Low Back Pain Protocols
|
|
|
- Jessica Morgan
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Low Back Pain Protocols Introduction: Diagnostic Triage And 1. Patient Group Adults aged 18 years and over with routine low back problems. Patients who have had recent surgery should be referred directly to Secondary Care. 2. Diagnostic Triage and Perform diagnostic triage to exclude serious spinal pathology, and distinguish a nerve root problem from simple back pain. See Section 1 for Triage and. X-ray and MRI guidelines are contained in Section Primary Care Management of simple Backache and Acute Distress Follow Flow Chart for Primary Care Management of simple backaches, or simple backache with distress in Section 3 C.S.A.G. DRAM ESR FBC MRI NSAID OT RTA Clinical Standards Advisory Committee Distress and Risk Assessment Erythrocyte sedimentation rate Full Blood Count Magnetic Resonance imaging n-steroidal Anti inflammatory Drug Occupational Therapy Road Traffic Accident
2 Diagnostic Triage Red Flags indicate possible serious spinal pathology Onset under age 20 or over age 55 Violent trauma: fall from height, RTA Constant, progressive, non-mechanical pain PMH Carcinoma, Systemic Steroids, drug abuse, HIV Systemically unwell, weight loss Thoracic pain Persisting severe restriction of lumbar flexion Widespread neurological symptoms or signs Structural deformity If there are suspicious clinical features or pain not settling, appropriate investigations e.g. FBC, ESR, plain X-rays, MRI should be considered Or Consider emergency referral if acute spinal cord injury or widespread neurological disorder suspected Cauda Equina Syndrome Difficulty with micturation Sphincter disturbance or faecal incontinence Widespread or progressive motor weakness in the legs or gait disturbance Saddle anaesthesia about the anus, perineum or genitals IMMEDIATELY LIAISE WITH ON-CALL ORTHOPAEDIC TEAM and CONSIDER EMERGENCY REFERRAL / ADMISSION Inflammatory Disorders (Ankylosing Spondylitis and related disorders) Gradual onset before age 40 Marked morning stiffness Persisting limitation spinal movements in all directions Peripheral joint involvement Iritis, skin ashes (psoriasis), colitis, urethral discharge Family history Undertake appropriate investigations e.g. consider FBC, ESR, HLA, B27, RA Factor, X-rays etc. Consider prompt referral into Secondary Care Rheumatology Simple Backache: Presentation age years Limbosacral region, buttocks and thighs Pain mechanical in nature varies with physical activity, varies with time Patient well Prognosis good 90% recover from acute attack in 6 weeks X-ray & Secondary Care Referrals t routinely required unless Red Flags are suspected on clinical examination. During initial management practice psychosocial approach this is fundamental to promote positive attitudes to activity and work. Provide reassurance nothing dangerous and expect recovery. Drug Therapy Prescribe analgesics at regular intervals not p.r.n. Start with paracetamol. If inadequate, substitute NSAIDs (e.g. Ibuprofen or Diclofenec) and then paracetamol weak Opioid compound (e.g. Co drydamol/co proxamol). Finally, consider adding a short course of muscle relaxant (e.g. Diazepam or Baclofen) Avoid strong Opioids if possible. Bed Rest Do not recommend or use bed rest as a treatment. Some patients may be confined to bed for a few days as a consequence of their pain but this should not be considered a treatment
3 Diagnostic Triage Activity Patients should be advised to stay as active as possible and to continue normal daily activities, increasing progressively over a few days or weeks. If working, advise to stay at work or return to work as soon as possible. Physiotherapy If not resolving, consider referral to Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy from 2 weeks. Simple Backache Unresolved Nerve Root Pain Unilateral leg pain worse than low back pain Radiates to foot or toes Numbness and paraesthesia in same distribution Nerve irritation signs reduced SLR which reproduces leg pain Motor, sensory or reflex change limited to one nerve root Prognosis reasonable 50% recover from acute attach within 6 weeks Physiotherapy treatment should be considered for patients who need additional help with pain relief or who are failing to return to normal activities Re-assess Review diagnostic triage consider X-ray, ESR and DRAM assessment Physiotherapy should be considered for patients who have not returned to ordinary activities and work by 6 weeks * Secondary care referral not required for one month, provided resolving. Give guarded positive messages, conservative management should suffice but may take a month or 2, full recovery expected but recurrence possible. Consider appropriate analgesia and refer to Acute Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy Service. t resolving at 6 weeks consider referral to MSK Tier 2 services or consider orthopaedic opinion if you feel surgery is indicated
4 Appendix 2 Extracted from the Clinical Standards Advisory Group Guidelines 1994 When to request an X-ray Plain X-rays of the lumbar spine are recommended for ruling out fractures in patients with acute low back problems when any of the following Red Flags are present: Recent significant trauma (any age) Recent mild trauma (patient over age of 50) History of prolonged steroid use, osteoporosis, patient over age of 50 Plain X-rays in combination with FBC and ESR may be useful for ruling out tumour or infection in patients with acute low back problems when any of the following Red Flags are present: Prior cancer or recent infection Fever over 100º F IV drug abuse Prolonged steroid use Low back pain worse with rest Unexplained weight loss In the presence of Red Flags, especially for tumour or infection, the use of other imaging studies such as bone scan, CT or MRI may be clinically indicated even if plain X-rays are negative. A bone scan is recommended to evaluate acute low back problems when spinal tumour, infection or occult fracture is suspected from Red Flags on medical history, physical examination, corroborative lab test or plain X-ray findings. Bone scans are contraindicated during pregnancy. Bone scans will be carried out in Secondary care only When to