Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System Clinician Manual
|
|
|
- Marilynn Barnett
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System Directions for Use CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale, distribution and use by or on the order of a physician REV B
2 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System Guarantees Boston Scientific Corporation reserves the right to modify, without prior notice, information relating to its products in order to improve their reliability or operating capacity. Drawings are for illustration purposes only. Trademarks All trademarks are the property of their respective holders Rev B ii of iv
3 Table of Contents Manual Overview... 1 Device and Product Description... 2 Implantable Pulse Generator...2 Leads...2 Lead Extension...2 Lead Splitter...3 Indications for Use... 4 Precision System Clinical Summary...4 Contraindications... 8 Safety Information... 9 Instructions for the Patient...9 Warnings...9 Precautions...9 Adverse Effects Instructions for the Physician Package Contents IPG Kit...13 Percutaneous Permanent Lead Kit...13 Percutaneous Trial Lead Kit...13 Lead Extension Kit x4 Splitter Kit...14 Surgical Paddle Lead Kit...14 Infinion 16 Lead Kit...14 Infinion 16 Trial Lead Kit...14 Infinion CX Lead Kit...15 Infinion CX Lead Trial Lead Kit...15 Splitter 2x8 Kit...15 Infinion 16 Trial Configuration Kit...15 Infinion 16 Configuration Kit...15 Sterilization, Handling, and Storage Sterilization...16 IPG Handling and Storage...16 Lead, Lead Extension, and Splitter Handling and Storage...17 Pre-Op Instructions Percutaneous Lead Placement in the Epidural Space Infinion CX Lead Placement in the Epidural Space with Entrada Needle...20 Lead Connection to Splitter...25 Surgical Paddle Lead Placement in the Epidural Space Connecting the OR Cable Assembly Intraoperative Stimulation Testing Securing the Trial Lead Securing the Infinion CX Trial Lead Permanent Lead Anchoring and Tunneling Anchoring the Lead...34 Tunneling the Lead or Lead Extension Rev B iii of iv
4 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System Connecting the Lead Extension...37 Connecting to the Trial Stimulator Removal of Trial Leads, Extensions, and Splitters Option A: Percutaneous Lead Removal after Temporary Trial...40 Option B: Lead Extension Removal after Permanent Trial...40 Option C: Splitter Removal after Trial...40 IPG Implantation Connecting to the IPG For Percutaneous Lead - Dual Lead Connection...42 For Infinion 16 Lead Connection...42 For Infinion CX Lead Connection...42 For Percutaneous Lead - Single Lead Connection...42 For Surgical Paddle Lead Connection...42 Programming with the Infinion 16 Lead and Infinion CX Lead...44 IPG Explant or Replacement Rechargeable Stimulator System IPG Battery Status...46 Charging Steps...47 Patient Remote Control...48 Device Linking...53 Searching...53 Clinician Options...54 Specifications and Technical Data Materials...59 Max Current Amp. per Electrode vs. Impedance...60 Registration Information Registering the Stimulator and Leads...63 Technical Service Limited Warranty - IPG Limited Warranty - Leads Limited Warranty - Externals Rev B iv of iv
5 Manual Overview Manual Overview This manual provides basic information for the trial, implantation, and operation of the Boston Scientific Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator (SCS) system. General surgical guidelines are presented in this manual for temporary and permanent implantation of Boston Scientific percutaneous leads, lead extensions, splitters, surgical paddle leads, and implantable pulse generator (IPG). These products are designed to aid in the management of chronic intractable pain. This manual also provides an overview of accessories for programming and charging the IPG, clinical and surgical considerations, storage and handling requirements, and relevant precautions concerning an implanted neurostimulator. Additional information on system components and operation can be found in the Bionic Navigator Software Guide Rev B 1 of 69
6 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System Device and Product Description The Precision system consists of an implantable pulse generator, temporary and permanent percutaneous leads, surgical paddle leads, and lead extensions, each packaged as a separate kit. Single use accessories and disposable tools are also included in these kits. Features of the Precision SCS System include: Stimulation electrode field navigation Sixteen independent current-controlled electrodes Four programmable stimulation areas per program; four possible programs Long-life operation High-range parameter capability Small size Two-foot programming range This product contains no detectable latex Implantable Pulse Generator The Precision Implantable Pulse Generator (IPG) system is intended to treat chronic pain by electrically stimulating the spinal cord. The multi-channel, multi-electrode device capability provides flexibility in conjunction with ease of programming. A rechargeable battery increases IPG longevity and output capability while reducing size and device replacement surgeries. The IPG is controlled by a handheld Remote Control, and can be engaged by a clinician computer using proprietary Bionic Navigator software. Periodically, the IPG battery requires replenishing with an RF charging device provided separately in the Patient Charging Kit. Leads The percutaneous and surgical paddle leads function as a component of the Precision SCS system by delivering electrical stimulation to the nerve structures in the dorsal aspect of the spinal cord, resulting in an inhibition of pain sensation. Surgical Paddle Lead The 2x8 Surgical Paddle Lead is available in lengths of 50 cm and 70 cm. The distal (paddle) end of the lead has two columns of eight evenly spaced planar electrodes. Each electrode is 3x2 mm 2 in area. On the proximal side, this lead employs 2 lead tails. The end of each tail has eight evenly spaced contacts, identical to the percutaneous leads. The right tail of the Paddle Lead is laser-etched to allow for ease of right and left identification. Each tail can be inserted into an IPG or into a lead extension. Percutaneous Leads The eight-contact percutaneous leads are available in lengths of 30 cm, 50 cm, and 70 cm. Each lead has eight electrode contacts located near the distal end. Each contact is 3 mm in length and is spaced 1, 4, or 6 mm from the adjacent contact. The 16 contact percutaneous lead (Infinion 16 Lead and Infinion CX Lead) is available in lengths of 50 cm and 70 cm. Each lead has 16 contacts located near the distal end. Each contact is 3 mm in length and is spaced 1 mm from the adjacent contact. The Infinion 16 lead must be inserted into a Splitter 2x8 which then connects to a Precision IPG s 8 contact ports or 8 contact OR Cables. Lead Extension Lead Extensions are designed to connect the percutaneous and paddle leads to the Precision IPG for spinal cord stimulation. The extension may be added to a lead to externalize the lead for a trial procedure or to extend the lead when a permanent IPG is implanted Rev B 2 of 69
7 Device and Product Description Lead extensions are available in lengths of 25 cm, 35 cm, and 55 cm. Each extension has eight electrode contacts located near the distal end. Each contact is 3 mm in length and is spaced 1 mm from the adjacent contact. The extension can be connected to either the Trial Stimulator (via an OR Cable Assembly included in the Leads Kit) or directly to the Precision IPG. Lead Splitter The 2x4 Splitters are designed to connect multiple percutaneous leads to the Precision IPG. The Linear leads may be inserted into a splitter for a maximum of four Linear leads per IPG. Four of the eight contacts of each Linear lead will be activated. Two configurations of 2x4 splitters are available: Distal 4 (D4) and Wide 4 (W4). The two versions offer different contact configurations. The Lead Splitter 2x8 is required to connect the Infinion 16 contact lead to the IPG. Only one Infinion 16 lead through one Splitter 2x8 can be connected to a Precision IPG Rev B 3 of 69
8 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System Indications for Use The Boston Scientific PRECISION Spinal Cord Stimulator System (PRECISION System) is indicated as an aid in the management of chronic intractable pain of the trunk and/or limbs, including unilateral or bilateral pain associated with the following: failed back surgery syndrome, intractable low back pain and leg pain. Precision System Clinical Summary Determination of the safety and effectiveness of the PRECISION System was based on available published clinical studies for similar implanted spinal cord stimulation systems. The PRECISION System is similar to the SCS systems reported in published literature in intended use, target patient population, technology, device design, and output characteristics. Therefore, the clinical data from the published literature described below represents evidence supporting the safety and effectiveness of the PRECISION System for the treatment chronic intractable pain of the trunk and/or limbs, including unilateral or bilateral pain associated with the following: failed back surgery syndrome, intractable low back and leg pain. Efficacy Evaluation Three (3) clinical literature studies were used to support the effectiveness of the PRECISION System (Ohnmeiss et al. 1996, Villavicencio et al. 2000, Hassenbusch SJ et al. 1995). The studies included a total of 116 patients that were implanted with an SCS system. A total of approximately 3166 device months of experience was depicted from the retrospective clinical evaluation. All three studies examined the effectiveness of SCS on patients with chronic pain of the trunk and/or limbs including unilateral or bilateral pain associated with the following: failed back surgery syndrome or intractable low back and leg pain. In all studies, a totally implantable spinal cord stimulator was used in association with a percutaneous and/or surgical lead. These studies provide the same diagnostic or therapeutic intervention for the same disease/ conditions and patient population as the PRECISION System. The prospective study by Ohnmeiss et al. 1996, examined the long-term effectiveness of SCS in patients with intractable leg pain. Forty patients were implanted with SCS systems and evaluated at 6 weeks, 12 months, and 24 months follow-up. Outcome measures included the VAS, pain drawings, medication use, SIP (Sickness Impact Profile), isometric lower extremity testing, and patient questionnaires. An intent-to-treat analysis was performed. After patients had SCS for 24 months, leg pain, pain when walking, standing pain, pain s effect on overall lifestyle, and the total analog scale scores were significantly improved from baseline. In this study, 25% of the implanted patients had greater than 50% improvement in pain rating. In addition, 3 patients from this study had their stimulators repositioned due to pain at the original location. Three patients had reoperations to adjust lead position; 1 patient required 2 reoperations, 1 patient had the device removed due to infection and later to have a new device implanted. A diabetic patient had skin problems which required device removal; a new device was later implanted. Two patients had the device removed due to unsatisfactory pain relief. The prospective study performed by Villavicencio et al included 41 patients with pain of various etiologies. The majority of the patients, 24 (59%), had Failed Back Surgery Syndrome (FBSS), 7 (17%) had Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS I and II), 4 (10%) had neuropathic pain syndrome, and 6 (15%) were diagnosed as stroke or other. Patients underwent an initial trial period for SCS with temporary leads. If the trial resulted in greater than 50% reduction in the patient s pain, as measured by the VAS, the patient was implanted with a SCS system. In this study, 27/41 patients, 66%, had permanent implants. All patients were examined after 6 weeks. Pain measurements were assessed at 3-6 month intervals for the first year and annually thereafter. The median long-term follow-up was 34 months. A total of 24/27 (89%), reported greater than 50% reduction in pain. Since the majority of the patients were treated for FBSS, this article supports the use of SCS for the treatment of FBSS Rev B 4 of 69
