A Parallel PSO Algorithm for a Watermarking Application on a GPU
|
|
|
- Adrian McCormick
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Parallel PSO Algorithm for a Watermarking Application on a GPU Edgar García Cano 1 and Katya Rodríguez 2 1 Posgrado en Ciencia e Ingeniería de la Computación, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico 2 Instituto de Investigaciones en Matemáticas Aplicadas y en Sistemas, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico [email protected], [email protected] Abstract. In this paper, a research about the usability, advantages and disadvantages of using Compute Unified Device Architecture (CUDA) is presented, implementing an algorithm based on populations called Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) [5]. In order to test the performance of the proposed algorithm, a hide watermark image application is put into practice. The PSO is used to optimize the positions where a watermark has to be inserted. This application uses the insertion/extraction algorithm proposed by Shieh et al. [1]. This algorithm was implemented for both sequential and CUDA architectures. The function used in the optimization algorithm has two objectives: fidelity and robustness. The measurement of fidelity and robustness is computed using Mean Squared Error (MSE) and Normalized Correlation (NC), respectively; these functions are evaluated using Pareto dominance. Keywords. Parallel particle swarm optimization, watermarking, CUDA, image security. Algoritmo paralelo PSO para una aplicación de marcas de agua en un GPU Resumen. En este artículo se presenta una investigación de la usabilidad, ventajas y desventajas de usar Compute Unified Device Architecture (CUDA) implementando un algoritmo basado en poblaciones, Optimización por Cúmulo de Partículas (PSO) [5]. Para probar el rendimiento del algoritmo propuesto, se realizó la implementación de una aplicación de marcas de agua ocultas. El PSO es usado para optimizar las posiciones donde la marca de agua debe ser insertada. Esta aplicación usa el algortimo de inserción/extracción propuesto por Shieh et al. [1]. El algortimo completo fue implementado para las arquitecturas secuenciales y CUDA. La función de optimización usada en el algoritmo de optimización es la unión de dos objetivos: fidelidad y robustez. La medición de la fidelidad y robustez es procesada usando el Error Cuadrático Medio (MSE) y la Correlación de Normalización (NC) respectivamente; estas funciones son evaluadas usando dominancia de Pareto. Palabras clave. Optimización por cúmulo de partículas en paralelo, marcas de agua, CUDA, seguridad en imágenes. 1 Introduction The digital age introduced a new way to share information (files, audio, video, image, etc.), and there is no guarantee that someone else may use it without authorization, that is why watermarking appeared as an innovative way to protect information. Digital watermarking is presented when a pattern is inserted in an image, video or audio file, it helps to copyright the information in the files. In the case of image watermarking, it is divided in two groups: visible and invisible watermarks. A visible watermark is a visible semitransparent text or image overlaid on the original image. It allows the original image to be viewed but still provides copyright protection by marking the image as its property. Visible watermarks are more robust against image transformation (especially if one uses a semi-transparent watermark placed over the whole image). Thus
2 382 Edgar García Cano and Katya Rodríguez they are preferable for strong copyright protection of intellectual property in digital format [2]. An invisible watermark is an embedded image that cannot be perceived with human eyes. Only electronic devices (or specialized software) can extract the hidden information to identify the copyright owner. Invisible watermarks are used to mark a specialized digital content (text, images or even audio content) to prove its authenticity [2]. Evolutionary computation, a subfield of Artificial Intelligence, uses models based on populations to solve optimization problems. Basically, these models were inspired by the mechanisms of natural evolution. Another set based on biological models and classified as bioinspired algorithms includes Ant Colony and Swarm-based algorithms. These are a different way to solve problems based on the behavior of animals or systems whose evolution lasts for centuries. In recent years, new and cheaper technologies such as CUDA architecture have emerged with the concept of massive parallelism for generalpurpose problems. The advantage of this technology is that every person with a personal computer has the possibility of taking advantage of the massive parallelism to accelerate procedures. The process of watermarking can be applied to copyright any sort of digital information. In some fields like financial banking, it is necessary to perform a process involving a big quantity of information as soon as possible. On one hand, this is a reason to look for a new and cheaper technology such as CUDA to accelerate the process. On the other hand, the need to improve the watermarking process against modifications such as cropping, rotation, flipping, scaling, changing colors, etc., was the reason to use an optimization process. The idea of using PSO as an optimization algorithm comes forward owing to the fact that it has few parameters to adjust. The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 offers an explanation of how the watermarking algorithm works and the metrics used to evaluate the watermarked image quality. In Section 3, an overview of the PSO algorithm is presented. Section 4 shows the optimization algorithm used in this work. In Section 5, tests and results are presented and analyzed. Finally, a discussion concerning advantages and disadvantages of using GPUs as a technology to implement algorithms based on populations is presented. 2 Methods With a vast volume of information flowing on the Internet, watermarking is widely used to protect the information authenticity. The need to copyright a huge quantity of digital files spending the less possible amount of time and avoiding information loss were the reasons to propose the use of an algorithm for watermarking Shieh algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization as an optimizer, and finally a GPU based in CUDA architecture to accelerate the process. 2.1 The Watermarking Algorithm Shieh et al. [1] have proposed an algorithm to insert and extract watermark based on Discrete Cosine Transformation (DCT). This transformation is used due to the fact that it is not necessary to have the original cover to extract the watermark. Dealing with a huge number of images, it would be very expensive to store all cover images for the watermark extraction. Figure 1 shows an adjustment of the Shieh algorithm used in this work. Once the original image is loaded in memory and after the DCT, the ratio values are calculated using DC and AC coefficients. Next step calculates the relation between the image content and the embedding frequency bands (polarities). Then, the watermark image is inserted in the selected bands of each 8x8 block. Quantization is used as an attack to the watermarked image, and it is necessary for the optimization process. Finally IDCT is computed and the watermarked image is obtained (see [3] for more details about the CUDA implementation) Watermarking Metrics In order to evaluate the performance of a watermark algorithm to hide the information, some metrics have been proposed. The watermark algorithm has to be capable to hide the mark data and to prevent distortions of the image. In order to propose a simpler way to measure the
3 A Parallel PSO algorithm for a Watermarking Application on a GPU 383 Table 1. Exclusive OR W W Output Fig. 1. Watermarking algorithm and the robustness spending the shortest time possible, the MSE and the NC were used. Watermark Fidelity. Fidelity represents the similarity of the watermarked image with the original image. Thus, mean squared error (see Equation 1) was utilized to measure fidelity. It ought to be close to zero to have a good correspondence between the nonwatermarked and the watermarked image. ( ) ( ) ( ) (1) Watermark Robustness. Robustness represents the resistance of the watermark against attacks (compression, rotation, scaling, among others) done on the watermarked image. The normalized correlation NC (see Equation 2) is used to measure robustness. It applies the logical operation exclusive disjunction, also called exclusive or. Bitwise operations are faster therefore, reduce the runtime. The NC value must be close to zero between the original watermark (W) and the extracted watermark (W ), to prevent a watermark image information loss. [ ( ) ( )] (2) Fig. 2. Block organization to calculate MSE and NC The exclusive or calculation is shown in Table1. The NC and the MSE are computed for each 8x8 block as shown in Fig. 2. This was carried out with the purpose of dividing, as much as possible, the data in GPU. When measuring the MSE in each block, just 64 comparisons are necessary, they are executed at the same time in the other blocks. In the sequential process, 512x512 evaluations one after another are needed for a 512x512 image size. The same case was applied for the NC: instead of being calculated for the whole image (as in the sequential form), it was computed for each block.
