Benedikt Ostendorf, Axel Scherer, Ulrich Mödder, and Matthias Schneider
|
|
|
- Oswin Cole
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 7, July 2004, pp DOI /art , American College of Rheumatology Diagnostic Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Forefeet in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis When Findings on Imaging of the Metacarpophalangeal Joints of the Hands Remain Normal Benedikt Ostendorf, Axel Scherer, Ulrich Mödder, and Matthias Schneider Objective. To investigate the diagnostic role of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the forefeet in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in whom findings on MR images of the hands are normal and conventional radiographs of the hands and feet do not show erosions. Methods. The study group comprised 25 patients with early RA (disease duration of <12 months) in whom erosions were not demonstrated on conventional radiographs of the hands and feet. These patients underwent MRI of the clinically dominant hand to detect signs of arthritis. If results of MRI of the hand were normal according to the Outcome Measures in Rheumatology Clinical Trials (OMERACT) RA-MRI scoring system (RAMRIS), MRI of the dominant forefoot was performed. The MRI protocol comprised coronal and sagittal T1-weighted spin-echo (before and after administration of contrast medium), coronal fatsuppressed short tau inversion recovery sequences, coronal and sagittal T2-weighted turbo spin-echo sequences, and axial fat-suppressed T1-weighted spinecho sequences after administration of contrast medium. MRI of the forefeet was analyzed on the basis of a modified RAMRIS. Results. MRI revealed pathologic findings in the hands of 15 of 25 patients (edema in 9 patients, synovitis in 12, erosions in 6, defects in 3). In 10 patients with a Benedikt Ostendorf, MD, Axel Scherer, MD, Ulrich Mödder, MD, Matthias Schneider, MD: Heinrich-Heine University of Duesseldorf, Duesseldorf, Germany. Address correspondence and reprint requests to Benedikt Ostendorf, MD, Center for Rheumatology, Department of Nephrology and Rheumatology, Heinrich-Heine University of Duesseldorf, Moorenstrasse 5, Duesseldorf, Germany. ostendorf@ med.uni-duesseldorf.de. Submitted for publication September 20, 2003; accepted in revised form March 5, mean disease duration of 9.4 weeks, hand MRI scans were normal according to RAMRIS. Four of these 10 patients had tenosynovitis of the finger flexor tendons (there was no OMERACT criterion for tenosynovitis). RAMRIS analysis of the corresponding MRI scans of the forefeet of these patients revealed signs of edema in 7 patients, synovitis in all 10 patients (at the third metatarsophalangeal [MTP] joint in 7, at the fourth MTP joint in 6, at the first MTP joint in 4, and at the fifth MTP joint in 2 patients), tenosynovitis of the foot flexor tendons in 2 patients, erosions at the second and third MTP joints in 1 patient, and a single defect at the first MTP joint in 1 patient. Conclusion. RAMRIS analysis of MRI scans of the forefeet detected synovitis and bone edema in patients with early RA in whom MRI of the finger joints was normal. MRI of the forefeet contributes an additional tool aimed at earlier and more accurate diagnosis and thus might allow an earlier decision to start appropriate medication in patients with early RA. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has a potential for disclosing early signs of inflammation and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) that is superior to that of conventional radiography and clinical examination of the knee (1,2), wrist (3,4), or hand and finger joints (5 9). Diagnosing destructive RA during its early stage is crucial to the implementation of active and aggressive treatment, which is expected to alleviate RA joint damage, thereby reducing functional deterioration and improving the long-term outcome (10 12). Conventional radiography of both the hands and feet is the traditional method used to diagnose RA (13). MRI investigations comparing images of the hands and feet of patients with early RA showed typical bony changes 2094
2 MRI OF FOREFEET IN DIAGNOSIS OF RA 2095 Table 1. Demographic and clinical details as well as hand MRI and forefeet MRI scoring data according to the OMERACT/RAMRIS (18,19) in 10 patients with early RA* OMERACT score, RAMRIS system, MTP joints 1 5 Patient/ age/sex Disease duration, weeks DAS28 OMERACT score, MRI MCP MTP Erosion Defect Bone edema Synovitis, method 1 (0 3 points) Synovitis, method 2 (millimeters) Sum score 1/43/M /34/F /71/M /52/F /26/F /69/F /39/F /31/F /36/M /39/F Sum score * The mean age of patients was 45.1 years; mean disease duration was 9.4 weeks; mean Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) was Patient 2 had tenosynovitis of the second through fourth hand flexor tendons (score 1 ); patient 4 had tenosynovitis of the second through fifth hand flexor tendons (score 1 ); patient 5 had tenosynovitis of the third hand extensor tendon (score 1 ); patient 8 had tenosynovitis of the fourth foot flexor tendon (score 1 ); patient 10 had tenosynovitis of the second hand flexor tendon (score 1 ). MRI magnetic resonance imaging; RA rheumatoid arthritis; OMERACT Outcome Measures in Rheumatology Clinical Trials; RAMRIS RA-MRI scoring system; MTP metatarsophalangeal; MCP metacarpophalangeal.
3 2096 OSTENDORF ET AL despite conventional radiographs being normal (14). The fact that conventional radiography has been found to reveal bony erosions in the foot earlier than in the hand joints (15,16) suggests that the feet may be primarily affected in very early RA (17). Therefore, the purpose of our study was to investigate, in patients with early RA and normal MR images of the hands, the diagnostic role of MRI of the forefeet for measuring features of early inflammation such as edema, synovitis, or even incipient osteodestruction, using the RA-MRI scoring system (RAMRIS) (18) of the Outcome Measures in Rheumatology Clinical Trials (OMERACT) group (19). PATIENTS AND METHODS Patients. Twenty-five patients (17 women and 8 men ages 18 years and older [mean age 49 years, range years]) with early RA diagnosed according to the criteria of the American College of Rheumatology (formerly, the American Rheumatism Association) (20) were recruited from the Early Arthritis Clinic of the Outpatient Department of Rheumatology of the Heinrich-Heine University. Patients with early RA (disease duration of 12 months) were eligible for the study. The mean disease duration was 5.89 months (range 6 weeks to 12 months). Medications used by the patients at the time of study entry included nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs; none of the patients had previously received disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) or corticosteroids. The assessment of general disease activity was based on the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) (Tables 1 and 2) (21,22). Conventional hand (posteroanterior, oblique) and foot (anteroposterior, oblique) radiographs were performed for all patients and were scored according to the method proposed by Larsen et al (23). Subject to their radiographs being graded as nonerosive (Larsen grade 0 or 1), 25 patients underwent MRI analysis of the clinically dominant hand to detect signs of arthritis according to RAMRIS (18). If MRI of the hand was normal according to RAMRIS (n 10), MRI of the clinically dominant forefoot was performed. Clinically dominant was defined as the site more tender to pressure and/or with signs of redness and/or hyperthermia and/or swelling. Protocol for MRI of the hand. A 1.5T MRI whole-body scanner (Siemens Magnetom Vision; Munich, Germany) was used for the MRI examinations. MRI of the second to fifth metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints of the dominant hand was performed. The hand was fixed within a flexible surface coil (CP flex large). MRI was used to obtain sequences, as follows: coronal T2-weighted turbo spin-echo (TSE) sequences (repetition time [TR]/echo time [TE] 3,500/100 msec, slice thickness 3 mm, field of view [FOV] cm, matrix size pixels, acquisition time 3 minutes, 50 seconds), coronal fatsuppressed short tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequences (TR/TE/inversion time [TI] 3,975/30/150 msec, slice thickness 3 mm, FOV cm, matrix size pixels, acquisition time 3 minutes, 30 seconds), and coronal T1-weighted SE sequences (TR/TE 500/15 msec, slice thickness 3 mm, FOV cm, matrix size pixels, acquisition time 6 minutes, 20 seconds) were obtained before and immediately after intravenous application of gadolinium diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (Gd-DTPA; 0.1 mmoles/kg of body weight) (Magnevist, Schering, Berlin). Axial T1-weighted fatsuppressed SE sequences (TR/TE 600/15 msec, slice thickness 3 mm, FOV 8 13 cm, matrix size pixels, acquisition time 4 minutes, 50 seconds) were obtained after administration