9 Indications for Use In this study, one patient required a revision because of electrode fracture. One patient required removal of the system due to local infection. One patient required replacement of the IPG due to mechanical failure. Overall, 16 of 27 (59%) patients required a total of 36 repositioning procedures. A retrospective analysis performed by Hassenbusch SJ et al included patients with chronic lower body pain, predominately neuropathic pain and pain either midline lower back and/or unilateral or bilateral leg pain treated over a 5 year period. The study was a comparison of SCS to spinal infusion of opioids. For patients with radicular pain involving one leg with or without unilateral buttock pain, a trial of SCS was recommended first. For patients with midline back pain and /or bilateral leg pain, a trial of long-term spinal infusion was recommended first. If the patients failed screening with either of these modalities, the other was then tested. If the treatment reduced the pain by 50%, the systems were internalized. A retrospective analysis of patients with unilateral leg and/or buttock pain treated initially with SCS and bilateral leg or mainly low back pain treated initially with spinal infusions of opioids was then done. In this study, 42 patients were screened; 26 (62%) patients received spinal stimulation; 16 (38%) received opioids via a spinal infusion pump. Five patients did not receive adequate pain relief with SCS; 3 (7%) of these patients underwent trial spinal infusions and had effective pain relief. There were 4 (10%) patients who underwent a trial of spinal infusion of opioid but did not receive adequate pain relief; these patients were not tested with SCS. Pain severity was rated using a verbal digital pain scale: On a scale of 0 to 10 where 0 is no pain and 10 is the worst pain you could ever imagine, what is your pain now? 16/26 patients (62%) had greater than 50% pain relief with SCS. In this study, 2/16 (13%) had greater than 50% pain relief with opioids. Mean follow-up was 2.1 ± 0.3 years. This analysis supports the use of SCS for intractable low back and leg pain. In this study, 7 (17%) patients suffered complications after implantation of the device; 5 (12%) patients required repositioning of catheter type electrodes and 2 patients required revision of the stimulator generator. Safety Evaluation Eleven studies were identified based on the detailed inclusion/exclusion criteria to demonstrate the safety of the PRECISION System. The studies included a total of 1056 patients that were trialed with SCS systems and 880 patients that received implants. The table below depicts the number of patients, the number of events, and the percentage of occurrences of each event compared to the total number of patients. It should be noted that citations cover both IPG and RF systems. The clinical experience reported in the literature on RF systems is relevant to determining the safety of totally implantable IPG systems Rev B 5 of 69
10 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System Risks Table 1: Summary of Risks Identified in the Retrospective Clinical Studies # Patients With Adverse Event Intent-to-Treat Basis N = 1056 Lead Migration % 19.9% Infection % 4.4% Epidural Hemorrhage 0 0% 0% Seroma 0 0% 0% Hematoma 1 0.1% 0.1% Paralysis 0 0% 0% CSF Leak 5 0.5% 0.6% Over/Under Stimulation, % 5.2% Ineffective Pain Control Intermittent Stimulation 0 0% 0% Pain Over Implant % 1.8% Allergic Reaction 6 0.6% 0.7% Skin Erosion 0 0% 0% Lead Breakage % 4.0% Hardware Malfunction % 2.5% Loose Connection 0 0% 0% Battery Failure 2 0.2% 0.2% Other % 5.1% Implanted Patient Basis N = 880 Clinical Experience-Safety Clinical data has been collected during a clinical study of the PRECISION System. As of January 15, 2004, 35 subjects were enrolled in the study at multiple sites and 26 subjects had a successful trial stimulation period and were implanted with the PRECISION System. The follow-up period for the 26 implanted patients ranged from 2 weeks to 6 months. The following major adverse events were reported. Table 2: Clinical Experience Safety Type Number of Resolution Patients Lead Migration 1 Lead repositioning and subsequent replacement Output malfunction 1 Device replaced Infection 1 Infection treated Pain 1 Lead explanted Other minor adverse events reported by at least one patient included: receiver malfunction, skin irritation, unpleasant stimulation, CSF leak, infection at implant site, lead migration, and OR cable malfunction. Two of the subjects reported multiple events Rev B 6 of 69
11 References Indications for Use Burchiel, K.J., V.C. Anderson, F.D. Brown, R.G. Fessler, W.A. Friedman, S. Pelofsky, R.L. Weiner, J. Oakley,and D. Shatin. Prospective, Multicenter Study of Spinal Cord Stimulation for Relief of Chronic Back and Extremity Pain. Spine, 21: , Hassenbusch, S.J., M. Stanton-Hicks, E.C. Covington. Spinal cord stimulation verses spinal infusion for low back and leg pain. Acta Neurochirgica, 64: , Kemler, M.A., G.A.M. Barendse, M. Van Kleef, H.C.W. De Vet, C.P.M. Rijks, C.A. Furnee and F.A.J.M. Van den Wilderberg. Spinal Cord Stimulation in Patients with Chronic Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy. New England J of Medicine, 343: , Kim S. H., R.R. Tasker, and M.Y. Oh. Spinal Cord Stimulation for Nonspecific Limb Pain versus Neuropathic Pain and Spontaneous versus Evoked Pain. Neurosurgery, 48(5): , Kumar, K., C. Toth, R. Nath, and P. Lang. Epidural Spinal Cord Stimulation for Treatment of Chronic Pain- Some Predictors of Success. A 15 year experience. Surg Neurol, 50: , Lang, P. The Treatment of Chronic Pain by Epidural Spinal Cord Stimulation. AXON, 18(4): 71-73, Ohnmeiss, D., R. Rashbaum, M. Bogdanffy. Prospective Outcome Evaluation of Spinal Cord Stimulation in Patients With Intractable Leg Pain. Spine, 21: , Rainov, N.G., V. Heidecke, and W. Burkert. Short Test-Period Spinal Cord Stimulation for Failed Back Surgery Syndrome. Minim Invasive Neurosurg, 39(2):41-44, Segal, R., B. Stacey, T. Rudy, S. Basser, J. Markham. Spinal Cord Stimulation Revisited. Neurological Research, 20: , Spieglemann, R. and W.A. Friedman. Spinal Cord Stimulation: A Contemporary Series. Neurosurg 28:65-71, Villavicencio, A.T., J.C. Leveque, L. Rubin, K. Bulsara, and J.P. Gorecki. Laminectomy versus percutaneous electrode placement for spinal cord stimulation. Neurosurgery, 46: , Rev B 7 of 69
12 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System Contraindications Patients contraindicated for permanent SCS therapy are those who: are unable to operate the SCS system have failed trial stimulation by failing to receive effective pain relief are poor surgical risks are pregnant Rev B 8 of 69
13 Safety Information Safety Information Instructions for the Patient Warnings Heat Due to Charging. Do not charge while sleeping. This may result in a burn.while charging, the Charger may become warm. It should be handled with care. Failure to use the Charger with either the Charging Belt or an adhesive patch, as shown, may result in a burn. If you experience pain or discomfort, cease charging and contact Boston Scientific. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Patients implanted with the Precision SCS system should not be subjected to MRI. MRI exposure may result in dislodgement of implanted components, heating of the neurostimulator, damage to the device electronics and/or voltage induction through the leads and Stimulator causing an uncomfortable or jolting sensation. Pediatric Use. The safety and effectiveness of spinal cord stimulation has not been established for pediatric use. Diathermy. Shortwave, microwave and/or therapeutic ultrasound diathermy should not be used on SCS patients. The energy generated by diathermy can be transferred through the Stimulator system, causing tissue damage at the lead site and resulting in severe injury or death. The IPG, whether it is turned on or off, may be damaged. Implanted Stimulation Devices. Spinal cord stimulators may interfere with the operation of implanted sensing stimulators such as pacemakers or cardioverter defibrillators. The effects of implanted stimulation devices on neurostimulators is unknown. Stimulator Damage. Burns may result if the pulse generator case is ruptured or pierced and patient tissue is exposed to battery chemicals. Do not implant the device if the case is damaged. Postural Changes. Patients should be advised that changes in posture or abrupt movements may cause decreases, or uncomfortable or painful increases in the perceived stimulation level. Patients should be advised to turn down the amplitude or turn off the IPG before making posture changes. If unpleasant sensations occur, the IPG should be turned off immediately. Electromagnetic Interference. Strong electromagnetic fields can potentially turn the Stimulator off, or cause uncomfortable or jolting stimulation. Patients should be counseled to avoid or exercise care around: Theft detectors or security screeners such as those used at entrances/exits of department stores, libraries, and other public establishments, and/or airport security screening devices. It is recommended thatpatients request assistance to bypass the device. If they must proceed through the device, the patient should turn off the Stimulator and proceed with caution, ensuring to move through the center of the screener as quickly as possible. Power lines or power generators Electric steel furnaces and arc welders Large, magnetized stereo speakers Precautions Physician training is required. Medical Devices/Therapies. The following medical therapies or procedures may turn stimulation off or may cause permanent damage to the Stimulator, particularly if used in close proximity to the device: lithotripsy electrocautery: Do not use monopolar cautery. See Instructions for the Physician on page 11 external defibrillation Rev B 9 of 69
