Explicit Option Pricing Formula for a Mean-Reverting Asset in Energy Markets
|
|
|
- Brooke Richardson
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Explicit Option Pricing Formula for a Mean-Reverting Asset in Energy Markets Anatoliy Swishchuk Mathematical & Computational Finance Lab Dept of Math & Stat, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada QMF 2007 Conference Sydney, Australia December 12-15, 2007 This research is supported by MITACS and NSERC
2 Outline Mean-Reverting Models (MRM): Deterministic vs. Stochastic MRM in Finance Markets: Variances or Volatilities (Not Asset Prices) MRM in Energy Markets: Asset Prices Change of Time Method (CTM) Mean-Reverting Model (MRM) Option Pricing Formula Drawback of One-Factor Models Future Work
3 Motivations for the Work Paper: Javaheri, Wilmott and Haug (2002) GARCH and Volatility Swaps, Wilmott Magazine, Jan Issue (they applied PDE approach to find a volatility swap for MRM and asked about the possible option pricing formula Paper: Bos, Ware and Pavlov (2002) On a Semi-Spectral Method for Pricing an Option on a Mean-Reverting Asset, Quantit. Finance J. (PDE approach, semi-spectral method to calculate numerically the solution)
4 Wilmott, Javaheri & Haug (2002) Model Wilmott, Javaheri & Haug (GARCH and Volatility Swaps, Wilmott Magazine, 2002)- volatility swap for -continuous-time GARCH(1,1) model
5 M. Yor s Results M. Yor On some exponential functions of Brownian motion, Adv. In Applied Probab., v. 24, No. 3, (1992), started the research for the integral of an exponential Brownian motion H. Matsumoto, M. Yor Exponential Functionals of Brownian motion, I: Probability laws at fixed time, Probability Surveys, v. 2 (2005), there is still no closed form probability density function, while the best result is a function with a double integral.
6 Mean-Reversion Effect Guitar String Analogy: if we pluck the guitar string, the string will revert to its place of equilibrium To measure how quickly this reversion back to the equilibrium location would happen we had to pluck the string Similarly, the only way to measure mean reversion is when the variances of asset prices in financial markets and asset prices in energy markets get plucked away from their non-event levels and we observe them go back to more or less the levels they started from
7 The Mean-Reverting Deterministic Process
8 Mean-Reverting Plot (a=4.6,l=2.5)
9 Meaning of Mean-Reverting Parameter The greater the mean-reverting parameter value, a, the greater is the pull back to the equilibrium level For a daily variable change, the change in time, dt, in annualized terms is given by 1/365 If a=365, the mean reversion would act so quickly as to bring the variable back to its equilibrium within a single day The value of 365/a gives us an idea of how quickly the variable takes to get back to the equilibrium-in days
10 Mean-Reverting Stochastic Process
11 Mean-Reverting Models in Financial Markets Stock (asset) Prices follow geometric Brownian motion The Variance of Stock Price follows Mean-Reverting Models Example: Heston Model
12 Mean-Reverting Models in Energy Markets Asset Prices follow Mean-Reverting Stochastic Processes Example: Continuous-Time GARCH Model (or Pilipovic One-Factor Model)
13 Mean-Reverting Models in Energy Markets
14 Change of Time: Definition and Examples Change of Time-change time from t to a nonnegative process T(t) with non-decreasing sample paths Example1 (Subordinator): X(t) and T(t)>0 are some processes, then X(T(t)) is subordinated to X(t); T(t) is change of time Example 2 (Time-Changed Brownian Motion): M(t)=B(T(t)), B(t)-Brownian motion Example 3 (Product Process):
15 Time-Changed Brownian Motion by Bochner Bochner (1949) ( Diffusion Equation and Stochastic Process, Proc. N.A.S. USA, v. 35)-introduced the notion of change of time (CT) (time-changed Brownian motion) Bochner (1955) ( Harmonic Analysis and the Theory of Probability, UCLA Press, 176)-further development of CT
16 Change of Time: First Intro into Financial Economics Clark (1973) ( A Subordinated Stochastic Process Model with Fixed Variance for Speculative Prices, Econometrica, 41, )-introduced Bochner s (1949) timechanged Brownian motion into financial economics: He wrote down a model for the log-price M as M(t)=B(T(t)), where B(t) is Brownian motion, T(t) is timechange (B and T are independent)
17 Change of Time: Short History. I. Feller (1966) ( An Introduction to Probability Theory, vol. II, NY: Wiley)-introduced subordinated processes X(T(t)) with Markov process X(t) and T(t) as a process with independent increments (i.e., Poisson process); T(t) was called randomized operational time Johnson (1979) ( Option Pricing When the Variance Rate is Changing, working paper, UCLA)- introduced time-changed SVM in continuous time Johnson & Shanno (1987) ( Option Pricing When the Variance is Changing, J. of Finan. & Quantit. Analysis, 22, )-studied the pricing of options using time-changing SVM
18 Change of Time: Short History. II. Ikeda & Watanabe (1981) ( SDEs and Diffusion Processes, North-Holland Publ. Co)-introduced and studied CTM for the solution of SDEs Barndorff-Nielsen, Nicolato & Shephard (2003) ( Some recent development in stochastic volatility modelling )-review and put in context some of their recent work on stochastic volatility (SV) modelling, including the relationship between subordination and SV (random time-chronometer) Carr, Geman, Madan & Yor (2003) ( SV for Levy Processes, mathematical Finance, vol.13)-used subordinated processes to construct SV for Levy Processes (T(t)-business time)
19 CT and Embedding Problem Embedding Problem was first terated by Skorokhod (1965)-sum of any sequence of i.r.v. with mean zero and finite variation could be embedded in Brownian motion (BM) using stopping time Dambis (1965) and Dubis and Schwartz (1965)-every continuous martingale could be time-changed BM Huff (1969)-every processes of pathwise bounded variation could be embedded in BM Monroe (1972)-every right continuous martingale could be embedded in a BM Monroe (1978)-local martingale can be embedded in BM
20 Change of Time: Simplest (Martingale) Case
21 Change of Time: Ito Integral s Case
22 Change of Time: SDE s Case
23 Geometric Brownian Motion SVM
24 Change of Time Method
25 Connection between phi_t and phi_t^(-1)
26 Solution for GBM Equation Using Change of Time
27 Explicit Expression for
28 Mean-Reverting SV Model
29 Solution of MRM by CTM
30 Explicit Expression for
31 Explicit Expression for
32 Comparison: Solution of GBM & MRM -GBM -MRM
33 Explicit Expression for S(t) where
34 Properties of
35 Properties of
36 Properties of eta(t)
37 Properties of Eta(t). II.
38 Mean Value of MRM S(t)
39 Dependence of ES(t) on T
40 Dependence of ES(t) on S_0 and T
41 Variance for S(t)
42 Dependence of Variance of S(t) on S_0 and T
43 Dependence of Volatility of S(t) on S_0 and T
44 European Call Option for MRM.I.
45 European Call Option. II.
46 Expression for C_T in the case of MRM C_T=BS(T)+A(T)
47 Expression for C_T=BS(T)+A(T).II.
48 Expression for BS(T)
49 Expression for y_0 for MRM
50 Expression for A(T).I.
51 Moment generating) function of Eta(T)
52 Expression for A(T)
53 European Call Option for MRM (Explicit Formula)
54 European Call Option for MRM in Risk-Neutral World
55
56
57 Dependence of C_T on T
58 Comparison of Three Solutions Heston Model Mean-Reverting Model Black-Scholes Model
59 Comparison: Heston Model (1993)
60 Explicit Solution for CIR Process: CTM
61 Comparison: Solutions to the Three Models -GBM -MRM -Heston model
62 Summary GBM Model 1. -martingale Mean-Reverting Model 2. Heston Model -sum of two martingales 3. -martingale
63 Problem -explicit expression? To calculate an option price for Heston model, for example We know all the moments at this moment, though
64 Drawback of One-Factor Mean- Reverting Models The long-term mean L remains fixed over time: needs to be recalibrated on a continuous basis in order to ensure that the resulting curves are marked to market The biggest drawback is in option pricing: results in a model-implied volatility term structure that has the volatilities going to zero as expiration time increases (spot volatilities have to be increased to non-intuitive levels so that the long term options do not lose all the volatility value-as in the marketplace they certainly do not)
65 Future Work Change of Time Method for Two- Factor Continuous-Time GARCH Model
66 The End Thank You for Your Attention and Time!
A spot price model feasible for electricity forward pricing Part II
 A spot price model feasible for electricity forward pricing Part II Fred Espen Benth Centre of Mathematics for Applications (CMA) University of Oslo, Norway Wolfgang Pauli Institute, Wien January 17-18
A spot price model feasible for electricity forward pricing Part II Fred Espen Benth Centre of Mathematics for Applications (CMA) University of Oslo, Norway Wolfgang Pauli Institute, Wien January 17-18
Monte Carlo Methods and Models in Finance and Insurance
 Chapman & Hall/CRC FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS SERIES Monte Carlo Methods and Models in Finance and Insurance Ralf Korn Elke Korn Gerald Kroisandt f r oc) CRC Press \ V^ J Taylor & Francis Croup ^^"^ Boca Raton
Chapman & Hall/CRC FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS SERIES Monte Carlo Methods and Models in Finance and Insurance Ralf Korn Elke Korn Gerald Kroisandt f r oc) CRC Press \ V^ J Taylor & Francis Croup ^^"^ Boca Raton
Mathematical Finance
 Mathematical Finance Option Pricing under the Risk-Neutral Measure Cory Barnes Department of Mathematics University of Washington June 11, 2013 Outline 1 Probability Background 2 Black Scholes for European
Mathematical Finance Option Pricing under the Risk-Neutral Measure Cory Barnes Department of Mathematics University of Washington June 11, 2013 Outline 1 Probability Background 2 Black Scholes for European
MATHEMATICAL FINANCE and Derivatives (part II, PhD)
 MATHEMATICAL FINANCE and Derivatives (part II, PhD) Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Marc CHESNEY Location: Time: Mon. 08.00 09.45 Uhr First lecture: 18.02.2008 Language: English Contents: Stochastic volatility models
MATHEMATICAL FINANCE and Derivatives (part II, PhD) Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Marc CHESNEY Location: Time: Mon. 08.00 09.45 Uhr First lecture: 18.02.2008 Language: English Contents: Stochastic volatility models
Modeling the Implied Volatility Surface. Jim Gatheral Stanford Financial Mathematics Seminar February 28, 2003
 Modeling the Implied Volatility Surface Jim Gatheral Stanford Financial Mathematics Seminar February 28, 2003 This presentation represents only the personal opinions of the author and not those of Merrill
Modeling the Implied Volatility Surface Jim Gatheral Stanford Financial Mathematics Seminar February 28, 2003 This presentation represents only the personal opinions of the author and not those of Merrill
ARBITRAGE-FREE OPTION PRICING MODELS. Denis Bell. University of North Florida
 ARBITRAGE-FREE OPTION PRICING MODELS Denis Bell University of North Florida Modelling Stock Prices Example American Express In mathematical finance, it is customary to model a stock price by an (Ito) stochatic
ARBITRAGE-FREE OPTION PRICING MODELS Denis Bell University of North Florida Modelling Stock Prices Example American Express In mathematical finance, it is customary to model a stock price by an (Ito) stochatic
Online Appendix. Supplemental Material for Insider Trading, Stochastic Liquidity and. Equilibrium Prices. by Pierre Collin-Dufresne and Vyacheslav Fos
 Online Appendix Supplemental Material for Insider Trading, Stochastic Liquidity and Equilibrium Prices by Pierre Collin-Dufresne and Vyacheslav Fos 1. Deterministic growth rate of noise trader volatility
Online Appendix Supplemental Material for Insider Trading, Stochastic Liquidity and Equilibrium Prices by Pierre Collin-Dufresne and Vyacheslav Fos 1. Deterministic growth rate of noise trader volatility
Volatility Index: VIX vs. GVIX
 I. II. III. IV. Volatility Index: VIX vs. GVIX "Does VIX Truly Measure Return Volatility?" by Victor Chow, Wanjun Jiang, and Jingrui Li (214) An Ex-ante (forward-looking) approach based on Market Price
I. II. III. IV. Volatility Index: VIX vs. GVIX "Does VIX Truly Measure Return Volatility?" by Victor Chow, Wanjun Jiang, and Jingrui Li (214) An Ex-ante (forward-looking) approach based on Market Price
Master of Mathematical Finance: Course Descriptions
 Master of Mathematical Finance: Course Descriptions CS 522 Data Mining Computer Science This course provides continued exploration of data mining algorithms. More sophisticated algorithms such as support
Master of Mathematical Finance: Course Descriptions CS 522 Data Mining Computer Science This course provides continued exploration of data mining algorithms. More sophisticated algorithms such as support
On Black-Scholes Equation, Black- Scholes Formula and Binary Option Price
 On Black-Scholes Equation, Black- Scholes Formula and Binary Option Price Abstract: Chi Gao 12/15/2013 I. Black-Scholes Equation is derived using two methods: (1) risk-neutral measure; (2) - hedge. II.
On Black-Scholes Equation, Black- Scholes Formula and Binary Option Price Abstract: Chi Gao 12/15/2013 I. Black-Scholes Equation is derived using two methods: (1) risk-neutral measure; (2) - hedge. II.
Markov modeling of Gas Futures
 Markov modeling of Gas Futures p.1/31 Markov modeling of Gas Futures Leif Andersen Banc of America Securities February 2008 Agenda Markov modeling of Gas Futures p.2/31 This talk is based on a working
Markov modeling of Gas Futures p.1/31 Markov modeling of Gas Futures Leif Andersen Banc of America Securities February 2008 Agenda Markov modeling of Gas Futures p.2/31 This talk is based on a working
Stephane Crepey. Financial Modeling. A Backward Stochastic Differential Equations Perspective. 4y Springer
 Stephane Crepey Financial Modeling A Backward Stochastic Differential Equations Perspective 4y Springer Part I An Introductory Course in Stochastic Processes 1 Some Classes of Discrete-Time Stochastic
Stephane Crepey Financial Modeling A Backward Stochastic Differential Equations Perspective 4y Springer Part I An Introductory Course in Stochastic Processes 1 Some Classes of Discrete-Time Stochastic
Oscillatory Reduction in Option Pricing Formula Using Shifted Poisson and Linear Approximation
 EPJ Web of Conferences 68, 0 00 06 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20146800006 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 Oscillatory Reduction in Option Pricing Formula Using Shifted Poisson
EPJ Web of Conferences 68, 0 00 06 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20146800006 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 Oscillatory Reduction in Option Pricing Formula Using Shifted Poisson
The Black-Scholes pricing formulas
 The Black-Scholes pricing formulas Moty Katzman September 19, 2014 The Black-Scholes differential equation Aim: Find a formula for the price of European options on stock. Lemma 6.1: Assume that a stock
The Black-Scholes pricing formulas Moty Katzman September 19, 2014 The Black-Scholes differential equation Aim: Find a formula for the price of European options on stock. Lemma 6.1: Assume that a stock
Monte Carlo Methods in Finance
 Author: Yiyang Yang Advisor: Pr. Xiaolin Li, Pr. Zari Rachev Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics State University of New York at Stony Brook October 2, 2012 Outline Introduction 1 Introduction
Author: Yiyang Yang Advisor: Pr. Xiaolin Li, Pr. Zari Rachev Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics State University of New York at Stony Brook October 2, 2012 Outline Introduction 1 Introduction
LOG-TYPE MODELS, HOMOGENEITY OF OPTION PRICES AND CONVEXITY. 1. Introduction
 LOG-TYPE MODELS, HOMOGENEITY OF OPTION PRICES AND CONVEXITY M. S. JOSHI Abstract. It is shown that the properties of convexity of call prices with respect to spot price and homogeneity of call prices as
LOG-TYPE MODELS, HOMOGENEITY OF OPTION PRICES AND CONVEXITY M. S. JOSHI Abstract. It is shown that the properties of convexity of call prices with respect to spot price and homogeneity of call prices as
On exponentially ane martingales. Johannes Muhle-Karbe
 On exponentially ane martingales AMAMEF 2007, Bedlewo Johannes Muhle-Karbe Joint work with Jan Kallsen HVB-Institut für Finanzmathematik, Technische Universität München 1 Outline 1. Semimartingale characteristics
On exponentially ane martingales AMAMEF 2007, Bedlewo Johannes Muhle-Karbe Joint work with Jan Kallsen HVB-Institut für Finanzmathematik, Technische Universität München 1 Outline 1. Semimartingale characteristics
Hedging Illiquid FX Options: An Empirical Analysis of Alternative Hedging Strategies
 Hedging Illiquid FX Options: An Empirical Analysis of Alternative Hedging Strategies Drazen Pesjak Supervised by A.A. Tsvetkov 1, D. Posthuma 2 and S.A. Borovkova 3 MSc. Thesis Finance HONOURS TRACK Quantitative
Hedging Illiquid FX Options: An Empirical Analysis of Alternative Hedging Strategies Drazen Pesjak Supervised by A.A. Tsvetkov 1, D. Posthuma 2 and S.A. Borovkova 3 MSc. Thesis Finance HONOURS TRACK Quantitative
General price bounds for discrete and continuous arithmetic Asian options
 General price bounds for discrete and continuous arithmetic Asian options 1 [email protected] in collaboration with Gianluca Fusai 1,2 [email protected] 1 Cass Business School, City
General price bounds for discrete and continuous arithmetic Asian options 1 [email protected] in collaboration with Gianluca Fusai 1,2 [email protected] 1 Cass Business School, City
QUANTIZED INTEREST RATE AT THE MONEY FOR AMERICAN OPTIONS
 QUANTIZED INTEREST RATE AT THE MONEY FOR AMERICAN OPTIONS L. M. Dieng ( Department of Physics, CUNY/BCC, New York, New York) Abstract: In this work, we expand the idea of Samuelson[3] and Shepp[,5,6] for
QUANTIZED INTEREST RATE AT THE MONEY FOR AMERICAN OPTIONS L. M. Dieng ( Department of Physics, CUNY/BCC, New York, New York) Abstract: In this work, we expand the idea of Samuelson[3] and Shepp[,5,6] for
Generation Asset Valuation with Operational Constraints A Trinomial Tree Approach
 Generation Asset Valuation with Operational Constraints A Trinomial Tree Approach Andrew L. Liu ICF International September 17, 2008 1 Outline Power Plants Optionality -- Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic Values
Generation Asset Valuation with Operational Constraints A Trinomial Tree Approach Andrew L. Liu ICF International September 17, 2008 1 Outline Power Plants Optionality -- Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic Values
The Behavior of Bonds and Interest Rates. An Impossible Bond Pricing Model. 780 w Interest Rate Models
 780 w Interest Rate Models The Behavior of Bonds and Interest Rates Before discussing how a bond market-maker would delta-hedge, we first need to specify how bonds behave. Suppose we try to model a zero-coupon
780 w Interest Rate Models The Behavior of Bonds and Interest Rates Before discussing how a bond market-maker would delta-hedge, we first need to specify how bonds behave. Suppose we try to model a zero-coupon
From CFD to computational finance (and back again?)
 computational finance p. 1/17 From CFD to computational finance (and back again?) Mike Giles [email protected] Oxford University Mathematical Institute Oxford-Man Institute of Quantitative Finance
computational finance p. 1/17 From CFD to computational finance (and back again?) Mike Giles [email protected] Oxford University Mathematical Institute Oxford-Man Institute of Quantitative Finance
Pricing Interest-Rate- Derivative Securities
 Pricing Interest-Rate- Derivative Securities John Hull Alan White University of Toronto This article shows that the one-state-variable interest-rate models of Vasicek (1977) and Cox, Ingersoll, and Ross
Pricing Interest-Rate- Derivative Securities John Hull Alan White University of Toronto This article shows that the one-state-variable interest-rate models of Vasicek (1977) and Cox, Ingersoll, and Ross
BROWNIAN MOTION DEVELOPMENT FOR MONTE CARLO METHOD APPLIED ON EUROPEAN STYLE OPTION PRICE FORECASTING
 International journal of economics & law Vol. 1 (2011), No. 1 (1-170) BROWNIAN MOTION DEVELOPMENT FOR MONTE CARLO METHOD APPLIED ON EUROPEAN STYLE OPTION PRICE FORECASTING Petar Koĉović, Fakultet za obrazovanje
International journal of economics & law Vol. 1 (2011), No. 1 (1-170) BROWNIAN MOTION DEVELOPMENT FOR MONTE CARLO METHOD APPLIED ON EUROPEAN STYLE OPTION PRICE FORECASTING Petar Koĉović, Fakultet za obrazovanje
Black-Scholes Option Pricing Model
 Black-Scholes Option Pricing Model Nathan Coelen June 6, 22 1 Introduction Finance is one of the most rapidly changing and fastest growing areas in the corporate business world. Because of this rapid change,
Black-Scholes Option Pricing Model Nathan Coelen June 6, 22 1 Introduction Finance is one of the most rapidly changing and fastest growing areas in the corporate business world. Because of this rapid change,
Rolf Poulsen, Centre for Finance, University of Gothenburg, Box 640, SE-40530 Gothenburg, Sweden. E-mail: [email protected].
 The Margrabe Formula Rolf Poulsen, Centre for Finance, University of Gothenburg, Box 640, SE-40530 Gothenburg, Sweden. E-mail: [email protected] Abstract The Margrabe formula for valuation of
The Margrabe Formula Rolf Poulsen, Centre for Finance, University of Gothenburg, Box 640, SE-40530 Gothenburg, Sweden. E-mail: [email protected] Abstract The Margrabe formula for valuation of
Pricing European and American bond option under the Hull White extended Vasicek model
 1 Academic Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics /August 2013/ UISA Pricing European and American bond option under the Hull White extended Vasicek model Eva Maria Rapoo 1, Mukendi Mpanda 2
1 Academic Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics /August 2013/ UISA Pricing European and American bond option under the Hull White extended Vasicek model Eva Maria Rapoo 1, Mukendi Mpanda 2
Binomial lattice model for stock prices
 Copyright c 2007 by Karl Sigman Binomial lattice model for stock prices Here we model the price of a stock in discrete time by a Markov chain of the recursive form S n+ S n Y n+, n 0, where the {Y i }
Copyright c 2007 by Karl Sigman Binomial lattice model for stock prices Here we model the price of a stock in discrete time by a Markov chain of the recursive form S n+ S n Y n+, n 0, where the {Y i }
Asian Option Pricing Formula for Uncertain Financial Market
 Sun and Chen Journal of Uncertainty Analysis and Applications (215) 3:11 DOI 1.1186/s4467-15-35-7 RESEARCH Open Access Asian Option Pricing Formula for Uncertain Financial Market Jiajun Sun 1 and Xiaowei
Sun and Chen Journal of Uncertainty Analysis and Applications (215) 3:11 DOI 1.1186/s4467-15-35-7 RESEARCH Open Access Asian Option Pricing Formula for Uncertain Financial Market Jiajun Sun 1 and Xiaowei
The Black-Scholes Formula
 FIN-40008 FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS SPRING 2008 The Black-Scholes Formula These notes examine the Black-Scholes formula for European options. The Black-Scholes formula are complex as they are based on the
FIN-40008 FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS SPRING 2008 The Black-Scholes Formula These notes examine the Black-Scholes formula for European options. The Black-Scholes formula are complex as they are based on the
Jung-Soon Hyun and Young-Hee Kim
 J. Korean Math. Soc. 43 (2006), No. 4, pp. 845 858 TWO APPROACHES FOR STOCHASTIC INTEREST RATE OPTION MODEL Jung-Soon Hyun and Young-Hee Kim Abstract. We present two approaches of the stochastic interest
J. Korean Math. Soc. 43 (2006), No. 4, pp. 845 858 TWO APPROACHES FOR STOCHASTIC INTEREST RATE OPTION MODEL Jung-Soon Hyun and Young-Hee Kim Abstract. We present two approaches of the stochastic interest
Simple Arbitrage. Motivated by and partly based on a joint work with T. Sottinen and E. Valkeila. Christian Bender. Saarland University
 Simple Arbitrage Motivated by and partly based on a joint work with T. Sottinen and E. Valkeila Saarland University December, 8, 2011 Problem Setting Financial market with two assets (for simplicity) on
Simple Arbitrage Motivated by and partly based on a joint work with T. Sottinen and E. Valkeila Saarland University December, 8, 2011 Problem Setting Financial market with two assets (for simplicity) on
BINOMIAL OPTIONS PRICING MODEL. Mark Ioffe. Abstract
 BINOMIAL OPTIONS PRICING MODEL Mark Ioffe Abstract Binomial option pricing model is a widespread numerical method of calculating price of American options. In terms of applied mathematics this is simple
BINOMIAL OPTIONS PRICING MODEL Mark Ioffe Abstract Binomial option pricing model is a widespread numerical method of calculating price of American options. In terms of applied mathematics this is simple
LECTURE 9: A MODEL FOR FOREIGN EXCHANGE
 LECTURE 9: A MODEL FOR FOREIGN EXCHANGE 1. Foreign Exchange Contracts There was a time, not so long ago, when a U. S. dollar would buy you precisely.4 British pounds sterling 1, and a British pound sterling
LECTURE 9: A MODEL FOR FOREIGN EXCHANGE 1. Foreign Exchange Contracts There was a time, not so long ago, when a U. S. dollar would buy you precisely.4 British pounds sterling 1, and a British pound sterling
Option Pricing with Time Varying Volatility
 Corso di Laurea Specialistica in Economia, curriculum Models and Methods of Quantitative Economics per la Gestione dell Impresa Prova finale di Laurea Option Pricing with Time Varying Volatility Relatore
Corso di Laurea Specialistica in Economia, curriculum Models and Methods of Quantitative Economics per la Gestione dell Impresa Prova finale di Laurea Option Pricing with Time Varying Volatility Relatore
3 Results. σdx. df =[µ 1 2 σ 2 ]dt+ σdx. Integration both sides will form
![3 Results. σdx. df =[µ 1 2 σ 2 ]dt+ σdx. Integration both sides will form 3 Results. σdx. df =[µ 1 2 σ 2 ]dt+ σdx. Integration both sides will form](/thumbs/36/17521817.jpg) Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 8, No. 1, 107-112 (2014) 107 Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/amis/080112 Forecasting Share Prices of Small Size Companies
Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 8, No. 1, 107-112 (2014) 107 Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/amis/080112 Forecasting Share Prices of Small Size Companies
Review of Basic Options Concepts and Terminology
 Review of Basic Options Concepts and Terminology March 24, 2005 1 Introduction The purchase of an options contract gives the buyer the right to buy call options contract or sell put options contract some
Review of Basic Options Concepts and Terminology March 24, 2005 1 Introduction The purchase of an options contract gives the buyer the right to buy call options contract or sell put options contract some
Volatility Jumps. April 12, 2010
 Volatility Jumps Viktor Todorov and George Tauchen April 12, 2010 Abstract The paper undertakes a non-parametric analysis of the high frequency movements in stock market volatility using very finely sampled
Volatility Jumps Viktor Todorov and George Tauchen April 12, 2010 Abstract The paper undertakes a non-parametric analysis of the high frequency movements in stock market volatility using very finely sampled
Risk-Neutral Valuation of Participating Life Insurance Contracts
 Risk-Neutral Valuation of Participating Life Insurance Contracts DANIEL BAUER with R. Kiesel, A. Kling, J. Russ, and K. Zaglauer ULM UNIVERSITY RTG 1100 AND INSTITUT FÜR FINANZ- UND AKTUARWISSENSCHAFTEN
Risk-Neutral Valuation of Participating Life Insurance Contracts DANIEL BAUER with R. Kiesel, A. Kling, J. Russ, and K. Zaglauer ULM UNIVERSITY RTG 1100 AND INSTITUT FÜR FINANZ- UND AKTUARWISSENSCHAFTEN
Derivatives: Principles and Practice
 Derivatives: Principles and Practice Rangarajan K. Sundaram Stern School of Business New York University New York, NY 10012 Sanjiv R. Das Leavey School of Business Santa Clara University Santa Clara, CA
Derivatives: Principles and Practice Rangarajan K. Sundaram Stern School of Business New York University New York, NY 10012 Sanjiv R. Das Leavey School of Business Santa Clara University Santa Clara, CA
The Heston Model. Hui Gong, UCL http://www.homepages.ucl.ac.uk/ ucahgon/ May 6, 2014
 Hui Gong, UCL http://www.homepages.ucl.ac.uk/ ucahgon/ May 6, 2014 Generalized SV models Vanilla Call Option via Heston Itô s lemma for variance process Euler-Maruyama scheme Implement in Excel&VBA 1.
Hui Gong, UCL http://www.homepages.ucl.ac.uk/ ucahgon/ May 6, 2014 Generalized SV models Vanilla Call Option via Heston Itô s lemma for variance process Euler-Maruyama scheme Implement in Excel&VBA 1.
Spikes. Shijie Deng 1. Georgia Institute of Technology. E-mail: [email protected]. First draft: November 20, 1998
 Stochastic Models of Energy ommodity Prices and Their Applications: Mean-reversion with Jumps and Spikes Shijie Deng Industrial and Systems Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA 3332-25
Stochastic Models of Energy ommodity Prices and Their Applications: Mean-reversion with Jumps and Spikes Shijie Deng Industrial and Systems Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA 3332-25
Grey Brownian motion and local times
 Grey Brownian motion and local times José Luís da Silva 1,2 (Joint work with: M. Erraoui 3 ) 2 CCM - Centro de Ciências Matemáticas, University of Madeira, Portugal 3 University Cadi Ayyad, Faculty of
Grey Brownian motion and local times José Luís da Silva 1,2 (Joint work with: M. Erraoui 3 ) 2 CCM - Centro de Ciências Matemáticas, University of Madeira, Portugal 3 University Cadi Ayyad, Faculty of
A new Feynman-Kac-formula for option pricing in Lévy models
 A new Feynman-Kac-formula for option pricing in Lévy models Kathrin Glau Department of Mathematical Stochastics, Universtity of Freiburg (Joint work with E. Eberlein) 6th World Congress of the Bachelier
A new Feynman-Kac-formula for option pricing in Lévy models Kathrin Glau Department of Mathematical Stochastics, Universtity of Freiburg (Joint work with E. Eberlein) 6th World Congress of the Bachelier
Numerical Methods for Pricing Exotic Options
 Imperial College London Department of Computing Numerical Methods for Pricing Exotic Options by Hardik Dave - 00517958 Supervised by Dr. Daniel Kuhn Second Marker: Professor Berç Rustem Submitted in partial
Imperial College London Department of Computing Numerical Methods for Pricing Exotic Options by Hardik Dave - 00517958 Supervised by Dr. Daniel Kuhn Second Marker: Professor Berç Rustem Submitted in partial
Valuation of Asian Options
 Valuation of Asian Options - with Levy Approximation Master thesis in Economics Jan 2014 Author: Aleksandra Mraovic, Qian Zhang Supervisor: Frederik Lundtofte Department of Economics Abstract Asian options
Valuation of Asian Options - with Levy Approximation Master thesis in Economics Jan 2014 Author: Aleksandra Mraovic, Qian Zhang Supervisor: Frederik Lundtofte Department of Economics Abstract Asian options
A non-gaussian Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process for electricity spot price modeling and derivatives pricing
 A non-gaussian Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process for electricity spot price modeling and derivatives pricing Thilo Meyer-Brandis Center of Mathematics for Applications / University of Oslo Based on joint work
A non-gaussian Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process for electricity spot price modeling and derivatives pricing Thilo Meyer-Brandis Center of Mathematics for Applications / University of Oslo Based on joint work
From CFD to computational finance (and back again?)
 computational finance p. 1/21 From CFD to computational finance (and back again?) Mike Giles [email protected] Oxford University Mathematical Institute Oxford-Man Institute of Quantitative Finance
computational finance p. 1/21 From CFD to computational finance (and back again?) Mike Giles [email protected] Oxford University Mathematical Institute Oxford-Man Institute of Quantitative Finance
CS 522 Computational Tools and Methods in Finance Robert Jarrow Lecture 1: Equity Options
 CS 5 Computational Tools and Methods in Finance Robert Jarrow Lecture 1: Equity Options 1. Definitions Equity. The common stock of a corporation. Traded on organized exchanges (NYSE, AMEX, NASDAQ). A common
CS 5 Computational Tools and Methods in Finance Robert Jarrow Lecture 1: Equity Options 1. Definitions Equity. The common stock of a corporation. Traded on organized exchanges (NYSE, AMEX, NASDAQ). A common
Flash crashes and order avalanches
 Flash crashes and order avalanches Friedrich Hubalek and Thorsten Rheinländer Vienna University of Technology November 29, 2014 Friedrich Hubalek and Thorsten Rheinländer (Vienna Flash University crashes
Flash crashes and order avalanches Friedrich Hubalek and Thorsten Rheinländer Vienna University of Technology November 29, 2014 Friedrich Hubalek and Thorsten Rheinländer (Vienna Flash University crashes
Black-Scholes Equation for Option Pricing
 Black-Scholes Equation for Option Pricing By Ivan Karmazin, Jiacong Li 1. Introduction In early 1970s, Black, Scholes and Merton achieved a major breakthrough in pricing of European stock options and there
Black-Scholes Equation for Option Pricing By Ivan Karmazin, Jiacong Li 1. Introduction In early 1970s, Black, Scholes and Merton achieved a major breakthrough in pricing of European stock options and there
On the Existence of a Unique Optimal Threshold Value for the Early Exercise of Call Options
 On the Existence of a Unique Optimal Threshold Value for the Early Exercise of Call Options Patrick Jaillet Ehud I. Ronn Stathis Tompaidis July 2003 Abstract In the case of early exercise of an American-style
On the Existence of a Unique Optimal Threshold Value for the Early Exercise of Call Options Patrick Jaillet Ehud I. Ronn Stathis Tompaidis July 2003 Abstract In the case of early exercise of an American-style
Lecture 1: Stochastic Volatility and Local Volatility
 Lecture 1: Stochastic Volatility and Local Volatility Jim Gatheral, Merrill Lynch Case Studies in Financial Modelling Course Notes, Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Fall Term, 2002 Abstract
Lecture 1: Stochastic Volatility and Local Volatility Jim Gatheral, Merrill Lynch Case Studies in Financial Modelling Course Notes, Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Fall Term, 2002 Abstract
The interest volatility surface
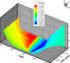 The interest volatility surface David Kohlberg Kandidatuppsats i matematisk statistik Bachelor Thesis in Mathematical Statistics Kandidatuppsats 2011:7 Matematisk statistik Juni 2011 www.math.su.se Matematisk
The interest volatility surface David Kohlberg Kandidatuppsats i matematisk statistik Bachelor Thesis in Mathematical Statistics Kandidatuppsats 2011:7 Matematisk statistik Juni 2011 www.math.su.se Matematisk
Stocks paying discrete dividends: modelling and option pricing
 Stocks paying discrete dividends: modelling and option pricing Ralf Korn 1 and L. C. G. Rogers 2 Abstract In the Black-Scholes model, any dividends on stocks are paid continuously, but in reality dividends
Stocks paying discrete dividends: modelling and option pricing Ralf Korn 1 and L. C. G. Rogers 2 Abstract In the Black-Scholes model, any dividends on stocks are paid continuously, but in reality dividends
The Black-Scholes-Merton Approach to Pricing Options
 he Black-Scholes-Merton Approach to Pricing Options Paul J Atzberger Comments should be sent to: atzberg@mathucsbedu Introduction In this article we shall discuss the Black-Scholes-Merton approach to determining
he Black-Scholes-Merton Approach to Pricing Options Paul J Atzberger Comments should be sent to: atzberg@mathucsbedu Introduction In this article we shall discuss the Black-Scholes-Merton approach to determining
More Exotic Options. 1 Barrier Options. 2 Compound Options. 3 Gap Options
 More Exotic Options 1 Barrier Options 2 Compound Options 3 Gap Options More Exotic Options 1 Barrier Options 2 Compound Options 3 Gap Options Definition; Some types The payoff of a Barrier option is path
More Exotic Options 1 Barrier Options 2 Compound Options 3 Gap Options More Exotic Options 1 Barrier Options 2 Compound Options 3 Gap Options Definition; Some types The payoff of a Barrier option is path
第 9 讲 : 股 票 期 权 定 价 : B-S 模 型 Valuing Stock Options: The Black-Scholes Model
 1 第 9 讲 : 股 票 期 权 定 价 : B-S 模 型 Valuing Stock Options: The Black-Scholes Model Outline 有 关 股 价 的 假 设 The B-S Model 隐 性 波 动 性 Implied Volatility 红 利 与 期 权 定 价 Dividends and Option Pricing 美 式 期 权 定 价 American
1 第 9 讲 : 股 票 期 权 定 价 : B-S 模 型 Valuing Stock Options: The Black-Scholes Model Outline 有 关 股 价 的 假 设 The B-S Model 隐 性 波 动 性 Implied Volatility 红 利 与 期 权 定 价 Dividends and Option Pricing 美 式 期 权 定 价 American
How To Understand The Theory Of Probability
 Graduate Programs in Statistics Course Titles STAT 100 CALCULUS AND MATR IX ALGEBRA FOR STATISTICS. Differential and integral calculus; infinite series; matrix algebra STAT 195 INTRODUCTION TO MATHEMATICAL
Graduate Programs in Statistics Course Titles STAT 100 CALCULUS AND MATR IX ALGEBRA FOR STATISTICS. Differential and integral calculus; infinite series; matrix algebra STAT 195 INTRODUCTION TO MATHEMATICAL
Martingale Pricing Applied to Options, Forwards and Futures
 IEOR E4706: Financial Engineering: Discrete-Time Asset Pricing Fall 2005 c 2005 by Martin Haugh Martingale Pricing Applied to Options, Forwards and Futures We now apply martingale pricing theory to the
IEOR E4706: Financial Engineering: Discrete-Time Asset Pricing Fall 2005 c 2005 by Martin Haugh Martingale Pricing Applied to Options, Forwards and Futures We now apply martingale pricing theory to the
OPTIONS, FUTURES, & OTHER DERIVATI
 Fifth Edition OPTIONS, FUTURES, & OTHER DERIVATI John C. Hull Maple Financial Group Professor of Derivatives and Risk Manage, Director, Bonham Center for Finance Joseph L. Rotinan School of Management
Fifth Edition OPTIONS, FUTURES, & OTHER DERIVATI John C. Hull Maple Financial Group Professor of Derivatives and Risk Manage, Director, Bonham Center for Finance Joseph L. Rotinan School of Management
Notes on Black-Scholes Option Pricing Formula
 . Notes on Black-Scholes Option Pricing Formula by De-Xing Guan March 2006 These notes are a brief introduction to the Black-Scholes formula, which prices the European call options. The essential reading
. Notes on Black-Scholes Option Pricing Formula by De-Xing Guan March 2006 These notes are a brief introduction to the Black-Scholes formula, which prices the European call options. The essential reading
Does Black-Scholes framework for Option Pricing use Constant Volatilities and Interest Rates? New Solution for a New Problem
 Does Black-Scholes framework for Option Pricing use Constant Volatilities and Interest Rates? New Solution for a New Problem Gagan Deep Singh Assistant Vice President Genpact Smart Decision Services Financial
Does Black-Scholes framework for Option Pricing use Constant Volatilities and Interest Rates? New Solution for a New Problem Gagan Deep Singh Assistant Vice President Genpact Smart Decision Services Financial
Math 526: Brownian Motion Notes
 Math 526: Brownian Motion Notes Definition. Mike Ludkovski, 27, all rights reserved. A stochastic process (X t ) is called Brownian motion if:. The map t X t (ω) is continuous for every ω. 2. (X t X t
Math 526: Brownian Motion Notes Definition. Mike Ludkovski, 27, all rights reserved. A stochastic process (X t ) is called Brownian motion if:. The map t X t (ω) is continuous for every ω. 2. (X t X t
Pricing Barrier Options under Local Volatility
 Abstract Pricing Barrier Options under Local Volatility Artur Sepp Mail: [email protected], Web: www.hot.ee/seppar 16 November 2002 We study pricing under the local volatility. Our research is mainly
Abstract Pricing Barrier Options under Local Volatility Artur Sepp Mail: [email protected], Web: www.hot.ee/seppar 16 November 2002 We study pricing under the local volatility. Our research is mainly
LogNormal stock-price models in Exams MFE/3 and C/4
 Making sense of... LogNormal stock-price models in Exams MFE/3 and C/4 James W. Daniel Austin Actuarial Seminars http://www.actuarialseminars.com June 26, 2008 c Copyright 2007 by James W. Daniel; reproduction
Making sense of... LogNormal stock-price models in Exams MFE/3 and C/4 James W. Daniel Austin Actuarial Seminars http://www.actuarialseminars.com June 26, 2008 c Copyright 2007 by James W. Daniel; reproduction
Stochastic Skew Models for FX Options
 Stochastic Skew Models for FX Options Peter Carr Bloomberg LP and Courant Institute, NYU Liuren Wu Zicklin School of Business, Baruch College Special thanks to Bruno Dupire, Harvey Stein, Arun Verma, and
Stochastic Skew Models for FX Options Peter Carr Bloomberg LP and Courant Institute, NYU Liuren Wu Zicklin School of Business, Baruch College Special thanks to Bruno Dupire, Harvey Stein, Arun Verma, and
Introduction to Arbitrage-Free Pricing: Fundamental Theorems
 Introduction to Arbitrage-Free Pricing: Fundamental Theorems Dmitry Kramkov Carnegie Mellon University Workshop on Interdisciplinary Mathematics, Penn State, May 8-10, 2015 1 / 24 Outline Financial market
Introduction to Arbitrage-Free Pricing: Fundamental Theorems Dmitry Kramkov Carnegie Mellon University Workshop on Interdisciplinary Mathematics, Penn State, May 8-10, 2015 1 / 24 Outline Financial market
Properties of the SABR model
 U.U.D.M. Project Report 2011:11 Properties of the SABR model Nan Zhang Examensarbete i matematik, 30 hp Handledare och examinator: Johan Tysk Juni 2011 Department of Mathematics Uppsala University ABSTRACT
U.U.D.M. Project Report 2011:11 Properties of the SABR model Nan Zhang Examensarbete i matematik, 30 hp Handledare och examinator: Johan Tysk Juni 2011 Department of Mathematics Uppsala University ABSTRACT
ELECTRICITY REAL OPTIONS VALUATION
 Vol. 37 (6) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 11 ELECTRICITY REAL OPTIONS VALUATION Ewa Broszkiewicz-Suwaj Hugo Steinhaus Center, Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science Wrocław University of Technology
Vol. 37 (6) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 11 ELECTRICITY REAL OPTIONS VALUATION Ewa Broszkiewicz-Suwaj Hugo Steinhaus Center, Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science Wrocław University of Technology
The Constant Elasticity of Variance Option Pricing Model
 The Constant Elasticity of Variance Option Pricing Model John Randal A thesis submitted to the Victoria University of Wellington in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
The Constant Elasticity of Variance Option Pricing Model John Randal A thesis submitted to the Victoria University of Wellington in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
Simulating Stochastic Differential Equations
 Monte Carlo Simulation: IEOR E473 Fall 24 c 24 by Martin Haugh Simulating Stochastic Differential Equations 1 Brief Review of Stochastic Calculus and Itô s Lemma Let S t be the time t price of a particular
Monte Carlo Simulation: IEOR E473 Fall 24 c 24 by Martin Haugh Simulating Stochastic Differential Equations 1 Brief Review of Stochastic Calculus and Itô s Lemma Let S t be the time t price of a particular
COMPLETE MARKETS DO NOT ALLOW FREE CASH FLOW STREAMS
 COMPLETE MARKETS DO NOT ALLOW FREE CASH FLOW STREAMS NICOLE BÄUERLE AND STEFANIE GRETHER Abstract. In this short note we prove a conjecture posed in Cui et al. 2012): Dynamic mean-variance problems in
COMPLETE MARKETS DO NOT ALLOW FREE CASH FLOW STREAMS NICOLE BÄUERLE AND STEFANIE GRETHER Abstract. In this short note we prove a conjecture posed in Cui et al. 2012): Dynamic mean-variance problems in
The real P&L in Black-Scholes and Dupire Delta hedging
 International Journal of Theoretical and Applied Finance c World Scientific Publishing Company The real P&L in Black-Scholes and Dupire Delta hedging MARTIN FORDE University of Bristol, Department of Mathematics,
International Journal of Theoretical and Applied Finance c World Scientific Publishing Company The real P&L in Black-Scholes and Dupire Delta hedging MARTIN FORDE University of Bristol, Department of Mathematics,
Barrier Options. Peter Carr
 Barrier Options Peter Carr Head of Quantitative Financial Research, Bloomberg LP, New York Director of the Masters Program in Math Finance, Courant Institute, NYU March 14th, 2008 What are Barrier Options?
Barrier Options Peter Carr Head of Quantitative Financial Research, Bloomberg LP, New York Director of the Masters Program in Math Finance, Courant Institute, NYU March 14th, 2008 What are Barrier Options?
Monte Carlo Simulation
 Monte Carlo Simulation Palisade User Conference 2007 Real Options Analysis Dr. Colin Beardsley, Managing Director Risk-Return Solutions Pty Limited www.riskreturnsolutions.com The Plot Today We will review
Monte Carlo Simulation Palisade User Conference 2007 Real Options Analysis Dr. Colin Beardsley, Managing Director Risk-Return Solutions Pty Limited www.riskreturnsolutions.com The Plot Today We will review
Introduction to portfolio insurance. Introduction to portfolio insurance p.1/41
 Introduction to portfolio insurance Introduction to portfolio insurance p.1/41 Portfolio insurance Maintain the portfolio value above a certain predetermined level (floor) while allowing some upside potential.
Introduction to portfolio insurance Introduction to portfolio insurance p.1/41 Portfolio insurance Maintain the portfolio value above a certain predetermined level (floor) while allowing some upside potential.
Alternative Price Processes for Black-Scholes: Empirical Evidence and Theory
 Alternative Price Processes for Black-Scholes: Empirical Evidence and Theory Samuel W. Malone April 19, 2002 This work is supported by NSF VIGRE grant number DMS-9983320. Page 1 of 44 1 Introduction This
Alternative Price Processes for Black-Scholes: Empirical Evidence and Theory Samuel W. Malone April 19, 2002 This work is supported by NSF VIGRE grant number DMS-9983320. Page 1 of 44 1 Introduction This
Fundamentals of Actuarial Mathematics. 3rd Edition
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2866022/ Fundamentals of Actuarial Mathematics. 3rd Edition Description: - Provides a comprehensive coverage of both the deterministic
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2866022/ Fundamentals of Actuarial Mathematics. 3rd Edition Description: - Provides a comprehensive coverage of both the deterministic
Numerical Methods for Pricing Exotic Options
 Numerical Methods for Pricing Exotic Options Dimitra Bampou Supervisor: Dr. Daniel Kuhn Second Marker: Professor Berç Rustem 18 June 2008 2 Numerical Methods for Pricing Exotic Options 0BAbstract 3 Abstract
Numerical Methods for Pricing Exotic Options Dimitra Bampou Supervisor: Dr. Daniel Kuhn Second Marker: Professor Berç Rustem 18 June 2008 2 Numerical Methods for Pricing Exotic Options 0BAbstract 3 Abstract
How To Price A Call Option
 Now by Itô s formula But Mu f and u g in Ū. Hence τ θ u(x) =E( Mu(X) ds + u(x(τ θ))) 0 τ θ u(x) E( f(x) ds + g(x(τ θ))) = J x (θ). 0 But since u(x) =J x (θ ), we consequently have u(x) =J x (θ ) = min
Now by Itô s formula But Mu f and u g in Ū. Hence τ θ u(x) =E( Mu(X) ds + u(x(τ θ))) 0 τ θ u(x) E( f(x) ds + g(x(τ θ))) = J x (θ). 0 But since u(x) =J x (θ ), we consequently have u(x) =J x (θ ) = min
Hedging Options In The Incomplete Market With Stochastic Volatility. Rituparna Sen Sunday, Nov 15
 Hedging Options In The Incomplete Market With Stochastic Volatility Rituparna Sen Sunday, Nov 15 1. Motivation This is a pure jump model and hence avoids the theoretical drawbacks of continuous path models.
Hedging Options In The Incomplete Market With Stochastic Volatility Rituparna Sen Sunday, Nov 15 1. Motivation This is a pure jump model and hence avoids the theoretical drawbacks of continuous path models.
Private Equity Fund Valuation and Systematic Risk
 An Equilibrium Approach and Empirical Evidence Axel Buchner 1, Christoph Kaserer 2, Niklas Wagner 3 Santa Clara University, March 3th 29 1 Munich University of Technology 2 Munich University of Technology
An Equilibrium Approach and Empirical Evidence Axel Buchner 1, Christoph Kaserer 2, Niklas Wagner 3 Santa Clara University, March 3th 29 1 Munich University of Technology 2 Munich University of Technology
An Analytical Pricing Formula for VIX Futures and Its Empirical Applications
 Faculty of Informatics, University of Wollongong An Analytical Pricing Formula for VIX Futures and Its Empirical Applications Song-Ping Zhu and Guang-Hua Lian School of Mathematics and Applied Statistics
Faculty of Informatics, University of Wollongong An Analytical Pricing Formula for VIX Futures and Its Empirical Applications Song-Ping Zhu and Guang-Hua Lian School of Mathematics and Applied Statistics
