Management of Chickenpox and Shingles Policy
|
|
|
- Alberta McDaniel
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Management of Chickenpox and Shingles Policy Version Number 3 Version Date June 2016 Owner Author First approval or date last reviewed Staff/Groups Consulted Director of Infection Prevention and Control Nurse Consultant Infection Control October 2010 Adapted from the Policy in use at Taunton & Somerset NHS Foundation Trust. The following groups have been consulted: Infection Control Doctor Medical Director Director of Infection Prevention and Control Associate Directors of Nursing Matrons Infection Prevention Control team Approved by IPCC July 2016 Next Review Due July 2019
2 1. RATIONALE 1.1. To set out the actions to be taken when caring for patients with suspected or confirmed chickenpox or shingles. To ensure that any non-immune individuals exposed are managed appropriately The aim of these guidelines is to provide healthcare workers with the necessary information in relation to: The infection prevention and control management of inpatients with chickenpox or shingles. The management of non-immune inpatients exposed to individuals with chickenpox or shingles. 2. KEY POINTS 2.1. Chickenpox is highly infectious and easily spread Chickenpox is usually a relatively mild infection in childhood but in adults and some groups (neonates, pregnant women, immunosuppressed) there may be more serious complications Shingles cannot be passed from person to person, however the virus from shingles lesions can cause chickenpox in those who have never had chickenpox before Staff who are not immune to chickenpox should not care for patients with either infective chickenpox or shingles If contact tracing of exposed patients is required this will be carried out by the Infection Prevention and Control Team (IPCT) in liaison with Public Health England (PHE). Contact tracing of exposed staff will be carried out by the Trust s Occupational Health Service in conjunction with Ward/Department managers. 3. BACKGROUND 3.1. Varicella zoster virus is a member of the Herpes virus family and causes two common infections, chickenpox and shingles. Chickenpox (varicella zoster) is the primary infection and usually results in lifetime immunity. Around 90% of the adult population born and raised in the UK are immune Chickenpox is not a notifiable disease in England and Wales Following chickenpox infection the virus remains dormant in dorsal root and cranial nerve ganglia and may be reactivated at a later date causing shingles (herpes zoster). 4. DEFINITION OF TERMS 4.1 Incubation period period of time from exposure to development of symptoms 4.2 Period of infectivity period of time when the individual is infectious 4.3 Maculopapular rash a large red area with confluent bumps
3 4.4 Vesicles small fluid filled blisters 4.5 Foetal varicella syndrome characterised by one or more of the following: skin scarring, eye defects, limb hypoplasia, neurological abnormalities and dysfunction of bladder and bowel sphincters. 4.6 Neonate baby from birth to 4 weeks of age. 4.7 Disseminated shingles widespread shingles. The virus affects multiple body systems and generally only occurs in those whose immune system is not fully functioning. 5. DUTIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES 5.1 The Director of Infection Prevention and Control (DIPC) is responsible for overseeing this policy and its implementation. 5.2 The Infection Prevention & Control (IP&C) Team are responsible for: Advising and supporting clinical staff in the management of inpatients with chickenpox or shingles. Carrying out necessary contact tracing and management of in-patients exposed to chickenpox or shingles in liaison with the clinical team caring for the patient. Liaising with Occupational Health regarding any patient or healthcare worker diagnosed with chickenpox or shingles so contact management of other staff can be initiated. 5.3 Occupational health (OH) is responsible for: Liaising with the IP&C team in the event of a member of staff developing chickenpox or shingles at work so contact management of patients can be initiated. Carrying out any necessary contact tracing and subsequent management of exposed staff. Advising staff exposed to or infected with chickenpox or shingles. 5.4 Ward managers / Matrons are responsible for ensuring all their staff are aware of and follow the actions of this policy. 5.5 All staff are responsible for: Ensuring the infection control precautions detailed in this policy are followed for any patient with suspected or confirmed chickenpox or shingles. Informing the IP&C team if a patient is admitted or develops chickenpox or shingles during their hospital stay. Informing the OH service if they are not immune and they develop chickenpox or shingles at work or are exposed to a case of chickenpox or shingles.
4 Following the actions of this policy. 6. CLINICAL FEATURES 6.1 Chickenpox usually begins with fever and malaise followed by a maculopapular rash progressing to vesicle formation, mainly over the trunk but extending to face, scalp and limbs. The rash often appears in 'crops' over the course of several days. The severity of chickenpox varies and it is possible to be infected but show no symptoms. 6.2 Chickenpox is usually a relatively mild infection but for adults and some groups (neonates, pregnant women, immune-suppressed) there may be more serious complications. These include viral pneumonia, secondary bacterial infections and encephalitis. In addition there are risks to the foetus or neonate if women develop chickenpox during pregnancy. The risks are related to gestation at the time of infection. 6.3 Shingles is caused by the reactivation of an individual's varicella virus and is a localised infection. It begins with increased sensitivity or a burning sensation over an area of skin, known as a dermatome, which follows the line of a nerve. A red vesicular rash then occurs over the same area. It most commonly occurs over one side of the chest, abdomen or around the eye (ophthalmic or facial shingles). 7 IMMUNITY 7.1 Chickenpox infection usually results in lifetime immunity to the virus so re-infection is very rare. A definite history of chickenpox or shingles indicates immunity however, this is a less reliable predictor of immunity for those born and raised outside of the UK and serology testing for the presence of varicella zoster antibodies may be required. A documented history of varicella vaccination (i.e. 2 doses of vaccine) is also satisfactory evidence of immunity. Post Vaccination testing is only considered in staff working with highly vulnerable patients. 7.2 For those who are immunosuppressed, a past history of chickenpox or shingles is not a definitive indication of immunity. For these individuals, serological confirmation of immunity should be considered in the event of exposure. 8. TRANSMISSION AND INFECTIVITY 8.1 Chickenpox is highly infectious. The virus is shed from both the naso-pharynx and vesicles on the skin, therefore transmission occurs via: Airborne spread of respiratory secretions. Direct contact with vesicles and vesicular fluid. Contact with clothing, bedding, equipment, etc. contaminated with respiratory secretions or vesicular fluid. 8.2 The incubation period for chickenpox is between 10 and 21 days following significant exposure to an individual with chickenpox or shingles. 8.3 Individuals are normally regarded as infectious from 2 days prior to the development of the rash until all the vesicles have crusted over, which usually occurs around 7 days after the onset of the rash. Infectivity may be prolonged in patients with altered immunity.
5 8.4 Significant exposure to chickenpox is assessed as: Face to face contact with a case of chickenpox (e.g. having a conversation). Being in the same room, bay or whole ward (if nightingale) for 15 minutes or longer with a case of chickenpox. Direct contact with a case of chickenpox at any point in the period of time 48 hours before the rash appears until all the vesicles have crusted over. 8.5 Shingles occurs from reactivation of the varicella virus that has lain dormant in nerve tissue following previous infection with chickenpox. Shingles cannot be passed from person to person, however individuals with shingles will shed varicella zoster virus from the vesicles. This can result in the development of chickenpox in those who have never had chickenpox before. 8.6 The route of transmission of varicella virus from an individual with shingles is via direct contact with vesicles or vesicular fluid. 8.7 Individuals are not infectious until appearance of the shingles rash. They then remain infectious until all the vesicles have crusted over. This is usually about 7 days after onset of the rash. 8.8 Significant exposure to shingles is assessed as: Close/direct contact with vesicles or vesicular fluid from an individual with shingles. Contact with a case of disseminated shingles. Contact with immunosuppressed individuals with shingles on any part of the body (viral shedding will be greater in these individuals). Contact with the case between the periods of onset of rash until all vesicles are crusted over. 9. VACCINATION & TREATMENT 9.1 Currently there is no widespread varicella vaccination programme in the UK however; since 2003 the Department of Health recommend chickenpox vaccination for all nonimmune healthcare workers. Vaccination may also be considered prophylactically (within three days of exposure) on advice of the Consultant Occupational Health Physician. 9.2 Chickenpox infection is usually self-limiting and management is usually based on symptom reduction. For some groups at risk of developing serious complications may require antiviral drugs or immunoglobulin. Treatment of shingles with antiviral drugs may reduce symptoms. The decision to initiate treatment of either chickenpox or shingles will be made by the clinician responsible for the patient. Advice is available from the Consultant Microbiologists.