14 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System radiation therapy ultrasonic scanning high-output ultrasound If any of the above is required by medical necessity, refer to Instructions for the Physician on page 11. Ultimately, however, the device may require explantation as a result of damage to the device. Automobiles and Other Equipment. Patients should not operate automobiles, other motorized vehicles, or potentially dangerous machinery/ equipment with therapeutic stimulation switched on. Stimulation must be turned off first. Sudden stimulation changes, if they occur, may distract patients from attentive operation of the vehicle or equipment. Post Operative. During the two weeks following surgery, it is important to use extreme care so that appropriate healing will secure the implanted components and close the surgical incisions: Do not lift objects of more than five pounds. Do not engage in rigorous physical activity such as twisting, bending, or climbing. If new leads were implanted, do not raise your arms above your head. Temporarily, there may be some pain in the area of the implant as the incisions heal. If discomfort continues beyond two weeks, contact your physician. If you notice excessive redness around the wound areas during this time, contact your physician to check for infection and administer proper treatment. In rare cases, adverse tissue reaction to implanted materials can occur during this period. Be sure to consult your physician before making lifestyle changes due to decreases in pain. Stimulator Location. Never attempt to change the orientation or flip the Stimulator. Do not finger or play with the Stimulator. If the Stimulator flips over in your body, it cannot be charged. If you know that the device has turned, or if stimulation cannot be turned on after charging, contact your physician to arrange an evaluation of the system. In some cases, the skin over your Stimulator may become very thin over time. If this occurs, contact your physician. Lead Location. In some instances a lead can move from its original location, and stimulation at the intended pain site can be lost. If this occurs, consult your physician who may able to restore stimulation by reprogramming the Stimulator in the clinic or repositioning the lead during another operation. Device Failure. Stimulators can fail at any time due to random component failure, loss of battery functionality, or lead breakage. If the device stops working even after complete charging (up to four hours), turn off the Stimulator and contact your physician so that the system can be evaluated. Storage, Handling and Transport. Do not expose the Remote Control or Charging System components to excessively hot or cold conditions. Do not leave the devices in your car or outdoors for extended periods of time. The sensitive electronics can be damaged by temperature extremes, particularly high heat. For proper operation, do not use the Charger if the ambient temperature is above 35 C (95 F). If the Remote Control or the Charging System is to be stored for a period of time without batteries, the storage temperature should not exceed -20 to 60 C (-4 to 140 F). Handle the system components and accessories with care. Do not drop them or submerge them in water. Although reliability testing has been performed to ensure quality manufacturing and performance, dropping the devices on hard surfaces or in water, or other rough handling, can permanently damage the components. (See Limited Warranty - IPG on page 65.) Component Disposal. Do not dispose of the Remote Control or Charger in fire. The battery in these devices can explode in fire. Dispose of used batteries in accordance with local regulations. The IPG should be explanted in the case of cremation, and returned to Boston Scientific. External devices to be disposed of per local regulatory requirements. Please contact your healthcare professional Rev B 10 of 69
15 Safety Information Remote Control, Charging System Cleaning. The components can be cleaned using alcohol or a mild detergent applied with a cloth or tissue. Residue from soapy detergents should be removed with a damp cloth. Do not use abrasive cleansers for cleaning. Cell Phones. While we do not anticipate any interference with cell phones, the full effects of interaction with cell phones are unknown at this time. If there is a concern or a problem is encountered, the physician should be contacted. Adverse Effects Potential risks are involved with any surgery. The possible risks of implanting a pulse generator as part of a system to deliver spinal cord stimulation include: Lead migration, resulting in undesirable changes in stimulation and subsequent reduction in pain relief. System failure, which can occur at any time due to random failure(s) of the components or the battery. These events, which may include device failure, lead breakage, hardware malfunctions, loose connections, electrical shorts or open circuits and lead insulation breaches, can result in ineffective pain control. Tissue reaction to implanted materials can occur. In some cases, the formation of reactive tissue around the lead in the epidural space can result in delayed onset of spinal cord compression and neurological/sensory deficit, including paralysis. Time to onset is variable, possibly ranging from weeks to years after implant. Skin erosion at the IPG site can occur over time. Possible surgical procedural risks are: temporary pain at the implant site, infection, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage and, although rare, epidural hemorrhage, seroma, hematoma and paralysis. External sources of electromagnetic interference may cause the device to malfunction and affect stimulation. Exposure to MRI can result in heating of tissue, image artifacts, induced voltages in the neurostimulator and/or leads, lead dislodgement. Undesirable stimulation may occur over time due to cellular changes in tissue around the electrodes, changes in electrode position, loose electrical connections and/or lead failure. The patient may experience painful electrical stimulation of the chest wall as a result of stimulation of certain nerve roots several weeks after surgery. Over time, the Stimulator may move from its original position. Weakness, clumsiness, numbness or pain below the level of implantation. Persistent pain at the IPG or lead site. In any event, instruct the patient to contact their physician to inform him/her. Instructions for the Physician Implanted Stimulation Devices. If such implanted devices are indicated for the patient, careful screening is required to determine if safe results can be achieved before permanently implementing concurrent electrical therapies. Postural Changes. Depending on the activity level of the patient, postural changes may affect stimulation intensity. Instruct patients to keep the Remote Control on hand at all times, and ensure that they understand how to adjust stimulation levels. Medical Devices/Therapies. If the patient is required to undergo lithotripsy, electrocautery, external defibrillation, radiation therapy, ultrasonic scanning, or high-output ultrasound: Turn off stimulation at least five minutes before the procedure or application Rev B 11 of 69
16 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System All equipment, including ground plates and paddles, must be used as far away from the IPG as possible. Bipolar electrocautery is recommended. Do not use monopolar electrocautery. Every effort should be taken to keep fields, including current, radiation, or high-output ultrasonic beams, away from the IPG. Equipment should be set to the lowest energy setting clinically indicated. Instruct patients to confirm IPG functionality following treatment by turning on the IPG and gradually increasing stimulation to the desired level Rev B 12 of 69
17 Package Contents Package Contents IPG Kit (1) Precision Implantable Pulse Generator (1) Hex Wrench (1) Tunneling Tool Assembly (1) IPG Pocket Template (2) Port Plugs (1) Device Registration Form/Temporary Patient Identification Card (1) Manual Percutaneous Permanent Lead Kit (1) Percutaneous Lead with pre-loaded Curved Stylet (1) Stylet Ring with a Curved and a Straight Stylet (4) Suture Sleeves (1) Insertion Needle with Stylet (1) Lead Blank (1) Steering Cap (1) OR Cable Assembly (2) Lead Position Labels left and right (non-sterile) (1) Device Registration Form/Temporary Patient Identification Card (1) Manual Percutaneous Trial Lead Kit (1) Percutaneous Lead with pre-loaded Curved Stylet (1) Suture Sleeve (1) Insertion Needle with Stylet (1) Steering Cap (1) OR Cable Assembly (2) Lead Position Labels left and right (non-sterile) (1) Manual (1) Device Registration Form/Temporary Patient Identification Card Lead Extension Kit (1) Lead Extension (1) Hex Wrench (1) Tunneling Tool Assembly (1) Device Registration Form/Temporary Patient Identification Card (1) Manual Rev B 13 of 69
18 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System 2x4 Splitter Kit (1) Splitter (1) Hex wrench (1) Manual and Insert (1) Device Registration Form/Temporary Patient Identification Card Surgical Paddle Lead Kit (1) Paddle Lead (4) Suture Sleeves (2) OR Cable Assemblies (2) Lead Position Labels left and right (non-sterile) (1) Device Registration Form/Temporary Patient Identification Card (1) Manual Infinion 16 Lead Kit (1) 16 Contact Lead with pre-loaded Curved Stylet (1) Stylet Ring with a Curved and a Straight Stylet (1) Straight Stylet (4) Suture Sleeves (1) Insertion Needle (1) Lead blank (2) Lead Position Labels left and right (non-sterile) (1) Manual (1) Product Registration Form/Temporary Patient Identification Card (1) Steering Cap Infinion 16 Trial Lead Kit (1) 16 Contact Percutaneous Lead with pre-loaded Curved Stylet (1) Suture Sleeve (1) Insertion Needle (2) Lead Position Labels left and right (non-sterile) (1) Manual (1) Product Registration Form/Temporary Patient Identification Card (1) Steering Cap Rev B 14 of 69
19 Package Contents Infinion CX Lead Kit (1) 16 Contact Percutaneous Infinion CX Lead with pre-loaded Curved Stylet (2) Suture Sleeves (2) Lead Position Labels left and right (non-sterile) (1) Manual (1) Product Registration Form/TemporaryPatient Identification Card (1) Steering Cap Infinion CX Lead Trial Lead Kit (1) 16 Contact Percutaneous Infinion CX Lead with pre-loaded Curved Stylet (2) Suture Sleeves (2) Lead Position Labels left and right (non-sterile) (1) Manual (1) Product Registration Form/Temporary Patient Identification Card (1) Steering Cap Splitter 2x8 Kit (1) Splitter 2x8 (1) Torque Wrench (1) Manual (1) Product Registration Form/Temporary Patient Identification Card Infinion 16 Trial Configuration Kit (1) Infinion 16 Trial Lead Kit (1) 2x8 Splitter Kit Infinion 16 Configuration Kit (1) Infinion 16 Lead Kit (1) 2x8 Splitter Kit Rev B 15 of 69
