Review for Test 1 : INCLUDES CHAPTERS 1, 2, 3 & 4 (For Friday class ONLY)
|
|
|
- Dwight Gordon
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review for Test 1 : INCLUDES CHAPTERS 1, 2, 3 & 4 (For Friday class ONLY) Name The following review includes 100 questions. On the test students will answer 33 questions selected from the review. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Accounting is the information system that provides information to various users. What process(es) does this include? A) processing the data into reports B) communicating the results to decisions makers C) measuring business activity D) all of the above 2) Many organizations have contributed to the process of creating and/or using generally accepted accounting principles. Which of the following organizations has the primary responsibility for formulating accounting standards? A) CMA B) AICPA C) SEC D) FASB 3) Which of the following is a licensed accountant who serves the general public rather than one particular company? A) FASB B) SEC C) CMA D) CPA 4) Accountants often refer to GAAP. What do the letters GAAP stand for when discussing accounting? A) Global accommodation accounting principles. B) Generate accurate accounting policies. C) Generally accepted accounting principles. D) Grandma's awesome apple pie. 5) Accounting information may be generated for a variety of purposes. The key product(s) of accounting is (are) which of the following documents? A) Remittance advices B) Spreadsheets C) Workpapers D) Financial statements 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Which of the following statements best defines accounting financial statements? 6) A) Financial statements are the verbal statements made to business news organizations by chief financial officers. B) Financial statements process information into reports. C) Financial statements are documents that report on a business in monetary terms, providing information to help people make informed business decisions. D) Financial statements are the information system that measures business activities. 7) The primary objective of financial reporting is to provide information useful for making investment and lending decisions. To be useful, information must possess certain characteristics. Which of the following is NOT one of the basic characteristics that accounting information must possess to be useful. A) relevance B) reliability C) an owner's equity section D) comparability 7) 1
2 8) Which of the following concepts (or principles) would be most likely to require that a person with three different businesses keep three different checking accounts? A) going-concern concept B) reliability concept C) entity concept D) cost principle 8) 9) Which of the following is a correct accounting equation? 9) A) Assets + Revenue = Liabilities + Expenses B) Assets + Liabilities = Owner's equity C) Assets = Liabilities + Owner's equity D) Assets + Revenue = Owner's equity 10) Owner's equity is $150, 000 and total liabilities are $90, 000. What would total assets be? 10) A) $180, 000 B) $60, 000 C) $240, 000 D) $300, ) A liability is paid with cash. How does paying this liability affect the accounting equation? 11) A) Assets decrease; liabilities decrease B) Liabilities decrease; owner's equity increases C) Assets increase; liabilities increase D) Assets increase; liabilities decrease 12) Which of the following amounts appears on both the statement of owner's equity and the balance sheet? A) ending owner's equity B) net income C) total assets D) total revenues 13) Which of the following is the detailed record of the changes in a particular asset, liability, or owner's equity? A) Trial balance B) Ledger C) Account D) Journal 14) Which of the following journal entries would be recorded if Jane Brown started a company by depositing cash of $6, 000 in the company's bank account? A) Jane Brown, Capital 6,000 Cash 6,000 B) Cash 6,000 Jane Brown, Capital 6,000 C) Accounts Payable 6,000 Cash 6,000 D) Jane Brown, Capital 6,000 Accounts Payable 6,000 12) 13) 14) 2
3 15) Which of the following journal entries would be recorded if a business purchased equipment for $2, 500 cash and supplies for $450 cash? A) Cash 2,950 Equipment 2,500 Supplies 450 B) Cash 2,500 Equipment 450 Accounts Receivable 2,950 C) Equipment 2,500 Supplies 450 Cash 2,950 D) Equipment 2,950 Cash 2,500 Supplies ) Case 2.1 The following transactions have been journalized and posted to the proper accounts. 1. Mark Call invested $7,000 cash in his new design services business. 2. Mark paid the first month's rent with $ Mark purchased equipment by paying $2,000 down and executing a note payable for $4, Mark purchased supplies for $850 cash. 5. Mark billed a client for $4,000 of design services completed 6. Mark received $3,000 of the account for the completed services. 16) Refer to Case 2.1. What is the balance in Cash? 16) A) $6,450 B) $8,450 C) $8,150 D) $7,850 17) Refer to Case 2.1. What is the balance in Accounts Receivable? 17) A) $1,000 B) $4,000 C) $8,500 D) $7,000 18) Refer to Case 2.1. What is the balance in Notes Payable? 18) A) $7,000 B) $4,000 C) $4,500 D) $1,000 19) Refer to Case 2.1. What is the balance in Service Revenue? 19) A) $3,150 B) $3,000 C) $1,000 D) $4,000 20) Refer to Case 2.1. What is the balance in Rent Expense? 20) A) $3,150 B) $3,000 C) $700 D) $2,700 3
4 21) Which of the following journal entries would be recorded if a business performed services for $400 cash and $1,000 on account? A) Cash 400 Accounts Receivable 1,000 Service Revenue 1,400 B) Cash 1,400 Accounts Receivable 1,000 Service Revenue 400 C) Service Revenue 1,000 Cash 400 Accounts Receivable 1,400 D) Service revenue 1,400 Cash 1,000 Accounts Payable ) 22) Which of the following is the book (or printout) holding all the accounts? 22) A) Journal B) Ledger C) Account D) Trial balance 23) Which of the following is the chronological record of transactions? 23) A) Ledger B) Trial balance C) Journal D) Account 24) Which of the following is a list of all the accounts with their balances? 24) A) Account B) Ledger C) Trial balance D) Journal 25) Which of the following accounts is NOT an example of an asset? 25) A) Cash B) Building C) Accounts Receivable D) Notes Payable 26) Which of the following accounts is NOT an example of a liability? 26) A) Accounts Payable B) Wages Payable C) Notes Payable D) Accounts Receivable 27) Which of the following accounts is NOT an example of owner's equity? 27) A) Cash B) Revenue C) Withdrawals D) Capital 28) Accountants record transactions first in which of the following? 28) A) Journal B) Chart of accounts C) Ledger D) Trial balance 29) After initially recording a transaction, the data is then copied, or posted, to which of the following? 29) A) Journal B) Trial balance C) Chart of accounts D) Ledger 30) Which of the following accounts is an asset? 30) A) Prepaid Expenses B) Service Revenue C) Accounts Payable D) Salary Expense 31) Which of the following accounts is a liability? 31) A) Salary Expense B) Service Revenue C) Accounts Payable D) Prepaid Expenses 4
