Reproductive Health. Caring for your reproductive health involves:
|
|
|
- Lesley Allen Evans
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reproductive Health A healthy reproductive system makes the miracle of life possible. Taking good care of your reproductive health is important because problems with this system can make it hard or impossible for you to become pregnant. Reproductive health problems also can be harmful to your overall health and emotional well-being and can make it hard to enjoy a sexual relationship. Fortunately, many reproductive health problems can be prevented or corrected if you take good care of your body and see your doctor for regular checkups and screenings. Caring for your reproductive health involves: l Learning how your reproductive system works and what is normal for you. Knowing these things will help you to tell if you need to see a doctor. l Keeping away from substances and chemicals that can harm your reproductive health and ability to produce healthy children. l Seeing your doctor for routine checkups and screenings. This way, problems can be found early, so they can be treated or kept from getting worse. l Protecting yourself from sexually transmitted infections (STIs), which are very common and easily spread. They can damage reproductive organs and make it hard to get pregnant or cause problems during pregnancy. l Incorporating family planning. Reproductive Health 153
2 Your reproductive system A woman has reproductive organs both inside and outside her body. All the organs play a role in the reproductive process, which includes: l menstrual cycle a woman s monthly cycle, which includes getting your period l conception when a woman s egg is fertilized by a man s sperm l pregnancy l childbirth Fallopian tube Vagina Ovary Uterus Cervix Here are the major reproductive organs and what they do: Ovaries These two small glands contain eggs (ova) and make hormones. One of the ovaries releases an egg about once a month as part of the menstrual cycle. This is called ovulation. Fallopian tube When an egg is released, it travels through the fallopian tube to the uterus. You will get pregnant if you have sex with a man, and his sperm fertilizes the egg on its way to your uterus. Uterus The uterus, or womb, is a hollow, pear-shaped organ. The tissue that lines the uterus is called the endometrium. If a fertilized egg attaches itself to the lining of the uterus, it may continue to develop into a fetus. The uterus expands as the fetus grows. The muscular walls of the uterus help to push the mature fetus out during birth. If pregnancy does not occur, the egg is shed along with the blood and tissue that lines the uterus. This is menstruation, also called getting your period. Cervix This narrow entryway connects the vagina and uterus. The cervix is flexible so that it can expand to let a baby pass through during birth. Reproductive health topics found elsewhere in this book: Cancer, including breast, cervical, endometrial, and uterine cancers...page 51 Menopause... page 224 Pregnancy, preconception care, infertility... page 169 Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)... page 119 Urinary incontinence... page The Healthy Woman: A Complete Guide for All Ages
3 Mons pubis Urinary opening Clitoris Labia (outer) Labia (inner) Vaginal opening Anus Vagina Also called the birth canal, the vagina stretches during childbirth. Caring for Your Vulva The vulva does not need special care. But there are a few things you can do to stay comfortable and prevent infections: Do not douche. Douching may make a woman more prone to vaginal infections and make it harder to get pregnant for women who want to. Wear only cotton underpants and avoid tight-fitting pants and pantyhose. Use a personal lubricant for intercourse if the vagina is dry or more lubrication is needed. Frequent use of lubricants that contain the spermicide nonoxynol-9 (N-9) can irritate the vulva and vagina and might increase the risk of infections, including HIV. Use a mirror to check your vulva once a month. If you notice any signs of problems, such as swelling, changes in color, or change in your usual discharge, contact your doctor. The external female genital organ is the vulva. The vulva has five parts: mons pubis, labia, clitoris, urinary opening, and vaginal opening. Know your period Chemicals a woman s body makes called hormones rise and fall during the month and make the menstrual cycle happen. Keep track of your menstrual cycle with a menstrual diary or calendar, so you can know what s normal for you. Make a note of the day your period starts and ends in your calendar and if your bleeding is heavier or lighter than usual. Most cycles are about 28 days long. Your period might not be the same every month. Also make a note of changes in your Reproductive Health 155
4 mood or body during your cycle. Some women have mild pain on one side of their abdomen during ovulation. You might also notice these symptoms in the days leading up to your period: l cramping, bloating, and sore breasts l food cravings l mood swings and irritability l headaches and fatigue Women whose symptoms are severe may have premenstrual syndrome (PMS). Let your doctor know if you have trouble coping with the symptoms of your period, especially mood swings. l l Regular periods: A sign of good health Sometimes women have problems with their menstrual cycle. These are some common menstrual problems: l Abnormal uterine bleeding includes very heavy or long-lasting periods (menorrhagia) (MEN-uh-RAY-jeeuh) or irregular bleeding. Uterine fibroids (FY-broidz) are the most common cause of menorrhagia in adult women. Young teenage girls often have longer cycles until their reproductive system is fully mature. Also, periods may become irregular as you near menopause. l Amenorrhea (ay-men-uh-ree-uh) occurs when a young woman hasn t started menstruating by age 16, or when a woman who used to have a regular period stops menstruating for at least 3 months. The most common cause is pregnancy. But amenorrhea can be a symptom of a disorder, such as polycystic ovary syndrome, premature ovarian failure, or thyroid problems. It is also a sign of a less common but serious condition called female athlete triad, which affects a woman s menstrual cycle, eating habits, and bone health. Competitive athletes and women who engage in a great deal of physical activity are at risk of this disorder. Dysmenorrhea (diss-men-uh-reeuh) is severe pain during a woman s period. The natural production of a hormone called prostaglandin (PROSS-tuh-GLAN-duhn) can cause intense cramping. It is a problem found mainly in girls and young women. In women in their 20s, 30s, and 40s, a condition such as uterine fibroids or endometriosis (EN-doh- MEE-tree-OH-suhss) may cause painful periods. Premature ovarian failure (POF) is when a woman s ovaries stop working normally before she is 40. POF is not the same as early menopause. Some women with POF still get a period 156 The Healthy Woman: A Complete Guide for All Ages