6 10.0 ACTION TO BE TAKEN IN EVENT OF CHICKENPOX/SHINGLES OCCURRING ON A WARD 10.1 Only staff with a definite history of chickenpox/shingles or a blood test demonstrating Immunity should provide care for any patient with suspected or confirmed chickenpox or shingles Patients with suspected or confirmed chickenpox or infectious shingles must not be nursed on Oncology wards or near other patients who are immunosuppressed unless there is an urgent clinical need. In this situation further advice can be obtained from the IPCT or on call microbiologists to help reduce the risks to other patients For patients with suspected or confirmed chickenpox or shingles on a ward the following action should be taken (see Flow Chart One) Isolate patient (index case) immediately. Difficulty in isolating should be escalated to the IP&C team / Clinical Site Manager. Instigate infection control precautions as detailed in Appendix A. Inform IPCT on Ext 4401 In conjunction with IPCT make a list of any individuals (patients, staff and visitors) that may have had contact with the index case (contacts). 11. MANAGEMENT OF CONTACTS 11.1 In the event of a patient developing chickenpox or shingles during their stay other patients, visitors and staff may be at risk of chickenpox infection if their exposure has been significant and they do not have immunity Managing contacts of an index case involves the following process: Assessment of immunity status of all contacts. Assessment of the significance and timing of the exposure of potentially nonimmune contacts. Deciding if prophylactic Varicella Zoster Immunoglobulin (VZIG) is required The following process should be followed for all potential contacts: Assess the immunity status of all the potential contacts using assessment criteria in Flow Chart Two. Assess the significance and timing of the exposure of all potentially nonimmune contacts using assessment criteria in Appendix B. All individuals who are potentially non-immune and are assessed as having had significant exposure should be listed on the form contained in Appendix C. These names should be given to either Occupational Health, PHE or IPCT, i.e. - Staff who are unvaccinated or without a definite history of chickenpox or shingles, and having a significant exposure to VZV, should either be excluded from contact with high-risk patients from 8 to 21 days after
7 - - exposure, or should be advised to inform OH before having patient contact if they feel unwell or develop a fever or rash. OH are able to provide VZ vaccination to staff who are proven non-immune and within three days of exposure as prophylaxis/to lessen the severity of the disease should it develop. Patient contacts who are not immune or for whom immunity is not definitive and have had significant exposure will be followed up by the IPCT. The need for prophylactic VZIG will be made by the Clinician responsible for the patients care in liaison with a Consultant Microbiologist. These patients should be managed as potentially infectious from 8 to 21 days after exposure to the index case. If VZIG is given they should be managed as potentially infectious from 8 to 28 days since VZIG extends the incubation period. Visitors or close family contacts to the index case will be assessed by the IPCT who will liaise with PHE as necessary. 12. VARICELLA ZOSTER EXPOSURE IN PREGNANCY 12.1 The majority of pregnant women will already be immune to chickenpox. If immune, exposure to individuals with either chickenpox or shingles presents no risks to mother or the foetus and no action is required Pregnant women who have never had chickenpox should avoid exposure to anyone with either chickenpox or shingles during the infectious period Pregnant women who have never had chickenpox or have no recollection of previous chickenpox or shingles who have significant contact with a case of chickenpox or shingles must have serology testing to check for presence of varicella zoster (VZ) antibodies. VZIG is recommended for all VZ antibody negative pregnant contacts exposed at any stage of pregnancy, providing VZIG can be given within 10 days of exposure If VZIG is given the pregnant woman should be managed as potentially infectious from 8-28 days after exposure. If VZIG is not given the pregnant woman should be managed as potentially infectious from 8-21days after exposure Any pregnant woman who has any exposure to chickenpox or shingles (regardless of whether or not they have received VZIG) should be asked to notify their Dr or midwife immediately if a rash develops VZIG has a short duration of effect and therefore a second dose may be required if a further exposure is reported and 3 weeks have elapsed since the last dose VZIG is not required as prophylaxis for non-immune women after delivery of the baby since they are no longer at high risk for complications of chickenpox once they have delivered. 13. VARICELLA ZOSTER INFECTION IN PREGNANCY 13.1 Pregnant women who develop chickenpox are at greater risk of complications themselves which may require hospitalisation e.g. viral pneumonia, haemorrhagic rash. The severity of complications seems to increase in later gestation.
8 13.2 Pregnant women with chickenpox must not be admitted to the maternity unit unless there is an overriding obstetric clinical need. If admission to the maternity unit is required they must not mix with other mothers or babies whilst still infectious. The same infection control measures should be applied as outlined in Appendix A Varicella zoster immunoglobulin (VZIG) has no therapeutic benefit once chickenpox has developed so is not indicated for maternal chickenpox during pregnancy. The use of antivirals should be made on an individual basis by the Clinician responsible for the patient with advice available from the Consultant Microbiologists There are risks to the foetus and/or new-born if the mother develops chickenpox during pregnancy. The severity of these risks depends on gestation at the time of infection Chickenpox in the first trimester does not increase the risk of miscarriage Chickenpox in the first 28 weeks of pregnancy is associated with foetal varicella syndrome. This is a serious condition that affects foetal development Maternal chickenpox around the time of birth exposes the neonate to varicella zoster virus and there is a risk the baby may be born with chickenpox. Elective delivery (including caesarean) should be avoided, where clinically possible, until 5-7 days after the onset of maternal rash to allow for the passive transfer of antibodies from mother to child. 14. NEONATAL EXPOSURE OR INFECTION 14.1 Neonates born to mothers who were immune to chickenpox will have passively acquired immunity. They are not at risk if exposed to cases of chickenpox or shingles unless they were born before 28 weeks gestation or weighed less than 1 kg at birth as they may lack these maternal antibodies VZIG is recommended for all non-immune neonates that are exposed to a case of chickenpox or shingles within the first 7 days of life VZIG prophylaxis is recommended in the following cases of neonatal exposure: Neonates born before 28 weeks gestation or who weighed less than 1 kg at birth Neonates born to mothers with no immunity to chickenpox Neonates born to mothers who develop chickenpox around or soon after delivery. If birth occurs within 7 days of onset of maternal rash the neonate should be given VZIG Neonates born to mothers who develop shingles around the time of delivery will have passive acquired immunity and are not at risk of developing chickenpox unless they were delivered before 28 weeks gestation or weighed less than 1 kg at birth Administration of VZIG does not guarantee the prevention of chickenpox in the neonate and extends the incubation period. All neonates who have received VZIG should be monitored for signs of infection up to 28 days from exposure or in the case
