SÜDAME RÜTMIHÄIRETE EPIDEMIOLOOGIA, JAOTUS JA PROGNOOS. RÜTMIHÄIRETE TEKKEPÕHJUSED JA RAVI KARDIOLOOGI PILGU LÄBI
|
|
|
- Audra Parker
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SÜDAME RÜTMIHÄIRETE EPIDEMIOLOOGIA, JAOTUS JA PROGNOOS. RÜTMIHÄIRETE TEKKEPÕHJUSED JA RAVI KARDIOLOOGI PILGU LÄBI Hasso Uuetoa Põhja-Eesti Regionaalhaigla Elektrofüsioloogia üksus
2 RÜTMIHÄIRETE JAOTUS
3 Rütmihäirete klassifikatsioon 1.Kestvuse ja püsivuse alusel Paroksüsmaalne / Intermiteeruv / Ebapüsiv Persistentne ehk kestev (ilma medikamentoosse ravita ja/või elektrilise kardioversioonita ei möödu). Permanentne ehk püsiv (medikamentoosse raviga ja/või elektrilise kardioversiooniga ka ei möödu või taastub koheselt uuesti )
4 Rütmihäirete klassifikatsioon 2. Vatsakeste töö regulaarsuse alusel REGULAARNE SVT (AVRT, AVNRT, AT) Kodade laperdus VT EBAREGULAARNE Kodade virvendus Kodade laperdus ebaregulaarse AV-ülejuhtega MAT Polümorfne VT Monomorfne VT, eriti käivitumise järgselt
5 Rütmihäirete klassifikatsioon 3. QRS-kompleksi laiuse alusel Kitsa QRS-komleksiga (<120 ms) SVT Fastsikularne VT Laia QRS-kompleksiga (>120 ms) VT SVT Vatsakese elektroodiga kardiostimulaator
6 Laia QRS kompleksi põhjused
7 Rütmihäirete klassifikatsioon 4.Vatsakeste sageduse alusel Tahhükardia Kodade töö aeglane või normaalne (VT ja siinus rütm) Kodade töö tahhükardiline (virvendus/laperdus/kodade tahhükardia) Normokardia Kodade töö tahhükardiline (virvendus/laperdus/kodade tahhükardia) Ventrikulo atriaalne dissotsatsioon (kodade töö aeglasem kui vatsakeste töö (idioventrikulaarne rütm) Bradükardia Kodade töö tahhükardiline (Fredericki sündroom) Kodade töö aeglane
8 Carotid sinus massage revealing flutter waves Atrial Flutter
9 BRADÜKARDIAD
10 Bradükardia klassifikatsioon Erutustekke häired ehk vajalik rütm jääb tekkimata (siinussõlme nõrkus) Erutusjuhte häired ehk rütm küll tekib, aga ei levi kogu südamele (sino-atrialne blokaad, atrioventrikulaarne blokaad)
11 Bradükardia põhjuse paiknemistase Siinussõlmes ja kodades (40-50 bpm) Atrio-ventrikulaarsõlmes (30-45 bpm) nn supra-his asendusrütmi QRS kompleks on kitsas (alla 120 ms) Vatsakestes (allpool His-Purkinje süsteemi) (20-30 bpm) nn infra-his - asendusrütmi QRS kompleks on lai (üle 120 ms)
12 Püsiv bardükardia Bradükardia kestvus Intermiteeruv / paroksüsmaalne bardükardia Ravi põhimõtted ei muutu, kuid diagnostika on raskendatud intermiteeruva bradükardia korral. Mööduva põhjusega bradükardia (medikamentoosne)
13 Bradükardiate põhjused Kongenitaalsed bradükardiad Isheemia Põletik (reumatism, borrelioos jt) Fibroos Medikamentoosne Kirurgilise ravi tagajärg (tüsistus või eesmärk) Ablatsioonravi tagajärg (tüsistus või eesmärk) Teadmata
14 Rütmihäirete ravi võimalused Medikamentoosne Mitte-medikamentoosne Invasiivne Semi-invasiivne (söögitoru kaudne) Instrumentaalne Kirurgiline
15 Bradükardiate ravi Medikamentoosne ravi: vähe efektiivne, ebakindla efektiga ja kõrvaltoimete rohke. Medikamentidest võib abi olla siis, kui QRS kompleks on kitsas probleem AV-sõlme tasemel või sellest kõrgemal ja allub sümpaatilise ning parasümpaatilise närvisüsteemi mõjutusele Atropiin Sümpatomimeetikumid (isoproterenool, salbutamool, dopamiin, dobutamiin jt) Aminofülliin Kardiostimulaator ehk tehisrütmur kas püsivate või korduvate bradükardiate raviks
16 Stimulatsiooni põhiprintsiibid Südame pumbafunktsiooni tagamiseks on oluline vatsakeste töö säilumine, selleks piisab elektroodi asetamisest paremasse vatsakesse. (VVI) Sellisel juhul häirub kodade ja vatsakeste normaalne aktivatsiooni järjekord ja sünkroonne töö: südame efektiivsus langeb 15-30% Kui AV-sõlme funktsioon on korras ehk bradükardia põhjus on siinussõlme või kodade tasemel, võib elektroodi asetada vaid kodadesse (AAI). Tõeliselt füsioloogiline stimulatsioon Kodade ja vatsakeste sünkroonse töö tagab kahe-kambri e DDD tüüpi stimulaator ( pseudo füsioloogiline).