20 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System Sterilization, Handling, and Storage Sterilization All Precision system implantable and surgical components are sterilized with ethylene oxide. Inspect the condition of the sterile package before opening the package and using the contents. Do not use the contents if the package is broken or torn, or if contamination is suspected because of a defective sterile package seal. Do not use any component that shows signs of damage. Do not resterilize the package or the contents. Obtain a sterile package from Boston Scientific. Do not use the product if the labeled Use By date has passed. All components are for single use only. Do not reuse. Do not use if package is opened or damaged Do not use if labeling is incomplete or illegible. WARNING: Contents supplied STERILE using an ethylene oxide (EO) process. Do not use if sterile barrier is damaged. If damage is found, call your Boston Scientific representative. For Single Use Only. Do Not Reuse. Do Not Resterilize. Do not use if package is damaged. For single patient use only. Do not reuse, reprocess or resterilize. Reuse, reprocessing or resterilization may compromise the structural integrity of the device and/or lead to device failure which, in turn, may result in patient injury, illness or death. Reuse, reprocessing or resterilization may also create a risk of contamination of the device and/or cause patient infection or cross-infection, including, but not limited to, the transmission of infectious disease(s) from one patient to another. Contamination of the device may lead to injury, illness or death of the patient. After use, dispose of product and packaging in accordance with hospital, administrative and/or local government policy. IPG Handling and Storage Handle the IPG and all components with care. Keep sharp instruments away from the components. Do not use the IPG if it has been dropped on a hard surface from a height of more than one foot. Do not incinerate an IPG. Improper disposal of the device could result in an explosion. Devices should be explanted in the case of cremation, and returned to Boston Scientific Neuromodulation. An explant kit is available. Store the IPG between 0 C and 45 C (32 F and 113 F). Devices should always be kept in temperature regulated areas within the acceptable temperature range. IPG damage can occur at temperatures outside of this range Rev B 16 of 69
21 Lead, Lead Extension, and Splitter Handling and Storage Sterilization, Handling, and Storage Avoid damaging the lead with sharp instruments or excessive force during surgery. Do not sharply bend or kink the lead, extension, or splitter. Do not tie suture(s) directly to the lead, extension, or splitter body; use the provided suture sleeves. For the Percutaneous Leads - avoid forcing the lead into the epidural space by carefully clearing a path using the lead blank. Avoid pulling an implanted lead taut; provide a stress relief loop at the insertion site to minimize tension on the lead. Avoid handling the lead with sharp instruments; use only rubber-tipped forceps. Take care when using sharp instruments such as hemostats or scalpels to prevent damaging the lead. Wipe off any body fluids from the lead connector end before connecting it to any other component. Fluid contamination of these connections could compromise the integrity of the stimulation circuit. Wipe off any body fluids from the lead stylet before inserting or reinserting it into the lead. Store components between 0 C and 45 C (32 F and 113 F) in an area where they are not exposed to liquids or excessive moisture. Temperatures outside of the stated range can cause damage Rev B 17 of 69
22 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System Pre-Op Instructions 1. Ensure that the IPG is fully charged prior to the permanent implant procedure. The approximate location of the IPG is marked on the IPG kit. Turn on the Charger and place it over the IPG to begin charging. 2. Check that the sterile package is intact. (See Sterilization, Handling, and Storage on page 16.) 3. Ensure that a Trial Stimulator is available for use. Install a new battery in the Trial Stimulator. 4. Be sure the Trial Stimulator and Remote Control stimulation settings have been reset. (See Device Linking on page 53.) 5. For trial procedures, ensure that a Patient Trial Kit is available, proceed to Percutaneous Lead Placement in the Epidural Space on page For permanent IPG implantation, proceed to Removal of Trial Leads, Extensions, and Splitters on page Rev B 18 of 69
23 Percutaneous Lead Placement in the Epidural Space Percutaneous Lead Placement in the Epidural Space Note: If using an Infinion CX Lead, proceed to Infinion CX Lead Placement in the Epidural Space with Entrada Needle on page Position, prep and drape the patient in the usual accepted manner. Inject a local anesthetic at the needle insertion site. 2. Under fluoroscopic guidance, place the insertion needle into the epidural space with the bevel facing up using an angle of 45 or less. CAUTION: Use only an insertion needle provided by Boston Scientific. Other needles may damage the lead. The stamped number 14 on the needle hub (or the triangle on the hub of the curved Epimed needle, sold separately) corresponds to the orientation of the bevel, which must face up. Turning the bevel ventral (down) may result in lead damage. An angle of more than 45 increases the risk of lead damage. WARNING: The angle of the insertion needle should be 45 or less. Steep angles increase the insertion force of the stylet and also present more of an opportunity for the stylet to pierce the lead and cause tissue damage. 3. Remove the needle stylet from the insertion needle and verify entry into the epidural space using the standard technique. 4. OPTIONAL. Under fluoroscopic guidance, insert the lead blank through the insertion needle and into the epidural space. Advance the lead blank to verify entry into the epidural space, then withdraw the blank. 5. While holding the lead stylet handle, place the steering cap over the proximal end of the stylet handle with moderate force until it is held in place. Then slowly insert the lead, with stylet, through the insertion needle. The lead stylet should extend to the tip of the lead. 6. OPTIONAL. If exchange of the lead stylet is desired, carefully pull out the existing stylet and insert the preferred stylet. While inserting the stylet into the lead, if resistance is encountered, withdraw the stylet approximately 3 cm, rotate the lead and/or stylet, and gently advance the stylet. If resistance is still encountered, repeat the above procedure until the stylet can be fully inserted. WARNING: Do not exchange the lead stylet while the electrode array of the lead is in the bevel of the insertion needle. If the electrode array is in the bevel area, remove the lead from the insertion needle before exchanging the stylet. Inserting the lead stylet in the lead while the electrode array is in the bevel of the insertion needle increases the risk of lead and tissue damage Rev B 19 of 69
24 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System WARNING: If the lead stylet is removed and reinserted, do not use excessive force when inserting the stylet into the lead. The use of instruments, such as forceps, to grasp the stylet during insertion is not recommended as this could result in applying excessive force and could increase the risk of lead and tissue damage. 7. Advance the lead to the appropriate vertebral level under fluoroscopic guidance. A sufficient length of lead (i.e., at least 10 cm, or approximately three vertebrae) should reside in the epidural space to aid in lead stabilization. 8. If use of a splitter is desired or you are using the Infinion 16 lead, continue to Lead Connection to Splitter on page 25. Otherwise, continue to Connecting the OR Cable Assembly on page 29. Infinion CX Lead Placement in the Epidural Space with Entrada Needle Infinion CX Lead The Infinion CX Lead has two tails to enable insertion into 8-contact IPG ports without the use of a Splitter 2x8. The two tails will not fit through a standard 14 gauge insertion needle or Epimed needle, therefore these needles are not compatible with the Infinion CX Lead. Do not use a standard 14 gauge introducer or Epimed needle to introduce the Infinion CX Lead. An Entrada Needle with peelable sheath is required to introduce the Infinion CX Lead into the epidural space and may be used with all percutaneous leads. Also, an anchor must be pre-loaded on the distal end of the Infinion CX Lead prior to inserting the lead into the Entrada Needle. For the Infinion CX Lead, the stylet may be in place within the lead when the Clik Anchor is loaded on the lead. Ensure that stylet is removed from the lead prior to locking the anchor. Entrada Needle Rev B 20 of 69
25 Percutaneous Lead Placement in the Epidural Space Fully Assembled Entrada Needle A A. Peelable sheath B C D B. Slotted Needle C. Loss of resistance (LOR) adaptor D. Needle stylet Entrada Needle Assembly A B C D A. Peelable Sheath B. Slotted needle inserts into sheath C. Insert LOR adaptor into slotted needle and lock on peelable sheath by turning clockwise D. Insert needle stylet into LOR adaptor and advance forward until fully seated into needle assembly. 1. Position, prep and drape the patient in the usual accepted manner. Inject a local anesthetic at the needle insertion site Rev B 21 of 69
26 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System 2. Verify that the Luer lock collar of the LOR adaptor is locked on the peelable sheath and that the needle stylet is fully inserted into the LOR adaptor hub before inserting the needle. To do so: A. Pull back the stylet cap to expose the clear LOR adaptor hub. B. Apply forward force to the LOR adaptor hub and rotate clockwise to fully engage onto the sheath luer connection. C. Straighten metal hub of LOR adaptor so that notch is facing up. D. Straighten the stylet cap with flat side facing up and advance forward to fully seat into the needle assembly. A B C D 3. Recommended for permanent or permanent-trial procedures: Cut down prior to inserting the Entrada Needle and insert needle into incision. Creating the incision before inserting the Entrada Needle provides a clear path for sliding the anchor into the incision. Insert Entrada Needle using an angle of 45 degrees or less Rev B 22 of 69
27 Percutaneous Lead Placement in the Epidural Space 4. Under fluoroscopic guidance, place the Entrada Needle into the epidural space with the stylet cap flat side facing up using an angle of 45 or less. CAUTION: Use only an Entrada Needle provided by Boston Scientific. Other needles may damage the lead. Turning the bevel ventral (down) may result in lead damage. An angle of more than 45 increases the risk of lead damage. WARNING: The angle of the insertion needle should be 45 or less. Steep angles increase the insertion force of the stylet and also present more of an opportunity for the stylet to pierce the lead and cause tissue damage. 5. Remove the needle stylet from the insertion needle and verify entry into the epidural space using the standard technique. Note: Hold onto sheath wings when attaching syringe to LOR needle. Note: Maintain positive pressure on the needle while performing LOR. Remove needle stylet Verify entry into the epidural space 6. OPTIONAL. Under fluoroscopic guidance, insert the lead blank through the LOR adaptor and into the epidural space. Advance the lead blank to verify entry into the epidural space, then withdraw the blank Rev B 23 of 69
