The EMT Instructional Guidelines in this section include all the topics and material at the EMR level PLUS the following material:
|
|
|
- Cameron Murphy
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Airway Management, Respiration and Artificial Ventilation EMR Applies knowledge (fundamental depth, foundational breadth) of general anatomy and physiology to assure a patent airway, adequate mechanical ventilation, and respiration while awaiting additional EMS response for patients of all ages. EMT Applies knowledge (fundamental depth, foundational breadth) of general anatomy and physiology to patient assessment and management in order to assure a patent airway, adequate mechanical ventilation, and respiration for patients of all ages. AEMT Applies knowledge (fundamental depth, foundational breadth) of additional upper airway anatomy and physiology to patient assessment and management in order to assure a patent airway, adequate mechanical ventilation, and respiration for patients of all ages. Paramedic Integrates complex knowledge of anatomy, physiology, and pathophysiology into the assessment to develop and implement a treatment plan with the goal of assuring a patent airway, adequate mechanical ventilation, and respiration for patients of all ages. EMR Fundamental depth, simple breadth Airway Management Within the scope of practice of the EMR Airway Anatomy o Upper Airway Tract Nose Mouth and oral cavity Jaw Throat/pharynx o Lower Airway Tract Trachea/windpipe Bronchi Lungs Airway Assessment o Signs of Adequate Airway Airway is open, can hear and feel air move in and out Patient is speaking in full sentences Sound of the voice is normal for the patient o Signs of Inadequate Airway Unusual sounds are heard with breathing (i.e. stridor or snoring) Awake patient is unable to speak or voice sounds hoarse
2 No air movement Apnea Airway obstruction o Swelling Due to Trauma or Infection Techniques of Assuring a Patent Airway (refer to current American Heart Association guidelines) o Manual Airway Maneuvers Head tilt/chin lift Jaw thrust maneuver Modified chin lift o Mechanical Airway Devices Oropharyngeal o Relief of Foreign Body Airway Obstruction o Upper Airway Suctioning Limitation Consider Age-Related Variations in Pediatric and Geriatric Patients EMT: EMR Material PLUS: Fundamental depth, foundational breadth The EMT Instructional Guidelines in this section include all the topics and material at the EMR level PLUS the following material: Airway Anatomy o Upper Airway Tract Nose warm and humidify air Mouth and oral cavity Jaw Pharynx Larynx o Lower Airway Tract Trachea Carina the bifurcation of the trachea into the two mainstem bronchi Bronchi Lungs Airway Assessment o Signs of Adequate Airway Airway is open, can hear/feel air move in and out Patient is speaking in full sentences Sound of the voice is normal for the patient
3 o Signs of Inadequate Airway (Not every sign listed below is present in every patient who has inadequate airway) Unusual sounds are heard with breathing Awake patient is unable to speak or sounds hoarse No air movement (apnea) Airway obstruction o Swelling Due to Trauma or Infection Techniques of Assuring a Patent Airway o Manual Airway Maneuvers -- review and elaborate on the manual airway maneuvers used by EMRs o Mechanical Airway Devices Review and elaborate on the mechanical airway maneuvers used by EMRs Nasopharyngeal o Relief of Foreign Body Airway Obstruction (refer to current American Heart Association guidelines) o Upper Airway Suctioning -- review and elaborate on all material from the EMR Level Consider Age-Related Variations in Pediatric and Geriatric Patients (see Special Patient Populations Section) AEMT: EMT Material PLUS: Fundamental depth, foundational breadth The AMT Instructional Guidelines in this section include all the topics and material at the EMT level PLUS the following material: Airway Anatomy o Sinuses o Upper Airway Tract Nose Mouth and Oral Cavity Jaw Pharynx Larynx o Jugular Notch o Lower Airway Tract Trachea Carina Bronchi Lungs o Support Structures Chest Cage Phrenic nerve Mediastinum Airway Assessment o Purpose
4 Identify inadequate airway Identify an unstable airway Identify potentially difficult airways o Procedure Gag Reflex Airway obstruction Work of breathing Laryngospasm Laryngeal edema Penetrating injuries Techniques of Assuring a Patent Airway o Manual Airway Maneuvers o Mechanical Airway Devices o Relief of Foreign Body Airway Obstruction (Refer to Current American Heart Association Guidelines) o Upper Airway Suctioning Review and elaborate on the upper airway suctioning material from the EMR and EMT levels for lower airway suctioning of the previously intubated patient o Blind Insertion Airway Devices Esophageal obturation (e.g., Combitube, PTL, Easytube, King LTD) Supraglottic devices (e.g., LMA, COBRA) Consider Age-Related Variations in Pediatric and Geriatric Patients Paramedic: AEMT Material PLUS: Complex depth, comprehensive breadth The Paramedic Instructional Guidelines in this section include all the topics and material at the AEMT level PLUS the following material: Airway Anatomy o Sinuses Frontal Sphenoid Ethmoid Maxillary o Upper Airway Tract Nose Mouth and Oral Cavity Jaw Pharynx Larynx o Jugular notch o Lower Airway Tract Trachea -- Spatial relationship to esophagus Carina -- Angle of Louis
5 Bronchi Lungs o Support Structures Chest Cage Phrenic nerve Mediastinum Airway Assessment o Purpose Identify inadequate airway Identify an unstable airway Identify potentially difficult airways o Procedure Gag Reflex Airway obstruction Work of breathing Laryngospasm Laryngeal edema Penetrating injuries o Anticipating the difficult airway Trauma/bleeding Vomiting History Mouth opening Mandibular length Mallampati classifications Obstructions Neck mobility Facial hair Techniques of assuring a patent airway o Manual airway maneuvers o Mechanical airway devices o Relief of Foreign Body Airway Obstruction Refer to current American Heart Association guidelines Removal of foreign body airway obstructions using direct laryngoscopy Airway suctioning o Blind insertion airway devices o Endotracheal intubation Direct laryngoscopy (visualized) Non-visualized o Percutaneous cricothyrotomy (including confirmation techniques) Limitations
6 Consider age-related variations in pediatric and geriatric patients o See Special Patient Populations section