17 Bradükardiate ohtlikkus Siinussõlme ja supra-his tasemel (Wencebachi perioodika) tekkivad bradükardiad ei ole otseselt eluohtlikud rütmihäired. Öine Wencenbachi perioodika on sage, eriti noortel. Möbitz II tüüpi AV-blokaad ja laia QRS kompleskiga asendusrütm on ohtlikke rütmihäirete tunnuseks. Kaasasündinud AV-blokaad: fr > 50 bpm rahuolekus, koormusel sagedus tõuseb ja ei teki VES, vatsake ei ole dilateerunud üldjoontes ohutu
18 TAHHÜKARDIAD
19 Tahhükardiliste rütmihäirete klassifikatsioon Tahhükardia mehhanismi alusel Re-entry (taassisestus) Tõusnud automatism Trigerdatud aktiivsus
20 Tahhükardiliste rütmihäirete klassifikatsioon Rütmihäire kolde lokaliseerumise alusel Ventrikulaarne Supraventrikulaarne Tõeliselt supraventrikulaarne rütmihäire kolle asub ainult kodades (kodade virvendus, -laperdus, kodade tahhükardia) NB! AV-ühenduse katkestamisel rütmihäire kestab edasi! Pseudo supraventrikulaarne re-entry ringis osalevad peale kodade ka AV-sõlm ja tihti ka osa vatsakeste müokardist WPW-sündroom. NB! AVühenduse katkestamisel rütmihäire ka katkeb! Teadmata/ebaselge lokalisatsiooniga
21 Pseudo supraventrikulaarne
22 Supraventrikulaarsed tahhükardiad Kodade virvendus (kohati võib täheldada kodede töös mingisugust regulaarsust, vatsakesed ebaregulaarsed v.a. Fredericki s.). Kodade laperdus (kodade töö regulaarne, vatsakeste töö võib olla ebaregulaarne) Tüüpiline nn saehammas Atüüpilised AV-nodaalne reentry tahhükardia (koda aeglane tee vatsakene - kiire tee) AV-reentry tahhükardia (koda AV sõlm vatsakene lisajuhte tee) Kodade tahhükardia Siinustahhükardia 90% juhtudel sekundaarne NB! rütmi aeglustamine võib lõppeda hemodünaamilise kollapsiga)
23 Supraventrikulaarseid rütmihäireid soodustavad faktorid
24 Lisajuhtetee ja WPW Manifestne delta laine EKG-l, lühike PQ aeg, (kui esinevad ka SVT hood siis WPW sündroom). Mitte manifestne või intermiteeruvalt manifestne lisajuhteteel on antegraadne (kdadelt vatsakestele) erutusjuhtivus olemas, kuid see ei ilmne, kuna erutus jõuab AV-sõlme kaudu vatsakesteni kiiremini (näiteks vasem lateraalne lisajuhtetee). Varjatud lisajuhtetee lisajuhtetee juhib erutust vaid retrograadselt (vatsakestelt kodadele), tavalisel EKG-l ei ole lisajuhteteele iseloomulike vihjeid. Tahhükardia ajal P sakk tuleb R sakist hiljem enam, kui 70 ms Tahhükardia võib olla: Ortodroomne kitsa QRS kompleksiga (erutus levib kodadelt vatsakesele AV-sõlme kaudu) Antidroomne laia QRS kompleksiga erutus levib kodadelt vatsakesele lisajuhtetee kaudu)
25 Varjatud lisajuhtetee ja WPW sündroom
26 Lisajuhtetee ja WPW-sündroom Accessory Pathway Accessory pathway Normal rhythm with WPW Tachycardia
27 Accessory Pathway Ablation
28 Ravimid WPW-korral
29 Lisajuhtetee ravivõimalused
30 AVNRT AV-sõlme re-entry tahhükardia Kõige sagedasem regulaarne tahhükardia Kahe osaline AV-sõlm Kiire juhtetee Aeglane juhtetee Avaldub enamasti hilisemas vanuses, kui WPW Enamasti südamesagedus kiirem, kui lisajuhtetee korral, kuna re-entry ring on lühem. ( bpm) Katkestatav vagaalsete võtete ja AV-sõlme mõjutavate ravimitega (Adenosiin valikravimiks) Kergesti ablatseeritav, kuid ca 1% totaalse AV-blokaadi oht
31 Supraventrikulaarsete rütmihäirete eristamine
32 ADENOSIINI TOIME PRO Katkestab AV-sõlme läbivad reentry tahhükardiad Tekitab lühiajalise AV-blokaadi / pausi Toime üli lühiaegne KONTRA Katkestab ajutiselt ka mitmed fokaalsed kodade tahhükardiad ja adenosiintundliku VT Võib tekitada asüstoolia Võib indutseerida AF Oht WPW korral. Võib süvendada isheemiat
33 ADENOSIINI TOIME Ravi ja diagnostika
34 Kodade laperdus (Atrial Flutter) AFL Normal sinus rhythm Atrial Flutter
35 A-Flutter Ablation A-flutter Reentry Circuit Septum Ablation Isthmus Ablation
36
37 Kodade virvendusarütmia Kõige sagedasem rütmihäire (kuni 2% elanikonnast, >80 aastastel ca 10%) 1/3 rütmihäirete tõttu hospialiseeritutest AF tõttu EU-s 4,5 mljn AF patsienti Aastas kulub nende raviks 13,5 miljardit EUROt AF patsiendi keskmine vanus 75 aastat 70% patsientidest jäävad eapiiridesse aastat 12 % patsientidest ei leita kaasuvat kardiopulmonaalset haigust (nn lone AFi) Uusi juhte <40 aastastel 0,1% aastas, tõustes 1,5% naistel ja 2% meestel vanemad kui 80 aastat Kodade virvendusega patsientide suremus on vähemalt 2 korda suurem
38 Südamehaigused ja AF 20,6% meestel ja 26,0% naistel, kellel tekkis kodadevirvendus Framingham i uuringus 38 aastase jälgimisperioodi jooksul esines kaasuvalt südamepuudulikkus (3,2% ja 2,9% ilma südamepuudulikuseta patsientidel tekkis vastavalt AF). AF sagedus on väisem nendel SP patsientidel, keda ravitakse AKEI-ga. Sama kehtib hüpertoonikute kohta, eriti ilmekalt vasaku vatsakese hüpertroofia ilmnemisel.
