revenue/ Accounts receivable/ Cash/Service revenue) account.
|
|
|
- Dorthy Jacobs
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The correct answer is shown. On December 27, a business completed a $400 service that had not yet been billed or recorded as of December 31. Demonstrate the required adjusting entry of the business by completing the following sentence. The required adjusting entry would be to debit the '\ccounts receivable (Unearned revenue/ Accounts receivable/ Cash/ Service revenue) account and credit (debivcredit) the Service revenue (Unearned revenue/ Accounts receivable/ Cash/Service revenue) account. ~Your answer is correct.
2 Describe the final step in the adjusting process. ~Your answer is correct. The final step is to post to a trial balance so financial statements can be prepared. The final step is to determine the correct balance of an account. The final step is to determine the current balance of an account. a The final step is to create an adjustingjournal entry. l
3 List the order in which financial statements are prepared. ~Your answer is correct. ~ 1 Income statement E} Statement of owner's equity E -:; Balance sheet ~ 4 Statement of cash flows
4 Explain your understanding of what unearned revenues are by selecting the statements below which are correct. (Check all that apply.) ~ Your answer is correct. ]
5 The correct answer is shown. By the end of the accounting period, employees have earned salaries of $650, but they will not be paid until the following pay period. Demonstrate the required adjusting entry by completing the following sentence. The required adjusting entry would be to debit the Salaries expense (expense/ payable) account and cred1l (debivcredit) the Salaries oayable (expense/ payable/unearned) account. ~Your answer is correct.
6 Choose the statement below that demonstrates the correct adjusting entry to recognize depreciation expense on a building. ~Your answer is correct. Debit Depreciation expense; credit Building. a Debit Accumulated depreciation; credit Depreciation expense. Debit Depreciation expense; credit Accumulated depreciation. Debit Building; credit Accumulated depreciation.
7 The correct answer is shown. Illustrate your understanding of how to use the adjusted trial balance to prepare an income statement by completing the following sentence. In order to prepare an income statement using the account balances on an adjusted trial balance, all of the r1:.wenues (revenues/liabilities) and their credit balances are transferred to the income statement as well as all of the ekp~nse;<:' (expenses/assets) and their d 3btL(debit/credit) balances. ~Your answer is correct.
8 The correct answer is shown. A company borrowed $10,000 from the bank at 5% interest. The loan has been outstanding for 45 days. Demonstrate the required adjusting entry for this company by completing the following sentence. The required adjusting entry would be to debit the Interest (expense/ payable/ receivable) expense account and (debitjcredit)cred1t the Interest oayaolc (expense/ payable/ receivable) account. ~Your answer is correct.
9 A 12-month insurance policy was purchased on Dec. 1 for $4,800 and the Prepaid insurance account was initially increased for the payment. The required adjusting journal entry on December 31 includes a: (Check all that apply.) ~ Your answer is correct. debit to Prepaid insurance for $400. credit to Insurance expense for $400. debit to Insurance expense for $4,800.
10 Choose the statement below which is true regarding adjustingjournal entries. ~Your answer is correct. An income statement account is never involved. A balance sheet account is never involved. a At least one income statement account and one balance sheet account are always involved. ] Cash is sometimes involved when payment is still due from a customer.
11 For the current year, Bubbles Office Supply had earned $600 of interest on investments. As of December 31, none of this interest had been received or recorded. Demonstrate the required half of the adjusting entry by choosing the correct statement below. ~Your answer is correct. Debit Interest revenue for $600. Credit Interest receivable for $600. a Debit Interest receivable for $600. Debit Cash for $600.
12 A plant asset can be defined by which of the following statements? (Check all that apply.) ~Your answer is correct. Its original cost is expensed in the period in which it was purchased. a It is reported on the balance sheet. ] a Its original cost (minus any salvage value) is expensed over its useful life. a It is a tangible long-term asset. ) It has a life within the business greater than one year.
13 The correct answer is shown. An adjusting journal entry is made at the c,nc (beginning/middle/end) of an accounting period. ~Your answer is correct.
14 The correct answer is shown. Illustrate your understanding of how to use the adjusted trial balance to prepare a statement of owner's equity by completing the following sentence. In order to prepare the statement of owner's equity, the balance of the Owner rapi1.al(capital, Cash) account balance as well as any debit balance in the witnr.frawals (Withdrawals, Supplies) account is transferred from the adjusted trial balance and is used along with the reported net income (loss) from the Income statement. V Your answer is correct.
15 Identify which group of accounts may require adjustments at the end of the accounting period. ~Your answer is correct. a Cash; Notes receivable; Land Unearned revenue; Supplies; Prepaid rent Utilities expense; Cash; Owner, Capital )
16 $800 of supplies were purchased at the beginning of the month and the Supplies account was increased. As of the end of the period, $200 of supplies still remain. Which of the following is the correct adjusting entry? ~Your answer is correct. Supplies expense would be debited for $200. Supplies would be credited for $200. lfl Supplies expense would be debited for $600. Supplies would be debited for $200.
17 $1,000 of cash was received in advance of performing services. By the end of the period, $300 had not yet been earned. (The Unearned revenue account was increased at the time of the initial cash receipt.) Demonstrate the required adjusting journal entry by selecting from the choices below. (Check all that apply.) ~ Your answer is correct. Unearned revenue would be debited for $300. Service revenue would be credited for $300.
18 The correct answer is shown. The matching principle aims to record Pxpe1'1SPS (expenses/assets/liabilities) in the same accounting period as the "evenues (expenses/revenues/assets) that are earned as a result of those costs. This principle is a major part of the '1 Justing (timing/adjusting/estimating) process. ~Your answer is correct.
19 Which of the following statements about t he Accumulated depreciation account is (are) correct? (Check all that apply.) ~ Your answer is correct. L!!J Read about this Accumulated depreciation accumulates the total depreciation taken on an asset since its purchase. Accumulated depreciation is an expense account. Accumulated depreciation is added to its plant asset on the income statement. The Accumulated depreciation account allows the original cost of the asset to remain in the plant asset account.
20 A $300,000 building was purchased on Dec 1. It is estimated that it will have a life of 20 years. Calculate depreciation expense for the month of December using straight-line depreciation. "Your answer is correct. $2,500 $0 $15,000. $1,250 ]
21 What is depreciation? Y'Your answer is correct. Depreciation is the process of determining the value of accounts receivable which will be collected in the current period. Depreciation is the process of allocating the costs of long-term assets over their expected useful life. Depreciation is the process of recognizing revenues earned within the current accounting period. '
22 Accrual basis accounting is defined as: (Check all that apply.) ~Your answer is correct. an accounting system that uses the matching principle to determine when to recognize revenues and expenses. an accounting system that uses the adjusting process to recognize revenues when earned and expenses when incurred. an accounting system which is consistent with generally accepted accounting principles. an accounting system that recognizes revenues when cash is received and records expenses when cash is paid.
