The accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging of the hands and feet in the diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis
|
|
|
- Buck Jefferson
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
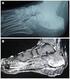
1 Joint Bone Spine 74 (2007) 362e367 Original article The accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging of the hands and feet in the diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis Cuneyt Calisir a, *, Ali Ilker Murat Aynaci a, Cengiz Korkmaz b a Department of Radiology, Osmangazi University, Medical Faculty, Eskisehir, Turkey b Department of Rheumatology, Osmangazi University, Medical Faculty, Eskisehir, Turkey Received 21 January 2006; accepted 5 July 2006 Available online 30 May Abstract Objective: To analyze MRI findings of early RA in the hand and foot joints and to determine any discrepancies between MRI findings in the hands and feet. Methods: Twenty one patients who fulfilled the 1987 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria for the diagnosis of RA at the onset underwent MRI of both hands and feet. Results: In 18 out of 21 patients, rheumatoid changes were observed in the hand and foot joints. However, rheumatoid changes were observed only in the hand joints of the three remaining patients. MRI revealed pathologic findings suggested RA in the hands of 21 of 21 patients. In the feet, MRI findings suggested RA in 18 of 21 patients. Bone erosions were seen in the hands of 14 patients (67%). Observers found as many bony changes in the hands as in the foot joints. MRI detected active synovitis in 17 patients (81%) in the hands and in 15 patients (71%) in the feet. MRI findings suggested bone edema in the hand and foot joints in 14 (63%) and 11 patients (52%), respectively. There was no significant difference between the MCP and MTP joints with respect to RA-based changes obtained in the MRI ( p > 0.05). Conclusion: Evidence of foot involvement is a frequent occurrence in early RA. Ó 2007 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved. Keywords: MRI; RA; Foot joints; Hand joints 1. Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic inflammatory disorder with estimated prevalence of 1% [1]. The chronic, bilateral, and symmetric joint lesions ultimately result in joint destruction and deformity [2]. Diagnosing RA during its early stage is important to the implementation of active and aggressive treatment, which is expected to prevent RA joint damage, thereby reducing functional decline and improving the longterm outcome [3,4]. The diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is based primarily on the 1987 revised criteria of the American College of Rheumatology, including clinical, biologic, and * Corresponding author. Tel.: þ /2802; fax: þ address: aynaci@yahoo.com (C. Calisir). radiological findings [5]. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been established as the most sensitive means for detection of active synovitis and bone erosions in early stage RA [6e8]. The joints of the hands are among the first to be affected by rheumatoid arthritis. Several studies have focused on MRI appearances of the hands [7,9,10]. However, there are only two reports on MRI characteristics of the feet in early RA [11,12]. In these studies, in early RA, MRI showed typical bony changes in hand and foot joints of those patients whose conventional radiographies were normal. In addition, radiography has been found to reveal bony erosions in the foot earlier than in the hand joints [13,14]. This suggests that the feet may be primarily affected by early RA. The study was performed to analyze MRI findings of early RA in hand and foot joints and to determine any discrepancies between MRI findings in the hands and feet X/$ - see front matter Ó 2007 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved. doi: /j.jbspin
2 C. Calisir et al. / Joint Bone Spine 74 (2007) 362e Methods 2.1. Patients Between 2001 and 2005, 21 patients who fulfilled the diagnosis of RA according to 1987 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria at the onset underwent MRI of their hands and feet. Our institutional review board approved the study protocol, and informed consents were obtained from all patients. The study group consisted of 19 women and 2 men with a mean age of 44.5 years (range 20e65 years). Hand (posteroanterior, oblique) and forefoot (anteroposterior, oblique) radiographs were available in all cases and showed no characteristic erosive changes of RA. MRI of the clinically dominant forefoot and hand was performed. Clinically dominant was defined as the site tenderer to pressure and/or with signs of redness and/or hyperthermia and/or swelling. Joints of the dominant hand and forefoot were evaluated in three separate areas, namely wrist or ankle, metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP) or metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP), and proximal interphalangeal joints (PIP). In all joints investigated, when at least one pathological joint was detected in a determined joint area, the area was noted as abnormal. The mean disease duration was 10 months. Medication at entry included non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids in 15 and 1 patients, respectively. None of the patients had previously received disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARD), and five patients were completely untreated MRI protocol MRI was performed with a 1.5 Tesla superconducting magnet (Vision Plus; Siemens, VB33C, Germany) equipped with a flex collimation coil of receiver property for examination of hand and an extremity collimation coil of receiver and transmitter property for examination of foot. Dominant hand was examined while in the prone position with arm hyper extended. In only one case, MRI of the dominant hand was not performed due to extensive shoulder pain experienced by the patient. Dominant foot was scanned while the patient was placed in the prone position with their feet parallel to the floor to prevent patients from moving and to evaluate three separate areas in the same coronal image. In all patients, coronal images of both hand and foot joints were obtained. Axial and sagittal images were not obtained to keep study time shorter since both hand and foot MRI were studied in most of the cases. The examinations consisted of the following sequences: spin echo T1 (SE T1) (TR/TE 400e500/12 ms), fast spin-echo T2 with fat saturation (FSE T2 FS) (TR/TE 4000e5000/45 ms), spin echo T1 with fat saturation (SE T1 FS) (615e660/12 ms) and after administration of i.v gadolinium diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (Gd DTPA; 0.1 mmoles/kg of body weight) (Magnevist, Schering, Berlin), and spin echo T1 with fat saturation (SE T1 FS) (615e660/12 ms). For imaging of hand, slice thickness was set as 3 mm, matrix as pixels, excitation as 1, field of view as 25 cm. For imaging of foot, slice thickness was set as 3 mm, matrix as pixels, excitation as 2, and field of view as 23 cm. In all cases, firstly, foot joints were examined by the sequences of T1, fat saturated T1 and T2. Later, hand joints were evaluated by the same sequences. Also, i.v contrast material was given without altering the position of the patient, and fat saturated T1 was obtained. After contrast enhanced study lasting approximately 1.5 min, position of patient was altered, and foot was examined with the same sequence. The overall examination time was about 17 min Analysis of MR images Two experienced MRI readers who were unaware of the patients identities evaluated MR images independently. Evaluation and scoring of MR images of both hand and foot joints was done separately for each patient. MR images were analyzed for bone erosions, synovitis, bone edema and tenosynovitis. Each variable was scored as absent (0) or present (1). In cases of difference of opinion between the MRI readers, a consensus was achieved. MRI criteria were similar to those described in the literature. A distinctive bone defect with cortical break was defined as bone erosion. Bone edema was defined as a lesion within the trabecular bone, with ill-defined margins and signal characteristics consistent with increased water content. Active synovitis was judged to be positive when an area that shows marked enhancement in the synovial compartment and synovial thickening (greater than the width of the joint capsule) were seen. Tenosynovitis was considered to be present when contrast material enhancement of the tendon sheath was observed. MR images of the same patients presented in a randomized fashion to the MRI readers were interpreted twice, with an interval of 5e11 months (mean 7 months) between the 2 interpretations to determine the intra-observer reliability Statistical analysis All statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS 10.0 software package. For assessment of intra- and inter-observer agreement, Cohen s kappa statistics were employed on all variables (erosion, bone edema, synovitis and tenosynovitis). The kappa statistic was interpreted as follows: 0.0e0.20: poor agreement, 0.21e0.40: fair agreement, 0.41e0.60: moderate agreement, 0.61e0.80: substantial agreement, 0.81e1.00: almost perfect agreement. Differences were considered statistically significant if p values were less than Fisher s chi-square test was used to compare the radiological findings of hand and foot. Values of p < 0.05 were considered to be significant. 3. Results 3.1. Hands MRI revealed pathologic findings suggesting RA in the hands of all patients. Rheumatoid changes were detected on MR images in 147 out of 231 joints. MR imaging detected erosions in 70 joints in 14 patients (67%) (Table 1). Wrist (n ¼ 37) and the MCP joints (n ¼ 29)