7 EMR Fundamental depth, simple breadth Respiration Anatomy of the Respiratory System o Includes All Airway Anatomy Covered in the Airway Management Section o Additional Respiratory System Anatomy o Vascular Structures That Support Respiration Pulmonary capillaries Heart and blood vessels Physiology of Respiration o Pulmonary Ventilation o Oxygenation o Respiration Pathophysiology of Respiration o Pulmonary Ventilation Interruption of nervous control Structural damage to the thorax Bronchoconstriction Disruption of airway patency o Oxygenation o Respiration External respiration Internal respiration Cellular respiration Assessment of Adequate and Inadequate Respiration (refer to current American Heart Association Guidelines) o Unresponsive Patient o Responsive Patient Management of Adequate and Inadequate Respiration o Assure Patent Airway (techniques described in Airway Management section) o Techniques for Assuring Adequate Respirations Supplemental Oxygen Therapy o Portable Oxygen Cylinder o Oxygen Delivery Devices Consider Age-Related Variations in Pediatric and Geriatric Patients EMT; EMR Material PLUS: Fundamental depth, foundational breadth The EMT Instructional Guidelines in this section include all the topics and material at the EMR level PLUS the following material: Anatomy of the Respiratory System o Includes All Airway Anatomy Covered in the Airway Management Section o Additional Respiratory System Anatomy
8 Chest cage Ribs Muscles Pleura Phrenic nerve innervations o Vascular Structures Which Support Respiration Pulmonary capillary structures The heart Arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins Tissue/cellular beds o Cells All cells perform a specific function Cells require chemicals in order to function, including oxygen, glucose, and electrolytes Respiratory regulation influenced by carbon dioxide and oxygen levels in the blood and spinal fluid Respiration; pulmonary ventilation the movement of air in and out of the lungs Physiology of Respiration o Pulmonary Ventilation Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Adequate ventilation is necessary for, but does not assure, adequate respiration The mechanics of ventilation Alveolar Ventilation o Oxygenation Oxygenation is the process of loading oxygen molecules onto hemoglobin molecules in the bloodstream Oxygenation is required for, but does not assure, internal respiration o Respiration Respiration is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide and is essential for life Adequate ventilation is required for, but does not assure, external respiration Adequate external ventilation and perfusion are required for, but do not assure, internal respiration Pathophysiology of Respiration o Pulmonary Ventilation Interruption of nervous control Structural damage to the thorax Bronchoconstriction Disruption of airway patency o Oxygenation o Respiration External Internal
9 Cellular o Circulation compromise Pathology typically related to derangement of pulmonary and systemic perfusion and oxygenation Typical disease processes o Cells Hypoxia Hypoglycemia Infection Assessment of Adequate and Inadequate Ventilation o Internal Respiration is Necessary for Life o It Is Sometimes Difficult to Assess Internal Respiration o It May Be Difficult to Determine If You Have a Respiration, Ventilation, or Oxygenation Problem as They May Coexist and One Can Cause Another o Assessment of Ventilation Signs of adequate ventilation Signs of inadequate ventilation (not every sign listed below is present in every patient who has inadequate ventilation and/or oxygenation) o Assessment of Respiration Ambient air is abnormal Level of consciousness Skin color/mucosa is not normal Assessment of oxygenation Management of Adequate and Inadequate Respiration o Assure an Adequate Airway o Supplemental Oxygen Therapy Ambient air is Oxygen Nitrogen Carbon dioxide Supplemental oxygen therapy replaces some of the inert gas with oxygen and can improve internal respiration Oxygen sources Oxygen delivery devices o Assisting Ventilation in Respiratory Distress/Failure Consider Age-Related Variations in Pediatric and Geriatric Patients (see Special Patient Populations) AEMT: EMT Material PLUS: Complex depth, foundational breadth Anatomy of the respiratory system
10 Fundamental depth, comprehensive breadth Physiology and pathophysiology of respiration Pulmonary ventilation Oxygenation Respiration External Internal Cellular Assessment and management of adequate and inadequate respiration Supplemental oxygen therapy The AMT Instructional Guidelines in this section include all the topics and material at the EMT level PLUS the following material: Anatomy of the Respiratory System o Includes All Airway Anatomy Covered in the Airway Management Section o Additional Respiratory System Anatomy o Chest Cage Ribs Muscles of respiration Pleura o Phrenic Nerve o Mediastinum Physiology of Respiration o Mechanics of Respiration Pulmonary ventilation Gas exchange Oxygenation Respiration Lung compliance Pathophysiology of Respiration o Pulmonary Ventilation Interruption of nervous control Structural damage to the thorax Bronchoconstriction Disruption of airway patency o Oxygenation o Respiration External Internal Cellular Assessment of Adequate and Inadequate Respiration Management of Adequate and Inadequate Respiration o Respiratory Compromise Assure an adequate airway Review supplemental oxygen therapy
11 Assisted positive pressure ventilations Supplemental Oxygen Therapy o Review of Oxygen Delivery Devices Used by EMTs s Age-Related Variations in Pediatric and Geriatric Patients Paramedic: AEMT Material PLUS: Complex depth, comprehensive breadth The Paramedic Instructional Guidelines in this section include all the topics and material at the AEMT level PLUS the following material: Anatomy of the Respiratory System o Includes all airway anatomy covered in the Airway Management section o Additional Respiratory System Anatomy Chest Cage Phrenic nerve Mediastinum Physiology of Respiration o Control of Respiration Nervous Control of Respiration Conscious Control of Respiration Chemical Control of Respiration o Mechanics of Respiration Pulmonary Ventilation Gas Exchange Gas Transport Ventilation perfusion ratio o Blood volume circulation disturbances due to Cardiac, Trauma, Systemic Vascular Resistance Orthostatic hypotension Oncotic fluid pressure Hydrostatic fluid pressure Capacitance of the venules and veins o Cardiac output and the role in adequate circulation maintenance Cardiac rate Stroke volume Role of alpha stimulation in the heart Role of beta stimulation in the heart Atrioventricular Synchronization Total peripheral Resistance o Buffer systems
12 Blood Respiratory Renal Pathophysiology of Respiration o Pulmonary ventilation Interruption of Nervous Control Structural Damage to the Thorax Bronchoconstriction Disruption of airway patency o Oxygenation o Respiration External Internal Cellular o Rapid ventilation, exhaustion, dead space air movement o Mechanical ventilation o Breathing against an elevated diaphragm o Decreases in lung compliance such as pneumonia, emphysema, and trauma o Ventilation-perfusion mismatch Ventilation defects Perfusion defects o Disruptions in oxygen transport associated with diminished oxygen carrying capacity Anemia Blood loss o Disruptions in effective circulation Shock Emboli Increased capillary permeability o Disruptions at the cellular level Acid-base balance Poisons/toxins Blood sugar changes Hormone effects Drugs Hypoxia Assessment of Adequate and Inadequate Respiration o Capnometry/Capnography /definition Management of Adequate and Inadequate Respiration o Respiratory Compromise Assure an adequate airway
