Gynaecology FAQ s. Correspondence address: 204 Fulham Road London SW10 9PJ Tel:
|
|
|
- Philomena Price
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gynaecology FAQ s Why is the cervical screening test important? Cervical cancer is not uncommon. In recent years the number of cases has fallen due to cervical screening tests. However, there are still over 2,000 new cases of cervical cancer diagnosed each year in the UK. Most of these occur in women who have never had a screening test, or who have not had one for many years. Cervical cancer can be prevented if you have regular screening tests What is cervical screening? Women are routinely invited to have regular cervical screening tests (smear tests) depending on their age this could be every 3 years in the UK on the NHS. The tests are done to prevent cervical cancer (and not to diagnose cancer as some people wrongly think). During each test some cells are removed from the cervix with a plastic brush. The cells are examined under a microscope to look for early changes that, if ignored and not treated, could develop into cancer of the cervix. If abnormal cells are found, these can be treated (removed). Cervical cytology smear results are reported as: Normal. Inadequate. Abnormal About 9 in 10 routine cervical screening tests results are normal. If your result is normal you should continue to attend for regular smear test, depending on your age and previous result history. A normal result means you have a very low chance of developing cervical cancer. It is not a guarantee that cervical cancer will not occur. I have never had sex - Do I need a cervical screening test? The test is recommended for all women - even if you have never had sex. However, the risk of getting cervical cancer is very low if you have never had sex. This is because the main cause of cervical cancer is a past infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a common virus that is normally passed on by having sex. There are other, less common types of cervical cancer, not caused by HPV, so women who have never had sex are still at risk When is the best time in the menstrual cycle to have cervical screening? Mid cycle (14 days after your last period) is the best time because a clearer background to the sample can be gained around this time. This is because the mucus plug is at its thinnest so the sample is less likely to contain mucus. Also, lining is at its thickest so the sample taken contains a full range of cells.
2 Can I have my cervical screening test when I am having my period? It is best to have your cervical screening test when you are not having your period. Ideally the test is best performed mid-cycle. With the new technology you can have the test done at any time but, if you are bleeding heavily, there may be too much blood and mucus on the brush, meaning too few cells from the cervix are removed. Can I have cervical screening when I am pregnant? If you are due your routine cervical screening test and you are pregnant, this should be deferred until after your baby is born. Usually it is advisable to wait until you are at least 6 weeks postnatal. This gives the cervix a chance to recover from pregnancy and childbirth. Tests performed earlier are more likely to be inadequate. I have had a hysterectomy - do I need to have a cervical screening test? This depends on the type of hysterectomy, and why it was done. Your doctor will advise you on this. In general, if you have a total hysterectomy (removal of the uterus and cervix) for a reason not due to cancer, then you no longer need cervical screening tests. Some types of hysterectomy leave the cervix (called subtotal hysterectomy), and some are done to remove a cancer. In these situations, a test of the cells of the remaining cervix, or of the top of the vagina (called the vault), may still be advised. What is HPV? Human papilloma viruses are known as HPV. They can affect the skin and the moist membranes that line parts of the body, including the cervix. There are more than 100 different types of human papilloma virus and each type has a different number. Some types of HPV can increase the risk of developing cervical cancer, particularly types 16, 18, 31, 33 and 45. They are called high risk types. Almost all women with cervical cancer have at least one of these types of HPV in the cells of their cervix. Of the different types of HPV, types 16 and 18 cause about 7 out of 10 (70%) cancers of the cervix. The other types cause most of the remaining 30% of cervical cancers. Do remember that most women with high risk HPV don t develop cervical cancer. Remember that regular cervical screening will pick up abnormal cervical cells before they become cancerous. Our gynecologists are able to provide HPV tests here at the centre. Do you offer the HPV vaccination? Yes we do - The HPV vaccine is most effective if it's given a few years before a girl becomes sexually active, so it's given to girls between the ages of 12 and 13. Gardasil - which provides protection against cervical cancer and genital warts The Gardasil vaccine provides complete protection against all the types of HPV that are known to cause cervical cancer. If you have been vaccinated for HPV you will still need to attend your future cervical screening appointments. When is the best time for an Early Pregnancy Scan? An Early Pregnancy Scan is the very first pregnancy scan between 6 weeks and 11 weeks to confirm your pregnancy is healthy, ongoing and to calculate the date when your baby is due. The sonographer or consultant will first try to scan you through your tummy (trans abdominally). If the image is unclear the operator will perform an internally scan (trans vaginally). Before 6 weeks is it not possible to always see any signs of pregnancy with current ultrasound technology and at this time we are able to offer a blood test to measure the hcg hormone level in your blood to test for positive pregnancies and indications of how many weeks pregnant you may be.
