A Rare Combination of Mixed Germ Cell Tumour of Testis- A Case Report
|
|
|
- Adelia Martin
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CASE REPORT A Rare Combination of Mixed Germ Cell Tumour of Testis- A Case Report *R Islam 1, Z Boksh 2, S Rahman 3, K Pasha 4 1 Dr. Rezaul Islam, Associate Professor & Head, Department of Surgery, Johurul Islam Medical College Hospital, JIMCH 2 Dr. Zahangir Boksh, Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Johurul Islam Medical College Hospital, JIMCH 3 Dr. Shafiqur Rahman, Associate Professor, Department of Radiology and imaging, Johurul Islam Medical College Hospital, JIMCH 4 Dr. Kamal Pasha, Assistant Professor, Department of Surgery,Johurul Islam Medical College Hospital, JIMCH *Corresponding Author ABSTRACT A 20 years old man presented with 4 year history of painless swelling of the left testis. He ignored this swelling until he started having pain in the abdomen. Ultrasonography revealed testicular malignancy with multiple para-aortic lymph nodes enlargements in the abdomen. His X-ray chest showed pulmonary metastasis. One tumor marker was raised. Histology revealed mixed germ cell tumour with a rare combination of seminoma and embryonal carcinoma. Because of this rare combination of 2 varieties of testicular germ cell tumor and extensive systemic metastasis we presented this case. We discussed the epidemiology, incidence, classification, staging, treatment and prognosis of testicular cancer. Key Words: Testicular cancer, Seminoma, Embryonal carcinoma, Orchiectomy Introduction Primary testicular tumors are the most common solid malignant tumor in men between the ages of 20 and 35 years. For unknown reasons, the incidence of this cancer has increased during the last century 1. Most testicular tumours are derived from the germ cells of the testis, although about 5% of testicular tumours are derived from other cells, including Leydig cells and lymphocytes (lymphoma) 2. The cause of testicular tumours is unknown, but several predisposing factors are recognized. Any solid, firm mass within the testis should be considered testicular cancer until proven otherwise. Prompt diagnosis and early treatment are required for cure. Testicular cancer may be painless, in which case they are sometimes ignored by the patient. In painful testicular swelling should be differentiated from epididymo-orchitis. The clinician should consider the full differential diagnosis of a testicular mass, which includes epididymo-orchitis, testicular torsion, hydrocele, hernia, hematoma, spermatocele, varicocele, and syphilitic gumma. In the past, metastatic testicular cancer was usually fatal, but recent advances in treatment, including high-dose chemotherapy and stem cell rescue, have considerably improved the prognosis. Indeed, testicular cancer is a bright spot in the oncological landscape and are now considered to be the model for treatment of solid tumors3. Testicular cancers are highly curable, even in patients with metastatic disease at diagnosis. The AKMMC J 2015; 6(1): prognosis depends upon the histologic type of cancer (seminoma versus non-seminoma), stage, and other features such as tumor marker and type of metastatic disease. Cure rates for good-risk disease is nearly 90-95%. Case Presentation A 20 years old male presented with four years history of painless swelling of the left testis. He ignored this swelling all this years probably due to lack of pain and he was ashamed of revealing to others. He came to the hospital as he experienced pain in his abdomen also. On examination his left testis was swollen, firm to hard in consistency and having smooth surface. It was oval in shape but size was about 10cm/6 cm. (Fig-A1)The testis was not fixed with the scrotal wall. He had vague lump and moderate tenderness in the lower abdomen on palpation. Ultrasonography showed a complex mass, partly solid and partly cystic in his left testis (Fig-B3). There was no fluid collection in the scrotum. This was typical combined solid and cystic component of mixed germ cell tumour. There were multiple enlarged para aortic lymph nodes in the abdomen.(fig-b1) His chest x-ray showed a huge cannon ball opacity occupying upper and mid zone of the Right lung.(fig-b2) Blood sample for serum marker was sent. β-hcg and LDH were found to be within normal limit.?-feto protein was 287 nmol/ml (normal < 10nmol/ml). Left