4 384 Edgar García Cano and Katya Rodríguez 2.2 Particle Swarm Optimization Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is a population-based stochastic optimization technique developed by Eberhart and Kennedy in 1995 inspired by social behavior of bird flocking or fish schooling [10]. PSO shares many similarities with evolutionary computation techniques such as Genetic Algorithms (GA). The system is initialized with a population of random solutions and searches for optima by updating iterations. However, unlike GA, PSO has no evolution operators such as crossover and mutation. In PSO, potential solutions, called particles, fly through the problem space by following the current optimum particles. It has been successfully applied to many problems in several fields such as biomedicine [7] and energy conversion [4]. Image analysis is one of the most frequent applications and it is performed for biomedical images [9], microwave imaging [6, 8], among others Basic PSO Algorithm Each particle keeps track of its coordinate in the problem space, which is associated with the best solution () achieved so far (this value is stored). This value is called pbest. Another best value that is tracked by the particle swarm optimizer is the best value, obtained so far by any particle in the neighborhood of a given particle. This location is called lbest. When the particle takes all the population as its topological neighbors, the best value is a global best and is called gbest. At each time step, the PSO concept consists of changing the velocity (acceleration) of each particle toward its lbest and gbest locations. Acceleration is weighted by a random term, with separate random numbers being generated for acceleration toward lbest and gbest locations. After finding the two best values (lbest and gbest), the particle i updates its velocity and position with Equations 3 and 4, where i = 1, 2, 3 NS. ( ) ( ) ( ( ) ( )) ( ( ) ( )) (3) ( ) ( ) ( ) (4) ϕ 1 and ϕ 2 are positive constants called acceleration coefficients, NS is the total number of particles in the swarm, r 1 and r 2 are random vectors, each component is generated within [0,1], and g represents the index of the best particle in the neighborhood. The other vectors X i =[x 1, x 2,, x id ] position of the i-th particle; V i = [v 1, v 2,,v id ] velocity of the i-th particle; B i best historical value for the i-th particle found, B i g best value found for the i-th particle in the neighborhood [5]. For details about the CUDA implementation see [3]. Algorithm 1. Basic PSO Algorithm 1: ize particles population 2: while do not get the max number of iterations or the optimal solution do 3: Calculate the for each particle i 4: Update B i if pbest is better than the last one 5: Calculate Big i of the neighbors 6: for each particle i do 7: Calculate V i according to 3 8: Update X i according to 4 9: Update best global solution (gbest) 10: end for 11: end while 2.3 The Optimization Algorithm The objective of optimization is to find the best frequency band set to insert the watermark within the image. Different frequency bands are tested through the iterations of the algorithm finding out the best solution. At the end of the execution the application has as results the watermarked image and a matrix with the whole best positions (frequency bands) to insert the complete watermark. The algorithm in charge of doing the watermark optimization is the PSO, and at the same time it uses Pareto dominance to evaluate the function through the MSE (fidelity) and NC (robustness). This process is detailed as follows. 1. Using the DCT idea to split the image in 8x8 blocks, each block is used as a swarm. An image of 512x512 has 4096 blocks; hence
5 each block will be a swarm. The number of particles by swarm is specified as a configuration parameter of the algorithm. 2. Each particle has a position vector. The vector size depends on the number of watermark bits used to be inserted in each block of the image. If the watermark size is 128x128 and if it is divided uniformly into 4096 blocks of the image, then 4 bits are inserted in each block. Each position corresponds to a band in the 8x8 block where the watermark bits are inserted. A Parallel PSO algorithm for a Watermarking Application on a GPU 385 At the beginning, all the swarms are initialized randomly (each swarm must have the same particle number). If 4 bits are to be inserted, 4 bands are required, and then 4 random numbers must be created between 1 and 63. This means that each particle will consist of 4 bands (position vectors). If each swarm has 5 particles, every particle has a set of 4 bands used to originate 5 different solutions. To generate solution 1, all the particles with index 1 are taken from every swarm and joined; to generate solution 2; all the particles with index 2 are taken from every swarm and joined, and so on. This procedure is shown in Fig. 3. Fig. 3. Generation of solutions taking particles P1 and P2 from the different swarms, bands B1, B2, B3 and B4 generate the corresponding solution 3. After the insertion and extraction operations, the MSE (see Equation 1) and the NC (see Equation 2) are calculated. Based on MSE and NC, the value is estimated. 4. One of the particles must be selected as the best global. Among the best options generated, one of them is chosen to be the best global. To choose the local best, the particle is considered to add up the MSE and the NC. If the new value is closer to zero than the old one, the new particle replaces the old one; otherwise the old one continues in the process. 5. In the last step, the velocity and the new position of the particles are calculated according to Equations 3 and 4. This generates the new bands and new iteration begins. Fig. 4 shows the whole algorithm. Fig. 4. The optimization algorithm
6 386 Edgar García Cano and Katya Rodríguez 3 Test and Results All tests were executed on two different servers with the features shown in Tables 2 and 3. In order to test the implementations, Fig. 5 shows the original image used in the algorithm and Fig. 6 shows the watermark image. For the experiments, the size of the images is 515x512 and they are in gray scale. 3.1 Results of the Algorithm Tables 4 and 5 show the runtime of the watermarking optimization. Parts A and B show five experiments with different number of iterations using the sequential and CUDA versions. These experiments were performed to compare the amount of time used for the algorithm and the quality of the results based on the idea that the operations executed in the GPU must be faster than the ones computed in the CPU. Part C of Tables 4 and 5 show the runtime for the sequential implementation with 10 and 30 Fig. 5. Original image (Barbara) Fig. 6. Watermark image ( 2012 BancTec, Inc., All rights reserved) Table 2. CPU server features Server name Cores CPU type Uxdea 8 Geogpus 8 Intel Xeon 2.4GHz Intel Xeon 3.47GHz Table 3. GPU server features Server name Cores GPU Uxdea 240 Tesla C1060 Geogpus 240 Tesla C1060 iterations, but without random number generation. This was made to compare CUDA runtime and check if CUDA implementation is faster than the sequential implementation without random numbers generation. Using random numbers in the sequential version produced a remarkable difference in time. The use of those numbers consumes a big quantity of time due to its necessity to spend time in the CPU to generate different numbers. For the sequential version, random numbers are generated using the C function drand48 that returns a pseudo-random number in the range [0.0,1.0). On the GPU, random numbers are generated using a library called curand. In the case of the GPU (Part D of Tables 4 and 5), random numbers are generated directly in the constant GPU memory; there is no need to transfer them from the host to the device. This is why the difference, in terms of runtime, between the option with random numbers and the option without random numbers in CUDA is minimal. Reviewing the values (Tables 4 and 5) of the initial and the final, it is noteworthy that the sequential version gives better results than the ones obtained from the GPU. For all the cases, the runtimes indicate that GPU is faster than CPU, even when all data have been loaded or when static numbers in the CPU version are used. Thus, it is possible to set up that, at least for this version of the application, if the user wants a good optimization for the watermarking, the sequential version must be used. However, if the user needs a quick approximation, the GPU version must be applied (for other results see [3]).