5 32) Which of the following accounts is an owner's equity account? 32) A) Capital B) Accrued Liability C) Accounts Payable D) Prepaid Expense 33) The accounting process of copying a transaction from the journal to the ledger is which of the following? A) Proofing B) Posting C) Journalizing D) Footing 33) 34) A chart of accounts is which of the following? 34) A) A list of all the accounts with their balances. B) A book (or printout) holding all the accounts. C) A list of all the accounts with their account numbers. D) A chronological record of transactions. 35) Which of the following groups of accounts have a normal debit balance? 35) A) Assets and liabilities B) Revenues and expenses C) Liabilities and owner's equity D) Assets and expenses 36) Which of the following accounts increase due to a credit? 36) A) Cash B) Owner's Capital C) Accounts Receivable D) Both A and B increase when credited. 37) Which of the following accounts decrease due to a credit? 37) A) Cash B) Owner's Capital C) Accounts Payable D) Both A and B decrease when credited. 38) Which of the following accounts increase due to a debit? 38) A) Cash B) Interest Payable C) Prepaid Insurance D) Both A and C increase when debited. 39) Which of the following accounts decrease due to a debit? 39) A) Prepaid Insurance B) Interest Payable C) Cash D) Both A and B decrease when debited. 40) An owner invests $20,000 in her business by depositing the cash in the business's checking account. Which of the following occurs? A) Cash is credited for $20,000. B) Cash is debited for $20,000. C) Owner's capital is debited for $20,000. D) Both B and C. 40) 41) A business purchases equipment for cash of $8,000. Which of the following occurs? 41) A) Cash is credited for $8,000. B) Cash is debited for $8,000. C) Equipment is debited for $8,000. D) Both A and C. 42) A business makes a cash payment of $12, 000 to a creditor. Which of the following occurs? 42) A) Cash is credited for $12, 000. B) Cash is debited for $12, 000. C) Accounts payable is credited for $12, 000. D) Both A and C. 5
6 43) A business completes services for $16,000 on account. Which of the following occurs? 43) A) Cash is debited for $16,000. B) Accounts receivable is debited for $16,000. C) Service revenue is credited for $16,000. D) Both B and C. 44) A business pays $500 cash for supplies. Which of the following occurs? 44) A) Cash is debited for $500. B) Accounts payable is credited for $500. C) Supplies is debited for $500. D) Both B and C. 45) A business receives cash in payment of accounts receivable. Which of the following occurs? 45) A) An asset is debited and an asset is credited. B) A liability is debited and a liability is credited. C) An asset is debited and a liability is credited. D) An asset is credited and a liability is debited. 46) An owner withdraws cash from his business. The cash will be used for personal purposes. Which of the following occurs? A) An asset is credited and a liability is debited. B) An asset is debited and an owner's equity account is credited. C) An asset is credited and an owner's equity account is debited. D) An asset is debited and a liability is credited. 46) 47) A business borrows cash by issuing a note payable. Which of the following occurs? 47) A) An asset is debited and a liability is credited. B) A liability is debited and a liability is credited. C) An asset is debited and an asset is credited. D) An asset is credited and a liability is debited. 48) The owner withdraws cash from the business. How does this withdrawal affect the accounting equation? A) Assets decrease; owner's equity decreases B) No effect on the assets, liabilities, or owner's equity C) Assets decrease; owner's equity increases D) Assets increase; liabilities decrease 48) 49) Assets are $150, 000 and total liabilities are $90, 000. What would total owner's equity be? 49) A) $60, 000 B) $240, 000 C) $300, 000 D) $180, ) Assets are $270, 000 and owner's equity is $90, 000. What would liabilities be? 50) A) $180, 000 B) $270, 000 C) $360, 000 D) $60, ) If a company is using the accrual method of accounting, when is revenue recorded? 51) A) When services are rendered, even though cash may be received at a later date. B) When cash is received, even though services may be rendered at a later date. C) Only when cash is received at the completion of the services. D) Only when cash is received after the completion of the services. 6
7 52) Under which of the following methods of accounting is an expense recorded when it is incurred, regardless of when cash is paid? A) Cash B) Accrual C) Deferral D) Receivable 52) 53) Under the accrual method of accounting, an expense is recorded at which of the following times? 53) A) When payment for the expense is made B) When the expense is incurred C) At the end of the accounting period D) Both A and C 54) Which of the following is the matching principle? 54) A) The principle that determines when to record revenue. B) The principle that determines when to record expenses. C) The principle that ensures that information is reported at regular intervals. D) None of the above. 55) What debit is required as part of an adjusting entry when a prepaid expense is initially recorded as an expense? A) A debit to an asset account B) A debit to an unearned expense account C) A debit to a contra account D) A debit to a deferred revenue account 56) What credit is required as part of an adjusting entry when an accrued expense is initially recorded as an expense? A) A credit to an unearned revenue account B) A credit to a liability account C) A credit to a revenue account D) A credit to a contra liability 55) 56) 57) An accrued expense is which of the following? 57) A) An expense that will be incurred and paid in the future B) An expense that the business has paid but not yet incurred C) An expense that the business has incurred but not yet paid D) An expense that has been paid and incurred 58) Unearned rent is an example of which of the following? 58) A) Accrued revenue B) An accrued expense C) Unearned revenue D) A prepaid expense 59) The Supplies account for Vulcan Detail Company had a balance of $3,200 at the beginning of the year. Additional supplies of $13,400 were purchased during the year. A physical count of the ending inventory of supplies revealed that $5,900 of supplies were still on hand. What was total supplies expense for the year? A) $9,100 B) $10,700 C) $4,300 D) $16,400 59) 60) The adjusting entry to record depreciation expense accomplishes which of the following? 60) A) Decreases a liability and increases a revenue B) Increases an asset and increases an expense C) Increases a contra-asset and increases an expense D) Decreases a liability and increases an expense 61) The beginning balance in the Supplies account was $3,000. Purchases of supplies during the year were $25,000. An inventory of supplies at year-end revealed that the ending balance in the Supplies account is $1,500. What is the amount of the adjusting entry? A) $25,000 B) $26,500 C) $3,000 D) $1,500 61) 7
8 62) A business acquires equipment for $140,000 on January 1. The equipment has a life of seven years. Which of the following is the adjusting entry required on December 31, 2008? A) Debit $140,000 to Equipment, credit $140,000 to Cash B) Debit $20,000 to Depreciation Expense, credit $20,000 to Equipment C) Debit $20,000 to Depreciation Expense, credit $20,000 to Accumulated Depreciation D) Debit $140,000 to Depreciation Expense, credit $140,000 to Accumulated Depreciation 62) 63) What type of account is an accrued expense and what is its normal balance? 63) A) Revenue, credit B) Asset, debit C) Expense, debit D) Liability, credit 64) Financial statements can be prepared from which of the following? 64) A) A general journal B) An unadjusted trial balance C) An adjusted trial balance D) A general ledger 65) How do the adjusting entries differ from other journal entries? 65) A) Adjusting entries never affect cash. B) Adjusting entries are made only at the end of the period. C) Adjusting entries debit or credit at least one income statement account and at least one balance sheet account. D) All of the above. 66) The adjusting process has two purposes. Which of the following represents these two purposes? 66) A) 1) Measure net income or loss and 2) Update the balance sheet B) 1) Compute ending capital and 2) Journalize the period's activity C) Both A and B are correct D) None of the above 67) Where does net income appear on a work sheet? 67) A) Net income appears in the Income Statement credit column and in the Balance Sheet debit column. B) Net income appears only in the Balance Sheet credit column. C) Net income appears only in the Income Statement debit column. D) Net income appears in the Balance Sheet credit column and in the Income Statement debit column. 68) Totals of various columns from the worksheet are shown below. What is net income or loss? 68) Income Statement Balance Sheet Debit Credit Debit Credit $6,800 $9,500 $7,400 $4,700 A) Net income of $2,700 B) Net loss of $6,800 C) Net income of $4,700 D) Net loss of $2,700 8
