Managing Alcohol Fermentation Good Fermentation Practices
|
|
|
- Elvin Neil Norris
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Managing Alcohol Fermentation Good Fermentation Practices Michigan Wine & Grape Conference, Grand Rapids February 24, 2010 Gordon Specht
2 Development and production of Yeast Bacteria and their derivatives
3 How to keep the yeast happy and minimize risks Good Fermentation Practices (GFP)
4 If Good Fermentation Practices are used... Sugar if not...higher risk of sluggish or stuck alcohol fermentation finish and... Fermentation Time
5 Factors affecting Fermentation Management - Key Interrelationships JUICE or MUST TEMPERATURE YEAST STRAIN CELL NUMBERS & HEALTH OPTIMUM FERMENTATION MANAGEMENT NUTRITIONAL FACTORS TOXIC FACTORS COMPETITIVE FACTORS
6 4 phases of Alcohol Fermentation Stationary Yeast Population Exponential Growth Decline 2-4 million Lag Fermentation time
7 In the winery Good Fermentation Practices should be used during > million 2-4 million 2-4 million Fermentation time
8 In the winery Good Fermentation Practices should be used during yeast rehydration > million 2-4 million 2-4 million Fermentation time
9 Good Fermentation Practice (GFP) at yeast rehydration stage: Proper Yeast Rehydration & Handling Addition of micronutrients Directly feed selected yeast with balance of key vitamins and minerals Why? They won t be used by ambient microbes or bound by must components Helps yeast population and health
10 Yeast Viability Viability: 70% = 49 x 10 6 live cells Viability: 43% = 23 x 10 6 live cells Control 18 C Goferm 18 C Hours Similar results at 24 C and 28 C, there is a strong positive effect on yeast viability when yeast stimulant GoFerm (minerals and Vitamins) added during yeast rehydration.
11 4 Easy Steps for Rehydrating Yeast and Inoculating Juice or Must
12 4 Easy Steps for Rehydrating Yeast and Inoculating Juice or Must
13 4 Easy Steps for Rehydrating Yeast and Inoculating Juice or Must
14 4 Easy Steps for Rehydrating Yeast and Inoculating Juice or Must
15 > million In the winery Good Fermentation Practices should be used during the beginning of yeast fermentation 2-4 million 2-4 million Fermentation time
16 GFP at beginning of fermentation: red musts If needed addition of complex nutrients at the end of yeast lag phase Under medium or low Yeast Available Nitrogen Conditions (YANC) Nitrogen as ammonia and alphaamino acids Additional survival factors sterols and unsaturated fatty acids Addition of oxygen as soon as the cap is formed (usually 15 g/l sugar fermented)
17 GFP at beginning of fermentation: red musts If needed addition of complex nutrients at the end of yeast lag phase Under medium or low Yeast Available Nitrogen Conditions (YANC) Nitrogen as ammonia and alphaamino acids Additional survival factors sterols and unsaturated fatty acids Addition of oxygen as soon as the cap is formed (usually 15 g/l sugar fermented)
18 > million In the winery Good Fermentation Practices should be used during the yeast exponential growth phase 2-4 million 2-4 million Fermentation time
19 GFP at yeast exponential growth phase Speed of yeast multiplication during growth phase
20 Don t grow yeast up too fast temperature management Low alcohol concentration High alcohol concentration Slow alcohol excretion
21 In the winery Good Fermentation Practices should be used during 1/3 1/2 through fermentation > million 2-4 million 2-4 million Fermentation time
22 GFP ~1/3 rd through the fermentation: red must If needed addition of complex nutrients at ~1/3 rd through the ferment under medium or low YANC Nitrogen as ammonia and alphaamino acids Additional survival factors sterols and unsaturated fatty acids Oxygen addition at one third of sugar depletion
23 GFP during peak of fermentation: red musts Maximum temperature reached under the cap Cap during the fermentation Fermenting Juice Yeast Biomass
24 In the winery Good Fermentation Practices should be used during the last ¼ of fermentation > million 2-4 million 2-4 million Fermentation time
25 GFP during the last quarter of fermentation: red musts Regular movement of the yeast during their death phase Deep punching down Bring the yeasts back up into suspension
26 Move your yeasts! Delestage Complete draining of fermenter O 2
27 GFP : whites Osmotic shock on the yeast Yeast cell content of stress resistant factors Addition of fatty acids, sterols, vitamins, amino acids and micronutrients at the inoculation step Temperature shock in cold juices Grape juice solids (pectic flakes) Oxygen addition as soon as the fermentation is active (usually 15 g/l sugar fermented) Oxygen addition at one third of sugar depletion Addition of ammonia at one third of sugar depletion Addition of fatty acids, sterols and alpha-amino acids at one third of sugar depletion Low temperature during the yeast death phase Regular movement of the yeast during their death phase
28 4 Easy Steps for Rehydrating Yeast and Inoculating Juice or Must
29 What are pectic flakes? After a cold settling with pectic enzymes Clear juice Pectic flakes Heavy solids
30 Special constraints : be even more careful applying GFP Large tanks (>25,000 gal.) or tall & narrow tanks : an important consideration Uncertain hygiene in the cellar End of harvest Other unknowns : personnel experience, training, knowledge of procedures, etc.
