American Heart Association
|
|
|
- Helena Robinson
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart Association
2 BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Written Examination Pretest 1. While at work in a hospital you find an adult victim who has collapsed. No one is available to help. After you ensure that the scene is safe, what should you do next? a. Check for unresponsiveness; if the victim is unresponsive, activate the emergency response system (or phone 911) and get the AED if available b. Phone 911 (or activate the emergency response system), then wait outside to direct the emergency responders c. Open the airway with a tongue-jaw lift and perform 2 finder sweeps to check if food is blocking the airway d. Perform CPR for 1 minute, then phone You work with an overweight 55-year-old dentist with no known history of heart disease. He begins to complain of sudden, severe, crushing pain under his breastbone, in the center of his chest. The pain has lasted more than 5 minutes. What problem should you think of right away, and what should you do? a. Heartburn; tell him to take an antacid b. Angina; phone his personal physician c. Heart attack; phone 911 d. Arrhythmia; drive him to an Emergency Department 3. You witnessed the collapse of a 45-year-old man. You are now performing CPR after sending someone to phone 911. You have done your best to ensure that the first 2 links in the Chain of Survival have been completed immediately. What is the third link in the chain, which will have the greatest effect on increasing this man s chance of survival? a. Arrival of paramedics who will administer drugs b. Transportation of the man to a hospital c. Arrival of a rescuer with a defibrillator d. Arrival of EMS personnel who can do CPR
3 4. You have been talking with a 60-year-old man. He is alert and has been conversing normally. All at once he complains of a sudden weakness on one side of his face and in one arm. He is also having trouble speaking. What is the most likely cause of his problem? a. A seizure b. A heart attack c. A stroke d. Diabetic coma 5. You remove a 3-year-old from the bottom of the shallow end of a swimming pool. You find that she is limp and unresponsive. No other person is available to help. When should you phone 911? a. After you have given the child 5 cycles of CPR b. As soon as you remove the child from the pool c. When you see that after sever minutes of CPR there is no response d. After giving a few ventilations and before beginning chest compressions 6. Which of the following best describes the steps common to the operation of all AEDs in the correct order? a. Power on the AED, attach pads, clear the victim and allow the AED to analyze the rhythm, clear the victim and deliver shock, if advised. b. Power on the AED, shave the victim s chest, attach pads, clear the victim and press the SHOCK button c. Power on the AED, attach pads, press the SHOCK button, clear the victim d. Power on the AED and press the SHOCK button immediately 7. You are responding to an emergency call for a child who was found unresponsive in her be with no sign of trauma. How should you open her airway? a. Place your fingers in her mouth and pull forward on the lower jaw b. Do the jaw-thrust maneuver c. Tilt her head and lift her chin d. Pull her tongue forward 8. Before providing rescue breathing for an unresponsive victim, you must check for breathing. You do this by listening and feeling for airflow through the victim s nose or mouth and by: a. Looking into the victim s mouth to see if anything is blocking the airway b. Shaking or tapping the victim s should to stimulate him to breathe
4 c. Checking the pupils d. Looking to see if the chest rises (and falls) as the victim breathes 9. Healthcare providers are cautioned to look for adequate breathing when they open the airway and check for breathing in an unresponsive victim. What is the best explanation for the requirement that the healthcare provider look for more than just the presence or absence of breathing? a. Healthcare providers often mistake effective breaths for absence of breaths and they start rescue breathing unnecessarily. b. Most adult victims of cardiac arrest actually stop breathing before the cardiac arrest, and the respiratory arrest precipitates the cardiac arrest c. Many victims of sudden cardiac arrest actually have a foreign body in the airway, which will require that you check and confirm that breathing is adequate. d. Some victims continue to demonstrate agonal or gasping breaths for several minutes after a cardiac arrest, but these breaths and breaths that are too slow or too shallow will not maintain oxygenation. 10. A choking adult becomes unresponsive while you are doing abdominal thrusts for severe choking. You ease the victim to the floor and send someone to activate your emergency response system. What should you do next? a. Perform a tongue-jaw lift and finger sweep for at least 2 minutes b. Begin CPR. When you open the airway, look for and remove the object (if seen) before giving rescue breaths c. Continue the Heimlich maneuver until the object comes out of the victim s airway then begin the steps of CPR d. Give chest thrusts for 2 minutes, then begin CPR 11. What is the best way for a rescuer to know that a rescue breath for an infant victim is effective? a. The stomach rises visibly b. The chest rises visibly c. An infant ventilation bag is completely compressed d. The rescuer can hear an air leak around the mask 12. A 3-year-old child is eating in the hospital playroom. She suddenly begins coughing repeatedly. Her cough then quickly becomes soft and weak. She is making highpitched noises while breathing in and seems to be in respiratory distress. Her skin is a bluish color. What is the most likely cause of her distress?