3 I have had a miscarriage do I need to see a gynaecologist? Any woman who has suffered a single miscarriage has an 80% chance of her next pregnancy being successful. Other than sympathy and reassurance, no clinical investigations or treatments are usually required. If, having suffered one miscarriage, the second pregnancy also ends in miscarriage then this woman has around 70% chance of her next pregnancy being successful. If the woman is even more unfortunate and suffers three consecutive miscarriages, she has around a 60% chance of her next pregnancy being successful. Therefore two or three consecutive miscarriages occur more frequently than chance alone, suggesting that in a proportion of these woman there may be an underlying cause, warranting investigation and treatment. Recurrent miscarriage is defined by the consecutive loss of two or more pregnancies with the same partner. What is a termination of pregnancy? Termination of pregnancy is a medical process of ending a pregnancy using pharmacological or surgical means. Having a termination is a personal choice and there can be many medical and social reasons for having one. In Great Britain (England, Scotland and Wales) it's legal for terminations to be carried out up to 24 weeks of pregnancy. However, in exceptional circumstances there isn't a strict upper limit. For example, you may be able to have an abortion after 24 weeks if your life is under serious threat, or if your baby will be born with a severe disability. Most women, however, have abortions before 12 weeks of pregnancy. Please speak to our gynaecologists at the centre to discuss pregnancy and termination options. Do you offer the emergency contraceptive pill? Our gynecologists offer contraceptives advice and can provide a whole range or contraception including the emergency contraceptive pill. The effectiveness of the emergency contraceptive pill decreases over time therefore speed in taking the contraceptive is of upmost importance. If it is taken within 24 hours of having unprotected sex, it can prevent 95% of pregnancies. Most women can use the emergency contraceptive pill. Our gynecologists are able to discuss emergency contraceptive option with you at the centre. How do I know which is the best coil for me? You would need to speak to your doctor and discus with them your reproductive history to work out weather a copper or hormone coil would best suit you Mirena Coil (levonorgestrel) Mirena is a small plastic T-shaped contraceptive device that contains the active ingredient levonorgestrel. It is an intrauterine system (IUS) that is inserted into the womb by a Dr. Once inserted it steadily releases levonorgestrel into the womb. Levonorgestrel is a synthetic form of the female sex hormone, progesterone. What is it used for? Contraception. Heavy or prolonged menstrual periods with no known cause. Protection from overgrowth of the womb lining oestrogen-only hormone replacement therapy (HRT) following the menopause. When can it be inserted? To provide contraception or treat heavy periods Mirena should ideally be inserted in the first seven days of your menstrual cycle (day one is the first day of your period). This will provide immediate protection against pregnancy. Mirena can be inserted at other times in your cycle if your doctor is sure you are not pregnant, but you will need to use an extra method of contraception (eg condoms) for the first seven days after it is inserted. If you have had a baby, Mirena should not be inserted until six weeks after the birth.
4 How long does it work for? The Mirena IUS provides protection from pregnancy for five years and must be removed by your doctor after this time if you are using it for contraception or heavy periods. (It can be removed earlier than this if required.) If you still want to use Mirena after five years it can be removed and replaced with a new one in the same visit. You won't need to use any extra contraception. If you don't want to keep using Mirena, but don't want to get pregnant, Mirena should be removed in the first few days of starting your period. If it is going to be removed at any other time in your cycle, it is important to use condoms to prevent pregnancy starting a week before Mirena is removed. This is because sperm can live for this long inside the vagina. If you have had Mirena fitted as part of your HRT you should have it removed after four years, because there are only limited data on its womb protective effect after this time. How is the Copper Coil ( IUD) different to the Mirena Coil? An intrauterine device (IUD) is a small, T-shaped contraceptive device made from plastic and copper that fits inside the womb (uterus). It used to be called a coil. It's a long-lasting and reversible method of contraception but it is not a barrier method. This means that an IUD can prevent pregnancy but won't stop you getting sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It's different to an intrauterine system (IUS) or mirena) which releases the hormone progestogen into the body. An IUD stops sperm from reaching the egg. It does this by releasing copper, which changes the make-up of the fluids in the womb and fallopian tubes. These changes prevent sperm from fertilising eggs. IUDs may also stop fertilised eggs from travelling along the fallopian tubes and implanting in the womb. Can I have my coil removed and have a new one inserted at the same time? Yes you can just mention this request when you make your appointment to see the gynaecologist. How long will my Mirena coil take to settle down after it has been inserted? The coil will take three to six months to settle down, if you required further advice please book an appointment to see your gynaecologist. I am experiencing heavy periods what should I do? Many women are troubled by heavy periods (menorrhagia), and some by bleeding between periods. In young women these symptoms are not always investigated but tend to be treated symptomatically i.e. by taking the oral contraceptive pill. In some cases bleeding will be due to an underlying problem, and an ultrasound scan may be performed to exclude or diagnose some of these conditions. Why could I be bleeding between periods? Bleeding between periods is often thought to be more likely to be associated with there being a underlying problem than heavy bleeding at the time of an expected period. Typically a polyp may be present on the cavity of the uterus, and this may be demonstrated by an ultrasound scan. However abnormalities of the cervix or infection may also be associated with this symptom and should be excluded. I suffer from absent or irregular periods what could be the reason? There are several reasons why periods may stop or become irregular. Many can be clarified on the basis of blood tests to measure the levels of circulating hormones. One condition called polycystic ovaries can be demonstrated using vaginal ultrasonography. This is one of the most common causes of irregular and absent periods.