13 Review supplemental oxygen therapy Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)/Bi-Level Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) Assisted positive pressure ventilations Supplemental Oxygen Therapy o Review and elaborate on the oxygen delivery devices used by EMRs, EMTs and AEMTs o Oxygen administration and the patient with hypercapnia Age-Related Variations in Pediatric and Geriatric Patients
14 EMR Fundamental depth, simple breadth Artificial Ventilation Assessment of Adequate and Inadequate Ventilation o Adequate Respiratory rate is normal Respiration depth is normal Effort of breathing is normal o Inadequate Abnormal work (effort) of breathing Abnormal breathing sounds Depth of breathing Rate of breathing Chest wall movement or damage Irregular respiratory pattern Oxygenation o Adequate Mental status considered normal for patient Skin color normal o Inadequate Ambient air is abnormal Mental status considered abnormal or altered for patient Skin color/mucosa is not normal Management of Adequate and Inadequate Ventilation o Patients With Adequate Ventilation o Patients With Inadequate Ventilation May be conscious or unconscious EMR must assist ventilation during respiratory distress/failure Ventilation of an Apneic Patient o To Oxygenate and Ventilate the Patient o Indications No breathing is noted Occasional gasping breathing is noted o Monitoring Patient o Limitation Differentiate Normal Ventilation From Positive Pressure Ventilation o Air Movement Positive pressure ventilation with pocket mask or bag-mask o Blood Movement Positive pressure ventilation o Esophageal Opening Pressure Positive pressure ventilation with a pocket mask or bag-mask
15 o Excess Rate or Depth of Ventilation Using Pocket Mask or Bag-Mask Can Harm the Patient as ventilating too fast or too deep may cause low blood pressure, vomiting, or decreased blood flow when the chest is compressed during CPR Consider Age-Related Variations in Pediatric and Geriatric Patients EMT: EMR Material PLUS: Fundamental depth, foundational breadth The EMT Instructional Guidelines in this section include all the topics and material at the EMR level PLUS the following material: The Management of Inadequate Ventilation o Assure an Adequate Airway o Supplemental Oxygen Therapy o Artificial Ventilation Devices Bag-valve-mask with reservoir Manually triggered ventilation device Automatic Transport Ventilator/Resuscitator o Ventilation of an Apneic Patient o Ventilation of the Protected Airway The Differences Between Normal and Positive Pressure Ventilation o Air Movement Positive pressure ventilation o Blood Movement Positive pressure ventilation o Airway Wall Pressure Positive pressure ventilation o Esophageal Opening Pressure Positive pressure ventilation Sellick s maneuver (cricoid pressure) o Over Ventilation (Either by Rate or Volume) Can Be Detrimental to the Patient Positive pressure ventilation may cause Hypotension
16 Gastric distention Other unintended consequences Consider Age-Related Variations in Pediatric and Geriatric Patients (see Special Patient Considerations) AEMT: EMT Material PLUS: Complex depth, foundational breadth The AMT Instructional Guidelines in this section include all the topics and material at the EMT level PLUS the following material: Comprehensive Ventilation Assessment o Purpose o Procedure o Minute Volume o Alveolar Volume o Evaluating the Effects of Artificial Ventilation o Pulse Oximetry The Management of Inadequate Ventilation o Assure an Adequate Airway o Supplemental Oxygen Therapy o Artificial Ventilation Devices Bag-valve-mask with reservoir Manually triggered ventilation device Automatic Transport Ventilator/Resuscitator o Ventilation of an Apneic Patient o Ventilation of the Protected Airway The Differences Between Normal and Positive Pressure Ventilation o Air Movement Positive pressure ventilation o Blood Movement
17 Positive pressure ventilation o Airway Wall Pressure Positive pressure ventilation o Esophageal Opening Pressure Positive pressure ventilation o Over Ventilation (Either by Rate or Volume) Can Be Detrimental to the Patient Hypotension Gastric distention Other unintended consequences Consider Age-Related Variations in Pediatric and Geriatric Patients PARAMEDIC: AEMT Material PLUS: Complex depth, comprehensive breadth The Paramedic Instructional Guidelines in this section include all the topics and material at the AEMT level PLUS the following material: Comprehensive ventilation assessment o Purpose o Procedure o Minute Volume o Alveolar Volume o Evaluating the effects of artificial ventilation o Pulse oximetry o Blood gas analysis ph PaCO2 PaO2 Bicarbonate Base déficit o Capnography Review Review of ventilation devices used by EMRs, EMTs and AEMTs o Manual devices
18 s o Mechanical devices s Assisting patient ventilations o Review of techniques used by EMRs, EMTs and AEMTs s o Review of the physiologic differences between normal and positive pressure ventilation o BiPAP/CPAP o Positive End Expiratory Pressure (PEEP) Age Related Variations in Pediatric and Geriatric Patients
Pediatric Airway Management
 Pediatric Airway Management Dec 2003 Dr. Shapiro I., PICU Adult Chain of Survival EMS CPR ALS Early Defibrillation Pediatric Chain of Survival Prevention CPR EMS ALS Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest SIDS
Pediatric Airway Management Dec 2003 Dr. Shapiro I., PICU Adult Chain of Survival EMS CPR ALS Early Defibrillation Pediatric Chain of Survival Prevention CPR EMS ALS Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest SIDS
Oxygenation. Chapter 21. Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing. Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing*
 Oxygenation Chapter 21 Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing Inspiration ~ breathing in Expiration ~ breathing out Ventilation ~ Movement of air in & out of the lungs Respiration ~ exchange of O2 & carbon
Oxygenation Chapter 21 Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing Inspiration ~ breathing in Expiration ~ breathing out Ventilation ~ Movement of air in & out of the lungs Respiration ~ exchange of O2 & carbon
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
EMS Course Requirements
 EMS Course Requirements The following outlines should be followed when creating your course syllabi. The minimum course hours must be met, but they can be exceeded depending on the needs of your class.
