microscope slide with a frosted end on a flat surface (usually the counter top of a laboratory bench). Attach label on the slide or write patient name, specimen identification number and date of preparation on the frosted surface. Place 2-3mm drop of blood approximately 1/4 from the frosted slide with a wooden applicator stick or glass capillary tube. Hold the slide by the narrow side between thumb and forefinger of one hand at the end farthest from the frosted end. Grasp a second slide ( spreader slide ) between thumb and forefinger of the other hand at the frosted end. Place edge of the spreader slide on the lower slide in front of the drop of blood (side farthest from the frosted end). Pull spreader slide toward the frosted end until it touches the drop of blood. Permit the blood to spread by capillary motion until it almost reaches the edges of the spreader slide. Push spreader slide forward at a 30º angle with a rapid even motion. Let the weight of the slide do the work or place a small drop of blood near an end of a slide. Notes: If you observe the smear as it is after fixing, you will see very little because all cells are very transparent. The erythrocytes are slightly visible, but the leukocytes are too pale, almost invisible and you will not see anything inside them. To be able to observe and recognize the different kinds of leukocyte, you must stain them. Featured StainRITE Ready-to-Use Hematology Stains StainRITE Wright-Giemsa Stain Solution StainRITE Wright-Giemsa Stain Phosphate Buffer ph 6.8 StainRITE Wright Stain Solution StainRITE Wright Stain Phosphate Buffer ph 6.8 StainRITE May-Grünwald Stain Solution StainRITE May-Grünwald Stain Phosphate Buffer ph 7.2 StainRITE Giemsa Stain (for May-Grünwald) 1L, 10L, 20L 100ml, 400ml StainRITE Stain Results Erythrocytes Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils Eosinophils Cytoplasm Basophils Lymphocytes and Monocytes Platelets StainRITE Wright-Giemsa Stain Solution (Cat. #24985) light pink to moderate purple, not grey or blue blue to dark blue to purple nuclei reddish purple lilac granules, pale pink cytoplasm blue to dark blue to purple nuclei, red to orange-red granules, blue cytoplasm purple to dark blue to black nuclei, purple granules dark purple nuclei, sky blue cytoplasm violet to purple granules StainRITE Wright Stain Solution (Cat. #24986) yellowish red dark blue nuclei, reddish lilac granulates, pale pink cytoplasm blue nuclei, red to orange-red granules, blue cytoplasm purple to dark blue nuclei, dark purple granules dark purple nuclei, sky blue cytoplasm violet to purple granules StainRITE May-Grünwald Stain Solution (Cat. #24981) light pink to moderate purple, not grey or blue blue to dark blue to purple nuclei, reddish purple lilac granules, pale pink cytoplasm blue to dark blue to purple nuclei, red to orangered granules, blue cytoplasm purple to dark blue to black nuclei, purple granules dark purple nuclei, sky blue cytoplasm violet to purple granules 2
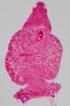
3 .... Use the Wright Stain, continued How are StainRITE Blood Stains Used? A peripheral blood smear was once prepared on nearly everyone who had a complete blood count (CBC) performed. In smaller labs blood cell counts are still done manually, while larger labs use automated blood cell counting instruments. If the presence of abnormal WBCs, RBCs or platelets is suspected a blood smear examined by a trained eye is still the best method for definitively evaluating and identifying immature and abnormal cells. There are many diseases, disorders and deficiencies that effect the blood cells function, lifespan, type and amount produced. Although usually only normal mature cells are released into the bloodstream, circumstances can force the bone marrow to release immature and/or malformed cells into the circulation. When is a Blood Smear Ordered? A Blood smear is primarily ordered to evaluate blood cell populations when there s a differential in the CBC performed with an automated blood cell counter indicating the presence of abnormal or immature cells. It may also be performed when a doctor suspects a deficiency, disease or disorder that is affecting blood cell production, such as anemias, abnormal production of cells or increased cell destruction. A blood smear may also be ordered when a patient is being treated or monitored for a blood cell-related disease. What is a Bone Marrow Aspirate / Biopsy? Bone marrow biopsy and aspiration procedures provide information about the status and capability for blood cell production. It is not routinely ordered, in fact the majority of people will never have one done. A bone marrow aspiration and/or biopsy is ordered to help evaluate blood cell production, diagnose leukemia, bone marrow disorder and a variety of stages of cancer that have spread into the marrow and to determine the cause of severe anemia. Severe anemia occurs due to decreased RBC production, increased loss, abnormal RBC production and/or to a vitamin or mineral deficiency or excess. Conditions that affect the bone marrow can affect the number, mixture and maturity of the cells and its fibrous structure. A bone marrow sample may also be evaluated and cultured for the presence of microorganisms such as fungus, bacteria and mycobacteria (such as that which causes Tuberculosis, TB) when the patient has a fever of an unknown origin. Additional marrow testing may be ordered when it is suspected that the patient has a chromosomal abnormality or disorder associated with iron storage that may cause iron to accumulate in the marrow. In histology a Trichrome Stain (Cat. #24205, #25088), Retic Stain (Cat. #25093) and Iron Stain (Cat. #24199) are also done. When a person is being treated for cancer, a bone marrow aspiration/ biopsy may be ordered to evaluate the response to therapy. It can determine whether suppressed marrow function is beginning to return to normal. Photo Courtesy of Biopsy of foot lesion: area of extended dermal necrosis with inflammatory infiltration. In the center PAS (periodic acid- Schiff stain) positive septate hyphae branching at an acute angle, x400 A CBC and reticulocyte are frequently ordered along with the bone marrow aspiration/biopsy. The results are used to help evaluate cell production in the marrow and compared to current cell populations in the blood. When is a Bone Marrow Aspirate / Biopsy Ordered? Bone marrow aspiration/biopsy may be ordered as a diagnostic procedure, for example when one of the following blood disorders is suspected: Aplastic Anemia Acute Leukemia Myelodysplastic Syndrome Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Myelofibrosis and Essential Thrombocythemia Multiple Myeloma Severe Thrombocytopenia and/or anemia and/or neutropenia It may be ordered when staging certain cancers. Staging is a careful and thorough examination and classification of how far the cancer has spread and what body organs are involved. These may include: Hodgkin s and Non-Hodgkin s Lymphomas Small Cell Carcinoma of the Lung (not frequently done anymore) It may be ordered for culturing in some cases, such as: Persistent fever is present in HIV/AIDS or other patients with a weak immune system, sometimes a PAS, GMS, Gram Stain is done in histology In patients suspected of having infectious diseases such as Brucellosis or Typhoid Fever A bone marrow biopsy and aspiration may also be ordered at intervals when a person is being treated for a cancer to evaluate whether marrow function is being suppressed, and if it is, when its function begins to recover. Supplementary Staining Products Gomori s Trichrome Stain Kit Masson Trichrome Stain Kit Retic Stain - Gordon & Sweet s Method Reticular Fibers Prussian Blue Reaction Demonstration of Iron Grocott Methenamine Silver Stain (GMS) for Fungus and PCP - Regular Room Temperature & Microwave Kit Kit to demonstrate ferric iron and ferritin. Not a true staining technique but rather a histochemical reaction. Protein is split off by hydrochloric acid, allowing the potassium ferrocyanide to combine with the ferric iron. Prussian Blue Reaction Demonstration of Iron (Cat. #24199) Staining of human kidney tissue, 100x 3