28 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System 7. The LOR adaptor must be removed prior to inserting lead. Unscrew Luer lock collar and remove LOR adaptor assembly from sheath while holding slotted needle in place. Note: An anchor must be loaded over the distal end of the Infinion CX Lead prior to inserting the lead into the Entrada Needle 8. While holding the lead stylet handle, place the steering cap over the proximal end of the stylet handle with moderate force until it is held in place. The lead stylet should extend to the tip of the lead. Slowly insert the Infinion CX Lead into the slotted needle, directing the distal lead tip into the needle lumen. 9. OPTIONAL. If exchange of the lead stylet is desired, carefully pull out the existing stylet and insert the Rev B 24 of 69
29 Percutaneous Lead Placement in the Epidural Space preferred stylet. The stylet must be inserted into the Infinion CX Lead tail with one marker band. While inserting the stylet into the lead, if resistance is encountered, withdraw the stylet approximately 3 cm, rotate the lead and/or stylet, and gently advance the stylet. If resistance is still encountered, repeat the above procedure until the stylet can be fully inserted. The stylet must be inserted into the Infinion CX Lead tail with one marker band WARNING: Do not exchange the lead stylet while the electrode array of the lead is in the bevel of the insertion needle. If the electrode array is in the bevel area, remove the lead from the insertion needle before exchanging the stylet. Inserting the lead stylet in the lead while the electrode array is in the bevel of the insertion needle increases the risk of lead and tissue damage. WARNING: If the lead stylet is removed and reinserted, do not use excessive force when inserting the stylet into the lead. The use of instruments, such as forceps, to grasp the stylet during insertion is not recommended as this could result in applying excessive force and could increase the risk of lead and tissue damage. 10. Advance the lead to the appropriate vertebral level under fluoroscopic guidance. A sufficient length of lead (i.e., at least 10 cm, or approximately three vertebrae) should reside in the epidural space to aid in lead stabilization. 11. If the needle must be repositioned during the procedure, or if inserting a second Infinion CX Lead through the same Entrada Needle with a new sheath, re-assemble needle outside of the body. Reassemble Entrada Needle using new sheath A B C D A. Sheath B. Insert slotted needle into new sheath C. Insert LOR adaptor into slotted needle and lock on peelable sheath by turning clockwise D. Insert needle stylet into LOR adaptor and advance forward until fully seated into needle assembly. CAUTION: Do not reinsert the needle stylet, LOR adaptor, or slotted needle into the sheath while the sheath is inserted within the patient. 12. Proceed with needle insertion and lead placement 13. Continue to Connecting the OR Cable Assembly on page 29 Lead Connection to Splitter 1. Carefully withdraw the stylets from the leads to be inserted into the splitter Rev B 25 of 69
30 Precision Spinal Cord Stimulator System 2. Wipe clean the proximal connector ends of the leads. 3. Select the desired splitter model. Note: A Splitter 2x8 must be used when implanting the Infinion 16 lead. 4. Check that the lead connector end can be easily inserted into the splitter without obstruction. If obstruction is encountered, loosen the set screws of the splitter by using the hex wrench provided, turning counterclockwise. Note: The set screw should only be loosened to an amount sufficient to insert a lead. Do not excessively loosen the set screw. This may cause the set screw to dislodge rendering the splitter unusable. 5. Insert proximal connector ends of desired leads into splitter receptacles until they are fully seated each lead bottoms out in receptacles and retention sleeves (long ring) are under the setscrew blocks of the splitter receptacles. Do not tighten set screw at this time. 6. Continue to Connecting the OR Cable Assembly on page 29, then proceed to step 7 below. 7. Check connections with an impedance measurement. If the impedance is satisfactory, proceed to Intraoperative Stimulation Testing on page 30 to confirm proper lead location. Note: Do not tighten set screw mechanical lock before intra-operative stimulation testing. Note: On the 2x4 Splitter, the shorter splitter receptacle corresponds to contacts 1-4, while the longer receptacle corresponds to contacts 5-8. Make note of which lead is connected to each splitter receptacle. Note: On the Splitter 2x8, one tail is laser-marked with bands, and corresponds to contacts 1-8 on the Infinion 16 percutaneous lead; the unmarked tail corresponds to contacts If lead repositioning is required, disconnect the splitter and reinsert the stylet before advancing the lead. Repeat steps 5 to 7 until satisfactory lead position is achieved Rev B 26 of 69
Percutaneous Leads. Directions for Use 91078744-02 REV A
 Percutaneous Leads Directions for Use CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale, distribution and use by or on the order of a physician. 91078744-02 REV A Guarantees Boston Scientific Corporation
Percutaneous Leads Directions for Use CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale, distribution and use by or on the order of a physician. 91078744-02 REV A Guarantees Boston Scientific Corporation
 Epimed Would Like To Congratulate The 20th Annual Budapest Conference The New Shape of Pain Relief SmalleST. ThiNNeST. CoNTouRed design. Precision Novi is the world s smallest, thinnest 16 contact primary
Epimed Would Like To Congratulate The 20th Annual Budapest Conference The New Shape of Pain Relief SmalleST. ThiNNeST. CoNTouRed design. Precision Novi is the world s smallest, thinnest 16 contact primary
Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) Therapy: Fact Sheet
 Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) Therapy: Fact Sheet What is SCS Therapy? Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) may be a life-changing 1 surgical option for patients to control their chronic neuropathic pain and
Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) Therapy: Fact Sheet What is SCS Therapy? Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) may be a life-changing 1 surgical option for patients to control their chronic neuropathic pain and
Spinal cord stimulation
 Spinal cord stimulation This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having spinal cord stimulation. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives, as well as what you can expect when you come to
Spinal cord stimulation This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having spinal cord stimulation. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives, as well as what you can expect when you come to
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: spinal_cord_stimulation 3/1980 10/2015 10/2016 10/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Spinal cord stimulation
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: spinal_cord_stimulation 3/1980 10/2015 10/2016 10/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Spinal cord stimulation
Boston Scientific Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) Systems
 Boston Scientific Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) Systems 91005942-03 REV B Boston Scientific Spinal Cord Stimulator Systems - Guarantees Boston Scientific Corporation reserves the right to modify, without
Boston Scientific Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) Systems 91005942-03 REV B Boston Scientific Spinal Cord Stimulator Systems - Guarantees Boston Scientific Corporation reserves the right to modify, without
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
NeuroPace. RNS System Patient Manual
 NeuroPace RNS System Patient Manual CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. 01/2013 DN 1013555 Rev 2 1 2013 NeuroPace, Inc. 2 This Manual supports: RNS Neurostimulator
NeuroPace RNS System Patient Manual CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. 01/2013 DN 1013555 Rev 2 1 2013 NeuroPace, Inc. 2 This Manual supports: RNS Neurostimulator
PAR Tablet 10 Quick Start Guide
 ParTech, Inc. 8383 Seneca Turnpike New Hartford, NY 13413 p.800.458.6898 www.partech.com PAR Tablet 10 Quick Start Guide PN 770505503 This material has been created in order to accommodate a wide range
ParTech, Inc. 8383 Seneca Turnpike New Hartford, NY 13413 p.800.458.6898 www.partech.com PAR Tablet 10 Quick Start Guide PN 770505503 This material has been created in order to accommodate a wide range
Special Control Guidance for Premarket Notifications for Totally Implanted Spinal Cord Stimulators for Pain Relief
 . na,:: t;. _ f _ 3.:. Druft 7 Not fvr Implementation Guidance for Industry Special Control Guidance for Premarket Notifications for Totally Implanted Spinal Cord Stimulators for Pain Relief Draft Guidance
. na,:: t;. _ f _ 3.:. Druft 7 Not fvr Implementation Guidance for Industry Special Control Guidance for Premarket Notifications for Totally Implanted Spinal Cord Stimulators for Pain Relief Draft Guidance
Neurostimulation: Orthopaedic Institute of Ohio 801 Medical Drive Lima, Ohio 45804 419-222-6622
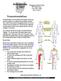 801 Medical Drive Lima, Ohio 45804 419-222-6622 Neurostimulation is the stimulation of the spinal cord by tiny electrical impulses. An implanted lead (a flexible insulated wire), which is powered by an
801 Medical Drive Lima, Ohio 45804 419-222-6622 Neurostimulation is the stimulation of the spinal cord by tiny electrical impulses. An implanted lead (a flexible insulated wire), which is powered by an
Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter
 Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter Instructions For Use Access Systems Product Description: The Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter is a tunneled, long-term catheter used to drain accumulated fluid
Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter Instructions For Use Access Systems Product Description: The Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter is a tunneled, long-term catheter used to drain accumulated fluid
CamSplice Assembly Manual
 Corning Cable Systems SRP-006-038 Issue 9, September 2000 Page 1 of 6 CamSplice Assembly Manual Table of Contents 1. General... 1 2. Precautions... 1 3. Tools and Materials... 2 4. Cable and Fiber Preparation...
Corning Cable Systems SRP-006-038 Issue 9, September 2000 Page 1 of 6 CamSplice Assembly Manual Table of Contents 1. General... 1 2. Precautions... 1 3. Tools and Materials... 2 4. Cable and Fiber Preparation...
Placement of Epidural Catheter for Pain Management Shane Bateman DVM, DVSc, DACVECC
 Placement of Epidural Catheter for Pain Management Shane Bateman DVM, DVSc, DACVECC Indications: Patients with severe abdominal or pelvic origin pain that is poorly responsive to other analgesic modalities.