of Gd-DTPA. Protocol for MRI of the forefoot. MR imaging of the forefoot was performed using the same hardware as that used for the hand examinations. MRI of the first to fifth metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints of the clinically dominant foot was performed. The sequences were obtained as follows: sagittal T2-weighted TSE sequences (TR/TE 3,700/96 msec, slice thickness 3 mm, FOV cm, matrix size pixels, acquisition time 4 minutes, 10 seconds), coronal fat-suppressed STIR sequences (TR/TE/TI 5,300/30/150 msec, slice thickness 3 mm, FOV cm, matrix size pixels, acquisition time 3 minutes, 40 seconds), and sagittal T1-weighted SE sequences (TR/TE 500/15 msec, slice thickness 3 mm, FOV cm, matrix size pixels, acquisition time 5 minutes, 30 seconds) were obtained before and immediately after intravenous application of Gd-DTPA (0.1 mmoles/kg of body weight). Axial T1-weighted fat-suppressed SE sequences (TR/TE 740/14 msec, slice thickness 3 mm, FOV cm, matrix size pixels, acquisition time 4 minutes, 40 seconds) were obtained after administration of Gd-DTPA. MRI evaluation. One experienced rheumatologist (BO) and 2 radiologists (AS and UM) blinded to each patient s identity and clinical data read and scored MR images of the hands and forefeet, in a consensual review. MRI evaluation and scoring of MR images of the hand were performed according to the OMERACT criteria and RAMRIS analysis (18). Definitions of lesions to be scored (OMERACT/ RAMRIS) (18,19). Synovitis was defined as an area in the synovial compartment that shows above-normal post gadolinium enhancement of a thickness greater than the width of the normal synovium. An MRI bone erosion was defined as a sharply marginated bone lesion, with correct juxtaarticular localization and typical signal characteristics, that is visible in 2 planes with a cortical break seen in at least 1 plane. An MRI bone defect was defined as a sharply marginated area of trabecular loss without a visible cortical break. MRI bone edema was defined as a lesion within the trabecular bone, with ill-defined margins and signal characteristics consistent with increased water content. Scoring system for the hand. Bone erosions. Each MCP joint was scored separately for bone erosions. The 0 10-point scale, based on the proportion of eroded bone compared with the assessed bone volume, which was judged on all available images, is as follows: 0 no erosion, % of bone eroded, % of bone eroded, and so forth. For long bones, the assessed bone volume is from the articular surface (or, if absent, its best estimated position) to a depth of 1 cm, whereas it is from the whole bone for carpal bones. Defect. For scoring of bone defects, the scale is 0 10, based on the volume of the defect, as for erosion. Bone edema. Bone edema is scored on a 0 3 scale based on the volume of edema, as follows: 0 no edema, 1
4 MRI OF FOREFEET IN DIAGNOSIS OF RA 2097 Table 2. Demographic and clinical details as well as MRI scoring data on the hands according to the OMERACT/RAMRIS (18,19) in 15 patients with early RA* OMERACT score, RAMRIS system, MCP joints I V Patient/ age/sex Disease duration, months DAS28 MRI, MCP Erosion Defect Bone edema (0 3 points) Synovitis, method 1 (0 3 points) Synovitis, method 2 (millimeters) Sum score 11/52/M /74/F /55/F /42/F /52/F /25/M /62/M /58/F /64/F /68/F /49/M /61/F /51/M /32/F /29/F Sum score * The mean age of patients was 51.6 years; mean disease duration was 8.3 months; mean Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) was Patients 11, 13, 14, 15, 16, 18, 21, 22, 23, 24, and 25 had tenosynovitis of the hand flexor tendons (score 1 ); patient 19 had tenosynovitis of hand extensor tendons (score 1 ). MRI magnetic resonance imaging; RA rheumatoid arthritis; OMERACT Outcome Measures in Rheumatology Clinical Trials; RAMRIS RA-MRI scoring system; MCP metacarpophalangeal.
5 2098 OSTENDORF ET AL Table 3. Parameter Correlation of clinical parameters and results of MRI forefoot analysis* DAS28 Disease duration Erosion Bone edema Synovitis, method 1 Synovitis, method 2 DAS Disease duration Erosion Bone edema Synovitis, method 1 Synovitis, method 2 * MRI magnetic resonance imaging; DAS28 Disease Activity Score in 28 joints; not significant; highly significant; moderately significant. 1 33% of bone edematous, % of bone edematous, and % of bone edematous. Synovitis. Synovitis was assessed in the second through fifth MCP joints (the first MCP joint was not scored), using 2 methods. For method 1, a 0 3-point scale is used. A score of 0 is normal, while scores of 1, 2, and 3 (mild, moderate, and severe, respectively) increase by thirds the presumed maximum volume of enhancing tissue in the synovial compartment. For method 2, the maximum thickness of enhancing tissue on the axial scan in the slice showing the most thickening is measured in millimeters. Scoring system for the forefoot. For the definition and scoring of joint pathology of the hands and forefeet, RAMRIS was adapted for MRI forefoot evaluation. Arthritic lesions of the forefoot region to be scored on MR images were synovitis, edema, erosion, and defects. In addition to these OMERACT criteria, we used and scored the appearance of tenosynovitis in the hands and feet (i.e., tissue surrounding the tendon showing high signal intensity on T2-weighted sequences, hypointense signal on T1-weighted images, and enhancement on the post Gd-DTPA images). Tenosynovitis was scored semiquantitatively, as follows: 0 not present, 1 present at the flexor tendons, and 1 present at the extensor tendons. In addition to the number of hand joints covered by RAMRIS for synovitis (the second to fifth MCP joints), we added the first MTP joint to the forefoot score, so that all 5 MTP joints (the first through fifth) could be analyzed. Bone edema was scored using a 0 10-point scale for the volume of edema, as follows: 0 no edema, % of bone affected, % of bone affected, and so forth. Statistical analysis. Pearson s chi-square test was used for statistical analysis. Two variables were considered not statistically independent if their chi-square value was highly significant at the 1% level ( ), moderately significant at less than or equal to the 10% level ( ), and not significant at greater than the 10% level. RESULTS According to RAMRIS analysis (18), 15 of the 25 patients with early RA who were investigated had pathologic findings of the hand by MRI. Signs of edema were detected in 9 of these 15 patients, synovitis in 12, erosions in 6, and defects in 3 (Table 2). In addition, signs of tenosynovitis (for which there was no OMERACT criterion), mostly affecting the flexor tendon sheaths, were observed in 12 patients. Synovitis and erosions were predominantly found at the second and third MCP joints, whereas bone edema was seen in all MCP joints, except the fifth MCP joint, without a significant joint pattern. In 10 of 25 patients with early RA (7 women and 3 men, age range years [mean 45 years]), MRI of the hand was normal for edema, synovitis, erosions, and/or defects (Table 1 and Figure 1). This finding must be emphasized, because a normal RAMRIS score for the hand was the inclusion criterion for the additional MRI investigation of the forefeet. In these 10 patients, disease duration ranged from 6 weeks to 16 weeks (mean 9.4 weeks) (Table 1). In patients with early RA and disease duration of 6 weeks (patients 3 and 7), MRI analysis of the forefeet revealed only mild signs of synovitis. In patients with disease duration of 8 10 weeks (patients 1, 2, 4, 8, 9, and 10), signs of bone edema were observed mostly at the second and third MTP joints, and synovitis was observed at the fourth MTP joint. In patients with disease duration of 12 weeks (patients 5 and 6), signs of edema were observed at the second, third, and fourth MTP joints; synovitis was observed at the first through fourth MTP joints in patient 5 and at the first through fifth MTP joints in patient 6. Erosions at the second and third MTP joints were observed in only 1 patient (patient 4), who had a disease duration of 8 weeks. No significant correlation of disease duration with any MRI parameter was demonstrated (Table 3). DAS28 scores in the 10 patients with normal hand MR images ranged from 3.67 to 4.81 (mean 4.22) (Table 1). Because the DAS28 does not include assessment of the feet in patients with RA, we clinically examined the forefeet joints. In 7 of 10 patients, the region of the first through fifth MTP joints was tender to pressure, but no signs of acute swelling were observed. In patients with early RA and a higher mean DAS28
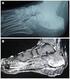