7 A Sequential (min) A Parallel PSO algorithm for a Watermarking Application on a GPU 387 Table 4. Runtime for PSO on Geogpus Final CUDA (s) Final B Sequential (min) 30 Iterations Final CUDA (s) Final C Sequential no random numbers Final 30 Iterations Final D CUDA no random numbers Final 30 Iterations Final
8 388 Edgar García Cano and Katya Rodríguez A Sequential (min) Table 5. Runtime for PSO on Uxdea Final CUDA (s) Final B C D Sequential (min) 30 Iterations Final CUDA (s) Final Sequential no random numbers Final 30 Iterations Final CUDA no random numbers Final 30 Iterations Final
9 A Parallel PSO algorithm for a Watermarking Application on a GPU Conclusions Since there is no standard configuration for the blocks, threads or memory treatment in the GPU, it is necessary to make analysis and design of the procedures involved in a particular application to take advantage of parallelism. In order to use parallel programing in a GPU, it is necessary to shift from sequential to parallel thinking and to learn how to divide a huge problem into small ones (divide and conquer), attempting to obtain the best performance. For example, in the calculation of the NC, only 4 threads were required to perform comparison, but in the case of the MSE 64, threads working at the same time were used. Therefore, the configuration of the blocks and threads for an application on a GPU must be carefully analyzed. Different options to implement the PSO were analyzed, but the version that uses as much swarms as the number of blocks to divide an image in the DCT was implemented. The idea was to divide a big problem into smaller ones, which suited the parallel paradigm. As it has been established, there is no standard configuration in CUDA architecture, so the accordance between configuration and the need of the function was achieved. The PSO has to evaluate two vectors: velocity and position. Position depends on velocity that is why velocity is to be computed first. If there are 4096 swarms 4096 blocks and each swarm has five particles, then each of them needs to update the velocity vector. The number of operations to be calculated in a CPU is 4096 (swarms) * 5 (particles) * 1 (operation) = operations one after another. In the case of the same operations on the GPU, the same operations are executed, but the difference is that there are 4096 swarms with 5 threads working in parallel computing one operation, hence there are threads working at the same time. If one thread in the CPU spends 1 second per operation, the runtime will be s, but in the case of the GPU there are threads working at the same time, and they spend 1 second to finish the calculus. In the last example, the speed of the processor is not considered, neither CPU nor GPU, nor the upload/download of the data to/from the GPU. The velocity vector needs random numbers to be calculated (see Equation 1). In order to generate random numbers, a library called curand was used. This library is useful because it is easy to generate a lot of numbers in a short time; the problem comes with the memory. If there is a big quantity of these numbers generated and held in global memory, there might be a shortage of space to store other data. In one iteration of the PSO, two random numbers are used to calculate the velocity value. If there are 4096 blocks with 5 particles each, random numbers for iteration are needed. There is another type of memory on the GPU, the constant memory. This memory is loaded in the GPU but it cannot be changed. This memory was considered to store the random numbers because they do not modify its value on the execution of the calculation of the velocity value. Another feature that has to be considered (from GPU to GPU) is the processor velocity. This is evident in the experiments because the Geogpus server is faster than the Uxdea server. The analysis done in the present work shows that the use of CUDA helps to improve the performance of the application and that an algorithm based on population can be implemented in it, as long as the developer is aware of the features of this technology. 5 Future Work The first phase of this project is focused on the implementation with the elemental CUDA features of a basic algorithm based on population; however, the CUDA architecture may be better exploited. The second phase will be focused on a combination of other CUDA features, such as streams, page locked memory and mapped memory. The aim of the third phase is to improve operations on the CPU and MPI to distribute tasks (in this case different swarms) in a cluster by mixing other technologies, such as Open MP. Acknowledgements The first author, postgraduate student in Computer Science and Engineering at the
10 390 Edgar García Cano and Katya Rodríguez National University of Mexico, expresses his gratitude to the support received from CONACYT (scholarship number 37617). The authors also express their gratitude to the support received from PAPIIT (project number ). References 1. Chin-Shiuh, S., Hsiang-Cheh, H., Feng-Hsing, W., & Jeng-Shyang, P. (2004). Genetic watermarking based on transform-domain techniques. Pattern Recognition, 37(3), ByteScout (s.f.). Retrieved from 3. García, E.E. (2012). A parallel bioinspired watermarking algorithm on a GPU. MSc thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, México, D.F. 4. Heo, J.S., Lee, K.Y., & Garduno-Ramirez, R. (2006). Multiobjective control of power plants using particle swarm optimization techniques. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 21(2), Mohemmed, A., Johnston, M., & Zhang, M. (2009). Particle swarm optimization based multiprototype ensembles. 11th Annual conference on Genetic and evolutionary computation (GECCO 09), Montreal, Canada, Donelli, M. & Massa, A. (2005). Computational approach based on a particle swarm optimizer for microwave imaging of two dimensional dielectric scatterers. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 53(5), Selvan, S.E., Xavier, C.C., Karssemeijer, N., Sequeira, J., Cherian, R.A., & Dhala, B.Y. (2006). Parameter estimation in stochastic mammogram model by heuristic optimization technique. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 10(4), Huang, T. & Mohan, A.S. (2007). A microparticle swarm optimizer for the reconstruction of microwave images. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 55(3), Wachowiak, M.P., Smolikova, R., Yufeng, Z., Zurada, J.M., & Elmaghraby, A.S. (2004). An approach to multimodal biomedical image registration utilizing particle swarm optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 8(3), Kennedy, J. & Eberhart, R. (1995). Particle swarm optimization. IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 4, Edgar García Cano received his Bachelor degree in Computer Engineering, and Master s degree in Computer Science from the National University of Mexico (UNAM), specializing in parallel programing and evolutionary computing. He worked as a teacher and IT consultant in the Engineering Faculty at UNAM for eight years. Currently, he is completing his Doctoral studies at the École de technologie superieure in Montreal, Canada. Katya Rodríguez received her Bachelor degree in Computer Engineering from the National University of Mexico in She obtained her Ph.D. from the University of Sheffield in She is currently a researcher at the Institute of Applied Mathematics and Systems Engineering, National University of Mexico. She has published a number of papers in international journals and conferences and has been a member of the Technical Program Committee for Conferences related to Evolutionary Computation. Her research interests are evolutionary and bioinspired algorithms, multi-objective optimization and its applications in diverse fields. Article received on 20/01/2013; accepted on 11/08/2013.
14.10.2014. Overview. Swarms in nature. Fish, birds, ants, termites, Introduction to swarm intelligence principles Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
 Overview Kyrre Glette kyrrehg@ifi INF3490 Swarm Intelligence Particle Swarm Optimization Introduction to swarm intelligence principles Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) 3 Swarms in nature Fish, birds,
Overview Kyrre Glette kyrrehg@ifi INF3490 Swarm Intelligence Particle Swarm Optimization Introduction to swarm intelligence principles Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) 3 Swarms in nature Fish, birds,
CLOUD DATABASE ROUTE SCHEDULING USING COMBANATION OF PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION AND GENETIC ALGORITHM
 CLOUD DATABASE ROUTE SCHEDULING USING COMBANATION OF PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION AND GENETIC ALGORITHM *Shabnam Ghasemi 1 and Mohammad Kalantari 2 1 Deparment of Computer Engineering, Islamic Azad University,
CLOUD DATABASE ROUTE SCHEDULING USING COMBANATION OF PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION AND GENETIC ALGORITHM *Shabnam Ghasemi 1 and Mohammad Kalantari 2 1 Deparment of Computer Engineering, Islamic Azad University,
Optimization of PID parameters with an improved simplex PSO
 Li et al. Journal of Inequalities and Applications (2015) 2015:325 DOI 10.1186/s13660-015-0785-2 R E S E A R C H Open Access Optimization of PID parameters with an improved simplex PSO Ji-min Li 1, Yeong-Cheng
Li et al. Journal of Inequalities and Applications (2015) 2015:325 DOI 10.1186/s13660-015-0785-2 R E S E A R C H Open Access Optimization of PID parameters with an improved simplex PSO Ji-min Li 1, Yeong-Cheng
A Novel Binary Particle Swarm Optimization
 Proceedings of the 5th Mediterranean Conference on T33- A Novel Binary Particle Swarm Optimization Motaba Ahmadieh Khanesar, Member, IEEE, Mohammad Teshnehlab and Mahdi Aliyari Shoorehdeli K. N. Toosi
Proceedings of the 5th Mediterranean Conference on T33- A Novel Binary Particle Swarm Optimization Motaba Ahmadieh Khanesar, Member, IEEE, Mohammad Teshnehlab and Mahdi Aliyari Shoorehdeli K. N. Toosi
International Journal of Software and Web Sciences (IJSWS) www.iasir.net
 International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research) ISSN (Print): 2279-0063 ISSN (Online): 2279-0071 International
International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research) ISSN (Print): 2279-0063 ISSN (Online): 2279-0071 International
BMOA: Binary Magnetic Optimization Algorithm
 International Journal of Machine Learning and Computing Vol. 2 No. 3 June 22 BMOA: Binary Magnetic Optimization Algorithm SeyedAli Mirjalili and Siti Zaiton Mohd Hashim Abstract Recently the behavior of
International Journal of Machine Learning and Computing Vol. 2 No. 3 June 22 BMOA: Binary Magnetic Optimization Algorithm SeyedAli Mirjalili and Siti Zaiton Mohd Hashim Abstract Recently the behavior of
School of Electrical, Electronic and Telecommunication Engineering, Universidad Industrial de Santander, Colombia. [email protected].