31 Good Fermentation Practices (GFP) Risk Management Very critical above ph 3.5! LYSOZYME Selected Yeast Viable Cells (cfu/ml) SO 2 Gluconobacter Lactobacillus Pediococcus SO 2 Acetobacter spontaneous Oenococcus Further Microbial control as needed HARVEST TRANSPORT AF AGEING
32
CONTROLLING MICROBIAL GROWTH IN WINE
 CONTROLLING MICROBIAL GROWTH IN WINE Section 3. Alcohol The alcohol content of wines is an important parameter in limiting microbial growth for only some of the enologically important organisms. The relative
CONTROLLING MICROBIAL GROWTH IN WINE Section 3. Alcohol The alcohol content of wines is an important parameter in limiting microbial growth for only some of the enologically important organisms. The relative
Guide to Wine Yeast Re-Hydration
 Guide to Wine Yeast Re-Hydration Another MoreManual! By Shea A.J. Comfort, YeastWhisperer Provided by A MoreFlavor!, Inc. Brand 1-800-600-0033 MoreWine s Guideline to Hydrating Active Dry Wine Yeast &
Guide to Wine Yeast Re-Hydration Another MoreManual! By Shea A.J. Comfort, YeastWhisperer Provided by A MoreFlavor!, Inc. Brand 1-800-600-0033 MoreWine s Guideline to Hydrating Active Dry Wine Yeast &
CONTROLLING MICROBIAL GROWTH IN WINE
 CONTROLLING MICROBIAL GROWTH IN WINE Learning Outcome. This chapter reviews the many practical features of importance involved in understanding wine microbiology. The student will gain an understanding
CONTROLLING MICROBIAL GROWTH IN WINE Learning Outcome. This chapter reviews the many practical features of importance involved in understanding wine microbiology. The student will gain an understanding
Composition of Grapes
 Composition of Grapes By Murli Dharmadhikari Grapes are the most important raw material for making wine. A good understanding of grape composition is essential to understanding the process of winemaking
Composition of Grapes By Murli Dharmadhikari Grapes are the most important raw material for making wine. A good understanding of grape composition is essential to understanding the process of winemaking
INTRODUCTION TO BACTERIA
 Morphology and Classification INTRODUCTION TO BACTERIA Most bacteria (singular, bacterium) are very small, on the order of a few micrometers µm (10-6 meters) in length. It would take about 1,000 bacteria,
Morphology and Classification INTRODUCTION TO BACTERIA Most bacteria (singular, bacterium) are very small, on the order of a few micrometers µm (10-6 meters) in length. It would take about 1,000 bacteria,
Exploring Lees Management
 Exploring Lees Management Good Practices for International Markets Dominique DELTEIL www.delteil-consultant.com Exploring Lees Management Good Practices for International Markets From 25 year R&D and consulting
Exploring Lees Management Good Practices for International Markets Dominique DELTEIL www.delteil-consultant.com Exploring Lees Management Good Practices for International Markets From 25 year R&D and consulting
Active Dry Wine Yeast* By Dr. Murli Dharmadhikari
 Active Dry Wine Yeast* By Dr. Murli Dharmadhikari Grape juice/must can be fermented by the yeasts present on grapes and in the winery. This kind of fermentation is often called natural or spontaneous fermentation.
Active Dry Wine Yeast* By Dr. Murli Dharmadhikari Grape juice/must can be fermented by the yeasts present on grapes and in the winery. This kind of fermentation is often called natural or spontaneous fermentation.
Fermentation and Ester Taints. Anita Oberholster
 Fermentation and Ester Taints Anita Oberholster Introduction: Aroma Compounds Grape derived provide varietal distinction Yeast and fermentation derived Esters Higher alcohols Carbonyls Volatile acids Volatile
Fermentation and Ester Taints Anita Oberholster Introduction: Aroma Compounds Grape derived provide varietal distinction Yeast and fermentation derived Esters Higher alcohols Carbonyls Volatile acids Volatile
The challenge of making mead is
 by Ken Schramm MASTERING MEAD Optimizing Honey Fermentation Photo courtesy of the National Honey Board The challenge of making mead is achieving the perfect honey fermentation clean, with zero or absolutely
by Ken Schramm MASTERING MEAD Optimizing Honey Fermentation Photo courtesy of the National Honey Board The challenge of making mead is achieving the perfect honey fermentation clean, with zero or absolutely
Medical Microbiology Culture Media :
 Lecture 3 Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology Culture Media : Culture media are used for recognition and identification (diagnosis) of microorganisms. The media are contained in plates (Petri dishes),
Lecture 3 Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology Culture Media : Culture media are used for recognition and identification (diagnosis) of microorganisms. The media are contained in plates (Petri dishes),
Microbial Nutrition And bacterial Classification Microbiology Unit-I. Muhammad Iqbal Lecturer KMU
 Microbial Nutrition And bacterial Classification Microbiology Unit-I Muhammad Iqbal Lecturer KMU Objectives At the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Define key terms. Identify the basic
Microbial Nutrition And bacterial Classification Microbiology Unit-I Muhammad Iqbal Lecturer KMU Objectives At the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Define key terms. Identify the basic
NUTRITION AND GROWTH OF BACTERIA
 3 NUTRITION AND GROWTH OF BACTERIA 3.1 INTRODUCTION Bacteria are prokaryotic organisms that do not contain chlorophyll. They are unicellular and do not show true branching. They differ from eukaryotes
3 NUTRITION AND GROWTH OF BACTERIA 3.1 INTRODUCTION Bacteria are prokaryotic organisms that do not contain chlorophyll. They are unicellular and do not show true branching. They differ from eukaryotes
Control of fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates
 Control of fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates Anneli Nilsson Department of Chemical Engineering II, Lund University P.O. Box 124, S-221 00 Lund, Sweden In this work substrate feeding rate to
Control of fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates Anneli Nilsson Department of Chemical Engineering II, Lund University P.O. Box 124, S-221 00 Lund, Sweden In this work substrate feeding rate to
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria in Agriculture Now a Real Option Guy Webb B.Sc. REM Agricultural Consultant
 Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria in Agriculture Now a Real Option Guy Webb B.Sc. REM Agricultural Consultant The Pursuit of Protein and Profit All agricultural enterprises, in essence, are based on the pursuit
Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria in Agriculture Now a Real Option Guy Webb B.Sc. REM Agricultural Consultant The Pursuit of Protein and Profit All agricultural enterprises, in essence, are based on the pursuit
Introduction. Introduction Nutritional Requirements. Six Major Classes of Nutrients. Water 12/1/2011. Regional Hay School -- Bolivar, MO 1
 Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
Bioremediation. Biodegradation
 Bioremediation A technology that encourages growth and reproduction of indigenous microorganisms (bacteria and fungi) to enhance biodegradation of organic constituents in the saturated zone Can effectively
Bioremediation A technology that encourages growth and reproduction of indigenous microorganisms (bacteria and fungi) to enhance biodegradation of organic constituents in the saturated zone Can effectively
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 10 BACTERIAL GROWTH Eye of Science / Science Photo Library WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? Increase in numbers is one of the requirements for infection. This increase is dependent upon bacterial growth.