Request an MRI Scan For use for patients requiring short protocol MRI scan, for screening purposes. Other views o full MRIs should be discussed with a Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon prior to being requested Short Protocol MRIs Patients can be divided into 2 broad categories: Back pain with sciatica and back pain without sciatica: Back Pain with Sciatica DIAGNOSIS Back pain with sciatica + worrying features such as cauda equina syndrome, or signs suggesting tumour or infection Back pain with no worrying features ACTION Immediate MRI and a consultant referral If the MRI is normal, no further investigations are needed. Plain films are only required if the MRI suggests the need for them imaging is required until after 6-8 weeks conservative treatment. If the patient fails to respond and surgery or percutaneous therapy is judged appropriate then the patient should have a full MRI Back Pain with no significant Radiation DIAGNOSIS Back pain with no significant radiation. If there is no improvement after 8 weeks If these patients fail to respond then it is possible to complete the rest of the MRI at a later stage prior to a Consultant referral ACTION Request a limited MRI utilising a Sagittal T and STIR sequence which should exclude significant pathology ie tumour, infection, pars defects, osteoporotic collapse. As there is no sciatica there is no need to look for compressive symptoms and thus the shorter scan NB: 40% of adults will have disc herniation yet be asymptomatic and therefore to search for this in the absence of clear neurology is often confusing These guidelines have been developed from the Oxford Nuffield Scheme
5 Appendix 3 Extracted from Clinical Standards Advisory Group Report 1994 Primary Care Management of Simple Backache Is the patient acutely distressed? PRIMARY MANAGEMENT OF SIMPLE BACKACHE Provide reassurance: nothing dangerous expect recovery Symptomatic measures: Analgesics, NSAIDs, local heat, cold Modified activities: Avoid aggravation Avoid debility PRIMARY MANAGEMENT OF SIMPLE BACKACHE & ACUTE DISTRESS Is acute distress settling? Provide reassurance: nothing dangerous expect recovery X-ray & Specialist not required Symptomatic measures: Analgesics, NSAIDs, Heat, cold, avoid narcotics if poss. <2/52 : sedation <2/52 Modified activities: bed rest 1-3 days Is the pain settling, even if still present? Adjust analgesics Progressively increase activity PHYSICAL THERAPY OR ACUTE PAIN SERVICE Adjust analgesics Physical Therapy Progressively increase activity RETURN TO WORK OR NORMAL ACTIVITY Consider physical therapy RETURN TO WORK OR NORMAL ACTIVITY REASSESS Review diagnostic triage. Consider X-ray & ESR Psychosocial & vocational assessment -VE +VE REFER OR MANAGE APPROPRIATELY CONTINUED PRIMARY CARE MANAGEMENT Patient information & advice Alternative symptomatic measures Physical Therapy Active rehabilitation programme RETURN TO WORK OR NORMAL ACTIVITY CONSIDER SECOND OPTION Specialist Physical Therapist G.P. with special interest RETURN TO WORK OR NORMAL ACTIVITY FAILED PRIMARY CARE MANAGEMENT SECONDARY REFERRAL TO BACK PAIN REHABILITATION SERVICE
Clinical Guideline. Low Back Pain Orthopaedics. Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department. 1 Purpose. 2 Background
 Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department Clinical Guideline Orthopaedics Review Officer: Katherine Isoardi Version no: 1 Approval date: 18/03/2015 Review date: 18/03/2017 Approving Officer Dr James
Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department Clinical Guideline Orthopaedics Review Officer: Katherine Isoardi Version no: 1 Approval date: 18/03/2015 Review date: 18/03/2017 Approving Officer Dr James
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
BACK PAIN PATHWAY DEFINTIONS
 BACK PAIN PATHWAY DEFINTIONS Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES) Current or imminent compression of the sacral nerve roots resulting in neurogenic bladder and bowel dysfunction. Symptoms typically include: severe
BACK PAIN PATHWAY DEFINTIONS Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES) Current or imminent compression of the sacral nerve roots resulting in neurogenic bladder and bowel dysfunction. Symptoms typically include: severe
Sample Treatment Protocol
 Sample Treatment Protocol 1 Adults with acute episode of LBP Definition: Acute episode Back pain lasting
Sample Treatment Protocol 1 Adults with acute episode of LBP Definition: Acute episode Back pain lasting
The Spine Center at Beth Israel Deaconess
 Spinal Pain The Spine Center at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center developed the following detailed eplanation of our care pathways for primary care providers to help support your interactions with patients
Spinal Pain The Spine Center at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center developed the following detailed eplanation of our care pathways for primary care providers to help support your interactions with patients
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: NEUROSURGERY
 Outpatient Referral Guidelines Page 1 1 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: NEUROSURGERY Essential Referral Content Date of birth Demographic Contact details (including mobile phone) Referring GP details Interpreter
Outpatient Referral Guidelines Page 1 1 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: NEUROSURGERY Essential Referral Content Date of birth Demographic Contact details (including mobile phone) Referring GP details Interpreter
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
Musculoskeletal: Acute Lower Back Pain
 Musculoskeletal: Acute Lower Back Pain Acute Lower Back Pain Back Pain only Sciatica / Radiculopathy Possible Cord or Cauda Equina Compression Possible Spinal Canal Stenosis Red Flags Initial conservative
Musculoskeletal: Acute Lower Back Pain Acute Lower Back Pain Back Pain only Sciatica / Radiculopathy Possible Cord or Cauda Equina Compression Possible Spinal Canal Stenosis Red Flags Initial conservative
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk. This reference summary explains herniated disks. It discusses symptoms and causes of the condition, as well as treatment options.
 Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Acute Low Back Pain. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
Spinal Surgery 2. Teaching Aims. Common Spinal Pathologies. Disc Degeneration. Disc Degeneration. Causes of LBP 8/2/13. Common Spinal Conditions
 Teaching Aims Spinal Surgery 2 Mr Mushtaque A. Ishaque BSc(Hons) BChir(Cantab) DM FRCS FRCS(Ed) FRCS(Orth) Hunterian Professor at The Royal College of Surgeons of England Consultant Orthopaedic Spinal
Teaching Aims Spinal Surgery 2 Mr Mushtaque A. Ishaque BSc(Hons) BChir(Cantab) DM FRCS FRCS(Ed) FRCS(Orth) Hunterian Professor at The Royal College of Surgeons of England Consultant Orthopaedic Spinal
Herniated Lumbar Disc
 Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Hitting a Nerve: The Triggers of Sciatica. Bruce Tranmer MD FRCS FACS
 Hitting a Nerve: The Triggers of Sciatica Bruce Tranmer MD FRCS FACS Disclosures I have no financial disclosures Objectives - Sciatica Historical Perspective What is Sciatica What can cause Sciatica Clinical
Hitting a Nerve: The Triggers of Sciatica Bruce Tranmer MD FRCS FACS Disclosures I have no financial disclosures Objectives - Sciatica Historical Perspective What is Sciatica What can cause Sciatica Clinical
Nerve Root Pain. Your back pain diagnosis. Contact Details. Spinal Triage Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre Windmill Road Headington Oxford OX3 7LD
 Nerve Root Pain Contact Details Spinal Triage Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre Windmill Road Headington Oxford OX3 7LD Phone: 01865 738051 Fax: 01865 738027 Web Site www.noc.nhs.uk Nerve Pain Patient Information
Nerve Root Pain Contact Details Spinal Triage Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre Windmill Road Headington Oxford OX3 7LD Phone: 01865 738051 Fax: 01865 738027 Web Site www.noc.nhs.uk Nerve Pain Patient Information
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back
 Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Advanced Practice Provider Academy
 (+)Dean T. Harrison, MPAS,PA C,DFAAPA Director of Mid Level Practitioners; Assistant Medical Director Clinical Evaluation Unit, Division of Emergency Medicine, Department of Surgery, Duke University Medical
(+)Dean T. Harrison, MPAS,PA C,DFAAPA Director of Mid Level Practitioners; Assistant Medical Director Clinical Evaluation Unit, Division of Emergency Medicine, Department of Surgery, Duke University Medical
Pathophysiology of Acute and Chronic Low Back Pain
 Pathophysiology of Acute and Chronic Low Back Pain Mary Beth Partyka MSN APN Adult Nurse Practitioner Adult Pain Service Advocate Christ Medical Center Presentation Objectives Review the incidence of acute
Pathophysiology of Acute and Chronic Low Back Pain Mary Beth Partyka MSN APN Adult Nurse Practitioner Adult Pain Service Advocate Christ Medical Center Presentation Objectives Review the incidence of acute
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck)
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome
 Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Physiotherapy fees and utilization guidelines for auto insurance accident claimants
 No. A-12/97 Property & Casualty ) Auto Physiotherapy fees and utilization guidelines for auto insurance accident claimants To the attention of all insurance companies licensed to transact automobile insurance
No. A-12/97 Property & Casualty ) Auto Physiotherapy fees and utilization guidelines for auto insurance accident claimants To the attention of all insurance companies licensed to transact automobile insurance
Practice Guidelines For Low Back Pain
 Consumers Guide Practice Guidelines For Low Back Pain Copyright 2008 American Chronic Pain Association Page 1 Written by: Penney Cowan Founder Executive Director American Chronic Pain Association Editors:
Consumers Guide Practice Guidelines For Low Back Pain Copyright 2008 American Chronic Pain Association Page 1 Written by: Penney Cowan Founder Executive Director American Chronic Pain Association Editors:
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236
 Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN. Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA
 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA MEDICAL ALGORITHM OF REALITY LOWER BACK PAIN Yes Patient will never get better until case
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA MEDICAL ALGORITHM OF REALITY LOWER BACK PAIN Yes Patient will never get better until case
BACK PAIN MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW
 2014 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: BACK PAIN MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2014 PQRS MEASURES IN BACK PAIN MEASURES GROUP: #148. Back Pain: Initial Visit #149. Back Pain: Physical Exam #150. Back Pain: Advice
2014 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: BACK PAIN MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2014 PQRS MEASURES IN BACK PAIN MEASURES GROUP: #148. Back Pain: Initial Visit #149. Back Pain: Physical Exam #150. Back Pain: Advice
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach
 Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