 A modified firefly-inspired algorithm for global computational optimization Iván Amaya a, Jorge Cruz b & Rodrigo Correa c a School of Electrical, Electronic and Telecommunication Engineering, Universidad
A modified firefly-inspired algorithm for global computational optimization Iván Amaya a, Jorge Cruz b & Rodrigo Correa c a School of Electrical, Electronic and Telecommunication Engineering, Universidad
A Binary Model on the Basis of Imperialist Competitive Algorithm in Order to Solve the Problem of Knapsack 1-0
 212 International Conference on System Engineering and Modeling (ICSEM 212) IPCSIT vol. 34 (212) (212) IACSIT Press, Singapore A Binary Model on the Basis of Imperialist Competitive Algorithm in Order
212 International Conference on System Engineering and Modeling (ICSEM 212) IPCSIT vol. 34 (212) (212) IACSIT Press, Singapore A Binary Model on the Basis of Imperialist Competitive Algorithm in Order
Dynamic Generation of Test Cases with Metaheuristics
 Dynamic Generation of Test Cases with Metaheuristics Laura Lanzarini, Juan Pablo La Battaglia III-LIDI (Institute of Research in Computer Science LIDI) Faculty of Computer Sciences. National University
Dynamic Generation of Test Cases with Metaheuristics Laura Lanzarini, Juan Pablo La Battaglia III-LIDI (Institute of Research in Computer Science LIDI) Faculty of Computer Sciences. National University
A RANDOMIZED LOAD BALANCING ALGORITHM IN GRID USING MAX MIN PSO ALGORITHM
 International Journal of Research in Computer Science eissn 2249-8265 Volume 2 Issue 3 (212) pp. 17-23 White Globe Publications A RANDOMIZED LOAD BALANCING ALGORITHM IN GRID USING MAX MIN ALGORITHM C.Kalpana
International Journal of Research in Computer Science eissn 2249-8265 Volume 2 Issue 3 (212) pp. 17-23 White Globe Publications A RANDOMIZED LOAD BALANCING ALGORITHM IN GRID USING MAX MIN ALGORITHM C.Kalpana
Dynamic Task Scheduling with Load Balancing using Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization
 Int. J. Open Problems Compt. Math., Vol. 2, No. 3, September 2009 ISSN 1998-6262; Copyright ICSRS Publication, 2009 www.i-csrs.org Dynamic Task Scheduling with Load Balancing using Hybrid Particle Swarm
Int. J. Open Problems Compt. Math., Vol. 2, No. 3, September 2009 ISSN 1998-6262; Copyright ICSRS Publication, 2009 www.i-csrs.org Dynamic Task Scheduling with Load Balancing using Hybrid Particle Swarm
Research on the Performance Optimization of Hadoop in Big Data Environment
 Vol.8, No.5 (015), pp.93-304 http://dx.doi.org/10.1457/idta.015.8.5.6 Research on the Performance Optimization of Hadoop in Big Data Environment Jia Min-Zheng Department of Information Engineering, Beiing
Vol.8, No.5 (015), pp.93-304 http://dx.doi.org/10.1457/idta.015.8.5.6 Research on the Performance Optimization of Hadoop in Big Data Environment Jia Min-Zheng Department of Information Engineering, Beiing
Optimal Tuning of PID Controller Using Meta Heuristic Approach
 International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174, Volume 7, Number 2 (2014), pp. 171-176 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Optimal Tuning of
International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174, Volume 7, Number 2 (2014), pp. 171-176 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Optimal Tuning of
Biogeography Based Optimization (BBO) Approach for Sensor Selection in Aircraft Engine
 Biogeography Based Optimization (BBO) Approach for Sensor Selection in Aircraft Engine V.Hymavathi, B.Abdul Rahim, Fahimuddin.Shaik P.G Scholar, (M.Tech), Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,
Biogeography Based Optimization (BBO) Approach for Sensor Selection in Aircraft Engine V.Hymavathi, B.Abdul Rahim, Fahimuddin.Shaik P.G Scholar, (M.Tech), Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,
Image Authentication Scheme using Digital Signature and Digital Watermarking
 www..org 59 Image Authentication Scheme using Digital Signature and Digital Watermarking Seyed Mohammad Mousavi Industrial Management Institute, Tehran, Iran Abstract Usual digital signature schemes for
www..org 59 Image Authentication Scheme using Digital Signature and Digital Watermarking Seyed Mohammad Mousavi Industrial Management Institute, Tehran, Iran Abstract Usual digital signature schemes for
A hybrid Approach of Genetic Algorithm and Particle Swarm Technique to Software Test Case Generation
 A hybrid Approach of Genetic Algorithm and Particle Swarm Technique to Software Test Case Generation Abhishek Singh Department of Information Technology Amity School of Engineering and Technology Amity
A hybrid Approach of Genetic Algorithm and Particle Swarm Technique to Software Test Case Generation Abhishek Singh Department of Information Technology Amity School of Engineering and Technology Amity
Flexible Neural Trees Ensemble for Stock Index Modeling
 Flexible Neural Trees Ensemble for Stock Index Modeling Yuehui Chen 1, Ju Yang 1, Bo Yang 1 and Ajith Abraham 2 1 School of Information Science and Engineering Jinan University, Jinan 250022, P.R.China
Flexible Neural Trees Ensemble for Stock Index Modeling Yuehui Chen 1, Ju Yang 1, Bo Yang 1 and Ajith Abraham 2 1 School of Information Science and Engineering Jinan University, Jinan 250022, P.R.China
XOR-based artificial bee colony algorithm for binary optimization
 Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences http:// journals. tubitak. gov. tr/ elektrik/ Research Article Turk J Elec Eng & Comp Sci (2013) 21: 2307 2328 c TÜBİTAK doi:10.3906/elk-1203-104
Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences http:// journals. tubitak. gov. tr/ elektrik/ Research Article Turk J Elec Eng & Comp Sci (2013) 21: 2307 2328 c TÜBİTAK doi:10.3906/elk-1203-104
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 20 th July 2015. Vol.77. No.2 2005-2015 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
 EFFICIENT LOAD BALANCING USING ANT COLONY OPTIMIZATION MOHAMMAD H. NADIMI-SHAHRAKI, ELNAZ SHAFIGH FARD, FARAMARZ SAFI Department of Computer Engineering, Najafabad branch, Islamic Azad University, Najafabad,
EFFICIENT LOAD BALANCING USING ANT COLONY OPTIMIZATION MOHAMMAD H. NADIMI-SHAHRAKI, ELNAZ SHAFIGH FARD, FARAMARZ SAFI Department of Computer Engineering, Najafabad branch, Islamic Azad University, Najafabad,
Méta-heuristiques pour l optimisation
 Méta-heuristiques pour l optimisation Differential Evolution (DE) Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) Alain Dutech Equipe MAIA - LORIA - INRIA Nancy, France Web : http://maia.loria.fr Mail : [email protected]
Méta-heuristiques pour l optimisation Differential Evolution (DE) Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) Alain Dutech Equipe MAIA - LORIA - INRIA Nancy, France Web : http://maia.loria.fr Mail : [email protected]
Wireless Sensor Networks Coverage Optimization based on Improved AFSA Algorithm
 , pp. 99-108 http://dx.doi.org/10.1457/ijfgcn.015.8.1.11 Wireless Sensor Networks Coverage Optimization based on Improved AFSA Algorithm Wang DaWei and Wang Changliang Zhejiang Industry Polytechnic College
, pp. 99-108 http://dx.doi.org/10.1457/ijfgcn.015.8.1.11 Wireless Sensor Networks Coverage Optimization based on Improved AFSA Algorithm Wang DaWei and Wang Changliang Zhejiang Industry Polytechnic College
Parallel Multi-Swarm Optimization Framework for Search Problems in Water Distribution Systems
 Parallel Multi-Swarm Optimization Framework for Search Problems in Water Distribution Systems Sarat Sreepathi 1, Downey Brill 2, Ranji Ranjithan 2, Gnanamanikam (Kumar) Mahinthakumar 2 {sarat s,brill,ranji,gmkumar}@ncsu.edu
Parallel Multi-Swarm Optimization Framework for Search Problems in Water Distribution Systems Sarat Sreepathi 1, Downey Brill 2, Ranji Ranjithan 2, Gnanamanikam (Kumar) Mahinthakumar 2 {sarat s,brill,ranji,gmkumar}@ncsu.edu
Curriculum Reform in Computing in Spain
 Curriculum Reform in Computing in Spain Sergio Luján Mora Deparment of Software and Computing Systems Content Introduction Computing Disciplines i Computer Engineering Computer Science Information Systems
Curriculum Reform in Computing in Spain Sergio Luján Mora Deparment of Software and Computing Systems Content Introduction Computing Disciplines i Computer Engineering Computer Science Information Systems
Bachelor Degree in Informatics Engineering Master courses
 Bachelor Degree in Informatics Engineering Master courses Donostia School of Informatics The University of the Basque Country, UPV/EHU For more information: Universidad del País Vasco / Euskal Herriko
Bachelor Degree in Informatics Engineering Master courses Donostia School of Informatics The University of the Basque Country, UPV/EHU For more information: Universidad del País Vasco / Euskal Herriko