4 400 Valley Road Warrington, PA PolyFacts Vol. 5 No. 1 BE OUR NEXT FEATURED AUTHOR Let us feature your article in the next PolyFacts issue. Showcase your research and experience using Polysciences products. If you have any suggestions or want to be a part of PolyFacts future issues please us at: marketing@polysciences.com BioSciences POLYSCIENCES Get it done Wright! C ATA L O G a Request py! o c E E R F Processing & Embedding Staining, Histology, Cytology Special Stains & Reagents Electrophoresis Products Microbiology Products Plus many others.. Visit StainRITE Ready-to-Use Stains for Hematology U.S. Corporate Headquarters 400 Valley Road, Warrington, PA (800) / (215) Fax 1(800) info@polysciences.com Polysciences Europe GmbH Handelsstrasse 3 D Eppelheim, Germany +(49) Fax +(49) info@polysciences.de
5 Science Solutions Fix Lymphoreticular Myeloid, Lymph Nodes and Bone Marrow Tissues Fixation is the most influential factor in the long series of steps between grossing the tissue and coverslipping the stained slide. Nearly all the steps can be reversed if a problem occurs. Tissue can be reverse processed and reprocessed. Most stains can be removed and restained to improve intensity. The one step in which errors are permanent and can not be undone is fixation. Understanding the importance of fixation is crucial to producing quality slides and interpreting results. For over 45 years, Polysciences, Inc. has set the standard for consistent, high quality fixatives and reagents. Our Acetic Acid Formalin for Bone Marrow and Lymph Nodes Fixative is designed to fix lymphoreticular myeloid, lymph nodes and bone marrow tissues. Procedure for bone marrow biopsies using Polysciences Acetic Acid Formalin for Bone Marrow & Lymph Node Fixative Aspirate 1. Allow aspirate to clot in petri dish 2. Transfer clot to specimen container filled with 10% NBF 3. Process as usual Microtoming 1. Cut both aspirate and bone cores at 2-3 microns. 2. Place 3 levels on one slide. Cut an extra slide of the last level and set aside on the back of the water bath in case a special stain is requested Bone Core Fixation 1. Immediately fix in Acetic Acid Formalin for Bone Marrow and Lymph Node Fixative (Cat. #24910) for a minimum of one hour 2. Fix overnight if brought in later than 2 hours before end of work day Decalcify first thing in the morning Bone Core Decalcification 1. Place fixed core and label in a plastic cassette. Super Decalcifier II: Heavy Duty (Cat. #24887) - will discolor metal. Decalcify in Deli-Cal Block Solution (Cat. #24900) for minutes. Do not leave periodically check 2. Test for decalcification by gently checking for pliability 3. Rinse in running tap water for approximately 2 minutes Processing 1. If biopsy arrived in afternoon, process with the rest of the specimens 2. If the biopsy is decalcified in the morning, hand process in 120cc plastic specimen cups, 15 minutes each container, start with 70% ethanol / speed process through processor, 15 minutes each station with heat and vacuum, starting with the first dehydrant station Staining 1. Hematoxylin approximately 5 minutes. Bone core 1 minute (check under the microscope before counterstaining) 2. Eosin for 10 dips, dehydrate, clear and coverslip Gold Standard Series: Acetic Acid Formalin for Bone Marrow & Lymph Node Fixative Designed to fix lymphoreticular myeloid, lymph nodes and bone marrow tissues Acetic Acid Formalin for Bone Marrow and Lymph Node Fixative 500ml, 1L Note: Over decalcification will result in poor or indifferent histological detail and staining characteristics. Reference: Adapted from Becky Scholes, HTL,MT(ASCP) H.I.S.T.O., The Official Newsletter of the Iowa Society for Histotechnology, Tech Tip Super Decalcifier I: Delicate Super Decalcifier I - Delicate is recommended for mildly calcified specimens such as bone marrow biopsies (core), and specimens that require fast diagnostic work such as immunohistochemistry, cytochemistry and special stain procedures. Ready-to-Use formula produces enhanced nuclear detail in both human and animal tissue. Environmentally safe and biodegradable. Save Time - Decalcify in as little as 3 hours! Ready-to-Use - for human and animal tissue Recommended for IHC, special stains and routine stains Enhanced nuclear detail Environmentally safe and biodegradable Super Decalcifier I: Delicate 500ml, 1L, Case (6 x liter) Human Degenerative Joint Disease, decalcified with Super Decalcifier I: Delicate and stained with H & E, 10X 4
6 Product Spotlight Gold Standard Series Gill s Hematoxylins Gill s Hematoxylin #1, for Cytology Formulated for routine cytology staining. This single strength formula optimally stains gynecological and nongynecological specimens. Can be used for staining filters and membranes. General purpose nuclear stain, progressive type. Used with hematoxylin and eosin staining. Gill s Hematoxylin #2, double strength for Histology & Cytology Used when a stronger or darker nuclear stain is required for cytology or immuno-histochemistry (IHC) conterstaining. Gill s #2 formulation is a double strength mixture and stains darker and more quickly than Gill s #1. General purpose nuclear stain, progressive type. Used with hematoxylin and eosin staining. Gill s Hematoxylin #3, triple strength for Histology Appropriate for routine histology staining where a darker nuclear stain is desired. This is a triple strength formula requiring shorter staining times. Formula is very stable and does not require filtering prior to each use. General purpose nuclear stain, progressive type. Used with hematoxylin and eosin staining. Gill s Hematoxylin Products Gill s Hematoxylin #1 Gill s Hematoxylin #2, double strength Gill s Hematoxylin #3, triple strength For our full line of Hematoxylin Eosin Bluing products, visit 500ml, 1000ml 500ml, 1000ml 500ml, 1000ml Cheek, Gill s Hematoxylin #1, 100X Breast, Gill s Hematoxylin #2, 100x Pancreas, Gill s Hematoxylin #3 and Scott s Eosin Y, 100x Additional Lab Products for Hematology Staining Flash Dip FNA / H. Pylori Kit High quality, rapid turnaround staining kit, serves many purposes in a cost conscious laboratory environment. Flash Dip is an optimal hematology stain for differential assessment of rapid blood smears, as well as for detecting H. pylori microorganism. Useful in applications such as: Fine Needle Aspirations, Frozen Sections, Blood Smears, Cytological Specimens, Bone Marrow Biopsies, Touch Preps and Microorganism Detection. Interprets result in less than 15 seconds! Sudan Black B, C.I , Certified This stain is specific for lipids. Sudan black B stains a variety of lipids, including neutral fat, phospholipids and sterols. Normal granulocyte precursors show increased sudanophilia that corresponds roughly to the number of granules. Promyelocytes contain a few sudanophilic granules and mature polymorphonuclear neutrophils contain large numbers of sudanophilic granules. Eosinophil granules are also sudanophilic, especially