5 a. An acute asthma attack causing a swelling of the airway b. Severe or complete airway obstruction with inadequate air exchange c. Infected and swollen vocal chords d. A seizure from a possible head injury 13. You are performing rescue breathing with a bag-mask device and oxygen for a nonbreathing child with signs of circulation. How often should you provide rescue breathings for the child? a. Approximately once every 3 seconds (20 breaths per minute) b. Approximately once every 4 seconds (15 breaths per minute) c. Approximately once every 5 seconds (10 to 12 breaths per minute) d. Approximately once every 10 seconds (6 breaths per minute) 14. A 52-year-old man collapses at the fitness center after a workout. To determine whether he is in cardiac arrest, you should check for signs of circulation. Part of this assessment is the pulse check. What is the preferred site for a pulse check in this adult victim? a. At the radial artery of the wrist b. At the brachial artery of the arm c. At the carotid artery of the neck d. On the chest over the heart 15. Where should you place your hands on the chest of a victim when you are performing chest compressions? a. On the top half of the breastbone b. Over the heart, on the left side of the chest at the nipple line c. Over the very bottom of the breastbone, on the xiphoid d. On the lower half of the breastbone, at the nipple line in the center of the chest 16. You are performing CPR on an unresponsive man who was found in his bed. What is your ratio of compressions to ventilations? a. 30 compressions, then 2 ventilations b. 5 compressions, then 1 ventilation c. 15 compressions, then 2 ventilations d. 30 compressions, then 5 ventilations
6 17. What is the correct rate or speed for performing compressions for a victim of any age? a. A rate of 30 times per minute b. A rate of 50 times per minute c. A rate of 80 times per minute d. A rate of 100 times per minute 18. A neighbor runs to you with his limp 5-year-old child. You verify that the child is unresponsive and send the neighbor to phone 911. You open the child s airway, determine that he is not breathing, and deliver 2 effective rescue breaths. You check for signs of circulation and find that the child has no signs of circulation (including no pulse). Which of the following choices best describes the technique you should use to perform chest compressions on this child? a. Use heal of both hands, one on top of the other b. Use the heal of one hand c. Use the tips of 2 fingers d. A or B 19. You are alone when you see a man collapse. You confirm that he is unresponsive and phone the emergency response number. There is no AED in sight. You return to the man and perform the steps of CPR. You open the airway and find that he has only agonal respirations. You deliver 2 effective breaths and check for signs of circulation. There are no signs of circulation, so you begin chest compressions. When should you recheck for signs of circulation? a. After each compression-ventilation cycle b. After the first compression-ventilation cycle c. After about 5 minutes of CPR d. After the first 5 cycles of 30 compressions and 2 ventilations (about 2 minutes) 20. Which of the following statements best describes why you should minimize interruptions when giving chest compressions to any victim of cardiac arrest? a. You do not need to worry about interrupting chest compressions b. Minimizing interruptions means you will not be as tired giving CPR c. Only advanced care professionals need to worry about minimizing interruptions d. If you minimize interruptions in chest compressions, you will increase the victim s chances of survival
American Heart Association. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
Northwestern Health Sciences University. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
American Heart Association. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest ANNOTATED ANSWER KEY February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest ANNOTATED ANSWER KEY February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses
Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer
 Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer
Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer
American Heart Association. BLS Instructor Course. Written Examination. July 2003
 American Heart Association BLS Instructor Course Written Examination July 2003 Basic Life Support Instructor Exam Part I Please do not mark on this examination. Record the best answer on the separate answer
American Heart Association BLS Instructor Course Written Examination July 2003 Basic Life Support Instructor Exam Part I Please do not mark on this examination. Record the best answer on the separate answer
BLS for Healthcare Providers Study Guide and Pretest
 BLS for Healthcare Providers Study Guide and Pretest Adult CPR 1-Rescuer CPR Sequence check for responsiveness if no response, activate 911 and get the AED open the airway look, listen, & feel for breathing
BLS for Healthcare Providers Study Guide and Pretest Adult CPR 1-Rescuer CPR Sequence check for responsiveness if no response, activate 911 and get the AED open the airway look, listen, & feel for breathing
Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course
 Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course Written by: Jay Snaric, MS And Kimberly Hickman, RN CPR St. Louis 44 Meramec Valley Plaza St. Louis MO 63088 www.stlcpr.com
Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course Written by: Jay Snaric, MS And Kimberly Hickman, RN CPR St. Louis 44 Meramec Valley Plaza St. Louis MO 63088 www.stlcpr.com
BLS PRETEST BASIC LIFE SUPPORT FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS (CREATED BY LAST MINUTE CPR & FIRST AID)
 BLS PRETEST BASIC LIFE SUPPORT FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS (CREATED BY LAST MINUTE CPR & FIRST AID) 1. THIS BLS FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS COURSE IS GIVEN TO: a. Nurses, Doctors, Paramedics, & Healthcare Workers.
BLS PRETEST BASIC LIFE SUPPORT FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS (CREATED BY LAST MINUTE CPR & FIRST AID) 1. THIS BLS FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS COURSE IS GIVEN TO: a. Nurses, Doctors, Paramedics, & Healthcare Workers.
Infant CPR. What You Need to Know. How to Do Infant CPR
 Infant CPR Infant CPR also called Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is emergency care given to a baby who has stopped breathing. This sheet has the steps for CPR for newborns or babies less than 1 year old.
Infant CPR Infant CPR also called Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is emergency care given to a baby who has stopped breathing. This sheet has the steps for CPR for newborns or babies less than 1 year old.
Infant CPR Skills Testing Checklist
 Infant CPR Skills Testing Checklist Student Name Date of Test Scenario: While you are pushing a baby in a stroller at the park, you notice something is wrong with the baby. You do not have a phone nearby.
Infant CPR Skills Testing Checklist Student Name Date of Test Scenario: While you are pushing a baby in a stroller at the park, you notice something is wrong with the baby. You do not have a phone nearby.