39 AFib-iga seotud haigused ja seisundid Cardiac causes Hypertensive heart disease Ischemic heart disease Valvular heart disease Rheumatic: mitral stenosis Non-rheumatic: aortic stenosis, mitral regurgitation Pericarditis Cardiac tumors: atrial myxoma Sick sinus syndrome Cardiomyopathy Hypertrophic Idiopathic dilated (? cause vs. effect) Post-coronary bypass surgery Pulmonary COPD Non-Cardiac causes Pneumonia Pulmonary embolism Metabolic Thyroid disease: hyperthyroidism Electrolyte disorder Toxic: alcohol ( holiday heart syndrome)
40 Ravimid, mis võivad põhjustada AFib-i
41 AFib esinemissagedus suureneb vanusega Curr Problems Cardiol 2005;30:
42 AFib esinemus kroonilise südamepuudulikkusega haigetel Curr Problems Cardiol 2005;30:
43 Aastane insultide tekkesagedus antikoagulantraviga ja ilma selleta Curr Problems Cardiol 2005;30:
44 Kodade virvenduse ravi ANTIKOAGULATSIOON VATSAKESTE SAGEDUSE KONTROLL Beeta blokaatorid Verapamiil, Diltiazeem Amiodaroon (Digoksiin toimib ainult rahuolekus) Siinusrütmi säilitav ravi Medikamentoosne, enamasti kombinatsioon mitmest ravimist Ablatsioon ravi (kateeter abaltsioon, kirurgiline ablatsioon) RATE versus RYTHM Control
45 AFib-i preventsioon AKE-inhibiitorite ja ARBidega
46 Atrial Fibrillation Macro re-entry circuits Cox, J.L., Atrial fibrillation I: A new classification system. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg,, (6): p
47 accounts for 1/3 of all patient discharges with arrhythmia as principal diagnosis. 4% Atrial Flutter 6% PVCs 6% PSVT 18% Unspecified 9% SSS 34% Atrial Fibrillation 8% Conduction Disease 3% SCD 10% VT Data source: Baily D. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992;19(3):41A. 2% VF
48 Total Hospitalization Days Based on Presenting Arrhythmia AF Atrial Flutter Cardiac arrest Conduction disease Junctional Premature beats Sick sinus syndrome VF VT Unspecified Presenting Arrhythmia Camm AJ. Am J Cardiol. 1996;78(8A):3-11.
49 Tahhükardiliste rütmihäirete ravi: Medikamentoosne Mittemedikamentoosne Implanteeritavad seadmed (Device-therapy) Kardioverterid-Defibrillaatorid, VF, VT, AF over-drive stimulaatorid, SVT, VT Ablatsioonravi Invasiivne ablatsioonravi (kateeterablatsioon) Kirurgiline ravi
50 Elektriline kardioversioon Valik meetod ebastabiilse patsiendi korral Kiire ja suhteliselt kindla efektiga Toimib nii ventrikulaarsetele kui ka supraventrikulaarsetele tahhükardiatele. Vajab narkoosi, kui patsient teadvusel Puudub kliiniliselt oluline järelmõju High Voltage shock
51 Medikamentoosne kardioversioon Mitmed antiarütmikumid võivad mõjutada stimulatsiooni / ICD defibrillatsiooni läve. Antiarütmikumid võivad mõjutada QRS-kompleksi kuju ja VT sagedust, mille tõttu ICD võib rütmihäiret mitte ära tunda. Ettevaatust ICD patsiendi korral ja talle püsiravi määramisel.
52 Hemodünaamiliselt stabiilne regularne tahhükardia Kitsas QRS Lai QRS SVT SVT + BBB Kindlalt SVT VT või ebaselge laia QRS Vagaalsed võtted Adenosiin I/V Verapamiil/Diltiazeem I/V Beeta-blokaator I/V SVT katkeb? Preeksitatsiooniga SVT Novokaiinamiid I/V Sotalool I/V Propafenoon I/V Lidokaiin I/V Amiodaroon I/V (Langenud EF korral) JAH Ibutiliid I/V \ Novokaiinamiid I/V \ AV juhtivust VT katkeb? EI SVT püsib Propafenoon I/V / + langetavad Flekainiid I/V / ravimid Ülestimulatsioon JAH EI VT püsib AV juhtivus langes Kardioversioon Kardioversioon
53 Rütmihäirete ravimite kõrvaltoimed Bradükardia, kuni sünkoobi tekkeni QT aja pikenemine ja sellega seotud eluohtlikud rütmihäired (v.a. Beeta-blokaatorid ja Cablokaatorid). Südame jõudluse vähenemine (negatiivne inotroopne toime
54 Sünkoop Süda Rütmihäired
55
56
57
58
59
60
61 Ohutud (?) Rütmhäirete patsiendi prognoos SVT AGA: AF üldsurevus vähemalt 2 korda tõusnud AF + Südamepuudulikkus ca 5 kordne surevuse tõus WPW ca 1% aastane surevus, VES (?) Ohtlikud VT Sünkoobiga kulgevad rütmihäired, eriti kellel kaasuv südamehaigus
62 Millised haiged tuleks võtta koheselt uuringutele? Kellel esineb ohtlik rütmihäire (VT, WPW ja AF koos lühima RR intervalliga alla 250 ms, AV-blokaad II (Möbitz II) või III aste. Kellel esines sünkoop, eeldatavalt rütmihäirega seotult. Kelle hemodünaamika rütmihäire ajal ebastabiilne. Kelle kaasuv südamehaigus rütmihäire ajal destabiliseerub südamepuudulikkus, stenokardia. Kellel antiarütmikumide manustamine põhjustab kõrvaltoimeid (QTc pikenemine, bradükardia, sünkoop)
63
64 Antiarütmikumide klassifikatsioon I klass e. Naatrium kanalite blokaatorid IA Kinidiin,Novokaiinamiid IB Lidokaiin, Mexilentiin IC Propafenoon, Flekaiinid, Disopüramiid II klass e. ß-adrenoblokaatorid III klass (Amiodaroon e.cordarone; Sotalool; Dofetiliid) IV klass e. Kaltsium-kanalite blokaatorid (Verapamiil, Diltiaseem)