6 MRI OF FOREFEET IN DIAGNOSIS OF RA 2099 Figure 1. Typical magnetic resonance image (axial T1-weighted fatsuppressed spin-echo sequences of the forefoot), after administration of gadolinium diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid, for each of the 10 patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Numbers 1 10 of these images correspond with the patient numbers in Table 1. be bone edema; sy synovitis; er erosion; de defect. ( 4.22; patients 2, 4, 5, 9, and 10), MRI showed signs of severe bone edema, mostly at the second through fourth MTP joints, and additionally showed signs of synovitis, primarily at the fourth MTP joint. Patients with a lower DAS28 ( 4.22; patients 1, 3, 6, 7, and 8) showed almost no signs of edema (patient 8 was given 1 point, by RAMRIS, for the fourth MTP joint), but patients 6, 7, and 8 did have severe synovitis, mostly at the third and fourth MTP joints. One patient with a DAS28 of 3.79 (patient 6) showed signs of severe synovitis in all MTP joints. A highly significant correlation of the DAS28 with the bone edema detected by MRI was found (Table 3). Independently of the clinical assessment, RAMRIS analysis of MR images of the MTP region (first through fifth MTP joints) revealed synovitis in all 10 patients (at the third MTP joint in 7 patients, at the fourth MTP joint in 6 patients, at the first MTP joint in 4 patients, and in the fifth MTP joint in 2 patients). According to method 1 (0 3-point scale, post contrast medium enhancement) (19), synovitis was scored highest at the fourth MTP joint (sum score 18), followed by the third MTP joint (sum score 16). Synovitis as scored by method 2 (thickness in millimeters) (19) was detected mostly at the third and fourth MTP joints (sum score 27 for both) and at the second MTP joint (sum score 16). The detection of bone edema was significantly correlated with the detection of synovitis measured by method 2 (OMERACT ) (Table 3). Tenosynovitis (no OMERACT criterion) was observed in 4 of the 10 patients with normal hand MR images (tenosynovitis of the second through fourth finger flexor tendons in 1 patient, of the second through fifth flexor tendons in 1 patient, of the third extensor tendon in 1 patient, and of the second flexor tendon in 1 patient (Table 1). No patient had tenosynovitis in both the hand and foot. Two patients with normal results of hand MRI had signs of tenosynovitis at the foot flexor tendons. Signs of bone edema were demonstrated in the MTP joints of 7 of 10 patients (in 15 of 50 MTP joints), and synovitis of different degrees, thicknesses, and extensions (scored by methods 1 and 2 [OMERACT]) (19) (Table 1) was observed in all 10 patients investigated (in 23 of 50 MTP joints). Bone edema was detected most intensively at the third and fourth MTP joints (sum score 23 for both). In general, no bone edema could be detected by MRI at the first MTP joint. Only 1 patient showed incipient edema at the fifth MTP joint. Predominant locations for bone edema and synovitis were the second through fourth MTP joints. Eight of 10 patients had no signs of osteodestruction. Slight erosions were found in only 1 patient, at the second and third MTP joints. In 1 patient, an isolated defect at the first MTP joint (1 point by RAMRIS) was detected. DISCUSSION Clinical, laboratory, and radiographic findings often differ in the early stages of RA, and at the time when erosions are first seen by conventional radiography, the disease is often quite established (13). Because the effectiveness of any treatment for RA should be judged on preservation of joint structure, accurate measurement of joint pathology and reliable indicators of
7 2100 OSTENDORF ET AL outcome are needed earlier in the disease process. In this context, MRI has become a valuable technique for early detection of bone erosions in RA (9). Reports of osteodestruction being detected by conventional radiography earlier and more frequently in the foot than in the hand joints (15 17) provide accumulating evidence that the foot may be primarily affected in the early stages of RA. Therefore, the purpose of our study was to evaluate the diagnostic role of forefoot MRI in early RA. In order to use MRI to assess and analyze incipient arthritis of the forefeet at the earliest time point, we focused on patients with early RA (disease duration of 12 months) who had not received treatment with DMARDs or corticosteroids. To evaluate the diagnostic value of an additional foot MRI scan, patients with early RA were included only when, primarily, conventional radiography of the hands and feet showed no erosions and, secondarily, MRI of the clinically dominant hand was normal according to the OMERACT/RAMRIS (18). In 10 (40%) of 25 patients with early RA, MR images of the hands were negative when scored for RAMRIS parameters such as edema, synovitis, or erosions. Strikingly, we found initial signs of arthritis in the forefoot region (MTP joints). For scoring these MRI findings we adapted the RAMRIS, which was originally developed for analysis of hand MRI (18,19). In addition to the OMERACT set of parameters and joints to be scored, we added the item tenosynovitis to the RAM- RIS, because tenosynovitis is often found early in the course of RA (24), a fact that was confirmed by our findings. To assess tenosynovitis, we simplified the scoring system described by McQueen et al (25) by differentiating absent and present inflammation only at the flexor or extension sheath group. A more detailed analysis of the thickness of the sheath or the degree of inflammation was not included. Because the first MTP joint often is involved in early RA (14), we moreover extended the set of joint regions by adding the first MTP joint. Conversely, inclusion of the first MTP joint will also introduce nonspecific MRI abnormalities from concomitant osteoarthritis, which is very frequent at that site (26). This is the first study to demonstrate that analysis and scoring of forefoot MR images are feasible by using the RAMRIS for hand RA (18). Analysis of MR images of the MTP joints, the earliest site of destructive changes in RA, revealed signs of erosion (at the second and third MTP joints) in 1 patient and an isolated defect at the first MTP joint in another patient; neither of these bony changes had been detected previously by plain radiography. The detection of bony alterations in only 2 patients is in contrast to the findings of Boutry et al (14), who detected bony erosions in 23 (77%) of 30 patients in different MTP joints (first through fifth). This difference might be explained by the longer disease duration of the patients with RA in that study (average duration 12 months), whereas the present study group was characterized by a very short mean disease duration of only 9.4 weeks (range 6 16 weeks). Signs of synovitis, scored by OMERACT methods 1 (points) and 2 (millimeters) (19), were found in all 10 of the patients in our study who had normal MRI of the hand, mostly at the second through fourth MTP joints, and overall in 23 (46%) of 50 MTP joints. Based on the fact that chronic synovitis might finally lead to bone damage, the early detection of synovitis by MRI, measured by either thickness or enhancement, seems to be an important prognostic marker (9). Conaghan et al showed that, in early RA, synovitis appears to be the primary abnormality, and bone damage occurs in proportion to the level of synovitis but not in the absence of synovitis (27). We observed synovitis, without erosive changes, at the fifth MTP joint in 2 patients (20%); the fifth MTP joint is where erosion is most likely to start, according to the findings on plain radiography (17). Boutry et al found synovitis at the fifth MTP joint in 22% of the investigated MTP joints, with no significant difference in appearance between the second through fifth MTP joints (14). In this context, it must be pointed out that our MRI protocol included use of a T1- weighted fat-suppressed SE sequence after gadolinium administration, which is not listed in the core set of MRI acquisitions proposed by OMERACT (19), although this sequence is known to display the highest contrast between enhanced synovitis and surrounding tissue. In addition to erosions and synovitis, we found signs of bone edema in 7 of 10 patients (when using T1-weighted fat-suppressed SE and STIR sequences), predominantly and most intensively at the third and fourth MTP joints (sum score 23) (Table 1). Bone edema is known as a very early marker of inflammation and, in addition to synovitis, as a strong individual predictor of bone erosion in the MRI evaluation of hand RA, carrying a 6.5-fold risk of bone damage at the same site within 1 year (25,28). Longitudinal studies of patients with early RA showed that the total synovial volume in the finger joints and the presence of bone edema seem to be predictive of the number of bone erosions 1 year later and may be used in screening (9). As shown in our study, bone edema seems to be a typical MRI feature in patients with early RA, which usually