3 364 C. Calisir et al. / Joint Bone Spine 74 (2007) 362e367 Table 1 Distribution of MRI findings in 21 patients suffering from RA Number of patients Bone edema Inflammation of synovium Hand Foot were the most frequently involved (Fig. S1; see the supplementary material associated with this article online) (Table 2). In the wrists, most common sites for erosions were capitate (n ¼ 12), lunate (n ¼ 10), scaphoid (n ¼ 8) (Fig. S2a). Bone edema was seen in 14 patients (67%) (Table 1). Bone erosion and bone edema were seen simultaneously in 64 (43%) out of 147 joints. Whereas, bone edema without evidence of a bone erosion was observed in five joints (PIP). Synovial contrast enhancement (active synovitis) was observed in 114 joints in 17 patients (81%) (Table 1). MR images revealed this frequency of involvement: MCP joints were involved 55 times, wrists 48 times (Fig. S2b), and PIP joints 11 times (Table 2). The 2nd (n ¼ 35) MCP joints were the most frequently involved. MR imaging detected tenosynovitis in 12 (57%) out of 21 patients. The most commonly affected site for tendon involvement was flexor digitorum tendon (n ¼ 8). Using clinical examination as a reference, the sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value (ppd) and negative predictive value (npd) of MRI in the detection of rheumatoid changes in the hands of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis respectively were 0.86, 0.90, 0.87, 0.95, and Feet Erosion MRI revealed pathologic findings suggesting RA in the feet of 18 of 21 patients (86%). Rheumatoid changes were seen in 114 out of 231 joints. Observers found erosions in 55 joints in 11 patients (52%) (Table 1). MTP joints (n ¼ 29) and ankle (n ¼ 22) were the most frequently involved (Table 2). In the ankles, talus (n ¼ 12) was the most frequently affected. In the MTP joints, the most common sites for erosions were the medial aspect of the 1st MTP (n ¼ 7), lateral aspect of the 5th MTP (n ¼ 6) and lateral aspect of the 3rd MTP (n ¼ 4) joints (Fig. S3a). However, no significant difference was found between the MTP joints. MR imaging detected bone edema in 11 patients Table 2 Distribution of rheumatoid changes in 231 joints from 21 patients suffering from RA Number of joints affected Bone edema Inflammation of synovium Erosion Wrist 32 (46%) 48 (42%) 37 (53%) MCP 30 (43%) 55 (48%) 29 (41%) Hand PIP 7 (11%) 11 (10%) 4 (6%) Total 69 (100%) 114 (100%) 70 (100%) Ankle 24 (46%) 33 (43%) 29 (53%) MTP 24 (46%) 37 (48%) 22 (40%) Foot PIP 4 (8%) 7 (9%) 4 (7%) Total 52 (100%) 77 (100%) 55 (100%) (52%) (Table 1). Bone erosion and bone edema were seen simultaneously in 48 (42%) out of 114 joints. Four MTP joints showed only bone edema without erosion. Isolated bone erosion was observed in three joints (one ankle, one MTP joint and one PIP joints). Synovial contrast enhancement (active synovitis) was observed in 77 joints in 15 patients (71%) (Table 1). MR images revealed this frequency of involvement: MTP joints were involved 37 times (Fig. S3b), ankle was involved 33 times (Fig. S4), and PIP joints were involved 7 times (Table 2). The 5th (n ¼ 17) MTP joints were the most frequently affected. MR imaging detected tenosynovitis in 8 (40%) out of 20 patients. Flexor digitorum tendons were more frequently involved than the extensor ones. Using clinical examination as a reference, the sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, ppd value and npd value of MRI in the detection of rheumatoid changes in the feet of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis respectively were 0.85, 0.82, 0.84, 0.81, and Hands versus feet In 18 out of 21 patients, rheumatoid changes were observed in the hand and foot joints. However, rheumatoid changes were observed only in the hand joints of the three remaining patients. Six patients had bone erosions in the hands without bony changes in the feet. In four patients, osseous abnormalities were seen only in the foot joints (Fig. S3a). There was no significant difference between the hand and foot joints in term of erosion ( p > 0.05). Four patients had rheumatoid changes in the MCP joints without changes in the MTP joints. Two patients had isolated rheumatoid changes in the MTP joints. There were no significant differences between the MCP and MTP joints in terms of rheumatoid changes ( p > 0.05). In two patients, active synovitis was seen only in the hand joints (Fig. S2b). In another patient, synovitis was diagnosed only in the foot joints. There was no significant difference between hand and foot joints in terms of synovitis Inter- and intra-observer reliabilities Inter-observer reliability values showed good to excellent agreement for variables in the hands (k ¼ 0.79 for synovitis, k ¼ 0.82 for bone edema and k ¼ 0.87 for erosion). Interobserver agreement between the readers was good to excellent with regard to variables in the feet (k ¼ 0.77 for synovitis, k ¼ 0.80 for bone edema, and k ¼ 0.84 for erosion). There was no significant difference between the hands and the feet in terms of kappa values. Intra-observer reliability values showed excellent agreement (k ¼ 0.89 for hands, k ¼ 0.85 for feet, and overall k ¼ 0.87). 4. Discussion Radiography of the hand and wrist is the traditional method used for diagnosing, staging, and following up on patients with
4 C. Calisir et al. / Joint Bone Spine 74 (2007) 362e rheumatoid arthritis. However, several studies have reported that MRI is more sensitive for detecting bone erosions in the early rheumatoid arthritis of the hand and wrist [15e19]. MRI is also documented in the literature as an effective imaging method in determination of inflammation of synovium, osseous and soft tissue abnormalities [7,14,18,20]. It is known that the synovial fluid and synovitis are related to each other especially in the long-term RA cases [21]. In a study by Boutry et al., it was indicated that both synovial thickening and effusion are expressions of the same process in RA [11]. Since rheumatoid pannus is hypervascular, numerous studies have shown that intravenous administration of contrast material with fat suppression techniques allows distinction between synovitis and joint effusion [22e24]. Data from earlier studies [25,26] also suggest that MR image acquisition should be performed quickly after gadolinium contrast injection (6e 11 min) to allow better delineation of synovium from joint effusion. In the present study, we imaged the joints with contrast-enhanced MR imaging with fat suppression. Contrast enhanced studies were completed in 6e7 min, and time intervals stated in the literature related to evaluation of synovitis were used. Thus synovitis could be reliably differentiated from the synovial fluid. Synovitis in RA has been studied by a number of groups using MRI. In these studies, MRI evidence of synovitis has been observed in the majority of early RA patients [27e29]. In this regard, it is predictable that active synovitis was observed in 81% of our series of patients. Erosive bony changes are more characteristic of early RA than of synovitis [17,18]. Conaghan et al. showed that, in early RA, synovitis appears to be the primary abnormality, and bone damage occurs in proportion to the level of synovitis but not in the absence of synovitis [30]. Several studies, however, have suggested that erosions occur in very early RA [31e33]. In Klarlund s study, MR imaging detected bone erosions of the MCP and PIP joints in 50% patients [15]. Boutry et al. reported a higher MR prevalence of bone erosion (80%) on patients who had median disease duration of 12 months [11]. In our study (average disease duration 10 months), we observed that the prevalence of erosion in the hand joints was similar to what was reported in that study. On the other hand, in a recent study in which the MTP joints of patients with early RA in whom findings on MR images of the hands were normal were examined, erosion was observed in only 2 (20%) of the patients, whereas synovitis was observed in all (100%) of the patients [12]. Our results are not in agreement with the results of that study. This difference might be explained by the shorter disease duration of the patients with RA in that study (average duration 9.4 weeks), whereas the present study group was characterized by longer mean disease duration of 10 months. Bone edema is known as a very early marker of inflammation and, in addition to synovitis, as a strong individual predictor of bone erosion [32,34]. STIR and T2 weighted sequences are