5 How would I know if I have endometriosis, what are the symptoms? Endometriosis is found in approximately 3-5% of women of child-bearing age. It is associated with infertility, since it occurs ten times more frequently in infertile women. Painful and heavier periods are the classic symptom. Typically the pain starts with the onset but does not necessarily last for the duration of the period. Some experience additional pelvic pain unrelated to their periods and this may be due to adhesions (scar tissue) that has formed due to endometriosis, or may be due to cysts of endometriosis. Painful intercourse is another classic symptom of endometriosis. What are fibroids? Fibroids are muscular tumors that grow in the wall of the uterus (womb). Fibroids are almost always benign (not cancerous). Fibroids can grow as a single tumor, or there can be many of them in the uterus. They can be as small as an apple seed or as big as a grapefruit. In unusual cases they can become very large. Fibroids are most common in women in their 40s and early 50s. Not all women with fibroids have symptoms. Some have pain and heavy menstrual bleeding. Fibroids also can put pressure on the bladder, causing frequent urination, or the rectum, causing rectal pressure. Should the fibroids get very large, they can cause the abdomen (tummy) to enlarge, making a woman look pregnant What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)? PCOS is a complex condition that effects the ovaries. There are characteristic changes in the appearance of the ovaries on an ultrasound scan: The ovaries are in generally a bit biger and polycystic, with many little follicles scattered under the surface of the ovary and almost non in the middle of the ovary. These follicles are all small and immature and generally do not grow to maturity and ovulate. So women with PCOS are less fertile and don t have regular periods. Other features of the condition are excess weight and body hair. The condition is relatively common. It affects up to 10per cent of all women between the ages of 15 and 50. In the general population, around 25 per cent of women will have PCOS but most have no symptoms or signs of PCOS and have no health problems. What are the symptoms of PCOS? - Infrequent periods - Increased facial and body hair - Acne - Infertility - Overweight and obesity - Miscarriage How is PCOS diagnosed? PCOS can be diagnosed through a blood test and an ultrasound examination performed by a specialist. What causes PCOS? It s not certain if women are born with this condition, PCOS seems to run in families. This means that something that includes the condition is inheritable, and therefore influenced by one or more genes. I have been experiencing pelvic pain what could it be? Pelvic pain is a common symptom in women of all ages. In some cases no specific cause can be found, but most find that being reassured that there is no serious underlying problem can be helpful. Taking a full history and a conventional gynaecological examination is an important part of the assessment of pelvic pain, with the addition of an ultrasound scan proving particularly helpful. A normal ultrasound scan can mean that it is unlikely that there is any significant underlying problem causing the pain.
6 How would I know if I had a sexually transmitted Infection (STI)? Some of the symptoms of STI s include blisters, warts, lesions, painful urination, itching, swelling, and unnatural bleeding or discharge. However, many STIs have no obvious symptoms, and eight out of ten people who have an STI s are currently unaware of their infection. If you have had any unprotected sexual contact, you should get tested. Many STI,s may remain dormant and undetectable for some time, so you could test negative for STIs and still be infected. This is why clinicians recommend that woman who have been sexually active in the past get tested annually, regardless of their current sexual activity. I have been experiencing bleeding after intercourse is this normal and what can I do? This is not a normal, so you would need to book an appointment with one of our gynaecologist and they will take it from there. I have been experiencing some discharge from my vagina for the pass few weeks what should I do? You should make an appointment to see one of our doctors for a health check to rule out any infections What is the Menopause? Menopause is the time in a woman's life when her periods stop and she can no longer become pregnant. It is a normal change in a woman's body. A woman will know she has reached menopause when she has not had a period for 12 months in a row ( when there are no other causes, such as pregnancy or illness, for this change). Most women experience menopause from 40 to 58 years of age, with a median age of 51.4 years. You will feel better by learning all you can about menopause and talking with your doctor about your health and your symptoms. If your symptoms are causing you discomfort or concern, your doctor can teach you about available therapeutic options and help you to make informed choices. How will I know I have started menopause? Menopause affects every woman differently. Your only symptom may be your period stopping or you may have other symptoms that include: Change in pattern of periods (They can be shorter or longer, lighter or heavier, or there may be more or less time between periods.) Hot flushes (sometimes called hot flashes) Night sweats (sometimes followed by a chill) Trouble sleeping through the night Vaginal dryness Urinary problems such as leaking, burning or pain when urinating, or leaking when sneezing, coughing, or laughing. Less interest in sexual intercourse Mood swings Trouble focusing or forgetfulness Hair loss or thinning on your head, or more hair growth on your face Changes in texture of your skin and nails. I thought I had started the menopause but now I have vaginal bleeding what could this be? A woman is considered to have started the menopause when a year has passed since her last period. Any bleeding after this time is always considered to be potentially abnormal. In fact only a small proportion of women who bleed after the menopause have anything significantly wrong but this bleeding should be investigated thoroughly by a Dr to rule out any abnormalities.