65 IB Lidokaiin, Mexilentiin Sobivad vaid ventrikulaarsete rütmihäirete raviks (ventrikulaarne ekstrasüstoolia, ventrikulaarne tahhükardia, vatsakeste fibrillatsiooni ärahoidmiseks) Mexilentiin on olemas ka suukaudse vormina
66 IA Kinidiin, Novokaiinamiid IC Propafenoon, Flekainiid Sobivad erinevate rütmihäirete raviks Supraventrikulaarsete Ventrikulaarsete Mõjutavad ka lisajuhtetee juhtivust Sobivad nii rütmihäirehoo lõpetamiseks kui ka uue hoo profülaktikaks
67 Propanolool Atenolool (Tenormin) II KLASS Beeta-blokaatorid Metoprolool (Betaloc, Seloken) Bisoprolool Karvedilool (Dilatrend) Nebivolool (Nebilet)
68 II KLASS Beeta-blokaatorid Tagasihoidliku antiarütmilise aktiivsusega Vähendavad katehoolamiinide toimega seotud rütmihäireid (koormusel, närveerimisel) Halvendava AV-juhtivust Aitavad langetada vatsakeste sagedust kodade virvenduse(laperduse) korral Vähendavad hapniku vajadust (Isheemiat) Lühendavad QT-aega
69 III Klass Amiodaroon e. Cordarone Sobib erinevate rütmihäirete raviks Nii hoo katkestamiseks kui ka uue hoo vältimiseks. Suukaudselt manustatuna ilmneb efekt alles küllastusannuse manustamisel (10 g) Sisaldab joodi, millega sageli tekivad kilpnäärme talitluse probleemid Kestval manustamisel ladestub silmade sarvkestas (nägemisehäired) ja kopsudesse (kopsufibroos)
70 III Klass Sotalool Valdavalt beeta-adrenoblokaator, millel lisaks muude antiarütmikumide omadusi. Võib pikendada QT aega ja põhjustada eluohtlike rütmihäirete tekke Seega ravi alustades oluline EKG kontroll
71 IV klass Verapamiil, Diltiaseem Sobivad valdavalt vaid supraventrikulaarsetele ja atrioventrikulaarsõlmega seotud rütmihäiretele Nii hoo raviks, kui ka uue hoo vältimiseks Erutusjuhtesüsteemiga seotud ventrikulaarne tahhükardia (fastsikulaarne) allub samuti verapamilile. Ei mõjuta lisajuhtetee juhtivust, seega ei sobi teadaoleva WPW-sündroomi korral Kuna laiendavad veresooni langetavad vererõhku Negatiivse inotroopse toime tõttu ei soovitata südamepuudulikkuse korral
72 ADENOSIIN Hetkeks katkestab AV-sõlme juhtivuse Kui esineb lisajuhtetee hakkab erutus kodadelt vatsakestele levima vaid lisajuhtetee kaudu Võib põhjustada kodade virvendust (ohtlik lisajuhtetee korral) NB! Adenosiini manustamise ajal on alaati otstarbekas samal ajal jooksvalt registreerida EKG-d, see annab väga olulise diagnostilise vihje rütmihäire tüübi ja edasiste ravivõimaluste kohta.
73 DIGOKSIIN Mõjutab uitnärvi (nervus vagus'e) toonust ehk suurendab parasümpaatilise närvisüsteemi mõju südamele Langetab AV-sõlme juhtivust kuid vaid rahuolekus Koormuse ajal aktiveerub sümpaatiline närvisüsteem ja digoksini mõju siis lakkab
74
75 ERROR: syntaxerror OFFENDING COMMAND: --nostringval-- STACK: (R tmih irete tekkepıhjused ja ravi.ppt [Read-Only]) /Title () /Subject (D: ) /ModDate () /Keywords (PDFCreator Version 0.8.0) /Creator (D: ) /CreationDate (indrekratsep) /Author -mark-
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias
 Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Normal Sinus Rhythm. Sinus Bradycardia. Sinus Tachycardia. Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example (NSR) & consistent. & consistent.
 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT. Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia
 PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART SA node His bundle Left bundle AV node Right
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART SA node His bundle Left bundle AV node Right
the basics Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital
 ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
Basics of Pacing. Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN
 Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Presenter Disclosure Information
 2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams
 Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology
 Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology Chapter 4: Endocrine, Nutritional, and Metabolic Diseases (E00-E89) The diabetes mellitus codes are combination codes
Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology Chapter 4: Endocrine, Nutritional, and Metabolic Diseases (E00-E89) The diabetes mellitus codes are combination codes
Syncope. enough to include disorders such as epileptic seizures and concussion. January 14-15, 2011 SCA Conference 1
 Syncope and Atypical Seizures Ravi Mandapati, M.D., FACC.; FHRS Director, Specialized Program for Arrhythmias in Congenital Heart Disease UCLA Cardiac Arrhythmia Center David Geffen School of Medicine
Syncope and Atypical Seizures Ravi Mandapati, M.D., FACC.; FHRS Director, Specialized Program for Arrhythmias in Congenital Heart Disease UCLA Cardiac Arrhythmia Center David Geffen School of Medicine
ACLS RHYTHM TEST. 2. A 74-year-old woman with chest pain. Blood pressure 192/90 and rates her pain 9/10.