5 When to Get Help for Problem Periods Problem periods often are a symptom of another condition, which may or may not need treatment. See your doctor if: you have not started menstruating by the age of 16 your period suddenly stops you are bleeding for more days than usual you are bleeding much more than usual your periods become irregular after having had regular, monthly cycles your period occurs more often than every 21 days or less often than every 45 days you suddenly feel very sick while or after using tampons, experiencing symptoms such as high fever, headache, throwing up, rash, or feeling faint you bleed between periods (more than just a few drops) you have severe pain during your period you have severe emotional or physical symptoms in the days before your period now and then. But getting pregnant is hard for women with POF. Women with POF also are more likely to develop certain conditions, including osteoporosis (OSS-tee-oh-puh-ROHsuhss), low thyroid function, and an autoimmune (aw-toh-ih-myoon) disease called Addison s disease. (See page 83 of the Autoimmune Diseases chapter for more information.) No treatment will restore ovary function. But some symptoms of POF and the risk of bone loss can be helped by hormone therapy. The cause of POF is not known. But it appears to run in some families. POF also occurs in some women who carry the mutated gene that causes Fragile X syndrome. Women with POF should talk to their doctors about being tested to see if l they are a carrier of this mutated gene. (See page 408 of the Appendix for information on genetic testing.) Premature menopause is when a woman s period stops completely before she is 40. This can occur naturally or because of medical treatment or surgery. Early menopause puts a woman at greater risk of heart disease and osteoporosis, but there are treatment options to lower these risks. Reproductive and gynecologic health There are many conditions and disorders that can affect the organs in a woman s abdominal and pelvic areas. We don t know what causes many reproductive health problems. But there are ways to manage symptoms or make them go Reproductive Health 157
6 away, such as with medicine, surgery, physical therapy, or lifestyle changes. The specific problem, your symptoms, your Disorder Endometrial hyperplasia (EN-doh-MEE-tree-uhl HEYE-pur-PLAY-zhee-uh) occurs when the lining of the uterus grows too thick. It is not cancer. But if the cells of the lining become abnormal, it can lead to cancer of the uterus. Endometriosis occurs when tissue that s like the uterine lining grows outside the uterus. It is very common, mainly affecting women in their 30s and 40s. It is one of the top three causes of infertility. Assisted reproductive technology (ART) helps many women with endometriosis become pregnant. (See the Pregnancy chapter on page 169 for more information on treating infertility.) Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs in the ovaries. In most cases, a cyst is completely normal: It does no harm and goes away by itself. Most women have them at some point in their lives. Often, a woman finds out about a cyst when she has a pelvic exam. Cysts are rarely cancerous in women younger than 50. See also, polycystic ovary syndrome. Painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia) (DISSpuh-ROO-nee-uh) can cause distress for a woman and her partner. Some causes of pain are: Vaginal dryness Infections Vaginismus spasms of the muscles around the vagina Uterine fibroids Scar tissue Past experiences, negative attitudes about sex, or fear of pain also can play a role Pelvic floor problems occur when tissues that support the pelvic organs weaken or are damaged. This can happen because of pregnancy, childbirth, weight gain, surgery, and normal aging. In uterine prolapse, the uterus drops into the vagina. In some cases this causes the cervix to come out through the vaginal opening. In vaginal prolapse, the top of the vagina loses support and can drop through the vaginal opening. age, and your desire to have children are factors that often guide treatment choices. Signs to look for Abnormal bleeding is the most common sign. Pelvic pain is the main symptom. Other types of pain include very painful periods; chronic pain in the belly, lower back, and pelvis; pain during sex; and pain during bowel movements or while passing urine. Difficulty becoming pregnant is another sign. Symptoms often improve after menopause. Cysts may not cause any symptoms. Some cysts may cause pain, discomfort, and irregular periods but not always. If you have cysts, watch for changes or acute symptoms. Call your doctor right away if you have: Sudden, severe pain in your pelvis or abdomen Pain with fever or throwing up Pain during sex can have many forms. Some women have pain outside the vagina, such as with vulvodynia. Some women feel like something is being bumped into when the penis is inside the vagina. You might feel pain every time you have sex or only now and then. It might be hard for women who have pain during sex to become aroused, even if they don t have pain all the time. You might notice a feeling of heaviness or pressure as if something is falling out of the vagina. It might also be hard to empty your bladder completely. You might also get frequent urinary tract infections. Sometimes, urinary and anal incontinence are signs of pelvic support problems. Kegel exercises can make your pelvic muscles stronger. (See page 256 of the Urologic and Kidney Health chapter for more information.) 158 The Healthy Woman: A Complete Guide for All Ages
7 Disorder Pelvic pain can have a number of causes. Often, it is a symptom of another condition, or infection. Sometimes, the reason for pelvic pain is not found. Pain that lasts a long time can disrupt a woman s quality of life and lead to depression. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormone imbalance problem, which can interfere with normal ovulation. This can lead to irregular periods and multiple cysts on the ovaries. PCOS is the most common cause of female infertility. Women with PCOS also are at higher risk of diabetes, high blood pressure, metabolic syndrome, heart disease, and perhaps fibroids and depression. Uterine fibroids are tumors or lumps that grow within the wall of the uterus. They are not cancer. Fibroids may grow as a single tumor or in clusters. A single fibroid can be 1 inch or less in size or grow to 8 inches across or more. Fibroids are very common, affecting at least one-quarter of all women. African American women and women who are overweight are at greater risk. Women who have given birth are at lower risk. Vaginitis is when the vagina is inflamed. It can happen for these reasons: Vaginal yeast infection an overgrowth of fungus, such as candida, which is normally present in the vagina Bacterial vaginosis an overgrowth of certain kinds of bacteria that are normally present in the vagina Sexually transmitted infections Allergy to douches, soaps, feminine sprays, spermicides, etc Vulvodynia is chronic pain and discomfort of the vulva. It can make it hard to sit comfortably, be active, or enjoy a sexual relationship. Over time, coping with pain can lower self-esteem and lead to depression. Signs to look for Pain comes in many forms. Acute pain lasts a short time. Chronic pelvic pain lasts for more than 6 months and