CHAPTER 10 BACTERIAL GROWTH Eye of Science / Science Photo Library WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? Increase in numbers is one of the requirements for infection. This increase is dependent upon bacterial growth.
Get It Right. Answers. Chapter 1: The Science of Life. A biologist studies all living things.
 Discover Biology 'N' Level Science Chapter 1 Chapter 1: The Science of Life A biologist studies all living things. In order to carry out the scientific method, we need to ask questions. Discover Biology
Discover Biology 'N' Level Science Chapter 1 Chapter 1: The Science of Life A biologist studies all living things. In order to carry out the scientific method, we need to ask questions. Discover Biology
What Is Humic Acid? Where Does It Come From?
 What Is Humic Acid? Humic and Fulvic acids are the final break-down constituents of the natural decay of plant and animal materials. These organic acids are found in pre-historic deposits. Humic matter
What Is Humic Acid? Humic and Fulvic acids are the final break-down constituents of the natural decay of plant and animal materials. These organic acids are found in pre-historic deposits. Humic matter
DIGESTION is the physical and
 Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Metabolism Dr.kareema Amine Al-Khafaji Assistant professor in microbiology, and dermatologist Babylon University, College of Medicine, Department of
 Metabolism Dr.kareema Amine Al-Khafaji Assistant professor in microbiology, and dermatologist Babylon University, College of Medicine, Department of Microbiology. Metabolism sum of all chemical processes
Metabolism Dr.kareema Amine Al-Khafaji Assistant professor in microbiology, and dermatologist Babylon University, College of Medicine, Department of Microbiology. Metabolism sum of all chemical processes
LAB PROCEDURE Alpha-Amino Nitrogen by NOPA
 LAB PROCEDURE Alpha-Amino Nitrogen by NOPA From: Method by Dr. Christian Butzke, U.C. Davis. The reagents have been changed slightly for better shelf life. In the original method, NaOH, boric acid, NAC,
LAB PROCEDURE Alpha-Amino Nitrogen by NOPA From: Method by Dr. Christian Butzke, U.C. Davis. The reagents have been changed slightly for better shelf life. In the original method, NaOH, boric acid, NAC,
Acidity in Wine: The importance of management through measurement
 Acidity in Wine: The importance of management through measurement The typical acidity measurements in grape juice and wine are ph and titratable acidity (TA). The ph measurement is used in the vineyard
Acidity in Wine: The importance of management through measurement The typical acidity measurements in grape juice and wine are ph and titratable acidity (TA). The ph measurement is used in the vineyard
General Properties Protein Nature of Enzymes Folded Shape of Enzymes H-bonds complementary
 Proteins that function as biological catalysts are called enzymes. Enzymes speed up specific metabolic reactions. Low contamination, low temperature and fast metabolism are only possible with enzymes.
Proteins that function as biological catalysts are called enzymes. Enzymes speed up specific metabolic reactions. Low contamination, low temperature and fast metabolism are only possible with enzymes.