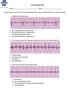 ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
Adult Cardiac Surgery ICD9 to ICD10 Crosswalks
 164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C38.0 Malignant neoplasm of heart 164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C45.2 Mesothelioma of pericardium 198.89 Secondary malignant neoplasm of other specified sites C79.89
164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C38.0 Malignant neoplasm of heart 164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C45.2 Mesothelioma of pericardium 198.89 Secondary malignant neoplasm of other specified sites C79.89
Automatic External Defibrillators
 Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians
 Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians May 19, 2015 Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent
Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians May 19, 2015 Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent
By the end of this continuing education module the clinician will be able to:
 EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
Preparing for ICD-10 for Physicians
 Preparing for ICD-10 for Physicians May 2011 Notices These coding suggestions and coverage guidelines do not replace seeking coding advice from the payer and/or your coding staff. The ultimate responsibility
Preparing for ICD-10 for Physicians May 2011 Notices These coding suggestions and coverage guidelines do not replace seeking coding advice from the payer and/or your coding staff. The ultimate responsibility
Introduction to Electrophysiology. Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery
 Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery David E. Lizotte, Jr. PA C, MPAS, FAPACVS President, Association of Physician Assistants in Cardiovascular Surgery Conflicts: None Indications 2008 Journal
Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery David E. Lizotte, Jr. PA C, MPAS, FAPACVS President, Association of Physician Assistants in Cardiovascular Surgery Conflicts: None Indications 2008 Journal
Electrophysiology Daymar College. Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011
 Electrophysiology Daymar College Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011 Electrical Conduction Pathway Chemical Basis for Impulse Formation Cardiac Action Potential Phases http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oqpffilde0e
Electrophysiology Daymar College Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011 Electrical Conduction Pathway Chemical Basis for Impulse Formation Cardiac Action Potential Phases http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oqpffilde0e
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL)
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001
 BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008
 Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS RHYTHM INTERPRETATION
 NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
Managing the Patient with Atrial Fibrillation
 Pocket Guide Managing the Patient with Atrial Fibrillation Updated April 2012 Editor Stephen R. Shorofsky, MD, Ph.D. Assistant Editors Anastasios Saliaris, MD Shawn Robinson, MD www.hrsonline.org DEFINITION
Pocket Guide Managing the Patient with Atrial Fibrillation Updated April 2012 Editor Stephen R. Shorofsky, MD, Ph.D. Assistant Editors Anastasios Saliaris, MD Shawn Robinson, MD www.hrsonline.org DEFINITION
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics
 Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
Catheter Ablation. A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias
 Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Introduction 2/9/2015
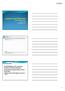 Thomas Haffey, D.O. FACC, FACOI, FNLA, CSOM February, 2015 Atrial Tachycardias Diagram summarizing types of atrial tachycardias often encountered in patients with a history of AF, including those seen
Thomas Haffey, D.O. FACC, FACOI, FNLA, CSOM February, 2015 Atrial Tachycardias Diagram summarizing types of atrial tachycardias often encountered in patients with a history of AF, including those seen
Atrial Fibrillation 2014 How to Treat How to Anticoagulate. Allan Anderson, MD, FACC, FAHA Division of Cardiology
 Atrial Fibrillation 2014 How to Treat How to Anticoagulate Allan Anderson, MD, FACC, FAHA Division of Cardiology Projection for Prevalence of Atrial Fibrillation: 5.6 Million by 2050 Projected number of
Atrial Fibrillation 2014 How to Treat How to Anticoagulate Allan Anderson, MD, FACC, FAHA Division of Cardiology Projection for Prevalence of Atrial Fibrillation: 5.6 Million by 2050 Projected number of
Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness
 Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
How should we treat atrial fibrillation in heart failure
 Advances in Cardiac Arrhhythmias and Great Innovations in Cardiology Torino, 23/24 Ottobre 2015 How should we treat atrial fibrillation in heart failure Matteo Anselmino Dipartimento Scienze Mediche Città
Advances in Cardiac Arrhhythmias and Great Innovations in Cardiology Torino, 23/24 Ottobre 2015 How should we treat atrial fibrillation in heart failure Matteo Anselmino Dipartimento Scienze Mediche Città
Cardiac Syncope. spot it, stop it! Syncope is Tranient Loss of Consciousness (T- LOC) due to: transient global cerebral hypoperfusion
 Definition Cardiac Syncope spot it, stop it! David Gareth Jones Heart Rhythm Centre Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Syncope is Tranient Loss of Consciousness (T- LOC) due to: transient
Definition Cardiac Syncope spot it, stop it! David Gareth Jones Heart Rhythm Centre Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Syncope is Tranient Loss of Consciousness (T- LOC) due to: transient
TABLE 1 Clinical Classification of AF. New onset AF (first detected) Paroxysmal (<7 days, mostly < 24 hours)
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Deborah Ritchie RN, MN, Robert S Sheldon MD, PhD Cardiovascular Research Group, University of Calgary, Alberta Partly
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Deborah Ritchie RN, MN, Robert S Sheldon MD, PhD Cardiovascular Research Group, University of Calgary, Alberta Partly
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
A 35 yo female presents increasing fatigue and shortness of breath for several days. She is found to be in atrial fibrillation.
 Ryan G. Aleong Cardiology Department University of Colorado A 35 yo female presents increasing fatigue and shortness of breath for several days. She is found to be in atrial fibrillation. 1. Initiation
Ryan G. Aleong Cardiology Department University of Colorado A 35 yo female presents increasing fatigue and shortness of breath for several days. She is found to be in atrial fibrillation. 1. Initiation
Palpitations & AF. Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust
 Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
Ngaire has Palpitations
 Ngaire has Palpitations David Heaven Cardiac Electrophysiologist/Heart Rhythm Specialist Middlemore, Auckland City and Mercy Hospitals Auckland Heart Group MCQ Ms A is 45, and a healthy marathon runner.
Ngaire has Palpitations David Heaven Cardiac Electrophysiologist/Heart Rhythm Specialist Middlemore, Auckland City and Mercy Hospitals Auckland Heart Group MCQ Ms A is 45, and a healthy marathon runner.
QRS Complexes. Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program
 6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation
 Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation Caroline McKillop Advisor: Dr. Tam Psenka 10-3-2007 Importance of Cardiac Guidelines -Used multiple times every day -Patient Safety -Part of Surgical Care Improvement Project
Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation Caroline McKillop Advisor: Dr. Tam Psenka 10-3-2007 Importance of Cardiac Guidelines -Used multiple times every day -Patient Safety -Part of Surgical Care Improvement Project
Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier
 Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier Most common dysrhythmia seen in ED, and incidence increasing with ageing population Presentation Common presentations: younger patients often
Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier Most common dysrhythmia seen in ED, and incidence increasing with ageing population Presentation Common presentations: younger patients often
Atrial Fibrillation Based on ESC Guidelines. Moshe Swissa MD Kaplan Medical Center
 Atrial Fibrillation Based on ESC Guidelines Moshe Swissa MD Kaplan Medical Center Epidemiology AF affects 1 2% of the population, and this figure is likely to increase in the next 50 years. AF may long
Atrial Fibrillation Based on ESC Guidelines Moshe Swissa MD Kaplan Medical Center Epidemiology AF affects 1 2% of the population, and this figure is likely to increase in the next 50 years. AF may long
12-Lead EKG Interpretation. Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P
 12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
Atrial Fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome. John Whitaker, Conn Sugihara and Michael Cooklin (Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust)
 Atrial Fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome John Whitaker, Conn Sugihara and Michael Cooklin (Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust) A 38 year old paramedic was admitted with symptoms
Atrial Fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome John Whitaker, Conn Sugihara and Michael Cooklin (Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust) A 38 year old paramedic was admitted with symptoms
Objectives. The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease. Lead II P-Wave Amplitude during COPD Exacerbation and after Treatment (50 pts.