Spine Trauma: When to Transfer. Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU
 Spine Trauma: When to Transfer Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU Disclosures Depuy Spine Consultant (teaching and courses) Department education and research funds Atlas Spine
Spine Trauma: When to Transfer Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU Disclosures Depuy Spine Consultant (teaching and courses) Department education and research funds Atlas Spine
Clinical guidance for MRI referral
 MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
Herniated Cervical Disc
 Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Acute low back pain. Key reviewers: Mr Chris Hoffman, Orthopaedic Surgeon, Mana Orthopaedics, Wellington
 Acute low back pain Key reviewers: Mr Chris Hoffman, Orthopaedic Surgeon, Mana Orthopaedics, Wellington Dr John MacVicar, Medical Director, Southern Rehab, Christchurch Key concepts: Acute low back pain
Acute low back pain Key reviewers: Mr Chris Hoffman, Orthopaedic Surgeon, Mana Orthopaedics, Wellington Dr John MacVicar, Medical Director, Southern Rehab, Christchurch Key concepts: Acute low back pain
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS?
 SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
.org. Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Low back pain. Quick reference guide. Issue date: May 2009. Early management of persistent non-specific low back pain
 Issue date: May 2009 Low back pain Early management of persistent non-specific low back pain Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Primary Care About this booklet This is a quick reference
Issue date: May 2009 Low back pain Early management of persistent non-specific low back pain Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Primary Care About this booklet This is a quick reference
Preventing & Treating Low Back Pain
 Preventing & Treating Low Back Pain An Introduction to Low Back Pain Low back pain is the number two reason that Americans see a health care practitioner second only to colds and flu. While most people
Preventing & Treating Low Back Pain An Introduction to Low Back Pain Low back pain is the number two reason that Americans see a health care practitioner second only to colds and flu. While most people
There are four main regions of the back; the cervical (C), thoracic (T), lumbar (L), and sacral (S) regions
 Low Back Pain Overview Low back pain is one of the most common disorders in the United States. About 80 percent of people have at least one episode of low back pain during their lifetime. Factors that
Low Back Pain Overview Low back pain is one of the most common disorders in the United States. About 80 percent of people have at least one episode of low back pain during their lifetime. Factors that
Return to same game if sx s resolve within 15 minutes. Return to next game if sx s resolve within one week Return to Competition
 Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
1st Edition 2015. Quick reference guide for the management of acute whiplash. associated disorders
 1 1st Edition 2015 Quick reference guide for the management of acute whiplash associated disorders 2 Quick reference guide for the management of acute whiplash associated disorders, 2015. This quick reference
1 1st Edition 2015 Quick reference guide for the management of acute whiplash associated disorders 2 Quick reference guide for the management of acute whiplash associated disorders, 2015. This quick reference
Management of spinal cord compression
 Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Fact Sheet. Queensland Spinal Cord Injuries Service. Pain Management Following Spinal Cord Injury for Health Professionals
 Pain Management Following Injury for Health Professionals and Introduction Pain is a common problem following SCI. In the case where a person with SCI does have pain, there are treatments available that
Pain Management Following Injury for Health Professionals and Introduction Pain is a common problem following SCI. In the case where a person with SCI does have pain, there are treatments available that
Treating Bulging Discs & Sciatica. Alexander Ching, MD
 Treating Bulging Discs & Sciatica Alexander Ching, MD Disclosures Depuy Spine Teaching and courses K2 Spine Complex Spine Study Group Disclosures Take 2 I am a spine surgeon I like spine surgery I believe
Treating Bulging Discs & Sciatica Alexander Ching, MD Disclosures Depuy Spine Teaching and courses K2 Spine Complex Spine Study Group Disclosures Take 2 I am a spine surgeon I like spine surgery I believe
Information on the Chiropractic Care of Lower Back Pain
 Chiropractic Care of Lower Back Pain Lower back pain is probably the most common condition seen the the Chiropractic office. Each month it is estimated that up to one third of persons experience some type
Chiropractic Care of Lower Back Pain Lower back pain is probably the most common condition seen the the Chiropractic office. Each month it is estimated that up to one third of persons experience some type
TABLE OF CONTENTS Page