does not improve with treatment. Describing your pain will help your doctor find out the cause. A pain diary is a good way to keep track of your pain. Signs of PCOS include: Irregular, infrequent periods Obesity Excess hair growth on the face, chest, stomach, thumbs, or toes Acne Trouble becoming pregnant Some women don t have any symptoms. But fibroids can cause: Heavy bleeding or painful periods Bleeding between periods Feeling full in the lower abdomen Frequent need to pass urine Pain during sex Lower back pain Infertility, more than one miscarriage, or early labor Most women with fibroids are able to become pregnant. Often, fibroids stop growing or shrink after menopause. Vaginitis may not always have symptoms. When it does, you might notice these signs: Burning Itching Redness or puffiness Abnormal discharge with a fishy odor or change in the way it normally looks. Yeast infections often cause cottage cheese like discharge. You might feel burning, stinging, rawness, or aching even though the vulva might look normal. Pain might be felt all over the vulva or in a single spot. Pain can be constant or come and go. You might feel pain only after touch or pressure, such as from using tampons, having sex, or riding a bike. Reproductive Health 159
8 Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is surgery to remove the uterus. It is the second most common surgery among women in the United States. Some reasons a woman might need a hysterectomy include: uterine fibroids endometriosis uterine prolapse cancer abnormal uterine bleeding In some cases, women have other treatment options, such as new medicines or procedures. These alternatives might offer lower risk and quicker recovery time. But they might have drawbacks, too. With your doctor, discuss all the treatment options that might help your problem. Consider getting a second opinion to help you make a wise choice. Breast health Breast health is important to a woman s sexual health, overall health, and breastfeeding. Your breasts will change at different times of your life. You might notice lumpiness or tenderness during your period. Your breasts might get bigger during pregnancy. As you get older, the milk-producing tissue of your breasts turns into soft, fatty tissue, which might feel different to you. It s important to know the way your breasts normally feel and look so you can tell your doctor if you notice changes. A change can be a sign of a problem, including breast cancer. Although not all lumps or breast changes mean you have cancer or a problem, any change in breast tissue should be checked by a doctor. Ask your doctor how you can do a self-exam. Checking your breasts once a month, a few days after your period ends, can alert you to these reasons to call your doctor: l a hard lump or knot in or near the breast or in your underarm l dimpling, puckering, or ridges of the skin on the breast l a change in the size or shape of your breast l clear or bloody fluid that leaks out of the nipple l itchy, scaly sore or rash on the nipple l unusual swelling, warmth, or redness You should also get a clinical breast exam as part of your regular checkup. This is done by your doctor. Women age 40 and older should have screening mammograms every 1 to 2 years. It is an x-ray of the breast. Ask your doctor how often you need one. A mammogram along with a clinical breast exam is the best way to find breast cancer. (See page 62 of the Cancer chapter for more information.) 160 The Healthy Woman: A Complete Guide for All Ages
9 Preventing unintended pregnancy About one-half of all pregnancies in the United States are unintended. Not having sex or using a safe and effective birth control method (contraception) is the best way to avoid pregnancy. Use this chart to learn about birth control methods, and talk to your doctor to find one that s right for you. Method How you get it Failure rate* (Number of pregnancies expected per 100 women) Methods range in effectiveness from light (most effective) to dark (least effective). Sterilization surgery for women Sterilization implant for women Sterilization surgery for men (vasectomy) Implantable rod Intrauterine device (IUD) One-time procedure, which is permanent One-time procedure, which is permanent One-time procedure, which is permanent One-time procedure, which lasts up to 3 years One-time procedure, which can stay in place for 5 to 10 years Less than 1 Less than 1 Less than 1 Less than 1 This method might not work as well for women who are overweight or obese. Less than 1 Some side effects and risks** Pain Bleeding Complications from surgery Ectopic (tubal) pregnancy Pain Ectopic (tubal) pregnancy Pain Bleeding Complications from surgery Acne Weight gain Cysts of the ovaries Mood changes Depression Hair loss Headache Upset stomach Dizziness Sore breasts Changes in period Lower interest in sex Cramps Bleeding between periods Pelvic inflammatory disease Infertility Tear or hole in the uterus Reproductive Health 161
10 Method How you get it Failure rate* (Number of pregnancies expected per 100 women) Methods range in effectiveness from light (most effective) to dark (least effective). Shot/injection Your doctor gives Less than 1 you one shot every 3 months Oral contraceptives (combination pill, or the pill ) Prescription 5 Being overweight may increase the chance of getting pregnant while using birth control pills. Oral contraceptives Prescription 5 (continuous/ Being overweight may increase the chance of getting extended use, or no-period pill ) pregnant while using birth control pills. Oral contraceptives Prescription 5 (progestin-only pill, Being overweight may increase the chance of getting or mini-pill ) pregnant while using birth control pills. Skin patch Prescription 5 The patch may be less effective in women weighing more than 198 pounds. Some side effects and risks** Bleeding between periods Weight gain Sore breasts Headaches Bone loss with long-term use Dizziness Upset stomach Changes in your period Changes in mood Weight gain High blood pressure Blood clots Heart attack Stroke New vision problems Same as combination pill Spotting or bleeding between periods Hard to know if pregnant Spotting or bleeding between periods Weight gain Sore breasts Similar to those for the combination pill Greater exposure to estrogen than with other methods Vaginal ring Prescription 5 Similar to those for the combination pill Swelling of the vagina Irritation Vaginal discharge Male condom Over the counter Allergic reaction 162 The Healthy Woman: A Complete Guide for All Ages