Projects - Neural and Evolutionary Computing
 Projects - Neural and Evolutionary Computing 2014-2015 I. Application oriented topics 1. Task scheduling in distributed systems. The aim is to assign a set of (independent or correlated) tasks to some
Projects - Neural and Evolutionary Computing 2014-2015 I. Application oriented topics 1. Task scheduling in distributed systems. The aim is to assign a set of (independent or correlated) tasks to some
HYBRID ACO-IWD OPTIMIZATION ALGORITHM FOR MINIMIZING WEIGHTED FLOWTIME IN CLOUD-BASED PARAMETER SWEEP EXPERIMENTS
 HYBRID ACO-IWD OPTIMIZATION ALGORITHM FOR MINIMIZING WEIGHTED FLOWTIME IN CLOUD-BASED PARAMETER SWEEP EXPERIMENTS R. Angel Preethima 1, Margret Johnson 2 1 Student, Computer Science and Engineering, Karunya
HYBRID ACO-IWD OPTIMIZATION ALGORITHM FOR MINIMIZING WEIGHTED FLOWTIME IN CLOUD-BASED PARAMETER SWEEP EXPERIMENTS R. Angel Preethima 1, Margret Johnson 2 1 Student, Computer Science and Engineering, Karunya
Improved Particle Swarm Optimization in Constrained Numerical Search Spaces
 Improved Particle Swarm Optimization in Constrained Numerical Search Spaces Efrén Mezura-Montes and Jorge Isacc Flores-Mendoza Abstract This chapter presents a study about the behavior of Particle Swarm
Improved Particle Swarm Optimization in Constrained Numerical Search Spaces Efrén Mezura-Montes and Jorge Isacc Flores-Mendoza Abstract This chapter presents a study about the behavior of Particle Swarm
2695 P a g e. IV Semester M.Tech (DCN) SJCIT Chickballapur Karnataka India
 Integrity Preservation and Privacy Protection for Digital Medical Images M.Krishna Rani Dr.S.Bhargavi IV Semester M.Tech (DCN) SJCIT Chickballapur Karnataka India Abstract- In medical treatments, the integrity
Integrity Preservation and Privacy Protection for Digital Medical Images M.Krishna Rani Dr.S.Bhargavi IV Semester M.Tech (DCN) SJCIT Chickballapur Karnataka India Abstract- In medical treatments, the integrity
DCT-JPEG Image Coding Based on GPU
 , pp. 293-302 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijhit.2015.8.5.32 DCT-JPEG Image Coding Based on GPU Rongyang Shan 1, Chengyou Wang 1*, Wei Huang 2 and Xiao Zhou 1 1 School of Mechanical, Electrical and Information
, pp. 293-302 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijhit.2015.8.5.32 DCT-JPEG Image Coding Based on GPU Rongyang Shan 1, Chengyou Wang 1*, Wei Huang 2 and Xiao Zhou 1 1 School of Mechanical, Electrical and Information
WATERMARKING FOR IMAGE AUTHENTICATION
 WATERMARKING FOR IMAGE AUTHENTICATION Min Wu Bede Liu Department of Electrical Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544, USA Fax: +1-609-258-3745 {minwu, liu}@ee.princeton.edu ABSTRACT A data
WATERMARKING FOR IMAGE AUTHENTICATION Min Wu Bede Liu Department of Electrical Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544, USA Fax: +1-609-258-3745 {minwu, liu}@ee.princeton.edu ABSTRACT A data
DYNA http://dyna.medellin.unal.edu.co/
 DYNA http://dyna.medellin.unal.edu.co/ Discrete Particle Swarm Optimization in the numerical solution of a system of linear Diophantine equations Optimización por Enjambre de Partículas Discreto en la
DYNA http://dyna.medellin.unal.edu.co/ Discrete Particle Swarm Optimization in the numerical solution of a system of linear Diophantine equations Optimización por Enjambre de Partículas Discreto en la
D A T A M I N I N G C L A S S I F I C A T I O N
 D A T A M I N I N G C L A S S I F I C A T I O N FABRICIO VOZNIKA LEO NARDO VIA NA INTRODUCTION Nowadays there is huge amount of data being collected and stored in databases everywhere across the globe.
D A T A M I N I N G C L A S S I F I C A T I O N FABRICIO VOZNIKA LEO NARDO VIA NA INTRODUCTION Nowadays there is huge amount of data being collected and stored in databases everywhere across the globe.
Web Service Selection using Particle Swarm Optimization and Genetic Algorithms
 Web Service Selection using Particle Swarm Optimization and Genetic Algorithms Simone A. Ludwig Department of Computer Science North Dakota State University Fargo, ND, USA [email protected] Thomas
Web Service Selection using Particle Swarm Optimization and Genetic Algorithms Simone A. Ludwig Department of Computer Science North Dakota State University Fargo, ND, USA [email protected] Thomas
Optimal PID Controller Design for AVR System
 Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 2, No. 3, pp. 259 270 (2009) 259 Optimal PID Controller Design for AVR System Ching-Chang Wong*, Shih-An Li and Hou-Yi Wang Department of Electrical Engineering,
Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 2, No. 3, pp. 259 270 (2009) 259 Optimal PID Controller Design for AVR System Ching-Chang Wong*, Shih-An Li and Hou-Yi Wang Department of Electrical Engineering,
Research Article Service Composition Optimization Using Differential Evolution and Opposition-based Learning
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 11(2): 229-234, 2015 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 2015 Maxwell Scientific Publication Corp. Submitted: May 20, 2015 Accepted: June
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 11(2): 229-234, 2015 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 2015 Maxwell Scientific Publication Corp. Submitted: May 20, 2015 Accepted: June
A resource schedule method for cloud computing based on chaos particle swarm optimization algorithm
 Abstract A resource schedule method for cloud computing based on chaos particle swarm optimization algorithm Lei Zheng 1, 2*, Defa Hu 3 1 School of Information Engineering, Shandong Youth University of
Abstract A resource schedule method for cloud computing based on chaos particle swarm optimization algorithm Lei Zheng 1, 2*, Defa Hu 3 1 School of Information Engineering, Shandong Youth University of
Image Compression through DCT and Huffman Coding Technique
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Rahul
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Rahul
DATABASE MAMMOGRAPHIC IMAGES UNDER PERUVIAN CASES AND DETECTION OF MICROCALCIFICATIONS BASED ON FRACTAL CHARACTERISTICS PROGRAMMATICALLY GPGPU
 VI International Conference on Computational Bioengineering ICCB 2015 M. Cerrolaza and S.Oller (Eds) DATABASE MAMMOGRAPHIC IMAGES UNDER PERUVIAN CASES AND DETECTION OF MICROCALCIFICATIONS BASED ON FRACTAL
VI International Conference on Computational Bioengineering ICCB 2015 M. Cerrolaza and S.Oller (Eds) DATABASE MAMMOGRAPHIC IMAGES UNDER PERUVIAN CASES AND DETECTION OF MICROCALCIFICATIONS BASED ON FRACTAL
Memory Allocation Technique for Segregated Free List Based on Genetic Algorithm
 Journal of Al-Nahrain University Vol.15 (2), June, 2012, pp.161-168 Science Memory Allocation Technique for Segregated Free List Based on Genetic Algorithm Manal F. Younis Computer Department, College
Journal of Al-Nahrain University Vol.15 (2), June, 2012, pp.161-168 Science Memory Allocation Technique for Segregated Free List Based on Genetic Algorithm Manal F. Younis Computer Department, College
JPEG compression of monochrome 2D-barcode images using DCT coefficient distributions
 Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Pre. JPEG compression of monochrome D-barcode images using DCT coefficient distributions Keng Teong Tan Hong Kong Baptist University Douglas Chai
Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Pre. JPEG compression of monochrome D-barcode images using DCT coefficient distributions Keng Teong Tan Hong Kong Baptist University Douglas Chai
A New Quantitative Behavioral Model for Financial Prediction
 2011 3rd International Conference on Information and Financial Engineering IPEDR vol.12 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore A New Quantitative Behavioral Model for Financial Prediction Thimmaraya Ramesh
2011 3rd International Conference on Information and Financial Engineering IPEDR vol.12 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore A New Quantitative Behavioral Model for Financial Prediction Thimmaraya Ramesh
Applying Particle Swarm Optimization to Software Testing
 Applying Particle Swarm Optimization to Software Testing Andreas Windisch DaimlerChrysler AG Research and Technology Alt-Moabit 96a, D-559 Berlin, Germany Phone: +49 3 39982 463 Stefan Wappler Technical
Applying Particle Swarm Optimization to Software Testing Andreas Windisch DaimlerChrysler AG Research and Technology Alt-Moabit 96a, D-559 Berlin, Germany Phone: +49 3 39982 463 Stefan Wappler Technical
Keywords Android, Copyright Protection, Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT), Digital Watermarking, Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT), YCbCr.
 Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Web Based Novel
Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Web Based Novel
COMPUTATIONIMPROVEMENTOFSTOCKMARKETDECISIONMAKING MODELTHROUGHTHEAPPLICATIONOFGRID. Jovita Nenortaitė
 ISSN 1392 124X INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND CONTROL, 2005, Vol.34, No.3 COMPUTATIONIMPROVEMENTOFSTOCKMARKETDECISIONMAKING MODELTHROUGHTHEAPPLICATIONOFGRID Jovita Nenortaitė InformaticsDepartment,VilniusUniversityKaunasFacultyofHumanities
ISSN 1392 124X INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND CONTROL, 2005, Vol.34, No.3 COMPUTATIONIMPROVEMENTOFSTOCKMARKETDECISIONMAKING MODELTHROUGHTHEAPPLICATIONOFGRID Jovita Nenortaitė InformaticsDepartment,VilniusUniversityKaunasFacultyofHumanities
Hybrid Evolution of Heterogeneous Neural Networks
 Hybrid Evolution of Heterogeneous Neural Networks 01001110 01100101 01110101 01110010 01101111 01101110 01101111 01110110 01100001 00100000 01110011 01101011 01110101 01110000 01101001 01101110 01100001
Hybrid Evolution of Heterogeneous Neural Networks 01001110 01100101 01110101 01110010 01101111 01101110 01101111 01110110 01100001 00100000 01110011 01101011 01110101 01110000 01101001 01101110 01100001
Improved PSO-based Task Scheduling Algorithm in Cloud Computing
 Journal of Information & Computational Science 9: 13 (2012) 3821 3829 Available at http://www.joics.com Improved PSO-based Tas Scheduling Algorithm in Cloud Computing Shaobin Zhan, Hongying Huo Shenzhen
Journal of Information & Computational Science 9: 13 (2012) 3821 3829 Available at http://www.joics.com Improved PSO-based Tas Scheduling Algorithm in Cloud Computing Shaobin Zhan, Hongying Huo Shenzhen
Dyna ISSN: 0012-7353 [email protected] Universidad Nacional de Colombia Colombia
 Dyna ISSN: 0012-7353 [email protected] Universidad Nacional de Colombia Colombia VELÁSQUEZ HENAO, JUAN DAVID; RUEDA MEJIA, VIVIANA MARIA; FRANCO CARDONA, CARLOS JAIME ELECTRICITY DEMAND FORECASTING USING
Dyna ISSN: 0012-7353 [email protected] Universidad Nacional de Colombia Colombia VELÁSQUEZ HENAO, JUAN DAVID; RUEDA MEJIA, VIVIANA MARIA; FRANCO CARDONA, CARLOS JAIME ELECTRICITY DEMAND FORECASTING USING
Effect of Using Neural Networks in GA-Based School Timetabling
 Effect of Using Neural Networks in GA-Based School Timetabling JANIS ZUTERS Department of Computer Science University of Latvia Raina bulv. 19, Riga, LV-1050 LATVIA [email protected] Abstract: - The school
Effect of Using Neural Networks in GA-Based School Timetabling JANIS ZUTERS Department of Computer Science University of Latvia Raina bulv. 19, Riga, LV-1050 LATVIA [email protected] Abstract: - The school
A Secure File Transfer based on Discrete Wavelet Transformation and Audio Watermarking Techniques
 A Secure File Transfer based on Discrete Wavelet Transformation and Audio Watermarking Techniques Vineela Behara,Y Ramesh Department of Computer Science and Engineering Aditya institute of Technology and
A Secure File Transfer based on Discrete Wavelet Transformation and Audio Watermarking Techniques Vineela Behara,Y Ramesh Department of Computer Science and Engineering Aditya institute of Technology and
International Journal of Computer Science Trends and Technology (IJCST) Volume 2 Issue 3, May-Jun 2014
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS A Survey of Data Mining: Concepts with Applications and its Future Scope Dr. Zubair Khan 1, Ashish Kumar 2, Sunny Kumar 3 M.Tech Research Scholar 2. Department of Computer
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS A Survey of Data Mining: Concepts with Applications and its Future Scope Dr. Zubair Khan 1, Ashish Kumar 2, Sunny Kumar 3 M.Tech Research Scholar 2. Department of Computer
A Robust and Lossless Information Embedding in Image Based on DCT and Scrambling Algorithms
 A Robust and Lossless Information Embedding in Image Based on DCT and Scrambling Algorithms Dr. Mohammad V. Malakooti Faculty and Head of Department of Computer Engineering, Islamic Azad University, UAE
A Robust and Lossless Information Embedding in Image Based on DCT and Scrambling Algorithms Dr. Mohammad V. Malakooti Faculty and Head of Department of Computer Engineering, Islamic Azad University, UAE
Multi-factor Authentication in Banking Sector
 Multi-factor Authentication in Banking Sector Tushar Bhivgade, Mithilesh Bhusari, Ajay Kuthe, Bhavna Jiddewar,Prof. Pooja Dubey Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Rajiv Gandhi College of Engineering
Multi-factor Authentication in Banking Sector Tushar Bhivgade, Mithilesh Bhusari, Ajay Kuthe, Bhavna Jiddewar,Prof. Pooja Dubey Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Rajiv Gandhi College of Engineering
International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
 DOI: 10.15662/ijareeie.2014.0307061 Economic Dispatch of Power System Optimization with Power Generation Schedule Using Evolutionary Technique Girish Kumar 1, Rameshwar singh 2 PG Student [Control system],
DOI: 10.15662/ijareeie.2014.0307061 Economic Dispatch of Power System Optimization with Power Generation Schedule Using Evolutionary Technique Girish Kumar 1, Rameshwar singh 2 PG Student [Control system],
Optimizing Configuration and Application Mapping for MPSoC Architectures
 Optimizing Configuration and Application Mapping for MPSoC Architectures École Polytechnique de Montréal, Canada Email : [email protected] 1 Multi-Processor Systems on Chip (MPSoC) Design Trends
Optimizing Configuration and Application Mapping for MPSoC Architectures École Polytechnique de Montréal, Canada Email : [email protected] 1 Multi-Processor Systems on Chip (MPSoC) Design Trends
GPUs for Scientific Computing
 GPUs for Scientific Computing p. 1/16 GPUs for Scientific Computing Mike Giles [email protected] Oxford-Man Institute of Quantitative Finance Oxford University Mathematical Institute Oxford e-research
GPUs for Scientific Computing p. 1/16 GPUs for Scientific Computing Mike Giles [email protected] Oxford-Man Institute of Quantitative Finance Oxford University Mathematical Institute Oxford e-research
Graphical Processing Units to Accelerate Orthorectification, Atmospheric Correction and Transformations for Big Data
 Graphical Processing Units to Accelerate Orthorectification, Atmospheric Correction and Transformations for Big Data Amanda O Connor, Bryan Justice, and A. Thomas Harris IN52A. Big Data in the Geosciences:
Graphical Processing Units to Accelerate Orthorectification, Atmospheric Correction and Transformations for Big Data Amanda O Connor, Bryan Justice, and A. Thomas Harris IN52A. Big Data in the Geosciences:
APPLICATION OF ADVANCED SEARCH- METHODS FOR AUTOMOTIVE DATA-BUS SYSTEM SIGNAL INTEGRITY OPTIMIZATION
 APPLICATION OF ADVANCED SEARCH- METHODS FOR AUTOMOTIVE DATA-BUS SYSTEM SIGNAL INTEGRITY OPTIMIZATION Harald Günther 1, Stephan Frei 1, Thomas Wenzel, Wolfgang Mickisch 1 Technische Universität Dortmund,
APPLICATION OF ADVANCED SEARCH- METHODS FOR AUTOMOTIVE DATA-BUS SYSTEM SIGNAL INTEGRITY OPTIMIZATION Harald Günther 1, Stephan Frei 1, Thomas Wenzel, Wolfgang Mickisch 1 Technische Universität Dortmund,
Speed Performance Improvement of Vehicle Blob Tracking System
 Speed Performance Improvement of Vehicle Blob Tracking System Sung Chun Lee and Ram Nevatia University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA 90089, USA [email protected], [email protected] Abstract. A speed
Speed Performance Improvement of Vehicle Blob Tracking System Sung Chun Lee and Ram Nevatia University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA 90089, USA [email protected], [email protected] Abstract. A speed
Solving Engineering Optimization Problems with the Simple Constrained Particle Swarm Optimizer