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION 3 CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS 5 EVALUATION AND TREATMENT OF ACUTE LOW BACK PROBLEMS IN ADULTS 9 SPECIAL STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC CONSIDERATIONS 15 PSYCHOLOGICAL RISK
TABLE OF CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION 3 CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS 5 EVALUATION AND TREATMENT OF ACUTE LOW BACK PROBLEMS IN ADULTS 9 SPECIAL STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC CONSIDERATIONS 15 PSYCHOLOGICAL RISK
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression
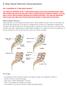 X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
INFORMATION FOR YOU. Lower Back Pain
 INFORMATION FOR YOU Lower Back Pain WHAT IS ACUTE LOWER BACK PAIN? Acute lower back pain is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced as aching, burning, stabbing, sharp
INFORMATION FOR YOU Lower Back Pain WHAT IS ACUTE LOWER BACK PAIN? Acute lower back pain is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced as aching, burning, stabbing, sharp
How To Get An Mri Of The Lumbar Spine W/O Contrast
 Date notice sent to all parties: May 27, 2014 IRO CASE #: ReviewTex, Inc. 1818 Mountjoy Drive San Antonio, TX 78232 (phone) 210-598-9381 (fax) 210-598-9382 [email protected] Notice of Independent Review
Date notice sent to all parties: May 27, 2014 IRO CASE #: ReviewTex, Inc. 1818 Mountjoy Drive San Antonio, TX 78232 (phone) 210-598-9381 (fax) 210-598-9382 [email protected] Notice of Independent Review
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
RNOH Physiotherapy Department (020 8909 5820) Rehabilitation guidelines for patients undergoing spinal surgery
 RNOH Physiotherapy Department (020 8909 5820) Rehabilitation guidelines for patients undergoing spinal surgery As a specialist orthopaedic hospital we recognise that our broad and often complex patient
RNOH Physiotherapy Department (020 8909 5820) Rehabilitation guidelines for patients undergoing spinal surgery As a specialist orthopaedic hospital we recognise that our broad and often complex patient
Lumbar Disc Herniation/Bulge Protocol
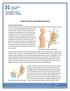 Lumbar Disc Herniation/Bulge Protocol Anatomy and Biomechanics The lumbar spine is made up of 5 load transferring bones called vertebrae. They are stacked in a column with an intervertebral disc sandwiched
Lumbar Disc Herniation/Bulge Protocol Anatomy and Biomechanics The lumbar spine is made up of 5 load transferring bones called vertebrae. They are stacked in a column with an intervertebral disc sandwiched
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
RNOH Physiotherapy Department (020 8909 5820) Rehabilitation guidelines for patients undergoing spinal surgery
 RNOH Physiotherapy Department (020 8909 5820) Rehabilitation guidelines for patients undergoing spinal surgery As a specialist orthopaedic hospital, we recognise that our broad and often complex patient
RNOH Physiotherapy Department (020 8909 5820) Rehabilitation guidelines for patients undergoing spinal surgery As a specialist orthopaedic hospital, we recognise that our broad and often complex patient
Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders
 Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Whiplash? The term whiplash might be confusing because it describes both a mechanism of injury and
Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Whiplash? The term whiplash might be confusing because it describes both a mechanism of injury and
Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery
 Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery Dr. Connie D Astolfo, DC, PhD (candidate) In past articles I have stressed that the causes of back pain can be very complex. This
Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery Dr. Connie D Astolfo, DC, PhD (candidate) In past articles I have stressed that the causes of back pain can be very complex. This
.org. Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
Guide to Claims against General Practitioners (GPs)
 Patients often build up a relationship of trust with their GP over a number of years. It can be devastating when a GP fails in his or her duty to a patient. Our medical negligence solicitors understand
Patients often build up a relationship of trust with their GP over a number of years. It can be devastating when a GP fails in his or her duty to a patient. Our medical negligence solicitors understand
NHS England National Pathfinder Projects. Trauma Programme of Care Pathfinder Project Low Back Pain and Radicular Pain. Report of the Clinical Group
 NHS England National Pathfinder Projects Trauma Programme of Care Pathfinder Project Low Back Pain and Radicular Pain Report of the Clinical Group National Pathway of Care for Low Back and Radicular Pain
NHS England National Pathfinder Projects Trauma Programme of Care Pathfinder Project Low Back Pain and Radicular Pain Report of the Clinical Group National Pathway of Care for Low Back and Radicular Pain
A self-help guide to managing back pain and enabling recovery