on the edge. Monocytes may be unstained or may contain a few discrete sudanophilic granules. Macrophages often contain sudanophilic material. In general, Sudan black B stain is similar to the peroxidase reaction in distinguishing acute lymphocytic leukemia from acute myelogenous leukemia. Periodic Acid Schiff s (PAS) Stain This reaction stains polysaccharides. Periodic acid oxidizes carbohydrates and similar compounds to aldehydes. Aldehydes can then react with the Schiff reagent (leukofuchsin) to release fuchsin and stain the cellular components containing oxidizable compounds. A variety of intracellular compounds react with the PAS reagents, but in the blood and marrow cells glycogen is the most abundant compound, as evidenced by amylase digestion that blocks the staining. In blood from samples, the cytoplasm of polymorphonuclear leukocytes stains intensely pink or red, with granular appearance in some cells. Monocyte cytoplasm stains faintly pink and may contain fine or coarse granules. Erythrocytes do not stain. Platelets stain intensely. In the normal marrow, the earliest granulocyte precursors do not stain. Cytoplasmic staining increases with increasing maturity of the granulocytic cells. The PAS reaction is helpful in the diagnosis of some cases of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and some subtypes of acute myeloid leukemia. Leishman Stain For staining bone marrow and blood smears to identify leucocytes, malarial parasites and trypanosomas. Terry s Polychrome Methylene Blue 2% Aqueous Excellent dye for nuclear and nucleolar details. Can be used to demonstrate erythrocyte alterations/inclusions and some erythrocyte parasites, as well as to visualize reticulocytes. Methylene blue is different from that in Romanowsky stains. In order to stain a slide with methylene blue a drop of stain is placed on a coverslip. The coverslip is then placed on an unfixed blood smear. An alternative method is to mix some stain with fresh blood before a blood smear is made. Additional Lab Products for Hematology Staining Flash Dip / H.Pylori Stain Kit Sudan Black B, C.I , Certified Terry s Polychrome Methylene Blue 2% aqueous Periodic Acid Schiff s (PAS) Stain Leishman Stain 250ml, 500ml 25g 470ml 25g 5
STAINING OF PBF AND INTERPRETATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL RED CELL MORPHOLOGY
 9 STAINING OF PBF AND INTERPRETATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL RED CELL MORPHOLOGY 9.1 INTRODUCTION A peripheral blood smear (peripheral blood film) is a glass microscope slide coated on one side with a thin
9 STAINING OF PBF AND INTERPRETATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL RED CELL MORPHOLOGY 9.1 INTRODUCTION A peripheral blood smear (peripheral blood film) is a glass microscope slide coated on one side with a thin
Preparation of Blood Films
 Preparation of Blood Films Principle: Blood film enables us to evaluate WBC, RBC, and PLT morphology, also, allows us to perform differential WBC count, furthermore estimation of WBC and platelets counts
Preparation of Blood Films Principle: Blood film enables us to evaluate WBC, RBC, and PLT morphology, also, allows us to perform differential WBC count, furthermore estimation of WBC and platelets counts
Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points)
 Pierce College Putman/Biol 242 Name: Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points) Reference: Marieb & Mitchell 9 th Ed: 29A (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7); 10 th Ed: Exercise 29 (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7). Pierce College
Pierce College Putman/Biol 242 Name: Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points) Reference: Marieb & Mitchell 9 th Ed: 29A (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7); 10 th Ed: Exercise 29 (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7). Pierce College
BLOOD FILM STAINING EFFECTS
 An Educational Supplement prepared by ALQEP May 2004 Introduction The stained peripheral blood film is one of the world s most widely and frequently used tests. Since its introduction in the late nineteenth
An Educational Supplement prepared by ALQEP May 2004 Introduction The stained peripheral blood film is one of the world s most widely and frequently used tests. Since its introduction in the late nineteenth
LABORATORY 2 Staining and processing of blood parasites Differential counts of leukocytes (giemsa stains)
 LABORATORY 2 Staining and processing of blood parasites Differential counts of leukocytes (giemsa stains) SPECIMENS TO BE STAINED 1. Thin and thick blood smears from a patient returning from Africa - case
LABORATORY 2 Staining and processing of blood parasites Differential counts of leukocytes (giemsa stains) SPECIMENS TO BE STAINED 1. Thin and thick blood smears from a patient returning from Africa - case
GIEMSA STAIN PREANALYTICAL CONSIDERATIONS
 GIEMSA STAIN PREANALYTICAL CONSIDERATIONS I. Principle Giemsa stain is used to differentiate nuclear and/or cytoplasmic morphology of platelets, RBCs, WBCs, and parasites (1,2). The most dependable stain
GIEMSA STAIN PREANALYTICAL CONSIDERATIONS I. Principle Giemsa stain is used to differentiate nuclear and/or cytoplasmic morphology of platelets, RBCs, WBCs, and parasites (1,2). The most dependable stain
White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes
 Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Granulocytes vs. Agranulocytes
 Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
Exercise 9: Blood. Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826.
 Exercise 9: Blood Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826. Blood Typing The membranes of human red blood cells (RBCs) contain a variety of cell surface proteins called
Exercise 9: Blood Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826. Blood Typing The membranes of human red blood cells (RBCs) contain a variety of cell surface proteins called
serology Agglutination Techniques and Blood Cell Identification
 Serology: Agglutination Techniques and Blood Cell Identification S erology is a branch of immunology dealing with techniques to identify and measure antigens, and to detect serum antibodies. Agglutination
Serology: Agglutination Techniques and Blood Cell Identification S erology is a branch of immunology dealing with techniques to identify and measure antigens, and to detect serum antibodies. Agglutination
A simple differential stain of blood smears using black Quink
 A simple differential stain of blood smears using black Quink Chris Thomas, 3 Hall End, Milton, Cambridge CB24 6AQ, chris@miltoncontact.com Published in: Micscape http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/artsep15/ct-quink-blood-stain.pdf
A simple differential stain of blood smears using black Quink Chris Thomas, 3 Hall End, Milton, Cambridge CB24 6AQ, chris@miltoncontact.com Published in: Micscape http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/artsep15/ct-quink-blood-stain.pdf
ABO-Rh Blood Typing Using Neo/BLOOD
 ABO-Rh Blood Typing Using Neo/BLOOD Objectives Determine the ABO and Rh blood type of unknown simulated blood samples. Prepare a simulated blood smear. Examine a prepared blood smear under the microscope
ABO-Rh Blood Typing Using Neo/BLOOD Objectives Determine the ABO and Rh blood type of unknown simulated blood samples. Prepare a simulated blood smear. Examine a prepared blood smear under the microscope
Blood. Functions of Blood. Components of Blood. Transporting. Distributing body heat. A type of connective tissue. Formed elements.
 Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
Laboratory 12 Blood Cells
 Laboratory 12 Blood Cells Objectives: Identify microscopically each of the following: erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs), the five types of leukocytes (white blood cells or WBCs), and thrombocytes
Laboratory 12 Blood Cells Objectives: Identify microscopically each of the following: erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs), the five types of leukocytes (white blood cells or WBCs), and thrombocytes
ABO-Rh Blood Typing With Synthetic Blood
 70-0101 ABO-Rh Blood Typing With Synthetic Blood Teacher s Manual World-Class Support for Science & Math The ability to type blood is an invaluable tool in the fields of medicine and criminology. Using
70-0101 ABO-Rh Blood Typing With Synthetic Blood Teacher s Manual World-Class Support for Science & Math The ability to type blood is an invaluable tool in the fields of medicine and criminology. Using
SEED Haematology. Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development February 2013
 SEED Haematology Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development February 2013 The role of the peripheral blood smear in the modern haematology laboratory Automated haematology cell counting The laboratory
SEED Haematology Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development February 2013 The role of the peripheral blood smear in the modern haematology laboratory Automated haematology cell counting The laboratory
MANUAL PLATELET COUNT
 MANUAL PLATELET COUNT Principle Whole blood is diluted with a 1% ammonium oxalate solution. The isotonic balance of the diluent is such that all erythrocytes are lysed while the leukocytes, platelets,
MANUAL PLATELET COUNT Principle Whole blood is diluted with a 1% ammonium oxalate solution. The isotonic balance of the diluent is such that all erythrocytes are lysed while the leukocytes, platelets,
Leukemias and Lymphomas: A primer
 Leukemias and Lymphomas: A primer Normal blood contains circulating white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets 700 red cells (oxygen) 1 white cell Neutrophils (60%) bacterial infection Lymphocytes
Leukemias and Lymphomas: A primer Normal blood contains circulating white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets 700 red cells (oxygen) 1 white cell Neutrophils (60%) bacterial infection Lymphocytes
HISTOLOGY LABORATORY. Microscope Orientation and Blood Smear Lab
 HISTOLOGY LABORATORY Microscope Orientation and Blood Smear Lab For practicing how to use the microscope DO NOT use the blood smear slide (it is too boring for the lower mags). Use a slide from the white
HISTOLOGY LABORATORY Microscope Orientation and Blood Smear Lab For practicing how to use the microscope DO NOT use the blood smear slide (it is too boring for the lower mags). Use a slide from the white
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 1 Urine Microscopic Examination The Complete Urinalysis Physical properties already covered Chemical analysis in the next unit Microscopic our current focus
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 1 Urine Microscopic Examination The Complete Urinalysis Physical properties already covered Chemical analysis in the next unit Microscopic our current focus
GLOSSARY of STAINS Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Periodic acid-schiff s (PAS) Masson s Trichrome Stain Gomori Trichrome Stain Silver Salts
 GLOSSARY of STAINS Your study and comprehension of the slides in your collection will be enhanced if you know something about the staining methods used in their preparation. The following list includes
GLOSSARY of STAINS Your study and comprehension of the slides in your collection will be enhanced if you know something about the staining methods used in their preparation. The following list includes
WHICH SAMPLES SHOULD BE SUBMITTED WHEN LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA IS SUSPECTED?
 WHICH SAMPLES SHOULD BE SUBMITTED WHEN LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA IS SUSPECTED? Which test should be submitted? The answer to this depends on the clinical signs, and the diagnostic question you are asking. If
WHICH SAMPLES SHOULD BE SUBMITTED WHEN LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA IS SUSPECTED? Which test should be submitted? The answer to this depends on the clinical signs, and the diagnostic question you are asking. If
Collect and label sample according to standard protocols. Gently invert tube 8-10 times immediately after draw. DO NOT SHAKE. Do not centrifuge.
 Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
Cardiovascular System. Blood Components
 Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
LAB: Blood Exploration
 Name: Period: Date: LAB: Blood Exploration Introduction A liquid called plasma makes up about half (55%) of the content of blood. Plasma contains proteins that help blood to clot, transport substances
Name: Period: Date: LAB: Blood Exploration Introduction A liquid called plasma makes up about half (55%) of the content of blood. Plasma contains proteins that help blood to clot, transport substances
CONTROL: For staining fungus; use a known positive such as those used for the GMS. Use skin, aorta or normal liver for positive PAS staining.
 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY - HISTOLOGY Date: STAINING MANUAL - CARBOHYDRATES Page: 1 of 3 PAS - McMANNUS' PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF'S - GLYCOGEN PURPOSE: Glycogen is present in skin, liver, parathyroid glands and skeletal
SURGICAL PATHOLOGY - HISTOLOGY Date: STAINING MANUAL - CARBOHYDRATES Page: 1 of 3 PAS - McMANNUS' PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF'S - GLYCOGEN PURPOSE: Glycogen is present in skin, liver, parathyroid glands and skeletal
Special histochemical stains are routinely used for the interpretation
 Technical Articles Special Stains in Interpretation of Liver Biopsies Rashmil Saxena, BFA, HT(ASCP) CM Division of Transplantation Department of Surgery, Indiana University Indianapolis, IN, USA Special
Technical Articles Special Stains in Interpretation of Liver Biopsies Rashmil Saxena, BFA, HT(ASCP) CM Division of Transplantation Department of Surgery, Indiana University Indianapolis, IN, USA Special
What is special about a stain, and why do we call some stains
 Technical Articles Evolution of Use of Special Stains Alton D. Floyd, PhD Independent Consultant Edwardsburg, MI, USA What is special about a stain, and why do we call some stains special? We all think
Technical Articles Evolution of Use of Special Stains Alton D. Floyd, PhD Independent Consultant Edwardsburg, MI, USA What is special about a stain, and why do we call some stains special? We all think
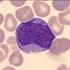
Hematology Morphology Critique
 Survey Slide: History: 60-year-old female presenting with pneumonia Further Laboratory Data: Hgb : 90 g/l RBC : 2.92 10 12 /L Hct : 0.25 L/L MCV : 87 fl MCH : 30.8 pg MCHC : 355 g/l RDW : 17.7 % WBC :
Survey Slide: History: 60-year-old female presenting with pneumonia Further Laboratory Data: Hgb : 90 g/l RBC : 2.92 10 12 /L Hct : 0.25 L/L MCV : 87 fl MCH : 30.8 pg MCHC : 355 g/l RDW : 17.7 % WBC :
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY - GRANULOCYTE FORMATION AND CHRONIC MYELOCYTIC LEUKEMIA