GOLDEN ENVIRO HERBA- EXTRACT DRAIN CLOG FREE. Pleasant lemon fragrance provides instant freshness Patented microbial technology
 GOLDEN ENVIRO HERBA- EXTRACT DRAIN CLOG FREE Application Sheet A clogged drain can stop kitchen operations - whether it is a busy restaurant or a dinner for two at home. Drain Clog Free combines fast-
GOLDEN ENVIRO HERBA- EXTRACT DRAIN CLOG FREE Application Sheet A clogged drain can stop kitchen operations - whether it is a busy restaurant or a dinner for two at home. Drain Clog Free combines fast-
AFDO 2010, Norfolk, VA James Marsden Regents Distinguished Professor Jasdeep Saini Kansas State University
 Strategies for Control of Listeria monocytogenes AFDO 2010, Norfolk, VA James Marsden Regents Distinguished Professor Jasdeep Saini Kansas State University Listeria monocytogenes Small Gram + rod, facultative
Strategies for Control of Listeria monocytogenes AFDO 2010, Norfolk, VA James Marsden Regents Distinguished Professor Jasdeep Saini Kansas State University Listeria monocytogenes Small Gram + rod, facultative
Ways of Making Terra Preta: Biochar Activation
 Ways of Making Terra Preta: Biochar Activation by Hans-Peter Schmidt (Delinat-Institute) Biochar is not a fertilizer, but rather a nutrient carrier and a habitat for microorganisms. First of all it has
Ways of Making Terra Preta: Biochar Activation by Hans-Peter Schmidt (Delinat-Institute) Biochar is not a fertilizer, but rather a nutrient carrier and a habitat for microorganisms. First of all it has
National Food Safety Standard Fermented Milk
 National Food Safety Standard of the People s Republic of China GB 19302-2010 National Food Safety Standard Fermented Milk Issued on 2010-03-26 Implemented on 2010-12-01 Published by Ministry of Health
National Food Safety Standard of the People s Republic of China GB 19302-2010 National Food Safety Standard Fermented Milk Issued on 2010-03-26 Implemented on 2010-12-01 Published by Ministry of Health
Topic 3: Nutrition, Photosynthesis, and Respiration
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the chemical reaction represented below and on your knowledge of biology. If this reaction takes place in an organism that requires sunlight to produce
1. Base your answer to the following question on the chemical reaction represented below and on your knowledge of biology. If this reaction takes place in an organism that requires sunlight to produce
ALL- GRAIN WHEAT- MASH VODKA
 ALL- GRAIN WHEAT- MASH VODKA Most home distillers make vodka from sugar and water fermented with turbo yeast. However, the majority of commercial vodka distilleries make their finest vodkas from Winter
ALL- GRAIN WHEAT- MASH VODKA Most home distillers make vodka from sugar and water fermented with turbo yeast. However, the majority of commercial vodka distilleries make their finest vodkas from Winter
Session 1 Fundamentals of Microbiology
 Session 1 Fundamentals of Microbiology Session overview Classification Microbial nomenclature Microbial growth Microbial death Spore formation Classification The Five Kingdom system is used to classify
Session 1 Fundamentals of Microbiology Session overview Classification Microbial nomenclature Microbial growth Microbial death Spore formation Classification The Five Kingdom system is used to classify
Mammalian digestive tracts
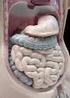 Mammalian digestive tracts Mouth: mastication, some digestive enzymes Esophagus: simple transport tube Stomach: most initial digestion, some physical processing Small intestine: digestion continues, some
Mammalian digestive tracts Mouth: mastication, some digestive enzymes Esophagus: simple transport tube Stomach: most initial digestion, some physical processing Small intestine: digestion continues, some
Lab Exercise 3: Media, incubation, and aseptic technique
 Lab Exercise 3: Media, incubation, and aseptic technique Objectives 1. Compare the different types of media. 2. Describe the different formats of media, plate, tube etc. 3. Explain how to sterilize it,
Lab Exercise 3: Media, incubation, and aseptic technique Objectives 1. Compare the different types of media. 2. Describe the different formats of media, plate, tube etc. 3. Explain how to sterilize it,
Spawning and Casing Supplements David M. Beyer, Penn State
 Spawning and Casing Supplements David M. Beyer, Penn State Spawning and Casing Supplements What is our current understanding of mushroom nutrition? What is the purpose of supplementation? How many years
Spawning and Casing Supplements David M. Beyer, Penn State Spawning and Casing Supplements What is our current understanding of mushroom nutrition? What is the purpose of supplementation? How many years
How To Get Healthy
 Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Fall 2-13 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Fall 2-13 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Understanding Feed Analysis Terminology
 Understanding Feed Analysis Terminology One of the most important steps in developing a ration suitable for dairy animals is feed testing. It is essential to have a starting point in order to formulate
Understanding Feed Analysis Terminology One of the most important steps in developing a ration suitable for dairy animals is feed testing. It is essential to have a starting point in order to formulate
Basic Chemistry And Fermentation
 Tonight's Lecture Basic Chemistry And Fermentation Wine 3 Introduction to Enology Review of basic chemistry Atoms & molecules Chemical bonding Acid-base chemistry Fermentation Chemistry of alcoholic fermentation
Tonight's Lecture Basic Chemistry And Fermentation Wine 3 Introduction to Enology Review of basic chemistry Atoms & molecules Chemical bonding Acid-base chemistry Fermentation Chemistry of alcoholic fermentation
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
The growth of Mos are effected by Chemical and Physical surroundings:
 The Continuous Culture of Microorganisms: Continuous Culture System! A microbial population of can be maintained in the exponential growth phase and at a constant biomass concentration for extended periods.!
The Continuous Culture of Microorganisms: Continuous Culture System! A microbial population of can be maintained in the exponential growth phase and at a constant biomass concentration for extended periods.!
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Level 3. Applying the Principles of Nutrition to a Physical Activity Programme Level 3
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
1. A covalent bond between two atoms represents what kind of energy? a. Kinetic energy b. Potential energy c. Mechanical energy d.
 1. A covalent bond between two atoms represents what kind of energy? a. Kinetic energy b. Potential energy c. Mechanical energy d. Solar energy A. Answer a is incorrect. Kinetic energy is the energy of
1. A covalent bond between two atoms represents what kind of energy? a. Kinetic energy b. Potential energy c. Mechanical energy d. Solar energy A. Answer a is incorrect. Kinetic energy is the energy of
Beneficial Microflora in Honey Bee Colonies
 Beneficial Microflora in Honey Bee Colonies Diana Sammataro, Ph.D. USDA-ARS Carl Hayden Bee Research Center Tucson, AZ Our Website: http://gears.tucson.ars.ag.gov Lactobacillus spp. Bifidobacterium spp.