EMS Course Requirements The following outlines should be followed when creating your course syllabi. The minimum course hours must be met, but they can be exceeded depending on the needs of your class.
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Responder Psychomotor Examination PATIENT ASSESSMENT/MANAGEMENT TRAUMA
 PATIENT ASSESSMENT/MANAGEMENT TRAUMA Scenario # Note: Areas denoted by ** may be integrated within sequence of Primary Survey/Resuscitation SCENE SIZE-UP Determines the mechanism of injury/nature of illness
PATIENT ASSESSMENT/MANAGEMENT TRAUMA Scenario # Note: Areas denoted by ** may be integrated within sequence of Primary Survey/Resuscitation SCENE SIZE-UP Determines the mechanism of injury/nature of illness
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Responder Psychomotor Examination BVM VENTILATION OF AN APNEIC ADULT PATIENT
 BVM VENTILATION OF AN APNEIC ADULT PATIENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Points Checks responsiveness NOTE: After checking responsiveness and breathing for at least 5 but no 1 Checks breathing
BVM VENTILATION OF AN APNEIC ADULT PATIENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Points Checks responsiveness NOTE: After checking responsiveness and breathing for at least 5 but no 1 Checks breathing
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Airway and Breathing Skills Levels Interpretive Guidelines
 Office of Emergency Medical Services and Trauma INDEX EFFECTIVE LAST REVIEW PAGES VERSION R-P11A 7/1/2011 7/1/2011 5 2011 Scope of Practice for EMS Personnel Emergency Medical Personnel are permitted to
Office of Emergency Medical Services and Trauma INDEX EFFECTIVE LAST REVIEW PAGES VERSION R-P11A 7/1/2011 7/1/2011 5 2011 Scope of Practice for EMS Personnel Emergency Medical Personnel are permitted to
ENT Emergencies. Injuries of the Neck. Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital
 ENT Emergencies Injuries of the Neck Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital Neck Injuries Blunt and Penetrating Trauma Blunt Injuries Blunt trauma direct/indirect Trauma to larynx
ENT Emergencies Injuries of the Neck Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital Neck Injuries Blunt and Penetrating Trauma Blunt Injuries Blunt trauma direct/indirect Trauma to larynx
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Technician Psychomotor Examination BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT
 BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Applies direct pressure to the wound 1 NOTE: The examiner must now inform the candidate that the wound continues to bleed.
BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Applies direct pressure to the wound 1 NOTE: The examiner must now inform the candidate that the wound continues to bleed.
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system
 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
81 First Responder Respiratory
 81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships
 Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log
 First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
American Heart Association
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer
 Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer
Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer
Pulmonary Diseases. Lung Disease: Pathophysiology, Medical and Exercise Programming. Overview of Pathophysiology
 Lung Disease: Pathophysiology, Medical and Exercise Programming Overview of Pathophysiology Ventilatory Impairments Increased airway resistance Reduced compliance Increased work of breathing Ventilatory
Lung Disease: Pathophysiology, Medical and Exercise Programming Overview of Pathophysiology Ventilatory Impairments Increased airway resistance Reduced compliance Increased work of breathing Ventilatory
1st Responder to Emergency Medical Responder Transition Course
 1st Responder to Emergency Medical Responder Transition Course Mandatory Training July 5, 2011 Authored by: Eddie Manley, Education Coordinator OSDH - EMS 1 st Responder to EMR Recommended Transition Course
1st Responder to Emergency Medical Responder Transition Course Mandatory Training July 5, 2011 Authored by: Eddie Manley, Education Coordinator OSDH - EMS 1 st Responder to EMR Recommended Transition Course
Virginia Office of Emergency Medical Services Scope of Practice - Procedures for EMS Personnel
 Specific tasks in this document shall refer to the Virginia Education Standards. AIRWAY TECHNIQUES Airway Adjuncts Airway Maneuvers Alternate Airway Devices Cricothyrotomy Obstructed Airway Clearance Intubation
Specific tasks in this document shall refer to the Virginia Education Standards. AIRWAY TECHNIQUES Airway Adjuncts Airway Maneuvers Alternate Airway Devices Cricothyrotomy Obstructed Airway Clearance Intubation
Emergency Medical Services Advanced Level Competency Checklist
 Emergency Services Advanced Level Competency Checklist EMS Service: Current License in State of Nebraska: # (Copy of license kept in file at station) Date of joining EMS Service: EMS Service Member Name:
Emergency Services Advanced Level Competency Checklist EMS Service: Current License in State of Nebraska: # (Copy of license kept in file at station) Date of joining EMS Service: EMS Service Member Name:
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPORT State Form 54407 (R / 5-13)
 EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT State Form 54407 (R / 5-3) INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street,
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT State Form 54407 (R / 5-3) INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street,
The EMT Instructional Guidelines in this section include all the topics and material at the EMR level PLUS the following material:
 Assessment EMR Use scene information and simple patient assessment findings to identify and manage immediate life threats and injuries within the scope of practice of the EMR. EMT Applies scene information
Assessment EMR Use scene information and simple patient assessment findings to identify and manage immediate life threats and injuries within the scope of practice of the EMR. EMT Applies scene information
National Registry Skill Sheets
 Bleeding Control/Shock Management BVM Ventilation of an Apneic Adult Patient Cardiac Arrest Management/AED Joint Immobilization Long Bone Immobilization Oxygen Administration By Non-Rebreather Mask Patient
Bleeding Control/Shock Management BVM Ventilation of an Apneic Adult Patient Cardiac Arrest Management/AED Joint Immobilization Long Bone Immobilization Oxygen Administration By Non-Rebreather Mask Patient
RECERTIFICATION PROTOCOL FOR EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES PERSONNEL MANUAL
 RECERTIFICATION PROTOCOL FOR EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES PERSONNEL MANUAL UTAH DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH DIVISION OF FAMILY HEALTH AND PREPAREDNESS BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AND PREPAREDNESS November
RECERTIFICATION PROTOCOL FOR EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES PERSONNEL MANUAL UTAH DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH DIVISION OF FAMILY HEALTH AND PREPAREDNESS BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AND PREPAREDNESS November
National Emergency Medical Services Education Standards. Emergency Medical Responder Instructional Guidelines
 National Emergency Medical Services Education Standards Emergency Medical Responder Instructional Guidelines EMR Education Standard Preparatory EMS Systems Uses simple knowledge of the Emergency Medical
National Emergency Medical Services Education Standards Emergency Medical Responder Instructional Guidelines EMR Education Standard Preparatory EMS Systems Uses simple knowledge of the Emergency Medical
EMR EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER Course Syllabus
 6111 E. Skelly Drive P. O. Box 477200 Tulsa, OK 74147-7200 EMR EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER Course Syllabus Course Number: HLTH-0009 OHLAP Credit: No OCAS Code: 9373 Course Length: 66 Hours Career Cluster:
6111 E. Skelly Drive P. O. Box 477200 Tulsa, OK 74147-7200 EMR EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER Course Syllabus Course Number: HLTH-0009 OHLAP Credit: No OCAS Code: 9373 Course Length: 66 Hours Career Cluster:
Emergency Medical Responder Mid-Course Knowledge Evaluation
 Emergency Medical Responder Mid-Course Knowledge Evaluation Please do not write on this sheet. Indicate your answers on the answer sheet provided. 1. Medical control is the process by which a physician
Emergency Medical Responder Mid-Course Knowledge Evaluation Please do not write on this sheet. Indicate your answers on the answer sheet provided. 1. Medical control is the process by which a physician
Target groups: Paramedics, nurses, respiratory therapists, physicians, and others who manage respiratory emergencies.
