Low-Field Compact Magnetic Resonance Imaging System for the Hand and Wrist in Rheumatoid Arthritis
|
|
|
- Darren Armstrong
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 23: (2006) Original Research Low-Field Compact Magnetic Resonance Imaging System for the Hand and Wrist in Rheumatoid Arthritis Hiroshi Yoshioka, MD, 1 * Satoshi Ito, MD, 2 Shinya Handa, BE, 3 Sadanori Tomiha, ME, 3 Katsumi Kose, PhD, 3 Tomoyuki Haishi, PhD, 4 Akito Tsutsumi, MD, 2 and Takayuki Sumida, MD 2 Purpose: To investigate the feasibility of an originally developed compact MRI system for evaluating rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and determine its advantages and disadvantages as an imaging modality for evaluating RA. Materials and Methods: We prospectively studied 13 healthy controls with no clinical symptoms of arthritis, and 13 patients with hand and wrist pains (including pain from RA) with a 0.2 T permanent-magnet compact MR imager. All MR images were obtained while the subjects were in a sitting position. Coronal three-dimensional spin-echo T1-weighted images and coronal two-dimensional short tau inversion recovery (STIR) images were obtained with image matrix and field of view (FOV) cm. Plain radiograph findings and MRI findings of patients were compared. Results: In three of the patients with suspected early RA (N 7), early RA was evaluated based on STIR images. All RA patients showed morphologic or signal intensity changes that allowed an evaluation of RA from MR findings. Four of five RA patients showed high signal intensity on STIR images in the wrist, proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint, or metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint that suggested synovitis. Multiple erosions in the hand and wrist were seen in four RA patients, with low signal intensity on T1-weighted images. Conclusion: RA was correctly evaluated, and early RA could be identified with the compact MRI system. However, the current system has limitations, such as the nonselective STIR sequence used and magnetic field inhomogeneity. Key Words: MR imaging; low-field MRI; compact MRI; rheumatoid arthritis; hand and wrist J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2006;23: Wiley-Liss, Inc. MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI), with its high soft-tissue contrast and absence of ionizing radiation, 1 Department of Radiology, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, USA. 2 Department of Rheumatology, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Japan. 3 Institute of Applied Physics, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Japan. 4 MR Technology Inc., Tsukuba, Japan. *Address reprint requests to: H.Y., Department of Radiology, Brigham and Women s Hospital, 75 Francis Street, Boston, MA hyoshioka@partners.org Received March 31, 2005; Accepted November 19, DOI /jmri Published online 2 February 2006 in Wiley InterScience (www. interscience.wiley.com). is a useful imaging tool for diagnosing musculoskeletal pathologies, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Numerous studies of RA have shown that MRI is much more sensitive than radiography or ultrasonography, especially for detecting early-stage RA (1 8). MRI is seven- to ninefold more sensitive than plain radiography for detecting erosions in early disease, and is able to detect lesions 6 12 months before they appear on plain radiographs (3,5,9 11). In one study, MRI identified more than twice as many erosions than ultrasonography and radiography, and was more sensitive than ultrasonography for detecting synovial disease (12). However, conventional whole-body, high-field MRI is more expensive (in terms of both startup costs and maintenance fees) and inconvenient for patients than radiography or ultrasonography. In addition, some metal objects, such as pacemakers and aneurysm clips, are contraindicated for whole-body MRI, and claustrophobic patients are sometimes unable to complete the examination. Low-field dedicated-extremity MR machines are now commercially available and have been applied to the evaluation of RA. Taouli et al (13) reported that conventional high-field MRI and low-field dedicated-extremity MRI were equivalent for evaluating RA synovitis. Using low-field dedicated-extremity MRI, Savnik et al (14) achieved a diagnostic accuracy for synovitis, bone marrow edema, joint effusion, and bone erosion of RA comparable to that of a high-field MRI system. Crues et al (15) reported that a portable MR system (0.2T) showed superior sensitivity for detecting bone damage compared to radiographs of the wrists and metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints. They reported that MRI identified bony erosion in 95% of patients, compared to 59% by radiographs. Peterfy (8) remarked that the introduction of effective therapies for RA has increased the technical requirements for imaging in rheumatology, and that low-field extremity MRI offers adequate performance at a lower cost and with greater comfort and convenience for the patient. However, one disadvantage of these low-field MRI systems is that the field of view (FOV) is too small to enable an assessment of the hand and wrist in one examination or one sequence. Kose et al (16) recently developed a compact MRI system for measuring bone density of the calcaneus, and demonstrated its potential for that purpose. Their 2006 Wiley-Liss, Inc. 370
2 Compact MRI for Hand and Wrist in RA 371 Figure 1. (a) Overview of the compact MRI systems for the hand and wrist, and (b) hand positioning at MR examination. Each subject sat in front of the magnet with his or her hand inserted into the RF coil for acquisition of MR images. entire system consisted of a permanent magnet, gradient coil assembly, RF probe, and portable MR console. It was small and could be installed in a space of 2 m 2 m. Kurimoto et al (17) developed two compact MRI systems for the hand, and reported that these systems successfully detected several hand injuries within a reasonable imaging time. These results suggest that compact MRI has the potential to be useful for imaging the musculoskeletal region. Accordingly, our purpose in this study was to investigate the feasibility of using our originally developed compact MRI with a relatively large FOV for evaluating RA with the subject in a sitting position, and to determine the advantages and disadvantages of this compact MRI system as an imaging modality for evaluating RA. MATERIALS AND METHODS We prospectively studied 13 normal controls with no clinical symptom of arthritis, and 13 patients with hand and wrist pains, with an originally developed compact MR imager (Fig. 1). The normal control group included eight men and five women (22 48 years old, mean age 34.1 years). The patient group consisted of 13 women (29 68 years old, mean age 50.2 years). Table 1 presents their clinical profiles. Before the MR examination was performed, seven patients were suspected of having early RA based on arthralgia and swelling of the hand joints, an inflammatory reaction, positivity for rheumatoid factor, morning stiffness, and duration of symptoms, but had not yet met the 1987 revised American Rheumatology Association (ARA) criteria for the classification of RA. These patients were defined as patients with suspected early RA. One of the seven patients with suspected early RA was later diagnosed with ovarian cancer, paraneoplastic syndrome, and amyopathic dermatomyositis, and one showed soft-tissue swelling of the hand and fever of unknown origin. Five patients already met the revised ARA criteria. These patients were defined as RA patients. Therefore, the patient group consisted of subjects with suspected early RA, RA, and soft-tissue swelling. The study was approved by the institutional review board of the institute in which the MR system was placed. Each control subject and patient gave written informed consent. The compact MRI system consisted of a permanent magnet, gradient coil set, RF coil, and MRI console. The total installation space was 6m 2 (Fig. 1a). The magnet was placed in an electromagnetic shield room (1.6 m (W) 2.0 m (H) 2.4 m (D)) to prevent external noise. The specifications of the permanent magnet were as follows: magnetic field 0.21 T; gap 25 cm; homogeneity 25 ppm over 15 cm diameter spherical volume (dsv); and weight 1350 kg. For uniform RF ex- Table 1 Patient Profile Patient # Sex Age Clinical diagnosis Duration of symptom (years) 1 F 48 Early RA suspect 1 2 F 36 Soft tissue swelling, fever of unknown origin 1 3 F 68 Early RA suspect a 1 4 F 56 Early RA suspect 1 5 F 57 Early RA suspect 1 6 F 29 Early RA suspect 1 7 F 55 Early RA suspect 1 8 F 61 Early RA suspect 1 9 F 29 RA 3 10 F 70 RA F 51 RA 3 12 F 39 RA F 54 RA 12 a The patient was later diagnosed with ovarian cancer, paraneoplastic syndrome, and amyopathic dermatomyositis.