well known for sensitive in detecting bone edema. Because STIR or T2-weighted sequences were not used by Boutry et al., detection of the early arthritis marker bone edema failed in that study [11]. Ostendorf et al. have shown bone edema in the foot joints of 70% of early stage RA patients whose hand joints were normal [12]. In similar to Ostendorf et al., we used T2 weighted imaging which probably allowed a more accurate assessment of bone edema. As shown in our and Ostendorf s study, bone edema seems to be a typical MRI feature in patients with early RA. However, in majority of the patients, we observed that edema was associated with erosion. This is not in agreement with the results of corresponding studies since they did not support the claim that edema could be strong individual predictor of bone erosion. In general, signs of edema are not detectable by clinical examination and imaging modalities such as conventional radiography and ultrasonography. Therefore, assessment of bone edema remains in the domain of MRI. Hand joints are usually affected in patients with RA [17]. Reports of osteodestruction being detected by conventional radiography earlier and more frequently in the foot than in the hand joints [13,14,35] provide accumulating evidence that the foot may be primarily affected in the early stages of RA. In view of this, MR imaging of the feet has potential applications in early diagnosis of RA. Several studies have focused on the MRI appearances of the hands [20,21,36,37]. However,to our knowledge, there are only two published studies describing the MR findings of early RA in the feet or comparing hand and foot involvement [11,12]. It should be noted that both studies were carried out using the axial MRI scans. Furthermore, in foot studies, only rheumatoid changes related to MTP joints were evaluated. In the study of Ostendorf, all patients whose hand MRI was normal showed rheumatoid changes in the foot joints. Based on this, it was thought that RA initially develops in the MTP joints. But in that study, only the MCP joints were evaluated and wrist joints were not examined. In this study, in 4 patients (19%) with RA, MCP joints were normal whereas wrist joints showed rheumatoid arthritis related MRI changes. Based on this result, we suggest that in the examination of hand with MRI, wrist joints have to be analyzed as well. Moreover, the exclusion of wrist joints may be interpreted as a deficiency of that study. In the present study, in the evaluation of the MCP and MTP joints, rheumatoid changes were found only in the MTP joints in two cases. In addition, changes were found only in the MCP joints in four cases. These findings do not support the idea that RA initially starts in the foot joints. Similarly, in the study of Boutry et al. with 30 cases, they observed same ratios of bone lesions in the MCP and MTP joints and proposed that, in the early detection of RA, if hand MRI examination was insufficient, MRI examination of the foot joints could help evaluation. The high sensitivity of our results might be explained by the fact that our patients mean disease duration (10 months) seems to be longer than usual for cases of early RA. Another factor contributing to the high sensitivity of our results might be the fact that none of the patients received disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARD). Unfortunately, in this study disease activity was not evaluated by using the Disease Activity Score 28-joint (DAS-28). This may be regarded as a limitation of the present study. Some groups [17,30,32,38,39] were selected to evaluate only the most symptomatic hand or the dominant hand at
5 366 C. Calisir et al. / Joint Bone Spine 74 (2007) 362e367 the side of the body in a whole-body system. Such assessment is more comfortable for the patient but may lead to falsenegative diagnosis in case of unilateral involvement. According to this, examination of clinically dominant hand and foot by MRI may be regarded as another limitation of the present study. To conclude, as the sensitivity of conventional radiography is especially low in detection of joint changes in the early stages of RA, MRI findings hold a very important role among other radiological modalities [40] in the time of diagnosis. MRI is insufficient or controversial, MRI of the feet can be used as additional diagnostic instrument in the diagnosis of early RA [41]. Supplementary information Supplementary figure (Figs. S1eS4) associated with this article can be found at at doi: /j.jbspin References [1] Gabriel SE, Crowson CS, O Fallon WM. The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis in Rochester, Minnesota, 1955e1985. Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:415e20. [2] Saraux A, Burdon V, Devauchelle V, Goff LP. Is hypocomplementemia useful for diagnosing or predicting extra-articular manifestations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis? Joint Bone Spine 2001;68:487e92. [3] Dawes PT, Fowler PD. Treatment of early rheumatoid arthritis: a review of current and future concepts and therapy. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1995;13:381e94. [4] Emery P, Marzo H, Proudman S. Management of patients with newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999;2(Suppl): 27e31. [5] Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1988;31: 315e24. [6] Sugimoto H, Takeda A, Masuyama J, Furuse M. Early-stage rheumatoid arthritis: diagnostic accuracy of MR imaging. Radiology 1996;198: 185e92. [7] Sugimoto H, Takeda A, Hyodoh K. Early-stage rheumatoid arthritis: prospective study of the effectiveness of MR imaging for diagnosis. Radiology 2000;216:569e75. [8] Peterfy CG. Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: current status and future directions. J Rheumatol 2001;28:1134e42. [9] Jevtic V, Watt I, Rozman B, Kos-Golja M, Rupenovic S, Logar D, et al. Precontrast and postcontrast (Gd-DTPA) magnetic resonance imaging of hand joints in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Radiol 1993; 48:176e81. [10] Goupille P, Roulot B, Akoka S, Avimadje AM, Garaud P, Naccache L, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging: a valuable method for the detection of synovial inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2001;28: 35e40. [11] Boutry N, Larde A, Lapegue F, Gervais E, Flipo R, Cotton A. Magnetic resonance imaging appearance of the hands and feet in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2003;30:671e9. [12] Ostendorf B, Scherer A, Mödder U, Scheider M. Diagnostic value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the forefeet in early rheumatoid arthritis when findings on imaging of the metacarpophalangeal joints of the hands remain normal. Arthritis Rheum 2004;50:2094e102. [13] Brook A, Corbett M. Radiographic changes in early rheumatoid disease. Ann Rheum Dis 1977;36:71e3. [14] Niwayama G. Rheumatoid arthritis. In: Resnick D, editor. Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; p. 866e970. [15] Klarlund M, Ostergaard M, Jensen KE, Madsen JL, Skjodt H, Lorenzen I, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging, radiography, and scintigraphy of the finger joints: one year follow up of patients with early arthritis- TIRA group. Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59:521e8. [16] McQueen FM, Benton N, Crabbe J, Robinson E, Yeoman S, McLean L, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis reveals a high prevalence of erosions at four months after symptom onset. Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:350e6. [17] Backhaus M, Kamradt T, Sandrock D, Loreck D, Fritz J, Wolf KJ, et al. Arthritis of the finger joints: a comprehensive approach comparing conventional radiography, scintigraphy, ultrasound and contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:1232e45. [18] Foley-Nolan D, Stack JP, Ryan M, Redmond U, Barry C, Enis J, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with plain film radiographs. Br J Rheumatol 1991;30:101e6. [19] Rominger MB, Bernreuter WK, Kenney PJ, Morgan SL, Blackburn WD, Alarcon GS. MR imaging of the hands in early rheumatoid arthritis: preliminary results. Radiographics 1993;13:37e46. [20] Klarlund M, Ostergaard M, Gideon P, Sorensen K, Jensen KE, Lorenzen I. Wrist and finger joint MR imaging in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Radiol 1999;40:400e9. [21] Savnik A, Malmskov H, Thomsen HS, Graff LB, Nielsen H, Danneskiold-Samsoe B, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist and finger joints in patients with inflammatory joint disease. J Rheumatol 2001;28:2193e200. [22] Kursunoglu-Brahme S, Riccio T, Weisman MH, Resnick D, Zvaifler N, Sanders ME, et al. Rheumatoid knee: role of gadopentetate-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 1990;176:831e5. [23] Konig H, Sieper J, Wolf KJ. Rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of hypervascular and fibrous pannus with dynamic MR imaging enhanced with Gd-DTPA. Radiology 1990;176:473e7. [24] Bjorkengren AG, Geborek P, Rydholm U, Holtas S, Petterson H. MR imaging of the knee in acute rheumatoid arthritis: synovial uptake of gadolinium-dota. AJR 1990;155:329e32. [25] Ostergaard M, Klarlund M. Importance of timing of post-contrast MRI in rheumatoid arthritis: what happens during the first 60 minutes after IV gadolinium-dtpa? Ann Rheum Dis 2001;60:1050e4. [26] Huang J, Stewart N, Crabbe J, Robinson E, McLean L, Yeoman S, et al. A 1-year follow-up study of dynamic magnetic resonance imaging in early rheumatoid arthritis reveals synovitis to be increased in shared epitope-positive patients and predictive of erosions at 1 year. Rheumatology 2000;39:407e16. [27] McQueen FM, Stewart N, Crabbe J, Robinson E, Yeoman S, Tan PLJ, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis reveals a high prevalence of erosions at four months after symptomonset. Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:350e6. [28] Jorgensen C, Cyteval C, Anaya JM, Baron MP, Lamarque JL, Sany J. Sensitivity of magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in very early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1993;11:163e8. [29] Tamai K, Yamato M, Yamaguchi T, Ohno W. Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging for the evaluation of synovitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1994;37:1151e7. [30] Conaghan P, Edmonds J, Emery P, Genant H, Gibbon W, Klarlund M, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: summary of OMER- ACT activities, current status, and plans. J Rheumatol 2001;28:1158e62. [31] Mc Gonagle D, Conaghan PG, O Connor P, Gibbon W, Green M, Wakefield R, et al. The relationship between synovitis and bone changes in early untreated rheumatoid arthritis: a controlled magnetic resonance imaging study. Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:1706e11. [32] McQueen FM, Stewart N, Crabbe J, Robinson E, Yeoman S, Tan PLJ, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis reveals progression of erosions despite clinical improvement. Ann Rheum Dis 1999;58:156e63. [33] McGonagle D, Green MJ, Proudman S, Richardson C, Veale D, O Connor P, et al. The majority of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
6 C. Calisir et al. / Joint Bone Spine 74 (2007) 362e have erosive disease at presentation when magnetic resonance imaging of the dominant hand is employed. Br J Rheumatol 1997;1(Suppl):121. [34] van der Heijde DM, van Leeuwen MA, van Riel PL, Koster AM, van t Hof MA, van Rijswijk MH, et al. Biannual radiographic assessments of hands and feet in a three-year prospective follow-up of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1992;35:26e33. [35] Scott DL, Coultan BL, Popert AJ. Long term progression of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 1986;45:373e8. [36] Ostergaard M, Hansen M, Stoltenberg M, Gideon P, Klarlund M, Jensen KE, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging-determined synovial membrane volume as a marker of disease activity and a predictor of progressive joint destruction in the wrists of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:918e29. [37] Mc Queen FM, Benton N, Crabbe J, Robinson E, Yeoman S, McLean L, et al. What is the fate of erosions in early rheumatoid arthritis? Tracking individual lesions using x rays and magnetic resonance imaging over the first two years of disease. Ann Rheum Dis 2001;60:859e68. [38] van der Heide, Jacobs JW, Bijlsma JW, Heurkens AH, van Booma- Frankfort C, van der Veen MJ, et al. The effectiveness of early treatment with secondline antirheumatic drugs: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 1996;124:699e707. [39] Savnik A, Malmskov H, Thomsen HS, Graff LB, Nielsen H, Danneskiold-Samsoe B, et al. MRI of the wrist and finger joints in inflammatory joint diseases at 1-year interval: MRI features to predict bone erosions. Eur Radiol 2002;12:1203e10. [40] Strunk J, Klingenberger P, Strube K, Bachmann G, Müller-Ladner U, Kluge A. Three-dimensional Doppler sonographic vascular imaging in regions with increased MR enhancement in inflamed wrists of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine 2006;73:518e22. [41] Gossec L, Fautrel B, Pham T, Combe B, Flipo RM, Goupille P, et al. Structural evaluation in the management of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: development of recommendations for clinical practice based on published evidence and expert opinion. Joint Bone Spine 2005;72: 229e34.
Benedikt Ostendorf, Axel Scherer, Ulrich Mödder, and Matthias Schneider
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 7, July 2004, pp 2094 2102 DOI 10.1002/art.20314 2004, American College of Rheumatology Diagnostic Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Forefeet in Early Rheumatoid
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 7, July 2004, pp 2094 2102 DOI 10.1002/art.20314 2004, American College of Rheumatology Diagnostic Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Forefeet in Early Rheumatoid
Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI. Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007
 Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007 Introduction RA most common type of inflammatory Arthritis with prevalence of 1% Accurate and
Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007 Introduction RA most common type of inflammatory Arthritis with prevalence of 1% Accurate and
Bone Erosions in Patients with RA: Exploring the Impact of the Anatomy of Interest on the Relationship Between MRI and X-ray Erosion Detection
 Bone Erosions in Patients with RA: Exploring the Impact of the Anatomy of Interest on the Relationship Between MRI and X-ray Erosion Detection Michael Tomizza, BSc, MSc Candidate October 15, 2014: Hamilton
Bone Erosions in Patients with RA: Exploring the Impact of the Anatomy of Interest on the Relationship Between MRI and X-ray Erosion Detection Michael Tomizza, BSc, MSc Candidate October 15, 2014: Hamilton
Treat to Target Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis: UK perspective. Dr Deirdre Shawe, North Hampshire Hospital, Basingstoke, UK
 Treat to Target Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis: UK perspective Dr Deirdre Shawe, North Hampshire Hospital, Basingstoke, UK What is the target? To achieve remission or low disease activity in Rheumatoid
Treat to Target Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis: UK perspective Dr Deirdre Shawe, North Hampshire Hospital, Basingstoke, UK What is the target? To achieve remission or low disease activity in Rheumatoid
Low-Field Compact Magnetic Resonance Imaging System for the Hand and Wrist in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 23:370 376 (2006) Original Research Low-Field Compact Magnetic Resonance Imaging System for the Hand and Wrist in Rheumatoid Arthritis Hiroshi Yoshioka, MD, 1 * Satoshi
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 23:370 376 (2006) Original Research Low-Field Compact Magnetic Resonance Imaging System for the Hand and Wrist in Rheumatoid Arthritis Hiroshi Yoshioka, MD, 1 * Satoshi
Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis
 REVIEW ARTICLE Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis Wilson Campos Tavares Junior 1, Renata Rolim 2, Adriana Maria Kakehasi 3 ABSTRACT Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory polyarthritis
REVIEW ARTICLE Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis Wilson Campos Tavares Junior 1, Renata Rolim 2, Adriana Maria Kakehasi 3 ABSTRACT Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory polyarthritis
Ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis
 Formosan Journal of Rheumatology 2009;23:1-7 Review Article Ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis Ying-Chou Chen 1, Tien-Tsai Cheng 1, Shih-Wei Hsu 2 1 Department of Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology,
Formosan Journal of Rheumatology 2009;23:1-7 Review Article Ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis Ying-Chou Chen 1, Tien-Tsai Cheng 1, Shih-Wei Hsu 2 1 Department of Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE THE DIAGNOSIS OF EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS USING MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY
 AL-AZHAR ASSIUT MEDICAL JOURNAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE THE DIAGNOSIS OF EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS USING MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY Sonya M. Rashad, Eman A.M. Alkady, Essam A.M. Abda and Marwa A.A. Galal,
AL-AZHAR ASSIUT MEDICAL JOURNAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE THE DIAGNOSIS OF EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS USING MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY Sonya M. Rashad, Eman A.M. Alkady, Essam A.M. Abda and Marwa A.A. Galal,
Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis Dr. Andrew K. Brown Senior Lecturer & Consultant Rheumatologist Content Practical RA Assessment Advantages of ultrasonography Potential
Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis Dr. Andrew K. Brown Senior Lecturer & Consultant Rheumatologist Content Practical RA Assessment Advantages of ultrasonography Potential
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nicole Klett,, M.D.