11 Method How you get it Failure rate* (Number Some side effects and of pregnancies expected per 100 women) risks** Methods range in effectiveness from light (most effective) to dark (least effective). Diaphragm with spermicide Prescription 15 Irritation Allergic reactions Urinary tract infection Toxic shock if left in too long Sponge with spermicide Over the counter Irritation Allergic reactions Hard time removing Toxic shock if left in too long Cervical cap with spermicide Prescription Irritation Allergic reactions Abnormal Pap smear Toxic shock if left in too long Female condom Over the counter 20 Irritation Allergic reactions Natural family planning Spermicide alone Ask your doctor or 25 None natural family planning instructor for information Over the counter 30 Irritation Spermicides can offer added Allergic reactions pregnancy protection if used Urinary tract infection with another barrier method, such as a condom. Emergency contraception if your primary method of birth control fails. It should not be used as a regu- Emergency contra- Over the counter for 15 Upset stomach lar birth control method. ception ( morningafter pill ) than 18 need a adults. Girls younger It must be used within 72 Vomiting hours of unprotected sex. prescription. Stomach pain Fatigue Headache *Failure rates depend on whether a birth control method is used correctly and consistently. Your chances of getting pregnant are lowest if birth control always is used correctly and every time you have sex. **Only condoms can protect against most sexually transmitted infections (STIs). The male latex condom offers the best protection against STIs if used correctly and all the time. Reproductive Health 163
12 Birth Control Warning Using the pill or patch may increase your risk of stroke or heart attack. Seek immediate medical care if you have any of the following: sudden change in vision, blurring, or flashing lights severe headache unusual leg pain, particularly in your calf chest pain, trouble breathing, or coughing up blood severe pain in your belly l l l Mammogram Women age 40 and older should have screening mammograms every 1 to 2 years. Pap test and pelvic exam Women should have a Pap test at least once every 3 years, beginning about 3 years after they begin to have sexual intercourse, but no later than age 21. Women who have had the HPV vaccine still need to have Pap tests. Sexually transmitted infection (STI) screening New partners should get tested for common STIs, including HIV, before becoming sexually active. See your doctor regularly, even if you re feeling fine Talk to your doctor about how often you need to schedule a general checkup and specific screenings or tests. This will depend on your age, risk factors, symptoms, and other issues. Here are guidelines for some of the exams, screenings, and vaccines you might need. l Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine It is recommended that girls 11 and 12 years of age get the HPV vaccine. Also, girls and women 13 through 26 years of age should get the vaccine if they did not get it when they were younger. For information on testing, see pages of the Sexually Transmitted Infections chapter. By taking steps to prevent problems and seeing your doctor for regular checkups, you can feel good knowing you re doing all you can to take care of your reproductive health at all stages of life. n For more information on the HPV vaccine, see page 134 of the Sexually Transmitted Infections chapter. 164 The Healthy Woman: A Complete Guide for All Ages
13 One Woman s Story Ihave long suffered from cramps, excessive bleeding, feeling bloated, and frequent urination. I thought that it was normal and did not complain to my parents. During my first trip to the OB-GYN, I learned that I had a uterine fibroid the size of a small gumball. My doctor suggested we monitor its growth but not take action. Consequently, each month I continued to deal with the same problems. During the birth of my daughter, a nurse suggested that I have the fibroid removed after I was back on my feet. I did have to use the bathroom even more frequently while pregnant, but I didn t blame it on the fibroid. With all of the excitement of having a new baby in the house, I forgot about Each month I had to take a couple of days off from work because of severe pain. addressing my problem. Also, my OB-GYN recommended we leave it alone because it would shrink as I aged. A move led to a new doctor who told me that the fibroid was about the size of an egg, but that we would continue to monitor the size. I was concerned that it had grown so significantly. The problems that I experienced continued to get worse over time, and it became increasingly more difficult to get my job done because of frequent trips to the ladies room. I was embarrassed to fly on an airplane because I did not want to disturb the people who sat in my row on the plane. Each month I had to take a couple of days off from work because of severe pain. I was very physically active, but I did not see any reduction in the size of my abdominal area. Finally, I decided to seek advice from an OB-GYN surgeon, who explained my options. We discussed laser technology to shrink the fibroid and a hysterectomy, although I was not prepared to experience menopause. After much consideration and discussions with my spouse, I determined that the best option for me was a myomectomy surgical removal of the fibroid. My hope was to minimize the changes to my body. The surgery was successful, and I learned that there were actually three fibroids connected to one another. Afterward, I no longer experienced excessive bleeding, cramps, bloating, or frequent urination. I recommend that every woman with these symptoms schedule regular checkups and talk about her options with her doctor. You may not have to suffer! Cordelia Chicago, Illinois Reproductive Health 165
14 For More Information Office on Women s Health, HHS 200 Independence Ave SW, Room 712E Washington, DC Web site: menstru.htm cysts.htm Phone number: (800) , (888) TDD Center for the Evaluation of Risks to Human Reproduction, NIH PO Box Research Triangle Park, NC Web site: Phone number: (919) Division of Reproductive Health, CDC 4770 Buford Hwy NE, MS K-20 Atlanta, GA Web site: Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, NIH PO Box 3006 Rockville, MD Web site: Phone number: (800) , (888) TTY Office of Women s Health, FDA 5600 Fishers Ln Rockville, MD Web site: Phone number: (888) American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists th St SW, PO Box Washington, DC Web site: Phone number: (202) Resource Center American Society for Reproductive Medicine 1209 Montgomery Hwy Birmingham, AL Web site: Association of Reproductive Health Professionals 2401 Pennsylvania Ave NW, Suite 350 Washington, DC Web site: Phone number: (202) Endometriosis Association 8585 N 76th Place Milwaukee, WI Web site: Planned Parenthood Federation of America 434 W 33rd St New York, NY Web site: Phone number: (800) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Association PO Box 3403 Englewood, CO Web site: The Healthy Woman: A Complete Guide for All Ages
Birth Control Options
 1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
Birth Control Methods
 page 1 Birth Control Methods Q: What is the best method of birth control (or contraception)? A: There is no best method of birth control. Each method has its pros and cons. All women and men can have control
page 1 Birth Control Methods Q: What is the best method of birth control (or contraception)? A: There is no best method of birth control. Each method has its pros and cons. All women and men can have control
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
All methods of birth control are MUCH SAFER than being pregnant! If 100 women use each method for a year, how many of them get pregnant?