Beneficial Microflora in Honey Bee Colonies Diana Sammataro, Ph.D. USDA-ARS Carl Hayden Bee Research Center Tucson, AZ Our Website: http://gears.tucson.ars.ag.gov Lactobacillus spp. Bifidobacterium spp.
Development of low-cost culture media for effective biosurfactant production
 Development of low-cost culture media for effective biosurfactant production Ana I. Rodrigues, Eduardo J. Gudiña, José A. Teixeira and Lígia R. Rodrigues CEB Centre of Biological Engineering, University
Development of low-cost culture media for effective biosurfactant production Ana I. Rodrigues, Eduardo J. Gudiña, José A. Teixeira and Lígia R. Rodrigues CEB Centre of Biological Engineering, University
OPTIMIZING BIOLOGICAL PHOSPHORUS REMOVAL FROM AN SBR SYSTEM MIDDLEBURY, VT. Paul Klebs, Senior Applications Engineer Aqua-Aerobic Systems, Inc.
 OPTIMIZING BIOLOGICAL PHOSPHORUS REMOVAL FROM AN SBR SYSTEM ABSTRACT MIDDLEBURY, VT Paul Klebs, Senior Applications Engineer Aqua-Aerobic Systems, Inc. The Middlebury Wastwater Treatment Plant, located
OPTIMIZING BIOLOGICAL PHOSPHORUS REMOVAL FROM AN SBR SYSTEM ABSTRACT MIDDLEBURY, VT Paul Klebs, Senior Applications Engineer Aqua-Aerobic Systems, Inc. The Middlebury Wastwater Treatment Plant, located
16 Very Important THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW About Cancer Cells
 16 Very Important THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW About Cancer Cells By Ingo Logé and Fitness Forever 1. Every person has cancer cells in the body. These cancer cells do not show up in the standard tests until
16 Very Important THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW About Cancer Cells By Ingo Logé and Fitness Forever 1. Every person has cancer cells in the body. These cancer cells do not show up in the standard tests until
Drain Ease Open. Application Sheet. Cleaning Solutions Drain
 Drain Ease Open Cleaning Solutions Drain Application Sheet A clogged drain can stop kitchen operations whether it is a busy restaurant or a dinner for two at home. Drain Ease Open combines fast-acting
Drain Ease Open Cleaning Solutions Drain Application Sheet A clogged drain can stop kitchen operations whether it is a busy restaurant or a dinner for two at home. Drain Ease Open combines fast-acting
ABCs OF WINE TASTING Worksheet
 Class 1: Module 1 1. The winemaking equation is: Grapes + Yeast = A. (The first letter of the answer is provided) 2. As grapes ripen on the vine, the amount of sugar contained in each berry increases /
Class 1: Module 1 1. The winemaking equation is: Grapes + Yeast = A. (The first letter of the answer is provided) 2. As grapes ripen on the vine, the amount of sugar contained in each berry increases /
Bioremediation of Petroleum Contamination. Augustine Ifelebuegu GE413
 Bioremediation of Petroleum Contamination Augustine Ifelebuegu GE413 Bioremediation Bioremediation is the use of living microorganisms to degrade environmental contaminants in the soil and groundwater
Bioremediation of Petroleum Contamination Augustine Ifelebuegu GE413 Bioremediation Bioremediation is the use of living microorganisms to degrade environmental contaminants in the soil and groundwater
Bioremediation. Introduction
 Bioremediation Introduction In the twentieth century, the ever increase in the global human population and industrialization led to the exploitation of natural resources. The increased usage of heavy metals
Bioremediation Introduction In the twentieth century, the ever increase in the global human population and industrialization led to the exploitation of natural resources. The increased usage of heavy metals
BIOREMEDIATION: A General Outline www.idem.in.gov Mitchell E. Daniels, Jr.