 LEUKEMIA Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing Education
LEUKEMIA Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing Education
MICROKROM MICROKROM. Basic Guidelines for Quality Staining with Romanowsky Stains
 MICROKROM M I C R O S C O P Y S TA I N S MICROKROM Basic Guidelines for Quality Staining with Romanowsky Stains Coral Clinical Systems A3, Gitanjali Tulip Block, Dr. A. Do Rego Bagh, Alto Santacruz, Bambolim
MICROKROM M I C R O S C O P Y S TA I N S MICROKROM Basic Guidelines for Quality Staining with Romanowsky Stains Coral Clinical Systems A3, Gitanjali Tulip Block, Dr. A. Do Rego Bagh, Alto Santacruz, Bambolim
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
 Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. Adult
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. Adult
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Collection of Blood and Preparation of Blood Smears. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Collection of Blood and Preparation of Blood Smears. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Select
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Collection of Blood and Preparation of Blood Smears. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Select
Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e. Chapter 17: Blood
 Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e Chapter 17: Blood This chapter begins a new unit. In this unit, the first four chapters deal with transportation one of the body's vital functions. It is important
Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e Chapter 17: Blood This chapter begins a new unit. In this unit, the first four chapters deal with transportation one of the body's vital functions. It is important
EQUIPMENT: Rinse glassware in DI water. Coplin jars, 60 C oven or waterbath, microwave
 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY - HISTOLOGY Date: STAINING MANUAL - CONNECTIVE TISSUE Page: 1 of 4 COLLAGEN - MASSON'S TRICHROME STAIN(TRI) PURPOSE: Used to differentiate between collagen and smooth muscle in tumors,
SURGICAL PATHOLOGY - HISTOLOGY Date: STAINING MANUAL - CONNECTIVE TISSUE Page: 1 of 4 COLLAGEN - MASSON'S TRICHROME STAIN(TRI) PURPOSE: Used to differentiate between collagen and smooth muscle in tumors,
Subtypes of AML follow branches of myeloid development, making the FAB classificaoon relaovely simple to understand.
 1 2 3 4 The FAB assigns a cut off of 30% blasts to define AML and relies predominantly on morphology and cytochemical stains (MPO, Sudan Black, and NSE which will be discussed later). Subtypes of AML follow
1 2 3 4 The FAB assigns a cut off of 30% blasts to define AML and relies predominantly on morphology and cytochemical stains (MPO, Sudan Black, and NSE which will be discussed later). Subtypes of AML follow
MANUAL PLATELET COUNT
 MANUAL PLATELET COUNT LAB OBJECTIVE The student will be able to perform, within K20% accuracy as compared to the automated result, five manual platelet counts using the Unopette system. and the light microscope.
MANUAL PLATELET COUNT LAB OBJECTIVE The student will be able to perform, within K20% accuracy as compared to the automated result, five manual platelet counts using the Unopette system. and the light microscope.
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES. 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions.
 KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
SWOG ONCOLOGY RESEARCH PROFESSIONAL (ORP) MANUAL VOLUME I RESPONSE ASSESSMENT LEUKEMIA CHAPTER 11A REVISED: OCTOBER 2015
 LEUKEMIA Response in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Response criteria in Acute Myeloid Leukemia for SWOG protocols is based on the review article Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults:
LEUKEMIA Response in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Response criteria in Acute Myeloid Leukemia for SWOG protocols is based on the review article Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults:
Hematology Sequence. Blood Labs ORIENTATION OBJECTIVES. c. Microscopic Exam of a Peripheral Blood Smear (several parts)
 Hematology Sequence Blood Labs ORIENTATION OBJECTIVES Objectives Procedure 1. Read the three sections that follow: a. Hematocrit b. Preparing a peripheral lood smear c. Microscopic Exam of a Peripheral
Hematology Sequence Blood Labs ORIENTATION OBJECTIVES Objectives Procedure 1. Read the three sections that follow: a. Hematocrit b. Preparing a peripheral lood smear c. Microscopic Exam of a Peripheral
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY RED BLOOD CELLS AND WHITE BLOOD CELLS IN URINALYSIS
 URINALYSIS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing
URINALYSIS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing
Cytology of Lymph Nodes
 Indications Cytology of Lymph Nodes Lymph node enlargement That was easy Mary Anna Thrall Don Meuten Indications Lymph node enlargement Suspect metastasis Normal sized lymph nodes are Normal Do NOT aspirate
Indications Cytology of Lymph Nodes Lymph node enlargement That was easy Mary Anna Thrall Don Meuten Indications Lymph node enlargement Suspect metastasis Normal sized lymph nodes are Normal Do NOT aspirate
Estimated New Cases of Leukemia, Lymphoma, Myeloma 2014
 ABOUT BLOOD CANCERS Leukemia, Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), non-hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), myeloma, myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are types of cancer that can affect the
ABOUT BLOOD CANCERS Leukemia, Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), non-hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), myeloma, myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are types of cancer that can affect the
ab176915 StayBlue/AP Plus Stain Kit Instructions for Use An immunohistochemical chromogen substrate for staining tissue sections
 ab176915 StayBlue/AP Plus Stain Kit Instructions for Use An immunohistochemical chromogen substrate for staining tissue sections This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab176915 StayBlue/AP Plus Stain Kit Instructions for Use An immunohistochemical chromogen substrate for staining tissue sections This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary. Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide
 Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Malignant Lymphomas and Plasma Cell Myeloma
 Malignant Lymphomas and Plasma Cell Myeloma Dr. Bruce F. Burns Dept. of Pathology and Lab Medicine Overview definitions - lymphoma lymphoproliferative disorder plasma cell myeloma pathogenesis - translocations
Malignant Lymphomas and Plasma Cell Myeloma Dr. Bruce F. Burns Dept. of Pathology and Lab Medicine Overview definitions - lymphoma lymphoproliferative disorder plasma cell myeloma pathogenesis - translocations
Hepatitis C. Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C
 Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
3. The Circulatory System
 3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
CHAPTER 3 OBSERVING MICROORGANISMS THROUGH A MICROSCOPE. I. UNITS OF MEASUREMENT - See Table 3.1 in text. + Fig. 3.2
 CHAPTER 3 OBSERVING MICROORGANISMS THROUGH A MICROSCOPE I. UNITS OF MEASUREMENT - See Table 3.1 in text. + Fig. 3.2 II. MICROSCOPY: THE INSTRUMENTS A. COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPY Figure 3.3 1. Have ocular