 Overview Estimated scenario time: 10 15 minutes Estimated debriefing time: 10 minutes Target groups: Paramedics, nurses, respiratory therapists, physicians, and others who manage respiratory emergencies.
Overview Estimated scenario time: 10 15 minutes Estimated debriefing time: 10 minutes Target groups: Paramedics, nurses, respiratory therapists, physicians, and others who manage respiratory emergencies.
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT. Angkana Lurngnateetape, MD. Department of Anesthesiology Siriraj Hospital
 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT Angkana Lurngnateetape, MD. Department of Anesthesiology Siriraj Hospital Perhaps the most important responsibility of the anesthesiologist is management of the patient s airway Miller
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT Angkana Lurngnateetape, MD. Department of Anesthesiology Siriraj Hospital Perhaps the most important responsibility of the anesthesiologist is management of the patient s airway Miller
National Emergency Medical Services Education Standards. Emergency Medical Responder Instructional Guidelines
 National Emergency Medical Services Education Standards Emergency Medical Responder Instructional Guidelines EMR Education Standard Preparatory EMS Systems Uses simple knowledge of the Emergency Medical
National Emergency Medical Services Education Standards Emergency Medical Responder Instructional Guidelines EMR Education Standard Preparatory EMS Systems Uses simple knowledge of the Emergency Medical
First Responder: The National EMS Scope of Practice changes the name to Emergency Medical Responder.
 APPROVED SCOPE 2/8/08 BOARD MTG First Responder: The National EMS Scope of Practice changes the name to Emergency Medical Responder. Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Description of the Profession The
APPROVED SCOPE 2/8/08 BOARD MTG First Responder: The National EMS Scope of Practice changes the name to Emergency Medical Responder. Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Description of the Profession The
Official Online ACLS Exam
 \ Official Online ACLS Exam Please fill out this form before you take the exam. Name : Email : Phone : 1. Hypovolemia initially produces which arrhythmia? A. PEA B. Sinus tachycardia C. Symptomatic bradyarrhythmia
\ Official Online ACLS Exam Please fill out this form before you take the exam. Name : Email : Phone : 1. Hypovolemia initially produces which arrhythmia? A. PEA B. Sinus tachycardia C. Symptomatic bradyarrhythmia
404 Section 5 Shock and Resuscitation. Scene Size-up. Primary Assessment. History Taking
 404 Section 5 and Resuscitation Scene Size-up Scene Safety Mechanism of Injury (MOI)/ Nature of Illness (NOI) Ensure scene safety and address hazards. Standard precautions should include a minimum of gloves
404 Section 5 and Resuscitation Scene Size-up Scene Safety Mechanism of Injury (MOI)/ Nature of Illness (NOI) Ensure scene safety and address hazards. Standard precautions should include a minimum of gloves
Oxygenation and Oxygen Therapy Michael Billow, D.O.