 TECHNICAL GUIDANCE DOCUMENT INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT BIOREMEDIATION: A General Outline www.idem.in.gov Mitchell E. Daniels, Jr. Thomas W. Easterly Governor Commissioner 100 N. Senate
TECHNICAL GUIDANCE DOCUMENT INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT BIOREMEDIATION: A General Outline www.idem.in.gov Mitchell E. Daniels, Jr. Thomas W. Easterly Governor Commissioner 100 N. Senate
Name Date Period. Keystone Review Enzymes
 Name Date Period Keystone Review Enzymes 1. In order for cells to function properly, the enzymes that they contain must also function properly. What can be inferred using the above information? A. Cells
Name Date Period Keystone Review Enzymes 1. In order for cells to function properly, the enzymes that they contain must also function properly. What can be inferred using the above information? A. Cells
The Goat s Digestive System. Roy Beckford UF/IFAS Lee County
 The Goat s Digestive System Roy Beckford UF/IFAS Lee County Ruminants The goat is a member of a class of animals called ruminants. These animals ruminate (chew their cud). Unlike us, they have special
The Goat s Digestive System Roy Beckford UF/IFAS Lee County Ruminants The goat is a member of a class of animals called ruminants. These animals ruminate (chew their cud). Unlike us, they have special
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
The Macroalgae Biorefinery (MAB3) with Focus on Cultivation, Bioethanol Production, Fish Feed and Sustainability Assessment
 The Macroalgae Biorefinery (MAB3) with Focus on Cultivation, Bioethanol Production, Fish Feed and Sustainability Assessment Dr. Anne-Belinda Bjerre Xiaoru Hou, Annette Bruhn, Michael Bo Rasmussen, Mette
The Macroalgae Biorefinery (MAB3) with Focus on Cultivation, Bioethanol Production, Fish Feed and Sustainability Assessment Dr. Anne-Belinda Bjerre Xiaoru Hou, Annette Bruhn, Michael Bo Rasmussen, Mette
Dietary Fiber and Alcohol. Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Spring 2014
 Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Spring 2014 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Spring 2014 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Enzymes: Practice Questions #1
 Enzymes: Practice Questions #1 1. Compound X increases the rate of the reaction below. Compound X is most likely A. an enzyme B. a lipid molecule C. an indicator D. an ADP molecule 2. The equation below
Enzymes: Practice Questions #1 1. Compound X increases the rate of the reaction below. Compound X is most likely A. an enzyme B. a lipid molecule C. an indicator D. an ADP molecule 2. The equation below
ANSWERS AND MARK SCHEMES. (a) 5 correct plots;;; (-1 mark each incorrect plot) 3
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 5 correct plots;;; (-1 mark each incorrect plot) 3 (b) 1600/4; = 400 kj; (i mark for correct working if answer incorrect) 2 (c) the more vigorous the activity the more energy used; 1 (d)
QUESTIONSHEET 1 5 correct plots;;; (-1 mark each incorrect plot) 3 (b) 1600/4; = 400 kj; (i mark for correct working if answer incorrect) 2 (c) the more vigorous the activity the more energy used; 1 (d)
Other Fruit Melomels for Experienced Dummies Curt Stock
 Other Fruit Melomels for Experienced Dummies Curt Stock Melomel is mead comprised of honey and fruit. Two varieties of melomels are Cyser (mead with apple cider) and Pyments (mead with wine grapes). This
Other Fruit Melomels for Experienced Dummies Curt Stock Melomel is mead comprised of honey and fruit. Two varieties of melomels are Cyser (mead with apple cider) and Pyments (mead with wine grapes). This
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline
 AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline I. How cells get energy. A. Cellular Respiration 1. Cellular respiration includes the various metabolic pathways that break down carbohydrates and other
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline I. How cells get energy. A. Cellular Respiration 1. Cellular respiration includes the various metabolic pathways that break down carbohydrates and other
NO-TILL AND NITROGEN FIXING INOCULANTS
 NO-TILL AND NITROGEN FIXING INOCULANTS Tom Wacek R & D Director for Urbana Laboratories St. Joseph, Missouri Nitrogen fixation is the utilization of the free gaseous nitrogen in the air by soil bacteria
NO-TILL AND NITROGEN FIXING INOCULANTS Tom Wacek R & D Director for Urbana Laboratories St. Joseph, Missouri Nitrogen fixation is the utilization of the free gaseous nitrogen in the air by soil bacteria
Respiration Worksheet. Respiration is the controlled release of energy from food. Types of Respiration. Aerobic Respiration
 Respiration Worksheet Respiration is the controlled release of energy from food The food involved in respiration is usually Internal respiration is controlled by which allow energy to be released in The
Respiration Worksheet Respiration is the controlled release of energy from food The food involved in respiration is usually Internal respiration is controlled by which allow energy to be released in The
1. Enzymes. Biochemical Reactions. Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism. 1. Enzymes. 2. ATP Production. 3. Autotrophic Processes
 Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism 1. Enzymes 2. ATP Production 3. Autotrophic Processes 1. Enzymes Biochemical Reactions All living cells depend on biochemical reactions to maintain homeostasis. All of the
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism 1. Enzymes 2. ATP Production 3. Autotrophic Processes 1. Enzymes Biochemical Reactions All living cells depend on biochemical reactions to maintain homeostasis. All of the
Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1
 Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1 1. Which statement best describes one of the events taking place in the chemical reaction? A. Energy is being stored as a result of aerobic respiration. B. Fermentation
Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1 1. Which statement best describes one of the events taking place in the chemical reaction? A. Energy is being stored as a result of aerobic respiration. B. Fermentation
Human Health, the Nutritional Quality of Harvested Food and Sustainable Farming Systems
 Human Health, the Nutritional Quality of Harvested Food and Sustainable Farming Systems by John B. Marler and Jeanne R. Wallin The alarming fact is that foods fruits, vegetables and grains now being raised
Human Health, the Nutritional Quality of Harvested Food and Sustainable Farming Systems by John B. Marler and Jeanne R. Wallin The alarming fact is that foods fruits, vegetables and grains now being raised