 Informatica 32 (2008) 319 326 319 Solving Engineering Optimization Problems with the Simple Constrained Particle Swarm Optimizer Leticia C. Cagnina and Susana C. Esquivel LIDIC, Universidad Nacional de
Informatica 32 (2008) 319 326 319 Solving Engineering Optimization Problems with the Simple Constrained Particle Swarm Optimizer Leticia C. Cagnina and Susana C. Esquivel LIDIC, Universidad Nacional de
International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational and Applied Sciences (IJETCAS) www.iasir.net
 International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research) International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational
International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research) International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational
ACO Based Dynamic Resource Scheduling for Improving Cloud Performance
 ACO Based Dynamic Resource Scheduling for Improving Cloud Performance Priyanka Mod 1, Prof. Mayank Bhatt 2 Computer Science Engineering Rishiraj Institute of Technology 1 Computer Science Engineering Rishiraj
ACO Based Dynamic Resource Scheduling for Improving Cloud Performance Priyanka Mod 1, Prof. Mayank Bhatt 2 Computer Science Engineering Rishiraj Institute of Technology 1 Computer Science Engineering Rishiraj
EVOLUTIONARY ALGORITHMS FOR FIRE AND RESCUE SERVICE DECISION MAKING
 EVOLUTIONARY ALGORITHMS FOR FIRE AND RESCUE SERVICE DECISION MAKING Dr. Alastair Clarke, Prof. John Miles and Prof. Yacine Rezgui Cardiff School of Engineering, Cardiff, UK ABSTRACT Determining high performance
EVOLUTIONARY ALGORITHMS FOR FIRE AND RESCUE SERVICE DECISION MAKING Dr. Alastair Clarke, Prof. John Miles and Prof. Yacine Rezgui Cardiff School of Engineering, Cardiff, UK ABSTRACT Determining high performance
Security Based Data Transfer and Privacy Storage through Watermark Detection
 Security Based Data Transfer and Privacy Storage through Watermark Detection Gowtham.T 1 Pradeep Kumar.G 2 1PG Scholar, Applied Electronics, Nandha Engineering College, Anna University, Erode, India. 2Assistant
Security Based Data Transfer and Privacy Storage through Watermark Detection Gowtham.T 1 Pradeep Kumar.G 2 1PG Scholar, Applied Electronics, Nandha Engineering College, Anna University, Erode, India. 2Assistant
Application of Neural Network in User Authentication for Smart Home System
 Application of Neural Network in User Authentication for Smart Home System A. Joseph, D.B.L. Bong, D.A.A. Mat Abstract Security has been an important issue and concern in the smart home systems. Smart
Application of Neural Network in User Authentication for Smart Home System A. Joseph, D.B.L. Bong, D.A.A. Mat Abstract Security has been an important issue and concern in the smart home systems. Smart
GA as a Data Optimization Tool for Predictive Analytics
 GA as a Data Optimization Tool for Predictive Analytics Chandra.J 1, Dr.Nachamai.M 2,Dr.Anitha.S.Pillai 3 1Assistant Professor, Department of computer Science, Christ University, Bangalore,India, [email protected]
GA as a Data Optimization Tool for Predictive Analytics Chandra.J 1, Dr.Nachamai.M 2,Dr.Anitha.S.Pillai 3 1Assistant Professor, Department of computer Science, Christ University, Bangalore,India, [email protected]
01219211 Software Development Training Camp 1 (0-3) Prerequisite : 01204214 Program development skill enhancement camp, at least 48 person-hours.
 (International Program) 01219141 Object-Oriented Modeling and Programming 3 (3-0) Object concepts, object-oriented design and analysis, object-oriented analysis relating to developing conceptual models
(International Program) 01219141 Object-Oriented Modeling and Programming 3 (3-0) Object concepts, object-oriented design and analysis, object-oriented analysis relating to developing conceptual models
Hybrid Algorithm using the advantage of ACO and Cuckoo Search for Job Scheduling
 Hybrid Algorithm using the advantage of ACO and Cuckoo Search for Job Scheduling R.G. Babukartik 1, P. Dhavachelvan 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Pondicherry University, Pondicherry, India {r.g.babukarthik,
Hybrid Algorithm using the advantage of ACO and Cuckoo Search for Job Scheduling R.G. Babukartik 1, P. Dhavachelvan 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Pondicherry University, Pondicherry, India {r.g.babukarthik,
Accelerating BIRCH for Clustering Large Scale Streaming Data Using CUDA Dynamic Parallelism
 Accelerating BIRCH for Clustering Large Scale Streaming Data Using CUDA Dynamic Parallelism Jianqiang Dong, Fei Wang and Bo Yuan Intelligent Computing Lab, Division of Informatics Graduate School at Shenzhen,
Accelerating BIRCH for Clustering Large Scale Streaming Data Using CUDA Dynamic Parallelism Jianqiang Dong, Fei Wang and Bo Yuan Intelligent Computing Lab, Division of Informatics Graduate School at Shenzhen,
Introduction To Genetic Algorithms
 1 Introduction To Genetic Algorithms Dr. Rajib Kumar Bhattacharjya Department of Civil Engineering IIT Guwahati Email: [email protected] References 2 D. E. Goldberg, Genetic Algorithm In Search, Optimization
1 Introduction To Genetic Algorithms Dr. Rajib Kumar Bhattacharjya Department of Civil Engineering IIT Guwahati Email: [email protected] References 2 D. E. Goldberg, Genetic Algorithm In Search, Optimization
Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization
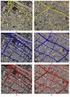 Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization Er.Harish Kundra Assistant Professor & Head Rayat Institute of Engineering & IT, Railmajra, Punjab,India. Dr. V.K.Panchal Director, DTRL,DRDO,
Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization Er.Harish Kundra Assistant Professor & Head Rayat Institute of Engineering & IT, Railmajra, Punjab,India. Dr. V.K.Panchal Director, DTRL,DRDO,
How Can Metaheuristics Help Software Engineers
 and Software How Can Help Software Engineers Enrique Alba [email protected] http://www.lcc.uma.es/~eat Universidad de Málaga, ESPAÑA Enrique Alba How Can Help Software Engineers of 8 and Software What s a
and Software How Can Help Software Engineers Enrique Alba [email protected] http://www.lcc.uma.es/~eat Universidad de Málaga, ESPAÑA Enrique Alba How Can Help Software Engineers of 8 and Software What s a
ultra fast SOM using CUDA
 ultra fast SOM using CUDA SOM (Self-Organizing Map) is one of the most popular artificial neural network algorithms in the unsupervised learning category. Sijo Mathew Preetha Joy Sibi Rajendra Manoj A
ultra fast SOM using CUDA SOM (Self-Organizing Map) is one of the most popular artificial neural network algorithms in the unsupervised learning category. Sijo Mathew Preetha Joy Sibi Rajendra Manoj A
Master in Science, specialty in Information Systems. ITESM. México, June 1984.
 LAURA CRUZ REYES Instituto Tecnológico de Cd. Madero División de Estudios de Posgrado e Investigación Juventino Rosas y Jesús Urueta Cd. Madero Tamaulipas México CP. 89440 Tel/Fax (52) 833 215 85 44 e-mail:
LAURA CRUZ REYES Instituto Tecnológico de Cd. Madero División de Estudios de Posgrado e Investigación Juventino Rosas y Jesús Urueta Cd. Madero Tamaulipas México CP. 89440 Tel/Fax (52) 833 215 85 44 e-mail:
Load balancing in a heterogeneous computer system by self-organizing Kohonen network
 Bull. Nov. Comp. Center, Comp. Science, 25 (2006), 69 74 c 2006 NCC Publisher Load balancing in a heterogeneous computer system by self-organizing Kohonen network Mikhail S. Tarkov, Yakov S. Bezrukov Abstract.
Bull. Nov. Comp. Center, Comp. Science, 25 (2006), 69 74 c 2006 NCC Publisher Load balancing in a heterogeneous computer system by self-organizing Kohonen network Mikhail S. Tarkov, Yakov S. Bezrukov Abstract.