 The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Gynaecology FAQ s. Correspondence address: 204 Fulham Road London SW10 9PJ Email: enquiries@missayida.com Tel: 02077514489
 Gynaecology FAQ s Why is the cervical screening test important? Cervical cancer is not uncommon. In recent years the number of cases has fallen due to cervical screening tests. However, there are still
Gynaecology FAQ s Why is the cervical screening test important? Cervical cancer is not uncommon. In recent years the number of cases has fallen due to cervical screening tests. However, there are still
patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015 Hormone Therapy Menopause is the time in a woman s life when she naturally stops having menstrual periods. Menopause marks the end of the
patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015 Hormone Therapy Menopause is the time in a woman s life when she naturally stops having menstrual periods. Menopause marks the end of the
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion.
 Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion. After the abortion I started re-thinking my birth control method. I am looking
Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion. After the abortion I started re-thinking my birth control method. I am looking
Summa Health System. A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy
 Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
GLOSSARY. A Abstinence: having no vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It is the only method that is 100% effective in preventing pregnancy and STI s.
 WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling IMPLANON (etonogestrel implant) Subdermal Use
 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling IMPLANON (etonogestrel implant) Subdermal Use IMPLANON does not protect against HIV infection (the virus that causes AIDS) or other sexually transmitted diseases. Read this
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling IMPLANON (etonogestrel implant) Subdermal Use IMPLANON does not protect against HIV infection (the virus that causes AIDS) or other sexually transmitted diseases. Read this
A Guide to Hysteroscopy. Patient Education
 A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
Client Information for Informed Consent TESTOSTERONE FOR TRANSGENDER PATIENTS
 Client Information for Informed Consent TESTOSTERONE FOR TRANSGENDER PATIENTS You want to take testosterone to masculinize your body. Before taking it, there are several things you need to know about.
Client Information for Informed Consent TESTOSTERONE FOR TRANSGENDER PATIENTS You want to take testosterone to masculinize your body. Before taking it, there are several things you need to know about.
Cervical cancer screening with the HPV test and the Pap test in women ages 30 and older
 Cervical cancer screening with the HPV test and the Pap test in women ages 30 and older When to get tested and how to make sense of your test results If you are 30 years or older and your Pap test is normal
Cervical cancer screening with the HPV test and the Pap test in women ages 30 and older When to get tested and how to make sense of your test results If you are 30 years or older and your Pap test is normal
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Hysterectomy. What is a hysterectomy? Why is hysterectomy done? Are there alternatives to hysterectomy?
 ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
Stay Healthy at Any Age!
 + Stay Healthy at Any Age! February 28, 2013 Kimberly Kelstone A Deaf Health Talk DHCC Partnership with REAP + Overview Introduction Normal healthy processes Diseases specific to women Screening tests
+ Stay Healthy at Any Age! February 28, 2013 Kimberly Kelstone A Deaf Health Talk DHCC Partnership with REAP + Overview Introduction Normal healthy processes Diseases specific to women Screening tests
Diseases that can be spread during sex
 Diseases that can be spread during sex Did you know... over 65 million people in the United States have a chronic, incurable sexually transmitted disease (STD)? and that every year another 19 million persons
Diseases that can be spread during sex Did you know... over 65 million people in the United States have a chronic, incurable sexually transmitted disease (STD)? and that every year another 19 million persons
Leader's Resource. Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms.
 Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know
 Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Hormone Therapy
 Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Heavy menstrual bleeding and what you can do about it!