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
Conversion of macroalgae to bioethanol and fish feed preliminary trials in the MAB3 project
 Conversion of macroalgae to bioethanol and fish feed preliminary trials in the MAB3 project Anne-Belinda Bjerre, Senior Scientist PhD Danish Technological Institute 3rd Danish Macroalgae conference Grenå
Conversion of macroalgae to bioethanol and fish feed preliminary trials in the MAB3 project Anne-Belinda Bjerre, Senior Scientist PhD Danish Technological Institute 3rd Danish Macroalgae conference Grenå
Functions of Blood. Collects O 2 from lungs, nutrients from digestive tract, and waste products from tissues Helps maintain homeostasis
 Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
LAB 4. Cultivation of Bacteria INTRODUCTION
 LAB 4. Cultivation of Bacteria Protocols for use of cultivation of bacteria, use of general growth, enriched, selective and differential media, plate pouring, determination of temperature range for growth
LAB 4. Cultivation of Bacteria Protocols for use of cultivation of bacteria, use of general growth, enriched, selective and differential media, plate pouring, determination of temperature range for growth
Eating Well with Diabetes. Cassie Vanderwall UW Health Nutrition Registered Dietitian Certified Personal Trainer Certified Diabetes Educator
 Eating Well with Diabetes Cassie Vanderwall UW Health Nutrition Registered Dietitian Certified Personal Trainer Certified Diabetes Educator Outline What is Diabetes? Diabetes Self-Management Eating Well
Eating Well with Diabetes Cassie Vanderwall UW Health Nutrition Registered Dietitian Certified Personal Trainer Certified Diabetes Educator Outline What is Diabetes? Diabetes Self-Management Eating Well
Ruminant Digestive System
 Ruminant Digestive System Complex structure with four compartments Source: Animal Feeding and Nutrition (Jurgens) Ruminant Characteristics Primarily herbivores Cattle, sheep, goats, deer, elk Camelids
Ruminant Digestive System Complex structure with four compartments Source: Animal Feeding and Nutrition (Jurgens) Ruminant Characteristics Primarily herbivores Cattle, sheep, goats, deer, elk Camelids
PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION
 reflect Wind turbines shown in the photo on the right are large structures with blades that move in response to air movement. When the wind blows, the blades rotate. This motion generates energy that is
reflect Wind turbines shown in the photo on the right are large structures with blades that move in response to air movement. When the wind blows, the blades rotate. This motion generates energy that is
Dr Erhard Briendenhann
 Dr Erhard Briendenhann Protein Research Foundation Soya processing nutritional and financial benefits Sponsored by: Protein Research Foundation SOYBEAN PROCESSING Nutritional and financial benefits Dr
Dr Erhard Briendenhann Protein Research Foundation Soya processing nutritional and financial benefits Sponsored by: Protein Research Foundation SOYBEAN PROCESSING Nutritional and financial benefits Dr
1. Lees. What are they?
 Published in Australian Grapegrower & Winemaker, 30 th Technical Issue Working with lees: key elements to wine maturing Author : Dominique DELTEIL, Scientific Director, ICV 1 In this magazine, we already
Published in Australian Grapegrower & Winemaker, 30 th Technical Issue Working with lees: key elements to wine maturing Author : Dominique DELTEIL, Scientific Director, ICV 1 In this magazine, we already
Using composting beds to treat acidity in saline drain water
 Government of Western Australia Department of Water Using composting beds to treat acidity in saline drain water Introduction Acidic saline water is common in drains used to manage shallow saline watertables
Government of Western Australia Department of Water Using composting beds to treat acidity in saline drain water Introduction Acidic saline water is common in drains used to manage shallow saline watertables
Effect Of Amino Acids On Plants
 Effect Of Amino Acids On Plants Agriculture production is a very intensive business and is related to better quality and better yield leading to better profitability Every farmer s dreams to achieve this
Effect Of Amino Acids On Plants Agriculture production is a very intensive business and is related to better quality and better yield leading to better profitability Every farmer s dreams to achieve this
Biological molecules:
 Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
Enzymes. Chapter 3. 3.1 Enzymes and catalysts. Vital mistake. What is an enzyme?
 Chapter 3 Enzymes Vital mistake We may not be able to see them, but enzymes are absolutely crucial to the lives of ourselves and all other living organisms. The Quarter Horse (Figure 3.1) is a breed of
Chapter 3 Enzymes Vital mistake We may not be able to see them, but enzymes are absolutely crucial to the lives of ourselves and all other living organisms. The Quarter Horse (Figure 3.1) is a breed of
Enzymes. A. a lipid B. a protein C. a carbohydrate D. a mineral
 Enzymes 1. All cells in multicellular organisms contain thousands of different kinds of enzymes that are specialized to catalyze different chemical reactions. Given this information, which of the following
Enzymes 1. All cells in multicellular organisms contain thousands of different kinds of enzymes that are specialized to catalyze different chemical reactions. Given this information, which of the following
Nutrient Removal at Wastewater Treatment Facilities. Nitrogen and Phosphorus. Gary M. Grey HydroQual, Inc. [email protected] 201 529 5151 X 7167
 Nutrient Removal at Wastewater Treatment Facilities Nitrogen and Phosphorus Gary M. Grey HydroQual, Inc. [email protected] 201 529 5151 X 7167 1 Agenda Nitrification and Denitrification Fundamentals
Nutrient Removal at Wastewater Treatment Facilities Nitrogen and Phosphorus Gary M. Grey HydroQual, Inc. [email protected] 201 529 5151 X 7167 1 Agenda Nitrification and Denitrification Fundamentals
Gas Analysis Mass Spectrometry Applications in Fermentation and Cell Culture Processes Written by Graham Lewis
 Gas Analysis Mass Spectrometry Applications in Fermentation and Cell Culture Processes Written by Graham Lewis Key Words Biotechnology Fermentation Off-gas Analysis Rapid Multistream Sampling Magnetic
Gas Analysis Mass Spectrometry Applications in Fermentation and Cell Culture Processes Written by Graham Lewis Key Words Biotechnology Fermentation Off-gas Analysis Rapid Multistream Sampling Magnetic
Which of the following can be determined based on this model? The atmosphere is the only reservoir on Earth that can store carbon in any form. A.