CHAPTER 3 OBSERVING MICROORGANISMS THROUGH A MICROSCOPE I. UNITS OF MEASUREMENT - See Table 3.1 in text. + Fig. 3.2 II. MICROSCOPY: THE INSTRUMENTS A. COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPY Figure 3.3 1. Have ocular
MODIFIED TRICHROME STAIN
 MODIFIED TRICHROME STAIN Preanalytical Considerations I. PRINCIPLE Modified trichrome stain for the microsporidia (Ryan-Blue). The diagnosis of intestinal microsporidiosis (Brachiola spp., Enterocytozoon
MODIFIED TRICHROME STAIN Preanalytical Considerations I. PRINCIPLE Modified trichrome stain for the microsporidia (Ryan-Blue). The diagnosis of intestinal microsporidiosis (Brachiola spp., Enterocytozoon
Functions of Blood. Collects O 2 from lungs, nutrients from digestive tract, and waste products from tissues Helps maintain homeostasis
 Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Cells. Introduction WSBCTC 1
 Cells Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are composed of cells. While there are several characteristics that are common to all cells, such as the presence of a cell membrane, cytoplasm,
Cells Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are composed of cells. While there are several characteristics that are common to all cells, such as the presence of a cell membrane, cytoplasm,
MANUAL WBC LAB OBJECTIVE
 MANUAL WBC LAB OBJECTIVE The student will be able to perform, within K20% accuracy as compared to the automated result, five manual white blood cell counts using the Unopette system. PRINCIPLE Free-flowing
MANUAL WBC LAB OBJECTIVE The student will be able to perform, within K20% accuracy as compared to the automated result, five manual white blood cell counts using the Unopette system. PRINCIPLE Free-flowing
What Leukemia Is. Understanding blood
 Leukemia is a malignant disease of the blood-forming cells. It involves white blood cells that do not mature and that reproduce too rapidly. Eventually, they replace the normal bone marrow, leaving insufficient
Leukemia is a malignant disease of the blood-forming cells. It involves white blood cells that do not mature and that reproduce too rapidly. Eventually, they replace the normal bone marrow, leaving insufficient
Stem Cell Transplantation
 Harmony Behavioral Health, Inc. Harmony Behavioral Health of Florida, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. HealthEase of Florida, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance
Harmony Behavioral Health, Inc. Harmony Behavioral Health of Florida, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. HealthEase of Florida, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance
Introduction. About 10,500 new cases of acute myelogenous leukemia are diagnosed each
 Introduction 1.1 Introduction: About 10,500 new cases of acute myelogenous leukemia are diagnosed each year in the United States (Hope et al., 2003). Acute myelogenous leukemia has several names, including
Introduction 1.1 Introduction: About 10,500 new cases of acute myelogenous leukemia are diagnosed each year in the United States (Hope et al., 2003). Acute myelogenous leukemia has several names, including
Reference Range: 0.5-1.6 mmol/l (arterial) 0.7-2.1 mmol/l (venous) CPT Code: 83605
 LACTIC ACID Fasting, arterial specimen preferred. Please note whether arterial or venous. 0.5 ml heparinized plasma. Green top or PST must be drawn, placed on ice, and spun within 15 minutes. Immediately
LACTIC ACID Fasting, arterial specimen preferred. Please note whether arterial or venous. 0.5 ml heparinized plasma. Green top or PST must be drawn, placed on ice, and spun within 15 minutes. Immediately
AURAMINE O STAIN. Preanalytical Considerations
 AURAMINE O STAIN Preanalytical Considerations I. PRINCIPLE Acid-fast mycobacteria resist decolorization by acid-alcohol after primary staining owing to the high lipid (mycolic acid) content in their cell
AURAMINE O STAIN Preanalytical Considerations I. PRINCIPLE Acid-fast mycobacteria resist decolorization by acid-alcohol after primary staining owing to the high lipid (mycolic acid) content in their cell
In order to be useful, a smear must have the following qualities:
 Smear Preparation and Simple Stain Objectives: Make bacterial smear slides (usually called smears) Distinguish cells on these slides using a simple stain procedure Unstained microbial cells are nearly
Smear Preparation and Simple Stain Objectives: Make bacterial smear slides (usually called smears) Distinguish cells on these slides using a simple stain procedure Unstained microbial cells are nearly
BLOOD-Chp. Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? What is the composition of blood? 3 major types of plasma proteins
 6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
What Does My Bone Marrow Do?
 What Does My Bone Marrow Do? the myelodysplastic syndromes foundation, inc. Illustrations by Kirk Moldoff Published by The Myelodysplastic Syndromes Foundation, Inc. First Edition, 2009. 2012. Table of
What Does My Bone Marrow Do? the myelodysplastic syndromes foundation, inc. Illustrations by Kirk Moldoff Published by The Myelodysplastic Syndromes Foundation, Inc. First Edition, 2009. 2012. Table of
Pleural and Pericardial fluids a one year analysis
 Pleural and Pericardial fluids a one year analysis Dr Olafsdottir Dr J Williams Department of Cytology, Llandough Hospital Contents Background Standards Aims/Questions Investigation group Results Conclusions
Pleural and Pericardial fluids a one year analysis Dr Olafsdottir Dr J Williams Department of Cytology, Llandough Hospital Contents Background Standards Aims/Questions Investigation group Results Conclusions
NEW YORK STATE CYTOHEMATOLOGY PROFICIENCY TESTING PROGRAM Glass Slide Critique ~ November 2010
 NEW YORK STATE CYTOHEMATOLOGY PROFICIENCY TESTING PROGRAM Glass Slide Critique ~ November 2010 Slide 081 Available data: 72 year-old female Diagnosis: MDS to AML WBC 51.0 x 10 9 /L RBC 3.39 x 10 12 /L
NEW YORK STATE CYTOHEMATOLOGY PROFICIENCY TESTING PROGRAM Glass Slide Critique ~ November 2010 Slide 081 Available data: 72 year-old female Diagnosis: MDS to AML WBC 51.0 x 10 9 /L RBC 3.39 x 10 12 /L
March 19, 2014. Dear Dr. Duvall, Dr. Hambrick, and Ms. Smith,
 Dr. Daniel Duvall, Medical Officer Center for Medicare, Hospital and Ambulatory Policy Group Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services 7500 Security Boulevard Baltimore, Maryland 21244 Dr. Edith Hambrick,
Dr. Daniel Duvall, Medical Officer Center for Medicare, Hospital and Ambulatory Policy Group Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services 7500 Security Boulevard Baltimore, Maryland 21244 Dr. Edith Hambrick,
Explain the role of blood and bloodstain patterns in forensics science. Analyze and identify bloodstain patterns by performing bloodstain analysis
 Lab 4 Blood Learning Objectives Explain the role of blood and bloodstain patterns in forensics science Analyze and identify bloodstain patterns by performing bloodstain analysis Introduction Blood, a
Lab 4 Blood Learning Objectives Explain the role of blood and bloodstain patterns in forensics science Analyze and identify bloodstain patterns by performing bloodstain analysis Introduction Blood, a
Haematology what does your blood test mean?