Hardware-Aware Analysis and. Presentation Date: Sep 15 th 2009 Chrissie C. Cui
 Hardware-Aware Analysis and Optimization of Stable Fluids Presentation Date: Sep 15 th 2009 Chrissie C. Cui Outline Introduction Highlights Flop and Bandwidth Analysis Mehrstellen Schemes Advection Caching
Hardware-Aware Analysis and Optimization of Stable Fluids Presentation Date: Sep 15 th 2009 Chrissie C. Cui Outline Introduction Highlights Flop and Bandwidth Analysis Mehrstellen Schemes Advection Caching
LBM BASED FLOW SIMULATION USING GPU COMPUTING PROCESSOR
 LBM BASED FLOW SIMULATION USING GPU COMPUTING PROCESSOR Frédéric Kuznik, frederic.kuznik@insa lyon.fr 1 Framework Introduction Hardware architecture CUDA overview Implementation details A simple case:
LBM BASED FLOW SIMULATION USING GPU COMPUTING PROCESSOR Frédéric Kuznik, frederic.kuznik@insa lyon.fr 1 Framework Introduction Hardware architecture CUDA overview Implementation details A simple case:
Scalability and Classifications
 Scalability and Classifications 1 Types of Parallel Computers MIMD and SIMD classifications shared and distributed memory multicomputers distributed shared memory computers 2 Network Topologies static
Scalability and Classifications 1 Types of Parallel Computers MIMD and SIMD classifications shared and distributed memory multicomputers distributed shared memory computers 2 Network Topologies static
A Novel Web Optimization Technique using Enhanced Particle Swarm Optimization
 A Novel Web Optimization Technique using Enhanced Particle Swarm Optimization P.N.Nesarajan Research Scholar, Erode Arts & Science College, Erode M.Venkatachalam, Ph.D Associate Professor & HOD of Electronics,
A Novel Web Optimization Technique using Enhanced Particle Swarm Optimization P.N.Nesarajan Research Scholar, Erode Arts & Science College, Erode M.Venkatachalam, Ph.D Associate Professor & HOD of Electronics,
A GENETIC ALGORITHM FOR RESOURCE LEVELING OF CONSTRUCTION PROJECTS
 A GENETIC ALGORITHM FOR RESOURCE LEVELING OF CONSTRUCTION PROJECTS Mahdi Abbasi Iranagh 1 and Rifat Sonmez 2 Dept. of Civil Engrg, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, 06800, Turkey Critical path
A GENETIC ALGORITHM FOR RESOURCE LEVELING OF CONSTRUCTION PROJECTS Mahdi Abbasi Iranagh 1 and Rifat Sonmez 2 Dept. of Civil Engrg, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, 06800, Turkey Critical path
An ACO Approach to Solve a Variant of TSP
 An ACO Approach to Solve a Variant of TSP Bharat V. Chawda, Nitesh M. Sureja Abstract This study is an investigation on the application of Ant Colony Optimization to a variant of TSP. This paper presents
An ACO Approach to Solve a Variant of TSP Bharat V. Chawda, Nitesh M. Sureja Abstract This study is an investigation on the application of Ant Colony Optimization to a variant of TSP. This paper presents
Web Mining using Artificial Ant Colonies : A Survey
 Web Mining using Artificial Ant Colonies : A Survey Richa Gupta Department of Computer Science University of Delhi ABSTRACT : Web mining has been very crucial to any organization as it provides useful
Web Mining using Artificial Ant Colonies : A Survey Richa Gupta Department of Computer Science University of Delhi ABSTRACT : Web mining has been very crucial to any organization as it provides useful
Performance Study of Parallel Programming Paradigms on a Multicore Clusters using Ant Colony Optimization for Job-flow scheduling problems
 Performance Study of Parallel Programming Paradigms on a Multicore Clusters using Ant Colony Optimization for Job-flow scheduling problems Nagaveni V # Dr. G T Raju * # Department of Computer Science and
Performance Study of Parallel Programming Paradigms on a Multicore Clusters using Ant Colony Optimization for Job-flow scheduling problems Nagaveni V # Dr. G T Raju * # Department of Computer Science and
Random forest algorithm in big data environment
 Random forest algorithm in big data environment Yingchun Liu * School of Economics and Management, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China Received 1 September 2014, www.cmnt.lv Abstract Random forest
Random forest algorithm in big data environment Yingchun Liu * School of Economics and Management, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China Received 1 September 2014, www.cmnt.lv Abstract Random forest
LOAD BALANCING IN CLOUD COMPUTING
 LOAD BALANCING IN CLOUD COMPUTING Neethu M.S 1 PG Student, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, LBSITW (India) ABSTRACT Cloud computing is emerging as a new paradigm for manipulating, configuring,
LOAD BALANCING IN CLOUD COMPUTING Neethu M.S 1 PG Student, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, LBSITW (India) ABSTRACT Cloud computing is emerging as a new paradigm for manipulating, configuring,
CS Master Level Courses and Areas COURSE DESCRIPTIONS. CSCI 521 Real-Time Systems. CSCI 522 High Performance Computing
 CS Master Level Courses and Areas The graduate courses offered may change over time, in response to new developments in computer science and the interests of faculty and students; the list of graduate
CS Master Level Courses and Areas The graduate courses offered may change over time, in response to new developments in computer science and the interests of faculty and students; the list of graduate
ACCELERATING SELECT WHERE AND SELECT JOIN QUERIES ON A GPU
 Computer Science 14 (2) 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.7494/csci.2013.14.2.243 Marcin Pietroń Pawe l Russek Kazimierz Wiatr ACCELERATING SELECT WHERE AND SELECT JOIN QUERIES ON A GPU Abstract This paper presents
Computer Science 14 (2) 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.7494/csci.2013.14.2.243 Marcin Pietroń Pawe l Russek Kazimierz Wiatr ACCELERATING SELECT WHERE AND SELECT JOIN QUERIES ON A GPU Abstract This paper presents
A Multi-Objective Performance Evaluation in Grid Task Scheduling using Evolutionary Algorithms
 A Multi-Objective Performance Evaluation in Grid Task Scheduling using Evolutionary Algorithms MIGUEL CAMELO, YEZID DONOSO, HAROLD CASTRO Systems and Computer Engineering Department Universidad de los
A Multi-Objective Performance Evaluation in Grid Task Scheduling using Evolutionary Algorithms MIGUEL CAMELO, YEZID DONOSO, HAROLD CASTRO Systems and Computer Engineering Department Universidad de los
Optimizing a 3D-FWT code in a cluster of CPUs+GPUs
 Optimizing a 3D-FWT code in a cluster of CPUs+GPUs Gregorio Bernabé Javier Cuenca Domingo Giménez Universidad de Murcia Scientific Computing and Parallel Programming Group XXIX Simposium Nacional de la
Optimizing a 3D-FWT code in a cluster of CPUs+GPUs Gregorio Bernabé Javier Cuenca Domingo Giménez Universidad de Murcia Scientific Computing and Parallel Programming Group XXIX Simposium Nacional de la
Praktikum Wissenschaftliches Rechnen (Performance-optimized optimized Programming)
 Praktikum Wissenschaftliches Rechnen (Performance-optimized optimized Programming) Dynamic Load Balancing Dr. Ralf-Peter Mundani Center for Simulation Technology in Engineering Technische Universität München
Praktikum Wissenschaftliches Rechnen (Performance-optimized optimized Programming) Dynamic Load Balancing Dr. Ralf-Peter Mundani Center for Simulation Technology in Engineering Technische Universität München
Minimizing Response Time for Scheduled Tasks Using the Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm in a Cloud Computing Environment
 Minimizing Response Time for Scheduled Tasks Using the Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm in a Cloud Computing Environment by Maryam Houtinezhad, Department of Computer Engineering, Artificial
Minimizing Response Time for Scheduled Tasks Using the Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm in a Cloud Computing Environment by Maryam Houtinezhad, Department of Computer Engineering, Artificial
QoS Guaranteed Intelligent Routing Using Hybrid PSO-GA in Wireless Mesh Networks
 BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 15, No 1 Sofia 2015 Print ISSN: 1311-9702; Online ISSN: 1314-4081 DOI: 10.1515/cait-2015-0007 QoS Guaranteed Intelligent Routing
BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 15, No 1 Sofia 2015 Print ISSN: 1311-9702; Online ISSN: 1314-4081 DOI: 10.1515/cait-2015-0007 QoS Guaranteed Intelligent Routing
A Study of Local Optima in the Biobjective Travelling Salesman Problem
 A Study of Local Optima in the Biobjective Travelling Salesman Problem Luis Paquete, Marco Chiarandini and Thomas Stützle FG Intellektik, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Alexanderstr. 10, Darmstadt,
A Study of Local Optima in the Biobjective Travelling Salesman Problem Luis Paquete, Marco Chiarandini and Thomas Stützle FG Intellektik, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Alexanderstr. 10, Darmstadt,
How To Use Neural Networks In Data Mining
 International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1449 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Neural Networks in Data Mining Priyanka Gaur Department of Information and
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1449 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Neural Networks in Data Mining Priyanka Gaur Department of Information and
Contents. Dedication List of Figures List of Tables. Acknowledgments
 Contents Dedication List of Figures List of Tables Foreword Preface Acknowledgments v xiii xvii xix xxi xxv Part I Concepts and Techniques 1. INTRODUCTION 3 1 The Quest for Knowledge 3 2 Problem Description
Contents Dedication List of Figures List of Tables Foreword Preface Acknowledgments v xiii xvii xix xxi xxv Part I Concepts and Techniques 1. INTRODUCTION 3 1 The Quest for Knowledge 3 2 Problem Description