 Oxygenation and Oxygen Therapy Michael Billow, D.O. The delivery of oxygen to all body tissues is the essence of critical care. Patients in respiratory distress/failure come easily to mind as the ones
Oxygenation and Oxygen Therapy Michael Billow, D.O. The delivery of oxygen to all body tissues is the essence of critical care. Patients in respiratory distress/failure come easily to mind as the ones
Northwestern Health Sciences University. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course
 Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course Written by: Jay Snaric, MS And Kimberly Hickman, RN CPR St. Louis 44 Meramec Valley Plaza St. Louis MO 63088 www.stlcpr.com
Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course Written by: Jay Snaric, MS And Kimberly Hickman, RN CPR St. Louis 44 Meramec Valley Plaza St. Louis MO 63088 www.stlcpr.com
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER REFRESHER TRAINING PROGRAM Ohio Approved Curriculum
 EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER REFRESHER TRAINING PROGRAM Ohio Approved Curriculum Instructor Course Guide Ohio Approved EMR Refresher 5-16-2012 Page 1 OHIO APPROVED EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER REFRESHER
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER REFRESHER TRAINING PROGRAM Ohio Approved Curriculum Instructor Course Guide Ohio Approved EMR Refresher 5-16-2012 Page 1 OHIO APPROVED EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER REFRESHER
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Chapter 26. Assisting With Oxygen Needs. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 26 Assisting With Oxygen Needs Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas. Oxygen It has no taste, odor, or color. It is a basic need required for life. Death occurs within minutes if breathing stops. Brain damage
Chapter 26 Assisting With Oxygen Needs Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas. Oxygen It has no taste, odor, or color. It is a basic need required for life. Death occurs within minutes if breathing stops. Brain damage
Community Ambulance Service of Minot ALS Standing Orders Legend
 Legend Indicates General Information and Guidelines Indicates Procedures Indicates Medication Administration Indicates Referral to Other Protocol Indicates Referral to Online Medical Direction Pediatric
Legend Indicates General Information and Guidelines Indicates Procedures Indicates Medication Administration Indicates Referral to Other Protocol Indicates Referral to Online Medical Direction Pediatric
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
OSDH EMS EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER
 OSDH EMS EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER Recommended Training Hours for National Education Standard OSDH 2011 Approved: Oklahoma Training and Licensure SubCommittee November 17 th, 2011 Approved: Oklahoma
OSDH EMS EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER Recommended Training Hours for National Education Standard OSDH 2011 Approved: Oklahoma Training and Licensure SubCommittee November 17 th, 2011 Approved: Oklahoma
Southern Stone County Fire Protection District Emergency Medical Protocols
 TITLE Pediatric Medical Assessment PM 2.4 Confirm scene safety Appropriate body substance isolation procedures Number of patients Nature of illness Evaluate the need for assistance B.L.S ABC s & LOC Focused
TITLE Pediatric Medical Assessment PM 2.4 Confirm scene safety Appropriate body substance isolation procedures Number of patients Nature of illness Evaluate the need for assistance B.L.S ABC s & LOC Focused
MECHINICAL VENTILATION S. Kache, MD
 MECHINICAL VENTILATION S. Kache, MD Spontaneous respiration vs. Mechanical ventilation Natural spontaneous ventilation occurs when the respiratory muscles, diaphragm and intercostal muscles pull on the
MECHINICAL VENTILATION S. Kache, MD Spontaneous respiration vs. Mechanical ventilation Natural spontaneous ventilation occurs when the respiratory muscles, diaphragm and intercostal muscles pull on the
Breathing and Holding Your Breath copyright, 2005, Dr. Ingrid Waldron and Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania 1
 Breathing and Holding Your Breath copyright, 2005, Dr. Ingrid Waldron and Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania 1 Introduction Everybody breathes all day, every day. Why?
Breathing and Holding Your Breath copyright, 2005, Dr. Ingrid Waldron and Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania 1 Introduction Everybody breathes all day, every day. Why?
Anatomy of the Respiratory System. The Respiratory System. Respiratory system functions mainly as gas exchange system for O 2 andco 2.
 The Respiratory System Respiratory system functions mainly as gas exchange system for O 2 andco 2! cellular respiration (energy production) closely tied to circulatory system General Functions of Respiratory
The Respiratory System Respiratory system functions mainly as gas exchange system for O 2 andco 2! cellular respiration (energy production) closely tied to circulatory system General Functions of Respiratory
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
 A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
Hypoxia and Oxygenation Hypoxia is a serious threat to patients and escorts alike when
 Chapter 4 2 71 Hypoxia and Oxygenation Hypoxia is a serious threat to patients and escorts alike when they fly. Air medical escorts need to understand what causes hypoxia, why some people are more likely
Chapter 4 2 71 Hypoxia and Oxygenation Hypoxia is a serious threat to patients and escorts alike when they fly. Air medical escorts need to understand what causes hypoxia, why some people are more likely
The Phoenix Document An Evolution from National Standard Curriculum to the Virginia EMS Education Standards
 The Phoenix Document An Evolution from National Standard Curriculum to the Virginia EMS Education Standards Training Levels Included: Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Last Revised: January 19, 2011 Page
The Phoenix Document An Evolution from National Standard Curriculum to the Virginia EMS Education Standards Training Levels Included: Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Last Revised: January 19, 2011 Page
EMR Instructional Guidelines. Preparatory
 EMR Instructional Guidelines Preparatory EMS Systems Uses simple knowledge of the EMS system, safety/well being of the EMR, medical/legal issues at the scene of an emergency while awaiting a higher level
EMR Instructional Guidelines Preparatory EMS Systems Uses simple knowledge of the EMS system, safety/well being of the EMR, medical/legal issues at the scene of an emergency while awaiting a higher level
Oxygen Therapy. Oxygen therapy quick guide V3 July 2012.
 PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in a compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in a liquid form. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the patient by means of plastic tubing
PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in a compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in a liquid form. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the patient by means of plastic tubing
Objectives. Burn Assessment and Management. Questions Regarding the Case Study. Case Study. Patient Assessment. Patient Assessment
 Objectives Burn Assessment and Management Discuss the mechanisms and complications of a thermal burn, electrical burn and an inhalation burn Explain the factors to consider when determining the severity
Objectives Burn Assessment and Management Discuss the mechanisms and complications of a thermal burn, electrical burn and an inhalation burn Explain the factors to consider when determining the severity
Adult Choking and CPR Manual
 Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