 The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
Atrial Fibrillation 2012: Latest Approaches to Diagnosis, Treatment, and Stroke Prevention
 Atrial Fibrillation 2012: Latest Approaches to Diagnosis, Treatment, and Stroke Prevention Michael G. Clark, PA-C, MPAS, Ph.D., AACC Fisher Cardiology and Electrophysiology Bedford, Texas Disclosures Speakers
Atrial Fibrillation 2012: Latest Approaches to Diagnosis, Treatment, and Stroke Prevention Michael G. Clark, PA-C, MPAS, Ph.D., AACC Fisher Cardiology and Electrophysiology Bedford, Texas Disclosures Speakers
The abbreviation EKG, for electrocardiogram,
 CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
ECG made extra easy. medics.cc
 ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
Atrial Fibrillation The High Risk Obese Patient
 Atrial Fibrillation The High Risk Obese Patient Frederick Schaller, D.O.,F.A.C.O.I. Professor and Vice Dean Touro University Nevada A 56 year old male with a history of hypertension and chronic stable
Atrial Fibrillation The High Risk Obese Patient Frederick Schaller, D.O.,F.A.C.O.I. Professor and Vice Dean Touro University Nevada A 56 year old male with a history of hypertension and chronic stable
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: Scope of the Problem. October 2015
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: Scope of the Problem October 2015 Purpose of the Presentation Review the worldwide incidence and prognosis associated with atrial fibrillation (AF) Identify the types of AF, clinical
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: Scope of the Problem October 2015 Purpose of the Presentation Review the worldwide incidence and prognosis associated with atrial fibrillation (AF) Identify the types of AF, clinical
Premature Ventricular Contractions. Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS
 Premature Ventricular Contractions Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Premature Ventricular Contractions: ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for Management of Patients With Ventricular
Premature Ventricular Contractions Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Premature Ventricular Contractions: ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for Management of Patients With Ventricular
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children
 Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
4/7/2015. Cardiac Rehabilitation: From the other side of the glass door. Chicago, circa 1999. Objectives. No disclosures, no conflicts
 Cardiac Rehabilitation: From the other side of the glass door No disclosures, no conflicts Charles X. Kim, MD, FACC, ABVM Objectives 1. Illustrate common CV benefits of CV rehab in real world practice.
Cardiac Rehabilitation: From the other side of the glass door No disclosures, no conflicts Charles X. Kim, MD, FACC, ABVM Objectives 1. Illustrate common CV benefits of CV rehab in real world practice.
Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia
 T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e clinical practice Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia Mark S. Link, M.D. This Journal feature begins with a case vignette
T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e clinical practice Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia Mark S. Link, M.D. This Journal feature begins with a case vignette
Lead avr: The Neglected Lead
 Chapter 22 Lead avr: The Neglected Lead M Chenniappan INTRODUCTION Lead avr, one of the 12 electrocardiographic leads, is frequently ignored in clinical medicine. In fact, many clinicians refer to the
Chapter 22 Lead avr: The Neglected Lead M Chenniappan INTRODUCTION Lead avr, one of the 12 electrocardiographic leads, is frequently ignored in clinical medicine. In fact, many clinicians refer to the
5 MILLION AMERICANS 1. Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) AFib affects an estimated
 A Patient s Guide To with Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) CAUSES RISK FACTORS SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENTS INSIDE The Healthy Heart... 2 Your Heart In AFib... 4 How Do You Get It?... 6 How Do You Know If You
A Patient s Guide To with Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) CAUSES RISK FACTORS SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENTS INSIDE The Healthy Heart... 2 Your Heart In AFib... 4 How Do You Get It?... 6 How Do You Know If You
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias
 8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
Surgeons Role in Atrial Fibrillation
 Atrial Fibrillation Surgeons Role in Atrial Fibrillation Steven J Feldhaus, MD, FACS 2015 Cardiac Symposium September 18, 2015 Stages of Atrial Fibrillation Paroxysmal (Intermittent) Persistent (Continuous)
Atrial Fibrillation Surgeons Role in Atrial Fibrillation Steven J Feldhaus, MD, FACS 2015 Cardiac Symposium September 18, 2015 Stages of Atrial Fibrillation Paroxysmal (Intermittent) Persistent (Continuous)
22 Arrhythmias. C. Scharf and F. Duru. Siegenthaler, Differential Diagnosis in Internal Medicine (ISBN9783131421418), 2007 Georg Thieme Verlag
 22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
Approach to the Patient with Syncope
 Syncope Case Study 38-year-old female with recurrent syncope occasionally occurring during emotional stressful times. Her physical examination and 12 lead EKG are normal. Approach to the Patient with Syncope
Syncope Case Study 38-year-old female with recurrent syncope occasionally occurring during emotional stressful times. Her physical examination and 12 lead EKG are normal. Approach to the Patient with Syncope
COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Question: How should the EGBS Coverage Guidance regarding ablation for atrial fibrillation be applied to the Prioritized List? Question source: Evidence
COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Question: How should the EGBS Coverage Guidance regarding ablation for atrial fibrillation be applied to the Prioritized List? Question source: Evidence
Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication.