 Earth s Cycles 1. Models are often used to explain scientific knowledge or experimental results. A model of the carbon cycle is shown below. Which of the following can be determined based on this model?
Earth s Cycles 1. Models are often used to explain scientific knowledge or experimental results. A model of the carbon cycle is shown below. Which of the following can be determined based on this model?
This is your LOVE MY HEART Journal. Index of Topics. You and Your Heart Activity 1: How Your Heart Functions.2 Activity 2: Break the Heart Code..
 This is your LOVE MY HEART Journal Use this workbook to learn about your heart and ways to keep your heart healthy. Talk with your family about the things that you do and learn in this book! Have fun!
This is your LOVE MY HEART Journal Use this workbook to learn about your heart and ways to keep your heart healthy. Talk with your family about the things that you do and learn in this book! Have fun!
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS
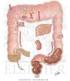 SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
What affects an enzyme s activity? General environmental factors, such as temperature and ph. Chemicals that specifically influence the enzyme.
 CH s 8-9 Respiration & Metabolism Metabolism A catalyst is a chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. An enzyme is a catalytic protein. Hydrolysis of sucrose by
CH s 8-9 Respiration & Metabolism Metabolism A catalyst is a chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. An enzyme is a catalytic protein. Hydrolysis of sucrose by
THESES OF DOCTORAL (Ph.D.) DISSERTATION
 THESES OF DOCTORAL (Ph.D.) DISSERTATION UNIVERSITY OF WEST HUNGARY FACULTY OF AGRICULTURAL AND FOOD SCIENCES MOSONMAGYARÓVÁR Institute of Food Science Head of Doctoral School: Prof. Dr. János Schmidt Corresponding
THESES OF DOCTORAL (Ph.D.) DISSERTATION UNIVERSITY OF WEST HUNGARY FACULTY OF AGRICULTURAL AND FOOD SCIENCES MOSONMAGYARÓVÁR Institute of Food Science Head of Doctoral School: Prof. Dr. János Schmidt Corresponding
Methyl groups, like vitamins, are
 Methyl groups are essential for the body to function properly and must be obtained from the diet The need for methyl groups increases under stress Chapter 11 Betaine a new B vitamin Methyl groups reduce
Methyl groups are essential for the body to function properly and must be obtained from the diet The need for methyl groups increases under stress Chapter 11 Betaine a new B vitamin Methyl groups reduce
Introduction to Beneficial Bacteria
 Name Introduction to Beneficial Bacteria Materials 11X17 paper Colored Pencils Markers Magazine Scissors Glue Procedure 1. Using your What is a Microbe? booklet and other handouts, answer the following
Name Introduction to Beneficial Bacteria Materials 11X17 paper Colored Pencils Markers Magazine Scissors Glue Procedure 1. Using your What is a Microbe? booklet and other handouts, answer the following
FEEDING THE DAIRY COW DURING LACTATION
 Department of Animal Science FEEDING THE DAIRY COW DURING LACTATION Dairy Cattle Production 342-450A Page 1 of 8 Feeding the Dairy Cow during Lactation There are main stages in the lactation cycle of the
Department of Animal Science FEEDING THE DAIRY COW DURING LACTATION Dairy Cattle Production 342-450A Page 1 of 8 Feeding the Dairy Cow during Lactation There are main stages in the lactation cycle of the
Wound Healing. Outline. Normal Wound Healing. Wounds and nutrition refresher UPHS evidence-based guideline for. wounds
 Wound Healing Clinical Nutrition Support Service Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Jung Kim, RD CNSD, LDN Tricia Stefankiewicz, MA, RD, CNSC, LDN Outline Wounds and nutrition refresher UPHS evidence-based
Wound Healing Clinical Nutrition Support Service Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Jung Kim, RD CNSD, LDN Tricia Stefankiewicz, MA, RD, CNSC, LDN Outline Wounds and nutrition refresher UPHS evidence-based
Liver, Gallbladder, Exocrine Pancreas KNH 406
 Liver, Gallbladder, Exocrine Pancreas KNH 406 2007 Thomson - Wadsworth LIVER Anatomy - functions With disease blood flow becomes obstructed Bile All bile drains into common hepatic duct Liver Bile complex
Liver, Gallbladder, Exocrine Pancreas KNH 406 2007 Thomson - Wadsworth LIVER Anatomy - functions With disease blood flow becomes obstructed Bile All bile drains into common hepatic duct Liver Bile complex
Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism)
 Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism) Large food molecules contain a lot of potential energy in the form of chemical bonds but it requires a lot of work to liberate the energy. Cells need
Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism) Large food molecules contain a lot of potential energy in the form of chemical bonds but it requires a lot of work to liberate the energy. Cells need
 Microalgae Grown in Photobioreactors for Mass Production of Biofuel Need for Sustainable Energy The Price of Energy is Going UP Oil reserves are depleting World demand for energy is increasing Economic
Microalgae Grown in Photobioreactors for Mass Production of Biofuel Need for Sustainable Energy The Price of Energy is Going UP Oil reserves are depleting World demand for energy is increasing Economic
Harvesting energy with fertilizers
 Harvesting energy with fertilizers Sustainable agriculture in Europe 1 Harvesting energy with fertilizers The reason for agriculture s existence is to supply energy to mankind. Agriculture converts solar
Harvesting energy with fertilizers Sustainable agriculture in Europe 1 Harvesting energy with fertilizers The reason for agriculture s existence is to supply energy to mankind. Agriculture converts solar