Placement of Epidural Catheter for Pain Management Shane Bateman DVM, DVSc, DACVECC Indications: Patients with severe abdominal or pelvic origin pain that is poorly responsive to other analgesic modalities.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Device LUMI-TENS
 Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Device LUMI-TENS Operation Manual Read Before Using LUMI-TENS-INS-LAB-RevA08 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO TENS INDICATIONS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Device LUMI-TENS Operation Manual Read Before Using LUMI-TENS-INS-LAB-RevA08 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO TENS INDICATIONS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS
ImageReady MRI Full Body Guidelines for Precision Montage MRI Spinal Cord Stimulator System
 ImageReady MRI Full Body Guidelines for Precision Montage MRI Spinal Cord Stimulator System CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale, distribution and use by or on the order of a physician. 91035972-01
ImageReady MRI Full Body Guidelines for Precision Montage MRI Spinal Cord Stimulator System CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale, distribution and use by or on the order of a physician. 91035972-01
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
PERCUTANEOUS PD CATHETER IMPLANTATION SYSTEM
 Place on Patient s Cranial Border of the Pubic Symphysis IMPLANTATION STENCIL Classic Exit Cuff Site PERCUTANEOUS PD CATHETER IMPLANTATION SYSTEM INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE VP 511 and VP-511M Implantation System
Place on Patient s Cranial Border of the Pubic Symphysis IMPLANTATION STENCIL Classic Exit Cuff Site PERCUTANEOUS PD CATHETER IMPLANTATION SYSTEM INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE VP 511 and VP-511M Implantation System
(English) NEXUS SPINE SPACER SYSTEM
 (English) NEXUS SPINE SPACER SYSTEM INDICATIONS FOR USE NEXUS Spine Spacer System, a GEO Structure is indicated for use in the thoraco-lumbar spine (i.e., T1 to L5) to replace a diseased vertebral body
(English) NEXUS SPINE SPACER SYSTEM INDICATIONS FOR USE NEXUS Spine Spacer System, a GEO Structure is indicated for use in the thoraco-lumbar spine (i.e., T1 to L5) to replace a diseased vertebral body
User Manual Table of Contents. Instructions for Using the LaserTouchOne Charging the Unit... 5 Holding the Device... 5 Treatment Steps...
 User Manual User Manual Table of Contents Introduction The LaserTouchOne... 3 Device Features and Controls (Photo of device)... 4 Product Contents... 4 Laser Safety... 4 Electrical Safety... 5 Instructions
User Manual User Manual Table of Contents Introduction The LaserTouchOne... 3 Device Features and Controls (Photo of device)... 4 Product Contents... 4 Laser Safety... 4 Electrical Safety... 5 Instructions
Biomet SpinalPak Non-Invasive Spine Fusion Stimulator System
 Biomet SpinalPak Non-Invasive Spine Fusion Stimulator System A Patient s Guide 100 Interpace Parkway Parsippany, NJ 07054 800-526-2579 www.biomet.com BNS231003 2009 EBI, LLC. All trademarks are the property
Biomet SpinalPak Non-Invasive Spine Fusion Stimulator System A Patient s Guide 100 Interpace Parkway Parsippany, NJ 07054 800-526-2579 www.biomet.com BNS231003 2009 EBI, LLC. All trademarks are the property
3. SEISCO PARTS & SERVICE REMOVAL AND REPAIR GUIDE
 4 3. SEISCO PARTS & SERVICE REMOVAL AND REPAIR GUIDE A. Changing the Control Board B. Replacing a Heating Element C. Thermistor Replacement D. High Limit Switch Replacement E. Level Detector Replacement
4 3. SEISCO PARTS & SERVICE REMOVAL AND REPAIR GUIDE A. Changing the Control Board B. Replacing a Heating Element C. Thermistor Replacement D. High Limit Switch Replacement E. Level Detector Replacement
Patient Information Guide Morpheus CT Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter
 Patient Information Guide Morpheus CT Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter IC 192 Rev C A measure of flexibility and strength. Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. What is the Morpheus CT PICC? 3. What
Patient Information Guide Morpheus CT Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter IC 192 Rev C A measure of flexibility and strength. Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. What is the Morpheus CT PICC? 3. What
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Department of Neurosciences Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG) Stimulation Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Department of Neurosciences Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG) Stimulation Information for patients We have recently seen you in clinic as you have had pain for a long period
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Department of Neurosciences Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG) Stimulation Information for patients We have recently seen you in clinic as you have had pain for a long period
Herniated Disk. This reference summary explains herniated disks. It discusses symptoms and causes of the condition, as well as treatment options.
 Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
ENGLISH...3 DEUTSCH...13 FRANÇAIS...23 ESPAÑOL...33 ITALIANO...43 PORTUGUÊS...53
 USERS GUIDE ENGLISH...3 DEUTSCH...13 FRANÇAIS...23 ESPAÑOL...33 ITALIANO...43 PORTUGUÊS...53 NEDERLANDS...63 SVENSKA...113 TABLE OF CONTENTS USERS MANUAL FOR CEFAR MYO XT AND CEFAR ACTIV XT ENGLISH 3 PRECAUTIONARY
USERS GUIDE ENGLISH...3 DEUTSCH...13 FRANÇAIS...23 ESPAÑOL...33 ITALIANO...43 PORTUGUÊS...53 NEDERLANDS...63 SVENSKA...113 TABLE OF CONTENTS USERS MANUAL FOR CEFAR MYO XT AND CEFAR ACTIV XT ENGLISH 3 PRECAUTIONARY
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Surgical Technique 2. Indications 4. Product Information 5. 1. Patient Positioning and Approach 2
 Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS Surgical Technique 2 1. Patient Positioning and Approach 2 2. Intervertebral Device Implanted 2 3. Buttress Plate Selection 2 4. Awl Insertion 2 5. Screw Insertion
Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS Surgical Technique 2 1. Patient Positioning and Approach 2 2. Intervertebral Device Implanted 2 3. Buttress Plate Selection 2 4. Awl Insertion 2 5. Screw Insertion
Economic aspects of Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS)
 Economic aspects of Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) Burden of Chronic Pain Chronic pain affects one in five adults in Europe 1. Up to 10 per cent of chronic pain cases are neuropathic in origin. 2 Chronic
Economic aspects of Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) Burden of Chronic Pain Chronic pain affects one in five adults in Europe 1. Up to 10 per cent of chronic pain cases are neuropathic in origin. 2 Chronic
Networkfleet 3500 Product Line Installation Guide
 Networkfleet 3500 Product Line Installation Guide Light/Medium Duty (L3500) Heavy Duty (H3500) Universal (U3500) www.networkcar.com/fleet Customer Care: (866) 227-7323 customercare@networkcar.com Table
Networkfleet 3500 Product Line Installation Guide Light/Medium Duty (L3500) Heavy Duty (H3500) Universal (U3500) www.networkcar.com/fleet Customer Care: (866) 227-7323 customercare@networkcar.com Table
Limited Warranty. CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale, distribution and use by or on the order of a physician.
 Limited Warranty CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale, distribution and use by or on the order of a physician. 91006760-01 REV C This page intentionally left blank. 91006760-01 REV C 1 of
Limited Warranty CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale, distribution and use by or on the order of a physician. 91006760-01 REV C This page intentionally left blank. 91006760-01 REV C 1 of
Nerve Blocks. What is a Nerve Block? What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Scan for mobile link. Nerve Blocks A nerve block is an injection to decrease inflammation or "turn off" a pain signal along a specific distribution of nerve. Imaging guidance may be used to place the needle
Scan for mobile link. Nerve Blocks A nerve block is an injection to decrease inflammation or "turn off" a pain signal along a specific distribution of nerve. Imaging guidance may be used to place the needle
Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion
 Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion Introduction Low back and leg pain caused by pinched nerves in the back is a common condition that limits your ability to move, walk, and work. This condition
Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion Introduction Low back and leg pain caused by pinched nerves in the back is a common condition that limits your ability to move, walk, and work. This condition
PBX Series Quick Fit Connector Bimetallic Steam Traps
 6262100/6 IM-P626-01 ST Issue 6 PBX Series Quick Fit Connector Bimetallic Steam Traps Installation and Maintenance Instructions 1. Safety information 2. General product information 3. Installation 4. Commissioning
6262100/6 IM-P626-01 ST Issue 6 PBX Series Quick Fit Connector Bimetallic Steam Traps Installation and Maintenance Instructions 1. Safety information 2. General product information 3. Installation 4. Commissioning
1.5 Tesla and 3 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Guidelines for the Senza System
 1.5 Tesla and 3 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Guidelines for the Senza System NEVRO CORP. All questions or concerns about Nevro products should be forwarded to: Nevro Corp. 1800 Bridge Parkway
1.5 Tesla and 3 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Guidelines for the Senza System NEVRO CORP. All questions or concerns about Nevro products should be forwarded to: Nevro Corp. 1800 Bridge Parkway
Scout Vessel Guard. A cover for vessels during anterior lumbar spine surgery.