 Heavy menstrual bleeding and what you can do about it! The intrauterine system as an alternative to hysterectomy. What is heavy menstrual bleeding? Do I have it? A woman s menstrual periods are considered
Heavy menstrual bleeding and what you can do about it! The intrauterine system as an alternative to hysterectomy. What is heavy menstrual bleeding? Do I have it? A woman s menstrual periods are considered
Ovarian Cystectomy / Oophorectomy
 Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
CONTRACEPTION LONG-ACTING REVERSIBLE CONTRACEPTIVES LARCS
 6 SAND HILL ROAD SUITE 102 FLEMINGTON, NJ 08822 PHONE 908-782-6700 FAX 908-788-5861 CONTRACEPTION LONG-ACTING REVERSIBLE CONTRACEPTIVES LARCS In 2014 the Academy of Pediatrics recommended that long-acting
6 SAND HILL ROAD SUITE 102 FLEMINGTON, NJ 08822 PHONE 908-782-6700 FAX 908-788-5861 CONTRACEPTION LONG-ACTING REVERSIBLE CONTRACEPTIVES LARCS In 2014 the Academy of Pediatrics recommended that long-acting
Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013
 Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013 Topics Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccines Pap smears Colposcopy Contraception Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Can I get pregnant? Miscarriage Abnormal Uterine
Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013 Topics Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccines Pap smears Colposcopy Contraception Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Can I get pregnant? Miscarriage Abnormal Uterine
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Menstruation
 Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
PILLS & RING INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS ON COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION INCLUDING BIRTH CONTROL PILLS & NUVA RING
 PILLS & RING INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS ON COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION INCLUDING BIRTH CONTROL PILLS & NUVA RING What is combined hormonal contraception? Birth control which contains two hormones
PILLS & RING INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS ON COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION INCLUDING BIRTH CONTROL PILLS & NUVA RING What is combined hormonal contraception? Birth control which contains two hormones
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
 Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding)
 Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
The menopausal transition usually has three parts:
 The menopausal transition usually has three parts: Perimenopause begins several years before a woman s last menstrual period, when the ovaries gradually produce less estrogen. In the last 1-2 years of
The menopausal transition usually has three parts: Perimenopause begins several years before a woman s last menstrual period, when the ovaries gradually produce less estrogen. In the last 1-2 years of
Now that your Doctor has prescribed Livial for you
 Now that your Doctor has prescribed Livial for you This educational brochure is only for use by patients prescribed LIVIAL The Menopause The term menopause refers to the very last menstrual period a woman
Now that your Doctor has prescribed Livial for you This educational brochure is only for use by patients prescribed LIVIAL The Menopause The term menopause refers to the very last menstrual period a woman
Intrauterine Device (IUD) THE FACTS
 Intrauterine Device (IUD) Quick Facts Effectiveness in Preventing Pregnancy: Use: Of 100 women using IUDs for a year, about one may become pregnant. IUDs are better at preventing pregnancy than condoms,
Intrauterine Device (IUD) Quick Facts Effectiveness in Preventing Pregnancy: Use: Of 100 women using IUDs for a year, about one may become pregnant. IUDs are better at preventing pregnancy than condoms,
There are four areas where you can expect changes to occur as your hormone therapy progresses.
 You are considering taking testosterone, so you should learn about some of the risks, expectations, long term considerations, and medications associated with medical transition. If is very important to
You are considering taking testosterone, so you should learn about some of the risks, expectations, long term considerations, and medications associated with medical transition. If is very important to
Post-Coital Hormonal Contraception Instructions for Use of Plan B, Plan B One-Step, Next Choice One Dose, My Way, Generic Levonorgestrel and Ella
 Post-Coital Hormonal Contraception Instructions for Use of Plan B, Plan B One-Step, Next Choice One Dose, My Way, Generic Levonorgestrel and Ella Several options for emergency birth control exist for women
Post-Coital Hormonal Contraception Instructions for Use of Plan B, Plan B One-Step, Next Choice One Dose, My Way, Generic Levonorgestrel and Ella Several options for emergency birth control exist for women
Please read these instructions carefully before using Poise* Bladder Supports
 For the Temporary Management of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Please read these instructions carefully before using Poise* Bladder Supports 500000023088 For the Temporary Management
For the Temporary Management of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Please read these instructions carefully before using Poise* Bladder Supports 500000023088 For the Temporary Management
Let s Learn the Basics about Cervical Cancer
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health October-December 2014 Let s Learn the Basics about Cervical Cancer What is cancer? The body is made up of millions and millions of living cells.
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health October-December 2014 Let s Learn the Basics about Cervical Cancer What is cancer? The body is made up of millions and millions of living cells.
What Athletic Trainers Need to Know About Gynecology
 What Athletic Trainers Need to Know About Gynecology Mona M. Shangold,, M.D. Director The Center for Women s Health and Sports Gynecology Philadelphia, PA Main Topics Normal development and function Effects
What Athletic Trainers Need to Know About Gynecology Mona M. Shangold,, M.D. Director The Center for Women s Health and Sports Gynecology Philadelphia, PA Main Topics Normal development and function Effects
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary
 X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer
 Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer Cervical Ovarian Uterine Vaginal Vulvar Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer Cervical Ovarian Uterine Vaginal Vulvar Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps
 Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps With today s medical advances the outlook for successful treatment of fibroids and polyps has never been better. You don t have to live with
Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps With today s medical advances the outlook for successful treatment of fibroids and polyps has never been better. You don t have to live with
Form ### Transgender Hormone Therapy - Estrogen Informed Consent SAMPLE
 What are the different medications that can help to feminize me? Estrogen - Different types of the hormone estrogen can help you appear more feminine. Estrogen is the female sex hormone. Androgen blocker
What are the different medications that can help to feminize me? Estrogen - Different types of the hormone estrogen can help you appear more feminine. Estrogen is the female sex hormone. Androgen blocker
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy
 What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
Endometriosis: An Overview
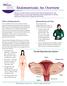 Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Where to get services How to use this brochure Questions to ask These choices don t work These choices might work Emergency Contraceptive Pills
 Where to get services How to use this brochure Questions to ask These choices don t work These choices might work Emergency Contraceptive Pills Abstinence Birth Control Pills Cervical Barriers Condoms
Where to get services How to use this brochure Questions to ask These choices don t work These choices might work Emergency Contraceptive Pills Abstinence Birth Control Pills Cervical Barriers Condoms
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects as many as 5 10% of women. PCOS has three key features: 1) high levels of hormones called androgens; 2) irregular menstrual
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects as many as 5 10% of women. PCOS has three key features: 1) high levels of hormones called androgens; 2) irregular menstrual
Title: Affordable Low Rate Health Insurance. Word Count: 329
 抮 抮 Title: Affordable Low Rate Health Insurance Word Count: 329 Summary: The easiest way to obtain affordable, low cost health insurance is to purchase a low cost health insurance plan through your employer.