9 of maternal chickenpox 28 days from onset of chickenpox in the mother. VZIG is of no benefit once neonatal chickenpox has developed Mothers with chickenpox should be allowed to breast feed. If they have lesions close to the nipple, they should express milk from the affected breast until the lesions have crusted. This expressed milk can be fed to the baby if they are covered by VZIG and/or antivirals. 15. IMMUNOSUPRESSED PATIENTS 15.1 Immunosuppressed patients are at risk of severe varicella infection. Vesicles may arise for several weeks prolonging the period of infectivity in these patients. There is an increased risk that the virus will disseminate throughout the organs of immunosuppressed individuals. In addition any that develop chickenpox or shingles will shed higher levels of the virus and therefore become a higher risk to other individuals that are not immune to chickenpox Immunosuppressed patients include the following conditions: Severe primary immunodeficiency. Malignant disease treated with immunosuppressive chemotherapy or radiotherapy (classed as immunosuppressed for at least 6 months after terminating such treatment). All patients who have received a solid organ transplant and are currently on immunosuppressant treatment. Patients who have received a bone marrow transplant until at least 12 months after finishing all immunosuppressant treatment or longer if the patient develops graft- versus- host disease. All patients receiving systemic high-dose steroids until at least 3 months after treatment has stopped. This includes children who receive prednisolone at a daily dose (or its equivalent) of 2mg/kg/day for at least one week or 1mg/kg/day for one month. For adults an equivalent dose is harder to define but immunosuppression should be considered in those who receive 40mg of prednisolone per day for more than one week. All patients receiving other types of immunosuppressant drugs (e.g. azathiopine, methotrexate etc.). All patients with immunosuppression due to HIV infection. Patients with gamma globulin deficiencies needing replacement therapy with HNIG do not require VZIG Any immunosuppressed patient that is exposed to a case of chickenpox or shingles should undergo the same process of assessment as any other contacts (see section 8 of these guidelines) The decision to give prophylactic VZIG is made on an individual basis. Wherever possible, immunosuppressed contacts should be tested for varicella zoster antibodies regardless of a previous history of chickenpox. If testing for antibodies will potentially delay the administration of VZIG beyond 7 days after initial contact with the index
10 case, then VZIG should be given on the basis of a negative history of chickenpox. If the patient has a positive history of chickenpox, serology results should be obtained first VZIG is not indicated in immunosuppressed contacts with detectable varicella zoster antibodies Patients with no detectable varicella zoster antibodies do require VZIG. The decision to administer VZIG should be made by the Clinician responsible for the patient in liaison with the Consultant Microbiologists. 16. IMPLEMENTATION, MONITORING AND EVALUATION Responsibility for implementation, monitoring and evaluation is identified in the Trust s Policy on Procedural Documents Daily monitoring is carried out by the IPCT of all patients isolated due to infection control reasons. This will include the monitoring of isolation practice for patients with either chickenpox or shingles Any issues identified from the monitoring process will be raised by the IPCT at the Infection Prevention & Control Committee (IPCC) if necessary Monitoring of these guidelines is overseen by the IPCC. 17. SOURCE REFERENCES AND ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS 17.1 Immunisation against Infectious Disease Chapter 34 (The Green Book), April Public Health England, Immunisation Against Infectious Disease (The Green Book) Public Health England, Immunoglobulin Handbook Guidance on Viral Rash in Pregnancy (Investigation, Diagnosis and Management of Viral Rash Illness, or Exposure to Viral Rash Illness, in Pregnancy). Health Protection Agency, January Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, Chickenpox in Pregnancy - Green Top Guideline 13, 2007.
11 Equality Impact Assessment Tool To be completed and attached to any procedural document when submitted to the appropriate committee for consideration and approval. Name of Document: Management of Chickenpox Policy 1. Does the policy/guidance affect one group less or more favourably than another on the basis of: Race Ethnic origins (including gypsies and travellers) Nationality Gender Culture Religion or belief Sexual orientation including lesbian, gay and bisexual people Yes/ Comments Age Disability 2. Is there any evidence that some groups are affected differently? 3. If you have identified potential discrimination, are any exceptions valid, legal and/or justifiable? 4. Is the impact of the policy/guidance likely to be negative? N/A 5. If so can the impact be avoided? N/A 6. What alternatives are there to achieving the policy/guidance without the impact? 7. Can we reduce the impact by taking different action? N/A N/A For advice or if you have identified a potential discriminatory impact of this procedural document, please refer it to The Equality & Diversity Lead, Yeovil Academy, together with any suggestions as to the action required to avoid/reduce this impact. Signed Lisa Eastmead-Hoare Date: 13/06/2016
12 FLOW CHART ONE ACTION TO BE TAKEN IN THE EVENT OF A CASE OF CHICKENPOX OR SHINGLES ON A WARD Isolate index case and deep clean bed space Inform IPCT Instigate infection control precautions (Appendix A) List potential contacts of index case (patients, staff and visitors) Assess immunity of all potential contacts using assessment in Flow Chart Two Contact is immune to Chickenpox Contact is not immune or immunity is unknown further action needed Assess significance of exposure using assessment in Appendix B Significant exposure has occurred complete contact list in Appendix C Exposure is not significant STAFF Refer to OH PATIENT or VISITOR Refer to IPCT further action needed
13 FLOW CHART TWO ASSESSMENT OF IMMUNITY TO CHICKENPOX OR SHINGLES Yes Has the contact had chickenpox or shingles before? Were they born or raised outside of the UK? OR Have they had a bone marrow transplant in the last 12 months? OR Are they immunosuppressed? Yes Consider serology testing to confirm immunity discuss with Microbiologist if necessary. Serology testing carried out. Yes Results Positive Antibodies Negative Antibodies Immunity cannot be confirmed Class as Immune Further Action Class as n-immune
VARICELLA ZOSTER (VZ) VIRUS, CHICKENPOX & SHINGLES GUIDANCE
 VARICELLA ZOSTER (VZ) VIRUS, CHICKENPOX & SHINGLES GUIDANCE Summary This guidance provides background information on varicella zoster (VZ), chickenpox and shingles and sets out the infection control measures
VARICELLA ZOSTER (VZ) VIRUS, CHICKENPOX & SHINGLES GUIDANCE Summary This guidance provides background information on varicella zoster (VZ), chickenpox and shingles and sets out the infection control measures
Chickenpox in pregnancy: what you need to know
 Chickenpox in pregnancy: what you need to know First published December 2003 Revised edition published November 2008 What is chickenpox? Chickenpox is a very infectious illness caused by a virus called
Chickenpox in pregnancy: what you need to know First published December 2003 Revised edition published November 2008 What is chickenpox? Chickenpox is a very infectious illness caused by a virus called
Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults
 Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults What is chickenpox? Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a very contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is spread easily through the
Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults What is chickenpox? Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a very contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is spread easily through the
SHINGLES (Herpes zoster infection)
 SHINGLES (Herpes zoster infection) What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about shingles. It will tell you what it is, what causes it, what can be
SHINGLES (Herpes zoster infection) What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about shingles. It will tell you what it is, what causes it, what can be
Ear Infections Chickenpox chickenpox
 Ear Chickenpox Infections chickenpox Chickenpox Chickenpox is a common, very contagious viral infection that over 90% of people get during childhood unless they have been immunised. After an infection,
Ear Chickenpox Infections chickenpox Chickenpox Chickenpox is a common, very contagious viral infection that over 90% of people get during childhood unless they have been immunised. After an infection,
Accent on Health Obgyn, PC HERPES Frequently Asked Questions
 1. What is herpes? 2. How common is herpes? 3. Is there a cure for herpes? 4. What is oral herpes (cold sores)? 5. How is oral herpes spread? 6. What is genital herpes? 7. How is genital herpes spread?