American Red Cross CPR Adult EXAMPLE ANSWER SHEET
 American Red Cross CPR Adult IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed by
American Red Cross CPR Adult IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed by
CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK
 CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: THE PROFESSIONAL RESCUER The Duty to Respond 2 Preventing the Spread of Bloodborne Pathogens 3 Taking Action
CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: THE PROFESSIONAL RESCUER The Duty to Respond 2 Preventing the Spread of Bloodborne Pathogens 3 Taking Action
Allina Emergency Medicine Education Healthcare Provider. CPR Study Guide. American Heart Association 2010 Guidelines
 Allina Emergency Medicine Education Healthcare Provider CPR Study Guide American Heart Association 2010 Guidelines The American Heart Association strongly promotes knowledge and proficiency in BLS< ACLS
Allina Emergency Medicine Education Healthcare Provider CPR Study Guide American Heart Association 2010 Guidelines The American Heart Association strongly promotes knowledge and proficiency in BLS< ACLS
Adult Choking and CPR Manual
 Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log
 First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
Pediatric Airway Management
 Pediatric Airway Management Dec 2003 Dr. Shapiro I., PICU Adult Chain of Survival EMS CPR ALS Early Defibrillation Pediatric Chain of Survival Prevention CPR EMS ALS Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest SIDS
Pediatric Airway Management Dec 2003 Dr. Shapiro I., PICU Adult Chain of Survival EMS CPR ALS Early Defibrillation Pediatric Chain of Survival Prevention CPR EMS ALS Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest SIDS
Module 5 ADULT RECOvERY POSITION STEP 1 POSITION ThE victim
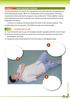 Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
Heart information. CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation
 Heart information CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation Contents 3 What is CPR? 3 What is cardiac arrest? 4 Heart attack and cardiac arrest 4 Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) 5 Danger 6 Response 7 Send
Heart information CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation Contents 3 What is CPR? 3 What is cardiac arrest? 4 Heart attack and cardiac arrest 4 Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) 5 Danger 6 Response 7 Send
81 First Responder Respiratory
 81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
CPR for the Professional Rescuer
 American Red Cross Video CPR for the Professional Rescuer As a professional rescuer, you are a key part of the emergency medical service (EMS) system. Whether you are paid or volunteer, in your position
American Red Cross Video CPR for the Professional Rescuer As a professional rescuer, you are a key part of the emergency medical service (EMS) system. Whether you are paid or volunteer, in your position
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd. Ready Reference
 Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
Procedure 17: Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
 Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation 349 Procedure 17: Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Introduction Cardiopulmonary arrest (CPA) occurs when a patient s heart and lungs stop functioning. In children, CPA usually
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation 349 Procedure 17: Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Introduction Cardiopulmonary arrest (CPA) occurs when a patient s heart and lungs stop functioning. In children, CPA usually
Adult Basic Life Support
 2 Adult Basic Life Support Introduction This chapter contains the guidelines for out-of-hospital, single rescuer, adult basic life support (BLS). Like the other guidelines in this publication, it is based
2 Adult Basic Life Support Introduction This chapter contains the guidelines for out-of-hospital, single rescuer, adult basic life support (BLS). Like the other guidelines in this publication, it is based
The purpose of this course is to outline the American Heart Association s guidelines for CPR, the use of AEDs, and the Heimlich maneuver.
 CPR Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed May, 2016, Expires May, 2018 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2016 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
CPR Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed May, 2016, Expires May, 2018 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2016 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE
 American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
Basic life support (BLS) Techniques
 module Basic life support (BLS) Techniques 1 01 04. Basic Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) 08. Adult basic life support sequence, according to European Resuscitation Guidelines 12. Recognition of cardiorespiratory
module Basic life support (BLS) Techniques 1 01 04. Basic Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) 08. Adult basic life support sequence, according to European Resuscitation Guidelines 12. Recognition of cardiorespiratory
Question-and-Answer Document 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR & ECC As of October 18, 2010
 Question-and-Answer Document 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR & ECC As of October 18, 2010 Q: What are the most significant changes in the 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR & ECC? A: Major changes for all rescuers,
Question-and-Answer Document 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR & ECC As of October 18, 2010 Q: What are the most significant changes in the 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR & ECC? A: Major changes for all rescuers,
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010.