3 372 Yoshioka et al. Table 2 Comparison Between Plain Radiography Findings and MRI Findings Patient # Plain radiography findings MR findings 1 Diffuse periarticular osteoporosis Small cystic change at left distal metacarpal head, otherwise normal 2 No abnormality T1 low, T2 high-intensity soft tissue mass in left dorsal hand 3 Diffuse periarticular osteoporosis, right MCP joints erosion Right 2nd and 3rd MCP joint synovitis suspect 4 Mild periarticular osteoporosis, bilateral 5th MCP erosion Bilateral wrist synovitis early RA suspect 5 Mild periarticular osteoporosis Ganglion cyst on left 4th flexor tendon 6 Left 2nd PIP joint soft tissue swelling suspect Left 2nd PIP joint synovitis early RA 7 No abnormality Bilateral 1st and left 5th flexor tenosynovitis early RA 8 Bilateral 2nd and 3rd DIP joint OA change Small cystic change at right distal metacarpal head, otherwise normal 9 a Periarticular osteoporosis Bilateral wrist synovitis 10 a Advanced RA change Bilateral erosions, marked joint deformity and ankylosis of hands and wrists 11 a Bilateral scaphoid erosion, left 2nd MCP joint erosion Multiple erosions in bilateral wrists and, right 5th and left 2nd MCP joint 12 a Advanced RA change Multiple erosions in bilateral wrists, bilateral MCP joints, right 1st IP, and right 2nd PIP joint 13 a Advanced RA change Multiple erosions in bilateral wrists and carpal ankylosis a The patient met the criteria for diagnosis of RA. citation over a hand, we developed a solenoid RF coil with an oval aperture (8.5 cm (H) 21 cm (W)). The subject sat in front of the magnet and inserted his or her hand into the RF coil to generate MR images (Fig. 1b). Coronal three-dimensional (3D) spin-echo (SE) T1- weighted images (repetition time (TR)/echo time (TE) 200/16 msec for control group and 160/16 msec for patients) were obtained with an image matrix of , FOV of cm cm 6.4 cm, and one acquisition. The scan time was 6.8 min for the control group and 5.5 min for the patients. Coronal two-dimensional (2D) short tau inversion recovery (STIR) images (TR/TE/inversion time (TI) 1400/50/ 130 msec) were also obtained with an image matrix of , no slice selection, an FOV of cm cm, and two acquisitions. The scan time was 6 min. The scan time with TR/TE/TI 1000/50/120 msec was shorter for one patient because of pain (scan time 4.3 min). Both hands of each subject were scanned, and the total examination time, including patient positioning, was 40 min. For all patients, plain radiographs of both hands were obtained prior to the MR examination and reported by radiologists in our institute as a routine reading. No normal control groups underwent plain radiographic examination. The MR images were read by a radiologist (H.Y.) who was unaware of the radiographic findings. RESULTS All but one of the 26 subjects underwent successful MR examinations of both hand and wrist without complications. The one exception was patient 11, who showed a motion artifact because of pain. Only one of the control subjects showed an abnormal finding (a cystic change in the proximal first metacarpal bone without any clinical symptoms). The findings from the plain radiograph and MR images of the patients are shown in Table 2. In the patients with suspected early RA, three had an evaluation by MRI of early RA due to proximal interphalangeal (PIP) synovitis, wrist synovitis, and flexor tenosynovitis. The PIP synovitis showed soft-tissue swelling around the joint and high signal intensity in and around the joint on STIR images (Fig. 2). The evaluation of wrist synovitis was based on findings of high signal intensity on STIR images in the intercarpal and radiocarpal joints. Linear high signal intensity over the wrist and digits with the STIR sequence affirmed an evaluation of tenosynovitis (Fig. 3). All RA patients showed morphologic changes, including dislocation or ankylosis, or signal-intensity changes that permitted an evaluation of RA from MR findings. Four of five RA patients showed a high signal intensity in the wrist, MCP, or PIP joint that suggested synovitis on STIR images. One patient (patient 10) showed no high signal intensity on STIR images, but had marked bilateral ulnar deviated deformity of the hand and wrist ankylosis. Multiple erosions in the hand and wrist were seen in four RA patients who exhibited low signal intensity on T1-weighted images (Fig. 4). DISCUSSION MRI has become an important imaging modality for evaluating RA. Bony erosion is an essential finding in the evaluation and assessment of RA, and MRI is highly sensitive for detecting erosions in the hands and wrists of patients with RA (3,5,10,15,18). Many MR studies have emphasized the usefulness of gadolinium contrast
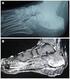
4 Compact MRI for Hand and Wrist in RA 373 Figure 2. MRI of the left hand of a 29-year-old woman with suspected early RA (patient 6). Her second PIP joint was swollen and showed slightly low signal intensity on (a) the T1- weighted image, and high signal intensity on (b) the STIR image (arrow), suggesting early RA. material in assessing active synovitis and destructive pannus (3,19 22). Most of these MR examinations were performed with high-field MRI systems. These systems can provide images with higher signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) and higher spatial resolution than low-field MRI systems. However, conventional whole-body, high-field MRI is expensive and inconvenient for patients and has some contraindications, such as the presence of metal objects (e.g., pacemakers, aneurysm clips, and cochlear implants) in the subject and claustrophobia. In general, the hand and wrist joints are among the first to be affected in RA, and they are of particular interest in the assessment of patients with suspected early RA (13,23). Therefore, for screening and early treatment of RA (especially early-stage RA), dedicated MRI of the hand may be useful for assessing RA if the system is less expensive, is more easily installed, improves patient comfort, and entails less patient risk than whole-body high-field MRI. The design of the low-field compact MRI system for the hand and wrist in this study was originally based on these concepts. Taouli et al (13) and Savnik et al (14) recently compared low-field dedicated-extremity MRI with high-field MRI for evaluating RA of the hand and wrist. Taouli et al (13) reported that the two systems performed equally well for cross-sectional grading of bone erosions, joint- Figure 3. T1-weighted images (a: left; b: right) and STIR images (c: left; d: right) of both hands of a 55-year-old woman with suspected early RA (patient 7). Linear high signal intensities over the bilateral wrists and first finger, and the left fifth finger on STIR (arrows) suggest tenosynovitis.