 Haematology what does your blood test mean? This document provides some reading material to be used in preparation for the Haematology what does your blood test mean? workshop at RMIT s Experience Health
Haematology what does your blood test mean? This document provides some reading material to be used in preparation for the Haematology what does your blood test mean? workshop at RMIT s Experience Health
Yvette Marie Miller, M.D. Executive Medical Officer American Red Cross October 20, 2012 45 th Annual Great Lakes Cancer Nursing Conference Troy, MI
 Yvette Marie Miller, M.D. Executive Medical Officer American Red Cross October 20, 2012 45 th Annual Great Lakes Cancer Nursing Conference Troy, MI Overview of Hematology, http://www.nu.edu.sa/userfiles/mhmorsy/h
Yvette Marie Miller, M.D. Executive Medical Officer American Red Cross October 20, 2012 45 th Annual Great Lakes Cancer Nursing Conference Troy, MI Overview of Hematology, http://www.nu.edu.sa/userfiles/mhmorsy/h
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Synovial Fluid. Synovial Fluid. Unit 4. Composition and formation. Functions. Reasons for analysis.
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 4 Synovial Fluid Synovial Fluid Composition and formation Secreted by cells of synovial membrane Very viscous, clear ultrafiltrate of plasma Contains Hyaluronic acid
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 4 Synovial Fluid Synovial Fluid Composition and formation Secreted by cells of synovial membrane Very viscous, clear ultrafiltrate of plasma Contains Hyaluronic acid
Enumeration and Viability of Nucleated Cells from Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, and Mobilized Peripheral Blood
 Application Note Primary Cell Analysis Enumeration and Viability of Nucleated Cells from Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, and Mobilized Peripheral Blood Cell Viability Introduction: Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, Stem
Application Note Primary Cell Analysis Enumeration and Viability of Nucleated Cells from Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, and Mobilized Peripheral Blood Cell Viability Introduction: Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, Stem
06-6542 n/a MYSTERY OF THE BLOOD STAIN (RE)
 DATA SHEET Order code Manufacturer code Description 06-6542 n/a MYSTERY OF THE BLOOD STAIN (RE) The enclosed information is believed to be correct, Information may change without notice due to product
DATA SHEET Order code Manufacturer code Description 06-6542 n/a MYSTERY OF THE BLOOD STAIN (RE) The enclosed information is believed to be correct, Information may change without notice due to product
Adult Medical-Surgical Nursing H A E M A T O L O G Y M O D U L E : L E U K A E M I A 2
 Adult Medical-Surgical Nursing H A E M A T O L O G Y M O D U L E : L E U K A E M I A 2 Leukaemia: Description A group of malignant disorders affecting: White blood cells (lymphocytes or leucocytes) Bone
Adult Medical-Surgical Nursing H A E M A T O L O G Y M O D U L E : L E U K A E M I A 2 Leukaemia: Description A group of malignant disorders affecting: White blood cells (lymphocytes or leucocytes) Bone
Touch DNA and DNA Recovery. H. Miller Coyle
 Touch DNA and DNA Recovery 1 2 What is the link between cell biology & forensic science? Cells are the trace substances left behind that can identify an individual. Cells contain DNA. There are two forms
Touch DNA and DNA Recovery 1 2 What is the link between cell biology & forensic science? Cells are the trace substances left behind that can identify an individual. Cells contain DNA. There are two forms
Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist
 Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist Basic Cytology Part 2 (Preparartion and normal morphology) Normal Morphology in Liquid based Gynecologic Cytology Speaker: Mr. Fung
Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist Basic Cytology Part 2 (Preparartion and normal morphology) Normal Morphology in Liquid based Gynecologic Cytology Speaker: Mr. Fung
CONTROL: Any tissue containing acid-fast organisms. Use Millipore filtered water in the waterbath and staining procedure.
 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY - HISTOLOGY Date: STAINING MANUAL - MICROORGANISMS Page: 1 of 3 ACID-FAST BACTERIA - ZIEHL-NEELSEN STAIN (AFB) PURPOSE: Used in the demonstration of acid-fast bacteria belonging to the
SURGICAL PATHOLOGY - HISTOLOGY Date: STAINING MANUAL - MICROORGANISMS Page: 1 of 3 ACID-FAST BACTERIA - ZIEHL-NEELSEN STAIN (AFB) PURPOSE: Used in the demonstration of acid-fast bacteria belonging to the
Please list four delivery functions of blood, two regulatory functions, and two protection functions. Delivery (distribution) functions
 Chapter 17 Blood Please list four delivery functions of blood, two regulatory functions, and two protection functions. Delivery (distribution) functions Names Period 1-3 - 2-4 - Regulatory functions 1-2
Chapter 17 Blood Please list four delivery functions of blood, two regulatory functions, and two protection functions. Delivery (distribution) functions Names Period 1-3 - 2-4 - Regulatory functions 1-2
Pre-Lab Questions. 1. What is cell theory? 2. What do all cells contain? 3. What is a prokaryote? 4. What is a eukaryote? 5. What is an organelle?
 Name: TOC# Background Ever since the first microscope was used, biologists have been interested in studying the cellular organization of all living things. After hundred s of years of observations by many
Name: TOC# Background Ever since the first microscope was used, biologists have been interested in studying the cellular organization of all living things. After hundred s of years of observations by many
I. ACID-BASE NEUTRALIZATION, TITRATION
 LABORATORY 3 I. ACID-BASE NEUTRALIZATION, TITRATION Acid-base neutralization is a process in which acid reacts with base to produce water and salt. The driving force of this reaction is formation of a
LABORATORY 3 I. ACID-BASE NEUTRALIZATION, TITRATION Acid-base neutralization is a process in which acid reacts with base to produce water and salt. The driving force of this reaction is formation of a
Blood, Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 4-Blood, Lymphatic and Immune Systems This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department
Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 4-Blood, Lymphatic and Immune Systems This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department
ab183294 TripleStain IHC Kit: M&M&R on rodent tissue (DAB, DAB/Ni & AP/Red)
 ab183294 TripleStain IHC Kit: M&M&R on rodent tissue (DAB, DAB/Ni & AP/Red) Instructions for Use For the detection of Rabbit and Mouse Primary antibodies on Rodent Tissue. This product is for research
ab183294 TripleStain IHC Kit: M&M&R on rodent tissue (DAB, DAB/Ni & AP/Red) Instructions for Use For the detection of Rabbit and Mouse Primary antibodies on Rodent Tissue. This product is for research
What You Will Learn in This Module: Testing for Pullorum-Typhoid Disease
 Module 5-B: Testing Poultry for Pullorum-Typhoid Disease This module applies only to individuals who have attended and successfully completed an Indiana State Poultry Association NPIP Blood Testing School
Module 5-B: Testing Poultry for Pullorum-Typhoid Disease This module applies only to individuals who have attended and successfully completed an Indiana State Poultry Association NPIP Blood Testing School
EXTRACTION OF DNA FROM CALF THYMUS CELLS Revised 2/1/96 Introduction
 Revised 2/1/96 Introduction Cells may be classified into two primary types depending on whether they have a discrete nucleus (eukaryotic) or do not (prokaryotic). Prokaryotes include bacteria, such as
Revised 2/1/96 Introduction Cells may be classified into two primary types depending on whether they have a discrete nucleus (eukaryotic) or do not (prokaryotic). Prokaryotes include bacteria, such as
LYMPHOMA. BACHIR ALOBEID, M.D. HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIVISION PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT Columbia University/ College of Physicians & Surgeons
 LYMPHOMA BACHIR ALOBEID, M.D. HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIVISION PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT Columbia University/ College of Physicians & Surgeons Normal development of lymphocytes Lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation:
LYMPHOMA BACHIR ALOBEID, M.D. HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIVISION PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT Columbia University/ College of Physicians & Surgeons Normal development of lymphocytes Lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation:
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Product name Company Cat # PowerPac Basic Power supply Bio Rad 165-6019 Mini Protean electrophoresis system Mini trans blot cell Bio Rad 170-3930
 SDS-PAGE and western blot for low molecular weight proteins (2-20kDa) Merav Marom Shamur, Smart Assays Aim: Analysis of low molecular weight proteins by SDS-PAGE and western blot under reducing conditions.