Module 5 ADULT RECOvERY POSITION STEP 1 POSITION ThE victim
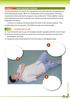 Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT POLICY
 PS1006 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT POLICY TITLE: NON-INVASIVE POSITIVE PRESSURE (NPPV) VENTILATION (CPAP/BIPAP) Job Title of Reviewer: EFFECTIVE DATE: REVISED DATE: POLICY TYPE: Director, Respiratory
PS1006 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT POLICY TITLE: NON-INVASIVE POSITIVE PRESSURE (NPPV) VENTILATION (CPAP/BIPAP) Job Title of Reviewer: EFFECTIVE DATE: REVISED DATE: POLICY TYPE: Director, Respiratory
Oxygen - update April 2009 OXG
 PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in liquid form, in a system adapted for ambulance use. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the
PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in liquid form, in a system adapted for ambulance use. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
ACLS Provider Manual Comparison Sheet Based on 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC. BLS Changes
 ACLS Provider Manual Comparison Sheet Based on 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC CPR Chest compressions, Airway, Breathing (C-A-B) BLS Changes New Old Rationale New science indicates the following order:
ACLS Provider Manual Comparison Sheet Based on 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC CPR Chest compressions, Airway, Breathing (C-A-B) BLS Changes New Old Rationale New science indicates the following order:
Emergency Medical Response INSTRUCTOR S MANUAL
 Emergency Medical Response INSTRUCTOR S MANUAL Contents Acknowledgments 3 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATION Chapter 1: Introduction 9 Course Purpose Course Objectives Course Participants Instructor Responsibilities
Emergency Medical Response INSTRUCTOR S MANUAL Contents Acknowledgments 3 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATION Chapter 1: Introduction 9 Course Purpose Course Objectives Course Participants Instructor Responsibilities
International EMS Registry. EMR Study Guide
 International EMS Registry EMR Study Guide 2012 This guide is to assist the student by highlighting the multiple areas of the EMR program. This guide is not designed to take the place of the EMR textbook
International EMS Registry EMR Study Guide 2012 This guide is to assist the student by highlighting the multiple areas of the EMR program. This guide is not designed to take the place of the EMR textbook
The Alberta College of Paramedics
 The Alberta College of Paramedics Alberta Occupational Competency Profile (AOCP) Upgrade Gap Training Program Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Airway Management Module Study Guide Table of Contents Acknowledgements
The Alberta College of Paramedics Alberta Occupational Competency Profile (AOCP) Upgrade Gap Training Program Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Airway Management Module Study Guide Table of Contents Acknowledgements
Difficult Pre-hospital Airway Management
 Difficult Pre-hospital Airway Management Frans L. Rutten, MD, FDSA Elisabeth Hospital Tilburg, The Netherlands In management of patients with an emergency, airway management and ventilatory care are the
Difficult Pre-hospital Airway Management Frans L. Rutten, MD, FDSA Elisabeth Hospital Tilburg, The Netherlands In management of patients with an emergency, airway management and ventilatory care are the
National Registry of EMTs Continued Competency Program. (NREMT Recertification Requirements) BETA Version 2
 National Registry of EMTs Continued Competency Program (NREMT Recertification Requirements) BETA Version 2 Massachusetts providers Issue date: 5/1/2013 The Four Principles of Continued Competency Professional
National Registry of EMTs Continued Competency Program (NREMT Recertification Requirements) BETA Version 2 Massachusetts providers Issue date: 5/1/2013 The Four Principles of Continued Competency Professional
STAGES OF SHOCK. IRREVERSIBLE SHOCK Heart deteriorates until it can no longer pump and death occurs.
 STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle?
 What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
Overview. Geriatric Overview. Chapter 26. Geriatrics 9/11/2012
 Chapter 26 Geriatrics Slide 1 Overview Trauma Common Medical Emergencies Special Considerations in the Elderly Medication Considerations Abuse and Neglect Expanding the Role of EMS Slide 2 Geriatric Overview
Chapter 26 Geriatrics Slide 1 Overview Trauma Common Medical Emergencies Special Considerations in the Elderly Medication Considerations Abuse and Neglect Expanding the Role of EMS Slide 2 Geriatric Overview
How To Treat A Pregnant Woman With A Miscarriage
 Special Patient Populations Obstetrics EMR Education Standard Recognizes and manages life threats based on simple assessment findings for a patient with special needs while awaiting additional emergency
Special Patient Populations Obstetrics EMR Education Standard Recognizes and manages life threats based on simple assessment findings for a patient with special needs while awaiting additional emergency
Idaho Transition Instructional Guidelines Emergency Medical Responder (EMR-2011)
 Idaho Transition Instructional Guidelines Emergency Medical Responder (EMR-2011) Idaho EMR Transition Instructional Guidelines Page 1 of 60 Preparatory EMS Systems EMR Education Standard Uses simple knowledge
Idaho Transition Instructional Guidelines Emergency Medical Responder (EMR-2011) Idaho EMR Transition Instructional Guidelines Page 1 of 60 Preparatory EMS Systems EMR Education Standard Uses simple knowledge
ACID- BASE and ELECTROLYTE BALANCE. MGHS School of EMT-Paramedic Program 2011
 ACID- BASE and ELECTROLYTE BALANCE MGHS School of EMT-Paramedic Program 2011 ACID- BASE BALANCE Ions balance themselves like a see-saw. Solutions turn into acids when concentration of hydrogen ions rises
ACID- BASE and ELECTROLYTE BALANCE MGHS School of EMT-Paramedic Program 2011 ACID- BASE BALANCE Ions balance themselves like a see-saw. Solutions turn into acids when concentration of hydrogen ions rises
LESSON 4 ORAL, NASOPHARYNGEAL, AND NASOTRACHEAL SUCTIONING.
 LESSON 4 ORAL, NASOPHARYNGEAL, AND NASOTRACHEAL SUCTIONING. 4-1. SUCTIONING a. Suctioning is a common nursing activity performed for the purpose of removing accumulated secretions from the patient's nose,
LESSON 4 ORAL, NASOPHARYNGEAL, AND NASOTRACHEAL SUCTIONING. 4-1. SUCTIONING a. Suctioning is a common nursing activity performed for the purpose of removing accumulated secretions from the patient's nose,
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Kansas Emergency Medical Services Education Standards EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER
 Kansas Emergency Medical Services Education Standards EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER Page 1 of 141 Page 2 of 141 Contents Preparatory EMS Systems (PR1) Page 5 Preparatory Research (PR2) Page 7 Preparatory
Kansas Emergency Medical Services Education Standards EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER Page 1 of 141 Page 2 of 141 Contents Preparatory EMS Systems (PR1) Page 5 Preparatory Research (PR2) Page 7 Preparatory
PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES
 P1 Pediatric Patient Care P2 Cardiac Arrest Initial Care and CPR P3 Neonatal Resuscitation P4 Ventricular Fibrillation / Ventricular Tachycardia P5 PEA / Asystole P6 Symptomatic Bradycardia P7 Tachycardia
P1 Pediatric Patient Care P2 Cardiac Arrest Initial Care and CPR P3 Neonatal Resuscitation P4 Ventricular Fibrillation / Ventricular Tachycardia P5 PEA / Asystole P6 Symptomatic Bradycardia P7 Tachycardia
PHSW Procedural Sedation Post-Test Answer Key. For the following questions, circle the letter of the correct answer(s) or the word true or false.