抮 抮 Title: Affordable Low Rate Health Insurance Word Count: 329 Summary: The easiest way to obtain affordable, low cost health insurance is to purchase a low cost health insurance plan through your employer.
the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD your guide to
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put
Chlamydia THE FACTS. How do people get Chlamydia?
 What is Chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection that is sexually transmitted and often causes no symptoms. If not treated, chlamydia can damage reproductive organs and make it difficult for
What is Chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection that is sexually transmitted and often causes no symptoms. If not treated, chlamydia can damage reproductive organs and make it difficult for
Chlamydia. Looking after your sexual health
 Chlamydia Looking after your sexual health 2 Chlamydia Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is very easy to treat and cure. Up to one in 10 sexually active young
Chlamydia Looking after your sexual health 2 Chlamydia Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is very easy to treat and cure. Up to one in 10 sexually active young
POINCIANA INTERNAL MEDICINE PA. Patient Name: Social Security Number: Date of Birth: / / Sex: M/F (Circle One) Married/Single/Divorced/Widow Address:
 Patient Name: Social Security Number: Date of Birth: / / Sex: M/F (Circle One) Married/Single/Divorced/Widow Address: (Street) (City/State/Zip) Home Phone: ( ) E Mail Address: Would you be interested in
Patient Name: Social Security Number: Date of Birth: / / Sex: M/F (Circle One) Married/Single/Divorced/Widow Address: (Street) (City/State/Zip) Home Phone: ( ) E Mail Address: Would you be interested in
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Laparoscopic Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy
 Laparoscopic Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy What is a? This is a surgery where your doctor uses a thin, lighted camera and small surgical tool placed through a small (1/2 inch) incision usually in the
Laparoscopic Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy What is a? This is a surgery where your doctor uses a thin, lighted camera and small surgical tool placed through a small (1/2 inch) incision usually in the
IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. your guide to
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD he the the the 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD he the the the 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your
Hysterectomy Vaginal hysterectomy Abdominal hysterectomy
 Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgery to remove a woman s uterus. The uterus is one of the organs of the female reproductive system and is about the size of a closed hand. You can no longer have children
Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgery to remove a woman s uterus. The uterus is one of the organs of the female reproductive system and is about the size of a closed hand. You can no longer have children
MULTILOAD cu 250 / cu 375
 MULTILOAD cu 250 / cu 375 CE 0336 Read all of this leaflet carefully before you decide to have Multiload Radiopaque inserted. This leaflet provides information that may help you in your decision to start
MULTILOAD cu 250 / cu 375 CE 0336 Read all of this leaflet carefully before you decide to have Multiload Radiopaque inserted. This leaflet provides information that may help you in your decision to start
Safe & Unsafe. abortion
 Safe & Unsafe Facts About abortion WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN UNSAFE AND SAFE ABORTION? What is unsafe abortion? Unsafe abortion is a procedure for terminating an unplanned pregnancy either by a person
Safe & Unsafe Facts About abortion WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN UNSAFE AND SAFE ABORTION? What is unsafe abortion? Unsafe abortion is a procedure for terminating an unplanned pregnancy either by a person
MEDICATION GUIDE. SORIATANE (sor-rye-uh-tane) (acitretin) Capsules
 Page 30 Please print: Patient name and address: Telephone: I have fully explained to the patient,, the nature and purpose of the treatment described above and the risks to females of childbearing potential.
Page 30 Please print: Patient name and address: Telephone: I have fully explained to the patient,, the nature and purpose of the treatment described above and the risks to females of childbearing potential.
Neuroendocrine Evaluation
 Neuroendocrine Evaluation When women have health concerns they usually prefer to discuss them with another woman. Dr. Vliet is a national expert on hormone-related problems and specializes in neuroendocrine
Neuroendocrine Evaluation When women have health concerns they usually prefer to discuss them with another woman. Dr. Vliet is a national expert on hormone-related problems and specializes in neuroendocrine
Birth Control M E T H O D S
 Birth Control M E T H O D S Adapted and reproduced with permission of Public Health, Region of Peel. Table of Contents z Introduction... 2 z Anatomy... 3 z Effectiveness... 4 z Hormonal Methods of Birth
Birth Control M E T H O D S Adapted and reproduced with permission of Public Health, Region of Peel. Table of Contents z Introduction... 2 z Anatomy... 3 z Effectiveness... 4 z Hormonal Methods of Birth
THE WELL. Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices WOMAN CENTRE
 THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
NovaSure: A Procedure for Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
 NovaSure: A Procedure for Heavy Menstrual Bleeding The one-time, five-minute procedure Over a million women 1 have been treated with NovaSure. NovaSure Endometrial Ablation (EA) is the simple, one-time,
NovaSure: A Procedure for Heavy Menstrual Bleeding The one-time, five-minute procedure Over a million women 1 have been treated with NovaSure. NovaSure Endometrial Ablation (EA) is the simple, one-time,
Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis. Looking after your sexual health
 Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Looking after your sexual health 2 Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Thrush is an infection that is caused by a yeast fungus. It is not a sexually transmitted infection but
Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Looking after your sexual health 2 Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Thrush is an infection that is caused by a yeast fungus. It is not a sexually transmitted infection but
progestog progestogen stogen-only pill progestogen progestogen-only pill he progestogen-only pill progestogen-onl progestogen-o the progestogenonly
 your guide to the progestogenonly pill Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you the progestogen rogestogen-only the progestogen-only pill progestogen-only pill stogen-only progestoge
your guide to the progestogenonly pill Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you the progestogen rogestogen-only the progestogen-only pill progestogen-only pill stogen-only progestoge
injections injections injections injections injections injection injections injections injections tions njections injections injections injections
 your guide to contraceptive Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you ions ections injection njections injection tions 2 Contraceptive Contraceptive contain a progestogen hormone
your guide to contraceptive Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you ions ections injection njections injection tions 2 Contraceptive Contraceptive contain a progestogen hormone
Saint Mary s Hospital. Hysterectomy. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Hysterectomy Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What is a hysterectomy? 4 Why is a hysterectomy necessary? 4 How common is it? 7 Things to consider before having a hysterectomy
Saint Mary s Hospital Hysterectomy Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What is a hysterectomy? 4 Why is a hysterectomy necessary? 4 How common is it? 7 Things to consider before having a hysterectomy
This is Jaydess. Patient Information. What is Jaydess? How does Jaydess work?
 , Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
, Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD the IUD. the IUD. the the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD.
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you I the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your uterus (womb).
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you I the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your uterus (womb).
Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place.
 What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
Hysterectomy. The time to take care of yourself
 Hysterectomy The time to take care of yourself The time to take care of yourself Women spend a lot of time taking care of others spouses, children, parents. We often overlook our own needs. But when our
Hysterectomy The time to take care of yourself The time to take care of yourself Women spend a lot of time taking care of others spouses, children, parents. We often overlook our own needs. But when our
Hormone Therapy with Tamoxifen
 What is hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer? Many breast cancers need estrogen and/or progesterone (female hormones), to grow and spread. When breast cancer is found, the cancer is tested for two proteins,
What is hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer? Many breast cancers need estrogen and/or progesterone (female hormones), to grow and spread. When breast cancer is found, the cancer is tested for two proteins,
The challenge of herpes
 The challenge of herpes Herpes is a common and personally challenging disease Herpes is very common. One out of four adults has genital herpes. When people first hear that they are infected, many become
The challenge of herpes Herpes is a common and personally challenging disease Herpes is very common. One out of four adults has genital herpes. When people first hear that they are infected, many become
Problems in Early Pregnancy
 Problems in Early Pregnancy Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered This information answers queries about issues that may arise in early pregnancy. Not all of these issues will apply to you. It provides
Problems in Early Pregnancy Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered This information answers queries about issues that may arise in early pregnancy. Not all of these issues will apply to you. It provides
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
LIPPES LOOP TRADEMARK. your intrauterine contraceptive
 LIPPES LOOP TRADEMARK your intrauterine contraceptive LIPPES LOOP Patient Information This brochure provides information on the use of In trauterine Contraceptive Devices (lud s). There are other birth
LIPPES LOOP TRADEMARK your intrauterine contraceptive LIPPES LOOP Patient Information This brochure provides information on the use of In trauterine Contraceptive Devices (lud s). There are other birth
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
MEDICAL HISTORY AND SCREENING FORM
 MEDICAL HISTORY AND SCREENING FORM The purpose of preventive exams is to screen for potential health problems and provide education to promote optimal health. It is best practice for chronic health problems
MEDICAL HISTORY AND SCREENING FORM The purpose of preventive exams is to screen for potential health problems and provide education to promote optimal health. It is best practice for chronic health problems
What are the differences between fibroid and ovarian cyst?
 DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
Family Planning for Women and Couples following Fistula Repair
 Family Planning for Women and Couples following Fistula Repair Fistula Care at EngenderHealth 440 Ninth Avenue, 13th Floor New York, NY, USA 10001 Tel: 212-561-8000 E-mail: fistulacare@engenderhealth.org
Family Planning for Women and Couples following Fistula Repair Fistula Care at EngenderHealth 440 Ninth Avenue, 13th Floor New York, NY, USA 10001 Tel: 212-561-8000 E-mail: fistulacare@engenderhealth.org
Disorders of the Vulva
 Disorders of the Vulva WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Certain health problems can affect the vulva (the outer part of the female genital area). Some problems are minor. Others
Disorders of the Vulva WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Certain health problems can affect the vulva (the outer part of the female genital area). Some problems are minor. Others
Why would you need a hysterectomy?
 Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
 Any further questions? Please contact the matron for Women s Health on 020 7288 5161 (answerphone) Monday - Thursday 9am - 5pm. For more information: Royal College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Recovering
Any further questions? Please contact the matron for Women s Health on 020 7288 5161 (answerphone) Monday - Thursday 9am - 5pm. For more information: Royal College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Recovering
contraception contraception contraception contracepti contraception contraception contraception aception contraception contraception contraception
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of that is best for you raception aception contracept contracepti contracep contracepti Your guide to This leaflet shows the available contraceptive methods,
your guide to Helping you choose the method of that is best for you raception aception contracept contracepti contracep contracepti Your guide to This leaflet shows the available contraceptive methods,
PROVERA (medroxyprogesterone acetate) Product Monograph Page 34 of 38
 PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION PR PROVERA* (medroxyprogesterone acetate) This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when PROVERA was approved for sale in Canada and is designed
PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION PR PROVERA* (medroxyprogesterone acetate) This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when PROVERA was approved for sale in Canada and is designed
Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD, Steve Livingston, MD, Lisa Townshend, ANP. Primary Care Provider:
 Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD, Steve Livingston, MD, Lisa Townshend, ANP Primary Care Provider: If you are considering hepatitis C treatment, please read this treatment
Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD, Steve Livingston, MD, Lisa Townshend, ANP Primary Care Provider: If you are considering hepatitis C treatment, please read this treatment
You and your doctor will talk about your condition and the treatment that is best for you.
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your surgery. If
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your surgery. If
Cancer Facts for Women
 2006, American Cancer Society, Inc. No.200700-Rev.03/08 The American Cancer Society is the nationwide community-based voluntary health organization dedicated to eliminating cancer as a major health problem
2006, American Cancer Society, Inc. No.200700-Rev.03/08 The American Cancer Society is the nationwide community-based voluntary health organization dedicated to eliminating cancer as a major health problem