SDS-PAGE and western blot for low molecular weight proteins (2-20kDa) Merav Marom Shamur, Smart Assays Aim: Analysis of low molecular weight proteins by SDS-PAGE and western blot under reducing conditions.
MUCICARMINE STAIN - SOUTHGATE S - MUCIN PURPOSE:
 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY - HISTOLOGY Date: STAINING MANUAL - CARBOHYDRATES Page: 1 of 2 MUCICARMINE STAIN - SOUTHGATE S - MUCIN PURPOSE: To stain mucin which is a secretion produced by a variety of epithelial
SURGICAL PATHOLOGY - HISTOLOGY Date: STAINING MANUAL - CARBOHYDRATES Page: 1 of 2 MUCICARMINE STAIN - SOUTHGATE S - MUCIN PURPOSE: To stain mucin which is a secretion produced by a variety of epithelial
ArtisanLink Staining System is an automated special stains slide
 Technical Tips Tips on using the ArtisanLink Special Staining System Jamie Nowacek, BS, HT(ASCP) CM, QIHC, PMP Dako North America, Inc. Carpinteria, CA, USA ArtisanLink Staining System is an automated
Technical Tips Tips on using the ArtisanLink Special Staining System Jamie Nowacek, BS, HT(ASCP) CM, QIHC, PMP Dako North America, Inc. Carpinteria, CA, USA ArtisanLink Staining System is an automated
The Diagnosis of Cancer in the Pathology Laboratory
 The Diagnosis of Cancer in the Pathology Laboratory Dr Edward Sheffield Christmas Select 74 Meeting, Queen s Hotel Cheltenham, 3 rd December 2014 Agenda Overview of the pathology of cancer How specimens
The Diagnosis of Cancer in the Pathology Laboratory Dr Edward Sheffield Christmas Select 74 Meeting, Queen s Hotel Cheltenham, 3 rd December 2014 Agenda Overview of the pathology of cancer How specimens
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
 Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
Preparation "Clinical Laboratory Technologist and Technician Overview"
 Clinical Laboratory Technologist and Technician Overview The Field - Preparation - Day in the Life - Earnings - Employment - Career Path Forecast - Professional Organizations The Field Clinical laboratory
Clinical Laboratory Technologist and Technician Overview The Field - Preparation - Day in the Life - Earnings - Employment - Career Path Forecast - Professional Organizations The Field Clinical laboratory
Gram Staining. The Most Commonly Used Differential Stain. Advantages:
 Gram Staining The Most Commonly Used Differential Stain Advantages: Can observe size and morphology (like other staining) Can find out additional information about the organism- primarily what type of
Gram Staining The Most Commonly Used Differential Stain Advantages: Can observe size and morphology (like other staining) Can find out additional information about the organism- primarily what type of
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition
 Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Protease Peptide Microarrays Ready-to-use microarrays for protease profiling
 Protocol Protease Peptide Microarrays Ready-to-use microarrays for protease profiling Contact us: InfoLine: +49-30-97893-117 Order per fax: +49-30-97893-299 Or e-mail: peptide@jpt.com www: www.jpt.com
Protocol Protease Peptide Microarrays Ready-to-use microarrays for protease profiling Contact us: InfoLine: +49-30-97893-117 Order per fax: +49-30-97893-299 Or e-mail: peptide@jpt.com www: www.jpt.com
Pathology No: SHS-CASE No. Date of Procedure: Client Name Address
 TEL #: (650) 725-5604 FAX #: (650) 725-7409 Med. Rec. No.: Date of Procedure: Sex: A ge: Date Received: Date of Birth: Account No.: Physician(s): Client Name Address SPECIMEN SUBMITTED: LEFT PIC BONE MARROW,
TEL #: (650) 725-5604 FAX #: (650) 725-7409 Med. Rec. No.: Date of Procedure: Sex: A ge: Date Received: Date of Birth: Account No.: Physician(s): Client Name Address SPECIMEN SUBMITTED: LEFT PIC BONE MARROW,
Hematology Reagents and Controls Our products for your critical process
 Part of a pure process Hematology Reagents and Controls Our products for your critical process 2 Reagents you can count on Mallinckrodt Baker s chemical expertise and 30 years of experience are the foundation
Part of a pure process Hematology Reagents and Controls Our products for your critical process 2 Reagents you can count on Mallinckrodt Baker s chemical expertise and 30 years of experience are the foundation
IKDT Laboratory. IKDT as Service Lab (CRO) for Molecular Diagnostics
 Page 1 IKDT Laboratory IKDT as Service Lab (CRO) for Molecular Diagnostics IKDT lab offer is complete diagnostic service to all external customers. We could perform as well single procedures or complex
Page 1 IKDT Laboratory IKDT as Service Lab (CRO) for Molecular Diagnostics IKDT lab offer is complete diagnostic service to all external customers. We could perform as well single procedures or complex
COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS
 COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS OBJECTIVES: Distinguish between plant and animals cells by their structures Demonstrate the benefit of stains Acquire ability to prepare wet mounts SAFETY: Methylene blue
COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS OBJECTIVES: Distinguish between plant and animals cells by their structures Demonstrate the benefit of stains Acquire ability to prepare wet mounts SAFETY: Methylene blue
Chapter 16: Innate Immunity
 Chapter 16: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity The Body s Defenses The body has 2 types of defense
Chapter 16: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity The Body s Defenses The body has 2 types of defense
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION
 PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