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Nicole Klett,, M.D. Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic Chronic Inflammatory Primarily targets the synovium of diarthrodial joints Etiology likely combination genetic and environmental Diarthrodial
Rheumatoid Arthritis Nicole Klett,, M.D. Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic Chronic Inflammatory Primarily targets the synovium of diarthrodial joints Etiology likely combination genetic and environmental Diarthrodial
Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital
 Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital Contents Definition/ epidemiology Diagnosis Importance of early diagnosis/ treatment Guidelines Evidence based treatment protocol Current
Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital Contents Definition/ epidemiology Diagnosis Importance of early diagnosis/ treatment Guidelines Evidence based treatment protocol Current
British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:1101-1105
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:1101-1105 REMISSION IN A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. AMERICAN RHEUMATISM ASSOCIATION PRELIMINARY REMISSION CRITERIA IN RELATION TO THE
British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:1101-1105 REMISSION IN A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. AMERICAN RHEUMATISM ASSOCIATION PRELIMINARY REMISSION CRITERIA IN RELATION TO THE
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz
 Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? RA is the second most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most often appears between
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? RA is the second most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most often appears between
Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis & Axial Spondyloarthritis
 Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis & Axial Spondyloarthritis 奇 美 醫 院 過 敏 免 疫 風 濕 科 陳 宏 安 Rheumatoid arthritis Most common chronic inflammatory joint disease Multisystem autoimmune disease of unknown
Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis & Axial Spondyloarthritis 奇 美 醫 院 過 敏 免 疫 風 濕 科 陳 宏 安 Rheumatoid arthritis Most common chronic inflammatory joint disease Multisystem autoimmune disease of unknown
1991 :super specialties perceptions
 Ved Chaturvedi, MD, DM Research & Referral Hospital New Delhi President Indian Rheumatology Association MSK Ultrasound..A decade experience of bedside MSK US by a clinician. Was it worth it.? 1991 :super
Ved Chaturvedi, MD, DM Research & Referral Hospital New Delhi President Indian Rheumatology Association MSK Ultrasound..A decade experience of bedside MSK US by a clinician. Was it worth it.? 1991 :super
Arthritis of the Hands
 Arthritis of the Hands On the Agenda Normal Osteoarthitis Rheumatoid arthritis CPPD crystal deposition Gout Psoriatic arthritis Normal Hand X-ray Osteoarthritis (DJD) Gradual degeneration of articular
Arthritis of the Hands On the Agenda Normal Osteoarthitis Rheumatoid arthritis CPPD crystal deposition Gout Psoriatic arthritis Normal Hand X-ray Osteoarthritis (DJD) Gradual degeneration of articular
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. Dr Bruce Kirkham Rheumatology Clinical Lead
 RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Dr Bruce Kirkham Rheumatology Clinical Lead RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) RA is a common disease: 0.8 per cent of the population RA more common in females: female to male ratio 3:1 RA
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Dr Bruce Kirkham Rheumatology Clinical Lead RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) RA is a common disease: 0.8 per cent of the population RA more common in females: female to male ratio 3:1 RA
DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO POSTGRADUATE EDUCTION ORTHOPAEDIC OFF-SERVICE GOALS & OBJECTIVES
 DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO POSTGRADUATE EDUCTION ORTHOPAEDIC OFF-SERVICE GOALS & OBJECTIVES GOAL #1 develop the ability to order and understand interpretation
DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO POSTGRADUATE EDUCTION ORTHOPAEDIC OFF-SERVICE GOALS & OBJECTIVES GOAL #1 develop the ability to order and understand interpretation
Ability of Oblique Foot Radiographs to Detect Erosions in Early Arthritis: Results in the ESPOIR Cohort
 Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 59, No. 12, December 15, 2008, pp 1729 1734 DOI 10.1002/art.24310 2008, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ability of Oblique Foot
Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 59, No. 12, December 15, 2008, pp 1729 1734 DOI 10.1002/art.24310 2008, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ability of Oblique Foot
The Widening Mortality Gap Between Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and the General Population
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 56, No. 11, November 2007, pp 3583 3587 DOI 10.1002/art.22979 2007, American College of Rheumatology The Widening Mortality Gap Between Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and the
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 56, No. 11, November 2007, pp 3583 3587 DOI 10.1002/art.22979 2007, American College of Rheumatology The Widening Mortality Gap Between Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and the
Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists
 Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists Case 27 yo female with 6 month history of right forearm and hand pain Works as secretary, symptoms are interfering with her job duties Complains that she
Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists Case 27 yo female with 6 month history of right forearm and hand pain Works as secretary, symptoms are interfering with her job duties Complains that she
ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 MEDIA BACKGROUNDER ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of arthritis (chronic inflammatory polyarthritis) that typically affects hands and feet, although any joint in the body
MEDIA BACKGROUNDER ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of arthritis (chronic inflammatory polyarthritis) that typically affects hands and feet, although any joint in the body
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations
 Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
A patientwithsystemicsclerosis andjointpain. Christian Beyer University Erlangen-Nuremberg(GER)
 A patientwithsystemicsclerosis andjointpain Christian Beyer University Erlangen-Nuremberg(GER) Whatisimportanttoyou? lungs GI tract fatigue heart skin muscles Raynaud s joints Whatisimportanttopatients?
A patientwithsystemicsclerosis andjointpain Christian Beyer University Erlangen-Nuremberg(GER) Whatisimportanttoyou? lungs GI tract fatigue heart skin muscles Raynaud s joints Whatisimportanttopatients?
Medical Policy Anti-CCP Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Medical Policy Anti-CCP Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy: Medicare Description References Authorization
Medical Policy Anti-CCP Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy: Medicare Description References Authorization
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Treat-to-Target
 Rheumatoid Arthritis and Treat-to-Target A Case of Need Encountering Opportunity Need RA affects approximately 1.5 million adults in the United States 1 20%-30% face permanent work disability if not treated
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Treat-to-Target A Case of Need Encountering Opportunity Need RA affects approximately 1.5 million adults in the United States 1 20%-30% face permanent work disability if not treated
Assessment of Proximal Finger Joint Inflammation in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis, Using a Novel Laser-Based Imaging Technique
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 46, No. 5, May 2002, pp 1177 1184 DOI 10.1002/art.10226 2002, American College of Rheumatology Assessment of Proximal Finger Joint Inflammation in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis,
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 46, No. 5, May 2002, pp 1177 1184 DOI 10.1002/art.10226 2002, American College of Rheumatology Assessment of Proximal Finger Joint Inflammation in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis,
Finger joint synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: quantitative assessment by magnetic resonance imaging
 Rheumatology 1999;38:66 72 Finger joint synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: quantitative assessment by magnetic resonance imaging M. Klarlund1,2, M. Østergaard1,2 and I. Lorenzen1 1Department of Rheumatology
Rheumatology 1999;38:66 72 Finger joint synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: quantitative assessment by magnetic resonance imaging M. Klarlund1,2, M. Østergaard1,2 and I. Lorenzen1 1Department of Rheumatology
NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Type III Hypersensitivity Response
 NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System Margaret H. Birney PhD, RN Lecture 12 Part 2 Joint Disorders (cont d) Rheumatoid Arthritis Definition: Autoimmune disorder occurring in genetically sensitive
NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System Margaret H. Birney PhD, RN Lecture 12 Part 2 Joint Disorders (cont d) Rheumatoid Arthritis Definition: Autoimmune disorder occurring in genetically sensitive
COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 17 December 2003 CPMP/EWP/556/95 rev 1/Final COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 17 December 2003 CPMP/EWP/556/95 rev 1/Final COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
ACT-RAY and MRI substudy
 Tocilizumab as Monotherapy or in Combination With Methotrexate associated with Early Reductions in Tissue Inflammation: 12-Week Results From a Magnetic Resonance Imaging Substudy of a Randomized Controlled
Tocilizumab as Monotherapy or in Combination With Methotrexate associated with Early Reductions in Tissue Inflammation: 12-Week Results From a Magnetic Resonance Imaging Substudy of a Randomized Controlled
2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis Published in the September 2010 Issues of A&Rand ARD Phases of the Project Phase 1 Data analysis Phase 2 Consensus process Predictors of
2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis Published in the September 2010 Issues of A&Rand ARD Phases of the Project Phase 1 Data analysis Phase 2 Consensus process Predictors of
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Disease RA Final.indd 2 15. 6. 10. 11:23
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease RA Final.indd 2 15. 6. 10. 11:23 Understanding what to expect can help you prepare for your transition into treatment. Rheumatoid Arthritis What You Need To Know About Rheumatoid
Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease RA Final.indd 2 15. 6. 10. 11:23 Understanding what to expect can help you prepare for your transition into treatment. Rheumatoid Arthritis What You Need To Know About Rheumatoid
Understanding and improving communications between people with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthcare professionals. RCUKCOMM00116w February 2014
 Understanding and improving communications between people with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthcare professionals RCUKCOMM00116w February 2014 This project has been funded by Roche Products Ltd &
Understanding and improving communications between people with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthcare professionals RCUKCOMM00116w February 2014 This project has been funded by Roche Products Ltd &
SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698
 SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698 Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging Biomarkers for Assessment of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Treatment: A sub-study of the I-SPY 2 TRIAL Version: 1.0 Date: May 28, 2012
SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698 Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging Biomarkers for Assessment of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Treatment: A sub-study of the I-SPY 2 TRIAL Version: 1.0 Date: May 28, 2012
INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D.