 PHSW Procedural Sedation Post-Test Answer Key 1 1. Define Procedural (Conscious) Sedation: A medically controlled state of depressed consciousness where the patient retains the ability to continuously
PHSW Procedural Sedation Post-Test Answer Key 1 1. Define Procedural (Conscious) Sedation: A medically controlled state of depressed consciousness where the patient retains the ability to continuously
BLS TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC
 BLS TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST - NON-TRAUMATIC (SJ-B101) effective 07/01/99 Defibrillation CPR Apply S-AED and assess rhythm as trained. Defib as indicated Simultaneous OXYGEN:
BLS TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST - NON-TRAUMATIC (SJ-B101) effective 07/01/99 Defibrillation CPR Apply S-AED and assess rhythm as trained. Defib as indicated Simultaneous OXYGEN:
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Pediatric Respiratory System: Basic Anatomy & Physiology. Jihad Zahraa Pediatric Intensivist Head of PICU, King Fahad Medical City
 Pediatric Respiratory System: Basic Anatomy & Physiology Jihad Zahraa Pediatric Intensivist Head of PICU, King Fahad Medical City Outline Introduction Developmental Anatomy Developmental Mechanics of Breathing
Pediatric Respiratory System: Basic Anatomy & Physiology Jihad Zahraa Pediatric Intensivist Head of PICU, King Fahad Medical City Outline Introduction Developmental Anatomy Developmental Mechanics of Breathing
NRP 2012 Putting New Resuscitation Guidelines into Practice
 Outreach Education Online Video Library for Healthcare Professionals NRP 2012 Putting New Resuscitation Guidelines into Practice. Jeanette Zaichkin, RN, MN, NNP-BC December 2, 2010 Program Handouts This
Outreach Education Online Video Library for Healthcare Professionals NRP 2012 Putting New Resuscitation Guidelines into Practice. Jeanette Zaichkin, RN, MN, NNP-BC December 2, 2010 Program Handouts This
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
Allina Emergency Medicine Education Healthcare Provider. CPR Study Guide. American Heart Association 2010 Guidelines
 Allina Emergency Medicine Education Healthcare Provider CPR Study Guide American Heart Association 2010 Guidelines The American Heart Association strongly promotes knowledge and proficiency in BLS< ACLS
Allina Emergency Medicine Education Healthcare Provider CPR Study Guide American Heart Association 2010 Guidelines The American Heart Association strongly promotes knowledge and proficiency in BLS< ACLS
Therapist Multiple-Choice Examination
 Therapist Multiple-Choice Examination Effective: January 2015 Detailed Content Outline Items are linked to open cells. Each scored form will include 20-item pretests. I. PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Therapist Multiple-Choice Examination Effective: January 2015 Detailed Content Outline Items are linked to open cells. Each scored form will include 20-item pretests. I. PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
CLINICAL SKILLS: THE 'DR ABCDE' ASSESSMENT
 CLINICAL SKILLS: THE 'DR ABCDE' ASSESSMENT The 'DR ABCDE' approach to assessing an acutely unwell patient should be at the front of every junior doctor's mind whenever they get bleeped or asked to see
CLINICAL SKILLS: THE 'DR ABCDE' ASSESSMENT The 'DR ABCDE' approach to assessing an acutely unwell patient should be at the front of every junior doctor's mind whenever they get bleeped or asked to see
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
State of Indiana EMR Psychomotor Skills Examination
 SECONDARY ASSESSMENT (Detailed Exam) *Credit should be given to candidates that use a brief exam f life-threatening injuries in the Primary Survey so long as it does not delay appropriate care. Head Neck
SECONDARY ASSESSMENT (Detailed Exam) *Credit should be given to candidates that use a brief exam f life-threatening injuries in the Primary Survey so long as it does not delay appropriate care. Head Neck
Scope of Practice Approved by the State Board of EMS (EMS Board), within the Division of EMS of the Ohio Department of Public Safety
 Scope of Practice Approved by the State Board of EMS (EMS Board), within the Division of EMS of the Ohio Department of Public Safety This document offers an at-a-glance view of the Scope of Practice for
Scope of Practice Approved by the State Board of EMS (EMS Board), within the Division of EMS of the Ohio Department of Public Safety This document offers an at-a-glance view of the Scope of Practice for
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 [email protected] www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 [email protected] www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
The Phoenix Document An Evolution from National Standard Curriculum to the Virginia EMS Education Standards
 An Evolution from National Standard Curriculum to the Virginia EMS Education Standards Training Levels Included: Emergency Medical Technician (EMT) Introduction: This document identifies the differences
An Evolution from National Standard Curriculum to the Virginia EMS Education Standards Training Levels Included: Emergency Medical Technician (EMT) Introduction: This document identifies the differences
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment
 Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
Neonatal Intubation. Purpose. Scope. Indications. Equipment Cardiorespiratory monitor SaO 2 monitor. Anatomic Considerations.
 Page 1 of 5 Purpose Scope Indications Neonatal Intubation To assure proper placement of endotracheal tubes for maximum ventilation using proper intubation procedures. The policy applies to all Respiratory
Page 1 of 5 Purpose Scope Indications Neonatal Intubation To assure proper placement of endotracheal tubes for maximum ventilation using proper intubation procedures. The policy applies to all Respiratory
Milwaukee School of Engineering [email protected]. Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version
 Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY KNR 182
 Human Anatomy and Physiology Notes (KNR 182) ; Page 92 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY KNR 182 Lecture Packet for Unit V Respiratory System Professor: Dale D. Brown, Ph.D. 5120 Dept of KNR Horton Fieldhouse
Human Anatomy and Physiology Notes (KNR 182) ; Page 92 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY KNR 182 Lecture Packet for Unit V Respiratory System Professor: Dale D. Brown, Ph.D. 5120 Dept of KNR Horton Fieldhouse
3100B Clinical Training Program. 3100B HFOV VIASYS Healthcare
 3100B Clinical Training Program 3100B HFOV VIASYS Healthcare HFOV at Alveolar Level Nieman,, G, SUNY 1999 Who DO We Treat? Only Pathology studied to date has been ARDS Questions about management of adults
3100B Clinical Training Program 3100B HFOV VIASYS Healthcare HFOV at Alveolar Level Nieman,, G, SUNY 1999 Who DO We Treat? Only Pathology studied to date has been ARDS Questions about management of adults