5 374 Yoshioka et al. Figure 4. MRI of both hands of a 39-year-old woman with RA (patient 12). a and b: T1- weighted images showed multiple low signal intensity erosions of the bilateral interphalangeal joints of the thumb, MCP joints, and wrist joints. c and d: STIR images show synovitis of the above joints as high signal intensity. space narrowing, and synovitis in RA. Both MRI techniques detected approximately twice as many erosions as detected by radiography (13). The Savnik et al (14) study showed that the volume of synovial membrane determined by extremity MRI was significantly correlated with and not significantly different from that determined with high-field MRI with gadolinium injection. Intraobserver variation was high for the two MR systems. Therefore, the performance of low-field dedicatedextremity MRI would be the same as that of high-field MRI for the evaluation of RA, including early-stage RA. The use of dedicated-extremity MRI for the evaluation of RA has several advantages over whole-body MRI. Compared to a whole-body MRI system, dedicated-extremity MRI requires a smaller installation space, costs less, offers greater patient comfort, and eliminates the problem of claustrophobia and potential biohazards associated with the presence of metal in or on the patient, since only the limb of interest is placed into the magnet bore. Therefore, it may be more feasible than conventional high-field MRI for evaluating patients with arthritis of the small joints (13). Savnik et al (14) reported that 64% of patients with arthritis of the hand and wrist preferred 0.2T extremity MRI to 1.5T high-field MRI because the former was more comfortable, less claustrophobic, and quieter. Of their patients, 20% reported experiencing mild to severe claustrophobia during the high-field MR examination. Lindegaard et al (10) also reported advantages of extremity MRI over whole-body MRI with regard to cost, comfort, and claustrophobia. In our study, these three Cs (cost, comfort, and claustrophobia), along with the small installation space, no maintenance, and no ionizing radiation, were the greatest advantages of extremity MRI. In addition, it had the technical advantage of a larger FOV (20.48 cm cm), which allowed us to obtain MR images that included the wrist joint to the PIP joint. Some earlier studies of extremity MRI had to use a smaller FOV and thus had limited anatomic coverage (13 15). With a smaller FOV, fewer joints can be examined in a given imaging series. In the present study, examinations of both hands, including positioning of subjects, could be performed within 40 min. Low-field compact MRI is insensitive to metal objects implanted anywhere but in the hand and wrist, and thus reduces the risk associated with the presence of metal in the body. Also, as Crues et al (15) mentioned, the unique features of the portable MR system allow it to be readily used in an office or point-of-care setting (e.g., a rheumatology office or clinic), improving overall patient management and operational efficiency. Generally, however, low-field dedicated-extremity MRI has the limitations of lower SNRs and longer acquisition times compared to conventional high-field MRI (13). Moreover, the present study had several limitations, as described below. First, the STIR images were obtained with a nonslice-selective sequence because STIR with multiple
6 Compact MRI for Hand and Wrist in RA 375 slices requires a longer scan time with an SE sequence. Thus, it was not possible to look at detailed anatomy with STIR. Also, it may be difficult to point out bone marrow edema. Non-slice-selective images were inadequate for assessing a large soft-tissue mass (in patient 2), since they could not show abnormal findings in detail because of the signal intensity of the normal structure overlying the lesion. However, joint effusion, synovitis, and tenosynovitis with STIR produced bright signals and enabled us to evaluate RA. Although we were able to evaluate erosion in 3D T1-weighted images in this study, we plan to use a multislice STIR sequence within a reasonable scan time as the next development in our compact MRI system. Second, we could not use a spectral fat-suppression technique because of close spectral peaks of fat and water in this study. On a low-field MR machine, it is difficult to obtain fat-suppressed T1-weighted images using a spectral fat-suppression technique, which is often combined with the use of gadolinium contrast. Fat-suppressed T1-weighted images with gadolinium were shown to be useful for diagnosing early and active RA in many earlier studies (4 6,21). In one study (13), synovitis was visible on coronal T1-weighted 3D gradient-recalled echo (GRE) and STIR low-field MR images as a fluid signal distending the joint cavity. Synovial tissue cannot be reliably differentiated from synovial fluid with these sequences. Discriminating between these two components of the synovial cavity typically requires the use of IV contrast materials. However, this increases the cost and time required for the examination. It would be difficult to study both hands and wrists, such as performed in this study, if contrast material were used. For screening both hands for RA, non-enhanced water-sensitive sequences, such as STIR, may be desirable. Third, in this study there was no established gold standard with which to compare the MRI and radiograph results, because no pathology specimens were available from the patients. It has not been proven that MR erosions are true erosions or that MR erosions will develop into radiographic erosions (1). Nevertheless, three patients with suspected early RA started antiinflammatory treatment after MRI evaluation, and the treatment was effective (i.e., joint pain and morning stiffness improved) in all three. Therefore, MRI helped physicians make decisions about treatment in a timely fashion. Fourth, image artifacts caused by inhomogeneity of the static field were sometimes seen around the wrists. To resolve this artifact, we should have shifted the hands slightly farther into the magnet. Fifth, our system cannot provide spatial resolution as high as that achievable with high-field MRI. However, as Peterfy (8) commented, the needs of radiology are different from those of mainstream rheumatology, and rheumatologists do not need highly sophisticated pulse sequence and contrast mechanisms. The ability to detect occult bone erosions and synovitis would be adequate to allow rheumatologists to initiate patient management and treatment. Sixth, typical erosions in RA measure 2 3 mm in maximum diameter. Our protocol uses 4-mm-thick images with mm in-plane resolution. With this resolution, changes in erosion that occur over small periods of time will not be reliable. We may combine a small surface coil with this system to detect a subtle change on high-resolution images in the future. Finally, the number of subjects in this study was small. We plan to perform a study with more patients after we have improved our compact MRI system, including the pulse sequence, magnet, gradient coils, and RF coil. To ensure the reliability of our compact MRI system, we need to assess intra- and interreader reproducibility for the evaluation of RA in future studies. In conclusion, normal controls and patients with hand and wrist pain, including those with suspected early RA and RA that met RA criteria, were examined with a prototype low-field hand and wrist dedicated compact MRI system. This system was able to evaluate RA correctly and suggest early RA. However, the system still has limitations, such as the use of a non-selective STIR sequence and magnetic field inhomogeneity. A large number of cohort studies are still necessary to improve the system. REFERENCES 1. Klarlund M, Ostergaard M, Gideon P, Sorensen K, Jensen KE, Lorenzen I. Wrist and finger joint MR imaging in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Radiol 1999;40: McQueen FM. Magnetic resonance imaging in early inflammatory arthritis: what is its role? Rheumatology (Oxf) 2000;39: Klarlund M, Ostergaard M, Jensen KE, Madsen JL, Skjodt H, Lorenzen I. Magnetic resonance imaging, radiography, and scintigraphy of the finger joints: one year follow up of patients with early arthritis. The TIRA Group. Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59: Ostergaard M, Szkudlarek M. Imaging in rheumatoid arthritis why MRI and ultrasonography can no longer be ignored. Scand J Rheumatol 2003;32: McQueen FM, Stewart N, Crabbe J, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis reveals a high prevalence of erosions at four months after symptom onset. Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57: Sugimoto H, Takeda A, Masuyama J, Furuse M. Early-stage rheumatoid arthritis: diagnostic accuracy of MR imaging. Radiology 1996;198: Sugimoto H, Takeda A, Hyodoh K. Early-stage rheumatoid arthritis: prospective study of the effectiveness of MR imaging for diagnosis. Radiology 2000;216: Peterfy CG. Is there a role for extremity magnetic resonance imaging in routine clinical management of rheumatoid arthritis? J Rheumatol 2004;31: McQueen F, Lassere M, Edmonds J, et al. OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging studies. Summary of OMER- ACT 6 MR imaging module. J Rheumatol 2003;30: Lindegaard H, Vallo J, Horslev-Petersen K, Junker P, Ostergaard M. Low field dedicated magnetic resonance imaging in untreated rheumatoid arthritis of recent onset. Ann Rheum Dis 2001;60: McQueen FM, Benton N, Crabbe J, et al. What is the fate of erosions in early rheumatoid arthritis? Tracking individual lesions using x rays and magnetic resonance imaging over the first two years of disease. Ann Rheum Dis 2001;60: Hoving JL, Buchbinder R, Hall S, et al. A comparison of magnetic resonance imaging, sonography, and radiography of the hand in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2004;31: Taouli B, Zaim S, Peterfy CG, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis of the hand and wrist: comparison of three imaging techniques. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2004;182: Savnik A, Malmskov H, Thomsen HS, et al. MRI of the arthritic small joints: comparison of extremity MRI (0.2 T) vs high-field MRI (1.5 T). Eur Radiol 2001;11:
7 376 Yoshioka et al. 15. Crues JV, Shellock FG, Dardashti S, James TW, Troum OM. Identification of wrist and metacarpophalangeal joint erosions using a portable magnetic resonance imaging system compared to conventional radiographs. J Rheumatol 2004;31: Kose K, Matsuda Y, Yoshioka H, et al. Development of a compact MRI system for trabecular bone volume fraction measurements. Magn Reson Med 2004;52: Kurimoto T, Furuya T, Kose K, et al. Compact hand MRI systems using permanent magnets. In: Proceedings of the 12th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Kyoto, Japan, p McGonagle D, Conaghan PG, O Connor P, et al. The relationship between synovitis and bone changes in early untreated rheumatoid arthritis: a controlled magnetic resonance imaging study. Arthritis Rheum 1999;42: Jevtic V, Watt I, Rozman B, et al. Precontrast and postcontrast (Gd-DTPA) magnetic resonance imaging of hand joints in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Radiol 1993;48: Konig H, Sieper J, Wolf KJ. Rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of hypervascular and fibrous pannus with dynamic MR imaging enhanced with Gd-DTPA. Radiology 1990;176: Nakahara N, Uetani M, Hayashi K, Kawahara Y, Matsumoto T, Oda J. Gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging of the wrist in rheumatoid arthritis: value of fat suppression pulse sequences. Skeletal Radiol 1996;25: Jevtic V, Watt I, Rozman B, et al. Prognostic value of contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA MRI for development of bone erosive changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol 1996;35: Scott DL, Coulton BL, Popert AJ. Long term progression of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 1986;45:
Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI. Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007
 Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007 Introduction RA most common type of inflammatory Arthritis with prevalence of 1% Accurate and
Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007 Introduction RA most common type of inflammatory Arthritis with prevalence of 1% Accurate and
Bone Erosions in Patients with RA: Exploring the Impact of the Anatomy of Interest on the Relationship Between MRI and X-ray Erosion Detection
 Bone Erosions in Patients with RA: Exploring the Impact of the Anatomy of Interest on the Relationship Between MRI and X-ray Erosion Detection Michael Tomizza, BSc, MSc Candidate October 15, 2014: Hamilton
Bone Erosions in Patients with RA: Exploring the Impact of the Anatomy of Interest on the Relationship Between MRI and X-ray Erosion Detection Michael Tomizza, BSc, MSc Candidate October 15, 2014: Hamilton
Treat to Target Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis: UK perspective. Dr Deirdre Shawe, North Hampshire Hospital, Basingstoke, UK
 Treat to Target Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis: UK perspective Dr Deirdre Shawe, North Hampshire Hospital, Basingstoke, UK What is the target? To achieve remission or low disease activity in Rheumatoid
Treat to Target Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis: UK perspective Dr Deirdre Shawe, North Hampshire Hospital, Basingstoke, UK What is the target? To achieve remission or low disease activity in Rheumatoid
Benedikt Ostendorf, Axel Scherer, Ulrich Mödder, and Matthias Schneider
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 7, July 2004, pp 2094 2102 DOI 10.1002/art.20314 2004, American College of Rheumatology Diagnostic Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Forefeet in Early Rheumatoid
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 7, July 2004, pp 2094 2102 DOI 10.1002/art.20314 2004, American College of Rheumatology Diagnostic Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Forefeet in Early Rheumatoid
The accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging of the hands and feet in the diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis
 Joint Bone Spine 74 (2007) 362e367 Original article The accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging of the hands and feet in the diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis Cuneyt Calisir a, *, Ali Ilker Murat
Joint Bone Spine 74 (2007) 362e367 Original article The accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging of the hands and feet in the diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis Cuneyt Calisir a, *, Ali Ilker Murat
Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis
 REVIEW ARTICLE Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis Wilson Campos Tavares Junior 1, Renata Rolim 2, Adriana Maria Kakehasi 3 ABSTRACT Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory polyarthritis
REVIEW ARTICLE Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis Wilson Campos Tavares Junior 1, Renata Rolim 2, Adriana Maria Kakehasi 3 ABSTRACT Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory polyarthritis
Arthritis of the Hands
 Arthritis of the Hands On the Agenda Normal Osteoarthitis Rheumatoid arthritis CPPD crystal deposition Gout Psoriatic arthritis Normal Hand X-ray Osteoarthritis (DJD) Gradual degeneration of articular
Arthritis of the Hands On the Agenda Normal Osteoarthitis Rheumatoid arthritis CPPD crystal deposition Gout Psoriatic arthritis Normal Hand X-ray Osteoarthritis (DJD) Gradual degeneration of articular
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nicole Klett,, M.D.
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Nicole Klett,, M.D. Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic Chronic Inflammatory Primarily targets the synovium of diarthrodial joints Etiology likely combination genetic and environmental Diarthrodial
Rheumatoid Arthritis Nicole Klett,, M.D. Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic Chronic Inflammatory Primarily targets the synovium of diarthrodial joints Etiology likely combination genetic and environmental Diarthrodial
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations
 Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES. Anthony Hewitt
 DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D.