 05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
Rheumatology Labs for Primary Care Providers. Robert Monger, M.D., F.A.C.P. 2015 Frontiers in Medicine
 Rheumatology Labs for Primary Care Providers Robert Monger, M.D., F.A.C.P. 2015 Frontiers in Medicine Objectives Review the Indications for and Interpretation of lab testing for the following diseases:
Rheumatology Labs for Primary Care Providers Robert Monger, M.D., F.A.C.P. 2015 Frontiers in Medicine Objectives Review the Indications for and Interpretation of lab testing for the following diseases:
Symptoms ongoing for 6/12, initially intermittent in nature.
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Case Study INTRODUCTION Each student will have watched the relevant MDT member carrying out their initial assessment on the same newly diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis patient. Videos
Rheumatoid Arthritis Case Study INTRODUCTION Each student will have watched the relevant MDT member carrying out their initial assessment on the same newly diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis patient. Videos
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents About Rheumatoid Arthritis 1 Definition 1 Signs and symptoms 1 Causes 1 Risk factors 1 Test and diagnosis 2 Treatment options 2 Lifestyle 3 References
Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents About Rheumatoid Arthritis 1 Definition 1 Signs and symptoms 1 Causes 1 Risk factors 1 Test and diagnosis 2 Treatment options 2 Lifestyle 3 References
Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013
 Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013 Measure Title USE OF IMAGING STUDIES FOR LOW BACK PAIN Disease State Musculoskeletal Indicator Classification Utilization Strength
Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013 Measure Title USE OF IMAGING STUDIES FOR LOW BACK PAIN Disease State Musculoskeletal Indicator Classification Utilization Strength
Imaging Rheumatoid Arthritis
 April 2002 Imaging Rheumatoid Arthritis Aimee Shu, Harvard Medical School, Year III Meet Ms. M 50-year old female 22-year history of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (RA) Followed at BIDMC rheumatology
April 2002 Imaging Rheumatoid Arthritis Aimee Shu, Harvard Medical School, Year III Meet Ms. M 50-year old female 22-year history of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (RA) Followed at BIDMC rheumatology
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain
 Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
Ultrasound of the small joints of the hands and feet: current status
 Skeletal Radiol (2008) 37:99 113 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0356-9 REVIEW ARTICLE Ultrasound of the small joints of the hands and feet: current status E. G. McNally Received: 8 December 2006 /Revised: 7 May
Skeletal Radiol (2008) 37:99 113 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0356-9 REVIEW ARTICLE Ultrasound of the small joints of the hands and feet: current status E. G. McNally Received: 8 December 2006 /Revised: 7 May
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments of Rheumatoid Foot and Ankle
 Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis, affecting about two to three million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is a symmetric disease, meaning that it will usually involve
Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis, affecting about two to three million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is a symmetric disease, meaning that it will usually involve
Treatment of Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Treatment of Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Zhanguo Li Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, People s Hospital Beijing University Medical School, China Contents Background Challenges Treatment strategies
Treatment of Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Zhanguo Li Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, People s Hospital Beijing University Medical School, China Contents Background Challenges Treatment strategies
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot
 The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk Pictorial review Abstract
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk Pictorial review Abstract
The Dedicated MRI Factbook. Esaote MRI: A world of difference
 The Dedicated MRI Factbook Esaote MRI: A world of difference Esaote Dedicated MRI Measures of Excellence Creativity in Healthcare is Esaote s motto which represents the philosophy that has been adopted
The Dedicated MRI Factbook Esaote MRI: A world of difference Esaote Dedicated MRI Measures of Excellence Creativity in Healthcare is Esaote s motto which represents the philosophy that has been adopted
It is worth noting that people with psoriasis can also develop other forms of arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
 Psoriatic Arthritis Main Colour - pantone 2597u Research - pantone 206u Children - pantone 123 4 What is psoriatic arthritis? Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory joint disease associated with psoriasis.
Psoriatic Arthritis Main Colour - pantone 2597u Research - pantone 206u Children - pantone 123 4 What is psoriatic arthritis? Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory joint disease associated with psoriasis.
Test Request Tip Sheet
 With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES. Anthony Hewitt
 DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis. A radiologic tour of a patient encounter
 Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Etanercept (Enbrel ) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis with Recent Onset Versus Established Disease: Improvement in Disability
 Etanercept (Enbrel ) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis with Recent Onset Versus Established Disease: Improvement in Disability SCOTT W. BAUMGARTNER, ROY M. FLEISCHMANN, LARRY W. MORELAND, MICHAEL H.
Etanercept (Enbrel ) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis with Recent Onset Versus Established Disease: Improvement in Disability SCOTT W. BAUMGARTNER, ROY M. FLEISCHMANN, LARRY W. MORELAND, MICHAEL H.
Psoriatic Arthritis: the Role of Radiologic Assessment in Diagnosis and Management
 Psoriatic Arthritis: the Role of Radiologic Assessment in Diagnosis and Management Stephanie W. Hu, HMS IV BIDMC Department of Radiology August 25, 2008 Overview Patient AC Psoriatic arthritis (PsA( PsA)
Psoriatic Arthritis: the Role of Radiologic Assessment in Diagnosis and Management Stephanie W. Hu, HMS IV BIDMC Department of Radiology August 25, 2008 Overview Patient AC Psoriatic arthritis (PsA( PsA)
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz
 Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the third most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the third most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most
A Topological Approach to Quantitation of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Topological Approach to Quantitation of Rheumatoid Arthritis Hamish Carr, John Ryan, Maria Joyce, Oliver Fitzgerald, Douglas Veale, Robin Gibney, and Patrick Brennan University College Dublin Summary.