9 69) In which of the columns of the worksheet would the owner's capital account be found? 69) A) In the Trial Balance credit column, the Adjusted Trial Balance credit column and the Balance Sheet credit column B) In the Trial Balance debit column, the Adjusted Trial Balance debit column and the Balance Sheet debit column C) In the Balance Sheet credit column and the Income Statement debit column D) In the Balance Sheet debit column and the Income Statement credit column 70) In which of the columns of the worksheet would the depreciation expense account be found? 70) A) In the Trial Balance credit column, the Adjusted Trial Balance debit column and the Income Statement debit column B) In the Adjusted Trial Balance debit column and the Income Statement debit column C) In the Trial Balance credit column, the Adjusted Trial Balance credit column and the Income Statement credit column D) In the Adjusted Trial Balance credit column and the Income Statement credit column 71) In which of the columns of the worksheet would the service revenue account be found? 71) A) In the Adjusted Trial Balance debit column and the Income Statement credit column B) In the Adjusted Trial Balance debit column and the Income Statement debit column C) In the Trial Balance credit column, the Adjusted Trial Balance credit column and the Income Statement credit column D) In the Trial Balance debit column, the Adjusted Trial Balance debit column and the Income Statement debit column 72) Which of the following accounts will be closed by debiting the Income Summary? 72) A) Depreciation Expense B) Accumulated Depreciation C) Service Revenue D) Accounts Payable 73) Revenues total $10,200. Expenses total $7,300. Owner's withdrawals total $2,600. What is the balance in the Income Summary account after closing net income or loss to the owner's capital account? A) Balance of $0 B) Credit balance of $2,900 C) Debit balance of $2,900 D) Credit balance of $300 74) Which of the following accounts has a remaining non-zero balance after the closing process is completed. A) The Accumulated Depreciation account has a non-zero balance. B) The Depreciation Expense account has a non-zero balance. C) The Service Revenue account has a non-zero balance. D) The Owner's Withdrawals account has a non-zero balance. 75) Net income for the year is $25,000. The owner withdrew $3,000 per month for personal living expenses. Which of the following occurs? A) The Owner's Capital account increases by $11,000. B) The Owner's Capital account decreases by $11,000. C) The Owner's Capital account decreases by $22,000. D) The Owner's Capital account increases by $22, ) 74) 75) 76) Which account has a balance equal to net income immediately before it is closed? 76) A) The Income Summary account B) The Owner's Capital account C) The Owner's Withdrawal account D) The Net Income account 9
10 77) To what account is the balance in the Income Summary closed? 77) A) The Income Summary is closed to the owner's capital or Retained Earnings account. B) The Income Summary is closed to the net income account. C) The Income Summary is closed to the owner's withdrawals account. D) None of the above. 78) Which of the following accounts are temporary accounts that must be closed at the end of the year? 78) A) Revenues, expenses and owner's capital B) Assets, liabilities and owner's equity C) Revenues, expenses and owner's withdrawals D) Assets, liabilities and owner's withdrawals 79) Revenues total $10,200. Expenses total $7,300. Owner's withdrawals total $2,600. What is the balance in the Income Summary account prior to closing net income or loss to the owner's capital account? A) Credit balance of $300 B) Balance of $0 C) Debit balance of $2,900 D) Credit balance of $2,900 79) 80) Which of the following does NOT appear on the work sheet? 80) A) Adjusting entries B) The adjusted trial balance C) The trial balance D) Closing entries 81) Which of the following accounts would appear in the Income Statement credit column? 81) A) Prepaid insurance B) Unearned service revenue C) Service revenue earned D) Depreciation expense 82) Which of the following statements is a TRUE statement concerning the work sheet? 82) A) The work sheet is a ledger. B) The work sheet is a document used to summarize data to prepare the financial statements. C) The work sheet is a journal. D) The work sheet is a financial statement. 83) Which of the following is the correct order of the steps of preparing the work sheet? I. Compute each account's adjusted balance by combining the trial balance and adjustment figures. Enter each account's adjusted amount in the Adjusted Trail Balance columns. II. Enter the account titles and their unadjusted balances in the Trial Balance columns of the work sheet and total the columns. III. Extend (copy) the asset, liability, and owner's equity amounts from the Adjusted Trial Balance to the Balance Sheet columns. Copy the revenue and expense amounts to the Income Statement columns. Total the statement columns. IV. Enter the adjusting entries in the Adjustments columns, and total the amounts. V. On the income statement column, compute net income. Enter net income as the balancing amount on the income statement and balance sheet columns. Total the income statement and balance sheet columns. A) III, V, IV, I, II B) I, II, III, IV, V C) IV, I, III, V, II D) II, IV, I, III, V 83) TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 84) Assets and liabilities are classified as either current or long-term to show their relative liquidity. 84) 10
11 85) Accountants often use a work sheet a document with several columns to summarize data for the financial statements. 85) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 86) To what account is the balance in the owner's withdrawals account closed? 86) A) The owner's withdrawals account is closed to the income summary account. B) The owner's withdrawals account is closed to the net income account. C) The owner's withdrawals account is closed to the cash account. D) The owner's withdrawals account is closed to the owner's capital account. 87) Which of the following is an asset that is expected to be converted to cash, sold, or consumed during the next year (or normal operating cycle if longer)? A) Liquid asset B) Long-term asset C) Quick asset D) Current asset 88) Which of the following is a debt that is due to be paid with cash, or with goods and services within the next year (or normal operating cycle if longer)? A) Liquid liability B) Long-term liability C) Current liability D) Quick liability 87) 88) TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 89) The first step in creating a work sheet is to enter the adjusting entries in the Adjustments columns. 89) 90) Prepaid rent is usually a long-term asset. 90) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 91) Which of the following accounts would appear in the Balance Sheet debit column? 91) A) Prepaid insurance B) Unearned service revenue C) Service revenue earned D) Depreciation expense 92) A business pays salaries of $140,000 on the first and fifteenth day of every month. Which of the following is the adjusting entry required on December 31, 2008? A) Debit $140,000 to Salaries Expense, credit $140,000 to Salaries Receivable B) Debit $140,000 to Salaries Expense, credit $140,000 to Salaries Payable C) Debit $140,000 to Salaries Receivable, credit $140,000 to Salaries Payable D) No adjusting entry required 92) 93) Salaries payable is an example of which of the following? 93) A) A prepaid expense B) Unearned revenue C) Accrued revenue D) An accrued expense 94) A prepaid expense is which of the following? 94) A) An expense that will be incurred and paid in the future B) An expense that has been paid and incurred C) An expense that the business has paid but not yet incurred D) An expense that the business has incurred but not yet paid 11