 ACLS Study Guide The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010. Please read the below information carefully This letter is to confirm your
ACLS Study Guide The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010. Please read the below information carefully This letter is to confirm your
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT REVISED STUDY GUIDE
 BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) REVISED STUDY GUIDE (2010 AHA Guidelines) NAME INSTRUCTOR COURSE DATE IT IS NOT THE INTENT OF THIS SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION PACKET TO REPLACE THE AMERICAN
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) REVISED STUDY GUIDE (2010 AHA Guidelines) NAME INSTRUCTOR COURSE DATE IT IS NOT THE INTENT OF THIS SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION PACKET TO REPLACE THE AMERICAN
How you can help save lives
 How you can help save lives Through Life Support Training Courses with THE INTERNATIONAL LIFE SUPPORT TRAINING CENTER (ILSTC) TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Page 3 Basic Life Support for Healthcare Provider
How you can help save lives Through Life Support Training Courses with THE INTERNATIONAL LIFE SUPPORT TRAINING CENTER (ILSTC) TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Page 3 Basic Life Support for Healthcare Provider
Presenters Alison Ellison Children s Healthcare of Atlanta Georgina Howard Therese McGuire Michael Tenoschok Georgia Department of Education
 CPR (Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation) and AED (Automated External Defibrillator) Information August 29, 2013 Today s Session will begin at 3:30 PM While you are waiting, please do the following: Configure
CPR (Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation) and AED (Automated External Defibrillator) Information August 29, 2013 Today s Session will begin at 3:30 PM While you are waiting, please do the following: Configure
Heartsaver Pediatric First Aid CPR AED Online Part 1 (90-1434) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) As of March 25, 2014
 Heartsaver Pediatric First Aid CPR AED Online Part 1 (90-1434) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) As of March 25, 2014 General Information: Q: What is Heartsaver Pediatric First Aid CPR AED Online Part
Heartsaver Pediatric First Aid CPR AED Online Part 1 (90-1434) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) As of March 25, 2014 General Information: Q: What is Heartsaver Pediatric First Aid CPR AED Online Part
2015 Interim Resources for BLS
 2015 Interim Resources for BLS Original Release: November 25, 2015 Starting in 2016, new versions of American Heart Association online courses will be released to reflect the changes published in the 2015
2015 Interim Resources for BLS Original Release: November 25, 2015 Starting in 2016, new versions of American Heart Association online courses will be released to reflect the changes published in the 2015
Emergency Medical Dispatching (EMD)
 Goals: Emergency Medical Dispatching (EMD) This program has been specifically designed to know how to use and be able to practice scenarios for Emergency Medical Dispatching. Objectives: Can explain how
Goals: Emergency Medical Dispatching (EMD) This program has been specifically designed to know how to use and be able to practice scenarios for Emergency Medical Dispatching. Objectives: Can explain how
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Responder Psychomotor Examination PATIENT ASSESSMENT/MANAGEMENT TRAUMA
 PATIENT ASSESSMENT/MANAGEMENT TRAUMA Scenario # Note: Areas denoted by ** may be integrated within sequence of Primary Survey/Resuscitation SCENE SIZE-UP Determines the mechanism of injury/nature of illness
PATIENT ASSESSMENT/MANAGEMENT TRAUMA Scenario # Note: Areas denoted by ** may be integrated within sequence of Primary Survey/Resuscitation SCENE SIZE-UP Determines the mechanism of injury/nature of illness
(Organization s Name)
 2 1 6 W A K E M A N P L A C E B R O O K L Y N, N E W Y O R K 1 1 2 2 0 W W W. A F O R U M F O R L I F E. O R G P H O N E 7 1 8 7 5 9 9 0 1 3 F A X 4 3 7 4 9 7 4 0 2 9 In association with the PROPOSAL FIRST
2 1 6 W A K E M A N P L A C E B R O O K L Y N, N E W Y O R K 1 1 2 2 0 W W W. A F O R U M F O R L I F E. O R G P H O N E 7 1 8 7 5 9 9 0 1 3 F A X 4 3 7 4 9 7 4 0 2 9 In association with the PROPOSAL FIRST
The science of medicine. The compassion to heal.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Responder Psychomotor Examination BVM VENTILATION OF AN APNEIC ADULT PATIENT
 BVM VENTILATION OF AN APNEIC ADULT PATIENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Points Checks responsiveness NOTE: After checking responsiveness and breathing for at least 5 but no 1 Checks breathing
BVM VENTILATION OF AN APNEIC ADULT PATIENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Points Checks responsiveness NOTE: After checking responsiveness and breathing for at least 5 but no 1 Checks breathing
CPR /AED for Professional Rescuers
 CPR /AED for Professional Rescuers In-Depth Instructor Resource Contents C-A-B (Compression-Airway-Breathing) 1,3... 3 CPR Barriers... 10 Adult CPR 1,3,4... 15 Child CPR 2... 17 Infant CPR 2... 19 Special
CPR /AED for Professional Rescuers In-Depth Instructor Resource Contents C-A-B (Compression-Airway-Breathing) 1,3... 3 CPR Barriers... 10 Adult CPR 1,3,4... 15 Child CPR 2... 17 Infant CPR 2... 19 Special
2015 Interim Resources for HeartCode ACLS
 2015 Interim Resources for HeartCode ACLS Original Release: November 25, 2015 Starting in 2016, new versions of American Heart Association online courses will be released to reflect the changes published
2015 Interim Resources for HeartCode ACLS Original Release: November 25, 2015 Starting in 2016, new versions of American Heart Association online courses will be released to reflect the changes published
Southern Stone County Fire Protection District Emergency Medical Protocols
 TITLE Pediatric Medical Assessment PM 2.4 Confirm scene safety Appropriate body substance isolation procedures Number of patients Nature of illness Evaluate the need for assistance B.L.S ABC s & LOC Focused
TITLE Pediatric Medical Assessment PM 2.4 Confirm scene safety Appropriate body substance isolation procedures Number of patients Nature of illness Evaluate the need for assistance B.L.S ABC s & LOC Focused
In-hospital resuscitation. Superseded by
 6 In-hospital resuscitation Introduction These guidelines are aimed primarily at healthcare professionals who are first to respond to an in-hospital cardiac arrest and may also be applicable to healthcare
6 In-hospital resuscitation Introduction These guidelines are aimed primarily at healthcare professionals who are first to respond to an in-hospital cardiac arrest and may also be applicable to healthcare
C-A-B. Compressions: Push hard and fast on the center of. Airway: Tilt the victim s head back and lift the chin to
 Center fr Prfessinal Practice f Nursing CPR Guidelines fr Health-Care Prviders C-A-B Cmpressins: Push hard and fast n the center f the victim s chest Airway: Tilt the victim s head back and lift the chin
Center fr Prfessinal Practice f Nursing CPR Guidelines fr Health-Care Prviders C-A-B Cmpressins: Push hard and fast n the center f the victim s chest Airway: Tilt the victim s head back and lift the chin
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPORT State Form 54407 (R / 5-13)
 EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT State Form 54407 (R / 5-3) INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street,
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT State Form 54407 (R / 5-3) INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street,
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT - ADULT
 BASIC LIFE SUPPORT - ADULT First Issued by/date BKW PCT May 2003 Issue Version Purpose of Issue/Description of Change 3 Policy reviewed. No changes in procedure or legislation since policy revised 12 months
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT - ADULT First Issued by/date BKW PCT May 2003 Issue Version Purpose of Issue/Description of Change 3 Policy reviewed. No changes in procedure or legislation since policy revised 12 months
Student Workbook. CPR & First Aid. for Childcare Providers. Emergency Response for the School and Childcare Environment.