 Scout Vessel Guard. A cover for vessels during anterior lumbar spine surgery. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction Scout Vessel Guard 2
Scout Vessel Guard. A cover for vessels during anterior lumbar spine surgery. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction Scout Vessel Guard 2
EXHIBIT C BOSTON SCIENTIFIC PRODUCTS AVAILABLE FOR NIH BRAIN INITIATIVE Page 1 of 9
 Page 1 of 9 NOTE: All systems and products should be considered as investigational-use only in the context of the NIH BRAIN Initiative. VERCISE DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION SYSTEM Description: 16-channel rechargeable
Page 1 of 9 NOTE: All systems and products should be considered as investigational-use only in the context of the NIH BRAIN Initiative. VERCISE DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION SYSTEM Description: 16-channel rechargeable
Open Discectomy. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
PICCs and Midline Catheters
 Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
POSEIDON 2-29, 2-25 & 2-22 POSEIDON 2-29, 2-25 & 2-22 XT
 POSEION 2-29, 2-25 & 2-22 POSEION 2-29, 2-25 & 2-22 XT Repair Manual Index A. Safety precautions 3 B. Technical data 4 C. Structure 5-6. Service / Repair 7-23 E. Tools 24 F. Function 25-26 G. Electric
POSEION 2-29, 2-25 & 2-22 POSEION 2-29, 2-25 & 2-22 XT Repair Manual Index A. Safety precautions 3 B. Technical data 4 C. Structure 5-6. Service / Repair 7-23 E. Tools 24 F. Function 25-26 G. Electric
Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative Technique
 *smith&nephew ANKLE TECHNIQUE GUIDE Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative Technique Prepared in Consultation with: C. Niek van Dijk, MD, PhD KNEE HIP SHOULDER EXTREMITIES Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative
*smith&nephew ANKLE TECHNIQUE GUIDE Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative Technique Prepared in Consultation with: C. Niek van Dijk, MD, PhD KNEE HIP SHOULDER EXTREMITIES Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative
Percutaneous Abscess Drainage
 Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Vaxcel PICCs Valved and Non-Valved. A Patient s Guide
 Vaxcel PICCs Valved and Non-Valved A Patient s Guide Information about your Vaxcel PICC is available by calling the Navilyst Medical Vascular Access Information Line 800.513.6876 Vaxcel Peripherally Inserted
Vaxcel PICCs Valved and Non-Valved A Patient s Guide Information about your Vaxcel PICC is available by calling the Navilyst Medical Vascular Access Information Line 800.513.6876 Vaxcel Peripherally Inserted
Patient Information. PORT-A-CATH Implantable Venous Access Systems
 Patient Information PORT-A-CATH Implantable Venous Access Systems Your doctor has prescribed treatment that requires the frequent administration of medications or other fluids directly into your bloodstream
Patient Information PORT-A-CATH Implantable Venous Access Systems Your doctor has prescribed treatment that requires the frequent administration of medications or other fluids directly into your bloodstream
Breast Implants: Local Complications and Adverse Outcomes
 Breast Implants: Local Complications and Adverse Outcomes This booklet highlights the most common problems associated with silicone gel-filled and saline-filled breast implants: those that occur in the
Breast Implants: Local Complications and Adverse Outcomes This booklet highlights the most common problems associated with silicone gel-filled and saline-filled breast implants: those that occur in the
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression
 X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
BRYAN. Cervical Disc System. Patient Information
 BRYAN Cervical Disc System Patient Information 3 BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION 1 BRYAN Cervical Disc System This patient information brochure
BRYAN Cervical Disc System Patient Information 3 BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION 1 BRYAN Cervical Disc System This patient information brochure
HP UPS R1500 Generation 3
 HP UPS R1500 Generation 3 Installation Instructions Part Number 650952-001 NOTE: The rating label on the device provides the class (A or B) of the equipment. Class B devices have a Federal Communications
HP UPS R1500 Generation 3 Installation Instructions Part Number 650952-001 NOTE: The rating label on the device provides the class (A or B) of the equipment. Class B devices have a Federal Communications
Aspira* Pleural Drainage Catheter
 Aspira* Pleural Drainage Catheter Instructions For Use Access Systems Product Description: The Aspira* Pleural Drainage Catheter is a tunneled, long-term catheter used to drain accumulated fluid from the
Aspira* Pleural Drainage Catheter Instructions For Use Access Systems Product Description: The Aspira* Pleural Drainage Catheter is a tunneled, long-term catheter used to drain accumulated fluid from the
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Device. Operation Manual Read Before Using
 Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Device Operation Manual Read Before Using TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO TENS INDICATIONS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS PRECAUTIONS/ADVERSE REACTIONS ABOUT
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Device Operation Manual Read Before Using TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO TENS INDICATIONS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS PRECAUTIONS/ADVERSE REACTIONS ABOUT
Cable Drum Machine. Operation Manual BC260 SERIES. Cleans 1 1/4" to 3" lines up to 50'
 Cable Drum Machine Operation Manual BC260 SERIES Cleans 1 1/4" to 3" lines up to 50' Used For: Sink, Shower & Floor Drains 42FM " WARNING - Read All Instructions, When Using Electric Tools, Basic Safety
Cable Drum Machine Operation Manual BC260 SERIES Cleans 1 1/4" to 3" lines up to 50' Used For: Sink, Shower & Floor Drains 42FM " WARNING - Read All Instructions, When Using Electric Tools, Basic Safety
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back
 Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS?
 SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials Giving a subcutaneous injection
 NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials What is a subcutaenous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous injection into the fatty
NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials What is a subcutaenous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous injection into the fatty
BARD MEDICAL DIVISION UROLOGICAL DRAINAGE. Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance. Patient Education Guide
 BARD MEDICAL DIVISION Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance Patient Education Guide WHAT IS A FOLEY CATHETER? Because of your medical problem, your body is having trouble completely emptying your bladder of
BARD MEDICAL DIVISION Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance Patient Education Guide WHAT IS A FOLEY CATHETER? Because of your medical problem, your body is having trouble completely emptying your bladder of
Information for the Patient About Surgical
 Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Trillium 40 Axis Spring Tensioner Wire Replacement Instructions
 Trillium 40 Axis Spring Tensioner Wire Replacement Instructions 1 Overview The objective is to replace the broken axis spring tensioner wire. This requires the following tasks: 1. Remove the seismometer
Trillium 40 Axis Spring Tensioner Wire Replacement Instructions 1 Overview The objective is to replace the broken axis spring tensioner wire. This requires the following tasks: 1. Remove the seismometer
Adult Forearm Fractures
 Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
MyoSure Hysteroscopic Tissue Removal System MyoSure XL Tissue Removal Device Instructions for Use
 MyoSure Hysteroscopic Tissue Removal System MyoSure XL Tissue Removal Device Instructions for Use PLEASE READ ALL INFORMATION CAREFULLY. ONLY Description The MyoSure Tissue Removal System consists of the
MyoSure Hysteroscopic Tissue Removal System MyoSure XL Tissue Removal Device Instructions for Use PLEASE READ ALL INFORMATION CAREFULLY. ONLY Description The MyoSure Tissue Removal System consists of the
Hand Injuries and Disorders
 Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
OPL BASIC. Dosing System for Professional Laundry machines. Contents
 OPL BASIC Dosing System for Professional Laundry machines Contents 1 Getting Started. Page 2 2 Installation. Page 4 3 Set Up & Operation. Page 8 4 Maintenance & Accessories. Page 10 5 Troubleshooting Page
OPL BASIC Dosing System for Professional Laundry machines Contents 1 Getting Started. Page 2 2 Installation. Page 4 3 Set Up & Operation. Page 8 4 Maintenance & Accessories. Page 10 5 Troubleshooting Page
Y O U R S U R G E O N S. choice of. implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y
 Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
Electrodiagnostic Testing
 Electrodiagnostic Testing Electromyogram and Nerve Conduction Study North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Electrodiagnostic Testing? The term electrodiagnostic testing covers a
Electrodiagnostic Testing Electromyogram and Nerve Conduction Study North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Electrodiagnostic Testing? The term electrodiagnostic testing covers a
Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances?
 Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances? Do you experience weakness, tingling, numbness, stiffness, or cramping in your legs, buttocks or
Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances? Do you experience weakness, tingling, numbness, stiffness, or cramping in your legs, buttocks or
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE
 LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
Contraindications: Malign or benign strictures in the upper part of esophagus close to the cricopharyngeal muscle.
 Manufactured by: ELLA CS, s.r.o. Milady Horákové 504 500 06 Hradec Králové 6 Czech Republic Phone: +420 49 527 91 11 Fax: +420 49 526 56 55 E-mail: volenec@ellacs.cz Instructions for Use FerX-ELLA Esophageal
Manufactured by: ELLA CS, s.r.o. Milady Horákové 504 500 06 Hradec Králové 6 Czech Republic Phone: +420 49 527 91 11 Fax: +420 49 526 56 55 E-mail: volenec@ellacs.cz Instructions for Use FerX-ELLA Esophageal
SALTER AIRE Plus COMPRESSOR Model 8350 / 8352 / 8353. Instruction Manual. Page 1 of 9
 SALTER AIRE Plus COMPRESSOR Model 8350 / 8352 / 8353 Instruction Manual Page 1 of 9 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...3 Important Safeguards..3 System Components...5 Setup and Operation...5 Setup...5 Operation....6
SALTER AIRE Plus COMPRESSOR Model 8350 / 8352 / 8353 Instruction Manual Page 1 of 9 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...3 Important Safeguards..3 System Components...5 Setup and Operation...5 Setup...5 Operation....6
Fire Risk Assessment Tool: Instructions for Use
 Fire Risk Assessment Tool: Instructions for Use Purpose of the Fire Risk Assessment Tool: To assist the perioperative team in determining and communicating the potential fire risk for each individual patient.
Fire Risk Assessment Tool: Instructions for Use Purpose of the Fire Risk Assessment Tool: To assist the perioperative team in determining and communicating the potential fire risk for each individual patient.
Ambulatory Surgery Center Coding and Payment Guide 2015
 Targeted Drug Delivery Ambulatory Surgery Center Coding and Payment Guide 2015 Flowonix Medical has compiled this coding information for your convenience. This information is gathered from third party
Targeted Drug Delivery Ambulatory Surgery Center Coding and Payment Guide 2015 Flowonix Medical has compiled this coding information for your convenience. This information is gathered from third party
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair
 A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
MEDICAL CONTESTED CASE HEARING NO 12090 M6-12-38043-01 DECISION AND ORDER
 MEDICAL CONTESTED CASE HEARING NO 12090 M6-12-38043-01 DECISION AND ORDER This case is decided pursuant to Chapter 410 of the Texas Workers Compensation Act and Rules of the Division of Workers Compensation
MEDICAL CONTESTED CASE HEARING NO 12090 M6-12-38043-01 DECISION AND ORDER This case is decided pursuant to Chapter 410 of the Texas Workers Compensation Act and Rules of the Division of Workers Compensation
Herniated Lumbar Disc
 Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
NEUROMODULATION THERAPY ACCESS COALITION POSITION STATEMENT ON SPINAL CORD NEUROSTIMULATION
 NEUROMODULATION THERAPY ACCESS COALITION POSITION STATEMENT ON SPINAL CORD NEUROSTIMULATION Introduction: Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) is an established treatment for chronic neuropathic pain, which can
NEUROMODULATION THERAPY ACCESS COALITION POSITION STATEMENT ON SPINAL CORD NEUROSTIMULATION Introduction: Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) is an established treatment for chronic neuropathic pain, which can
User Guide Nokia Portable Wireless Charging Plate DC-50
 User Guide Nokia Portable Wireless Charging Plate DC-50 Issue 1.1 EN User Guide Nokia Portable Wireless Charging Plate DC-50 Contents For your safety 3 About your accessory 4 Keys and parts 5 Top up your
User Guide Nokia Portable Wireless Charging Plate DC-50 Issue 1.1 EN User Guide Nokia Portable Wireless Charging Plate DC-50 Contents For your safety 3 About your accessory 4 Keys and parts 5 Top up your
ArtisanLink Staining System is an automated special stains slide
 Technical Tips Tips on using the ArtisanLink Special Staining System Jamie Nowacek, BS, HT(ASCP) CM, QIHC, PMP Dako North America, Inc. Carpinteria, CA, USA ArtisanLink Staining System is an automated
Technical Tips Tips on using the ArtisanLink Special Staining System Jamie Nowacek, BS, HT(ASCP) CM, QIHC, PMP Dako North America, Inc. Carpinteria, CA, USA ArtisanLink Staining System is an automated
INSERTABLE CARDIAC MONITORING SYSTEM. UNLOCK the ANSWER. Your heart and long-term monitoring
 INSERTABLE CARDIAC MONITORING SYSTEM UNLOCK the ANSWER Your heart and long-term monitoring UNLOCK the ANSWER Irregular heartbeats can be related to a variety of conditions, including unexplained fainting,
INSERTABLE CARDIAC MONITORING SYSTEM UNLOCK the ANSWER Your heart and long-term monitoring UNLOCK the ANSWER Irregular heartbeats can be related to a variety of conditions, including unexplained fainting,
Instructions for Use. Device Description The AMPLATZER Vascular Plug II is a self-expandable nitinol mesh occlusion device (see Figure 1).