 In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
PRO-CPR. 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview. (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material)
 PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
Life Threatening EKG s In The Office. Joseph A Manfredi, MD, FACC, FHRS GHS Cardiovascular Symposium
 Life Threatening EKG s In The Office Joseph A Manfredi, MD, FACC, FHRS GHS Cardiovascular Symposium January 24 th, 2015 Disclosures Speaker Honorariums: STJM, Boston Scientific Advisory role: Medtronic
Life Threatening EKG s In The Office Joseph A Manfredi, MD, FACC, FHRS GHS Cardiovascular Symposium January 24 th, 2015 Disclosures Speaker Honorariums: STJM, Boston Scientific Advisory role: Medtronic
Antiarrhythmic drug pharmacology
 Antiarrhythmic drug pharmacology Samuel C. Dudley, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. 6/7/2003 1 Setting the membrane potential Nernst E eq [ S] = 61log i [ S] o Current I Na Equil. Pot. +60 mv Effect on E m Depolarize
Antiarrhythmic drug pharmacology Samuel C. Dudley, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. 6/7/2003 1 Setting the membrane potential Nernst E eq [ S] = 61log i [ S] o Current I Na Equil. Pot. +60 mv Effect on E m Depolarize
Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. in general practice. 22 BPJ Issue 39
 Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION in general practice 22 BPJ Issue 39 What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in primary care. It is often
Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION in general practice 22 BPJ Issue 39 What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in primary care. It is often
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS -
 Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
Clinical Guideline for the Management of Pot Operative Atrial Fibrillation
 Clinical Guideline for the Management of Pot Operative Atrial Fibrillation 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. Atrial Fibrillation is the most common cardiac arrhythmia with a prevalence of around 0.5%
Clinical Guideline for the Management of Pot Operative Atrial Fibrillation 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. Atrial Fibrillation is the most common cardiac arrhythmia with a prevalence of around 0.5%
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
UNIVERSITA' DEGLI STUDI DI ROMA TOR VERGATA
 SYSTEMATIC PATHOLOGY I IIIYear Scientific Field DISCIPLINE TUTOR Systematic Pathology I MED/21 MED/10 Thoracic Surgery Respiratory Diseases Tommaso Claudio Mineo Paola Rogliani MED/10 Respiratory Diseases
SYSTEMATIC PATHOLOGY I IIIYear Scientific Field DISCIPLINE TUTOR Systematic Pathology I MED/21 MED/10 Thoracic Surgery Respiratory Diseases Tommaso Claudio Mineo Paola Rogliani MED/10 Respiratory Diseases
Karen Bain James Cook University Hospital Middlesbrough
 Karen Bain James Cook University Hospital Middlesbrough Electrophysiology Electrophysiology... Is the study of the heart s electrical system Assesses the function of each component of cardiac conduction
Karen Bain James Cook University Hospital Middlesbrough Electrophysiology Electrophysiology... Is the study of the heart s electrical system Assesses the function of each component of cardiac conduction
THE CANADIAN CARDIOVASCULAR SOCIETY DATA DICTIONARY ATRIAL FIBRILLATION/FLUTTER DATA ELEMENTS AND DEFINITIONS
 THE CANADIAN CARDIOVASCULAR SOCIETY DATA DICTIONARY A CCS Consensus Document ATRIAL FIBRILLATION/FLUTTER DATA ELEMENTS AND DEFINITIONS FINAL VERSION v1.1 Last Updated: July 16, 2013 Copyright 2013 The
THE CANADIAN CARDIOVASCULAR SOCIETY DATA DICTIONARY A CCS Consensus Document ATRIAL FIBRILLATION/FLUTTER DATA ELEMENTS AND DEFINITIONS FINAL VERSION v1.1 Last Updated: July 16, 2013 Copyright 2013 The
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION IN THE 21 ST CENTURY TIMOTHY DOWLING, D.O. FAMILY PHYSICIAN
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION IN THE 21 ST CENTURY TIMOTHY DOWLING, D.O. FAMILY PHYSICIAN GOALS AND OBJECTIVES At The end of this talk you should understand: What is Atrial Fibrillation Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION IN THE 21 ST CENTURY TIMOTHY DOWLING, D.O. FAMILY PHYSICIAN GOALS AND OBJECTIVES At The end of this talk you should understand: What is Atrial Fibrillation Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
Understanding the Electrocardiogram. David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem
 Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Guideline for the management of arrhythmias
 Guideline for the management of arrhythmias The following guideline is approved only for use at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. It is provided as supporting information for the
Guideline for the management of arrhythmias The following guideline is approved only for use at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. It is provided as supporting information for the
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND ANAESTHESIA
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND ANAESTHESIA Dr AD Theron, SHO in Anaesthesia, Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital, Exeter, UK. E-mail: drabrietheron@yahoo.co.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the commonest arrhythmias.
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND ANAESTHESIA Dr AD Theron, SHO in Anaesthesia, Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital, Exeter, UK. E-mail: drabrietheron@yahoo.co.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the commonest arrhythmias.
GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS. (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support)
 AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
Management of Atrial Fibrillation in Heart Failure
 Disadvantages of AV Junction Ablation Persistent AFib- no AV synchrony Ongoing risk of thromboembolism Life-long dependency on pacemaker Comparison of LA Ablation vs. AVN Ablation LA Ablation AVN Ablation
Disadvantages of AV Junction Ablation Persistent AFib- no AV synchrony Ongoing risk of thromboembolism Life-long dependency on pacemaker Comparison of LA Ablation vs. AVN Ablation LA Ablation AVN Ablation
CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY, ARRHYTHMIAS AND PACING. Medical Knowledge. Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational
 Know the histology and gross anatomy of the normal sinoatrial node, atrial conduction pathways, atrioventricular (AV) junction and nod, His bundle, conduction fascicles and terminal intra-ventricular conduction
Know the histology and gross anatomy of the normal sinoatrial node, atrial conduction pathways, atrioventricular (AV) junction and nod, His bundle, conduction fascicles and terminal intra-ventricular conduction
JAPI VOL. 52 NOVEMBER 2004 www.japi.org 883
 Review Article Wide Complex Tachycardia : Recognition and Management in the Emergency Room IB Ray Abstract Cardiac arrhythmias often present as urgent medical conditions requiring immediate care. Patient
Review Article Wide Complex Tachycardia : Recognition and Management in the Emergency Room IB Ray Abstract Cardiac arrhythmias often present as urgent medical conditions requiring immediate care. Patient
Visited 9/14/2011. What is Atrial Fibrillation? What you need to know about Atrial Fibrillation. The Normal Heart Rhythm. 1 of 7 9/14/2011 10:50 AM
 1 of 7 9/14/2011 10:50 AM Current URL: What you need to know about Atrial Fibrillation What is atrial fibrillation? What causes atrial fibrillation? How is atrial fibrillation diagnosed? What are the dangers
1 of 7 9/14/2011 10:50 AM Current URL: What you need to know about Atrial Fibrillation What is atrial fibrillation? What causes atrial fibrillation? How is atrial fibrillation diagnosed? What are the dangers
Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome
 Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome R. Thomas Collins II, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Internal Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Arkansas Children s Hospital
Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome R. Thomas Collins II, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Internal Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Arkansas Children s Hospital
What to Know About. Atrial Fibrillation
 Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
ACCIDENT AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT/CARDIOLOGY
 Care Pathway Triage category ATRIAL FIBRILLATION PATHWAY ACCIDENT AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT/CARDIOLOGY AF/ FLUTTER IS PRIMARY REASON FOR PRESENTATION YES NO ONSET SYMPTOMS OF AF./../ TIME DURATION OF AF
Care Pathway Triage category ATRIAL FIBRILLATION PATHWAY ACCIDENT AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT/CARDIOLOGY AF/ FLUTTER IS PRIMARY REASON FOR PRESENTATION YES NO ONSET SYMPTOMS OF AF./../ TIME DURATION OF AF
Chest Pain in Young Athletes. Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego cdavis@rchsd.