 05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis Dr. Andrew K. Brown Senior Lecturer & Consultant Rheumatologist Content Practical RA Assessment Advantages of ultrasonography Potential
Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis Dr. Andrew K. Brown Senior Lecturer & Consultant Rheumatologist Content Practical RA Assessment Advantages of ultrasonography Potential
Integra. MCP Joint Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra MCP Joint Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION Integra MCP Patient Information This brochure summarizes information about the use, risks, and benefits of the Integra MCP finger implant. Be sure to discuss
Integra MCP Joint Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION Integra MCP Patient Information This brochure summarizes information about the use, risks, and benefits of the Integra MCP finger implant. Be sure to discuss
Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists
 Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists Case 27 yo female with 6 month history of right forearm and hand pain Works as secretary, symptoms are interfering with her job duties Complains that she
Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists Case 27 yo female with 6 month history of right forearm and hand pain Works as secretary, symptoms are interfering with her job duties Complains that she
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain
 Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
Ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis
 Formosan Journal of Rheumatology 2009;23:1-7 Review Article Ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis Ying-Chou Chen 1, Tien-Tsai Cheng 1, Shih-Wei Hsu 2 1 Department of Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology,
Formosan Journal of Rheumatology 2009;23:1-7 Review Article Ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis Ying-Chou Chen 1, Tien-Tsai Cheng 1, Shih-Wei Hsu 2 1 Department of Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology,
5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio
 5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio 29 5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio In the preceding chapters we have learned how an MR signal is generated and how the collected signal is processed
5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio 29 5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio In the preceding chapters we have learned how an MR signal is generated and how the collected signal is processed
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons
 MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis & Axial Spondyloarthritis
 Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis & Axial Spondyloarthritis 奇 美 醫 院 過 敏 免 疫 風 濕 科 陳 宏 安 Rheumatoid arthritis Most common chronic inflammatory joint disease Multisystem autoimmune disease of unknown
Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis & Axial Spondyloarthritis 奇 美 醫 院 過 敏 免 疫 風 濕 科 陳 宏 安 Rheumatoid arthritis Most common chronic inflammatory joint disease Multisystem autoimmune disease of unknown
A patientwithsystemicsclerosis andjointpain. Christian Beyer University Erlangen-Nuremberg(GER)
 A patientwithsystemicsclerosis andjointpain Christian Beyer University Erlangen-Nuremberg(GER) Whatisimportanttoyou? lungs GI tract fatigue heart skin muscles Raynaud s joints Whatisimportanttopatients?
A patientwithsystemicsclerosis andjointpain Christian Beyer University Erlangen-Nuremberg(GER) Whatisimportanttoyou? lungs GI tract fatigue heart skin muscles Raynaud s joints Whatisimportanttopatients?
Arthroscopy of the Hand and Wrist
 Arthroscopy of the Hand and Wrist Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure whereby a small camera is inserted through small incisions of a few millimeters each around a joint to view the joint directly.
Arthroscopy of the Hand and Wrist Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure whereby a small camera is inserted through small incisions of a few millimeters each around a joint to view the joint directly.
Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital
 Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital Contents Definition/ epidemiology Diagnosis Importance of early diagnosis/ treatment Guidelines Evidence based treatment protocol Current
Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital Contents Definition/ epidemiology Diagnosis Importance of early diagnosis/ treatment Guidelines Evidence based treatment protocol Current
GE 3.0T NPW,TRF,FAST,F R NPW,TRF,FAST,F R
 GE 3.0T 3.0T WRIST Invivo 8CH Wrist Coil Sequence Ax T2 Cor PD Cor PDFS Cor T1 Cor PD (Small FOV) FOV (mm) 80 80 80 80 40 Matrix 384x224 384x256 320x256 384x320 320x192 Phase Direction RL RL RL RL RL #
GE 3.0T 3.0T WRIST Invivo 8CH Wrist Coil Sequence Ax T2 Cor PD Cor PDFS Cor T1 Cor PD (Small FOV) FOV (mm) 80 80 80 80 40 Matrix 384x224 384x256 320x256 384x320 320x192 Phase Direction RL RL RL RL RL #
ACT-RAY and MRI substudy
 Tocilizumab as Monotherapy or in Combination With Methotrexate associated with Early Reductions in Tissue Inflammation: 12-Week Results From a Magnetic Resonance Imaging Substudy of a Randomized Controlled
Tocilizumab as Monotherapy or in Combination With Methotrexate associated with Early Reductions in Tissue Inflammation: 12-Week Results From a Magnetic Resonance Imaging Substudy of a Randomized Controlled
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD
 Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
SPECT/CT Wrist. Wrist pain 3/27/2012
 Wrist pain Wrist joint - complicated anatomy complex biomechanics Imaging and management of wrist pain presents a significant challenge Significant economic burden SPECT/CT Wrist HK Mohan GSTT London Intra-capsular
Wrist pain Wrist joint - complicated anatomy complex biomechanics Imaging and management of wrist pain presents a significant challenge Significant economic burden SPECT/CT Wrist HK Mohan GSTT London Intra-capsular
ORIGINAL ARTICLE THE DIAGNOSIS OF EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS USING MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY
 AL-AZHAR ASSIUT MEDICAL JOURNAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE THE DIAGNOSIS OF EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS USING MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY Sonya M. Rashad, Eman A.M. Alkady, Essam A.M. Abda and Marwa A.A. Galal,
AL-AZHAR ASSIUT MEDICAL JOURNAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE THE DIAGNOSIS OF EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS USING MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY Sonya M. Rashad, Eman A.M. Alkady, Essam A.M. Abda and Marwa A.A. Galal,
1991 :super specialties perceptions
 Ved Chaturvedi, MD, DM Research & Referral Hospital New Delhi President Indian Rheumatology Association MSK Ultrasound..A decade experience of bedside MSK US by a clinician. Was it worth it.? 1991 :super
Ved Chaturvedi, MD, DM Research & Referral Hospital New Delhi President Indian Rheumatology Association MSK Ultrasound..A decade experience of bedside MSK US by a clinician. Was it worth it.? 1991 :super
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
 In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698
 SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698 Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging Biomarkers for Assessment of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Treatment: A sub-study of the I-SPY 2 TRIAL Version: 1.0 Date: May 28, 2012
SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698 Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging Biomarkers for Assessment of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Treatment: A sub-study of the I-SPY 2 TRIAL Version: 1.0 Date: May 28, 2012
Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition
 www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
Musculoskeletal Trauma of the Wrist
 September 2000 Musculoskeletal Trauma of the Wrist Murat Akalin, Harvard Medical School, Year- IV Gillian Lieberman, MD The Wrist Most common site of injury in entire skeleton Distal radius and ulna fractures
September 2000 Musculoskeletal Trauma of the Wrist Murat Akalin, Harvard Medical School, Year- IV Gillian Lieberman, MD The Wrist Most common site of injury in entire skeleton Distal radius and ulna fractures
Scaphoid and Other Wrist Injuries in the Emergency Department