12 95) Accrued revenue is which of the following? 95) A) Revenue that has been collected and earned B) Revenue that the business has collected but not yet earned C) Revenue that will be collected and earned in the future D) Revenue that the business has earned but not collected 96) Unearned revenue is which of the following? 96) A) Revenue that the business has collected but not yet earned B) Revenue that will be collected and earned in the future C) Revenue that the business has earned but not collected D) Revenue that has been collected and earned 97) What credit is required as part of an adjusting entry when an accrued revenue is initially recorded as revenue? A) A credit to a contra liability B) A credit to an unearned revenue account C) A credit to a liability account D) A credit to a revenue account 98) What debit is required as part of an adjusting entry when unearned income is initially recorded as revenue? A) A debit to an asset account B) A debit to a contra account C) A debit to an unearned expense account D) A debit to a deferred revenue account 97) 98) 99) Which of the following is the time-period concept? 99) A) The concept that ensures that information is reported at regular intervals. B) The concept that determines when to record expenses. C) The concept that determines when to record revenue. D) None of the above. 100) Under which of the following methods of accounting is an expense recorded ONLY when cash is paid? A) Receivable B) Cash C) Deferral D) Accrual 100) 12
Basic Accounting Principles
 Basic Accounting Principles Basic Accounting Model The basic accounting model represents the relationship between assets (what the company owns), liabilities (what the company owes), and owner s equity
Basic Accounting Principles Basic Accounting Model The basic accounting model represents the relationship between assets (what the company owns), liabilities (what the company owes), and owner s equity
How To Calculate A Trial Balance For A Company
 THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
Accounting Cycle. Matching Principle
 CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
Completing the Accounting Cycle
 C H A P T E R 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Flow of Accounting Information (slide 1 of 5) End-of-Period Spreadsheet (Work
C H A P T E R 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Flow of Accounting Information (slide 1 of 5) End-of-Period Spreadsheet (Work
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments
 Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and
 Name: Due Date: December 12, 2011 Score: out of a possible 47 Course value: 7.5% Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and Worksheets A series of transactions are presented and their journal entries
Name: Due Date: December 12, 2011 Score: out of a possible 47 Course value: 7.5% Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and Worksheets A series of transactions are presented and their journal entries
ACCT1115. Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013
 ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
Accounting II Second Semester Final
 Name: Class: Date: Accounting II Second Semester Final Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Profit is the difference between:
Name: Class: Date: Accounting II Second Semester Final Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Profit is the difference between:
PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING MODEL
 CHAPTER 1 PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING MODEL OBJECTIVES The objectives of this part are: To introduce a definition of accounting, the need for accounting information, and the various accounting
CHAPTER 1 PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING MODEL OBJECTIVES The objectives of this part are: To introduce a definition of accounting, the need for accounting information, and the various accounting
Accumulated Depreciation Equipment
 Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle > DO IT! Worksheet Balance sheet: Extend assets to debit column. Extend liabilities to credit column. Extend contra assets to credit column. Extend drawings account
Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle > DO IT! Worksheet Balance sheet: Extend assets to debit column. Extend liabilities to credit column. Extend contra assets to credit column. Extend drawings account
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS. Lecture Outline
 CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers
 Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
Dr. M. D. Chase BA 201 Examination 1J
 Dr. M. D. Chase BA 201 Examination 1J Instructions: 1. Place your Name, Code Number of the Examination and the Examination Number on your Scantron form. Failure to follow these instructions will result
Dr. M. D. Chase BA 201 Examination 1J Instructions: 1. Place your Name, Code Number of the Examination and the Examination Number on your Scantron form. Failure to follow these instructions will result
> DO IT! Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts. Timing Concepts. Adjusting Entries for Deferrals D-12. Solution
 Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts Timing Concepts Review the glossary terms. Study carefully the revenue recognition principle, the expense recognition principle, and the time period assumption. Several
Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts Timing Concepts Review the glossary terms. Study carefully the revenue recognition principle, the expense recognition principle, and the time period assumption. Several
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle. Appendix 4A: Reversing entries
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
Chapter 1. Introduction to Accounting and Business
 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting and Business Learning Objective 1 Describe the nature of a business, the role of accounting, and ethics in business. Nature of Business and Accounting A business
1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting and Business Learning Objective 1 Describe the nature of a business, the role of accounting, and ethics in business. Nature of Business and Accounting A business
Chapter 5 Accrual Adjustments and Financial Statement Preparation. Revenue recognition Matching expenses to revenues Expenses related to periods
 Chapter 5 Accrual Adjustments and Financial Statement Preparation Revenue recognition Matching expenses to revenues Expenses related to periods 1 The Measurement of Income major function of accounting
Chapter 5 Accrual Adjustments and Financial Statement Preparation Revenue recognition Matching expenses to revenues Expenses related to periods 1 The Measurement of Income major function of accounting
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries -
 COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries - Worksheet Overview Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Account Titles Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit
COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries - Worksheet Overview Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Account Titles Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit
In the event of a tie, the score on the last ten questions will be used as a tie-breaker.
 NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING II 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING II 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
Accrual vs Deferral Accrual vs Cash Basis
 1 - Accrual vs Deferral Accrual vs Cash Basis - understanding debits and credits a transaction either increases or decreases the balance of accounts. increases and decreases in accounts are based on the
1 - Accrual vs Deferral Accrual vs Cash Basis - understanding debits and credits a transaction either increases or decreases the balance of accounts. increases and decreases in accounts are based on the
Objective Evidence. Unit of Measurement. Accounting Period Cycle. Business Entity. Going Concern. Adequate Disclosure. Matching Expenses with Revenue
 Accounting Concept: A source document is prepared for each transaction Objective Evidence Accounting Concept: Business transactions are stated in numbers that have common values; that is, using a common
Accounting Concept: A source document is prepared for each transaction Objective Evidence Accounting Concept: Business transactions are stated in numbers that have common values; that is, using a common
Study Guide - Final Exam Accounting I
 Study Guide - Final Exam Accounting I True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. Entries in a sales journal affect account balances in both the accounts receivable ledger
Study Guide - Final Exam Accounting I True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. Entries in a sales journal affect account balances in both the accounts receivable ledger
Time Period Assumption
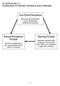 ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance
 6-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance 6 Section 1: Closing Entries Section Objectives 1. Journalize and post
6-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance 6 Section 1: Closing Entries Section Objectives 1. Journalize and post
Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle
 Page 1 of 27 Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied the fundamental steps in recording accounting information by
Page 1 of 27 Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied the fundamental steps in recording accounting information by
Review of Accounting Principles
 Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
Accruals, Deferrals,
 12-1 McGraw-Hill 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Accruals, Deferrals, 12 and the Worksheet Section 1: Calculating and Recording Adjustments Section Objectives 1. Determine
12-1 McGraw-Hill 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Accruals, Deferrals, 12 and the Worksheet Section 1: Calculating and Recording Adjustments Section Objectives 1. Determine
SOLUTIONS. Learning Goal 16
 Learning Goal 16: Prepare Closing Entries S1 Learning Goal 16 Multiple Choice 1. d 2. a 3. b 4. d Because drawing is closed directly into the capital account, not into income summary. 5. c 6. b This a
Learning Goal 16: Prepare Closing Entries S1 Learning Goal 16 Multiple Choice 1. d 2. a 3. b 4. d Because drawing is closed directly into the capital account, not into income summary. 5. c 6. b This a
CHAPTER 3 The Accounting Information System
 CHAPTER 3 The Accounting Information System 3-1 LECTURE OUTLINE Chapter 3 provides a review of accounting procedures throughout the accounting cycle. Depending on time constraints and students accounting
CHAPTER 3 The Accounting Information System 3-1 LECTURE OUTLINE Chapter 3 provides a review of accounting procedures throughout the accounting cycle. Depending on time constraints and students accounting
CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY. True-False Statements
 CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 4
CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 4
Chapter 13 Financial Statements and Closing Procedures
 Chapter 13 - Financial Statements and Closing Procedures Chapter 13 Financial Statements and Closing Procedures TEACHING OBJECTIVES 13-1) Prepare a classified income statement from the worksheet. 13-2)
Chapter 13 - Financial Statements and Closing Procedures Chapter 13 Financial Statements and Closing Procedures TEACHING OBJECTIVES 13-1) Prepare a classified income statement from the worksheet. 13-2)
'i*,; V' Your answer is correct! Match the Item on the left wlth the definition on the rtght.
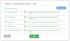 Match the Item on the left wlth the definition on the rtght. V' Your answer is correct! ~ Income statement """' ~ Reports a business's revenues and expenses for a period of time. ~ Balance sheet 1rt1 ~
Match the Item on the left wlth the definition on the rtght. V' Your answer is correct! ~ Income statement """' ~ Reports a business's revenues and expenses for a period of time. ~ Balance sheet 1rt1 ~
The Statement of Cash Flows
 CHAPTER The Statement of Cash Flows OBJECTIVES After careful study of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Define operating, investing, and financing activities. 2. Know the categories of inflows and
CHAPTER The Statement of Cash Flows OBJECTIVES After careful study of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Define operating, investing, and financing activities. 2. Know the categories of inflows and
CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS
 CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS TIME PERIOD ASSUMPTION The time period (or periodicity) assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods generally a
CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS TIME PERIOD ASSUMPTION The time period (or periodicity) assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods generally a
Accrual Accounting Process
 Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 3 THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM OVERVIEW Accounting information must be accumulated and summarized before it can be communicated and analysed. In this chapter, we will discuss the steps involved
CHAPTER 3 THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM OVERVIEW Accounting information must be accumulated and summarized before it can be communicated and analysed. In this chapter, we will discuss the steps involved
Preparing Financial Statements
 Carroll_CH03_023-040.qxd 8/10/06 4:37 PM Page 23 CHAPTER 3 Preparing Financial Statements OBJECTIVES F After reading this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the general process by which
Carroll_CH03_023-040.qxd 8/10/06 4:37 PM Page 23 CHAPTER 3 Preparing Financial Statements OBJECTIVES F After reading this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the general process by which
revenue/ Accounts receivable/ Cash/Service revenue) account.
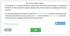 The correct answer is shown. On December 27, a business completed a $400 service that had not yet been billed or recorded as of December 31. Demonstrate the required adjusting entry of the business by
The correct answer is shown. On December 27, a business completed a $400 service that had not yet been billed or recorded as of December 31. Demonstrate the required adjusting entry of the business by
CHAPTER 4 The Mechanics of Financial Accounting
 CHAPTER 4 The Mechanics of Financial Accounting SYNOPSIS This chapter covers the mechanics underlying preparation of financial statements and how they help to ensure that a company s transactions are accurately
CHAPTER 4 The Mechanics of Financial Accounting SYNOPSIS This chapter covers the mechanics underlying preparation of financial statements and how they help to ensure that a company s transactions are accurately
Accounting Notes. Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value
 Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
The General Journal and the General Ledger
 4-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 4 The General Journal and the General Ledger Section 1: The General Journal Section Objectives 1. Record transactions in
4-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 4 The General Journal and the General Ledger Section 1: The General Journal Section Objectives 1. Record transactions in
CHAPTER II GENERAL LEDGER ACCOUNTS
 CHAPTER II GENERAL LEDGER ACCOUNTS A general ledger is basic to an accounting system. The General Ledger of a fund is a summary record containing the balance of assets, liabilities, deferred revenues,
CHAPTER II GENERAL LEDGER ACCOUNTS A general ledger is basic to an accounting system. The General Ledger of a fund is a summary record containing the balance of assets, liabilities, deferred revenues,
Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed
 Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of accounting?
Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of accounting?
Financial Statements Tutorial
 Financial Statement Review: Financial Statements Tutorial There are four major financial statements used to communicate information to external users (creditors, investors, suppliers, etc.) - 1. Balance
Financial Statement Review: Financial Statements Tutorial There are four major financial statements used to communicate information to external users (creditors, investors, suppliers, etc.) - 1. Balance
CHAE Review. Capital Leases & Forms of Business
 CHAE Review Financial Statements, Capital Leases & Forms of Business This is a complete review of the two volume text book, Certified Hospitality Accountant Executive Study Guide, as published by The Educational
CHAE Review Financial Statements, Capital Leases & Forms of Business This is a complete review of the two volume text book, Certified Hospitality Accountant Executive Study Guide, as published by The Educational
Glossary of Accounting Terms Peter Baskerville
 Glossary of Accounting Terms Peter Baskerville Account for or 'bring to account': An accounting phrase used to describe the recording of a financial transaction that is required under the generally accepted
Glossary of Accounting Terms Peter Baskerville Account for or 'bring to account': An accounting phrase used to describe the recording of a financial transaction that is required under the generally accepted
EXERCISES. Does not normally require adjustment. Normally requires adjustment (AE).
 EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
CHAPTER 5 THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE: REPORTING FINANCIAL RESULTS
 CHAPTER 5 THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE: REPORTING FINANCIAL RESULTS OVERVIEW OF BRIEF EXERCISES, EXERCISES, PROBLEMS AND CRITICAL THINKING CASES Brief Exercises Topic Learning Objectives Skills B. Ex. 5.1 B. Ex.
CHAPTER 5 THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE: REPORTING FINANCIAL RESULTS OVERVIEW OF BRIEF EXERCISES, EXERCISES, PROBLEMS AND CRITICAL THINKING CASES Brief Exercises Topic Learning Objectives Skills B. Ex. 5.1 B. Ex.
Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings
 Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Adjusting entries are made at the end of the accounting period to record all revenues and expenses that
Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Adjusting entries are made at the end of the accounting period to record all revenues and expenses that
Chapter 5 Accounting for Merchandising Operations
 Chapter 5 Accounting for Merchandising Operations Purchase Transactions Purchaser records goods at cost. When goods are returned, purchaser reduces Inventory. On September 5, De La Hoya Company buys merchandise
Chapter 5 Accounting for Merchandising Operations Purchase Transactions Purchaser records goods at cost. When goods are returned, purchaser reduces Inventory. On September 5, De La Hoya Company buys merchandise
SOLUTIONS. Learning Goal 15
 Learning Goal 15: Prepare a Classified S1 Learning Goal 15 Multiple Choice 1. b 2. c 3. a 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. c Their importance in paying current liabilities is the main reason current assets are shown
Learning Goal 15: Prepare a Classified S1 Learning Goal 15 Multiple Choice 1. b 2. c 3. a 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. c Their importance in paying current liabilities is the main reason current assets are shown
1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000.
 Rallis Page 1 Name: _ Date: 1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000. A) True B) False 2. If total liabilities decreased by
Rallis Page 1 Name: _ Date: 1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000. A) True B) False 2. If total liabilities decreased by
The worksheet for Hancock Company shows the following in the financial statement
 Chapter 4 Do it! Susan Elbe is preparing a worksheet. Explain to Susan how she should extend the following adjusted trial balance accounts to the financial statement columns of the worksheet. Cash Accumulated
Chapter 4 Do it! Susan Elbe is preparing a worksheet. Explain to Susan how she should extend the following adjusted trial balance accounts to the financial statement columns of the worksheet. Cash Accumulated
The Work Sheet and the Closing Process
 C H A P T E R 4 The Work Sheet and the Closing Process A systematic approach is essential for efficient and accurate processing of large amounts of information. Whether work sheets are on paper or computerized,
C H A P T E R 4 The Work Sheet and the Closing Process A systematic approach is essential for efficient and accurate processing of large amounts of information. Whether work sheets are on paper or computerized,
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE. Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations:
 TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize revenue until next year after the games are played.
 CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
SMART TOUCH LEARNING Balance Sheet May 31, 2013 $ 4,800. $ 48,700 Accounts receivable 2,600. 900 Inventory 30,500. 100 Supplies.
 3 The Adjusting Process Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWNS? SMART TOUCH LEARNING ance Sheet May 31, 2013 Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWES?
3 The Adjusting Process Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWNS? SMART TOUCH LEARNING ance Sheet May 31, 2013 Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWES?
PART A: TRUE/FALSE (1 point each):
 CHABOT COLLEGE General Accounting (BUS-7) Dmitriy Kalyagin PART A: TRUE/FALSE (1 point each): EXAM #4 (Chapters 10, 12, 13) 1. Employees who are exempt from the FLSA are entitled for overtime pay for hours
CHABOT COLLEGE General Accounting (BUS-7) Dmitriy Kalyagin PART A: TRUE/FALSE (1 point each): EXAM #4 (Chapters 10, 12, 13) 1. Employees who are exempt from the FLSA are entitled for overtime pay for hours
Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows
 Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows The Statement of Cash Flows describes the cash inflows and outflows for the firm based upon three categories of activities. Operating Activities: Generally include transactions
Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows The Statement of Cash Flows describes the cash inflows and outflows for the firm based upon three categories of activities. Operating Activities: Generally include transactions
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM
 ILLUSTRATION 3-1 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM ASSETS Increase Decrease + DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING REAL (PERMANENT) ACCOUNTS = LIABILITIES + Rules of Thumb + If the "normal balance" for an account is a
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM ASSETS Increase Decrease + DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING REAL (PERMANENT) ACCOUNTS = LIABILITIES + Rules of Thumb + If the "normal balance" for an account is a
When to Debit and Credit in Accounting
 When to Debit and Credit in Accounting Journal entries show a firm s transactions throughout a period of time; for example, when a company purchases supplies a journal entry will show the amount of supplies
When to Debit and Credit in Accounting Journal entries show a firm s transactions throughout a period of time; for example, when a company purchases supplies a journal entry will show the amount of supplies
CHAPTER 3: PREPARING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
 CHAPTER 3: PREPARING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS I. TIMING AND REPORTING A. The Accounting Period Time period assumption an organization s activities can be divided into specific time periods. Examples: a month,
CHAPTER 3: PREPARING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS I. TIMING AND REPORTING A. The Accounting Period Time period assumption an organization s activities can be divided into specific time periods. Examples: a month,
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions
 Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
Accounting for Changes and Errors
 CHAPTER Accounting for Changes and Errors OBJECTIVES After careful study of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Identify the types of accounting changes. 2. Explain the methods of disclosing an accounting
CHAPTER Accounting for Changes and Errors OBJECTIVES After careful study of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Identify the types of accounting changes. 2. Explain the methods of disclosing an accounting
The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET. Initial Paid-in Capital. An Example Entity. Transaction 2.