8 MRI OF FOREFEET IN DIAGNOSIS OF RA 2101 might not be found in patients with only nonspecific arthralgia (29). Because T1-weighted fat-suppressed SE and STIR sequences were not used by Boutry et al, detection of the early arthritis marker bone edema failed in that study (14). In general, signs of edema are not detectable by clinical examination and imaging modalities such as conventional radiography and ultrasonography; therefore, assessment of bone edema remains the domain of the MRI technique. Concerning clinical data, we found bone edema combined with synovitis as a sign of early inflammation in the forefeet region in the 5 patients who had a higher mean DAS28 ( 4.22). In patients with lower disease activity (DAS ), only synovitis of mild degree (1 point by RAMRIS) was detected, with almost no signs of edema. Statistical analysis (Pearson s chi-square test) revealed a significant correlation of the DAS28 with the detection of bone edema and a moderate correlation with the assessment of synovitis measured in millimeters (Table 3). This finding is in contrast to the DAS28 core criteria set (21,22), which does not include joint tenderness and swelling of the feet in patients with RA, and to the results reported by Klarlund et al (6), who found only a poor correlation of the synovial membrane volume measured by quantitative MRI of finger joints with the presence of inflammation and laboratory markers (e.g., erythrocyte sedimentation rate and rheumatoid factor). A limitation of our study was the MRI investigation of only 1 extremity (hand or foot), with the risk of arthritic lesions remaining undetected, although singleextremity MRI delivers higher MRI quality. In this study we mainly focused on MCP joints and not on the total hand including the wrist, in order to have more precise MRI analysis of that joint region, which is the primary site of RA. Another point of discussion is the transfer and extension of the existing MRI hand scoring system RAMRIS (19) to another joint region, such as the forefoot. Further studies are therefore needed to validate use of RAMRIS for evaluation of the rheumatoid joints of the foot in terms of interreader agreement and active-controlled clinical trials assessing treatment effects on MRI parameters such as edema and synovitis, which should be potentially reversible. The results of our study strongly suggest that MRI of the forefeet can be used as an additional diagnostic instrument in early RA, particularly in patients whose clinical features persist but whose conventional radiographs do not demonstrate erosions, and for whom even MRI findings of the hands are normal. In this context, the introduction of MRI of the forefoot supports accurate measurement of joint pathology in terms of defining the diagnosis of early RA more effectively, i.e., with greater precision and at an earlier stage. This may then facilitate decision-making regarding first-line medication, such as DMARD therapy. REFERENCES 1. Reiser MF, Bongartz GP, Erlemann R, Schneider M, Pauly T, Sittek H, et al. Gadolinium-DTPA in rheumatoid arthritis and related diseases: first results with dynamic magnetic resonance imaging. Skeletal Radiol 1989;18: Kursunoglu-Brahme S, Riccio T, Weisman MH, Resnick D, Zvaifler N, Sanders ME, et al. Rheumatoid knee: role of gadopentetate-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 1990;176: Gilkeson G, Polisson R, Sinclair H, Vogler J, Rice J, Caldwell D, et al. Early detection of carpal erosions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a pilot study of magnetic resonance imaging. J Rheumatol 1988;15: Corvetta A, Giovagnoni A, Baldelli S, Ercolani P, Pomponio G, Luchetti MM, et al. MR imaging of rheumatoid hand lesions: comparison with conventional radiology in 31 patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1992;10: Jevtic V, Watt I, Rozman B, Kos-Golja M, Rupenovic S, Logar D, et al. Precontrast and postcontrast (Gd-DTPA) magnetic resonance imaging of hand joints in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Radiol 1993;48: Klarlund M, Ostergaard M, Lorenzen I. Finger joint synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: quantitative assessment by magnetic resonance imaging. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999;38: Gasson J, Gandy SJ, Hutton CW, Jacoby RK, Summers IR, Vennart W. Magnetic resonance imaging of rheumatoid arthritis in metacarpophalangeal joints. Skeletal Radiol 2000;29: Ostendorf B, Peters R, Dann P, Becker A, Scherer A, Wedekind F, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and miniarthroscopy of metacarpophalangeal joints: sensitive detection of morphologic changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2001;44: Savnik A, Malmskov H, Thomsen HS, Graff LB, Nielsen H, Danneskiold-Sansoe B, et al. MRI of the wrist and finger joints in inflammatory joint diseases at 1-year interval: MRI features to predict bone erosions. Eur Radiol 2002;12: Dawes PT, Fowler PD. Treatment of early rheumatoid arthritis: a review of current and future concepts and therapy. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1995;13: Young A, van der Heijde DM. Can we predict aggressive disease? Baillieres Clin Rheumatol 1997;11: Emery P, Marzo H, Proudman S. Management of patients with newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999;38 Suppl 2: Taouli B, Guermazi A, Sack KE, Genant HK. Imaging of the hand and wrist in RA. Ann Rheum Dis 2002;61: Boutry N, Larde A, Lapegue F, Solau-Gervais E, Flipo RM, Cotten A. Magnetic resonance imaging appearance of the hands and feet in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2003;30: Brook A, Corbett M. Radiographic changes in early rheumatoid disease. Ann Rheum Dis 1977;36: Resnick D, Niwayma G. Rheumatoid arthritis. In: Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; p
9 2102 OSTENDORF ET AL 17. Van der Heijde DM, van Leeuwen MA, van Riel PL, Koster AM, van t Hof MA, van Rijswijk MH, et al. Biannual radiographic assessments of hands and feet in a three-year prospective followup of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1992; 35: Ostergaard M, Peterfy C, Conaghan P, McQueen F, Bird P, Ejbjerg B, et al. OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies: core set of MRI acquisitions, joint pathology definitions, and the OMERACT RA-MRI scoring system. J Rheumatol 2003;30: Conaghan P, Edmonds J, Emery P, Genant H, Gibbon W, Klarlund M, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: summary of OMERACT activities, current status, and plans. J Rheumatol 2001;28: Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1988;31: Van der Heijde DM, van t Hof M, van Riel PL, van de Putte LB. Development of a disease activity score based on judgment in clinical practice by rheumatologists. J Rheumatol 1993;20: Prevoo ML, van t Hof MA, Kuper HH, van Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight joint counts: development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1995;38: Larsen A, Dale K, Eek M. Radiographic evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis and related conditions by standard reference films. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1977;18: Grassi W, De Angelis R, Lamanna G, Cervini C. The clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Radiol 1998;27 Suppl 1:S McQueen FM, Stewart N, Crabbe J, Robinson E, Yeoman S, Tan PL, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis reveals a high prevalence of erosions at four months after symptom onset. Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57: Muehleman C, Bareither D, Huch K, Cole AA, Kuettner KE. Prevalence of degenerative morphological changes in the joints of the lower extremity. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 1997;5: Conaghan PG, O Connor P, McGonagle D, Astin P, Wakefield RJ, Gibbon WW, et al. Elucidation of the relationship between synovitis and bone damage: a randomized magnetic resonance imaging study of individual joints in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2003;48: McQueen FM, Benton N, Perry D, Crabbe J, Robinson E, Yeoman S, et al. Bone edema scored on magnetic resonance imaging scans of the dominant carpus at presentation predicts radiographic joint damage of the hands and feet six years later in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2003;48: McGonagle D, Conaghan PG, O Connor P, Gibbon W, Green M, Wakefield R, et al. The relationship between synovitis and bone changes in early untreated rheumatoid arthritis: a controlled magnetic resonance imaging study. Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:
The accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging of the hands and feet in the diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis
 Joint Bone Spine 74 (2007) 362e367 Original article The accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging of the hands and feet in the diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis Cuneyt Calisir a, *, Ali Ilker Murat
Joint Bone Spine 74 (2007) 362e367 Original article The accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging of the hands and feet in the diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis Cuneyt Calisir a, *, Ali Ilker Murat
Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI. Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007
 Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007 Introduction RA most common type of inflammatory Arthritis with prevalence of 1% Accurate and
Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007 Introduction RA most common type of inflammatory Arthritis with prevalence of 1% Accurate and
Bone Erosions in Patients with RA: Exploring the Impact of the Anatomy of Interest on the Relationship Between MRI and X-ray Erosion Detection
 Bone Erosions in Patients with RA: Exploring the Impact of the Anatomy of Interest on the Relationship Between MRI and X-ray Erosion Detection Michael Tomizza, BSc, MSc Candidate October 15, 2014: Hamilton
Bone Erosions in Patients with RA: Exploring the Impact of the Anatomy of Interest on the Relationship Between MRI and X-ray Erosion Detection Michael Tomizza, BSc, MSc Candidate October 15, 2014: Hamilton
Treat to Target Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis: UK perspective. Dr Deirdre Shawe, North Hampshire Hospital, Basingstoke, UK
 Treat to Target Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis: UK perspective Dr Deirdre Shawe, North Hampshire Hospital, Basingstoke, UK What is the target? To achieve remission or low disease activity in Rheumatoid
Treat to Target Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis: UK perspective Dr Deirdre Shawe, North Hampshire Hospital, Basingstoke, UK What is the target? To achieve remission or low disease activity in Rheumatoid
Low-Field Compact Magnetic Resonance Imaging System for the Hand and Wrist in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 23:370 376 (2006) Original Research Low-Field Compact Magnetic Resonance Imaging System for the Hand and Wrist in Rheumatoid Arthritis Hiroshi Yoshioka, MD, 1 * Satoshi
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 23:370 376 (2006) Original Research Low-Field Compact Magnetic Resonance Imaging System for the Hand and Wrist in Rheumatoid Arthritis Hiroshi Yoshioka, MD, 1 * Satoshi
Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis
 REVIEW ARTICLE Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis Wilson Campos Tavares Junior 1, Renata Rolim 2, Adriana Maria Kakehasi 3 ABSTRACT Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory polyarthritis
REVIEW ARTICLE Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis Wilson Campos Tavares Junior 1, Renata Rolim 2, Adriana Maria Kakehasi 3 ABSTRACT Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory polyarthritis
Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis Dr. Andrew K. Brown Senior Lecturer & Consultant Rheumatologist Content Practical RA Assessment Advantages of ultrasonography Potential
Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis Dr. Andrew K. Brown Senior Lecturer & Consultant Rheumatologist Content Practical RA Assessment Advantages of ultrasonography Potential
Ability of Oblique Foot Radiographs to Detect Erosions in Early Arthritis: Results in the ESPOIR Cohort
 Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 59, No. 12, December 15, 2008, pp 1729 1734 DOI 10.1002/art.24310 2008, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ability of Oblique Foot
Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 59, No. 12, December 15, 2008, pp 1729 1734 DOI 10.1002/art.24310 2008, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ability of Oblique Foot
Ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis
 Formosan Journal of Rheumatology 2009;23:1-7 Review Article Ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis Ying-Chou Chen 1, Tien-Tsai Cheng 1, Shih-Wei Hsu 2 1 Department of Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology,
Formosan Journal of Rheumatology 2009;23:1-7 Review Article Ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis Ying-Chou Chen 1, Tien-Tsai Cheng 1, Shih-Wei Hsu 2 1 Department of Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology,
ACT-RAY and MRI substudy
 Tocilizumab as Monotherapy or in Combination With Methotrexate associated with Early Reductions in Tissue Inflammation: 12-Week Results From a Magnetic Resonance Imaging Substudy of a Randomized Controlled
Tocilizumab as Monotherapy or in Combination With Methotrexate associated with Early Reductions in Tissue Inflammation: 12-Week Results From a Magnetic Resonance Imaging Substudy of a Randomized Controlled
British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:1101-1105
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:1101-1105 REMISSION IN A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. AMERICAN RHEUMATISM ASSOCIATION PRELIMINARY REMISSION CRITERIA IN RELATION TO THE
British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:1101-1105 REMISSION IN A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. AMERICAN RHEUMATISM ASSOCIATION PRELIMINARY REMISSION CRITERIA IN RELATION TO THE
Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital
 Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital Contents Definition/ epidemiology Diagnosis Importance of early diagnosis/ treatment Guidelines Evidence based treatment protocol Current
Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital Contents Definition/ epidemiology Diagnosis Importance of early diagnosis/ treatment Guidelines Evidence based treatment protocol Current
ORIGINAL ARTICLE THE DIAGNOSIS OF EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS USING MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY
 AL-AZHAR ASSIUT MEDICAL JOURNAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE THE DIAGNOSIS OF EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS USING MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY Sonya M. Rashad, Eman A.M. Alkady, Essam A.M. Abda and Marwa A.A. Galal,
AL-AZHAR ASSIUT MEDICAL JOURNAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE THE DIAGNOSIS OF EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS USING MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY Sonya M. Rashad, Eman A.M. Alkady, Essam A.M. Abda and Marwa A.A. Galal,
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz
 Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? RA is the second most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most often appears between
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? RA is the second most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most often appears between
Symptoms ongoing for 6/12, initially intermittent in nature.
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Case Study INTRODUCTION Each student will have watched the relevant MDT member carrying out their initial assessment on the same newly diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis patient. Videos
Rheumatoid Arthritis Case Study INTRODUCTION Each student will have watched the relevant MDT member carrying out their initial assessment on the same newly diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis patient. Videos
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations
 Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis & Axial Spondyloarthritis
 Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis & Axial Spondyloarthritis 奇 美 醫 院 過 敏 免 疫 風 濕 科 陳 宏 安 Rheumatoid arthritis Most common chronic inflammatory joint disease Multisystem autoimmune disease of unknown
Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis & Axial Spondyloarthritis 奇 美 醫 院 過 敏 免 疫 風 濕 科 陳 宏 安 Rheumatoid arthritis Most common chronic inflammatory joint disease Multisystem autoimmune disease of unknown
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nicole Klett,, M.D.
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Nicole Klett,, M.D. Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic Chronic Inflammatory Primarily targets the synovium of diarthrodial joints Etiology likely combination genetic and environmental Diarthrodial
Rheumatoid Arthritis Nicole Klett,, M.D. Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic Chronic Inflammatory Primarily targets the synovium of diarthrodial joints Etiology likely combination genetic and environmental Diarthrodial
The Widening Mortality Gap Between Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and the General Population
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 56, No. 11, November 2007, pp 3583 3587 DOI 10.1002/art.22979 2007, American College of Rheumatology The Widening Mortality Gap Between Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and the
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 56, No. 11, November 2007, pp 3583 3587 DOI 10.1002/art.22979 2007, American College of Rheumatology The Widening Mortality Gap Between Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and the
Temporomandibular Joint Imaging Using CBCT: Technology Now Captures Reality!