 Student Workbook CPR & First Aid for Childcare Providers Emergency Response for the School and Childcare Environment 2010 Guidelines Emergency Index 42 65 51 35 28 49 39 7 60 33 35 20 49 43 46 42 24 26
Student Workbook CPR & First Aid for Childcare Providers Emergency Response for the School and Childcare Environment 2010 Guidelines Emergency Index 42 65 51 35 28 49 39 7 60 33 35 20 49 43 46 42 24 26
Armstrong Medical Little Joe. 1 Manikin 1 Red Cross-branded Carrying Case
 Category Ambu CPR Pal Trainer Ambu Multi Man Armstrong Medical Actar D-Fib Armstrong Medical Little Joe Laerdal Little Anne Laerdal Resusci Anne Prestan Professional Adult Manikin Retail Price $257.89/each
Category Ambu CPR Pal Trainer Ambu Multi Man Armstrong Medical Actar D-Fib Armstrong Medical Little Joe Laerdal Little Anne Laerdal Resusci Anne Prestan Professional Adult Manikin Retail Price $257.89/each
EMS SKILL CARDIAC EMERGENCY: AUTOMATED EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATION (AED)
 EMS SKILL CARDIAC EMERGENCY: AUTOMATED EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATION (AED) PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE Demonstrate competency in assessing signs of cardiopulmonary arrest and performing defibrillation using a semi-automated
EMS SKILL CARDIAC EMERGENCY: AUTOMATED EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATION (AED) PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE Demonstrate competency in assessing signs of cardiopulmonary arrest and performing defibrillation using a semi-automated
LIFE SUPPORT TRAINING CENTER
 LIFE SUPPORT TRAINING CENTER (LSTC) Contents Preface Page 1 Basic Life Support Page 3 Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Page 5 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Page 7 Neonatal Resuscitation Program
LIFE SUPPORT TRAINING CENTER (LSTC) Contents Preface Page 1 Basic Life Support Page 3 Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Page 5 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Page 7 Neonatal Resuscitation Program
Official Online ACLS Exam
 \ Official Online ACLS Exam Please fill out this form before you take the exam. Name : Email : Phone : 1. Hypovolemia initially produces which arrhythmia? A. PEA B. Sinus tachycardia C. Symptomatic bradyarrhythmia
\ Official Online ACLS Exam Please fill out this form before you take the exam. Name : Email : Phone : 1. Hypovolemia initially produces which arrhythmia? A. PEA B. Sinus tachycardia C. Symptomatic bradyarrhythmia
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Technician Psychomotor Examination BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT
 BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Applies direct pressure to the wound 1 NOTE: The examiner must now inform the candidate that the wound continues to bleed.
BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Applies direct pressure to the wound 1 NOTE: The examiner must now inform the candidate that the wound continues to bleed.
CPR & AED Awareness Survey
 CPR & AED Awareness Survey Created for: Philips Medical Systems & the American Heart Association SUBJECTS FOR QUESTIONNAIRE 400 SCREENER 500 AWARENESS AND KNOWLEDGE OF SCA, CPR, AED 600 EXPERIENCE WITH
CPR & AED Awareness Survey Created for: Philips Medical Systems & the American Heart Association SUBJECTS FOR QUESTIONNAIRE 400 SCREENER 500 AWARENESS AND KNOWLEDGE OF SCA, CPR, AED 600 EXPERIENCE WITH
National Registry Skill Sheets
 Bleeding Control/Shock Management BVM Ventilation of an Apneic Adult Patient Cardiac Arrest Management/AED Joint Immobilization Long Bone Immobilization Oxygen Administration By Non-Rebreather Mask Patient
Bleeding Control/Shock Management BVM Ventilation of an Apneic Adult Patient Cardiac Arrest Management/AED Joint Immobilization Long Bone Immobilization Oxygen Administration By Non-Rebreather Mask Patient
Chapter Review Questions
 1 Chapter Review Questions Chapter 1 1. True or false: As an Emergency Medical Responder, your first priority when responding to any emergency scene is patient care. 2. True or false: The first step in
1 Chapter Review Questions Chapter 1 1. True or false: As an Emergency Medical Responder, your first priority when responding to any emergency scene is patient care. 2. True or false: The first step in
19.109 AUTOMATED EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR
 19.109 AUTOMATED EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR References: American Heart Association Healthcare Provider (CPR/AED) Ohio Revised Code Chapter 2305.235 Immunity of Person Involved with Providing Automated External
19.109 AUTOMATED EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR References: American Heart Association Healthcare Provider (CPR/AED) Ohio Revised Code Chapter 2305.235 Immunity of Person Involved with Providing Automated External
Training Manikin Requirements for American Red Cross Certification Courses
 Training Manikin Requirements for American Red Cross Certification Courses Introduction We are pleased to announce the release of the requirements for training manikins. These requirements apply to all
Training Manikin Requirements for American Red Cross Certification Courses Introduction We are pleased to announce the release of the requirements for training manikins. These requirements apply to all
FIRST AID TEST. 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988. www.schoolbusing.com. Revised April 21, 2008 - 1 -
 FIRST AID TEST 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988 www.schoolbusing.com Revised April 21, 2008-1 - West County Transportation Agency This test was developed to help school bus driver
FIRST AID TEST 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988 www.schoolbusing.com Revised April 21, 2008-1 - West County Transportation Agency This test was developed to help school bus driver
Fainting - Syncope. This reference summary explains fainting. It discusses the causes and treatment options for the condition.
 Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Case Scenarios
 Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Case Scenarios ACLS Respiratory Arrest Case Out-of-Hospital Scenario You are a paramedic and respond to the scene of a possible cardiac arrest. A young man lies motionless
Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Case Scenarios ACLS Respiratory Arrest Case Out-of-Hospital Scenario You are a paramedic and respond to the scene of a possible cardiac arrest. A young man lies motionless
Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel
 Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel Management of Life-Threatening Allergies in the School Setting Dover and Sherborn Schools EpiPen Administration This program is designed
Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel Management of Life-Threatening Allergies in the School Setting Dover and Sherborn Schools EpiPen Administration This program is designed
ACLS Provider Manual Comparison Sheet Based on 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC. BLS Changes
 ACLS Provider Manual Comparison Sheet Based on 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC CPR Chest compressions, Airway, Breathing (C-A-B) BLS Changes New Old Rationale New science indicates the following order:
ACLS Provider Manual Comparison Sheet Based on 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC CPR Chest compressions, Airway, Breathing (C-A-B) BLS Changes New Old Rationale New science indicates the following order:
EMT B Practice Test. Practice Questions:
 EMT B Practice Test Practice Questions: Questions 1 to 3 pertain to the following scenario: You and your partner are called to the home of a 75-year-old man complaining of severe pain in the chest and
EMT B Practice Test Practice Questions: Questions 1 to 3 pertain to the following scenario: You and your partner are called to the home of a 75-year-old man complaining of severe pain in the chest and
CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION This chapter will cover the following topics: Introduction: The basic concepts of providing disaster first aid and the equipment required to safely respond to
CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION This chapter will cover the following topics: Introduction: The basic concepts of providing disaster first aid and the equipment required to safely respond to
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
Why and how to have end-of-life discussions with your patients:
 Why and how to have end-of-life discussions with your patients: A guide with a suggested script and some basic questions to use The medical literature consistently shows that physicians can enhance end-of-life
Why and how to have end-of-life discussions with your patients: A guide with a suggested script and some basic questions to use The medical literature consistently shows that physicians can enhance end-of-life
OPTIONAL LESSON Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector
 OPTIONAL LESSON Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector Lesson Length: 54 minutes GUIDANCE FOR THE INSTRUCTOR To complete this lesson and meet the lesson objectives, you must: Discuss all points in the
OPTIONAL LESSON Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector Lesson Length: 54 minutes GUIDANCE FOR THE INSTRUCTOR To complete this lesson and meet the lesson objectives, you must: Discuss all points in the
Emergency Scenario. Chest Pain
 Emergency Scenario Chest Pain This emergency scenario reviews chest pain in a primary care patient, and is set up for roleplay and case review with your staff. 1) The person facilitating scenarios can
Emergency Scenario Chest Pain This emergency scenario reviews chest pain in a primary care patient, and is set up for roleplay and case review with your staff. 1) The person facilitating scenarios can
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPORT
 Reset Form EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street, Room E239 Indianapolis,
Reset Form EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street, Room E239 Indianapolis,
First Aid Multiple Choice Test
 First Aid Multiple Choice Test Answer all 25 questions by circling the correct answer. This is an open-book test. Answers are contained in The Boy Scout Handbook. Patrol Troop 1. When making a 911 call,
First Aid Multiple Choice Test Answer all 25 questions by circling the correct answer. This is an open-book test. Answers are contained in The Boy Scout Handbook. Patrol Troop 1. When making a 911 call,
WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK TO WRIST
 GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
100018 100016 100017. Scope of Course Public Safety First Aid and CPR Course Content. (a) The initial course of instruction shall at a minimum
 100018 100016 100017. Scope of Course Public Safety First Aid and CPR Course Content. (a) The initial course of instruction shall at a minimum consist of not less than fifteen (15) hours in first aid and
100018 100016 100017. Scope of Course Public Safety First Aid and CPR Course Content. (a) The initial course of instruction shall at a minimum consist of not less than fifteen (15) hours in first aid and
U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 CARDIAC IMPAIRMENT SUBCOURSE MD0571 EDITION 100
 U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 CARDIAC IMPAIRMENT SUBCOURSE MD0571 EDITION 100 DEVELOPMENT This subcourse is approved for resident and correspondence
U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 CARDIAC IMPAIRMENT SUBCOURSE MD0571 EDITION 100 DEVELOPMENT This subcourse is approved for resident and correspondence
Frontline First Aid EMR Scenario Examples
 Course Type: Start Date: Instructors initial scenarios as they are completed CPR-AED Scenarios CPR with Hypothermia Load and Go CPR with Obstructed Airway Continue CPR after airway clears with NO obvious
Course Type: Start Date: Instructors initial scenarios as they are completed CPR-AED Scenarios CPR with Hypothermia Load and Go CPR with Obstructed Airway Continue CPR after airway clears with NO obvious