 The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET 2001 Richard S. Barr Transaction: Any event that affects the entity's financial position and requires recording Every accounting transaction
The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET 2001 Richard S. Barr Transaction: Any event that affects the entity's financial position and requires recording Every accounting transaction
Accounting Skills Assessment Practice Exam Page 1 of 10
 NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
CHAPTER 12 ACCRUALS, DEFERRALS, AND THE WORKSHEET
 CHAPTER 12 ACCRUALS, DEFERRALS, AND THE WORKSHEET Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students may assess that an unexpected decline in sales would mean surplus inventory which would have to be reduced
CHAPTER 12 ACCRUALS, DEFERRALS, AND THE WORKSHEET Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students may assess that an unexpected decline in sales would mean surplus inventory which would have to be reduced
Definition of Accounting
 SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES Lesson 1: Definition of Accounting 1. What is accounting? What are its main functions? Accounting is the process of financially measuring, recording, summarizing and communicating
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES Lesson 1: Definition of Accounting 1. What is accounting? What are its main functions? Accounting is the process of financially measuring, recording, summarizing and communicating
Fundamentals of Financial Accounting
 Fundamentals of Financial Accounting CHAPTER I Accounting in action. What is accounting? Accounting is the recording of financial transactions plus storing, sorting, retrieving, summarizing, and presenting
Fundamentals of Financial Accounting CHAPTER I Accounting in action. What is accounting? Accounting is the recording of financial transactions plus storing, sorting, retrieving, summarizing, and presenting
Learning Objectives: Quick answer key: Question # Multiple Choice True/False. 14.1 Describe the important of accounting and financial information.
 0 Learning Objectives: 14.1 Describe the important of accounting and financial information. 14.2 Differentiate between managerial and financial accounting. 14.3 Identify the six steps of the accounting
0 Learning Objectives: 14.1 Describe the important of accounting and financial information. 14.2 Differentiate between managerial and financial accounting. 14.3 Identify the six steps of the accounting
Salem Community College Course Syllabus. Section I. Course Title: Principles Of Accounting I. Course Code: ACC121
 Salem Community College Course Syllabus Section I Course Title: Principles Of Accounting I Course Code: ACC121 Lecture Hours: 4 Lab Hours: 0 Credits: 4 Course Description: An introduction to accounting
Salem Community College Course Syllabus Section I Course Title: Principles Of Accounting I Course Code: ACC121 Lecture Hours: 4 Lab Hours: 0 Credits: 4 Course Description: An introduction to accounting
Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II
 Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II Part One (30%) 1. Give the Chinese/English of the following terms: (5%) subsidiary ledger 统 制 账 户 purchase requisition 现 金 溢 缺 petty cash fund 永 续 盘 存 制
Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II Part One (30%) 1. Give the Chinese/English of the following terms: (5%) subsidiary ledger 统 制 账 户 purchase requisition 现 金 溢 缺 petty cash fund 永 续 盘 存 制
The Nature of Accounting Systems
 Basic Accounting & Budgeting February 4, 2009 The Nature of Accounting Systems Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, summarizing, reporting and interpreting information about the economic
Basic Accounting & Budgeting February 4, 2009 The Nature of Accounting Systems Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, summarizing, reporting and interpreting information about the economic
The Accounting Process
 GAAP LITERATURE The Accounting Process Chapter 3 TRADITIONAL: Original pronouncements, issued by the FASB. SEPT. 2009 CHANGE: Codification issued by the FASB. DIFFERENCE: Codification is listed by topic
GAAP LITERATURE The Accounting Process Chapter 3 TRADITIONAL: Original pronouncements, issued by the FASB. SEPT. 2009 CHANGE: Codification issued by the FASB. DIFFERENCE: Codification is listed by topic
Chapter 21 The Statement of Cash Flows Revisited
 Chapter 21 The Statement of Cash Flows Revisited AACSB assurance of learning standards in accounting and business education require documentation of outcomes assessment. Although schools, departments,
Chapter 21 The Statement of Cash Flows Revisited AACSB assurance of learning standards in accounting and business education require documentation of outcomes assessment. Although schools, departments,
In the event of a tie, the score on the last ten questions will be used as a tie-breaker.
 NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING I 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING I 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
CHAPTER 4. Adjusting the accounts and preparing financial statements CONTENTS
 CHAPTER 4 Adjusting the accounts and preparing financial statements CONTENTS Demonstration problem 4.1 Adjusting entries and corrections 4.2 Adjusting centries and effect on financial statements 4.3 Adjusting
CHAPTER 4 Adjusting the accounts and preparing financial statements CONTENTS Demonstration problem 4.1 Adjusting entries and corrections 4.2 Adjusting centries and effect on financial statements 4.3 Adjusting
Basic Accounting. Supplement for Using Simply Accounting Version 8.0 for Windows by. M. Purbhoo and D. Purbhoo
 Basic Accounting Supplement for Using Simply Accounting Version 8.0 for Windows by M. Purbhoo and D. Purbhoo Basic Accounting Contents: Accounting Theory 3 Basic Accounting 3 Balance Sheet 3 Income Statement
Basic Accounting Supplement for Using Simply Accounting Version 8.0 for Windows by M. Purbhoo and D. Purbhoo Basic Accounting Contents: Accounting Theory 3 Basic Accounting 3 Balance Sheet 3 Income Statement
how to prepare a cash flow statement
 business builder 4 how to prepare a cash flow statement zions business resource center zions business resource center 2 how to prepare a cash flow statement A cash flow statement is important to your business
business builder 4 how to prepare a cash flow statement zions business resource center zions business resource center 2 how to prepare a cash flow statement A cash flow statement is important to your business
Accounting Principles Dr. Mishari Alfraih. Adjusting the Accounts
 Accrual- vs. Cash-Basis Accounting Accrual-Basis Accounting Adjusting the Accounts Transactions recorded in the periods in which the events occur Revenues are recognized when earned, rather than when cash
Accrual- vs. Cash-Basis Accounting Accrual-Basis Accounting Adjusting the Accounts Transactions recorded in the periods in which the events occur Revenues are recognized when earned, rather than when cash
Chapter 16 Accounting for Income Taxes
 DEFERRED TAX ASSETS AND DEFERRED TAX LIABILITIES Fundamental Concepts There are fundamental differences in the amount of income and expenses reported for GAAP and income tax purposes. The objective for
DEFERRED TAX ASSETS AND DEFERRED TAX LIABILITIES Fundamental Concepts There are fundamental differences in the amount of income and expenses reported for GAAP and income tax purposes. The objective for
Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle
 Course Schedule Course Modules Review and Practice Exam Preparation Resources Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied
Course Schedule Course Modules Review and Practice Exam Preparation Resources Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied
Bookkeeping Proficiency
 Bookkeeping Proficiency (Exam) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials. Take a quick tour by visiting www.accountingcoach.com/quicktour. Table of Contents (click
Bookkeeping Proficiency (Exam) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials. Take a quick tour by visiting www.accountingcoach.com/quicktour. Table of Contents (click
How To Balance Sheet
 Page 1 of 6 Balance Sheet Accounts The Chart of Accounts is normally arranged or grouped by the Major Types of Accounts. The Balance Sheet Accounts (Assets, Liabilities, & Equity) are presented first,
Page 1 of 6 Balance Sheet Accounts The Chart of Accounts is normally arranged or grouped by the Major Types of Accounts. The Balance Sheet Accounts (Assets, Liabilities, & Equity) are presented first,
Authored for ENMU Tutoring Services. By Jessica Huff
 By Jessica Huff The standard accounting equation is Assets=Liabilities + Stockholders Equity. Depending on which item someone is looking at will determine what the normal balance is. The normal balance
By Jessica Huff The standard accounting equation is Assets=Liabilities + Stockholders Equity. Depending on which item someone is looking at will determine what the normal balance is. The normal balance
CHAPTER 2 THE RECORDING PROCESS SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY. True-False Statements. Multiple Choice Questions
 CHAPTER 2 THE RECORDING PROCESS sg st SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 3 K 25.
CHAPTER 2 THE RECORDING PROCESS sg st SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 3 K 25.
Welcome to the financial reports topic. 5-1-1
 Welcome to the financial reports topic. 5-1-1 We will explore the effect of standard processes in SAP Business One on Financial Reports: such as the Balance Sheet, the Trial Balance, and the Profit and
Welcome to the financial reports topic. 5-1-1 We will explore the effect of standard processes in SAP Business One on Financial Reports: such as the Balance Sheet, the Trial Balance, and the Profit and
MIDTERM EXAMINATION. Afaaq_tariq@yahoo.com. Fall 2009
 MIDTERM EXAMINATION Afaaq_tariq@yahoo.com Fall 2009 FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis Asslam O Alikum FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis (Session 3) solved by Afaaq n Shani Bhai with reference n numerical
MIDTERM EXAMINATION Afaaq_tariq@yahoo.com Fall 2009 FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis Asslam O Alikum FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis (Session 3) solved by Afaaq n Shani Bhai with reference n numerical
Century 21 Accounting, 8e General Journal Chapter Outlines
 Century 21 Accounting, 8e General Journal Chapter Outlines PART 1 Chapter 1 ACCOUNTING FOR A SERVICE BUSINESS ORGANIZED AS A PROPRIETORSHIP Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting
Century 21 Accounting, 8e General Journal Chapter Outlines PART 1 Chapter 1 ACCOUNTING FOR A SERVICE BUSINESS ORGANIZED AS A PROPRIETORSHIP Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting
Accrual Accounting and the Financial Statements
 Accrual Accounting and the Financial Statements 3 LEARNING OBJECTIVES SPOTLIGHT Le Château has been selling fashion apparel, footwear, and accessories in Canada for over 50 years. What started as a single,
Accrual Accounting and the Financial Statements 3 LEARNING OBJECTIVES SPOTLIGHT Le Château has been selling fashion apparel, footwear, and accessories in Canada for over 50 years. What started as a single,
TOPIC LEARNING OBJECTIVE
 Topic Mapping 1 Transaction Analysis Understand the effect of various types of transactions on the accounting equation, accounting journal and accounting ledger. Concepts and Skills Accounting Equation
Topic Mapping 1 Transaction Analysis Understand the effect of various types of transactions on the accounting equation, accounting journal and accounting ledger. Concepts and Skills Accounting Equation
RECORDING OF TRANSACTIONS (JOURNAL ENTRIES, LEDGER AND TRIAL BALANCE)
 Source Document : RECORDING OF TRANSACTIONS (JOURNAL ENTRIES, LEDGER AND TRIAL BALANCE) A document which provides evidence of the transactions is called the Source Document such as Cash memo, Invoice etc.
Source Document : RECORDING OF TRANSACTIONS (JOURNAL ENTRIES, LEDGER AND TRIAL BALANCE) A document which provides evidence of the transactions is called the Source Document such as Cash memo, Invoice etc.
Accruals and prepayments
 Accruals and prepayments Introduction These are adjustments which need to be carried out before the financial statements can be produced. The adjustments are necessary as accounts are prepared in accordance
Accruals and prepayments Introduction These are adjustments which need to be carried out before the financial statements can be produced. The adjustments are necessary as accounts are prepared in accordance
CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS
 CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS Key Terms and Concepts to Know Double entry accounting: Debits and Credits Total debits must always equal total credits Accounting Books: Accounts General Journal
CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS Key Terms and Concepts to Know Double entry accounting: Debits and Credits Total debits must always equal total credits Accounting Books: Accounts General Journal
How To Account For A Company
 Institution: Great Bay Community College Course: Introduction to Accounting and Financial Reporting I, ACCT 113 Required Text: Fundamentals of Accounting Principles, Latest edition; Larson Packet Contents:
Institution: Great Bay Community College Course: Introduction to Accounting and Financial Reporting I, ACCT 113 Required Text: Fundamentals of Accounting Principles, Latest edition; Larson Packet Contents:
ACC 255 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (NEW MATERIAL)
 Page 1 ACC 255 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (NEW MATERIAL) Complete these sample exam problems/objective questions and check your answers with the solutions at the end of the review file and identify where
Page 1 ACC 255 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (NEW MATERIAL) Complete these sample exam problems/objective questions and check your answers with the solutions at the end of the review file and identify where