A Topological Approach to Quantitation of Rheumatoid Arthritis Hamish Carr, John Ryan, Maria Joyce, Oliver Fitzgerald, Douglas Veale, Robin Gibney, and Patrick Brennan University College Dublin Summary.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Application of high frequency color Doppler ultrasound in the monitoring of rheumatoid arthritis treatment
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: 1807-1812, 2014 Application of high frequency color Doppler ultrasound in the monitoring of rheumatoid arthritis treatment GUIMIN ZHENG 1, LEI WANG 2, XIUCHUAN
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: 1807-1812, 2014 Application of high frequency color Doppler ultrasound in the monitoring of rheumatoid arthritis treatment GUIMIN ZHENG 1, LEI WANG 2, XIUCHUAN
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy
 Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy Hans T.M. van Schie DVM, PhD UTC Imaging, Netherlands Scoring with Patellar Tendinopathy? no one size
Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy Hans T.M. van Schie DVM, PhD UTC Imaging, Netherlands Scoring with Patellar Tendinopathy? no one size
SPECT/CT Wrist. Wrist pain 3/27/2012
 Wrist pain Wrist joint - complicated anatomy complex biomechanics Imaging and management of wrist pain presents a significant challenge Significant economic burden SPECT/CT Wrist HK Mohan GSTT London Intra-capsular
Wrist pain Wrist joint - complicated anatomy complex biomechanics Imaging and management of wrist pain presents a significant challenge Significant economic burden SPECT/CT Wrist HK Mohan GSTT London Intra-capsular
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons
 MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
EFSUMB EUROPEAN FEDERATION OF SOCIETIES FOR ULTRASOUND IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY Building a European Ultrasound Community
 MINIMUM TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PRACTICE OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND IN EUROPE Appendix 12: Musculoskeletal Musculoskeletal ultrasound comprises a wide range of different examinations increasingly performed
MINIMUM TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PRACTICE OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND IN EUROPE Appendix 12: Musculoskeletal Musculoskeletal ultrasound comprises a wide range of different examinations increasingly performed
Psoriatic Arthritis. Title. Understanding and Managing. in All the Wrong Places. Clinical Features. Etiology of Psoriatic Arthritis
 Focus on CME at Memorial University Understanding and Managing Title Psoriatic Arthritis in All the Wrong Places Proton Rahman MD, MSc, FRCPC Although Baron Jean-Luis Aubert offered the first case description
Focus on CME at Memorial University Understanding and Managing Title Psoriatic Arthritis in All the Wrong Places Proton Rahman MD, MSc, FRCPC Although Baron Jean-Luis Aubert offered the first case description
Early identification and treatment - the Norwegian perspective. Till Uhlig Dept of Rheumatology Diakonhjemmet Hospital Oslo, Norway
 Early identification and treatment - the Norwegian perspective Till Uhlig Dept of Rheumatology Diakonhjemmet Hospital Oslo, Norway Oslo Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry (ORAR) Very early Arthritis Clinic
Early identification and treatment - the Norwegian perspective Till Uhlig Dept of Rheumatology Diakonhjemmet Hospital Oslo, Norway Oslo Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry (ORAR) Very early Arthritis Clinic
A ctive rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterised by
 290 REVIEW Early referral recommendation for newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis: evidence based development of a clinical guide P Emery, F C Breedveld, M Dougados, J R Kalden, M H Schiff, J S Smolen...
290 REVIEW Early referral recommendation for newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis: evidence based development of a clinical guide P Emery, F C Breedveld, M Dougados, J R Kalden, M H Schiff, J S Smolen...
Disease Therapy Management (DTM) Enhances Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
 A WHITE PAPER BY Disease Therapy Management (DTM) Enhances Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Increased adherence rates deliver improved outcomes for patients FALL 2010 The Benefits of DTM for Rheumatoid Arthritis
A WHITE PAPER BY Disease Therapy Management (DTM) Enhances Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Increased adherence rates deliver improved outcomes for patients FALL 2010 The Benefits of DTM for Rheumatoid Arthritis
What s new in clinical assesment of ankylosing spondylitis?
 What s new in clinical assesment of ankylosing spondylitis? Désirée van der Heijde Professor of Rheumatology Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, Norway Content
What s new in clinical assesment of ankylosing spondylitis? Désirée van der Heijde Professor of Rheumatology Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, Norway Content
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
 In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
(Intro to Arthritis with a. Arthritis) Manager of Education & Services for the Vancouver Island Region of The Arthritis Society
 Arthritis 101 (Intro to Arthritis with a Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis) by Cari Taylor by Cari Taylor Manager of Education & Services for the Vancouver Island Region of The Arthritis Society What You Will
Arthritis 101 (Intro to Arthritis with a Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis) by Cari Taylor by Cari Taylor Manager of Education & Services for the Vancouver Island Region of The Arthritis Society What You Will
Youth Thrower s Elbow
 Youth Thrower s Elbow Description Youth Thrower s elbow is an inflammatory condition involving the growth plate of the humerus, near the inner elbow at the medial epicondyle.(figure 1) This condition is
Youth Thrower s Elbow Description Youth Thrower s elbow is an inflammatory condition involving the growth plate of the humerus, near the inner elbow at the medial epicondyle.(figure 1) This condition is
Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Original Policy Date January /2014
 MP 2.04.81 Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis Medical Policy Section 2.0 Original Policy Date January /2014 Last Review Status/Date 1/2014 Disclaimer Our medical policies are designed for informational
MP 2.04.81 Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis Medical Policy Section 2.0 Original Policy Date January /2014 Last Review Status/Date 1/2014 Disclaimer Our medical policies are designed for informational
Psoriatic Arthritis. Ewa Olech, MD Division of Rheumatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Las Vegas
 Psoriatic Arthritis Ewa Olech, MD Division of Rheumatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Las Vegas The Spectrum of Spondyloarthritis Characteristics of the Spondyloarthritis Sacroiliac & spinal
Psoriatic Arthritis Ewa Olech, MD Division of Rheumatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Las Vegas The Spectrum of Spondyloarthritis Characteristics of the Spondyloarthritis Sacroiliac & spinal
Rheumatoid Arthritis Information
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Information Definition Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term disease that leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It can also affect other organs. Alternative
Rheumatoid Arthritis Information Definition Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term disease that leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It can also affect other organs. Alternative
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview. Christine Pham MD
 Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND COURSE - BASIC LEVEL- Graz, November 2 nd 4 th, 2016
 MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND COURSE - BASIC LEVEL- Graz, November 2 nd 4 th, 2016 Dear colleague, musculoskeletal ultrasound is increasingly used by rheumatologist and other health professionals for diagnostic
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND COURSE - BASIC LEVEL- Graz, November 2 nd 4 th, 2016 Dear colleague, musculoskeletal ultrasound is increasingly used by rheumatologist and other health professionals for diagnostic
Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 10/11/2015 History Child with several month history of weakness, arthralgias and palpable abnormalities at the knee Diagnosis Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 10/11/2015 History Child with several month history of weakness, arthralgias and palpable abnormalities at the knee Diagnosis Juvenile Dermatomyositis
I. INCLUSION AND EXCLUSION CRITERIA
 Page 1 of 5 I. INCLUSION AND EXCLUSION CRITERIA INCLUSION CRITERIA Yes No 1. Patient is diagnosed with according to the American College of Rheumatology 1987 revised criteria. 2. All 4 grandparents are
Page 1 of 5 I. INCLUSION AND EXCLUSION CRITERIA INCLUSION CRITERIA Yes No 1. Patient is diagnosed with according to the American College of Rheumatology 1987 revised criteria. 2. All 4 grandparents are
Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition
 www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
Evolution of Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis: How Do the 2010 Criteria Perform?