1. What is herpes? 2. How common is herpes? 3. Is there a cure for herpes? 4. What is oral herpes (cold sores)? 5. How is oral herpes spread? 6. What is genital herpes? 7. How is genital herpes spread?
Pregnancy and Tuberculosis. Information for clinicians
 Pregnancy and Tuberculosis Information for clinicians When to suspect Tuberculosis (TB)? Who is at risk of TB during pregnancy? Recent research suggests that new mothers are at an increased risk of TB
Pregnancy and Tuberculosis Information for clinicians When to suspect Tuberculosis (TB)? Who is at risk of TB during pregnancy? Recent research suggests that new mothers are at an increased risk of TB
41 Viral rashes and skin infections
 41 Viral rashes and skin infections Clinical There are several kinds of skin infections caused by viruses, and these are best considered in the four categories that group together similar symptoms for
41 Viral rashes and skin infections Clinical There are several kinds of skin infections caused by viruses, and these are best considered in the four categories that group together similar symptoms for
Zika Virus. Fred A. Lopez, MD, MACP Richard Vial Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases
 Zika Virus Fred A. Lopez, MD, MACP Richard Vial Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases What is the incubation period for Zika virus infection? Unknown but likely to be several
Zika Virus Fred A. Lopez, MD, MACP Richard Vial Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases What is the incubation period for Zika virus infection? Unknown but likely to be several
How can herpes simplex spread to an infant?
 CHAPTER 3 HERPES AND PREGNANCY As an expectant parent eagerly awaiting the birth of your new baby, you are probably taking a number of steps to ensure your baby s health. One step many experts recommend
CHAPTER 3 HERPES AND PREGNANCY As an expectant parent eagerly awaiting the birth of your new baby, you are probably taking a number of steps to ensure your baby s health. One step many experts recommend
EVALUATING THE PATIENT WITH AN ACUTE, GENERALIZED VESICULAR OR PUSTULAR RASH ILLNESS AND DETERMINING THE RISK OF SMALLPOX
 EVALUATING THE PATIENT WITH AN ACUTE, GENERALIZED VESICULAR OR PUSTULAR RASH ILLNESS AND DETERMINING THE RISK OF SMALLPOX Many rash illnesses can present with vesicles and pustules. The purpose of this
EVALUATING THE PATIENT WITH AN ACUTE, GENERALIZED VESICULAR OR PUSTULAR RASH ILLNESS AND DETERMINING THE RISK OF SMALLPOX Many rash illnesses can present with vesicles and pustules. The purpose of this
Chickenpox (Varicella)
 Chickenpox (Varicella) DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report within 24 hours confirmed or suspected cases of varicella
Chickenpox (Varicella) DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report within 24 hours confirmed or suspected cases of varicella
ROYAL HOSPITAL FOR WOMEN
 HEPATITIS B POSITIVE MOTHERS AND THEIR BABIES This LOP is developed to guide clinical practice at the Royal Hospital for Women. Individual patient circumstances may mean that practice diverges from this
HEPATITIS B POSITIVE MOTHERS AND THEIR BABIES This LOP is developed to guide clinical practice at the Royal Hospital for Women. Individual patient circumstances may mean that practice diverges from this
Pregnancy and Tuberculosis. Patient and Public information sheet
 Pregnancy and Tuberculosis Patient and Public information sheet Who is at risk of TB? Anyone can catch TB, but it is possible that pregnant women have a slightly higher risk of TB. Some people are more
Pregnancy and Tuberculosis Patient and Public information sheet Who is at risk of TB? Anyone can catch TB, but it is possible that pregnant women have a slightly higher risk of TB. Some people are more
Laboratory confirmation requires isolation of Bordetella pertussis or detection of B. pertussis nucleic acid, preferably from a nasopharyngeal swab.
 Pertussis Epidemiology in New Zealand New Zealand has continued to experience outbreaks of pertussis in recent decades. This is in part due to historically low immunisation rates and in part because immunity
Pertussis Epidemiology in New Zealand New Zealand has continued to experience outbreaks of pertussis in recent decades. This is in part due to historically low immunisation rates and in part because immunity
Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.
 Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.org/ Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) is a common, mild, childhood
Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.org/ Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) is a common, mild, childhood
INFECTION CONTROL MANUAL
 Page 1 of 19 Key Words: staff, communicable diseases, diseases, infectious diseases Policy Applies to: All staff employed by Mercy Hospital, Credentialed Specialists and Allied Health Professionals involved
Page 1 of 19 Key Words: staff, communicable diseases, diseases, infectious diseases Policy Applies to: All staff employed by Mercy Hospital, Credentialed Specialists and Allied Health Professionals involved
Health Professionals Advice: Azithromycin now fully funded 3 December 2012
 Health Professionals Advice: Azithromycin now fully funded 3 December 2012 SITUATION UPDATE The Pertussis epidemic has continued all year, and is expected to continue throughout 2013. Between 1 January
Health Professionals Advice: Azithromycin now fully funded 3 December 2012 SITUATION UPDATE The Pertussis epidemic has continued all year, and is expected to continue throughout 2013. Between 1 January
Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management. March 2010
 Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management March 2010 Infectious Agent Bordetella pertussis (a bacterium) Clinical Features Infants and Young
Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management March 2010 Infectious Agent Bordetella pertussis (a bacterium) Clinical Features Infants and Young
NHS FORTH VALLEY Guidelines for Hepatitis B Vaccination in High Risk Groups
 NHS FORTH VALLEY Guidelines for Hepatitis B Vaccination in High Risk Groups Approved 01/04/2012 Version 1.0 Date of First Issue 01/04/2012 Review Date 01/02/2014 Date of Issue 01/04/2012 EQIA Yes Author
NHS FORTH VALLEY Guidelines for Hepatitis B Vaccination in High Risk Groups Approved 01/04/2012 Version 1.0 Date of First Issue 01/04/2012 Review Date 01/02/2014 Date of Issue 01/04/2012 EQIA Yes Author
A guide for people with genital herpes
 A guide for people with genital herpes Contents Getting the facts 4 The key facts 6 What is genital herpes? 8 Genital herpes symptoms 10 Getting tested 12 The first outbreak 14 Recurrent outbreaks 16 Common
A guide for people with genital herpes Contents Getting the facts 4 The key facts 6 What is genital herpes? 8 Genital herpes symptoms 10 Getting tested 12 The first outbreak 14 Recurrent outbreaks 16 Common
The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. Management and post-exposure prophylaxis for suspected cases of pertussis (Whooping Cough)
 The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Management and post-exposure prophylaxis for suspected cases of pertussis (Whooping Cough) Version No.: 5.0 Effective From: 2 May 2013 Expiry Date:
The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Management and post-exposure prophylaxis for suspected cases of pertussis (Whooping Cough) Version No.: 5.0 Effective From: 2 May 2013 Expiry Date:
Safety Alerts Management Policy
 Safety Alerts Management Policy Version Number 1.1 Version Date February 2014 Policy Owner Author First approval or date last reviewed Staff/Groups Consulted Director of Nursing and Clinical Governance
Safety Alerts Management Policy Version Number 1.1 Version Date February 2014 Policy Owner Author First approval or date last reviewed Staff/Groups Consulted Director of Nursing and Clinical Governance
Mother s blood test to check her unborn baby s blood group
 Mother s blood test to check her unborn baby s blood group This leaflet explains why it is important to have a blood test to check the baby s blood group, so that only those who need it, receive anti-d
Mother s blood test to check her unborn baby s blood group This leaflet explains why it is important to have a blood test to check the baby s blood group, so that only those who need it, receive anti-d
I B2.4. Design of the patient information leaflet for VariQuin
 (English translation of official Dutch version) I B2.4. Design of the patient information leaflet for VariQuin Information for the Patient: Read this package leaflet carefully when you have some time to
(English translation of official Dutch version) I B2.4. Design of the patient information leaflet for VariQuin Information for the Patient: Read this package leaflet carefully when you have some time to
2.1 When a breastfeeding woman is admitted to hospital, the support she needs depends on the nature of her illness and the treatment needed
 CARE OF BREASTFEEDING WOMEN ADMITTED TO HOSPITAL, CLINICAL GUIDELINE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1 Breastfeeding is known to be one of the most powerful health protective influences and as such,
CARE OF BREASTFEEDING WOMEN ADMITTED TO HOSPITAL, CLINICAL GUIDELINE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1 Breastfeeding is known to be one of the most powerful health protective influences and as such,
What is whooping cough. (pertussis)? Information and Prevention. Ocument dn
 What is whooping cough Ocument dn (pertussis)? Information and Prevention IMPORTANT Pertussis (or whooping cough) is a highly contagious infection that can cause uncontrollable, violent coughing. If you
What is whooping cough Ocument dn (pertussis)? Information and Prevention IMPORTANT Pertussis (or whooping cough) is a highly contagious infection that can cause uncontrollable, violent coughing. If you
MANAGEMENT OF INFANTS BORN TO HIV POSITIVE MOTHERS
 MANAGEMENT OF INFANTS BORN TO HIV POSITIVE MOTHERS Introduction Perinatal management of infants born to HIV-infected mothers requires a coordinated multidisciplinary team approach. The consultant leads
MANAGEMENT OF INFANTS BORN TO HIV POSITIVE MOTHERS Introduction Perinatal management of infants born to HIV-infected mothers requires a coordinated multidisciplinary team approach. The consultant leads
CMV: Your questions answered
 The basics about the virus CMV: Your questions answered What is CMV? CMV, or Cytomegalovirus, is a common virus that can infect people of all ages. Once CMV is in a person s body, it stays there for life.