23 Review the following statements and determine which is (are) correct regarding an adjusted trial balance and how it is used In preparing financial statements. (Check all that apply.) '-'Your answer Is correct. L!J Read about this The income statement Is the first financial statement prepared after preparing the adjusted trial balance. Fi nancial statements are prepared more easily using the adjusted trial balance than with the general ledger. The ending Owner, Capital account balance on the balance sheet is transferred from the statement of owner's equity. H The adjusted trial balance includes all accounts and balances appearing In financial statements. ) The ending Owner, Capital account balance on the balance sheet is taken directly from the adjusted trial balance. The balance sheet is t he first financial statement prepared.
24 The correct answer is shown. Explain your understanding of a contra account by filling in the following blanks. A contra account is an account that is linked with another account (reportjaccounvstatement). It has a(n) oppos1t\.,, (similar/opposite) balance and is subtractec (added/subtracted) to/from the other account's balance. ~ Your answer Is correct.
25 The correct answer is shown. $200 of supplies were purchased at the beginning of the period and recorded as an asset. During the period, $90 of supplies were used. The adjustment to show the supplies used up would cause ssets (assets/ liabilities/ expenses) to be reduced and expenses(expenses/ liabilities,/revenues) to be increased, so net income would decline. ~Your answer is correct.
26 The correct answer is shown. Illustrate your understanding of how to use the adjusted trial balance to prepare the balance sheet by completing the following sentence. In order to prepare a balance sheet using the account balances on an adjusted trial balance, all of the ~ssets (expenses/ assets) and their debit balances are transferred to the balance sheet as well as all of the li'3bi ities (liabilities/ revenues) and their credit(debitjcredit) balances. ~ Your answer is correct.
27 What is the book value of an asset? ~Your answer is correct. Book value is the original cost of an asset plus its accumulated depreciation a Book value is the difference between the original cost of an asset and its fair market value. Book value is the original cost of an asset less its accumulated depreciation. ) Book value is another name for the original cost of an asset.
28 Which of the following refers to the preparation of an adjusted trial balance? (Check all that apply.) V Your answer is correct. I M Read about this An adjusted trial balance is a list of accounts and balances prepared before adjustments are posted. The debit and credit column totals don't have to equal each other on an adjusted trial balance. If+ The debit and credit column totals must balance. ilfl An adjusted trial balance is prepared after adjustments have been posted. ilfl New accounts may need to be added because of the adjusting process. ilfl Accounts are generally listed in the same order as listed in the chart of accounts. ilfl An adjusted trial balance has one debit column and one credit column.
29 Cash basis accounting is defined as: ~Your answer is correct. an accounting system which is consistent with generally accepted accounting principles an accounting system that uses the adjusting process to recognize revenues when earned and expenses when incurred an accounting system which recognizes revenues when cash is received and records expenses when cash is paid an accounting system that uses the matching principle to determine when to recognize revenues and expenses
30 Which of the following accounts would be considered a prepaid expense or prepaid asset account? (Check all that apply.) ~ Your answer is correct. Accounts payable a Prepaid rent a Prepaid insurance lflsupplies Owner, Capital
31 Which of the following lists of assets would be classified as plant assets? a ~Your answer is correct. Buildings, Equipment Land, Accounts receivable ) Buildings, Office supplies Equipment, Cash
32 Explain the difference between the unadjusted and the adjusted trial balance. ~ Your answer is correct. The adjusted trial balance contains only the accounts which were adjusted. The unadjusted trial balance contains all of the remaining accounts. The unadjusted trial balance is more accurate and should be used to prepare financial statements. a The adjusted trial balance is prepared after adjusting entries have been recorded and posted. J The unadjusted trial balance is more up to date than the adjusted trial balance.
33 What is needed in order to figure interest expense? (Check all that apply.) ~ Your answer is correct. M Read about this Salvage value Original cost of asset a Annual interest rate Years of useful life a Principal amount owed Fraction of year since last payment
34 StoryBook Company provided services to several customers during the month of December. These services have not yet been paid by the customers. StoryBook should record the following adjusting entry at the end of December: ~ Your answer is correct. credit accounts payable debit services revenue debit cash
35 The correct answer is shown. The formula to figure out the profit margin of a company is 1Pt iricome (Net income/ Accounts receivable/ Net sales) divided by r et sales (Net income/ Cash/ Net sales). ~Your answer is correct.
36 The correct answer is shown. On December 1, 2015, a company pays $3,600 for a 36-month insurance policy. After one month, accrual accounting requires $100 (100/3,600) of insurance expense be reported on the income statement ending December 31, However, if cash basis accounting is used, $3,600 (100/3,600) of insurance expense would be reported at the time of purchase. ~Your answer is correct.
37 A business has a $10,000 loan from a bank at 8% annual interest. Calculate the amount of interest to accrue if the loan has been outstanding for 45 days. Use a 360 day year...,your answer is correct. $800 $360. $100 $98.63 )
38 Define the Salaries payable account by selecting the appropriate statement below. ~Your answer is correct. It reports amounts owed to employees and is reported on the income statement. It is increased with a debit and is considered an asset account. a It reports amounts owed to employees and is a liability. It reports amounts owed to employees and is an asset. )
39 The Fish Aquarium obtained funds from a bank and owes interest on a note at the end of the month. The required adjusting journal entry will ~Your answer is correct. debit interest expense and credit cash a debit interest expense and credit interest payable debit interest payable and credit interest expense ] debit interest payable and credit cash
40 What is the effect of an accrued expense (such as salaries expense) adjustment on the income statement and the balance sheet? (Check all that apply.) ~Your answer is correct. a Expenses are increased. a Net income is reduced. Total liabilities are reduced. ] Net income is increased. a A liability (such as salaries payable) will be increased.
41 The correct answer is shown. A calendar-year-end reporting period is defined as a I./ (1 / 3 / 12) -month period which ends on December (December/January/March) 31st. '-'Your answer is correct.
42 Describe the effect of the adjusting entry to show the earned amount of a previously recorded unearned revenue on the income statement and on the balance sheet by choosing the correct statements below. (Check all that apply.) ~ Your answer is correct. if! Total liabilities are reduced. Total liabilities are increased. If I Net income is increased.
43 tven t h e f o II owing. m f ormat1on f or M ouse nc., c alculate its profit margin for the year $ in thousands Net income $ 500 $450 Net sales Accounts receivable ~ Your answer is correct. 7%
44 The correct answer is shown. Describe the difference that exists between U.S. GAAP and IFRS in adjusting accounts by completing the following sentence. bo1'1(both/neither) U.S. GAAP anj (and/nor) IFRS provide guidance for adjusting accounts at period end which include deferrals and accruals. ~Your answer is correct.