 A self-help guide to managing back pain and enabling recovery The aim of this publication is to help people with back pain to begin to get back in control of their symptoms. By following the advice in
A self-help guide to managing back pain and enabling recovery The aim of this publication is to help people with back pain to begin to get back in control of their symptoms. By following the advice in
Test Request Tip Sheet
 With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK)
 THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
Spine conditionsnew treatments. Ben Okafor FRCS FRCS.orth Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Spine conditionsnew treatments Ben Okafor FRCS FRCS.orth Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Certainties of life Death Taxes Back pain New Advances Minimal access surgery Indirect Lumbar decompression Dynamic
Spine conditionsnew treatments Ben Okafor FRCS FRCS.orth Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Certainties of life Death Taxes Back pain New Advances Minimal access surgery Indirect Lumbar decompression Dynamic
LUMBAR. Hips R L B R L B LUMBAR. Hips R L B R L B LUMBAR. Hips R L B R L B
 1 Patient Name In order to properly assess your condition, we must understand how much your BACK/LEG (SCIATIC) PAIN has affected your ability to manage everyday activities. For each item below, please
1 Patient Name In order to properly assess your condition, we must understand how much your BACK/LEG (SCIATIC) PAIN has affected your ability to manage everyday activities. For each item below, please
MANAGING BACK PAIN GETTING YOU BACK INTO ACTION MANAGING BACK PAIN. www.healthcare-rm.com
 H E A L T H R I S K M A N A G E M E N T MANAGING BACK PAIN MANAGING BACK PAIN GETTING YOU BACK INTO ACTION GETTING YOU BACK INTO ACTION www.healthcare-rm.com Who is this for? CONTENTS Introduction about
H E A L T H R I S K M A N A G E M E N T MANAGING BACK PAIN MANAGING BACK PAIN GETTING YOU BACK INTO ACTION GETTING YOU BACK INTO ACTION www.healthcare-rm.com Who is this for? CONTENTS Introduction about
Spine University s Guide to Transient Osteoporosis
 Spine University s Guide to Transient Osteoporosis 2 Introduction The word osteoporosis scares many people because they ve heard about brittle bone disease. They may know someone who has had it or seen
Spine University s Guide to Transient Osteoporosis 2 Introduction The word osteoporosis scares many people because they ve heard about brittle bone disease. They may know someone who has had it or seen
Surgery for cervical disc prolapse or cervical osteophyte
 Mr Paul S. D Urso MBBS(Hons), PhD, FRACS Neurosurgeon Provider Nº: 081161DY Epworth Centre Suite 6.1 32 Erin Street Richmond 3121 Tel: 03 9421 5844 Fax: 03 9421 4186 AH: 03 9483 4040 email: [email protected]
Mr Paul S. D Urso MBBS(Hons), PhD, FRACS Neurosurgeon Provider Nº: 081161DY Epworth Centre Suite 6.1 32 Erin Street Richmond 3121 Tel: 03 9421 5844 Fax: 03 9421 4186 AH: 03 9483 4040 email: [email protected]
Clinical Reasoning The patient presents with no red flags and no indications of maladaptive behaviour in regard to fear avoidance.
 The McKenzie Institute International 2014 Vol. 3, No. 3 CASE REVIEW: A CLINICIAN S PERSPECTIVE Case Review: 35-Year-Old Male with History of Low Back Pain Brian Østergaard Sørensen, PT, Dip.MDT Introduction
The McKenzie Institute International 2014 Vol. 3, No. 3 CASE REVIEW: A CLINICIAN S PERSPECTIVE Case Review: 35-Year-Old Male with History of Low Back Pain Brian Østergaard Sørensen, PT, Dip.MDT Introduction
Acute Oncology Service Patient Information Leaflet
 Spinal cord compression Acute Oncology Service Patient Information Leaflet Introduction If you have been diagnosed with cancer, you need to know about spinal cord compression and the warning signs. What
Spinal cord compression Acute Oncology Service Patient Information Leaflet Introduction If you have been diagnosed with cancer, you need to know about spinal cord compression and the warning signs. What
Balloon Kyphoplasty. Balloon Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat vertebral body compression fractures.
 Balloon Kyphoplasty Overview Balloon Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat vertebral body compression fractures. The technique is designed to: Reduce and stabilise the fracture in a controlled
Balloon Kyphoplasty Overview Balloon Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat vertebral body compression fractures. The technique is designed to: Reduce and stabilise the fracture in a controlled
This booklet can also be provided in large print on request. Please call 01865 738126. Spinal Stenosis. The Oxford Spine Unit
 This booklet can also be provided in large print on request. Please call 01865 738126 Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre NHS Trust NHS Spinal Team Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre Windmill Road Headington Oxford OX3
This booklet can also be provided in large print on request. Please call 01865 738126 Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre NHS Trust NHS Spinal Team Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre Windmill Road Headington Oxford OX3
LOW BACK PAIN: SHOULD I HAVE AN MRI?