The basics about the virus CMV: Your questions answered What is CMV? CMV, or Cytomegalovirus, is a common virus that can infect people of all ages. Once CMV is in a person s body, it stays there for life.
2 P age. Babies from Birth to Age 2
 Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
MUMPS PUBLIC FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program MUMPS PUBLIC FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Date: April 17, 2014 DESCRIPTION OF MUMPS What is mumps? Mumps is a disease that is caused by
New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program MUMPS PUBLIC FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Date: April 17, 2014 DESCRIPTION OF MUMPS What is mumps? Mumps is a disease that is caused by
HPA National Measles Guidelines Local & Regional Services
 HPA National Measles Guidelines Local & Regional Services Version 1.2: 28 th October 2010 1 Table of Contents Title: Page No: 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. RATIONALE FOR PUBLIC HEALTH ACTION...3 3. SURVEILLANCE
HPA National Measles Guidelines Local & Regional Services Version 1.2: 28 th October 2010 1 Table of Contents Title: Page No: 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. RATIONALE FOR PUBLIC HEALTH ACTION...3 3. SURVEILLANCE
PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CLOSE CONTACTS OF PERTUSSIS INFECTION
 PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CLOSE CONTACTS OF PERTUSSIS INFECTION Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL PROTOCOL NO. 1.03 Policy Group Infection Control Committee
PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CLOSE CONTACTS OF PERTUSSIS INFECTION Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL PROTOCOL NO. 1.03 Policy Group Infection Control Committee
Whooping Cough Vaccine for Pregnant Women
 Whooping Cough Vaccine for Pregnant Women What is whooping cough (pertussis)? Whooping cough (also known as pertussis) is a highly contagious illness that can be life threatening. The disease is most serious
Whooping Cough Vaccine for Pregnant Women What is whooping cough (pertussis)? Whooping cough (also known as pertussis) is a highly contagious illness that can be life threatening. The disease is most serious
The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. Laundry Management Policy
 The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Laundry Management Policy Version No.: 4.1 Effective From: 20 December 2013 Expiry Date: 31 December 2016 Date Ratified: 20 December 2013 Ratified
The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Laundry Management Policy Version No.: 4.1 Effective From: 20 December 2013 Expiry Date: 31 December 2016 Date Ratified: 20 December 2013 Ratified
Tuberculosis Exposure Control Plan for Low Risk Dental Offices
 Tuberculosis Exposure Control Plan for Low Risk Dental Offices A. BACKGROUND According to the CDC, approximately one-third of the world s population, almost two billion people, are infected with tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis Exposure Control Plan for Low Risk Dental Offices A. BACKGROUND According to the CDC, approximately one-third of the world s population, almost two billion people, are infected with tuberculosis.
35-40% of GBS disease occurs in the elderly or in adults with chronic medical conditions.
 What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
Infection Prevention and Control Policy
 Infection Prevention and Control Policy Version: 1 Version: Ratified By: Quality Sub Committee Ratified By: Date Ratified: vember 2014 Date Ratified: Date Policy Comes Into Effect: vember 2014 Date Policy
Infection Prevention and Control Policy Version: 1 Version: Ratified By: Quality Sub Committee Ratified By: Date Ratified: vember 2014 Date Ratified: Date Policy Comes Into Effect: vember 2014 Date Policy
The flu vaccination WINTER 2016/17. Who should have it and why. Flu mmunisation 2016/17
 The flu vaccination WINTER 2016/17 Who should have it and why Flu mmunisation 2016/17 The flu vaccination 1 Winter 2016/17 Helping to protect everyone, every winter This leaflet explains how you can help
The flu vaccination WINTER 2016/17 Who should have it and why Flu mmunisation 2016/17 The flu vaccination 1 Winter 2016/17 Helping to protect everyone, every winter This leaflet explains how you can help
Thinking of getting pregnant?
 Thinking of getting pregnant? Make sure you re protected against German measles the safest way to protect the health of you and your baby Catching German measles (rubella) can be very serious for your
Thinking of getting pregnant? Make sure you re protected against German measles the safest way to protect the health of you and your baby Catching German measles (rubella) can be very serious for your
INFUSE Bone Graft. Patient Information Brochure
 INFUSE Bone Graft Patient Information Brochure This Patient Guide is designed to help you decide whether or not to have surgery using INFUSE Bone Graft to treat your broken tibia (lower leg). There are
INFUSE Bone Graft Patient Information Brochure This Patient Guide is designed to help you decide whether or not to have surgery using INFUSE Bone Graft to treat your broken tibia (lower leg). There are
OET: Listening Part A: Influenza
 Listening Test Part B Time allowed: 23 minutes In this part, you will hear a talk on critical illnesses due to A/H1N1 influenza in pregnant and postpartum women, given by a medical researcher. You will
Listening Test Part B Time allowed: 23 minutes In this part, you will hear a talk on critical illnesses due to A/H1N1 influenza in pregnant and postpartum women, given by a medical researcher. You will
Yes, I know I have genital herpes:
 Counseling Messages for Herpes Simplex Type II (HSV-II) Genital herpes Always take the time to attend to the participant s feelings and emotional state; for some people, this is the most devastating news
Counseling Messages for Herpes Simplex Type II (HSV-II) Genital herpes Always take the time to attend to the participant s feelings and emotional state; for some people, this is the most devastating news
SOGC recommendation on ZIKA virus exposure for clinicians caring for pregnant women and those who intend to get pregnant
 SOGC recommendation on ZIKA virus exposure for clinicians caring for pregnant women and those who intend to get pregnant Foreword The rapid emergence of Zika virus as a potential causative agent for fetal
SOGC recommendation on ZIKA virus exposure for clinicians caring for pregnant women and those who intend to get pregnant Foreword The rapid emergence of Zika virus as a potential causative agent for fetal
Whooping cough and pregnancy
 Whooping cough and pregnancy Your questions answered on how to help protect your baby 2014 edition the safest way to protect yourself and your baby 1 There is a lot of whooping cough around at the moment
Whooping cough and pregnancy Your questions answered on how to help protect your baby 2014 edition the safest way to protect yourself and your baby 1 There is a lot of whooping cough around at the moment
Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women
 Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control & Prevention Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women from Recommendations of the Advisory
Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control & Prevention Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women from Recommendations of the Advisory
Rubella. Questions and answers
 Rubella Questions and answers What is rubella? Rubella, or German measles, is a mild disease caused by a virus. Before the MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) vaccine was used, rubella used to be common in
Rubella Questions and answers What is rubella? Rubella, or German measles, is a mild disease caused by a virus. Before the MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) vaccine was used, rubella used to be common in
FAQs HIV & AIDS. What is HIV? A virus that reduces the effectiveness of your immune system, meaning you are less protected against disease.
 HIV & AIDS What is HIV? A virus that reduces the effectiveness of your immune system, meaning you are less protected against disease. What does HIV stand for? Human Immunodeficiency Virus Where did HIV
HIV & AIDS What is HIV? A virus that reduces the effectiveness of your immune system, meaning you are less protected against disease. What does HIV stand for? Human Immunodeficiency Virus Where did HIV
BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE.
 DON T GET OR GIVE THE FLU THIS YEAR THANK YOU Vaccination is the only protection. www.immunisation.ie BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE. FLU VACCINE 2013-2014 Healthcare workers prevent the spread of flu and
DON T GET OR GIVE THE FLU THIS YEAR THANK YOU Vaccination is the only protection. www.immunisation.ie BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE. FLU VACCINE 2013-2014 Healthcare workers prevent the spread of flu and
MINISTRY OF HEALTH PANDEMIC INFLUENZA A / H1N1 2009 VACCINE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 Government of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago MINISTRY OF HEALTH PANDEMIC INFLUENZA A / H1N1 2009 VACCINE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Influenza vaccines are one of the most effective ways to protect
Government of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago MINISTRY OF HEALTH PANDEMIC INFLUENZA A / H1N1 2009 VACCINE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Influenza vaccines are one of the most effective ways to protect
Developed in response to: Health and Social Act 2008 Contributes to CQC Core Standard Outcome 8
 Management of H1N1 (Swine Flu) Patients Policy Register No: 09061 Status: Public Developed in response to: Health and Social Act 2008 Contributes to CQC Core Standard Outcome 8 number: Consulted With Post/Committee/Group
Management of H1N1 (Swine Flu) Patients Policy Register No: 09061 Status: Public Developed in response to: Health and Social Act 2008 Contributes to CQC Core Standard Outcome 8 number: Consulted With Post/Committee/Group
School of Health & Rehabilitation Sciences INFORMATION FOR HEALTH CARE STUDENTS RE: VACCINATIONS AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES
 School of Health & Rehabilitation Sciences INFORMATION FOR HEALTH CARE STUDENTS RE: VACCINATIONS AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES Adults as well as children need protection against infectious diseases. As Health
School of Health & Rehabilitation Sciences INFORMATION FOR HEALTH CARE STUDENTS RE: VACCINATIONS AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES Adults as well as children need protection against infectious diseases. As Health
Clinical description 2 Laboratory test for diagnosis 3. Incubation period 4 Mode of transmission 4 Period of communicability 4
 Tuberculosis Contents Epidemiology in New Zealand 2 Case definition 2 Clinical description 2 Laboratory test for diagnosis 3 Case classification 3 Spread of infection 4 Incubation period 4 Mode of transmission
Tuberculosis Contents Epidemiology in New Zealand 2 Case definition 2 Clinical description 2 Laboratory test for diagnosis 3 Case classification 3 Spread of infection 4 Incubation period 4 Mode of transmission
Lymphomas after organ transplantation
 Produced 21.03.2011 Revision due 21.03.2011 Lymphomas after organ transplantation People who have undergone an organ transplant are more at risk of developing lymphoma known as post-transplant lymphoproliferative
Produced 21.03.2011 Revision due 21.03.2011 Lymphomas after organ transplantation People who have undergone an organ transplant are more at risk of developing lymphoma known as post-transplant lymphoproliferative
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth. What are the symptoms of a DVT during pregnancy?
 Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
SWINE FLU: FROM CONTAINMENT TO TREATMENT
 SWINE FLU: FROM CONTAINMENT TO TREATMENT SWINE FLU: FROM CONTAINMENT TO TREATMENT INTRODUCTION As Swine Flu spreads and more people start to catch it, it makes sense to move from intensive efforts to contain
SWINE FLU: FROM CONTAINMENT TO TREATMENT SWINE FLU: FROM CONTAINMENT TO TREATMENT INTRODUCTION As Swine Flu spreads and more people start to catch it, it makes sense to move from intensive efforts to contain
Severe Combined Immune Deficiency (SCID)
 Severe Combined Immune Deficiency (SCID) ASCIA EDUCATION RESOURCES (AER) PATIENT INFORMATION Severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) is the most serious form of primary immune deficiency and is usually
Severe Combined Immune Deficiency (SCID) ASCIA EDUCATION RESOURCES (AER) PATIENT INFORMATION Severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) is the most serious form of primary immune deficiency and is usually
Resource Document 6: Tetanus Immunization. I. Introduction
 Resource Document 6: Tetanus Immunization I. Introduction Attention must be directed to adequate tetanus prophylaxis in the multiply injured patient, particularly if open-extremity trauma is present. The
Resource Document 6: Tetanus Immunization I. Introduction Attention must be directed to adequate tetanus prophylaxis in the multiply injured patient, particularly if open-extremity trauma is present. The
TEMPORARY PROGRAMME PERTUSSIS VACCINATION FOR PREGNANT WOMEN
 TEMPORARY PROGRAMME PERTUSSIS VACCINATION FOR PREGNANT WOMEN Richard Smithson Neil Irvine Maureen McCartney Consultant Health Protection October 2012 Pertussis/whooping cough The disease Whooping Cough
TEMPORARY PROGRAMME PERTUSSIS VACCINATION FOR PREGNANT WOMEN Richard Smithson Neil Irvine Maureen McCartney Consultant Health Protection October 2012 Pertussis/whooping cough The disease Whooping Cough
The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. National Early Warning Score (NEWS) Policy
 The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust National Early Warning Score (NEWS) Policy Version.: 1.0 Effective From: 3 December 2014 Expiry Date: 3 December 2016 Date Ratified: 1 September 2014
The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust National Early Warning Score (NEWS) Policy Version.: 1.0 Effective From: 3 December 2014 Expiry Date: 3 December 2016 Date Ratified: 1 September 2014
Vaccination against pertussis (Whooping cough) for pregnant women- 2014. Information for healthcare professionals
 Vaccination against pertussis (Whooping cough) for pregnant women- 2014 Information for healthcare professionals About Public Health England Public Health England s mission is to protect and improve the
Vaccination against pertussis (Whooping cough) for pregnant women- 2014 Information for healthcare professionals About Public Health England Public Health England s mission is to protect and improve the
Pennsylvania Hospital & Surgery Center of Pennsylvania Hospital ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY MANUAL
 Page 1 Issued: March 1978 Committee Approval: Human Resources Employee Health Infection Control Administrative Policy Review Committee: January 1982 December 1986 June 1989 April 1991 December 1993 March
Page 1 Issued: March 1978 Committee Approval: Human Resources Employee Health Infection Control Administrative Policy Review Committee: January 1982 December 1986 June 1989 April 1991 December 1993 March
Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) - the replacement of Repevax with Boostrix -IPV an update for registered healthcare practitioners
 Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) - the replacement of Repevax with Boostrix -IPV an update for registered healthcare practitioners Questions and Answers May 2014 Health Protection Scotland
Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) - the replacement of Repevax with Boostrix -IPV an update for registered healthcare practitioners Questions and Answers May 2014 Health Protection Scotland
Pre-employment Health Assessment Questionnaire
 Pre-employment Health Assessment Questionnaire (for use from 1 October 2010) University Occupational Health Service 10 Parks Road Oxford OX1 3PD Telephone: (01865) 282676 Fax: (01865) 282678 (+44 1865
Pre-employment Health Assessment Questionnaire (for use from 1 October 2010) University Occupational Health Service 10 Parks Road Oxford OX1 3PD Telephone: (01865) 282676 Fax: (01865) 282678 (+44 1865
Interim Guidance for Medical Schools on health checks for active and latent Tuberculosis in medical students returning from elective periods overseas
 Interim Guidance for Medical Schools on health checks for active and latent Tuberculosis in medical students returning from elective periods overseas This document has been developed by: Dr Mathina Darmalingam
Interim Guidance for Medical Schools on health checks for active and latent Tuberculosis in medical students returning from elective periods overseas This document has been developed by: Dr Mathina Darmalingam
Immunization FAQs Required Vaccines for 2014-15 School Year
 Immunization Schedules and Documentation Immunization FAQs Required Vaccines for 2014-15 School Year 1. Question: What is the difference between the recommended immunization schedule and the Colorado School
Immunization Schedules and Documentation Immunization FAQs Required Vaccines for 2014-15 School Year 1. Question: What is the difference between the recommended immunization schedule and the Colorado School
Chickenpox and Shingles Vaccines
 Chickenpox and Shingles Vaccines The chicken pox/shingles connection DISCLAIMER: The following is not intended as advice on whether or not to receive a chicken pox, shingles, or any other vaccine. The
Chickenpox and Shingles Vaccines The chicken pox/shingles connection DISCLAIMER: The following is not intended as advice on whether or not to receive a chicken pox, shingles, or any other vaccine. The
Alzheimer s and Herpes Zoster
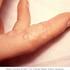 The relationship between Alzheimer's and herpes zoster should be studied. A solid link between herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV1) and Alzheimer's has been found. See: "Cold Sore Virus Linked To Alzheimer's
The relationship between Alzheimer's and herpes zoster should be studied. A solid link between herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV1) and Alzheimer's has been found. See: "Cold Sore Virus Linked To Alzheimer's
UCSF Communicable Disease Surveillance and Vaccination Policy
 Office of Origin: Occupational Health Program I. PURPOSE To provide a sustainable, healthy and safe working environment for UCSF research laboratory staff, and animal research care staff and to prevent
Office of Origin: Occupational Health Program I. PURPOSE To provide a sustainable, healthy and safe working environment for UCSF research laboratory staff, and animal research care staff and to prevent
PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH 2015 PAHAN 307 04-02-ADV Pertussis in Centre County
 PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH 2015 PAHAN 307 04-02-ADV Pertussis in Centre County DATE: 04/02/2015 TO: Health Alert Network FROM: Karen M. Murphy, PhD, RN, Acting Secretary of Health SUBJECT: DISTRIBUTION:
PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH 2015 PAHAN 307 04-02-ADV Pertussis in Centre County DATE: 04/02/2015 TO: Health Alert Network FROM: Karen M. Murphy, PhD, RN, Acting Secretary of Health SUBJECT: DISTRIBUTION:
When an occupational exposure occurs, the source patient should be evaluated for both hepatitis B and hepatitis C. (AII)
 XI. OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO HEPATITIS B AND C RECOMMENDATION: When an occupational exposure occurs, the source patient should be evaluated for both hepatitis B and hepatitis C. (AII) The risk of transmission
XI. OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO HEPATITIS B AND C RECOMMENDATION: When an occupational exposure occurs, the source patient should be evaluated for both hepatitis B and hepatitis C. (AII) The risk of transmission
Explanation of Immunization Requirements
 Explanation of Immunization Requirements CONTENTS Hepatitis A... 2 Hepatitis B... 3 Influenza... 4 Measles (Rubella), Mumps, and Rubella (MMR)... 5 Pertussis (Tdap)... 6 Tuberculosis (TB) Test... 7 Varicella/Chicken
Explanation of Immunization Requirements CONTENTS Hepatitis A... 2 Hepatitis B... 3 Influenza... 4 Measles (Rubella), Mumps, and Rubella (MMR)... 5 Pertussis (Tdap)... 6 Tuberculosis (TB) Test... 7 Varicella/Chicken
General Colorado Immunization Guidelines... 3. Varicella (Chickenpox) Disease and Varicella Vaccine... 4. DTaP/Tdap/Td Vaccines...
 General Colorado Immunization Guidelines... 3 What is the difference between Colorado school required immunizations and immunizations that are recommended?... 3 What is the 4 day grace period for vaccines
General Colorado Immunization Guidelines... 3 What is the difference between Colorado school required immunizations and immunizations that are recommended?... 3 What is the 4 day grace period for vaccines
Hepatitis B Pathway stages to protection Actions, roles, responsibilities and standards
 Hepatitis B Pathway stages to protection Actions, roles, responsibilities and standards Start Pathway stages colour code: Action Midwifery role Risk areas Specialist services role Primary care role Paediatric
Hepatitis B Pathway stages to protection Actions, roles, responsibilities and standards Start Pathway stages colour code: Action Midwifery role Risk areas Specialist services role Primary care role Paediatric
HIV/AIDS: General Information & Testing in the Emergency Department
 What Is HIV? HIV/AIDS: General Information & Testing in the Emergency Department HIV is the common name for the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. HIV is a retrovirus. This means it can enter the body s own
What Is HIV? HIV/AIDS: General Information & Testing in the Emergency Department HIV is the common name for the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. HIV is a retrovirus. This means it can enter the body s own
Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis)
 Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis) About whooping cough What is whooping cough? Whooping cough is a highly contagious illness caused by bacteria. It mainly affects the respiratory
Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis) About whooping cough What is whooping cough? Whooping cough is a highly contagious illness caused by bacteria. It mainly affects the respiratory
Plan early - get your vaccinations in time for full protection. To prepare for your trip, schedule an appointment: (910) 347-2154, option #2.