45 Which of the following could be a logical or realistic accounting period for a business that is creating financial statements? (Check all that apply.) ~Your answer is correct. a Six-month period a One-year period a One-month period ] ] ] Five-year period
46 The revenue recognition principle states that revenue: ~Your answer is correct. should be recorded when payment has been received is recognized when expenses are paid a should be recorded when it is earned should be recorded at the end of the accounting cycle
47 The correct answer is shown. Cash received from a customer for unearned subscription revenue can initially be recorded as either a(n) revenue (revenue/expense) or a(n) I abil1t1 (liability/expense). No matter how an unearned revenue was initially recorded, after the adjusting entry, net income will be identical. ~ Your answer is correct.
48 Mouse Inc. uses the alternative method of accounting for prepayments and purchased a $1,200, 6-month insurance policy. The company immediately debited the Insurance expense account. By the end of the period, $400 of the policy had expired. Demonstrate the required adjustment needed at the end of the period. ~ Your answer is correct. Credit Prepaid insurance $800. Debit Prepaid insurance for $400. Debit Insurance expense $400. a Debit Prepaid insurance $800.
49 Which of the following statements accurately explains how to use a worksheet to enter adjustments? (Check all that apply.) L!J Read about this ~ Your answer is correct. The adjustments column totals must balance before moving on to the Adjusted Trial Balance columns. As new accounts are added, they are added to the bottom of the worksheet below the other accounts. Each adjustment is identified by a letter in parentheses that serves as a cross-reference to the debit and credit side of the adjustment. Only t he debited or credited account of each adj ustment needs to be shown-not both accounts.
50 What defines a fiscal year for a business? ~Your answer is correct. It is any period which consists of 12 consecutive months. It is a year in which financial statements are audited. It is any period which consists of 48 consecutive weeks. It is a 12-month period always ending on December 31.
51 Rather than debiting an asset account, which of the following statements explains an alternate recording procedure to journalize prepaid expenses, such as prepaid rent or supplies. (Check all that apply.) ~Your answer is correct. Record all prepaid expenses with credits to liability accounts. Record all prepaid expenses with debits to expense accounts. a Record all prepaid expenses with credits to expense accounts Any unused prepaids existing at end of period are transferred to asset accounts.
52 Mouse Inc. received a $2,500 prepayment of rent from one of its tenants and immediately credited the Rent revenue account. By the end of the period, $500 of the rent had not been earned by Mouse Inc.. Demonstrate the required adjustment needed at the end of the period. ~ Your answer is correct. Credit Rent revenue $500. Credit Unearned rent for $2,000. a Debit Rent revenue for $500. ) Credit Rent revenue $2,000.
53 Which of the following statements best explains the posting process of adjusting entries? Y'Vour answer Is correct. a Posting is done as soon as possible after the adjustments are journalized. ) Posting is done after the adjusted trial balance is prepared. Posting to the ledger is never completed for adjusting entries. Posting is done after financial statements are prepared.
54 Rather than crediting the Unearned rent account for $400 of prepaid rent received from a customer, which of the following statements explains an alternate recording procedure to journalize this receipt? (Check all that apply.) V Your answer is correct. Record receipt with a debit to the Rent revenue account. Record receipt with a credit to the Rent revenue account. Any unused portion of the prepayment still existing at the end of the period will be transferred to the Unearned rent account Record the receipt of $400 with a debit to the Unearned rent account.
55 A prepaid expense (such as supplies or prepaid rent) can initially be recorded as either an expense or as an asset. Demonstrate your understanding of adj usting for prepaid expenses by selecting the statement that is correct. ~ Your answer is correct. If a prepaid expense was initially recorded as an expense, then expenses will be higher on the income statement If prepaid expense was initially recorded as an asset, then assets will be higher on t he balance sheet. No matter how a prepaid expense was initially recorded, after adjustment, the financial statements will be identical. If prepaid expense was initially recorded as an asset, then net income will be lower.
56 Which of the following statements correctly define(s) a profit margin? (Check all that apply.) ~ Your answer is correct. Profit margin is the ratio of a business's net income to its net sales. Profit margin is also called return on sales. Profit margin is the ratio of a business's net income to its accounts receivables. Profit margin is the amount of revenue received on a sale. Profit margin is a useful measure of a business's operating results.
57 What is the date primarily used in adjusting entries? ~Your answer is correct. The date is unimportant a The first day of the period The last day of the period The original date of the transaction being adjusted
58 Explain your understanding of what an accrued expense is by selecting the statements below which are correct. (Check all that apply.) ~ Your answer is correct. They refer to earnings which have been earned, but not yet billed. They are reported on an income statement. They are also called accounts receivable. ]
59 McDarrel's records $500 of accrued salaries on December 31. Three days later, on January 3, total salaries of $4,000 (including the $500 accrued at year end) are paid. Demonstrate the required journal entry on January 3 by selecting from the choices below. (Check all that apply.) ~ Your answer is correct. Cash would be credited for $4,000. On January 3, cash will be credited for entire weekly pay period of 5 days. Salaries payable will be credited for $500.
60 At the end of the previous year, a customer owed Chocolates R US $500. On January 31 of the current year, the customer paid $900 total, which included the $500 owed plus $400 owed for the current month of January. What would be the journal entry on January 31 that reflects this? (Check all that apply.) ~ Your answer is correct. Service revenue will be credited for $900.
61 Describe the effect of an accrued revenue adjustment on the income statement and the balance sheet by choosing f rom the statements below. (Check all that apply.) ~ Your answer is correct. Net income is reduced. ]
62 Which of the following statements describes why accrual accounting better reflects a business's performance? (Check all that apply.) ~Your answer is correct. Revenues are always recorded in the period in which they are earned. It provides a better focus and understanding of how cash is spent and why it is received. Expenses are always recognized in the period in which they are incurred. Comparability of financial statements is improved.
63 Identify the statement(s) below which is (are) correct regarding the use of estimates in accounting. (Check all that apply.) ~ Your answer is correct. Predictions of revenues and expenses are based on expectations and sometimes included on financial statements. When following the matching principle, sometimes estimates are used because the actual expense or revenue amount is not yet known. Matching expenses with revenues often requires us to predict certain events which we are not always able to do. Estimates of revenues and expenses are used in budgeting, but not on actual financial statements.
64 Which of the accounts below are considered accrued expenses? '-'Your answer is correct. Owner, Capital, Owner,Withdrawal Unearned revenue, Utility expense a Cash, Building, Equipment Wages expense, Interest expense )
65 Which of the following adjustments would be required at the end of the period? (Check all that apply.) a ~Your answer is correct. Unearned (deferred) revenues Cash accrued expenses a Prepaid (deferred) expenses Owner, Capital deferral adjustment a Accrued expenses a Accrued revenues I
66 Determine which statement(s) below correctly describe(s) the similarities that exist between U.S. GAAP and IFRS in preparing financial statements. (Check all that apply.) ~ Your answer Is correct. Both IFRS and U.S. GAAP require the income statement to be prepared quarterly. Both U.S. GAAP and IFRS balance sheets require current items to be separated from noncurrent a items. Both U.S. GAAP and IFRS prepare the same four basic financial statements. Both U.S. GAAP and IFRS balance sheets normally present noncurrent items first and equity before liabilities.
67 Which of the following describes accrued revenue? (Check all that apply).., Your answer is correct. The adjustment causes an increase in an asset account and an increase in a revenue account. Adjustments involve increasing both an expense account and a liability account. a Accounts receivable is usually increased when accruing revenues. a They refer to earnings which have been earned but not yet billed. They refer to revenues that are earned in a period, but have not been received and are unrecorded.
68 Which of the following is (are) true regarding timeliness and the importance of periodic reporting? (Check all that apply.) ~Your answer is correct. The value of information is often linked to its t imeliness. Decision makers require financial statements that are audited to insure reliability. Businesses report financial information at regular intervals to insure timeliness of data.
Accounting Cycle. Matching Principle
 CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
CHAPTER 3: PREPARING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
 CHAPTER 3: PREPARING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS I. TIMING AND REPORTING A. The Accounting Period Time period assumption an organization s activities can be divided into specific time periods. Examples: a month,
CHAPTER 3: PREPARING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS I. TIMING AND REPORTING A. The Accounting Period Time period assumption an organization s activities can be divided into specific time periods. Examples: a month,
CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS
 CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS TIME PERIOD ASSUMPTION The time period (or periodicity) assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods generally a
CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS TIME PERIOD ASSUMPTION The time period (or periodicity) assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods generally a
Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and
 Name: Due Date: December 12, 2011 Score: out of a possible 47 Course value: 7.5% Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and Worksheets A series of transactions are presented and their journal entries
Name: Due Date: December 12, 2011 Score: out of a possible 47 Course value: 7.5% Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and Worksheets A series of transactions are presented and their journal entries
Chapter 5 Accrual Adjustments and Financial Statement Preparation. Revenue recognition Matching expenses to revenues Expenses related to periods
 Chapter 5 Accrual Adjustments and Financial Statement Preparation Revenue recognition Matching expenses to revenues Expenses related to periods 1 The Measurement of Income major function of accounting
Chapter 5 Accrual Adjustments and Financial Statement Preparation Revenue recognition Matching expenses to revenues Expenses related to periods 1 The Measurement of Income major function of accounting
Accrual accounting ACCRUAL VERSUS CASH BASIS OF ACCOUNTING. ACCRUAL VERSUS CASH BASIS OF ACCOUNTING continued. Chapter 3
 Chapter 3 Accrual accounting concepts PowerPoint presentation by Anne Abraham University of Wollongong 2009 John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd ACCRUAL VERSUS CASH BASIS OF ACCOUNTING Accrual-based accounting
Chapter 3 Accrual accounting concepts PowerPoint presentation by Anne Abraham University of Wollongong 2009 John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd ACCRUAL VERSUS CASH BASIS OF ACCOUNTING Accrual-based accounting
> DO IT! Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts. Timing Concepts. Adjusting Entries for Deferrals D-12. Solution
 Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts Timing Concepts Review the glossary terms. Study carefully the revenue recognition principle, the expense recognition principle, and the time period assumption. Several
Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts Timing Concepts Review the glossary terms. Study carefully the revenue recognition principle, the expense recognition principle, and the time period assumption. Several
Time Period Assumption
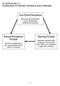 ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
The Work Sheet and the Closing Process
 C H A P T E R 4 The Work Sheet and the Closing Process A systematic approach is essential for efficient and accurate processing of large amounts of information. Whether work sheets are on paper or computerized,
C H A P T E R 4 The Work Sheet and the Closing Process A systematic approach is essential for efficient and accurate processing of large amounts of information. Whether work sheets are on paper or computerized,
'i*,; V' Your answer is correct! Match the Item on the left wlth the definition on the rtght.
 Match the Item on the left wlth the definition on the rtght. V' Your answer is correct! ~ Income statement """' ~ Reports a business's revenues and expenses for a period of time. ~ Balance sheet 1rt1 ~
Match the Item on the left wlth the definition on the rtght. V' Your answer is correct! ~ Income statement """' ~ Reports a business's revenues and expenses for a period of time. ~ Balance sheet 1rt1 ~
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments
 Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
How To Calculate A Trial Balance For A Company
 THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle
 Page 1 of 27 Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied the fundamental steps in recording accounting information by
Page 1 of 27 Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied the fundamental steps in recording accounting information by
ACCT1115. Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013
 ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle. Appendix 4A: Reversing entries
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance
 6-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance 6 Section 1: Closing Entries Section Objectives 1. Journalize and post
6-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance 6 Section 1: Closing Entries Section Objectives 1. Journalize and post
SMART TOUCH LEARNING Balance Sheet May 31, 2013 $ 4,800. $ 48,700 Accounts receivable 2,600. 900 Inventory 30,500. 100 Supplies.
 3 The Adjusting Process Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWNS? SMART TOUCH LEARNING ance Sheet May 31, 2013 Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWES?
3 The Adjusting Process Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWNS? SMART TOUCH LEARNING ance Sheet May 31, 2013 Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWES?
Chapter 13 Financial Statements and Closing Procedures
 Chapter 13 - Financial Statements and Closing Procedures Chapter 13 Financial Statements and Closing Procedures TEACHING OBJECTIVES 13-1) Prepare a classified income statement from the worksheet. 13-2)
Chapter 13 - Financial Statements and Closing Procedures Chapter 13 Financial Statements and Closing Procedures TEACHING OBJECTIVES 13-1) Prepare a classified income statement from the worksheet. 13-2)
Accumulated Depreciation Equipment
 Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle > DO IT! Worksheet Balance sheet: Extend assets to debit column. Extend liabilities to credit column. Extend contra assets to credit column. Extend drawings account
Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle > DO IT! Worksheet Balance sheet: Extend assets to debit column. Extend liabilities to credit column. Extend contra assets to credit column. Extend drawings account
Which of the following accounts impact equity? (Check all that apply.) Owner, Withdrawal. Expenses. Liabilities. Owner, Capital. Revenue.
 Which of the following accounts impact equity? (Check all that apply.) a Owner, Withdrawal & Expenses a Liabilities Owner, Capital & Revenue Assets ) ) ) ) The correct answer is shown. The T- account for
Which of the following accounts impact equity? (Check all that apply.) a Owner, Withdrawal & Expenses a Liabilities Owner, Capital & Revenue Assets ) ) ) ) The correct answer is shown. The T- account for
Adjusting Accounts and Preparing Financial Statements
 wil79549_ch03_0090-0133 07/30/2008 5:36 pm Page 90 pinnacle 201:MHBR055:mhwiL19:wiL19ch03: A Look Back Chapter 2 explained the analysis and recording of transactions. We showed how to apply and interpret
wil79549_ch03_0090-0133 07/30/2008 5:36 pm Page 90 pinnacle 201:MHBR055:mhwiL19:wiL19ch03: A Look Back Chapter 2 explained the analysis and recording of transactions. We showed how to apply and interpret
ACC 211/212: Double Entry Logs
 ACC 211/212: Double Entry Logs Journal Entries: o Credits are always indented (account name and value). o The sum of debits will always equal the sum of credits. o The month name is required only for the
ACC 211/212: Double Entry Logs Journal Entries: o Credits are always indented (account name and value). o The sum of debits will always equal the sum of credits. o The month name is required only for the
Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings
 Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Adjusting entries are made at the end of the accounting period to record all revenues and expenses that
Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Adjusting entries are made at the end of the accounting period to record all revenues and expenses that
Basic Accounting Principles
 Basic Accounting Principles Basic Accounting Model The basic accounting model represents the relationship between assets (what the company owns), liabilities (what the company owes), and owner s equity
Basic Accounting Principles Basic Accounting Model The basic accounting model represents the relationship between assets (what the company owns), liabilities (what the company owes), and owner s equity
The Adjusting Process
 Chapter 03.qxd 5/21/08 7:07 PM Page 99 C H A P T E R 3 AP Photo/Jeff Kravitz Fo r Sa le The Adjusting Process M A R V E L D E N T E R T A I N M E N T, N ot o you subscribe to any magazines? Most of us
Chapter 03.qxd 5/21/08 7:07 PM Page 99 C H A P T E R 3 AP Photo/Jeff Kravitz Fo r Sa le The Adjusting Process M A R V E L D E N T E R T A I N M E N T, N ot o you subscribe to any magazines? Most of us
Completing the Accounting Cycle
 C H A P T E R 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Flow of Accounting Information (slide 1 of 5) End-of-Period Spreadsheet (Work
C H A P T E R 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Flow of Accounting Information (slide 1 of 5) End-of-Period Spreadsheet (Work
Accounting Notes. Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value
 Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
PART A: TRUE/FALSE (1 point each):
 CHABOT COLLEGE General Accounting (BUS-7) Dmitriy Kalyagin PART A: TRUE/FALSE (1 point each): EXAM #4 (Chapters 10, 12, 13) 1. Employees who are exempt from the FLSA are entitled for overtime pay for hours
CHABOT COLLEGE General Accounting (BUS-7) Dmitriy Kalyagin PART A: TRUE/FALSE (1 point each): EXAM #4 (Chapters 10, 12, 13) 1. Employees who are exempt from the FLSA are entitled for overtime pay for hours
CHAPTER 4. Adjusting the accounts and preparing financial statements CONTENTS
 CHAPTER 4 Adjusting the accounts and preparing financial statements CONTENTS Demonstration problem 4.1 Adjusting entries and corrections 4.2 Adjusting centries and effect on financial statements 4.3 Adjusting
CHAPTER 4 Adjusting the accounts and preparing financial statements CONTENTS Demonstration problem 4.1 Adjusting entries and corrections 4.2 Adjusting centries and effect on financial statements 4.3 Adjusting
Accrual Accounting and the Financial Statements
 Accrual Accounting and the Financial Statements 3 LEARNING OBJECTIVES SPOTLIGHT Le Château has been selling fashion apparel, footwear, and accessories in Canada for over 50 years. What started as a single,
Accrual Accounting and the Financial Statements 3 LEARNING OBJECTIVES SPOTLIGHT Le Château has been selling fashion apparel, footwear, and accessories in Canada for over 50 years. What started as a single,
Preparing Financial Statements
 Carroll_CH03_023-040.qxd 8/10/06 4:37 PM Page 23 CHAPTER 3 Preparing Financial Statements OBJECTIVES F After reading this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the general process by which
Carroll_CH03_023-040.qxd 8/10/06 4:37 PM Page 23 CHAPTER 3 Preparing Financial Statements OBJECTIVES F After reading this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the general process by which
Accounting II Second Semester Final
 Name: Class: Date: Accounting II Second Semester Final Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Profit is the difference between:
Name: Class: Date: Accounting II Second Semester Final Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Profit is the difference between:
Chapter 3. Adjusting the accounts. Appendix 3A: An alternative method of recording deferrals
 1 Chapter 3 Adjusting the accounts Appendix 3A: An alternative method of recording deferrals 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare adjusting entries for prepaid expenses originally recorded in an expense account
1 Chapter 3 Adjusting the accounts Appendix 3A: An alternative method of recording deferrals 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare adjusting entries for prepaid expenses originally recorded in an expense account
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize revenue until next year after the games are played.
 CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
Module 6 Intro to Adjusting Entries
 Module 6 Intro to Adjusting Entries Entries required at the end of each accounting period to recognize on accrual basis: Revenues earned for the period Expenses that match the revenue earned And to report
Module 6 Intro to Adjusting Entries Entries required at the end of each accounting period to recognize on accrual basis: Revenues earned for the period Expenses that match the revenue earned And to report
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE. Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations:
 TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
Accrual Accounting Process
 Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
EXERCISES. Does not normally require adjustment. Normally requires adjustment (AE).
 EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
Accrual vs Deferral Accrual vs Cash Basis
 1 - Accrual vs Deferral Accrual vs Cash Basis - understanding debits and credits a transaction either increases or decreases the balance of accounts. increases and decreases in accounts are based on the
1 - Accrual vs Deferral Accrual vs Cash Basis - understanding debits and credits a transaction either increases or decreases the balance of accounts. increases and decreases in accounts are based on the
Adjusting Entries and the Work Sheet
 Heintz & Parry th Edition Chapter 5 th Edition College Accounting Adjusting Entries and the Work Sheet 1 Prepare end-of-period adjustments. END-OF-PERIOD ADJUSTMENTS Changes occur that affect the business
Heintz & Parry th Edition Chapter 5 th Edition College Accounting Adjusting Entries and the Work Sheet 1 Prepare end-of-period adjustments. END-OF-PERIOD ADJUSTMENTS Changes occur that affect the business
Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle
 Course Schedule Course Modules Review and Practice Exam Preparation Resources Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied
Course Schedule Course Modules Review and Practice Exam Preparation Resources Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied
The worksheet for Hancock Company shows the following in the financial statement
 Chapter 4 Do it! Susan Elbe is preparing a worksheet. Explain to Susan how she should extend the following adjusted trial balance accounts to the financial statement columns of the worksheet. Cash Accumulated
Chapter 4 Do it! Susan Elbe is preparing a worksheet. Explain to Susan how she should extend the following adjusted trial balance accounts to the financial statement columns of the worksheet. Cash Accumulated
Review of Accounting Principles
 Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers
 Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING MODEL
 CHAPTER 1 PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING MODEL OBJECTIVES The objectives of this part are: To introduce a definition of accounting, the need for accounting information, and the various accounting
CHAPTER 1 PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING MODEL OBJECTIVES The objectives of this part are: To introduce a definition of accounting, the need for accounting information, and the various accounting
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS. Lecture Outline
 CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
SOLUTIONS. Learning Goal 16
 Learning Goal 16: Prepare Closing Entries S1 Learning Goal 16 Multiple Choice 1. d 2. a 3. b 4. d Because drawing is closed directly into the capital account, not into income summary. 5. c 6. b This a
Learning Goal 16: Prepare Closing Entries S1 Learning Goal 16 Multiple Choice 1. d 2. a 3. b 4. d Because drawing is closed directly into the capital account, not into income summary. 5. c 6. b This a
MIDTERM EXAMINATION. [email protected]. Fall 2009
 MIDTERM EXAMINATION [email protected] Fall 2009 FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis Asslam O Alikum FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis (Session 3) solved by Afaaq n Shani Bhai with reference n numerical
MIDTERM EXAMINATION [email protected] Fall 2009 FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis Asslam O Alikum FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis (Session 3) solved by Afaaq n Shani Bhai with reference n numerical
Reporting and Analyzing Cash Flows QUESTIONS
 Chapter 12 Reporting and Analyzing Cash Flows QUESTIONS 1. The purpose of the cash flow statement is to report all major cash receipts (inflows) and cash payments (outflows) during a period. It helps users
Chapter 12 Reporting and Analyzing Cash Flows QUESTIONS 1. The purpose of the cash flow statement is to report all major cash receipts (inflows) and cash payments (outflows) during a period. It helps users
How To Account For Revenue Under Accrual Accounting
 BAT 4M: Chapter 3 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 01. (a) Under the time period assumption, an accountant is required to determine the relevance of each business transaction to specific accounting periods, and its
BAT 4M: Chapter 3 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 01. (a) Under the time period assumption, an accountant is required to determine the relevance of each business transaction to specific accounting periods, and its
Chapter 5 Accounting for Merchandising Operations
 Chapter 5 Accounting for Merchandising Operations Purchase Transactions Purchaser records goods at cost. When goods are returned, purchaser reduces Inventory. On September 5, De La Hoya Company buys merchandise
Chapter 5 Accounting for Merchandising Operations Purchase Transactions Purchaser records goods at cost. When goods are returned, purchaser reduces Inventory. On September 5, De La Hoya Company buys merchandise
1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000.
 Rallis Page 1 Name: _ Date: 1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000. A) True B) False 2. If total liabilities decreased by
Rallis Page 1 Name: _ Date: 1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000. A) True B) False 2. If total liabilities decreased by
The Matching Concept and the Adjusting Process
 The Matching Concept and the Adjusting Process o b j e c t i v e s After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 4 Explain how the matching concept relates to the accrual basis of accounting. Explain
The Matching Concept and the Adjusting Process o b j e c t i v e s After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 4 Explain how the matching concept relates to the accrual basis of accounting. Explain
Reporting and Interpreting Liabilities Irwin/McGraw-Hill
 Chapter 9 Reporting and Interpreting Liabilities Business Background The acquisition of assets is financed from two sources: Debt - funds from creditors Equity - funds from owners Business Background The
Chapter 9 Reporting and Interpreting Liabilities Business Background The acquisition of assets is financed from two sources: Debt - funds from creditors Equity - funds from owners Business Background The
COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries -
 COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries - Worksheet Overview Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Account Titles Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit
COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries - Worksheet Overview Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Account Titles Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit
How To Adjust For The Year End
 ACCOUNTING 30S WORKSHEET ON ADJUSTING ENTRIES Put on your thinking caps and sharpen your pencils boys and girls it's time to practice with adjusting entries! 1. Give in general journal form the year-end
ACCOUNTING 30S WORKSHEET ON ADJUSTING ENTRIES Put on your thinking caps and sharpen your pencils boys and girls it's time to practice with adjusting entries! 1. Give in general journal form the year-end
Study Guide - Final Exam Accounting I
 Study Guide - Final Exam Accounting I True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. Entries in a sales journal affect account balances in both the accounts receivable ledger
Study Guide - Final Exam Accounting I True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. Entries in a sales journal affect account balances in both the accounts receivable ledger
Accounting Skills Assessment Practice Exam Page 1 of 10
 NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 3 THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM OVERVIEW Accounting information must be accumulated and summarized before it can be communicated and analysed. In this chapter, we will discuss the steps involved
CHAPTER 3 THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM OVERVIEW Accounting information must be accumulated and summarized before it can be communicated and analysed. In this chapter, we will discuss the steps involved
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions
 Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
Adjusting the Accounts
 HOSP 1210 (Financial Acct) Learning Centre Adjusting the Accounts Anytime we prepare financial statements or reach the end of an accounting period, there are account adjustments that need to be made to
HOSP 1210 (Financial Acct) Learning Centre Adjusting the Accounts Anytime we prepare financial statements or reach the end of an accounting period, there are account adjustments that need to be made to
E2-2: Identifying Financing, Investing and Operating Transactions?
 E2-2: Identifying Financing, Investing and Operating Transactions? Listed below are eight transactions. In each case, identify whether the transaction is an example of financing, investing or operating
E2-2: Identifying Financing, Investing and Operating Transactions? Listed below are eight transactions. In each case, identify whether the transaction is an example of financing, investing or operating
Supplement to CHAPTER 3 CLOSING ENTRIES AND THE WORK SHEET
 Supplement to CHAPTER 3 CLOSING ENTRIES AND THE WORK SHEET Answers to Review Questions 1. No, the work sheet cannot be used as a substitute for the financial statements. It is a tool used in preparing
Supplement to CHAPTER 3 CLOSING ENTRIES AND THE WORK SHEET Answers to Review Questions 1. No, the work sheet cannot be used as a substitute for the financial statements. It is a tool used in preparing
ACCOUNTING COMPETENCY EXAM SAMPLE EXAM. 2. The financial statement or statements that pertain to a stated period of time is (are) the:
 ACCOUNTING COMPETENCY EXAM SAMPLE EXAM 1. The accounting process does not include: a. interpreting d. observing b. reporting e. classifying c. purchasing 2. The financial statement or statements that pertain
ACCOUNTING COMPETENCY EXAM SAMPLE EXAM 1. The accounting process does not include: a. interpreting d. observing b. reporting e. classifying c. purchasing 2. The financial statement or statements that pertain
CHAPTER 4 Accrual Accounting Concepts Study Objectives
 CHAPTER 4 Accrual Accounting Concepts Study Objectives Explain the revenue recognition principle and the matching principle. Differentiate between the cash basis and the accrual basis of accounting. Explain
CHAPTER 4 Accrual Accounting Concepts Study Objectives Explain the revenue recognition principle and the matching principle. Differentiate between the cash basis and the accrual basis of accounting. Explain
CHAPTER 4 The Mechanics of Financial Accounting
 CHAPTER 4 The Mechanics of Financial Accounting SYNOPSIS This chapter covers the mechanics underlying preparation of financial statements and how they help to ensure that a company s transactions are accurately
CHAPTER 4 The Mechanics of Financial Accounting SYNOPSIS This chapter covers the mechanics underlying preparation of financial statements and how they help to ensure that a company s transactions are accurately
RAPID REVIEW Chapter Content
 RAPID REVIEW BASIC ACCOUNTING EQUATION (Chapter 2) INVENTORY (Chapters 5 and 6) Basic Equation Assets Owner s Equity Expanded Owner s Owner s Assets Equation = Liabilities Capital Drawing Revenues Debit
RAPID REVIEW BASIC ACCOUNTING EQUATION (Chapter 2) INVENTORY (Chapters 5 and 6) Basic Equation Assets Owner s Equity Expanded Owner s Owner s Assets Equation = Liabilities Capital Drawing Revenues Debit
Glossary of Accounting Terms Peter Baskerville
 Glossary of Accounting Terms Peter Baskerville Account for or 'bring to account': An accounting phrase used to describe the recording of a financial transaction that is required under the generally accepted
Glossary of Accounting Terms Peter Baskerville Account for or 'bring to account': An accounting phrase used to describe the recording of a financial transaction that is required under the generally accepted
Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed
 Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of accounting?
Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of accounting?
Accounting Principles Critical to Success Presented By: C. P. Krishnan. www.cakintl.com
 Accounting Principles Critical to Success Presented By: C. P. Krishnan Basic Accounting You Need to Know Assets, Liabilities, Equity, Income, & Expenses Assets Includes what you have and what people owe
Accounting Principles Critical to Success Presented By: C. P. Krishnan Basic Accounting You Need to Know Assets, Liabilities, Equity, Income, & Expenses Assets Includes what you have and what people owe
TOPIC LEARNING OBJECTIVE
 Topic Mapping 1 Transaction Analysis Understand the effect of various types of transactions on the accounting equation, accounting journal and accounting ledger. Concepts and Skills Accounting Equation
Topic Mapping 1 Transaction Analysis Understand the effect of various types of transactions on the accounting equation, accounting journal and accounting ledger. Concepts and Skills Accounting Equation
CHAPTER 12 ACCRUALS, DEFERRALS, AND THE WORKSHEET
 CHAPTER 12 ACCRUALS, DEFERRALS, AND THE WORKSHEET Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students may assess that an unexpected decline in sales would mean surplus inventory which would have to be reduced
CHAPTER 12 ACCRUALS, DEFERRALS, AND THE WORKSHEET Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students may assess that an unexpected decline in sales would mean surplus inventory which would have to be reduced
CHAPTER 10 Financial Statements NOTE
 NOTE In practice, accruals accounts and prepayments accounts are implied rather than drawn up. It is common for expense accounts to show simply a balance c/d and a balance b/d. The accrual or prepayment
NOTE In practice, accruals accounts and prepayments accounts are implied rather than drawn up. It is common for expense accounts to show simply a balance c/d and a balance b/d. The accrual or prepayment
Midterm Fall 2012 Solution
 Midterm Fall 2012 Solution Instructions: 1) Answers for the multiple-choice questions must be recorded on the UW answer card. All other questions must be answered in the space provided on the examination
Midterm Fall 2012 Solution Instructions: 1) Answers for the multiple-choice questions must be recorded on the UW answer card. All other questions must be answered in the space provided on the examination
Accounting for Changes and Errors
 CHAPTER Accounting for Changes and Errors OBJECTIVES After careful study of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Identify the types of accounting changes. 2. Explain the methods of disclosing an accounting
CHAPTER Accounting for Changes and Errors OBJECTIVES After careful study of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Identify the types of accounting changes. 2. Explain the methods of disclosing an accounting
CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives
 CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives Chapter 1 Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting Equation After studying Chapter 1, you will be able to: 1. Define accounting
CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives Chapter 1 Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting Equation After studying Chapter 1, you will be able to: 1. Define accounting
In the event of a tie, the score on the last ten questions will be used as a tie-breaker.
 NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING II 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING II 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
Accounting Principles Dr. Mishari Alfraih. Adjusting the Accounts
 Accrual- vs. Cash-Basis Accounting Accrual-Basis Accounting Adjusting the Accounts Transactions recorded in the periods in which the events occur Revenues are recognized when earned, rather than when cash
Accrual- vs. Cash-Basis Accounting Accrual-Basis Accounting Adjusting the Accounts Transactions recorded in the periods in which the events occur Revenues are recognized when earned, rather than when cash
CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY. Multiple Choice Questions
 sg st a CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 C 9. 2 C 17. 5 C
sg st a CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 C 9. 2 C 17. 5 C
Preparing cash budgets
 3 Preparing cash budgets this chapter covers... In this chapter we will examine in detail how a cash budget is prepared. This is an important part of your studies, and you will need to be able to prepare
3 Preparing cash budgets this chapter covers... In this chapter we will examine in detail how a cash budget is prepared. This is an important part of your studies, and you will need to be able to prepare
Chapter 07 - Accounts and Notes Receivable. Chapter Outline
 Chapter 07 - Accounts and Receivable I. Accounts Receivable A receivable is an amount due from another party. Accounts Receivable are amounts due from customers for credit sales. A. Recognizing Accounts
Chapter 07 - Accounts and Receivable I. Accounts Receivable A receivable is an amount due from another party. Accounts Receivable are amounts due from customers for credit sales. A. Recognizing Accounts
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO School of Accounting and Finance
 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO School of Accounting and Finance AFM 101 Professor Shari Mann Professor Donna Psutka Professor Mindy Wolfe Mid-Term Examination Fall 2010 Date and Time: October 21, 2010, 6:30 8:00pm
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO School of Accounting and Finance AFM 101 Professor Shari Mann Professor Donna Psutka Professor Mindy Wolfe Mid-Term Examination Fall 2010 Date and Time: October 21, 2010, 6:30 8:00pm
Fundamentals of Financial Accounting
 Fundamentals of Financial Accounting CHAPTER I Accounting in action. What is accounting? Accounting is the recording of financial transactions plus storing, sorting, retrieving, summarizing, and presenting
Fundamentals of Financial Accounting CHAPTER I Accounting in action. What is accounting? Accounting is the recording of financial transactions plus storing, sorting, retrieving, summarizing, and presenting
The Statement of Cash Flows
 CHAPTER The Statement of Cash Flows OBJECTIVES After careful study of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Define operating, investing, and financing activities. 2. Know the categories of inflows and
CHAPTER The Statement of Cash Flows OBJECTIVES After careful study of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Define operating, investing, and financing activities. 2. Know the categories of inflows and
a. $ 65,000. b. $ 80,000. c. $130,000. d. $145,000.
 注 意 1. 本 試 題 卷 共 50 題, 總 分 100 分 第 01-15 題, 每 題 1.75 分, 合 計 26.25 分 ; 第 16-35 題, 每 題 2 分, 合 計 40 分 ; 第 36-50 題, 每 題 2.25 分, 合 計 33.75 答 錯 不 倒 扣 2. 請 將 答 案 按 試 題 題 號, 依 序 填 入 答 案 卡 1.FastForward had cash
注 意 1. 本 試 題 卷 共 50 題, 總 分 100 分 第 01-15 題, 每 題 1.75 分, 合 計 26.25 分 ; 第 16-35 題, 每 題 2 分, 合 計 40 分 ; 第 36-50 題, 每 題 2.25 分, 合 計 33.75 答 錯 不 倒 扣 2. 請 將 答 案 按 試 題 題 號, 依 序 填 入 答 案 卡 1.FastForward had cash
CHAPTER 4 THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE: ACCRUALS AND DEFERRALS
 CHAPTER 4 THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE: ACCRUALS AND DEFERRALS OVERVIEW OF BRIEF EXERCISES, EXERCISES, PROBLEMS, AND CRITICAL THINKING CASES Brief Exercises B. Ex. 4.1 B. Ex. 4.2 B. Ex. 4.3 B. Ex. 4.4 Topic Deferred
CHAPTER 4 THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE: ACCRUALS AND DEFERRALS OVERVIEW OF BRIEF EXERCISES, EXERCISES, PROBLEMS, AND CRITICAL THINKING CASES Brief Exercises B. Ex. 4.1 B. Ex. 4.2 B. Ex. 4.3 B. Ex. 4.4 Topic Deferred
Advanced Financial Accounting
 Advanced Financial Accounting Sample Paper 2 Questions & Suggested Solutions Page 1 of 27 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES PLEASE READ CAREFULLY Candidates must indicate clearly whether they are answering the
Advanced Financial Accounting Sample Paper 2 Questions & Suggested Solutions Page 1 of 27 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES PLEASE READ CAREFULLY Candidates must indicate clearly whether they are answering the
Chapter 2. Analyzing transactions
 1 Chapter 2 Analyzing transactions 2 Learning objectives 1. Explain the steps in the accounting cycle and each step s supporting documentation 2. Explain the purpose of source documents 3. Describe an
1 Chapter 2 Analyzing transactions 2 Learning objectives 1. Explain the steps in the accounting cycle and each step s supporting documentation 2. Explain the purpose of source documents 3. Describe an
Accruals, Deferrals,
 12-1 McGraw-Hill 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Accruals, Deferrals, 12 and the Worksheet Section 1: Calculating and Recording Adjustments Section Objectives 1. Determine
12-1 McGraw-Hill 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Accruals, Deferrals, 12 and the Worksheet Section 1: Calculating and Recording Adjustments Section Objectives 1. Determine
Glossary of Accounting Terms
 Glossary of Accounting Terms Account - Something to which transactions are assigned. Accounts in MYOB are in one of eight categories: Asset Liability Equity Income Cost of sales Expense Other income Other
Glossary of Accounting Terms Account - Something to which transactions are assigned. Accounts in MYOB are in one of eight categories: Asset Liability Equity Income Cost of sales Expense Other income Other
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO School of Accounting and Finance
 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO School of Accounting and Finance AFM 101 Professor Duane Kennedy Mid-Term Examination Fall 2008 Date and Time: October 16, 2008, 7:15 8:45pm Pages: 16, including cover Name: Student
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO School of Accounting and Finance AFM 101 Professor Duane Kennedy Mid-Term Examination Fall 2008 Date and Time: October 16, 2008, 7:15 8:45pm Pages: 16, including cover Name: Student
3 Accrual Accounting & Income
 29366_10_ch3_p125-196 12/12/07 5:50 PM Page 125 3 Accrual Accounting & Income SPOTLIGHT STARBUCKS CORPORATION Starbucks has changed coffee from a breakfast drink to an experience. The corporation began
29366_10_ch3_p125-196 12/12/07 5:50 PM Page 125 3 Accrual Accounting & Income SPOTLIGHT STARBUCKS CORPORATION Starbucks has changed coffee from a breakfast drink to an experience. The corporation began
Student Solutions Manual to Accompany. Introduction to Financial Accounting. David Annand. Based on International Financial Reporting Standards
 Student Solutions Manual to Accompany Introduction to Financial Accounting Based on International Financial Reporting Standards David Annand Copyright 2014 David Annand Published by David Annand 4910C
Student Solutions Manual to Accompany Introduction to Financial Accounting Based on International Financial Reporting Standards David Annand Copyright 2014 David Annand Published by David Annand 4910C
Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II
 Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II Part One (30%) 1. Give the Chinese/English of the following terms: (5%) subsidiary ledger 统 制 账 户 purchase requisition 现 金 溢 缺 petty cash fund 永 续 盘 存 制
Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II Part One (30%) 1. Give the Chinese/English of the following terms: (5%) subsidiary ledger 统 制 账 户 purchase requisition 现 金 溢 缺 petty cash fund 永 续 盘 存 制
Chapter 1 Accounting in action
 Chapter 1 Accounting in action What is Accounting Accounting is the financial information system that consists of three basic activities-it identifies, records, and communicates the economic events of
Chapter 1 Accounting in action What is Accounting Accounting is the financial information system that consists of three basic activities-it identifies, records, and communicates the economic events of
Dr. M. D. Chase BA 201 Examination 1J
 Dr. M. D. Chase BA 201 Examination 1J Instructions: 1. Place your Name, Code Number of the Examination and the Examination Number on your Scantron form. Failure to follow these instructions will result
Dr. M. D. Chase BA 201 Examination 1J Instructions: 1. Place your Name, Code Number of the Examination and the Examination Number on your Scantron form. Failure to follow these instructions will result
CHAPTER 3. BE3-2 Advertising. Dec. 31 Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 to adjust. BE3-3 Bere Co.
 CHAPTER 3 BE3-2 Advertising Advertising Supplies Supplies Expense 8700 7200 7200 1500 7200 Dec. Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 BE3-3 Bere Co. Prepaid Insurance Insurance Expense
CHAPTER 3 BE3-2 Advertising Advertising Supplies Supplies Expense 8700 7200 7200 1500 7200 Dec. Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 BE3-3 Bere Co. Prepaid Insurance Insurance Expense