 Temporomandibular Joint Imaging Using CBCT: Technology Now Captures Reality! Dale A. Miles BA, DDS, MS, FRCD (C) Diplomate, American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology Diplomate, American Board
Temporomandibular Joint Imaging Using CBCT: Technology Now Captures Reality! Dale A. Miles BA, DDS, MS, FRCD (C) Diplomate, American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology Diplomate, American Board
DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO POSTGRADUATE EDUCTION ORTHOPAEDIC OFF-SERVICE GOALS & OBJECTIVES
 DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO POSTGRADUATE EDUCTION ORTHOPAEDIC OFF-SERVICE GOALS & OBJECTIVES GOAL #1 develop the ability to order and understand interpretation
DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO POSTGRADUATE EDUCTION ORTHOPAEDIC OFF-SERVICE GOALS & OBJECTIVES GOAL #1 develop the ability to order and understand interpretation
Finger joint synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: quantitative assessment by magnetic resonance imaging
 Rheumatology 1999;38:66 72 Finger joint synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: quantitative assessment by magnetic resonance imaging M. Klarlund1,2, M. Østergaard1,2 and I. Lorenzen1 1Department of Rheumatology
Rheumatology 1999;38:66 72 Finger joint synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: quantitative assessment by magnetic resonance imaging M. Klarlund1,2, M. Østergaard1,2 and I. Lorenzen1 1Department of Rheumatology
Healing of erosive changes in rheumatoid arthritis
 Healing of erosive changes in rheumatoid arthritis R. Rau, G. Herborn, S. Wassenberg Please address correspondence to: Rolf Rau, MD, PhD, Rheumatologie, Evangelisches Fachkrankenhaus, Rosenstrasse 2, 40882
Healing of erosive changes in rheumatoid arthritis R. Rau, G. Herborn, S. Wassenberg Please address correspondence to: Rolf Rau, MD, PhD, Rheumatologie, Evangelisches Fachkrankenhaus, Rosenstrasse 2, 40882
ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 MEDIA BACKGROUNDER ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of arthritis (chronic inflammatory polyarthritis) that typically affects hands and feet, although any joint in the body
MEDIA BACKGROUNDER ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of arthritis (chronic inflammatory polyarthritis) that typically affects hands and feet, although any joint in the body
1991 :super specialties perceptions
 Ved Chaturvedi, MD, DM Research & Referral Hospital New Delhi President Indian Rheumatology Association MSK Ultrasound..A decade experience of bedside MSK US by a clinician. Was it worth it.? 1991 :super
Ved Chaturvedi, MD, DM Research & Referral Hospital New Delhi President Indian Rheumatology Association MSK Ultrasound..A decade experience of bedside MSK US by a clinician. Was it worth it.? 1991 :super
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
 In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists
 Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists Case 27 yo female with 6 month history of right forearm and hand pain Works as secretary, symptoms are interfering with her job duties Complains that she
Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists Case 27 yo female with 6 month history of right forearm and hand pain Works as secretary, symptoms are interfering with her job duties Complains that she
2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis Published in the September 2010 Issues of A&Rand ARD Phases of the Project Phase 1 Data analysis Phase 2 Consensus process Predictors of
2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis Published in the September 2010 Issues of A&Rand ARD Phases of the Project Phase 1 Data analysis Phase 2 Consensus process Predictors of
Arthritis of the Hands
 Arthritis of the Hands On the Agenda Normal Osteoarthitis Rheumatoid arthritis CPPD crystal deposition Gout Psoriatic arthritis Normal Hand X-ray Osteoarthritis (DJD) Gradual degeneration of articular
Arthritis of the Hands On the Agenda Normal Osteoarthitis Rheumatoid arthritis CPPD crystal deposition Gout Psoriatic arthritis Normal Hand X-ray Osteoarthritis (DJD) Gradual degeneration of articular
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Disease RA Final.indd 2 15. 6. 10. 11:23
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease RA Final.indd 2 15. 6. 10. 11:23 Understanding what to expect can help you prepare for your transition into treatment. Rheumatoid Arthritis What You Need To Know About Rheumatoid
Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease RA Final.indd 2 15. 6. 10. 11:23 Understanding what to expect can help you prepare for your transition into treatment. Rheumatoid Arthritis What You Need To Know About Rheumatoid
Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Original Policy Date January /2014
 MP 2.04.81 Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis Medical Policy Section 2.0 Original Policy Date January /2014 Last Review Status/Date 1/2014 Disclaimer Our medical policies are designed for informational
MP 2.04.81 Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis Medical Policy Section 2.0 Original Policy Date January /2014 Last Review Status/Date 1/2014 Disclaimer Our medical policies are designed for informational
Understanding and improving communications between people with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthcare professionals. RCUKCOMM00116w February 2014
 Understanding and improving communications between people with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthcare professionals RCUKCOMM00116w February 2014 This project has been funded by Roche Products Ltd &
Understanding and improving communications between people with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthcare professionals RCUKCOMM00116w February 2014 This project has been funded by Roche Products Ltd &
COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 17 December 2003 CPMP/EWP/556/95 rev 1/Final COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 17 December 2003 CPMP/EWP/556/95 rev 1/Final COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
A patientwithsystemicsclerosis andjointpain. Christian Beyer University Erlangen-Nuremberg(GER)
 A patientwithsystemicsclerosis andjointpain Christian Beyer University Erlangen-Nuremberg(GER) Whatisimportanttoyou? lungs GI tract fatigue heart skin muscles Raynaud s joints Whatisimportanttopatients?
A patientwithsystemicsclerosis andjointpain Christian Beyer University Erlangen-Nuremberg(GER) Whatisimportanttoyou? lungs GI tract fatigue heart skin muscles Raynaud s joints Whatisimportanttopatients?
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. Dr Bruce Kirkham Rheumatology Clinical Lead
 RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Dr Bruce Kirkham Rheumatology Clinical Lead RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) RA is a common disease: 0.8 per cent of the population RA more common in females: female to male ratio 3:1 RA
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Dr Bruce Kirkham Rheumatology Clinical Lead RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) RA is a common disease: 0.8 per cent of the population RA more common in females: female to male ratio 3:1 RA
Early identification and treatment - the Norwegian perspective. Till Uhlig Dept of Rheumatology Diakonhjemmet Hospital Oslo, Norway
 Early identification and treatment - the Norwegian perspective Till Uhlig Dept of Rheumatology Diakonhjemmet Hospital Oslo, Norway Oslo Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry (ORAR) Very early Arthritis Clinic
Early identification and treatment - the Norwegian perspective Till Uhlig Dept of Rheumatology Diakonhjemmet Hospital Oslo, Norway Oslo Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry (ORAR) Very early Arthritis Clinic
Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem
 Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem Professor Dr John George University of Malaya Research Imaging Centre University of Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Abstract: Aim:
Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem Professor Dr John George University of Malaya Research Imaging Centre University of Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Abstract: Aim:
Etanercept (Enbrel ) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis with Recent Onset Versus Established Disease: Improvement in Disability
 Etanercept (Enbrel ) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis with Recent Onset Versus Established Disease: Improvement in Disability SCOTT W. BAUMGARTNER, ROY M. FLEISCHMANN, LARRY W. MORELAND, MICHAEL H.
Etanercept (Enbrel ) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis with Recent Onset Versus Established Disease: Improvement in Disability SCOTT W. BAUMGARTNER, ROY M. FLEISCHMANN, LARRY W. MORELAND, MICHAEL H.
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain
 Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis at an early stage
 Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis at an early stage P. Miossec and J. Tebib Definition Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the most frequent chronic inflammatory arthritis. It affects about 0.5% of the population,
Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis at an early stage P. Miossec and J. Tebib Definition Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the most frequent chronic inflammatory arthritis. It affects about 0.5% of the population,
Rheumatology Labs for Primary Care Providers. Robert Monger, M.D., F.A.C.P. 2015 Frontiers in Medicine
 Rheumatology Labs for Primary Care Providers Robert Monger, M.D., F.A.C.P. 2015 Frontiers in Medicine Objectives Review the Indications for and Interpretation of lab testing for the following diseases:
Rheumatology Labs for Primary Care Providers Robert Monger, M.D., F.A.C.P. 2015 Frontiers in Medicine Objectives Review the Indications for and Interpretation of lab testing for the following diseases:
A Topological Approach to Quantitation of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Topological Approach to Quantitation of Rheumatoid Arthritis Hamish Carr, John Ryan, Maria Joyce, Oliver Fitzgerald, Douglas Veale, Robin Gibney, and Patrick Brennan University College Dublin Summary.
A Topological Approach to Quantitation of Rheumatoid Arthritis Hamish Carr, John Ryan, Maria Joyce, Oliver Fitzgerald, Douglas Veale, Robin Gibney, and Patrick Brennan University College Dublin Summary.
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES. Anthony Hewitt
 DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Assessment of Proximal Finger Joint Inflammation in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis, Using a Novel Laser-Based Imaging Technique
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 46, No. 5, May 2002, pp 1177 1184 DOI 10.1002/art.10226 2002, American College of Rheumatology Assessment of Proximal Finger Joint Inflammation in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis,
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 46, No. 5, May 2002, pp 1177 1184 DOI 10.1002/art.10226 2002, American College of Rheumatology Assessment of Proximal Finger Joint Inflammation in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis,
.org. Arthritis of the Hand. Description
 Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Medical Policy Manual. Topic: Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis Date of Origin: June 2014
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis Date of Origin: June 2014 Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed Date: June 2014 Policy No: 67 Effective Date: September 1, 2014 IMPORTANT
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis Date of Origin: June 2014 Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed Date: June 2014 Policy No: 67 Effective Date: September 1, 2014 IMPORTANT
Imaging Rheumatoid Arthritis
 April 2002 Imaging Rheumatoid Arthritis Aimee Shu, Harvard Medical School, Year III Meet Ms. M 50-year old female 22-year history of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (RA) Followed at BIDMC rheumatology
April 2002 Imaging Rheumatoid Arthritis Aimee Shu, Harvard Medical School, Year III Meet Ms. M 50-year old female 22-year history of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (RA) Followed at BIDMC rheumatology
DISEASE COURSE IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: AN OBSERVATIONAL STUDY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES DISEASE COURSE IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: AN OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Teodora Serban 1,2, Iulia Satulu 2, Oana Vutcanu 2, Mihaela Milicescu 1,2, Carina Mihai 1,2, Mihai Bojinca 1,2, Victor
ORIGINAL ARTICLES DISEASE COURSE IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: AN OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Teodora Serban 1,2, Iulia Satulu 2, Oana Vutcanu 2, Mihaela Milicescu 1,2, Carina Mihai 1,2, Mihai Bojinca 1,2, Victor
INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D.