 Evolution of Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis: How Do the 2010 Criteria Perform? Elizabeth C. Ortiz, MD*, Shuntaro Shinada, MD KEYWORDS Rheumatoid arthritis Classification criteria Inflammatory
Evolution of Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis: How Do the 2010 Criteria Perform? Elizabeth C. Ortiz, MD*, Shuntaro Shinada, MD KEYWORDS Rheumatoid arthritis Classification criteria Inflammatory
Radiographic development during three decades in a patient with psoriatic arthritis mutilans
 Case Report Radiographic development during three decades in a patient with psoriatic arthritis mutilans Acta Radiologica Open 4(7) 1 5! The Foundation Acta Radiologica 2015 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalspermissions.nav
Case Report Radiographic development during three decades in a patient with psoriatic arthritis mutilans Acta Radiologica Open 4(7) 1 5! The Foundation Acta Radiologica 2015 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalspermissions.nav
Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases
 September 2002 Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases Natalie J. M. Dailey, Harvard Medical Student Year III Our Patient s Presenting Story 70 year old male Presents to the hospital for laparascopic
September 2002 Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases Natalie J. M. Dailey, Harvard Medical Student Year III Our Patient s Presenting Story 70 year old male Presents to the hospital for laparascopic
PREVALENCE OF HAND SYMPTOMS, IMPAIRMENTS AND ACTIVITY LIMITATIONS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN RELATION TO DISEASE
 J Rehabil Med 1; : 91 91 ORIGINAL REPORT PREVALENCE OF HAND SYMPTOMS, IMPAIRMENTS AND ACTIVITY LIMITATIONS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN RELATION TO DISEASE DURATION Noortje C. A. Horsten, MD 1, Jennie Ursum,
J Rehabil Med 1; : 91 91 ORIGINAL REPORT PREVALENCE OF HAND SYMPTOMS, IMPAIRMENTS AND ACTIVITY LIMITATIONS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN RELATION TO DISEASE DURATION Noortje C. A. Horsten, MD 1, Jennie Ursum,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure
Ultrasound For Rheumatologists: Focus on Hands and Feet
 THE RHEUMATISM SOCIETY OF THE DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA PRESENTS Ultrasound For Rheumatologists: Focus on Hands and Feet September 12, 2015 2730 University Boulevard West Westfield North Building 7th Floor
THE RHEUMATISM SOCIETY OF THE DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA PRESENTS Ultrasound For Rheumatologists: Focus on Hands and Feet September 12, 2015 2730 University Boulevard West Westfield North Building 7th Floor
Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis at an early stage
 Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis at an early stage P. Miossec and J. Tebib Definition Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the most frequent chronic inflammatory arthritis. It affects about 0.5% of the population,
Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis at an early stage P. Miossec and J. Tebib Definition Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the most frequent chronic inflammatory arthritis. It affects about 0.5% of the population,
Assessment of Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis with 18 F-FDG PET
 Assessment of Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis with F-FDG PET Catherine Beckers, MD 1 ; Clio Ribbens, MD, PhD 2 ;Béatrice André, MD 2 ; Stefaan Marcelis, MD 3 ; Olivier Kaye, MD, PhD 2 ; Luc Mathy,
Assessment of Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis with F-FDG PET Catherine Beckers, MD 1 ; Clio Ribbens, MD, PhD 2 ;Béatrice André, MD 2 ; Stefaan Marcelis, MD 3 ; Olivier Kaye, MD, PhD 2 ; Luc Mathy,
Multiple Myeloma. Abstract. Introduction
 Multiple Myeloma Abstract Multiple Myeloma is a plasma cell cancer that causes an overproduction of plasma cells. Multiple Myeloma is a difficult disease to diagnosis because symptoms might not be present
Multiple Myeloma Abstract Multiple Myeloma is a plasma cell cancer that causes an overproduction of plasma cells. Multiple Myeloma is a difficult disease to diagnosis because symptoms might not be present
Arthroscopy of the Hand and Wrist
 Arthroscopy of the Hand and Wrist Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure whereby a small camera is inserted through small incisions of a few millimeters each around a joint to view the joint directly.
Arthroscopy of the Hand and Wrist Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure whereby a small camera is inserted through small incisions of a few millimeters each around a joint to view the joint directly.
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program. 2011-2012 Assessment Report
 Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program 2011-2012 Assessment Report I. Introduction II. III. Mission, Objectives, and Student Learning Outcomes a. Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program Mission
Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program 2011-2012 Assessment Report I. Introduction II. III. Mission, Objectives, and Student Learning Outcomes a. Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program Mission
11/8/2011. Administrative Definitions of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rising Prevalence Regardless of Definition Used. No Disclosures. Background.
 Administrative Definitions of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rising Prevalence Regardless of Definition Used Christine A. Peschken, Carol A. Hitchon, Hui Chen, Allan Garland, Hani S. El-Gabalawy, Charles N. Bernstein
Administrative Definitions of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rising Prevalence Regardless of Definition Used Christine A. Peschken, Carol A. Hitchon, Hui Chen, Allan Garland, Hani S. El-Gabalawy, Charles N. Bernstein
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Update 2014 Mark Hulsey, MD FACR Rheumatoid Arthritis Key Features Symptoms >6 weeks duration Often lasts the remainder of the patient s life Inflammatory synovitis Palpable synovial
Rheumatoid Arthritis Update 2014 Mark Hulsey, MD FACR Rheumatoid Arthritis Key Features Symptoms >6 weeks duration Often lasts the remainder of the patient s life Inflammatory synovitis Palpable synovial
LATE-ONSET RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: IS PITTING OEDEMA OF THE HANDS AT ONSET A GOOD PROGNOSTIC INDICATOR?
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1997;36:214 219 LATE-ONSET RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: IS PITTING OEDEMA OF THE HANDS AT ONSET A GOOD PROGNOSTIC INDICATOR? B. B. BHAKTA and C. T. PEASE Rheumatology and Rehabilitation
British Journal of Rheumatology 1997;36:214 219 LATE-ONSET RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: IS PITTING OEDEMA OF THE HANDS AT ONSET A GOOD PROGNOSTIC INDICATOR? B. B. BHAKTA and C. T. PEASE Rheumatology and Rehabilitation
Healing of erosive changes in rheumatoid arthritis
 Healing of erosive changes in rheumatoid arthritis R. Rau, G. Herborn, S. Wassenberg Please address correspondence to: Rolf Rau, MD, PhD, Rheumatologie, Evangelisches Fachkrankenhaus, Rosenstrasse 2, 40882
Healing of erosive changes in rheumatoid arthritis R. Rau, G. Herborn, S. Wassenberg Please address correspondence to: Rolf Rau, MD, PhD, Rheumatologie, Evangelisches Fachkrankenhaus, Rosenstrasse 2, 40882
Psoriatic arthritis in practice : How to detect? How to diagnose? Pascal RICHETTE Hôpital Lariboisière, Paris. Copyright
 Psoriatic arthritis in practice : How to detect? How to diagnose? Pascal RICHETTE Hôpital Lariboisière, Paris The patient: a 57 year-old man, with a history of psoriatic nail dystrophy for 10 years Past
Psoriatic arthritis in practice : How to detect? How to diagnose? Pascal RICHETTE Hôpital Lariboisière, Paris The patient: a 57 year-old man, with a history of psoriatic nail dystrophy for 10 years Past
RHEUMATOLOGY ICD-10 CROSSWALK
 RHEUMATOLOGY ICD-10 CROSSWALK ICD is revised periodically and is currently in its tenth edition and will be implemented in the United States on October 1, 2015. There is an annual minor update and three-yearly
RHEUMATOLOGY ICD-10 CROSSWALK ICD is revised periodically and is currently in its tenth edition and will be implemented in the United States on October 1, 2015. There is an annual minor update and three-yearly
USE OF ULTRASOUND FOR DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW-UP OF PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS
 USE OF ULTRASOUND FOR DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW-UP OF PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS Rusmir Husic, 1 Anja Ficjan, 1 Christina Duftner, 2 *Christian Dejaco 1 1. Division of Rheumatology and Immunology, Medical University
USE OF ULTRASOUND FOR DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW-UP OF PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS Rusmir Husic, 1 Anja Ficjan, 1 Christina Duftner, 2 *Christian Dejaco 1 1. Division of Rheumatology and Immunology, Medical University
X-Plain Rheumatoid Arthritis Reference Summary
 X-Plain Rheumatoid Arthritis Reference Summary Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating
X-Plain Rheumatoid Arthritis Reference Summary Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating
