Barrett s oesophagus: specimen handling and reporting
|
|
|
- Wesley Jackson
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Barrett s oesophagus: specimen handling and reporting Professor Neil A Shepherd Gloucester and Cheltenham, UK
2 The role of the pathologist in Barrett s oesophagus 1. Diagnosis 2. Typing 3. Assessing response to treatment 4. The diagnosis of neoplasia and surveillance
3 The role of the pathologist in Barrett s oesophagus 1. Diagnosis 2. Typing 3. Assessing response to treatment 4. The diagnosis of neoplasia and surveillance
4 Barrett s oesophagus at endoscopy
5 Endoscopist vs. the pathologist long segment CLO is on the whole an endoscopic diagnosis short segment may need pathology much more USSCLO (cardia IM) is entirely a pathological diagnosis
6 The pathologist reporting CLO Perfect world download endoscopy report & images Real world Clinical information:? Barrett s oesophagus full knowledge of site of generous biopsies with diagnostic features two (if you re lucky) scrappy biopsies without specific features
7
8 Reporting CLO Hellier & Shepherd, 2005 Diagnostic for CLO: Native oesophageal structures are present with juxtaposition to metaplastic glandular mucosa, whether intestinalised or not About 10 to 15% of biopsy sets Takubo et al 1995, UKBOR 2003 Biopsies corroborative of an endoscopic diagnosis of CLO: Intestinalised metaplastic glandular mucosa with or without non-organoid arrangement, villous architecture, patchwork of different glandular types, etc. This could potentially still represent incomplete intestinal metaplasia in the stomach, especially in a hiatus hernia or IM at the cardia. Biopsies in keeping with, but not specific for, CLO: Gastric-type mucosa of either fundic or cardiac type without IM. Patchwork appearance is still possible, as is a non-organoid arrangement. Such appearances could, however, represent the oesophago-gastric junction or the stomach within or without a hiatus hernia.
9 the IM/goblet cell question should Barrett s be defined/diagnosed by showing intestinal metaplasia/goblet cells on biopsy?
10 The influence of the number of biopsies on the demonstration of IM in classical CLO Harrison et al, % with IM vs number of biopsies taken
11 The influence of the number of biopsies on the demonstration of IM in classical CLO >9 No of Biopsies United Kingdom Barrett s Oesophagus Registry (UKBOR) study diagnostic biopsies of 200 patients Mandalia & Shepherd, 2010
12 Definition of Barrett's esophagus: time for a rethink is intestinal metaplasia dead? Riddell RH, Odze RD: Am J Gastroenterol, 2009 goblet cells are uncommon in pediatric patients with BE small percentage of adults have CLO without goblet cells the chances of detecting goblet cells proportional to the length of CLO sampling error common interpretation & differentiation of goblet cells vs. pseudogoblet cells difficult in some circumstances. goblet cells have been shown to wax and wane over the natural history of BE background non-goblet epithelium in BE is biologically intestinalised background non-goblet epithelium in BE shows molecular abnormalities similar to the goblet cell-containing epithelium well-defined risk of neoplasia in patients with esophageal columnar metaplasia without goblet cells a diagnosis of BE should not require demonstration of goblet cells in mucosal biopsies guidelines for the diagnosis of BE need to consider revisions that take into account new data
13 Intestinal differentiation in metaplastic, non-goblet columnar epithelium in the esophagus 89 patients with CLO immunohistochemistry for markers of intestinal differentiation: MUC2, DAS-1, villin and cdx2 metaplastic esophageal columnar epithelium without goblet cells shows phenotypic evidence of intestinal differentiation supports the theory that squamous epithelium converts initially to non-goblet columnar epithelium before goblet cell metaplasia Hahn HP et al, Am J Surg Pathol, 2009
14 Pathology and the diagnosis of CLO the IM/goblet cell/specialised IM story was always tosh and has now been shown to be by the two best known GI pathologists worldwide the BSG reporting guidelines are still valid there are pathological features of CLO that are still diagnostic (juxtaposed native structures, hybrid glands,? MLE) but these are all unusual I (and others) am becoming more and more convinced that pathology has little or no role in the diagnosis of CLO except when there is stricturing, ulceration or short segment disease (but even then it is difficult pathologically)
15 The role of the pathologist in Barrett s oesophagus 1. Diagnosis 2. Typing 3. Assessing response to treatment 4. The diagnosis of neoplasia and surveillance
16 Typing Barrett s oesophagus: Paull et al, 1976 fundic is it really hiatus hernia? cardiac it may be intestinalised, it s just that we can t see it on H&E intestinal incomplete, complete pancreatic half-way houses hybrid glands, multilayered epithelium
17 The role of the pathologist in Barrett s oesophagus 1. Diagnosis 2. Typing 3. Assessing response to treatment 4. The diagnosis of neoplasia and surveillance
18 Surface squamous re-epithelialisation, especially after ablation therapy
19 Squamous re-epithelialisation with mimicry of glandular dysplasia
20 Squamous re-epithelialisation over glandular dysplasia mimicking invasive adenocarcinoma
21 The role of the pathologist in Barrett s oesophagus 1. Diagnosis 2. Typing 3. Assessing response to treatment 4. The diagnosis of neoplasia and surveillance
22 EMR in Barrett s oesophagus
23
24 Management of dysplasia H Barr, NA Shepherd Indefinite for dysplasia early re-evaluation with extensive biopsies following a course of PPI. Low grade dysplasia extensive biopsies after intensive acid suppression for 8-12 weeks. 6-monthly surveillance as long as disease is stable. High grade dysplasia if changes persist after intensive acid suppression and HGD is confirmed by two pathologists, oesophagectomy in specialised unit recommended. ablative therapy for patients unfit for surgery.
25 The average long segment CLO surveillance case with Seattle biopsies 40 biopsy pots 352 individual sections
26 From microscope to smart endoscope for the diagnosis of neoplasia in Barrett s oesophagus
27 Newer techniques for the in-situ detection of neoplastic change in CLO magnification and high resolution endoscopy chromo-endoscopy auto-fluorescence endoscopy narrow band imaging microscopic tools confocal microscopy multiphoton microscopy in situ molecular analysis FISH spectroscopic analysis fluorescence spectroscopy light scattering spectroscopy optical coherence spectroscopy Raman (inelastic) spectroscopy
28 Standard endoscopic view of CLO with HGD: no lesion identified
29 Auto-fluorescence image: purple is abnormal and showed HGD on histology
30 Narrow band image of same abnormal area: HGD on histology
31 Chromo-endoscopy with indigo carmine dye-spray: HGD on histology - now for EMR
32 Management of neoplasia in CLO: the present (in some places) and the future less major surgery trimodal endoscopy means the endoscopist spends the time and not the pathologist!! directed biopsies after such endoscopy and not random Seattle protocols EMR to determine the indication for major surgery more sensible patient-directed management
33
34
35 The limitations of biopsy and advantages of EMR Biopsy EMR Size Size is important Depth - no submucosa in stomach - usually no submucosa in oesophagus Depth - usually submucosa in both stomach and oesophagus Artefact Less artefact (depends on size)
36 Nice low grade dysplasia in EMR EMR makes histological assessment so much easier
37 Uses of EMR in the upper GI tract good-sized biopsy of lesion which has provided difficult/equivocal pathological results in repeated standard biopsy procedures complete excision of benign tumorous nodules with ability to judge completeness of excision (cf multiple biopsy chews) (eg GCTs of oesophagus, some endocrine tumours of stomach) complete excision and complete pathological assessment of early gastric cancers to provide definitive pathology and thus a guide to further management of neoplastic lesions of the oesophagus
38 69F. Long history of achalasia. Nodule close to OGJ. Multiple biopsies at three endoscopic sittings had provided equivocal results. EMR.
39 Oesophageal EMR Olympus/Keymed inject submucosa and form pseudopolyp, direct snare Cook Duette band EMR band ligation and snare methodology and subsequent therapy likely influences how important margins are
40 Problem with EMR for early CLO neoplasia Metachronous lesions during FU: 30% Combine with ablative therapy.
41 Oesophageal EMR Practicalities size and number depends on preferred technique of endoscopist (please make em big!) specimen preparation don t let them leave the band still attached! orientation adequate fixation specimen dissection depends on size we are more interested in the deep margin than peripheral margins
42 close collaboration with endoscopist and assistant to identify important landmarks resect en bloc if possible keep specimen(s) intact pin out on cork mark margins embed whole specimen(s) for histology
43 Oesophageal EMR by HB: size matters size number less than 6 mm mm 76 greater than 10 mm 46
44 Oesophageal EMR size matters
45 Oesophageal EMR band artefact
46 Oesophageal EMRs
47
48 Margin fragment
49 Oesophageal EMR The final diagnostic step and the first therapeutic step Jacques Bergman, 2007
50 The rationale for EMR in CLO Histological assessment of EMR Intramucosal pathology Submucosal involvement by carcinoma Endoscopic treatment and/or survelliance Referral for surgery
51 The rationale for EMR in CLO: risk of lymph node metastatic disease intramucosal disease Bergman, 2007 submucosal disease adenocarcinoma 2.0% 24.6% squamous cell carcinoma 3.6% 26% For mucosal disease, the surgical mortality outweighs the risk of metastasis
52 What are the diagnostic pathological issues in oesophageal EMR?
53 HGD versus intramucosal carcinoma
54 Entrapped and submucosal glands mimicking submucosal adenocarcinoma
55 Reporting oesophageal EMRs is it Barrett s? are there treatment effects? neoplasia diagnosis depth of spread lymphovascular spread peripheral margins status deep margin status
56 Oesophageal EMR by HB diagnosis and complete excision CLO only 21 Squamous only 9 Gastric mucosa only 7 LGD excised 5 LGD at margins 9 HGD excised 9 HGD at margins 36 IMC excised 4 IMC at margins 12 Ca into SM excised 8 Ca into SM at margins 17 Total 137
57 Low grade dysplasia at margins
58 Oesophageal EMR in Gloucestershire we have now done about 600 number of normals reflects endoscopic difficulties benign nodules in CLO, hiatus hernia, etc LGD and HGD often at margins reflects endoscopic difficulties matters less because of subsequent ablative therapy IMC often at margins don t know the implications of this but one suspects that this, too, will be successfully ablated submucosal adenocarcinoma (ironically) more often clear of margins but doesn t matter much as this is an indication for radical surgery
59 Oesophageal EMR pathology is important, mainly to confirm or refute: the presence of malignancy if present, depth of malignancy margins matter less (but this does depend on subsequent management strategy)
60 CLO and the double muscularis mucosae and entrapment of dysplastic epithelium Takubo et al, 1991, Lewis et al, 2008
61 CLO and the double muscularis mucosae Takubo et al, 1991, Lewis et al, 2008
62 Lewis JT, Wang KK, Abraham SC. Muscularis mucosae duplication and the musculo-fibrous anomaly in endoscopic mucosal resections for Barrett esophagus: implications for staging of adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 2008; 32: EMR specimens from 100 patients from 1999 to 2006 prolapse changes in 65 (54%) cases & gland entrapment in 67 (56%). 33 cases of IMAC, tumor invaded lamina propria in 10 (30%), inner or single MM in 14 (42%), space between duplicated MM in 5 (15%), and outer MM layer in 4(12%). lymphatic invasion was seen in 2 (10%) cases in which tumor reached the space between MM layers. overstaging of carcinoma in 7% due to misinterpretation of anatomy one case where deep MM was interpreted as muscularis propria.
63 Staging of adenocarcinoma in EMRs European/Bergmann pt1 m1, m2, m3 Bayreuth/Vieth pt1 m1, m2, m3, m4 spread into the true submucosa remains the most important arbiter for resection need more data on the niceties of intramucosal staging
64 pt 1 (m1) pt 1 (m2) pt 1 (m3) pt 1 (m4) pt 1 (sm1)
65 Frequency of vessel permeation in Barrett s adenocarcinoma Invasion n L1 Barrett-Ca pt1 m (0,8%) m m m (2,8%) Barrett-Ca pt1 sm (13,3%) sm (12,5%) sm (26,3%) Vieth et al, 2005
66 Is it in the submucosa?
67 Is it in the submucosa?
68 retrospective analysis of post-emr biopsies in 33 patients who underwent gastric EMR inflammation (100%), stromal edema (97.0%), foveolar hyperplasia (78.8%), ectatic vessels (66.7%), epithelial atypia (60.6%), increased glandular mitoses (57.6%), epithelial anisonucleosis (54.5%), fibrinopurulent materials (51.5%), ischemia (48.5%), stromal hemorrhage (33.3%), mucin depletion (12.1%), clear cell degeneration (15.2%), and signet-ring cell-like change (6.1%) clear cell degeneration and signet-ring cell-like change in areas of ischaemia (1-16 days post-emr) degenerative glands were usually embedded in a nondesmoplastic stroma and showed anisonucleosis of glandular epithelia. mimics of residual adenocarcinoma, namely clear cell degeneration and signet-ring cell-like change, should be judiciously assessed to avoid unnecessary surgery Mitsuhashi T, Lauwers GY, et al, Am J Surg Pathol 2006; 30: 650-6
69 Mitsuhashi T, Lauwers GY, et al, Am J Surg Pathol 2006; 30: 650-6
70 Mitsuhashi T, Lauwers GY, et al, Am J Surg Pathol 2006; 30: 650-6
71 Artefact to the left and carcinoma to the right Mitsuhashi T, Lauwers GY, et al, Am J Surg Pathol 2006; 30: 650-6
72 The pathology of oesophageal EMR: take home messages the most important assessment is the differentiation of in-situ and intramucosal disease, on the one hand, from submucosal adenocarcinoma, on the other lymphovascular spread is important and is proportional to depth of spread margins may be less important depending on local management strategy duplicated mm, entrapped glands & prolapse changes cause consternation the jury is still out on the utility of intramucosal staging & which system EMRs ease the pathological burden and are generally easier to assess than straggly biopsies don t let them biopsy shortly after an oesophageal or gastric EMR!
How to report Upper GI EMR/ESD specimens
 Section of Pathology and Tumour Biology How to report Upper GI EMR/ESD specimens Dr.H.Grabsch Warning. Most of the criteria, methodologies, evidence presented in this talk are based on studies in early
Section of Pathology and Tumour Biology How to report Upper GI EMR/ESD specimens Dr.H.Grabsch Warning. Most of the criteria, methodologies, evidence presented in this talk are based on studies in early
EMR Can anyone do this?
 EMR Can anyone do this? Norio Fukami, MD University of Colorado Piecemeal resection? 1 Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) Endoscopic removal of premalignant or
EMR Can anyone do this? Norio Fukami, MD University of Colorado Piecemeal resection? 1 Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) Endoscopic removal of premalignant or
Learning Luncheon 7: Endoscopic Mucosal Resection: When, Where and How?
 Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR): When, Where, and Charles J. Lightdale, MD Columbia University New York, NY Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) EMR developed for removal of sessile or flat neoplasms
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR): When, Where, and Charles J. Lightdale, MD Columbia University New York, NY Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) EMR developed for removal of sessile or flat neoplasms
Captivator EMR Device
 Device Clinical Article and Abstract Summary Endoscopic Mucosal Bergman et al: EMR Training Tips Bergman et al: EMR Learning Curve ASGE: EMR & ESD Guidelines Bergman et al: Captivator EMR vs Cook Duette
Device Clinical Article and Abstract Summary Endoscopic Mucosal Bergman et al: EMR Training Tips Bergman et al: EMR Learning Curve ASGE: EMR & ESD Guidelines Bergman et al: Captivator EMR vs Cook Duette
These parameters cannot, at the present time, be determined by non-invasive imaging techniques.
 Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Upper Gastrointestinal Lesions Kenneth K. Wang, M.D. Chairman, WEO Publication and Guidelines Committee Professor of Medicine, Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota Upper gastrointestinal
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Upper Gastrointestinal Lesions Kenneth K. Wang, M.D. Chairman, WEO Publication and Guidelines Committee Professor of Medicine, Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota Upper gastrointestinal
Evolution of Barrett s esophagus
 Endoscopic Treatment and Surveillance of Esophageal Cancer: GI Perspective Charles J. Lightdale, MD Columbia University New York, NY Evolution of Barrett s esophagus Squamous esophagus Chronic inflammation
Endoscopic Treatment and Surveillance of Esophageal Cancer: GI Perspective Charles J. Lightdale, MD Columbia University New York, NY Evolution of Barrett s esophagus Squamous esophagus Chronic inflammation
Endoscopic Resection for Barrett s Esophagus and Early Cancer 2014 Masters of Minimally Invasive Surgery
 Endoscopic Resection for Barrett s Esophagus and Early Cancer 2014 Masters of Minimally Invasive Surgery Matthew Hartwig, M.D. Duke Cancer Institute Case Presentation: Patient ER 51 y/o man with schizophrenia
Endoscopic Resection for Barrett s Esophagus and Early Cancer 2014 Masters of Minimally Invasive Surgery Matthew Hartwig, M.D. Duke Cancer Institute Case Presentation: Patient ER 51 y/o man with schizophrenia
Endoscopic Therapy for Early Esophageal Cancer: EMR and ESD
 Endoscopic Therapy for Early Esophageal Cancer: EMR and ESD AATS Toronto April 26, 2014 Lorenzo Ferri MD PhD David S. Mulder Chair in Surgery Associate Professor of Surgery and Oncology Disclosures Olympus
Endoscopic Therapy for Early Esophageal Cancer: EMR and ESD AATS Toronto April 26, 2014 Lorenzo Ferri MD PhD David S. Mulder Chair in Surgery Associate Professor of Surgery and Oncology Disclosures Olympus
Cancer of the Cardia/GE Junction: Surgical Options
 Cancer of the Cardia/GE Junction: Surgical Options Michael A Smith, MD Associate Chief Thoracic Surgery Center for Thoracic Disease St Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center Phoenix, AZ Michael Smith, MD
Cancer of the Cardia/GE Junction: Surgical Options Michael A Smith, MD Associate Chief Thoracic Surgery Center for Thoracic Disease St Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center Phoenix, AZ Michael Smith, MD
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (E.S.D.) vs. Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (E.M.R.) in Colombia. Advocating E.M.R.
 Controversies in Gastroenterology Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (E.S.D.) vs. Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (E.M.R.) in Colombia. Advocating E.M.R. Raúl Cañadas Garrido, MD. 1 1 Internist-Gastroenterologist.
Controversies in Gastroenterology Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (E.S.D.) vs. Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (E.M.R.) in Colombia. Advocating E.M.R. Raúl Cañadas Garrido, MD. 1 1 Internist-Gastroenterologist.
Endoscopic mucosal resection for treatment of early gastric cancer
 Gut 2001;48:225 229 225 Endoscopic mucosal resection for treatment of early gastric cancer H Ono, H Kondo, T Gotoda, K Shirao, H Yamaguchi, D Saito, K Hosokawa, T Shimoda, S Yoshida Department of Endoscopy
Gut 2001;48:225 229 225 Endoscopic mucosal resection for treatment of early gastric cancer H Ono, H Kondo, T Gotoda, K Shirao, H Yamaguchi, D Saito, K Hosokawa, T Shimoda, S Yoshida Department of Endoscopy
Endotherapy for high grade dysplasia & early oesophageal neoplasia in Barrett s oesophagus: A single centre retrospective audit
 Endotherapy for high grade dysplasia & early oesophageal neoplasia in Barrett s oesophagus: A single centre retrospective audit U Duffy, K Gowland, AI Morris, HL Smart Department of Gastroenterology, Royal
Endotherapy for high grade dysplasia & early oesophageal neoplasia in Barrett s oesophagus: A single centre retrospective audit U Duffy, K Gowland, AI Morris, HL Smart Department of Gastroenterology, Royal
ESD for colorectal lesions I am in favour. Alessandro Repici, MD Digestive Endoscopy Unit IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas Milano, Italy
 ESD for colorectal lesions I am in favour Alessandro Repici, MD Digestive Endoscopy Unit IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas Milano, Italy Surgery for early colonic lesions 51 pts referred for lap colectomy
ESD for colorectal lesions I am in favour Alessandro Repici, MD Digestive Endoscopy Unit IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas Milano, Italy Surgery for early colonic lesions 51 pts referred for lap colectomy
How to treat early gastric cancer. Surgery
 How to treat early gastric cancer Surgery Mark I. van Berge Henegouwen Department of Surgery, AMC, Amsterdam Director upper GI surgical unit Academic Medical Center Upper GI surgery at AMC 100 oesophagectomies
How to treat early gastric cancer Surgery Mark I. van Berge Henegouwen Department of Surgery, AMC, Amsterdam Director upper GI surgical unit Academic Medical Center Upper GI surgery at AMC 100 oesophagectomies
Center for Endoscopic Research & Therapeutics
 Center for Endoscopic Research & Therapeutics 5758 South Maryland Avenue (MC9028) Chicago, Illinois 60637 (773) 702-1459 www.uchospitals.edu Center for Endoscopic Research & Therapeutics To refer a patient
Center for Endoscopic Research & Therapeutics 5758 South Maryland Avenue (MC9028) Chicago, Illinois 60637 (773) 702-1459 www.uchospitals.edu Center for Endoscopic Research & Therapeutics To refer a patient
Endoscopic submucosal dissection: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline
 Guideline 829 Endoscopic submucosal dissection: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline Authors Institutions Pedro Pimentel-Nunes 1, Mário Dinis-Ribeiro 1, Thierry Ponchon 2, Alessandro
Guideline 829 Endoscopic submucosal dissection: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline Authors Institutions Pedro Pimentel-Nunes 1, Mário Dinis-Ribeiro 1, Thierry Ponchon 2, Alessandro
Changes in Breast Cancer Reports After Second Opinion. Dr. Vicente Marco Department of Pathology Hospital Quiron Barcelona. Spain
 Changes in Breast Cancer Reports After Second Opinion Dr. Vicente Marco Department of Pathology Hospital Quiron Barcelona. Spain Second Opinion in Breast Pathology Usually requested when a patient is referred
Changes in Breast Cancer Reports After Second Opinion Dr. Vicente Marco Department of Pathology Hospital Quiron Barcelona. Spain Second Opinion in Breast Pathology Usually requested when a patient is referred
Endoscopic Management of Barrett s High-Grade Dysplasia and Early Stage Esophageal Cancer
 VOLUME 10, ISSUE 2, YEAR 2011 Endoscopic Management of Barrett s High-Grade Dysplasia and Early Stage Esophageal Cancer James L. Wise, MD Duluth, MN. Introduction: In recent years there has been intense
VOLUME 10, ISSUE 2, YEAR 2011 Endoscopic Management of Barrett s High-Grade Dysplasia and Early Stage Esophageal Cancer James L. Wise, MD Duluth, MN. Introduction: In recent years there has been intense
Understanding your pathology report
 Understanding your pathology report 2 Contents Contents Introduction 3 What is a pathology report? 3 Waiting for your results 4 What s in a pathology report? 4 Information about your breast cancer 5 What
Understanding your pathology report 2 Contents Contents Introduction 3 What is a pathology report? 3 Waiting for your results 4 What s in a pathology report? 4 Information about your breast cancer 5 What
Photodynamic Therapy for the Treatment of Barrett s Esophagus: A Systematic Review and Economic Evaluation
 Health Technology & Policy Series; 29:1 Photodynamic Therapy for the Treatment of Barrett s Esophagus: A Systematic Review and Economic Evaluation FINAL REPORT August 29 Submitted to: The Alberta Health
Health Technology & Policy Series; 29:1 Photodynamic Therapy for the Treatment of Barrett s Esophagus: A Systematic Review and Economic Evaluation FINAL REPORT August 29 Submitted to: The Alberta Health
The digestive system. Medicine and technology. Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies
 The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
HOW I DO IT Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) in the esophagus
 HOW I DO IT (EMR) in the esophagus AUTHORSHIP How I do it: Horst Neuhaus, MD Department of Internal Medicine Evangelisches Krankenhaus Düsseldorf Germany Comment Hiroyasu Makuuchi, MD Professor and Chairman
HOW I DO IT (EMR) in the esophagus AUTHORSHIP How I do it: Horst Neuhaus, MD Department of Internal Medicine Evangelisches Krankenhaus Düsseldorf Germany Comment Hiroyasu Makuuchi, MD Professor and Chairman
Bridging Techniques. What s between EMR and Traditional Surgery? Elisabeth C. McLemore, MD, FACS, FASCRS
 Bridging Techniques What s between EMR and Traditional Surgery? Elisabeth C. McLemore, MD, FACS, FASCRS Associate Professor of Surgery Assistant Program Director, General Surgery Residency Disclosures
Bridging Techniques What s between EMR and Traditional Surgery? Elisabeth C. McLemore, MD, FACS, FASCRS Associate Professor of Surgery Assistant Program Director, General Surgery Residency Disclosures
YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...3 The Basics...4 Sections of a Pathology Report...7
UNDERSTANDING YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...3 The Basics...4 Sections of a Pathology Report...7
This is a prospective study that analyzed the factors associated with cancer progression after
 Sample Peer-Review of a Fictitious Manuscript Reviewer A s Comments to Authors: This is a prospective study that analyzed the factors associated with cancer progression after EMR of Barrett s esophagus
Sample Peer-Review of a Fictitious Manuscript Reviewer A s Comments to Authors: This is a prospective study that analyzed the factors associated with cancer progression after EMR of Barrett s esophagus
PROTOCOL OF THE RITA DATA QUALITY STUDY
 PROTOCOL OF THE RITA DATA QUALITY STUDY INTRODUCTION The RITA project is aimed at estimating the burden of rare malignant tumours in Italy using the population based cancer registries (CRs) data. One of
PROTOCOL OF THE RITA DATA QUALITY STUDY INTRODUCTION The RITA project is aimed at estimating the burden of rare malignant tumours in Italy using the population based cancer registries (CRs) data. One of
Safety of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Barrett s Esophagus
 1440 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTIONS nature publishing group see CMErelated editorial on page x Safety of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Barrett s Esophagus Yutaka Tomizawa, MD 1, Prasad G. Iyer, MD 1, Louis
1440 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTIONS nature publishing group see CMErelated editorial on page x Safety of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Barrett s Esophagus Yutaka Tomizawa, MD 1, Prasad G. Iyer, MD 1, Louis
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus
 PRACTICE GUIDELINES nature publishing group 1 ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Nichol as J. Sha he e n, M D, M PH, FAC G 1, Gary W. Falk, MD, MS, FACG 2, Prasad G.
PRACTICE GUIDELINES nature publishing group 1 ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Nichol as J. Sha he e n, M D, M PH, FAC G 1, Gary W. Falk, MD, MS, FACG 2, Prasad G.
HER2 Status: What is the Difference Between Breast and Gastric Cancer?
 Ask the Experts HER2 Status: What is the Difference Between Breast and Gastric Cancer? Bharat Jasani MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Marco Novelli MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Josef Rüschoff, MD Robert Y. Osamura, MD, FIAC
Ask the Experts HER2 Status: What is the Difference Between Breast and Gastric Cancer? Bharat Jasani MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Marco Novelli MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Josef Rüschoff, MD Robert Y. Osamura, MD, FIAC
The Diagnosis of Cancer in the Pathology Laboratory
 The Diagnosis of Cancer in the Pathology Laboratory Dr Edward Sheffield Christmas Select 74 Meeting, Queen s Hotel Cheltenham, 3 rd December 2014 Agenda Overview of the pathology of cancer How specimens
The Diagnosis of Cancer in the Pathology Laboratory Dr Edward Sheffield Christmas Select 74 Meeting, Queen s Hotel Cheltenham, 3 rd December 2014 Agenda Overview of the pathology of cancer How specimens
POEM Procedure for. Esophageal Achalasia
 POEM Procedure for Esophageal Achalasia POEM (Per-Oral endoscopic myotomy) is an incisionless procedure to treat esophageal achalasia, totally performed by endoscopy, without cutting the surface of the
POEM Procedure for Esophageal Achalasia POEM (Per-Oral endoscopic myotomy) is an incisionless procedure to treat esophageal achalasia, totally performed by endoscopy, without cutting the surface of the
Challenges in gastric, appendiceal and rectal NETs Leuven, 29.11.2014
 Challenges in gastric, appendiceal and rectal NETs Leuven, 29.11.2014 Prof. Dr. Chris Verslype, Leuven Prof. Dr. Aurel Perren, Bern Menue Challenges: 1. Gastric NET 2. Appendiceal NET 3. Rectal NET SEER,
Challenges in gastric, appendiceal and rectal NETs Leuven, 29.11.2014 Prof. Dr. Chris Verslype, Leuven Prof. Dr. Aurel Perren, Bern Menue Challenges: 1. Gastric NET 2. Appendiceal NET 3. Rectal NET SEER,
ERBEJET 2. The versatility of waterjet surgery: ERBEJET 2 with hybrid instruments WATERJET SURGERY
 ERBEJET 2 The versatility of waterjet surgery: ERBEJET 2 with hybrid instruments WATERJET SURGERY Gentle interventions in surgery and endoscopy Waterjet surgery with hybrid technology Waterjet surgery
ERBEJET 2 The versatility of waterjet surgery: ERBEJET 2 with hybrid instruments WATERJET SURGERY Gentle interventions in surgery and endoscopy Waterjet surgery with hybrid technology Waterjet surgery
What is Barrett s esophagus? How does Barrett s esophagus develop?
 Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a pre-cancerous condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth
Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a pre-cancerous condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Guidelines for reporting histopathology of cervical carcinoma
 Guidelines for reporting histopathology of cervical carcinoma Naveena Singh, Consultant Pathologist Introduction Cancer management is multidisciplinary Histopathology report has a MAJOR impact on management
Guidelines for reporting histopathology of cervical carcinoma Naveena Singh, Consultant Pathologist Introduction Cancer management is multidisciplinary Histopathology report has a MAJOR impact on management
Ovarian mucinous lesions. Ovarian mucinous lesions: Common diagnostic dilemmas. Ovarian mucinous lesions: problematic issues
 Ovarian mucinous lesions Ovarian mucinous lesions: Common diagnostic dilemmas Karuna Garg, MD University of California San Francisco Intestinal or usual type Seromucinous (Endocervical mucinous or Mullerian
Ovarian mucinous lesions Ovarian mucinous lesions: Common diagnostic dilemmas Karuna Garg, MD University of California San Francisco Intestinal or usual type Seromucinous (Endocervical mucinous or Mullerian
Digestive System Digestive Tract
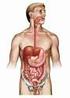 Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
Use of stents in esophageal cancer" Hans Gerdes, M.D. Director, GI Endoscopy Unit Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
 Use of stents in esophageal cancer" Hans Gerdes, M.D. Director, GI Endoscopy Unit Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Features of esophageal cancer Esophageal cancer is an abnormal growth that arises
Use of stents in esophageal cancer" Hans Gerdes, M.D. Director, GI Endoscopy Unit Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Features of esophageal cancer Esophageal cancer is an abnormal growth that arises
ORIGINAL ARTICLE: Clinical Endoscopy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: Clinical Endoscopy Endotherapy for superficial adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: an American experience Shreyas Saligram, MD, MRCP, 1 Jennifer Chennat, MD, 1 Huankai Hu, MD, 2 Jon M. Davison,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE: Clinical Endoscopy Endotherapy for superficial adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: an American experience Shreyas Saligram, MD, MRCP, 1 Jennifer Chennat, MD, 1 Huankai Hu, MD, 2 Jon M. Davison,
Endoscopic eradication of Barrett s esophagus
 TECHNICAL REVIEW Endoscopic eradication of Barrett s esophagus Sachin Wani, MD, Hari Sayana, MD, Prateek Sharma, MD Kansas City, Missouri, USA Barrett s esophagus (BE) is the premalignant lesion of esophageal
TECHNICAL REVIEW Endoscopic eradication of Barrett s esophagus Sachin Wani, MD, Hari Sayana, MD, Prateek Sharma, MD Kansas City, Missouri, USA Barrett s esophagus (BE) is the premalignant lesion of esophageal
Endo Conference: Large Polypectomy & EMR
 Endo Conference: Large Polypectomy & EMR Dr. Whang Feb 3, 2015 VOGELGRAM: genetic pathway of colorectal cancer & genes affected by point mutations Outline I. Baseline Colonoscopy II. Colon Polyps III.
Endo Conference: Large Polypectomy & EMR Dr. Whang Feb 3, 2015 VOGELGRAM: genetic pathway of colorectal cancer & genes affected by point mutations Outline I. Baseline Colonoscopy II. Colon Polyps III.
Horizon Scanning in Surgery: Application to Surgical Education and Practice
 Horizon Scanning in Surgery: Application to Surgical Education and Practice Cryotherapy for Esophageal Cancer May 2012 American College of Surgeons Division of Education Prepared by the Australian Safety
Horizon Scanning in Surgery: Application to Surgical Education and Practice Cryotherapy for Esophageal Cancer May 2012 American College of Surgeons Division of Education Prepared by the Australian Safety
Outline. Workup for metastatic breast cancer. Metastatic breast cancer
 Metastatic breast cancer Immunostain Update: Diagnosis of metastatic breast carcinoma, emphasizing distinction from GYN primary 1/3 of breast cancer patients will show metastasis 1 st presentation or 20-30
Metastatic breast cancer Immunostain Update: Diagnosis of metastatic breast carcinoma, emphasizing distinction from GYN primary 1/3 of breast cancer patients will show metastasis 1 st presentation or 20-30
Barrett s Esophagus and Endoscopic Therapy
 Barrett s Esophagus and Endoscopic Therapy John A. Dumot, DO Department of Gastroenterology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: Research support from CSA Medical Inc. [email protected] Objectives Relationship
Barrett s Esophagus and Endoscopic Therapy John A. Dumot, DO Department of Gastroenterology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: Research support from CSA Medical Inc. [email protected] Objectives Relationship
Histopathology of Colorectal Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation Therapy
 The Open Pathology Journal, 2009, 3, 91-98 91 Open Access Histopathology of Colorectal Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation Therapy Maura O Neil * and Ivan Damjanov Department of Pathology and Laboratory
The Open Pathology Journal, 2009, 3, 91-98 91 Open Access Histopathology of Colorectal Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation Therapy Maura O Neil * and Ivan Damjanov Department of Pathology and Laboratory
h. Large intestine 3
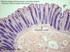 (1) General features (a) Large intestine is last organ of digestive tract proper divided into 3 or 4 regions cecum appendix in humans colon rectum 1 b) No villi lumenal epithelium has microvilli This brush
(1) General features (a) Large intestine is last organ of digestive tract proper divided into 3 or 4 regions cecum appendix in humans colon rectum 1 b) No villi lumenal epithelium has microvilli This brush
Melanoma The Skin Understanding Cancer
 Melanoma A form of cancer that begins in melanocytes (cells that make the pigment melanin). It may begin in a mole (skin melanoma), but can also begin in other pigmented tissues, such as in the eye or
Melanoma A form of cancer that begins in melanocytes (cells that make the pigment melanin). It may begin in a mole (skin melanoma), but can also begin in other pigmented tissues, such as in the eye or
Post-DDW OAG Course - Therapeutic Endoscopy
 Post-DDW OAG Course - Therapeutic Endoscopy June 13, 2015 Jeffrey Mosko Division of Gastroenterology St. Michael's Hospital University of Toronto [email protected] Program Name: Post-DDW OAG course CanMEDS
Post-DDW OAG Course - Therapeutic Endoscopy June 13, 2015 Jeffrey Mosko Division of Gastroenterology St. Michael's Hospital University of Toronto [email protected] Program Name: Post-DDW OAG course CanMEDS
Small & Large Intestines
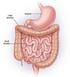 Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination
 Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
Pathology of lung cancer
 Pathology of lung cancer EASO COURSE ON LUNG CANCER AND MESOTHELIOMA DAMASCUS (SYRIA), MAY 3-4, 2007 Gérard ABADJIAN MD Pathologist Associate Professor, Saint Joseph University Pathology Dept. Hôtel-Dieu
Pathology of lung cancer EASO COURSE ON LUNG CANCER AND MESOTHELIOMA DAMASCUS (SYRIA), MAY 3-4, 2007 Gérard ABADJIAN MD Pathologist Associate Professor, Saint Joseph University Pathology Dept. Hôtel-Dieu
Cytology : first alert of mesothelioma? Professor B. Weynand, UCL Yvoir, Belgium
 Cytology : first alert of mesothelioma? Professor B. Weynand, UCL Yvoir, Belgium Introduction 3 cavities with the same embryologic origin the mesoderme Pleura Exudates Pleura Peritoneum Pericardium 22%
Cytology : first alert of mesothelioma? Professor B. Weynand, UCL Yvoir, Belgium Introduction 3 cavities with the same embryologic origin the mesoderme Pleura Exudates Pleura Peritoneum Pericardium 22%
Esophagus Cancer. What is cancer?