 05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Treat-to-Target
 Rheumatoid Arthritis and Treat-to-Target A Case of Need Encountering Opportunity Need RA affects approximately 1.5 million adults in the United States 1 20%-30% face permanent work disability if not treated
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Treat-to-Target A Case of Need Encountering Opportunity Need RA affects approximately 1.5 million adults in the United States 1 20%-30% face permanent work disability if not treated
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION
 Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 65, No. 2, February 2013, pp 220 226 DOI 10.1002/acr.21787 2013, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Foot-Related Health Care Use in Patients With Rheumatoid
Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 65, No. 2, February 2013, pp 220 226 DOI 10.1002/acr.21787 2013, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Foot-Related Health Care Use in Patients With Rheumatoid
Prognostic factors in rheumatoid arthritis
 Prognostic factors in rheumatoid arthritis Thesis Éva Palkonyai M.D. Semmelweis University, Budapest School of Ph.D. Studies Supervisor: Péter Gergely MD, D.Sci Budapest 2006. 1 Contents 1. Introduction
Prognostic factors in rheumatoid arthritis Thesis Éva Palkonyai M.D. Semmelweis University, Budapest School of Ph.D. Studies Supervisor: Péter Gergely MD, D.Sci Budapest 2006. 1 Contents 1. Introduction
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure
Treatment of Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Treatment of Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Zhanguo Li Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, People s Hospital Beijing University Medical School, China Contents Background Challenges Treatment strategies
Treatment of Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Zhanguo Li Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, People s Hospital Beijing University Medical School, China Contents Background Challenges Treatment strategies
Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents About Rheumatoid Arthritis 1 Definition 1 Signs and symptoms 1 Causes 1 Risk factors 1 Test and diagnosis 2 Treatment options 2 Lifestyle 3 References
Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents About Rheumatoid Arthritis 1 Definition 1 Signs and symptoms 1 Causes 1 Risk factors 1 Test and diagnosis 2 Treatment options 2 Lifestyle 3 References
Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013
 Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013 Measure Title USE OF IMAGING STUDIES FOR LOW BACK PAIN Disease State Musculoskeletal Indicator Classification Utilization Strength
Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013 Measure Title USE OF IMAGING STUDIES FOR LOW BACK PAIN Disease State Musculoskeletal Indicator Classification Utilization Strength
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis. A radiologic tour of a patient encounter
 Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
LATE-ONSET RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: IS PITTING OEDEMA OF THE HANDS AT ONSET A GOOD PROGNOSTIC INDICATOR?
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1997;36:214 219 LATE-ONSET RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: IS PITTING OEDEMA OF THE HANDS AT ONSET A GOOD PROGNOSTIC INDICATOR? B. B. BHAKTA and C. T. PEASE Rheumatology and Rehabilitation
British Journal of Rheumatology 1997;36:214 219 LATE-ONSET RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: IS PITTING OEDEMA OF THE HANDS AT ONSET A GOOD PROGNOSTIC INDICATOR? B. B. BHAKTA and C. T. PEASE Rheumatology and Rehabilitation
The Vectra DA Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis Date of Origin: June 2014 Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed Date: May 2015 Policy No: 67 Effective Date: July 1, 2015 IMPORTANT
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis Date of Origin: June 2014 Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed Date: May 2015 Policy No: 67 Effective Date: July 1, 2015 IMPORTANT
ANTIBODIES AGAINST CITRULLINATED PEPTIDES IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE
 ANTIBODIES AGAINST CITRULLINATED PEPTIDES IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE Principal investigators: Dr Raimon Sanmartí Sala Hospital Clínic i Provincial de Barcelona
ANTIBODIES AGAINST CITRULLINATED PEPTIDES IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE Principal investigators: Dr Raimon Sanmartí Sala Hospital Clínic i Provincial de Barcelona
Psoriatic Arthritis. Title. Understanding and Managing. in All the Wrong Places. Clinical Features. Etiology of Psoriatic Arthritis
 Focus on CME at Memorial University Understanding and Managing Title Psoriatic Arthritis in All the Wrong Places Proton Rahman MD, MSc, FRCPC Although Baron Jean-Luis Aubert offered the first case description
Focus on CME at Memorial University Understanding and Managing Title Psoriatic Arthritis in All the Wrong Places Proton Rahman MD, MSc, FRCPC Although Baron Jean-Luis Aubert offered the first case description
We should not forget the foot: relations between signs and symptoms, damage, and function in rheumatoid arthritis
 Clin Rheumatol (2011) 30:1475 1479 DOI 10.1007/s10067-011-1780-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE We should not forget the foot: relations between signs and symptoms, damage, and function in rheumatoid arthritis Henriëtte
Clin Rheumatol (2011) 30:1475 1479 DOI 10.1007/s10067-011-1780-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE We should not forget the foot: relations between signs and symptoms, damage, and function in rheumatoid arthritis Henriëtte
Imaging of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Imaging of Rheumatoid Arthritis Lisa C. Vasanth, MD, MSc a, *, Helene Pavlov, MD b, Vivian Bykerk, BSc, MD, FRCPC c KEYWORDS Rheumatoid arthritis Imaging Radiography KEY POINTS Increased awareness of the
Imaging of Rheumatoid Arthritis Lisa C. Vasanth, MD, MSc a, *, Helene Pavlov, MD b, Vivian Bykerk, BSc, MD, FRCPC c KEYWORDS Rheumatoid arthritis Imaging Radiography KEY POINTS Increased awareness of the
SPECT/CT Wrist. Wrist pain 3/27/2012
 Wrist pain Wrist joint - complicated anatomy complex biomechanics Imaging and management of wrist pain presents a significant challenge Significant economic burden SPECT/CT Wrist HK Mohan GSTT London Intra-capsular
Wrist pain Wrist joint - complicated anatomy complex biomechanics Imaging and management of wrist pain presents a significant challenge Significant economic burden SPECT/CT Wrist HK Mohan GSTT London Intra-capsular
The importance of early treatment for the prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis
 Published 19 September 2013, doi:10.4414/smw.2013.13865 Cite this as: The importance of early treatment for the prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis Diego Kyburz a, Axel Finckh b a Rheumaklinik, Universitätsspital
Published 19 September 2013, doi:10.4414/smw.2013.13865 Cite this as: The importance of early treatment for the prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis Diego Kyburz a, Axel Finckh b a Rheumaklinik, Universitätsspital
PREVALENCE OF HAND SYMPTOMS, IMPAIRMENTS AND ACTIVITY LIMITATIONS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN RELATION TO DISEASE
 J Rehabil Med 1; : 91 91 ORIGINAL REPORT PREVALENCE OF HAND SYMPTOMS, IMPAIRMENTS AND ACTIVITY LIMITATIONS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN RELATION TO DISEASE DURATION Noortje C. A. Horsten, MD 1, Jennie Ursum,
J Rehabil Med 1; : 91 91 ORIGINAL REPORT PREVALENCE OF HAND SYMPTOMS, IMPAIRMENTS AND ACTIVITY LIMITATIONS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN RELATION TO DISEASE DURATION Noortje C. A. Horsten, MD 1, Jennie Ursum,
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments of Rheumatoid Foot and Ankle
 Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis, affecting about two to three million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is a symmetric disease, meaning that it will usually involve
Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis, affecting about two to three million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is a symmetric disease, meaning that it will usually involve
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz
 Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the third most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the third most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most
Predictors of Physical Therapy Use in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Predictors of Physical Therapy Use in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Maura Iversen,, PT, DPT, SD, MPH 1,2,3 Ritu Chhabriya,, MSPT 4 Nancy Shadick, MD 2,3 1 Department of Physical Therapy, Northeastern
Predictors of Physical Therapy Use in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Maura Iversen,, PT, DPT, SD, MPH 1,2,3 Ritu Chhabriya,, MSPT 4 Nancy Shadick, MD 2,3 1 Department of Physical Therapy, Northeastern
NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Type III Hypersensitivity Response
 NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System Margaret H. Birney PhD, RN Lecture 12 Part 2 Joint Disorders (cont d) Rheumatoid Arthritis Definition: Autoimmune disorder occurring in genetically sensitive
NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System Margaret H. Birney PhD, RN Lecture 12 Part 2 Joint Disorders (cont d) Rheumatoid Arthritis Definition: Autoimmune disorder occurring in genetically sensitive
A pilot study of the primary care management of knee osteoarthritis in the Northern States of Malaysia.