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Scaphoid and Other Wrist Injuries in the Emergency Department SCOPE (Area): SCOPE (Staff): Emergency Department and Fracture Clinic Medical, Nursing, Patient Service Assistants
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Scaphoid and Other Wrist Injuries in the Emergency Department SCOPE (Area): SCOPE (Staff): Emergency Department and Fracture Clinic Medical, Nursing, Patient Service Assistants
(Intro to Arthritis with a. Arthritis) Manager of Education & Services for the Vancouver Island Region of The Arthritis Society
 Arthritis 101 (Intro to Arthritis with a Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis) by Cari Taylor by Cari Taylor Manager of Education & Services for the Vancouver Island Region of The Arthritis Society What You Will
Arthritis 101 (Intro to Arthritis with a Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis) by Cari Taylor by Cari Taylor Manager of Education & Services for the Vancouver Island Region of The Arthritis Society What You Will
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
GE Medical Systems Training in Partnership. Module 8: IQ: Acquisition Time
 Module 8: IQ: Acquisition Time IQ : Acquisition Time Objectives...Describe types of data acquisition modes....compute acquisition times for 2D and 3D scans. 2D Acquisitions The 2D mode acquires and reconstructs
Module 8: IQ: Acquisition Time IQ : Acquisition Time Objectives...Describe types of data acquisition modes....compute acquisition times for 2D and 3D scans. 2D Acquisitions The 2D mode acquires and reconstructs
GE Medical Systems Training in Partnership. Module 12: Spin Echo
 Module : Spin Echo Spin Echo Objectives Review the SE PSD. Review the concepts of T, T, and T*. Spin Echo PSD RF Gz Gy 90 80 Gx Spin Echo - SE Spin echo is a standard pulse sequence on Signa MRi/LX and
Module : Spin Echo Spin Echo Objectives Review the SE PSD. Review the concepts of T, T, and T*. Spin Echo PSD RF Gz Gy 90 80 Gx Spin Echo - SE Spin echo is a standard pulse sequence on Signa MRi/LX and
2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis Published in the September 2010 Issues of A&Rand ARD Phases of the Project Phase 1 Data analysis Phase 2 Consensus process Predictors of
2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis Published in the September 2010 Issues of A&Rand ARD Phases of the Project Phase 1 Data analysis Phase 2 Consensus process Predictors of
X-ray (Radiography) - Bone
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department
 Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department Taylor Sittler MS IV - UMASS Images courtesy of Jim Wu, MD, Sanjay Shetty, MD and Mary Hochman, MD Diagnostic Errors in the ED Taylor Sittler, MS IV
Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department Taylor Sittler MS IV - UMASS Images courtesy of Jim Wu, MD, Sanjay Shetty, MD and Mary Hochman, MD Diagnostic Errors in the ED Taylor Sittler, MS IV
MRI SEQUENCES. 1 Gradient Echo Sequence
 5 An MRI sequence is an ordered combination of RF and gradient pulses designed to acquire the data to form the image. In this chapter I will describe the basic gradient echo, spin echo and inversion recovery
5 An MRI sequence is an ordered combination of RF and gradient pulses designed to acquire the data to form the image. In this chapter I will describe the basic gradient echo, spin echo and inversion recovery
Multiple Myeloma. Abstract. Introduction
 Multiple Myeloma Abstract Multiple Myeloma is a plasma cell cancer that causes an overproduction of plasma cells. Multiple Myeloma is a difficult disease to diagnosis because symptoms might not be present
Multiple Myeloma Abstract Multiple Myeloma is a plasma cell cancer that causes an overproduction of plasma cells. Multiple Myeloma is a difficult disease to diagnosis because symptoms might not be present
.org. Arthritis of the Hand. Description
 Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis. A radiologic tour of a patient encounter
 Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
7/16/2010. Pulse Sequences and Acquisition Techniques for Breast MRI. Objectives. ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program Launched May 2010
 Pulse Sequences and Acquisition Techniques for Breast MRI ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program Launched May 2010 Ron Price Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN 37232 Information available:
Pulse Sequences and Acquisition Techniques for Breast MRI ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program Launched May 2010 Ron Price Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN 37232 Information available:
A Patient's Guide to Arthritis of the Finger Joints
 Introduction A Patient's Guide to Arthritis of the Finger Joints When you stop to think about how much you use your hands, it's easy to see why the joints of the fingers are so important. Arthritis of
Introduction A Patient's Guide to Arthritis of the Finger Joints When you stop to think about how much you use your hands, it's easy to see why the joints of the fingers are so important. Arthritis of
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT
 Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7
 Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Type III Hypersensitivity Response
 NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System Margaret H. Birney PhD, RN Lecture 12 Part 2 Joint Disorders (cont d) Rheumatoid Arthritis Definition: Autoimmune disorder occurring in genetically sensitive
NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System Margaret H. Birney PhD, RN Lecture 12 Part 2 Joint Disorders (cont d) Rheumatoid Arthritis Definition: Autoimmune disorder occurring in genetically sensitive
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a valuable diagnostic study that has been used
Magnetic Resonance Imaging North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a valuable diagnostic study that has been used
RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION
 Jeff Husband MD Objectives Evaluate, diagnose and manage common wrist injuries due to high energy trauma in athletes Appropriately use radiographs, CT scans and MRI Know when to refer patients for additional
Jeff Husband MD Objectives Evaluate, diagnose and manage common wrist injuries due to high energy trauma in athletes Appropriately use radiographs, CT scans and MRI Know when to refer patients for additional
ORIGINAL PAPER WATER FAT SEPARATION USING THE SINGLE ACQUISITION SANDWICH TYPE 3-POINT DIXON METHOD TO OPTIMIZE KNEE JOINT SCANS
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 63. 41 ~ 49, 2000 ORIGINAL PAPER WATER FAT SEPARATION USING THE SINGLE ACQUISITION SANDWICH TYPE 3-POINT DIXON METHOD TO OPTIMIZE KNEE JOINT SCANS ERIKO SHIBAHARA 1, HIROSHI FUKATSU
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 63. 41 ~ 49, 2000 ORIGINAL PAPER WATER FAT SEPARATION USING THE SINGLE ACQUISITION SANDWICH TYPE 3-POINT DIXON METHOD TO OPTIMIZE KNEE JOINT SCANS ERIKO SHIBAHARA 1, HIROSHI FUKATSU
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Temporomandibular Joint Imaging Using CBCT: Technology Now Captures Reality!
 Temporomandibular Joint Imaging Using CBCT: Technology Now Captures Reality! Dale A. Miles BA, DDS, MS, FRCD (C) Diplomate, American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology Diplomate, American Board
Temporomandibular Joint Imaging Using CBCT: Technology Now Captures Reality! Dale A. Miles BA, DDS, MS, FRCD (C) Diplomate, American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology Diplomate, American Board
NERVE COMPRESSION DISORDERS
 Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Ryan Klinefelter, MD Associate Professor of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Medical Center NERVE COMPRESSION DISORDERS 1 Carpal
Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Ryan Klinefelter, MD Associate Professor of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Medical Center NERVE COMPRESSION DISORDERS 1 Carpal
Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist
 Page 1 of 6 Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist Doctors commonly diagnose a sprained wrist after a patient falls on an outstretched hand. However, if pain and swelling don't go away, doctors become suspicious
Page 1 of 6 Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist Doctors commonly diagnose a sprained wrist after a patient falls on an outstretched hand. However, if pain and swelling don't go away, doctors become suspicious
Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma. Magee, 2008. pg.
 PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging
 Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 10/11/2015 History Child with several month history of weakness, arthralgias and palpable abnormalities at the knee Diagnosis Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 10/11/2015 History Child with several month history of weakness, arthralgias and palpable abnormalities at the knee Diagnosis Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz
 Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? RA is the second most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most often appears between
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? RA is the second most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most often appears between
Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy
 Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy Hans T.M. van Schie DVM, PhD UTC Imaging, Netherlands Scoring with Patellar Tendinopathy? no one size
Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy Hans T.M. van Schie DVM, PhD UTC Imaging, Netherlands Scoring with Patellar Tendinopathy? no one size
Magnetic Resonance Imaging H IROSHI Y OSHIOKA,MD,PH D, PHILIPP M. SCHLECHTWEG,MD,
 CHAPTER 3 Magnetic Resonance Imaging H IROSHI Y OSHIOKA,MD,PH D, PHILIPP M. SCHLECHTWEG,MD, and K ATSUMI K OSE,PH D 34 K E Y F A C T S l Clinical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measures the spatial distribution
CHAPTER 3 Magnetic Resonance Imaging H IROSHI Y OSHIOKA,MD,PH D, PHILIPP M. SCHLECHTWEG,MD, and K ATSUMI K OSE,PH D 34 K E Y F A C T S l Clinical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measures the spatial distribution
X-ray (Radiography) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
Ultrasound of the small joints of the hands and feet: current status
 Skeletal Radiol (2008) 37:99 113 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0356-9 REVIEW ARTICLE Ultrasound of the small joints of the hands and feet: current status E. G. McNally Received: 8 December 2006 /Revised: 7 May
Skeletal Radiol (2008) 37:99 113 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0356-9 REVIEW ARTICLE Ultrasound of the small joints of the hands and feet: current status E. G. McNally Received: 8 December 2006 /Revised: 7 May
MANUAL OSTEOPATHY JOINT MOBILIZATION FOR TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 MANUAL OSTEOPATHY JOINT MOBILIZATION FOR TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Student; Liu Ai Cao, RMT Investigative Project as required by National Academy of Osteopathy June 2011 Professor: Dr. Shahin Pourgol,
MANUAL OSTEOPATHY JOINT MOBILIZATION FOR TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Student; Liu Ai Cao, RMT Investigative Project as required by National Academy of Osteopathy June 2011 Professor: Dr. Shahin Pourgol,
Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem
 Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem Professor Dr John George University of Malaya Research Imaging Centre University of Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Abstract: Aim:
Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem Professor Dr John George University of Malaya Research Imaging Centre University of Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Abstract: Aim:
A Diagnostic Chest XRay: Multiple Myeloma
 Daniela Marinho Tridente, VI FCMSCSP October 2013 A Diagnostic Chest XRay: Multiple Myeloma Daniela Marinho Tridente, VI FCMSCSP Our Learning Agenda Introduction of our patient His imaging data and findings
Daniela Marinho Tridente, VI FCMSCSP October 2013 A Diagnostic Chest XRay: Multiple Myeloma Daniela Marinho Tridente, VI FCMSCSP Our Learning Agenda Introduction of our patient His imaging data and findings
Systemic condition affecting synovial tissue Hypertrohied synovium destroys. Synovectomy. Tenosynovectomy Tendon Surgery Arthroplasty Arthrodesis
 Surgical Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Wrist Raj Bhatia Consultant Hand & Orthopaedic Surgeon Bristol Royal Infirmary & Avon Orthopaedic Centre Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic condition affecting
Surgical Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Wrist Raj Bhatia Consultant Hand & Orthopaedic Surgeon Bristol Royal Infirmary & Avon Orthopaedic Centre Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic condition affecting
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
I. INCLUSION AND EXCLUSION CRITERIA
 Page 1 of 5 I. INCLUSION AND EXCLUSION CRITERIA INCLUSION CRITERIA Yes No 1. Patient is diagnosed with according to the American College of Rheumatology 1987 revised criteria. 2. All 4 grandparents are
Page 1 of 5 I. INCLUSION AND EXCLUSION CRITERIA INCLUSION CRITERIA Yes No 1. Patient is diagnosed with according to the American College of Rheumatology 1987 revised criteria. 2. All 4 grandparents are
Psoriatic Arthritis: the Role of Radiologic Assessment in Diagnosis and Management
 Psoriatic Arthritis: the Role of Radiologic Assessment in Diagnosis and Management Stephanie W. Hu, HMS IV BIDMC Department of Radiology August 25, 2008 Overview Patient AC Psoriatic arthritis (PsA( PsA)
Psoriatic Arthritis: the Role of Radiologic Assessment in Diagnosis and Management Stephanie W. Hu, HMS IV BIDMC Department of Radiology August 25, 2008 Overview Patient AC Psoriatic arthritis (PsA( PsA)
.org. Osteochondroma. Solitary Osteochondroma
 Osteochondroma Page ( 1 ) An osteochondroma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops during childhood or adolescence. It is an abnormal growth that forms on the surface of a bone near the growth
Osteochondroma Page ( 1 ) An osteochondroma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops during childhood or adolescence. It is an abnormal growth that forms on the surface of a bone near the growth
X-ray (Radiography), Chest
 X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases
 September 2002 Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases Natalie J. M. Dailey, Harvard Medical Student Year III Our Patient s Presenting Story 70 year old male Presents to the hospital for laparascopic
September 2002 Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases Natalie J. M. Dailey, Harvard Medical Student Year III Our Patient s Presenting Story 70 year old male Presents to the hospital for laparascopic
DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO POSTGRADUATE EDUCTION ORTHOPAEDIC OFF-SERVICE GOALS & OBJECTIVES
 DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO POSTGRADUATE EDUCTION ORTHOPAEDIC OFF-SERVICE GOALS & OBJECTIVES GOAL #1 develop the ability to order and understand interpretation
DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO POSTGRADUATE EDUCTION ORTHOPAEDIC OFF-SERVICE GOALS & OBJECTIVES GOAL #1 develop the ability to order and understand interpretation
Wrist Fractures. Wrist Defined: Carpal Bones Distal Radius Distal Ulna
 Wrist Fractures Wrist Fractures Wrist Defined: Carpal Bones Distal Radius Distal Ulna Wrist Fractures Wrist Joints: CMC Intercarpal Radiocarpal DRUJ drudge Wrist Fractures Wrist Fractures: (that we are
Wrist Fractures Wrist Fractures Wrist Defined: Carpal Bones Distal Radius Distal Ulna Wrist Fractures Wrist Joints: CMC Intercarpal Radiocarpal DRUJ drudge Wrist Fractures Wrist Fractures: (that we are
It is worth noting that people with psoriasis can also develop other forms of arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
 Psoriatic Arthritis Main Colour - pantone 2597u Research - pantone 206u Children - pantone 123 4 What is psoriatic arthritis? Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory joint disease associated with psoriasis.