 The Onslow County Health Department Travel Clinic offers a complete line of immunizations and prescriptions to protect you while traveling abroad. The most appropriate immunizations and travel medications
The Onslow County Health Department Travel Clinic offers a complete line of immunizations and prescriptions to protect you while traveling abroad. The most appropriate immunizations and travel medications
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept ): risks of miscarriage and birth defects. Patient guide. Key points to remember
 Mycophenolate (CellCept ): risks of miscarriage and birth defects Patient guide Key points to remember Mycophenolate (CellCept ) causes birth defects and miscarriages Follow the contraceptive advice given
Mycophenolate (CellCept ): risks of miscarriage and birth defects Patient guide Key points to remember Mycophenolate (CellCept ) causes birth defects and miscarriages Follow the contraceptive advice given
CROSS HEALTH CARE BOUNDARIES MATERNITY CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 CROSS HEALTH CARE BOUNDARIES MATERNITY CLINICAL GUIDELINE Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Obstetric Early Warning Score Guideline Implementation
CROSS HEALTH CARE BOUNDARIES MATERNITY CLINICAL GUIDELINE Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Obstetric Early Warning Score Guideline Implementation
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women
 Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
Cord blood banking: information for parents
 Cord blood banking: information for parents Published August 2006 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What is cord blood? 2 Why is cord blood useful? 3 How is cord blood
Cord blood banking: information for parents Published August 2006 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What is cord blood? 2 Why is cord blood useful? 3 How is cord blood
Tuberculosis: FAQs. What is the difference between latent TB infection and TB disease?
 Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy. Chapter 7
 Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy Chapter 7 An unborn baby makes no IgG (antibody) and only slowly starts producing it after birth. However, starting at about the sixth month of pregnancy, the
Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy Chapter 7 An unborn baby makes no IgG (antibody) and only slowly starts producing it after birth. However, starting at about the sixth month of pregnancy, the
Solid Organ Transplantation
 Solid Organ Transplantation Infection Prevention And Control Transplant Atlantic 2011 October 13/2011 Kathy Hart Introduction In the past several years, the drugs that we use, the surgeries themselves,
Solid Organ Transplantation Infection Prevention And Control Transplant Atlantic 2011 October 13/2011 Kathy Hart Introduction In the past several years, the drugs that we use, the surgeries themselves,
FOR INFORMATION CONTACT:
 NEWS RELEASE FOR INFORMATION CONTACT: Caroline Calderone Baisley Deborah C. Travers Director of Health Director of Family Health Tel [203] 622-7836 Tel [203] 622-7854 September 10, 2014 For Immediate Release
NEWS RELEASE FOR INFORMATION CONTACT: Caroline Calderone Baisley Deborah C. Travers Director of Health Director of Family Health Tel [203] 622-7836 Tel [203] 622-7854 September 10, 2014 For Immediate Release
Factsheet September 2012. Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women. Introduction
 Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis.
Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis.
AV1300 STAFF INFLUENZA IMMUNIZATION AND EXCLUSION POLICY
 AV1300 STAFF INFLUENZA IMMUNIZATION AND EXCLUSION POLICY 1.0 PURPOSE To help ensure that those at greatest risk of complications and death from influenza are optimally protected through the appropriate
AV1300 STAFF INFLUENZA IMMUNIZATION AND EXCLUSION POLICY 1.0 PURPOSE To help ensure that those at greatest risk of complications and death from influenza are optimally protected through the appropriate
LEHMAN COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF NURSING ANNUAL HEALTH CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
 ANNUAL HEALTH CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS Each student in the Department of Nursing must have current health clearance prior to each clinical nursing course (NUR 301, 303, 304, 400, 405, 409). Health clearance
ANNUAL HEALTH CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS Each student in the Department of Nursing must have current health clearance prior to each clinical nursing course (NUR 301, 303, 304, 400, 405, 409). Health clearance
The link between cervical cancer and HPV (human papillomavirus)
 The link between cervical cancer and HPV (human papillomavirus) The link between cervical cancer and HPV Key facts: HPV is a virus (the human papillomavirus). Almost all abnormal Pap smear results are
The link between cervical cancer and HPV (human papillomavirus) The link between cervical cancer and HPV Key facts: HPV is a virus (the human papillomavirus). Almost all abnormal Pap smear results are
STAFF SCREENING AND IMMUNISATION POLICY
 2GETHER NHS FOUNDATION TRUST GLOUCESTERSHIRE HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST NHS GLOUCESTERSHIRE GLOUCESTERSHIRE CARE SERVICES STAFF SCREENING AND IMMUNISATION POLICY Version: 1 Consultation: Ratified by:
2GETHER NHS FOUNDATION TRUST GLOUCESTERSHIRE HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST NHS GLOUCESTERSHIRE GLOUCESTERSHIRE CARE SERVICES STAFF SCREENING AND IMMUNISATION POLICY Version: 1 Consultation: Ratified by:
Appendix 3 Exposure Incident Report Form
 Appendix 3 Exposure Incident Report Form January, 2015 Page 1 of 6 Please see the following pages for the Exposure Incident Report Form. Guidelines for the Management of Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids
Appendix 3 Exposure Incident Report Form January, 2015 Page 1 of 6 Please see the following pages for the Exposure Incident Report Form. Guidelines for the Management of Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids
Chapter 3. Immunity and how vaccines work
 Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Fact Sheet for Health Care Providers: Interpreting Results from the Aptima Zika Virus Assay. June 17, 2016
 Dear Health Care Provider: Fact Sheet for Health Care Providers: Interpreting Results from the Aptima Zika Virus Assay June 17, 2016 The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued an Emergency
Dear Health Care Provider: Fact Sheet for Health Care Providers: Interpreting Results from the Aptima Zika Virus Assay June 17, 2016 The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued an Emergency
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil (filgrastim)
 EMA/475472/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil (filgrastim) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure
EMA/475472/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil (filgrastim) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure
Delaware. Downloaded 01/2011
 Delaware Downloaded 01/2011 3.0 CNA Training Program Requirements 3.3 Curriculum Content 3.3.2 Environmental Needs Of The Resident Key Concepts: Introduces the nursing assistant to the need to keep residents
Delaware Downloaded 01/2011 3.0 CNA Training Program Requirements 3.3 Curriculum Content 3.3.2 Environmental Needs Of The Resident Key Concepts: Introduces the nursing assistant to the need to keep residents
Nurse Aide Training Program Application Checklist
 Nurse Aide Training Program Application Checklist The following checklist must be completed before enrolling in the Nurse Aide Training course: Complete, sign, and date the Application Form Have the physical
Nurse Aide Training Program Application Checklist The following checklist must be completed before enrolling in the Nurse Aide Training course: Complete, sign, and date the Application Form Have the physical
William Atkinson, MD, MPH Hepatitis B Vaccine Issues June 16, 2016
 William Atkinson, MD, MPH Hepatitis B Vaccine Issues June 16, 2016 Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) The recommendations to be discussed are primarily those of the ACIP composed of 15
William Atkinson, MD, MPH Hepatitis B Vaccine Issues June 16, 2016 Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) The recommendations to be discussed are primarily those of the ACIP composed of 15
INFANT IMMUNISATION GUIDELINES
 INFANT IMMUNISATION GUIDELINES For all immunisations it is imperative that parental consent is obtained prior to proceeding. Use the Immunisation Consent and Administration Form. Once administered, fax
INFANT IMMUNISATION GUIDELINES For all immunisations it is imperative that parental consent is obtained prior to proceeding. Use the Immunisation Consent and Administration Form. Once administered, fax
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR VAGINAL BIRTH AFTER CAESAREAN SECTION (VBAC)
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR VAGINAL BIRTH AFTER CAESAREAN SECTION (VBAC) 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. Due to a rise in the caesarean section rate there are increasing numbers of pregnant women who
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR VAGINAL BIRTH AFTER CAESAREAN SECTION (VBAC) 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. Due to a rise in the caesarean section rate there are increasing numbers of pregnant women who