7 What is urinary incontinence? Many women experience a small amount of urine leakage on an occasional basis, and it causes them little bother and they able to continue with their lives as normal yet for a significant number of women, urinary incontinence may be serious enough to involve having to change their clothes and to avoid performing certain tasks or exercises. For these women, advice from a health professional is appropriate. The commonest is called stress urinary incontinence (SUI). This is when the bladder sphincter just gives way under pressure and a small amount of urine escapes on straining, for example when coughing, laughing, sneezing or doing physical exercise. Stress incontinence is usually the result of weakening of the muscles in the pelvic floor that surround the bladder. This often happens during pregnancy, following childbirth or after the menopause. What does the well women s health screen contain? It contains a full discussion & history check, symptom check, blood tests, a smear test, swab tests to check for infection and a body examination from your doctor such as basic breast & abdomen check to rule out any abnormalities Gynaecology Scanning: Does it matter if I am having my period when I come to have my scan? No - unless the period is very heavy it makes no difference to the scan I need an abdominal scan what will happen? For an abdominal scan you will lie on your back on a couch. The sonographer will apply gel to the skin on your abdomen over the area to be examined. The gel allows the sensor to slide easily over the skin and helps to produce clear pictures. I need to have a transvaginal scan what does this mean? A TV scan is used to examine the reproductive organs (womb, fallopian tubes and ovaries) in women. You usually need to lie on your back on a couch with your feet up in stirrups. A lubricated probe (the size of a tampon) is inserted two or three inches into your vagina and most women tolerate this procedure very well.
Birth Control Options
 1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. your guide to
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD he the the the 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD he the the the 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your
IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD the IUD. the IUD. the the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD.
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you I the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your uterus (womb).
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you I the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your uterus (womb).
THE WELL. Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices WOMAN CENTRE
 THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD your guide to
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put
Copper intra-uterine device (IUD)
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Copper intra-uterine device (IUD) Page What is an inter-uterine device? 3 How does it work? 4 Would an IUD be suitable for me? 5 Are there any risks or complications?
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Copper intra-uterine device (IUD) Page What is an inter-uterine device? 3 How does it work? 4 Would an IUD be suitable for me? 5 Are there any risks or complications?
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion.
 Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion. After the abortion I started re-thinking my birth control method. I am looking
Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion. After the abortion I started re-thinking my birth control method. I am looking
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Heavy menstrual bleeding and what you can do about it!
 Heavy menstrual bleeding and what you can do about it! The intrauterine system as an alternative to hysterectomy. What is heavy menstrual bleeding? Do I have it? A woman s menstrual periods are considered
Heavy menstrual bleeding and what you can do about it! The intrauterine system as an alternative to hysterectomy. What is heavy menstrual bleeding? Do I have it? A woman s menstrual periods are considered
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know
 Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Intrauterine Device (IUD) THE FACTS
 Intrauterine Device (IUD) Quick Facts Effectiveness in Preventing Pregnancy: Use: Of 100 women using IUDs for a year, about one may become pregnant. IUDs are better at preventing pregnancy than condoms,
Intrauterine Device (IUD) Quick Facts Effectiveness in Preventing Pregnancy: Use: Of 100 women using IUDs for a year, about one may become pregnant. IUDs are better at preventing pregnancy than condoms,
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding)
 Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
Summa Health System. A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy
 Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
A Guide to Hysteroscopy. Patient Education
 A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013
 Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013 Topics Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccines Pap smears Colposcopy Contraception Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Can I get pregnant? Miscarriage Abnormal Uterine
Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013 Topics Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccines Pap smears Colposcopy Contraception Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Can I get pregnant? Miscarriage Abnormal Uterine
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
progestog progestogen stogen-only pill progestogen progestogen-only pill he progestogen-only pill progestogen-onl progestogen-o the progestogenonly
 your guide to the progestogenonly pill Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you the progestogen rogestogen-only the progestogen-only pill progestogen-only pill stogen-only progestoge
your guide to the progestogenonly pill Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you the progestogen rogestogen-only the progestogen-only pill progestogen-only pill stogen-only progestoge
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
Although the flush is the classic menopausal symptom that we ve
 24 MENOPAUSE: ANSWERS AT YOUR FINGERTIPS HOW LONG DO SYMPTOMS LAST? The duration of early symptoms is very variable from a few months to many years and the severity varies between individuals. On average,
24 MENOPAUSE: ANSWERS AT YOUR FINGERTIPS HOW LONG DO SYMPTOMS LAST? The duration of early symptoms is very variable from a few months to many years and the severity varies between individuals. On average,
What are the differences between fibroid and ovarian cyst?
 DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
GLOSSARY. A Abstinence: having no vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It is the only method that is 100% effective in preventing pregnancy and STI s.
 WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
Cervical Cancer. What you should know. making cancer less frightening by enlightening
 Cervical Cancer What you should know making cancer less frightening by enlightening cervical cancer the facts Around 325 women are diagnosed with cervical cancer in Ireland each year It is the most common
Cervical Cancer What you should know making cancer less frightening by enlightening cervical cancer the facts Around 325 women are diagnosed with cervical cancer in Ireland each year It is the most common
Ovarian Cystectomy / Oophorectomy
 Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Hysterectomy. What is a hysterectomy? Why is hysterectomy done? Are there alternatives to hysterectomy?
 ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
The main surgical options for treating early stage cervical cancer are:
 INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
CERVICAL CANCER What every woman should know What is a cervix?
 CERVICAL CANCER What every woman should know What is a cervix? The cervix is the entrance to the womb from the vagina. It is the narrow, lower part of the uterus that is the passageway connecting the uterus
CERVICAL CANCER What every woman should know What is a cervix? The cervix is the entrance to the womb from the vagina. It is the narrow, lower part of the uterus that is the passageway connecting the uterus
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer
 Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
HPV is very common and usually clears up on its own
 What is HPV? All cervical cancers are linked to a very common virus called the human papillomavirus or HPV. HPV usually doesn t cause any harm and most people will be infected with it at some point in
What is HPV? All cervical cancers are linked to a very common virus called the human papillomavirus or HPV. HPV usually doesn t cause any harm and most people will be infected with it at some point in
Saint Mary s Hospital. Ovarian Cysts. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
implant contraceptiv contraceptive contraceptive raceptiv contraceptive implant contraceptive contraceptive ontraceptive implant ontraceptive im
 your guide to the contraceptive implant Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you contra ontraceptive im contraceptive implant mpl ceptive contraceptive contracepti ntraceptive
your guide to the contraceptive implant Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you contra ontraceptive im contraceptive implant mpl ceptive contraceptive contracepti ntraceptive
Information for you Abortion care
 Information for you Abortion care Published in February 2012 This information is for you if you are considering having an abortion. It tells you: how you can access abortion services the care you can expect
Information for you Abortion care Published in February 2012 This information is for you if you are considering having an abortion. It tells you: how you can access abortion services the care you can expect
contraception contraception contraception contracepti contraception contraception contraception aception contraception contraception contraception
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of that is best for you raception aception contracept contracepti contracep contracepti Your guide to This leaflet shows the available contraceptive methods,
your guide to Helping you choose the method of that is best for you raception aception contracept contracepti contracep contracepti Your guide to This leaflet shows the available contraceptive methods,
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
Cervical Cancer. Cervical smear test. The cervix. Dysplasia. Cervical cancer. The female reproductive system
 INFORMATION SHEET Cervical Cancer This information sheet has been written to provide you with information about cervical cancer (cancer of the cervix). The sheet has information about the different types
INFORMATION SHEET Cervical Cancer This information sheet has been written to provide you with information about cervical cancer (cancer of the cervix). The sheet has information about the different types
Saint Mary s Hospital. Hysterectomy. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Hysterectomy Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What is a hysterectomy? 4 Why is a hysterectomy necessary? 4 How common is it? 7 Things to consider before having a hysterectomy
Saint Mary s Hospital Hysterectomy Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What is a hysterectomy? 4 Why is a hysterectomy necessary? 4 How common is it? 7 Things to consider before having a hysterectomy
This is Jaydess. Patient Information. What is Jaydess? How does Jaydess work?
 , Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
, Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A.
 Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A. Craig R. Sweet, M.D. www.dreamababy.com Fertility@DreamABaby.com Excellence, Experience & Ethics Endometriosis Awareness Week/Month Common Questions
Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A. Craig R. Sweet, M.D. www.dreamababy.com Fertility@DreamABaby.com Excellence, Experience & Ethics Endometriosis Awareness Week/Month Common Questions
Out-patient hysteroscopy. Information for patients
 Out-patient hysteroscopy Information for patients Important If there is any chance you may be pregnant please tell a member of the team immediately. We will not be able to perform a hysteroscopy if you
Out-patient hysteroscopy Information for patients Important If there is any chance you may be pregnant please tell a member of the team immediately. We will not be able to perform a hysteroscopy if you
Endometriosis Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women and Children s Group
 Endometriosis Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women and Children s Group This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that
Endometriosis Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women and Children s Group This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that
abortion abortion abortion abortion abortion abortion abortion on abortio abortion ortion abortion abortion abortion abortion abortio
 Abortion Your questions answered abortio bortion ion ortion on abortio 2 Are you pregnant but not sure you want to have the baby? Do you need more information about your pregnancy choices? Unplanned pregnancy
Abortion Your questions answered abortio bortion ion ortion on abortio 2 Are you pregnant but not sure you want to have the baby? Do you need more information about your pregnancy choices? Unplanned pregnancy
Chlamydia. Looking after your sexual health
 Chlamydia Looking after your sexual health 2 Chlamydia Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is very easy to treat and cure. Up to one in 10 sexually active young
Chlamydia Looking after your sexual health 2 Chlamydia Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is very easy to treat and cure. Up to one in 10 sexually active young
LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY
 LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 About this information This leaflet is for you if you have a cyst on one or both ovaries and are considering surgery.
LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 About this information This leaflet is for you if you have a cyst on one or both ovaries and are considering surgery.
injections injections injections injections injections injection injections injections injections tions njections injections injections injections
 your guide to contraceptive Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you ions ections injection njections injection tions 2 Contraceptive Contraceptive contain a progestogen hormone
your guide to contraceptive Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you ions ections injection njections injection tions 2 Contraceptive Contraceptive contain a progestogen hormone
Stay Healthy at Any Age!
 + Stay Healthy at Any Age! February 28, 2013 Kimberly Kelstone A Deaf Health Talk DHCC Partnership with REAP + Overview Introduction Normal healthy processes Diseases specific to women Screening tests
+ Stay Healthy at Any Age! February 28, 2013 Kimberly Kelstone A Deaf Health Talk DHCC Partnership with REAP + Overview Introduction Normal healthy processes Diseases specific to women Screening tests
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
 Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
Cervical cancer screening with the HPV test and the Pap test in women ages 30 and older
 Cervical cancer screening with the HPV test and the Pap test in women ages 30 and older When to get tested and how to make sense of your test results If you are 30 years or older and your Pap test is normal
Cervical cancer screening with the HPV test and the Pap test in women ages 30 and older When to get tested and how to make sense of your test results If you are 30 years or older and your Pap test is normal
The menopausal transition usually has three parts:
 The menopausal transition usually has three parts: Perimenopause begins several years before a woman s last menstrual period, when the ovaries gradually produce less estrogen. In the last 1-2 years of
The menopausal transition usually has three parts: Perimenopause begins several years before a woman s last menstrual period, when the ovaries gradually produce less estrogen. In the last 1-2 years of
The Centre For Women s Reproductive Care HYSTERECTOMY
 The Centre For Women s Reproductive Care Baringa Private Hospital, 31 Mackays Rd Coffs Harbour NSW 2450 Harvey Ward MB ChB, BSc(Med), FCOG (SA), MMed (O&G), FRANZCOG Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Phone:
The Centre For Women s Reproductive Care Baringa Private Hospital, 31 Mackays Rd Coffs Harbour NSW 2450 Harvey Ward MB ChB, BSc(Med), FCOG (SA), MMed (O&G), FRANZCOG Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Phone:
What could endometriosis mean for me?
 Endometriosis: what you need to know Published November 2007 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a very common condition where cells of the lining of the womb (the endometrium) are found elsewhere,
Endometriosis: what you need to know Published November 2007 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a very common condition where cells of the lining of the womb (the endometrium) are found elsewhere,
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Menstruation
 Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Birth Control Methods
 page 1 Birth Control Methods Q: What is the best method of birth control (or contraception)? A: There is no best method of birth control. Each method has its pros and cons. All women and men can have control
page 1 Birth Control Methods Q: What is the best method of birth control (or contraception)? A: There is no best method of birth control. Each method has its pros and cons. All women and men can have control
Bard: Continence Therapy. Stress Urinary Incontinence. Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle.
 Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Becoming knowledgeable about urinary incontinence Uterus Normal Pelvic Anatomy
Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Becoming knowledgeable about urinary incontinence Uterus Normal Pelvic Anatomy
Young Women and Long-Acting Reversible Contraception. Safe, Reliable, and Cost-Effective Birth Control
 ISSUES AT A GLANCE Young Women and Long-Acting Reversible Contraception Safe, Reliable, and Cost-Effective Birth Control In 2012, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) revised
ISSUES AT A GLANCE Young Women and Long-Acting Reversible Contraception Safe, Reliable, and Cost-Effective Birth Control In 2012, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) revised
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME
 POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC)
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Regional Genetic Department Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Information for women with an increased lifetime risk of breast and ovarian cancer What
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Regional Genetic Department Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Information for women with an increased lifetime risk of breast and ovarian cancer What
l family plan natural natural family p natural family planning ily natural family plannin natural fami atural family planning your guide to
 your guide to natural family planning Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you natural family pla al family plannin natural family planning natural family plann atural fam natural
your guide to natural family planning Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you natural family pla al family plannin natural family planning natural family plann atural fam natural
Ask us about LARC. LARC stands for Long Acting Reversible Contraception. Types of LARC are: Contraceptive implant IUS IUD Contraceptive injection
 Ask us about LARC LARC stands for Long Acting Reversible Contraception. Types of LARC are: Contraceptive implant IUS IUD Contraceptive injection visit our website Long Acting Reversible Contraception (LARC)
Ask us about LARC LARC stands for Long Acting Reversible Contraception. Types of LARC are: Contraceptive implant IUS IUD Contraceptive injection visit our website Long Acting Reversible Contraception (LARC)
NHS cervical screening Helping you decide
 NHS cervical screening Helping you decide What is cervical cancer? 2 What causes cervical cancer? 2 What is cervical screening? 3 Cervical screening results 6 What is a colposcopy? 8 What are the benefits
NHS cervical screening Helping you decide What is cervical cancer? 2 What causes cervical cancer? 2 What is cervical screening? 3 Cervical screening results 6 What is a colposcopy? 8 What are the benefits
TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY- MEDICAL
 TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY- MEDICAL Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 8 You have been offered a medical termination of pregnancy using mifepristone. You will have been given some verbal
TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY- MEDICAL Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 8 You have been offered a medical termination of pregnancy using mifepristone. You will have been given some verbal
after you ve had you after you ve had your baby after you ve after you ve had your baby fter you ve had your baby after contraceptive choices
 your guide to contraceptive choices after you ve had your baby Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you after you ve had you ve had your bab after you ve had your baby after
your guide to contraceptive choices after you ve had your baby Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you after you ve had you ve had your bab after you ve had your baby after
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Reproductive Health. Caring for your reproductive health involves:
 Reproductive Health A healthy reproductive system makes the miracle of life possible. Taking good care of your reproductive health is important because problems with this system can make it hard or impossible
Reproductive Health A healthy reproductive system makes the miracle of life possible. Taking good care of your reproductive health is important because problems with this system can make it hard or impossible
Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps
 Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps With today s medical advances the outlook for successful treatment of fibroids and polyps has never been better. You don t have to live with
Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps With today s medical advances the outlook for successful treatment of fibroids and polyps has never been better. You don t have to live with
OUTPATIENT HYSTEROSCOPY SERVICES JASMINE SUITE
 OUTPATIENT HYSTEROSCOPY SERVICES JASMINE SUITE Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 This information is for patients having a hysteroscopy (diagnostic or operative). It explains what
OUTPATIENT HYSTEROSCOPY SERVICES JASMINE SUITE Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 This information is for patients having a hysteroscopy (diagnostic or operative). It explains what
Clinical Interruption of Pregnancy (Medical/Surgical Abortion)
 Clinical Interruption of Pregnancy (Medical/Surgical Abortion) Approximately one fifth of all pregnancies in the United States end in abortion (Ventura et al., 2009). According to the CDC (2011a), there
Clinical Interruption of Pregnancy (Medical/Surgical Abortion) Approximately one fifth of all pregnancies in the United States end in abortion (Ventura et al., 2009). According to the CDC (2011a), there
Leader's Resource. Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms.
 Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Once a woman has had a hysterectomy, she will no longer have menstrual periods and cannot have a child. She no longer needs to use contraception.
 Hysterectomy Summary Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the womb (uterus), with or without the cervix. Hysterectomy is used to treat a number of conditions, including heavy or painful periods, fibroids
Hysterectomy Summary Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the womb (uterus), with or without the cervix. Hysterectomy is used to treat a number of conditions, including heavy or painful periods, fibroids
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
HYDROSALPINX PATIENT INFORMATION
 What is a Hydrosalpinx? Hydrosalpinx, derived from Greek, is a word literally meaning water tube. A Hydrosalpinx is a blocked, dilated, fluid filled-fallopian tube usually caused by a previous tubal infection.
What is a Hydrosalpinx? Hydrosalpinx, derived from Greek, is a word literally meaning water tube. A Hydrosalpinx is a blocked, dilated, fluid filled-fallopian tube usually caused by a previous tubal infection.
All methods of birth control are MUCH SAFER than being pregnant! If 100 women use each method for a year, how many of them get pregnant?