Michigan Adult Cardiac Protocols CARDIAC ARREST GENERAL. Date: May 31, 2012 Page 1 of 5
 Date: May 31, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all adult cardiac arrests. Medical cardiac arrest patients undergoing attempted resuscitation should not be transported
Date: May 31, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all adult cardiac arrests. Medical cardiac arrest patients undergoing attempted resuscitation should not be transported
TN Emergency Medical Services
 TN Emergency edical ODULES AND UNITS ES System ES Providers: ER and ET Safety and Wellness Body echanics System Communication Documentation Therapeutic Communication Legal and Ethical Issues Intro to Respiratory
TN Emergency edical ODULES AND UNITS ES System ES Providers: ER and ET Safety and Wellness Body echanics System Communication Documentation Therapeutic Communication Legal and Ethical Issues Intro to Respiratory
AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION UPDATES:
 INTRODUCTION TO CPR AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION UPDATES: October 18, 2010 If a bystander is not trained in CPR, the bystander should provide compression-only CPR (see below) for the adult victim who suddenly
INTRODUCTION TO CPR AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION UPDATES: October 18, 2010 If a bystander is not trained in CPR, the bystander should provide compression-only CPR (see below) for the adult victim who suddenly
IN CASE OF EMERGENCY. Emergency Telephone Number 112
 IN CASE OF EMERGENCY Emergency Telephone Number 112 Police, Fire, Ambulance Dial 112 in case of fire, medical emergency, serious or life threatening traffic or other accident. Tell the operator: What has
IN CASE OF EMERGENCY Emergency Telephone Number 112 Police, Fire, Ambulance Dial 112 in case of fire, medical emergency, serious or life threatening traffic or other accident. Tell the operator: What has
Emergency Medical Technician - Basic
 Washington State Specific Objectives for Emergency Medical Technician - Basic OFFICE OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL AND TRAUMA PREVENTION September 1996 Emergency Medical Technician - Basic Definition: Emergency
Washington State Specific Objectives for Emergency Medical Technician - Basic OFFICE OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL AND TRAUMA PREVENTION September 1996 Emergency Medical Technician - Basic Definition: Emergency
What to do during... Medical Emergencies
 What to do during... Calling 911 Reacting in an Emergency Performing CPR Providing Rescue Breathing Delivering Abdominal Thrusts Formulating an Emergency Action Plan Assembling Your First Aid Kit Preparing
What to do during... Calling 911 Reacting in an Emergency Performing CPR Providing Rescue Breathing Delivering Abdominal Thrusts Formulating an Emergency Action Plan Assembling Your First Aid Kit Preparing
Target groups: Paramedics, nurses, respiratory therapists, physicians, and others who manage respiratory emergencies.
 Overview Estimated scenario time: 10 15 minutes Estimated debriefing time: 10 minutes Target groups: Paramedics, nurses, respiratory therapists, physicians, and others who manage respiratory emergencies.
Overview Estimated scenario time: 10 15 minutes Estimated debriefing time: 10 minutes Target groups: Paramedics, nurses, respiratory therapists, physicians, and others who manage respiratory emergencies.
SHAKEN BABY SYNDROME:
 SHAKEN BABY SYNDROME: A SAFETY MANUAL FOR HAND IN HAND CHILD CARE SHAKEN BABY SYNDROME BACKGROUND: The dangers of shaking a baby are becoming more and more apparent, often with disastrous results. The
SHAKEN BABY SYNDROME: A SAFETY MANUAL FOR HAND IN HAND CHILD CARE SHAKEN BABY SYNDROME BACKGROUND: The dangers of shaking a baby are becoming more and more apparent, often with disastrous results. The
Obstetric Emergencies
 Obstetric Emergencies Dr. Si Lay Khaing Senior Lecturer/ O&G Specialist Faculty of Medicine University of Malaya 15 th March 2014 Abstract Life Saving, The obstetric patient is unique in medicine as two
Obstetric Emergencies Dr. Si Lay Khaing Senior Lecturer/ O&G Specialist Faculty of Medicine University of Malaya 15 th March 2014 Abstract Life Saving, The obstetric patient is unique in medicine as two
Diuretics: You may get diuretic medicine to help decrease swelling in your brain. This may help your brain get better blood flow.
 Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
American Red Cross First Aid EXAMPLE ANSWER SHEET
 American Red Cross First Aid Exam A IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed
American Red Cross First Aid Exam A IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed
How To Treat A Pregnant Woman With A Miscarriage
 Special Patient Populations Obstetrics EMR Education Standard Recognizes and manages life threats based on simple assessment findings for a patient with special needs while awaiting additional emergency
Special Patient Populations Obstetrics EMR Education Standard Recognizes and manages life threats based on simple assessment findings for a patient with special needs while awaiting additional emergency
Emergency Medical Services Division. DNR Guidelines Draft
 Emergency Medical Services Division Draft Ross Elliott EMS Director Robert Barnes, M.D. Medical Director 1 Revision Log 01/01/1992 Initial draft 08/01/2013 POLST Addition Kern County Public Health Services
Emergency Medical Services Division Draft Ross Elliott EMS Director Robert Barnes, M.D. Medical Director 1 Revision Log 01/01/1992 Initial draft 08/01/2013 POLST Addition Kern County Public Health Services
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE
 Systems of Care and Continuous Quality Improvement Universal elements of a system of care have been identified to provide stakeholders with a common framework with which to assemble an integrated resuscitation
Systems of Care and Continuous Quality Improvement Universal elements of a system of care have been identified to provide stakeholders with a common framework with which to assemble an integrated resuscitation
Purpose To guide registered nurses who may manage clients experiencing sudden or unexpected life-threatening cardiac emergencies.