 DATE: / / HG SY EH CQ RL AS JZ Name: (Last, First, M.I.) M F DOB: / / Decision Point LOW BACK PAIN: SHOULD I HAVE AN MRI? You may want to have a say in this decision, or you may simply want to follow your
DATE: / / HG SY EH CQ RL AS JZ Name: (Last, First, M.I.) M F DOB: / / Decision Point LOW BACK PAIN: SHOULD I HAVE AN MRI? You may want to have a say in this decision, or you may simply want to follow your
Neck Pain Frequently Asked Questions. Moe R. Lim, MD UNC Orthopaedics (919-96B-ONES) UNC Spine Center (919-957-6789)
 Neck Pain Frequently Asked Questions Moe R. Lim, MD UNC Orthopaedics (919-96B-ONES) UNC Spine Center (919-957-6789) Neck Pain Human Spine 25 bones Cervical (7) Thoracic (12) Lumbar (5) Sacrum Human Spine
Neck Pain Frequently Asked Questions Moe R. Lim, MD UNC Orthopaedics (919-96B-ONES) UNC Spine Center (919-957-6789) Neck Pain Human Spine 25 bones Cervical (7) Thoracic (12) Lumbar (5) Sacrum Human Spine
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide
 Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients
 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients Lukas P. Zebala, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopaedic and Neurological Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients Lukas P. Zebala, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopaedic and Neurological Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of
Appointment Types First outpatient. Clinic Types CATS Spine CATS Hip and Knee CATS General Orthopaedic Injection Clinic Podiatry/Foot and Ankle
 Clinic Types CATS Spine CATS Hip and Knee CATS General Orthopaedic Injection Clinic Podiatry/Foot and Ankle Conditions Treated Ankle & foot pain & stiffness Back pain & stiffness Carpal Tunnel/ Nerve impingement/entrapment
Clinic Types CATS Spine CATS Hip and Knee CATS General Orthopaedic Injection Clinic Podiatry/Foot and Ankle Conditions Treated Ankle & foot pain & stiffness Back pain & stiffness Carpal Tunnel/ Nerve impingement/entrapment
4.2 Spinal Cord Compression
 4.2 Spinal Cord Compression AO Protocol Name: Metastatic Spinal Cord Compression (MSCC) AO Type: Type I (New Cancer), Type III (Cancer Complication) Author: ST Introduction: MSCC can cause irreversible
4.2 Spinal Cord Compression AO Protocol Name: Metastatic Spinal Cord Compression (MSCC) AO Type: Type I (New Cancer), Type III (Cancer Complication) Author: ST Introduction: MSCC can cause irreversible
GUIDELINES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPINAL STABILITY THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE. CP57 Version: V3
 GUIDELINES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPINAL STABILITY THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE Procedure Reference: Document Owner: CP57 Version: V3 Dr V. Misra Accountable Committee: Acute Oncology Group Network
GUIDELINES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPINAL STABILITY THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE Procedure Reference: Document Owner: CP57 Version: V3 Dr V. Misra Accountable Committee: Acute Oncology Group Network
Open Discectomy. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
Spina Bifida Occulta. Lo-Call 1890 20 22 60. Occulta Means Hidden
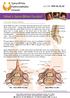 Occulta Means Hidden Spina Bifida Occulta is not easily detected because skin covers the area, such as the spinal cord, spinal bone or nerve roots, which may be affected. Spina Bifida Occulta can affect
Occulta Means Hidden Spina Bifida Occulta is not easily detected because skin covers the area, such as the spinal cord, spinal bone or nerve roots, which may be affected. Spina Bifida Occulta can affect
A Syndrome (Pattern) Approach to Low Back Pain. History
 A Syndrome (Pattern) Approach to Low Back Pain Hamilton Hall MD FRCSC Professor, Department of Surgery, University of Toronto Medical Director, CBI Health Group Executive Director, Canadian Spine Society
A Syndrome (Pattern) Approach to Low Back Pain Hamilton Hall MD FRCSC Professor, Department of Surgery, University of Toronto Medical Director, CBI Health Group Executive Director, Canadian Spine Society
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion
 Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
White Paper: Reducing Utilization Concerns Regarding Spinal Fusion and Artificial Disc Implants
 White Paper: Reducing Utilization Concerns Regarding Spinal Fusion and Artificial Disc Implants For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Back pain is one of the most
White Paper: Reducing Utilization Concerns Regarding Spinal Fusion and Artificial Disc Implants For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Back pain is one of the most
LOW BACK INJURIES PROGRAM OF CARE PROGRAM OF CARE 4TH EDITION 2014
 LOW BACK INJURIES PROGRAM OF CARE PROGRAM OF CARE 4TH EDITION 2014 GUIDE Acknowledgements Acknowledgements The WSIB would like to acknowledge the significant contributions of the following regulated Health
LOW BACK INJURIES PROGRAM OF CARE PROGRAM OF CARE 4TH EDITION 2014 GUIDE Acknowledgements Acknowledgements The WSIB would like to acknowledge the significant contributions of the following regulated Health