Psoriatic Arthritis Main Colour - pantone 2597u Research - pantone 206u Children - pantone 123 4 What is psoriatic arthritis? Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory joint disease associated with psoriasis.
Cervical Spine: Postmortem Assessment of Accident Injuries Comparison of Radiographic, MR Imaging, Anatomic, and Pathologic Findings
 Cervical Spine: Postmortem Assessment of Accident Injuries Comparison of Radiographic, MR Imaging, Anatomic, and Pathologic Findings 1 Radiology, November, 2001;221:340-346. Axel Stäbler, MD, Jurik Eck,
Cervical Spine: Postmortem Assessment of Accident Injuries Comparison of Radiographic, MR Imaging, Anatomic, and Pathologic Findings 1 Radiology, November, 2001;221:340-346. Axel Stäbler, MD, Jurik Eck,
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Test Request Tip Sheet
 With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Common wrist injuries in sport. Chris Milne Sports Physician Hamilton,NZ
 Common wrist injuries in sport Chris Milne Sports Physician Hamilton,NZ Overview / Classification Acute injuries Simple - wrist sprain Not so simple 1 - Fracture of distal radius/ulna 2 - Scaphoid fracture
Common wrist injuries in sport Chris Milne Sports Physician Hamilton,NZ Overview / Classification Acute injuries Simple - wrist sprain Not so simple 1 - Fracture of distal radius/ulna 2 - Scaphoid fracture
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
EFSUMB EUROPEAN FEDERATION OF SOCIETIES FOR ULTRASOUND IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY Building a European Ultrasound Community
 MINIMUM TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PRACTICE OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND IN EUROPE Appendix 12: Musculoskeletal Musculoskeletal ultrasound comprises a wide range of different examinations increasingly performed
MINIMUM TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PRACTICE OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND IN EUROPE Appendix 12: Musculoskeletal Musculoskeletal ultrasound comprises a wide range of different examinations increasingly performed
NOTEWORTHY DECISION SUMMARY. Decision: WCAT-2004-02435-RB Panel: Beatrice Anderson Decision Date: May 10, 2004
 NOTEWORTHY DECISION SUMMARY Decision: WCAT-2004-02435-RB Panel: Beatrice Anderson Decision Date: May 10, 2004 Referrals to Board of Issue for Determination - Completion of Appeals after Referral - Section
NOTEWORTHY DECISION SUMMARY Decision: WCAT-2004-02435-RB Panel: Beatrice Anderson Decision Date: May 10, 2004 Referrals to Board of Issue for Determination - Completion of Appeals after Referral - Section
What a Difference MRI Makes
 Consultant s Corner What a Difference MRI Makes Nathaniel A. White, DVM, MS, DACVS Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University Natasha M. Werpy, DVM Colorado State University Consultant s Corner
Consultant s Corner What a Difference MRI Makes Nathaniel A. White, DVM, MS, DACVS Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University Natasha M. Werpy, DVM Colorado State University Consultant s Corner
Treatment of Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Treatment of Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Zhanguo Li Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, People s Hospital Beijing University Medical School, China Contents Background Challenges Treatment strategies
Treatment of Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Zhanguo Li Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, People s Hospital Beijing University Medical School, China Contents Background Challenges Treatment strategies
Cirrus 0.2T. MRI for Everyone. North America, Asia, Europe. contact: kturek@mri-tech.pl
 Cirrus 0.2T MRI for Everyone North America, Asia, Europe contact: kturek@mri-tech.pl MRI-TECH inc. Cirrus MRI system for all your needs: Low costs Low maintenance High quality Open geometry Imaging of
Cirrus 0.2T MRI for Everyone North America, Asia, Europe contact: kturek@mri-tech.pl MRI-TECH inc. Cirrus MRI system for all your needs: Low costs Low maintenance High quality Open geometry Imaging of
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
 Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
MEDICAL CENTRES AND SCANS
 MEDICAL CENTRES AND SCANS Lúnasa 2013 MEDICAL, SCIENTIFIC AND WELFARE COMMITTEE INTRODUCTION Technology is a critical component of modern day sports medicine. Whilst providing a cutting edge in terms of
MEDICAL CENTRES AND SCANS Lúnasa 2013 MEDICAL, SCIENTIFIC AND WELFARE COMMITTEE INTRODUCTION Technology is a critical component of modern day sports medicine. Whilst providing a cutting edge in terms of
How To Choose A Biologic Drug
 North Carolina Rheumatology Association Position Statements I. Biologic Agents A. Appropriate delivery, handling, storage and administration of biologic agents B. Indications for biologic agents II. III.
North Carolina Rheumatology Association Position Statements I. Biologic Agents A. Appropriate delivery, handling, storage and administration of biologic agents B. Indications for biologic agents II. III.
Symptoms ongoing for 6/12, initially intermittent in nature.
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Case Study INTRODUCTION Each student will have watched the relevant MDT member carrying out their initial assessment on the same newly diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis patient. Videos
Rheumatoid Arthritis Case Study INTRODUCTION Each student will have watched the relevant MDT member carrying out their initial assessment on the same newly diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis patient. Videos
Enthesitis: an autoinflammatory lesion linking nail and joint involvement in psoriatic disease
 DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03363.x JEADV Blackwell Publishing Ltd REVIEW ARTICLE Enthesitis: an autoinflammatory lesion linking nail and joint involvement in psoriatic disease D McGonagle* NIHR, Leeds
DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03363.x JEADV Blackwell Publishing Ltd REVIEW ARTICLE Enthesitis: an autoinflammatory lesion linking nail and joint involvement in psoriatic disease D McGonagle* NIHR, Leeds
IFSSH Scientific Committee on. Wrist Biomechanics and Instability
 IFSSH Scientific Committee on Wrist Biomechanics and Instability Chair: Hisao Moritomo (Japan) Committee: Emmanuel Apergis (Greece) Guillaume Herzberg (France) Scott Wolfe (USA) Jose Maria Rotella (Argentina)
IFSSH Scientific Committee on Wrist Biomechanics and Instability Chair: Hisao Moritomo (Japan) Committee: Emmanuel Apergis (Greece) Guillaume Herzberg (France) Scott Wolfe (USA) Jose Maria Rotella (Argentina)
MRI Department Goals. Effective Ways to Improve Patient Cooperation and Safety in MRI Exam. Lecture Topics
 Effective Ways to Improve Patient Cooperation and Safety in MRI Exam lowens2@clarian.org Lecture Topics MRI patient preparation Department MRI Safety Policies and Procedures MRI patient safety screening
Effective Ways to Improve Patient Cooperation and Safety in MRI Exam lowens2@clarian.org Lecture Topics MRI patient preparation Department MRI Safety Policies and Procedures MRI patient safety screening
Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries
 1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