 What is cancer? Esophagus Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person s life,
What is cancer? Esophagus Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person s life,
Update on Mesothelioma
 November 8, 2012 Update on Mesothelioma Intro incidence and nomenclature Update on Classification Diagnostic specimens Morphologic features Epithelioid Histology Biphasic Histology Immunohistochemical
November 8, 2012 Update on Mesothelioma Intro incidence and nomenclature Update on Classification Diagnostic specimens Morphologic features Epithelioid Histology Biphasic Histology Immunohistochemical
Frozen Section Diagnosis
 Frozen Section Diagnosis Dr Catherine M Corbishley Honorary Consultant Histopathologist St George s Healthcare NHS Trust and lead examiner final FRCPath Practical 2008-2011 Frozen Section Diagnosis The
Frozen Section Diagnosis Dr Catherine M Corbishley Honorary Consultant Histopathologist St George s Healthcare NHS Trust and lead examiner final FRCPath Practical 2008-2011 Frozen Section Diagnosis The
Success rate of curative endoscopic mucosal resection with circumferential mucosal incision assisted by submucosal injection of sodium hyaluronate
 Success rate of curative endoscopic mucosal resection with circumferential mucosal incision assisted by submucosal injection of sodium hyaluronate Hironori Yamamoto, MD, Hiroshi Kawata, MD, Keijiro Sunada,
Success rate of curative endoscopic mucosal resection with circumferential mucosal incision assisted by submucosal injection of sodium hyaluronate Hironori Yamamoto, MD, Hiroshi Kawata, MD, Keijiro Sunada,
Esophageal cancer. Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth
 Esophageal cancer Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth Epidemiology 8th most common cancer worldwide Male/Female ratio: 3,5-4 Mean age at Dx 64 yrs Epidemiology in Switzerland 500-550 new cases/yr 400-450 deaths/yr
Esophageal cancer Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth Epidemiology 8th most common cancer worldwide Male/Female ratio: 3,5-4 Mean age at Dx 64 yrs Epidemiology in Switzerland 500-550 new cases/yr 400-450 deaths/yr
Lenox Hill Hospital Department of Surgery General Surgery Goals and Objectives
 Lenox Hill Hospital Department of Surgery General Surgery Goals and Objectives Medical Knowledge and Patient Care: Residents must demonstrate knowledge and application of the pathophysiology and epidemiology
Lenox Hill Hospital Department of Surgery General Surgery Goals and Objectives Medical Knowledge and Patient Care: Residents must demonstrate knowledge and application of the pathophysiology and epidemiology
Core curriculum for EMR and ablative techniques
 Communication from the ASGE Training Committee CORE CURRICULUM Core curriculum for EMR and ablative techniques This document was prepared by the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) Training
Communication from the ASGE Training Committee CORE CURRICULUM Core curriculum for EMR and ablative techniques This document was prepared by the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) Training
CPT COD1NG UPDATES Gastroenterology CPT Advisors
 2014 CPT COD1NG UPDATES Gastroenterology CPT Advisors Joel V. Brill, MD, AGA CPT Advisor Daniel C. DeMarco, MD, ACG CPT Advisor Glenn D. Littenberg, MD, ASGE CPT Advisor The American College of Gastroenterology
2014 CPT COD1NG UPDATES Gastroenterology CPT Advisors Joel V. Brill, MD, AGA CPT Advisor Daniel C. DeMarco, MD, ACG CPT Advisor Glenn D. Littenberg, MD, ASGE CPT Advisor The American College of Gastroenterology
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond. Adriana Corben, M.D.
 Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Male. Female. Death rates from lung cancer in USA
 Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Avastin: Glossary of key terms
 Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Australian clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of Barrett s esophagus and early esophageal adenocarcinoma
 bs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/jgh.12913 SOLICITED REVIEW Australian clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of Barrett s esophagus and early esophageal adenocarcinoma David C Whiteman,*
bs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/jgh.12913 SOLICITED REVIEW Australian clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of Barrett s esophagus and early esophageal adenocarcinoma David C Whiteman,*
Endoscopic treatment of Common Esophageal disorders
 Endoscopic treatment of Common Esophageal disorders November 7, 2015 Shivangi T. Kothari, MD Assistant Professor, Medicine Associate Director of Endoscopy Co-Director Developmental Endoscopy Lab at UR
Endoscopic treatment of Common Esophageal disorders November 7, 2015 Shivangi T. Kothari, MD Assistant Professor, Medicine Associate Director of Endoscopy Co-Director Developmental Endoscopy Lab at UR
Introduction: Tumor Swelling / new growth / mass. Two types of growth disorders: Non-Neoplastic. Secondary / adaptation due to other cause.
 Disorders of Growth Introduction: Tumor Swelling / new growth / mass Two types of growth disorders: Non-Neoplastic Secondary / adaptation due to other cause. Neoplastic. Primary growth abnormality. Non-Neoplastic
Disorders of Growth Introduction: Tumor Swelling / new growth / mass Two types of growth disorders: Non-Neoplastic Secondary / adaptation due to other cause. Neoplastic. Primary growth abnormality. Non-Neoplastic
THYROID CANCER. I. Introduction
 THYROID CANCER I. Introduction There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the US. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer than men by a ratio of 3:1, and it is more common in
THYROID CANCER I. Introduction There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the US. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer than men by a ratio of 3:1, and it is more common in
Thursday, November 3, 2005
 Thursday, November 3, 2005 8:30-10:30 a. m. Gastric Tumors, Session 1 Chairman: P. Ruszniewski, Clichy, France 9:00-9:30 a. m. Working Group Sessions Pathology and Genetics Group leaders: G. Rindi, Parma,
Thursday, November 3, 2005 8:30-10:30 a. m. Gastric Tumors, Session 1 Chairman: P. Ruszniewski, Clichy, France 9:00-9:30 a. m. Working Group Sessions Pathology and Genetics Group leaders: G. Rindi, Parma,
LOWER GI ENDOSCOPIES So why is CMS yanking our chain? General Concepts for all GI Endoscopy Procedures
 LOWER GI ENDOSCOPIES We have lots of changes to lower GI coding for 2015 to talk about. Code definitions have been revised and many new codes have been added to this chapter. First the good news: All these
LOWER GI ENDOSCOPIES We have lots of changes to lower GI coding for 2015 to talk about. Code definitions have been revised and many new codes have been added to this chapter. First the good news: All these
Polyps. Hyperplasias. CAP 2011: Course AP104. The High Risk Benign Endometrium. Mutter and Nucci 1
 Course AP104 Endometrial Hyperplasia A morphologic Definition Hyperplasias Hormonal Effect or Precancer? George L. Mutter, MD Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA Endometrial
Course AP104 Endometrial Hyperplasia A morphologic Definition Hyperplasias Hormonal Effect or Precancer? George L. Mutter, MD Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA Endometrial
Surgery for oesophageal cancer
 Surgery for oesophageal cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding oesophageal cancer (cancer of the gullet). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Surgery for oesophageal cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding oesophageal cancer (cancer of the gullet). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