IMPAIRMENT RATING 5 TH EDITION MODULE II
 IMPAIRMENT RATING 5 TH EDITION MODULE II THE SPINE AND ALTERATION OF MOTION SEGMENT INTEGRITY (AOMSI) PRESENTED BY: RONALD J. WELLIKOFF, D.C., FACC, FICC In conjuction with: The chapter on the spine includes
IMPAIRMENT RATING 5 TH EDITION MODULE II THE SPINE AND ALTERATION OF MOTION SEGMENT INTEGRITY (AOMSI) PRESENTED BY: RONALD J. WELLIKOFF, D.C., FACC, FICC In conjuction with: The chapter on the spine includes
Management of Low back pain
 Management of Low back pain Dr Prabhu Gandhimani MD;FRCA;FIPP;FFPMRCA Kingston Hospital Queen Mary s Hospital, Roehampton New Victoria,Parkside Hospital and Putney ( NHS Choose and Book) Incidence About
Management of Low back pain Dr Prabhu Gandhimani MD;FRCA;FIPP;FFPMRCA Kingston Hospital Queen Mary s Hospital, Roehampton New Victoria,Parkside Hospital and Putney ( NHS Choose and Book) Incidence About
EUROPEAN GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE NONSPECIFIC LOW BACK PAIN IN PRIMARY CARE
 EUROPEAN GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE NONSPECIFIC LOW BACK PAIN IN PRIMARY CARE Maurits van Tulder, Annette Becker, Trudy Bekkering, Alan Breen, Maria Teresa Gil del Real, Allen Hutchinson, Bart
EUROPEAN GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE NONSPECIFIC LOW BACK PAIN IN PRIMARY CARE Maurits van Tulder, Annette Becker, Trudy Bekkering, Alan Breen, Maria Teresa Gil del Real, Allen Hutchinson, Bart
This is my information booklet: Introduction
 Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
15 things you might not know about back pain
 15 things you might not know about back pain Mary O Keeffe (University of Limerick), Dr Kieran O Sullivan (University of Limerick), Dr Derek Griffin (Tralee Physiotherapy Clinic) Managing back pain costs
15 things you might not know about back pain Mary O Keeffe (University of Limerick), Dr Kieran O Sullivan (University of Limerick), Dr Derek Griffin (Tralee Physiotherapy Clinic) Managing back pain costs
Orthopaedic Approach to Back Pain. Seth Cheatham, MD
 Orthopaedic Approach to Back Pain Seth Cheatham, MD 262 Seth A. Cheatham, MD VCU Sports Medicine I have no financial disclosures. Focus on clinical situations where a referral to an orthopaedic surgeon
Orthopaedic Approach to Back Pain Seth Cheatham, MD 262 Seth A. Cheatham, MD VCU Sports Medicine I have no financial disclosures. Focus on clinical situations where a referral to an orthopaedic surgeon
BRYAN. Cervical Disc System. Patient Information
 BRYAN Cervical Disc System Patient Information 3 BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION 1 BRYAN Cervical Disc System This patient information brochure
BRYAN Cervical Disc System Patient Information 3 BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION 1 BRYAN Cervical Disc System This patient information brochure
Whiplash Associated Disorder
 Whiplash Associated Disorder The pathology Whiplash is a mechanism of injury, consisting of acceleration-deceleration forces to the neck. Mechanism: Hyperflexion/extension injury Stationary vehicle hit
Whiplash Associated Disorder The pathology Whiplash is a mechanism of injury, consisting of acceleration-deceleration forces to the neck. Mechanism: Hyperflexion/extension injury Stationary vehicle hit
Approach to Back Pain
 Approach to Back Pain Year 3 Clerkship Guide, Family Medicine Department Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry Objectives 1. Define acute low back pain. 2. Define chronic back pain. 3. What is the
Approach to Back Pain Year 3 Clerkship Guide, Family Medicine Department Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry Objectives 1. Define acute low back pain. 2. Define chronic back pain. 3. What is the
Spine University s Guide to Vertebral Osteonecrosis (Kummel's Disease)
 Spine University s Guide to Vertebral Osteonecrosis (Kummel's Disease) 2 Introduction Kummel's disease is a collapse of the vertebrae (the bones that make up the spine). It is also called vertebral osteonecrosis.
Spine University s Guide to Vertebral Osteonecrosis (Kummel's Disease) 2 Introduction Kummel's disease is a collapse of the vertebrae (the bones that make up the spine). It is also called vertebral osteonecrosis.
Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario
 Page 1 Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario Injury Descriptions Developed from Newfoundland claim study injury definitions No injury Death Psychological
Page 1 Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario Injury Descriptions Developed from Newfoundland claim study injury definitions No injury Death Psychological
Psoriatic Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz
 Psoriatic Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects one in six New Zealanders over the age of 15 years. Psoriatic arthritis usually appears in people between the ages of 30 to 50.
Psoriatic Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects one in six New Zealanders over the age of 15 years. Psoriatic arthritis usually appears in people between the ages of 30 to 50.

 More information >>> HERE
More information >>> HERE