 Chest Pain in Young Athletes Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego cdavis@rchsd.org 858-966-5855 None Disclosures Chest Pain: the good news and the bad news:
Chest Pain in Young Athletes Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego cdavis@rchsd.org 858-966-5855 None Disclosures Chest Pain: the good news and the bad news:
The debate: Should all AF patients see an EP consultant?
 The debate: Should all AF patients see an EP consultant? Pre-debate show of hands in favour of the motion The argument for the motion: Dr Nick Kelland The argument against the motion: Dr Andy McCoye Discussion
The debate: Should all AF patients see an EP consultant? Pre-debate show of hands in favour of the motion The argument for the motion: Dr Nick Kelland The argument against the motion: Dr Andy McCoye Discussion
RUSSELLS HALL HOSPITAL EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT
 RUSSELLS HALL HOSPITAL EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT CLINICAL GUIDELINE ATRIAL FIBRILLATION March 2011 For quick links to AF algorithms: UNSTABLE PATIENT STABLE PATIENT - 1 - Introduction Atrial fibrillation is
RUSSELLS HALL HOSPITAL EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT CLINICAL GUIDELINE ATRIAL FIBRILLATION March 2011 For quick links to AF algorithms: UNSTABLE PATIENT STABLE PATIENT - 1 - Introduction Atrial fibrillation is
Management of Atrial Fibrillation in the Emergency Department
 Management of Atrial Fibrillation in the Emergency Department Ref: Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America, 2005 Introduction AfAf is most common cardiac arrhythmia Sequelae: : range from none to devastating:
Management of Atrial Fibrillation in the Emergency Department Ref: Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America, 2005 Introduction AfAf is most common cardiac arrhythmia Sequelae: : range from none to devastating:
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation DISCLOSURES. Heart Beat Anatomy. I have no financial conflicts to disclose
 Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
How do you decide on rate versus rhythm control?
 How do you decide on rate versus rhythm control? Dr. Mark O Neill Consultant Cardiologist & Electrophysiologist Assumptions Camm et al. EHJ 2010;Sept 25 epub Choice of strategy: Criteria for consideration
How do you decide on rate versus rhythm control? Dr. Mark O Neill Consultant Cardiologist & Electrophysiologist Assumptions Camm et al. EHJ 2010;Sept 25 epub Choice of strategy: Criteria for consideration
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study
 Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
NAME OF THE HOSPITAL: 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3
 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
Combined Epicardial and Endocardial Ablation for Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation. Ashkan Babaie MD Providence Portland Medical Center
 Combined Epicardial and Endocardial Ablation for Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation Ashkan Babaie MD Providence Portland Medical Center 1 Disclosures None 2 Cox-Maze III The Godfather Cure rates > 95% in
Combined Epicardial and Endocardial Ablation for Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation Ashkan Babaie MD Providence Portland Medical Center 1 Disclosures None 2 Cox-Maze III The Godfather Cure rates > 95% in
2320-6691 2015; 3(3B):1132-1136 ISSN 2347-954X
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3B):1132-1136 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3B):1132-1136 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Appropriate Use Criteria for ICD/CRT Online Appendix Guideline Mapping and References Document
 Appropriate Use Criteria for ICD/CRT Online Appendix Guideline Mapping and References Document Section 1: Secondary Prevention Table 1.1 CAD: VF or Hemodynamically Unstable VT Associated With Acute (
Appropriate Use Criteria for ICD/CRT Online Appendix Guideline Mapping and References Document Section 1: Secondary Prevention Table 1.1 CAD: VF or Hemodynamically Unstable VT Associated With Acute (
Projected Number of Adults With AF in the US. Review the growing incidence and importance of AF in the population
 Atrial Fibrillation Troy E. Rhodes, MD, PhD Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Electrophysiology Ohio State University Medical Center Learning Objectives Review the growing incidence and importance of
Atrial Fibrillation Troy E. Rhodes, MD, PhD Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Electrophysiology Ohio State University Medical Center Learning Objectives Review the growing incidence and importance of
Anatomy Review. Heart Murmurs. Surface Topography of the Heart 7/19/2011. The Base of the Heart and Erb s Point
 James A Mathey PA C, MPA CAPA WORKSHOP 2010 Heart Murmurs Anatomy Review 4 Classic Auscultatory Areas: Aortic 2ICS R SB Pulmonic 2ICS L SB Tricuspid 4 th L Lower SB Mitral 5ICS MCL Surface Topography of
James A Mathey PA C, MPA CAPA WORKSHOP 2010 Heart Murmurs Anatomy Review 4 Classic Auscultatory Areas: Aortic 2ICS R SB Pulmonic 2ICS L SB Tricuspid 4 th L Lower SB Mitral 5ICS MCL Surface Topography of
Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure: A Cause or a Consequence
 Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure: A Cause or a Consequence Rajat Deo, MD, MTR Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Cardiology, Electrophysiology Section University of Pennsylvania November
Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure: A Cause or a Consequence Rajat Deo, MD, MTR Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Cardiology, Electrophysiology Section University of Pennsylvania November
Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain
 Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain Vikranth Gongidi, DO FACC FACOI Indian River Medical Center Vero Beach, FL No Disclosures Outline Background Chest pain pathway Indications for stress test Stress test
Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain Vikranth Gongidi, DO FACC FACOI Indian River Medical Center Vero Beach, FL No Disclosures Outline Background Chest pain pathway Indications for stress test Stress test