 The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
Hysterectomy. The time to take care of yourself
 Hysterectomy The time to take care of yourself The time to take care of yourself Women spend a lot of time taking care of others spouses, children, parents. We often overlook our own needs. But when our
Hysterectomy The time to take care of yourself The time to take care of yourself Women spend a lot of time taking care of others spouses, children, parents. We often overlook our own needs. But when our
All you need to know about Endometriosis. Nordica Fertility Centre, Lagos, Asaba, Abuja
 All you need to know about Endometriosis October, 2015 About The Author Nordica Lagos Fertility Centre is one of Nigeria's leading centres for world class Assisted Reproductive Services, with comfort centres
All you need to know about Endometriosis October, 2015 About The Author Nordica Lagos Fertility Centre is one of Nigeria's leading centres for world class Assisted Reproductive Services, with comfort centres
MULTILOAD cu 250 / cu 375
 MULTILOAD cu 250 / cu 375 CE 0336 Read all of this leaflet carefully before you decide to have Multiload Radiopaque inserted. This leaflet provides information that may help you in your decision to start
MULTILOAD cu 250 / cu 375 CE 0336 Read all of this leaflet carefully before you decide to have Multiload Radiopaque inserted. This leaflet provides information that may help you in your decision to start
Endometriosis. Information and advice. Page 12 Patient Information
 Endometriosis Information and advice Page 12 Patient Information Contents page What is Endometriosis?... page 3 Symptoms page 5 Treatments.. page 7 Further information and support.. page 9 Contact us page
Endometriosis Information and advice Page 12 Patient Information Contents page What is Endometriosis?... page 3 Symptoms page 5 Treatments.. page 7 Further information and support.. page 9 Contact us page
ency emergency contra-
 your guide to emergency contraception Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you emergency cont gency contrace emergency contraception ency emergency contra- emergen mergency contraception
your guide to emergency contraception Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you emergency cont gency contrace emergency contraception ency emergency contra- emergen mergency contraception
Now that your Doctor has prescribed Livial for you
 Now that your Doctor has prescribed Livial for you This educational brochure is only for use by patients prescribed LIVIAL The Menopause The term menopause refers to the very last menstrual period a woman
Now that your Doctor has prescribed Livial for you This educational brochure is only for use by patients prescribed LIVIAL The Menopause The term menopause refers to the very last menstrual period a woman
Copper-Bearing Intrauterine Device
 CHAPTER 9 Copper-Bearing Intrauterine Device This chapter describes primarily the TCu-380A intrauterine device (for the Levonorgestrel Intrauterine Device, see p. 157). Key Points for Providers and Clients
CHAPTER 9 Copper-Bearing Intrauterine Device This chapter describes primarily the TCu-380A intrauterine device (for the Levonorgestrel Intrauterine Device, see p. 157). Key Points for Providers and Clients
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients
 Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
CONTRACEPTION LONG-ACTING REVERSIBLE CONTRACEPTIVES LARCS
 6 SAND HILL ROAD SUITE 102 FLEMINGTON, NJ 08822 PHONE 908-782-6700 FAX 908-788-5861 CONTRACEPTION LONG-ACTING REVERSIBLE CONTRACEPTIVES LARCS In 2014 the Academy of Pediatrics recommended that long-acting
6 SAND HILL ROAD SUITE 102 FLEMINGTON, NJ 08822 PHONE 908-782-6700 FAX 908-788-5861 CONTRACEPTION LONG-ACTING REVERSIBLE CONTRACEPTIVES LARCS In 2014 the Academy of Pediatrics recommended that long-acting
Let s Learn the Basics about Cervical Cancer
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health October-December 2014 Let s Learn the Basics about Cervical Cancer What is cancer? The body is made up of millions and millions of living cells.
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health October-December 2014 Let s Learn the Basics about Cervical Cancer What is cancer? The body is made up of millions and millions of living cells.
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015 Hormone Therapy Menopause is the time in a woman s life when she naturally stops having menstrual periods. Menopause marks the end of the
patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015 Hormone Therapy Menopause is the time in a woman s life when she naturally stops having menstrual periods. Menopause marks the end of the
Endometriosis: An Overview
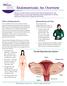 Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
In Vitro Fertilization
 Patient Education In Vitro Fertilization What to expect This handout describes how to prepare for and what to expect when you have in vitro fertilization. It provides written information about this process,
Patient Education In Vitro Fertilization What to expect This handout describes how to prepare for and what to expect when you have in vitro fertilization. It provides written information about this process,
Why would you need a hysterectomy?
 Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
 Any further questions? Please contact the matron for Women s Health on 020 7288 5161 (answerphone) Monday - Thursday 9am - 5pm. For more information: Royal College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Recovering
Any further questions? Please contact the matron for Women s Health on 020 7288 5161 (answerphone) Monday - Thursday 9am - 5pm. For more information: Royal College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Recovering
Problems in Early Pregnancy
 Problems in Early Pregnancy Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered This information answers queries about issues that may arise in early pregnancy. Not all of these issues will apply to you. It provides
Problems in Early Pregnancy Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered This information answers queries about issues that may arise in early pregnancy. Not all of these issues will apply to you. It provides