 Vascular Plug II Instructions for Use Device Description The AMPLATZER Vascular Plug II is a self-expandable nitinol mesh occlusion device (see Figure 1). A B Figure 1. AMPLATZER Vascular Plug II A. Nitinol
Vascular Plug II Instructions for Use Device Description The AMPLATZER Vascular Plug II is a self-expandable nitinol mesh occlusion device (see Figure 1). A B Figure 1. AMPLATZER Vascular Plug II A. Nitinol
PATIENT GUIDE. Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL
 PATIENT GUIDE Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL Introduction The following information is presented as a guideline for your reference. The best
PATIENT GUIDE Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL Introduction The following information is presented as a guideline for your reference. The best
Spinal Injections. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Spinal Injections North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Spinal Injection? Your doctor has suggested that you have a spinal injection to help reduce pain and improve function. This
Spinal Injections North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Spinal Injection? Your doctor has suggested that you have a spinal injection to help reduce pain and improve function. This
Portable Air Conditioner
 Portable Air Conditioner Owner's Manual Model:3 in 1 12,000 Btu/h Series 3 Please read this owner s manual carefully before operation and retain it for future reference. CONTENTS 1. SUMMARY...1 2. PORTABLE
Portable Air Conditioner Owner's Manual Model:3 in 1 12,000 Btu/h Series 3 Please read this owner s manual carefully before operation and retain it for future reference. CONTENTS 1. SUMMARY...1 2. PORTABLE
HOW TO USE THE LIFEPAK 1000 DEFIBRILLATOR 3
 3 How to Use the LIFEPAK 1000 Defibrillator HOW TO USE THE LIFEPAK 1000 DEFIBRILLATOR 3 This section provides an overview of information and instructions for using the LIFEPAK 1000 defibrillator. Modes
3 How to Use the LIFEPAK 1000 Defibrillator HOW TO USE THE LIFEPAK 1000 DEFIBRILLATOR 3 This section provides an overview of information and instructions for using the LIFEPAK 1000 defibrillator. Modes
UPLIFT Height Adjustable Standing Desk (T-Frame) DIRECTIONS FOR ASSEMBLY AND USE - - ALSO - - Watch our assembly video
 UPLIFT Height Adjustable Standing Desk (T-Frame) DIRECTIONS FOR ASSEMBLY AND USE - - ALSO - - Watch our assembly video http://bit.ly/9ywwh! CAUTION MAKE SURE NO OBSTACLES ARE IN THE DESK S PATH AND ALL
UPLIFT Height Adjustable Standing Desk (T-Frame) DIRECTIONS FOR ASSEMBLY AND USE - - ALSO - - Watch our assembly video http://bit.ly/9ywwh! CAUTION MAKE SURE NO OBSTACLES ARE IN THE DESK S PATH AND ALL
Contractor Number 11302. Oversight Region Region IV
 Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Spinal Cord Stimulators for Chronic Pain (L32549) Contractor Information Contractor Name Palmetto GBA opens in new window Contractor Number 11302 Contractor Type MAC
Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Spinal Cord Stimulators for Chronic Pain (L32549) Contractor Information Contractor Name Palmetto GBA opens in new window Contractor Number 11302 Contractor Type MAC
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
INSTRUCTION MANUAL PLEASE READ ALL THE INSTRUCTIONS COMPLETELY BEFORE USE AND SAVE THIS MANUAL FOR FUTURE REFERENCE
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL PLEASE READ ALL THE INSTRUCTIONS COMPLETELY BEFORE USE AND SAVE THIS MANUAL FOR FUTURE REFERENCE m Before Use Please read IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS on page 10 before use. It is important
INSTRUCTION MANUAL PLEASE READ ALL THE INSTRUCTIONS COMPLETELY BEFORE USE AND SAVE THIS MANUAL FOR FUTURE REFERENCE m Before Use Please read IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS on page 10 before use. It is important
Physician Coding and Payment Guide 2015
 Targeted Drug Delivery Physician Coding and Payment Guide 2015 Flowonix Medical has compiled this coding information for your convenience. This information is gathered from third party sources and is subject
Targeted Drug Delivery Physician Coding and Payment Guide 2015 Flowonix Medical has compiled this coding information for your convenience. This information is gathered from third party sources and is subject
Posterior Cervical Decompression
 Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement
 A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness
RNS System User Manual
 2015 NeuroPace, Inc. Rev Date: 2015-04 DN 1015882 Rev 2 This Manual supports: ii RNS Neurostimulator: model RNS-300M with firmware version 7.0 NeuroPace Cortical Strip Lead: models CL-315-10, CL-325-10,
2015 NeuroPace, Inc. Rev Date: 2015-04 DN 1015882 Rev 2 This Manual supports: ii RNS Neurostimulator: model RNS-300M with firmware version 7.0 NeuroPace Cortical Strip Lead: models CL-315-10, CL-325-10,
Introduction. Planned surgical procedures
 Guidelines for the perioperative management of patients with implantable pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defibrillators, where the use of surgical diathermy/electrocautery is anticipated. Introduction
Guidelines for the perioperative management of patients with implantable pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defibrillators, where the use of surgical diathermy/electrocautery is anticipated. Introduction
Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter
 Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter UHN A Patient s Guide What is a Pleural Effusion? There is a small space between the outside of your lung and the chest wall (ribs). This space is called the pleural space.
Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter UHN A Patient s Guide What is a Pleural Effusion? There is a small space between the outside of your lung and the chest wall (ribs). This space is called the pleural space.
ON-Q * Catheters and Introducers
 Instructions For Use ON-Q * Catheters and Introducers MANUFACTURED BY: Kimberly-Clark 1400 Holcomb Bridge Road Roswell, GA 30076 USA Kimberly-Clark N.V. Da Vincilaan 1 1935 Zaventem, Belgium Figure 1 4
Instructions For Use ON-Q * Catheters and Introducers MANUFACTURED BY: Kimberly-Clark 1400 Holcomb Bridge Road Roswell, GA 30076 USA Kimberly-Clark N.V. Da Vincilaan 1 1935 Zaventem, Belgium Figure 1 4
PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide
 PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide medcompnet.com 1 table of contents Introduction 4 What is a PICC or Midline Catheter? 4 How is the PICC or Midline Catheter Inserted? 6 Catheter Care
PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide medcompnet.com 1 table of contents Introduction 4 What is a PICC or Midline Catheter? 4 How is the PICC or Midline Catheter Inserted? 6 Catheter Care
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study
 Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine
Battery Charger For Nickel Cadmium and Nickel-Metal Hydride Rechargeable Batteries Model PSN Series
 Battery Charger For Nickel Cadmium and Nickel-Metal Hydride Rechargeable Batteries Model PSN Series Operating Instructions WARNING CONCERNING THE REMOVAL OF COVER: CAUTION: TO PREVENT THE RISK OF ELECTRIC
Battery Charger For Nickel Cadmium and Nickel-Metal Hydride Rechargeable Batteries Model PSN Series Operating Instructions WARNING CONCERNING THE REMOVAL OF COVER: CAUTION: TO PREVENT THE RISK OF ELECTRIC
Intrathecal Baclofen for CNS Spasticity
 Intrathecal Baclofen for CNS Spasticity Last Review Date: November 13, 2015 Number: MG.MM.ME.31bC5 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or
Intrathecal Baclofen for CNS Spasticity Last Review Date: November 13, 2015 Number: MG.MM.ME.31bC5 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or
LOW BACK PAIN: SHOULD I HAVE AN MRI?
 DATE: / / HG SY EH CQ RL AS JZ Name: (Last, First, M.I.) M F DOB: / / Decision Point LOW BACK PAIN: SHOULD I HAVE AN MRI? You may want to have a say in this decision, or you may simply want to follow your
DATE: / / HG SY EH CQ RL AS JZ Name: (Last, First, M.I.) M F DOB: / / Decision Point LOW BACK PAIN: SHOULD I HAVE AN MRI? You may want to have a say in this decision, or you may simply want to follow your
Instructions: Part I. Charge the Power Bank. Method 1. Charge the Power Bank via Computer USB Terminal.
 Instructions: Part I. Charge the Power Bank Method 1 Charge the Power Bank via Computer USB Terminal. Connect the provided USB power cable to the micro- USB plug connector tip (the tip marked "M10"). Step
Instructions: Part I. Charge the Power Bank Method 1 Charge the Power Bank via Computer USB Terminal. Connect the provided USB power cable to the micro- USB plug connector tip (the tip marked "M10"). Step