 Emergency Cardiac Care: Decision Support Tool #1 RN-Initiated Emergency Cardiac Care Without Cardiac Monitoring/Manual Defibrillator or Emergency Cardiac Drugs Decision support tools are evidence-based
Emergency Cardiac Care: Decision Support Tool #1 RN-Initiated Emergency Cardiac Care Without Cardiac Monitoring/Manual Defibrillator or Emergency Cardiac Drugs Decision support tools are evidence-based
ADMINISTERING EMERGENCY OXYGEN
 FACT SHEET ADMINISTERING EMERGENCY OXYGEN Emergency oxygen can be given for many breathing and cardiac emergencies. It can help improve hypoxia (insufficient oxygen reaching the cells) and reduce pain
FACT SHEET ADMINISTERING EMERGENCY OXYGEN Emergency oxygen can be given for many breathing and cardiac emergencies. It can help improve hypoxia (insufficient oxygen reaching the cells) and reduce pain
Team Leader. Ensures high-quality CPR at all times Assigns team member roles Ensures that team members perform well. Bradycardia Management
 ACLS Megacode Case 1: Sinus Bradycardia (Bradycardia VF/Pulseless VT Asystole Out-of-Hospital Scenario You are a paramedic and arrive on the scene to find a 57-year-old woman complaining of indigestion.
ACLS Megacode Case 1: Sinus Bradycardia (Bradycardia VF/Pulseless VT Asystole Out-of-Hospital Scenario You are a paramedic and arrive on the scene to find a 57-year-old woman complaining of indigestion.
Oxygen - update April 2009 OXG
 PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in liquid form, in a system adapted for ambulance use. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the
PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in liquid form, in a system adapted for ambulance use. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the
EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES POLICIES AND PROCEDURES Policy Number 613. Date: July 1, 2016. Date: July 1, 2016. Effective Date: July 1, 2016
 COUNTY OF VENTURA HEALTH CARE AGENCY Policy Title: Do Not Resuscitate APPROVED: Administration: Steven L. Carroll, EMT-P APPROVED: Medical Director: Angelo Salvucci, M.D. Origination Date: October 1, 1993
COUNTY OF VENTURA HEALTH CARE AGENCY Policy Title: Do Not Resuscitate APPROVED: Administration: Steven L. Carroll, EMT-P APPROVED: Medical Director: Angelo Salvucci, M.D. Origination Date: October 1, 1993
Bleeding Control for the Injured
 Bleeding Control for the Injured Bleeding Control (1 of 2) The focus of this training is on recognition of life-threatening bleeding with appropriate medical treatment. This training will show you the
Bleeding Control for the Injured Bleeding Control (1 of 2) The focus of this training is on recognition of life-threatening bleeding with appropriate medical treatment. This training will show you the
Scenario 2 Is it ever safe enough?
 IRECA BLS Competition 2011 Scenario 2 Is it ever safe enough? Team Name Captain Name Judge 1 Judge 2 The Event: You are dispatched to a shooting for two injured at a local bar. Witnesses have told police
IRECA BLS Competition 2011 Scenario 2 Is it ever safe enough? Team Name Captain Name Judge 1 Judge 2 The Event: You are dispatched to a shooting for two injured at a local bar. Witnesses have told police
3/24/2014. Waubonsee Community College Safety Day 2014. Why do we need a First Aid Program?
 Waubonsee Community College Safety Day 2014 Why do we need a First Aid Program? 4,383 workers were killed on the job in 2012 Total recordable non fatal cases: 2,976,400 in 2012 Cases involving days away
Waubonsee Community College Safety Day 2014 Why do we need a First Aid Program? 4,383 workers were killed on the job in 2012 Total recordable non fatal cases: 2,976,400 in 2012 Cases involving days away
Why are you being seen at Frontier Diagnostic Sleep Center?
 8425 South 84th Street Suite B Omaha, NE 68127 Phone: 402.339.7378 Fax: 402.339.9455 SLEEP QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: ADDRESS: Last First MI Street Address DATE City State Zip PHONE: ( ) BIRTHDATE: HEIGHT: WEIGHT:
8425 South 84th Street Suite B Omaha, NE 68127 Phone: 402.339.7378 Fax: 402.339.9455 SLEEP QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: ADDRESS: Last First MI Street Address DATE City State Zip PHONE: ( ) BIRTHDATE: HEIGHT: WEIGHT:
Cardiac Arrest Pediatric Ventricular Fibrillation / Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Protocol revised October 2008
 Cardiac Arrest Pediatric Ventricular Fibrillation / Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Protocol revised October 2008 Preamble In contrast to cardiac arrest in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in pediatric
Cardiac Arrest Pediatric Ventricular Fibrillation / Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Protocol revised October 2008 Preamble In contrast to cardiac arrest in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in pediatric
INFLUENZA (FLU) Flu and You
 Influenza (Flu) What is the flu? The flu is an illness caused by flu viruses. The flu may make people cough and have a sore throat and fever. They may also have a runny or stuffy nose, feel tired, have
Influenza (Flu) What is the flu? The flu is an illness caused by flu viruses. The flu may make people cough and have a sore throat and fever. They may also have a runny or stuffy nose, feel tired, have
Vtial sign #1: PULSE. Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation. Factors that influence pulse rate: Importance of Vital Signs
 Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation Elma I. LeDoux, MD, FACP, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Vtial sign #1: PULSE Reflects heart rate (resting 60-90/min) Should be strong and regular Use 2
Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation Elma I. LeDoux, MD, FACP, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Vtial sign #1: PULSE Reflects heart rate (resting 60-90/min) Should be strong and regular Use 2