 A pilot study of the primary care management of knee osteoarthritis in the Northern States of Malaysia. Arshad A and Rashid R Putra Specialist Centre, Alor Setar, Kedah, Malaysia ABSTRACT ORIGINAL ARTICLE
A pilot study of the primary care management of knee osteoarthritis in the Northern States of Malaysia. Arshad A and Rashid R Putra Specialist Centre, Alor Setar, Kedah, Malaysia ABSTRACT ORIGINAL ARTICLE
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
Shared care protocol for the management of patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis treated with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
 Tameside Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and NHS Tameside and Glossop Shared care protocol for the management of patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis treated with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
Tameside Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and NHS Tameside and Glossop Shared care protocol for the management of patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis treated with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
Medical Policy Anti-CCP Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Medical Policy Anti-CCP Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy: Medicare Description References Authorization
Medical Policy Anti-CCP Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy: Medicare Description References Authorization
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot
 The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk Pictorial review Abstract
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk Pictorial review Abstract
Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 10/11/2015 History Child with several month history of weakness, arthralgias and palpable abnormalities at the knee Diagnosis Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 10/11/2015 History Child with several month history of weakness, arthralgias and palpable abnormalities at the knee Diagnosis Juvenile Dermatomyositis
A ctive rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterised by
 290 REVIEW Early referral recommendation for newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis: evidence based development of a clinical guide P Emery, F C Breedveld, M Dougados, J R Kalden, M H Schiff, J S Smolen...
290 REVIEW Early referral recommendation for newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis: evidence based development of a clinical guide P Emery, F C Breedveld, M Dougados, J R Kalden, M H Schiff, J S Smolen...
Test Request Tip Sheet
 With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
Application of high frequency color Doppler ultrasound in the monitoring of rheumatoid arthritis treatment
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: 1807-1812, 2014 Application of high frequency color Doppler ultrasound in the monitoring of rheumatoid arthritis treatment GUIMIN ZHENG 1, LEI WANG 2, XIUCHUAN
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: 1807-1812, 2014 Application of high frequency color Doppler ultrasound in the monitoring of rheumatoid arthritis treatment GUIMIN ZHENG 1, LEI WANG 2, XIUCHUAN
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND COURSE - BASIC LEVEL- Graz, November 2 nd 4 th, 2016
 MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND COURSE - BASIC LEVEL- Graz, November 2 nd 4 th, 2016 Dear colleague, musculoskeletal ultrasound is increasingly used by rheumatologist and other health professionals for diagnostic
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND COURSE - BASIC LEVEL- Graz, November 2 nd 4 th, 2016 Dear colleague, musculoskeletal ultrasound is increasingly used by rheumatologist and other health professionals for diagnostic
Comparison of treatment outcome in Rheumatoid Arthritis patients treated with single and two DMARDs in combination with Corticosteroids
 International Journal of Drug Development & Research July-September 2012 Vol. 4 Issue 3 ISSN 0975-9344 Available online http://www.ijddr.in Covered in Official Product of Elsevier, The Netherlands SJR
International Journal of Drug Development & Research July-September 2012 Vol. 4 Issue 3 ISSN 0975-9344 Available online http://www.ijddr.in Covered in Official Product of Elsevier, The Netherlands SJR
Other Noninfectious Diseases. Chapter 31 Lesson 3
 Other Noninfectious Diseases Chapter 31 Lesson 3 Diabetes Diabetes- a chronic disease that affects the way body cells convert food into energy. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death by disease
Other Noninfectious Diseases Chapter 31 Lesson 3 Diabetes Diabetes- a chronic disease that affects the way body cells convert food into energy. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death by disease
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons
 MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition
 www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis to Target : the patient version of the international recommendations
 Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis to Target : the patient version of the international recommendations Data presented from the publication: M. de Wit, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:891-5. Epub Apr 7, 2011.
Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis to Target : the patient version of the international recommendations Data presented from the publication: M. de Wit, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:891-5. Epub Apr 7, 2011.
Arthritis in Children: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis By Kerry V. Cooke
 Reading Comprehension Read the following essay on juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Then use the information in the text to answer the questions that follow. Arthritis in Children: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
Reading Comprehension Read the following essay on juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Then use the information in the text to answer the questions that follow. Arthritis in Children: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy
 Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy Hans T.M. van Schie DVM, PhD UTC Imaging, Netherlands Scoring with Patellar Tendinopathy? no one size
Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy Hans T.M. van Schie DVM, PhD UTC Imaging, Netherlands Scoring with Patellar Tendinopathy? no one size
The Dedicated MRI Factbook. Esaote MRI: A world of difference
 The Dedicated MRI Factbook Esaote MRI: A world of difference Esaote Dedicated MRI Measures of Excellence Creativity in Healthcare is Esaote s motto which represents the philosophy that has been adopted
The Dedicated MRI Factbook Esaote MRI: A world of difference Esaote Dedicated MRI Measures of Excellence Creativity in Healthcare is Esaote s motto which represents the philosophy that has been adopted
Sacroiliitis In Routine Mri For Low Back Ache
 643 Low back Sacroiliitis In Routine Mri For Low Back Ache CM SREEDHAR, MN SREE RAM, A ALAM, IK INDRAJIT, K SHANMUGANANDAN Abstract Low backache is a common clinical presentation in medical practice and
643 Low back Sacroiliitis In Routine Mri For Low Back Ache CM SREEDHAR, MN SREE RAM, A ALAM, IK INDRAJIT, K SHANMUGANANDAN Abstract Low backache is a common clinical presentation in medical practice and
Evolution of Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis: How Do the 2010 Criteria Perform?
 Evolution of Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis: How Do the 2010 Criteria Perform? Elizabeth C. Ortiz, MD*, Shuntaro Shinada, MD KEYWORDS Rheumatoid arthritis Classification criteria Inflammatory
Evolution of Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis: How Do the 2010 Criteria Perform? Elizabeth C. Ortiz, MD*, Shuntaro Shinada, MD KEYWORDS Rheumatoid arthritis Classification criteria Inflammatory
What s new in clinical assesment of ankylosing spondylitis?
 What s new in clinical assesment of ankylosing spondylitis? Désirée van der Heijde Professor of Rheumatology Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, Norway Content
What s new in clinical assesment of ankylosing spondylitis? Désirée van der Heijde Professor of Rheumatology Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, Norway Content
Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Systemic condition affecting synovial tissue Hypertrohied synovium destroys. Synovectomy. Tenosynovectomy Tendon Surgery Arthroplasty Arthrodesis
 Surgical Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Wrist Raj Bhatia Consultant Hand & Orthopaedic Surgeon Bristol Royal Infirmary & Avon Orthopaedic Centre Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic condition affecting
Surgical Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Wrist Raj Bhatia Consultant Hand & Orthopaedic Surgeon Bristol Royal Infirmary & Avon Orthopaedic Centre Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic condition affecting
It is worth noting that people with psoriasis can also develop other forms of arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
 Psoriatic Arthritis Main Colour - pantone 2597u Research - pantone 206u Children - pantone 123 4 What is psoriatic arthritis? Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory joint disease associated with psoriasis.
Psoriatic Arthritis Main Colour - pantone 2597u Research - pantone 206u Children - pantone 123 4 What is psoriatic arthritis? Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory joint disease associated with psoriasis.
(Intro to Arthritis with a. Arthritis) Manager of Education & Services for the Vancouver Island Region of The Arthritis Society
 Arthritis 101 (Intro to Arthritis with a Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis) by Cari Taylor by Cari Taylor Manager of Education & Services for the Vancouver Island Region of The Arthritis Society What You Will
Arthritis 101 (Intro to Arthritis with a Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis) by Cari Taylor by Cari Taylor Manager of Education & Services for the Vancouver Island Region of The Arthritis Society What You Will