2 51 AKMMC J 2015 : 6(1) radical orchiectomy was done through inguinal approach. His abdominal lump and tenderness were reduced within a week of orchiectomy. Histology of the tumor showed combined variety of testicular carcinoma. On gross view the tumour had solid and cystic component.(fig-a2) Microscopy revealed a combination of seminoma(fig-a3) and embryonal carcinoma(fig-a4) After healing of the wound patient was sent to oncologist in national Cancer Institute for further chemotherapy and radiotherapy. (1. Clinical picture, Figure-A 2.Gross picture of the bisected tumour, 3. Photo micrograph of the Seminoma component, 4.Embryonal carcinoma component) Figure B (1.Enlarged multiple paraaortic lymph nodes on USG, 2.A large cannon ball of pulmonary metastasis 3.Solid and cystic component of the mixed tumour on USG of scrotum) Discussion R Islam, Z Boksh, S Rahman et al Testicular cancer can occur at any age but is most common between the ages of 15 and 35 years. There is also secondary peak in incidence after age 60. Seminoma is rare in boys younger than 10 years of age but is the most common histologic type in men older than 60. Various risk factors have been associated with testicular tumors, but the specific etiology is not known. Cryptorchidism, genetic predisposition, family history and prior testicular cancers are important etiological factor. Painless swelling or nodule of one testicle is the most common presenting symptom. On physical exam this mass/nodule can not be separated from the testis. Quick loss of testicular sensation could be presenting symptom also. Our patient presented with long 4 years history of slow growing painless swelling of the testis. Disseminated disease have symptom of lymphatic or hematogenous spread. Presenting symptoms could be neck mass in supraclavicular lymph node, anorexia, nausea and other gastrointestinal symptom. Bulky retroperitoneal disease could present as back pain. Cough, chest pain, hemoptysis and shortness of breath could be presenting symptom of mediastinal lymadenopathy or lung metastatic disease. Our patient did not have symptoms of chest symptom despite of pulmonary metastasis. 4 Classification 4 Approximately 95% of testicular tumors are germ cell tumors. These are divided into two types: pure seminoma (no nonseminomatous element present) and nonseminomatous germ cell tumors (NSGCT) A. Germ cell Tumour 1. Seminoma 2. Non-seminoma (Teratoma) B. Mixed germ cell tumour C. Yolk sac tumour D. Sex cord stromal tumor( Sertoli cell, Leydig cell tumor) E. Lymphoma Seminoma Seminoma constitutes roughly 50% of pure germ cell tumors. A seminomatous component is present in 20% of mixed germ cell tumors. Serum tumor markers are usually at normal levels, but if syncytio-trophoblastic giant cells are present, β-hcg may be elevated.
3 A Rare Combination of Mixed Germ Cell Tumour of Testis- A Case Report Nonseminoma Embryonal carcinomas constitute about 2% of all testicular germ cell tumors but are the histological type in 85% of mixed germ cell tumors. They have large pleomorphic cells with different architectural patterns. Teratocarcinomas are part of the mixed germ cell tumor and are generally benign but have the potential for metastasis. They have elements from all three germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm. Choriocarcinomas are the least common type of nonseminoma but are very aggressive. Widespread hematological metastasis can occur very early in the disease course; the retroperitoneum may be spared. Choriocarcinomas are associated with increased levels of β-hcg. Yolk cell tumors, also called endodermal sinus tumor, are the most common testicular tumor in infants and young children. In adults, pure yolk cell tumors are rare, but yolk cell elements are found in approximately 40% of mixed germ cell tumors. Yolk cell tumors are associated with elevated alpha fetoprotein levels but they do not produce β-hcg. Mixed germ cell tumors have two or more germ cell types. These constitute approximately one third of testicular cancer. Mixed germ cell tumors behave like nonseminomas. The average age at diagnosis is older than 30 years. Our case falls in this category as it has two components seminoma and embryonal carcinoma. Diagnostic Workup Ultrasongram of the scrotum- USG has 100% accuracy for diagnosis of testicular malignancy. Seminoma appears as hypoechoic homogenous appearance. Nonseminoma appears as complex cystic and solid masses. Our patient showed typical combined solid and cystic component of mixed germ cell tumour. USG of the abdomen and Chest x-ray are minimum requirement for staging of the tumour. USG or CT Scan of the abdomen is necessary to see the enlargement of the para-aortic lymph nodes in the abdomen. This was very much positive in our case. Chest x-ray shows pulmonary metastasis in the form of multiple cannon ball especially in non-seminoma. This cannon ball in our case is due to the non-seminomatous component of the tumour. Tumour Markers Blood must be taken for marker evaluation before surgical removal of the testis. This is important for staging and also for postoperative follow up and to know the response of the treatment and surveillance. α-fetoprotein (AFP) is produced by the yolk sac elements and is elevated 52 in 50-70% of NSGCT. It is not usually elevated in pure seminoma. Its half-life is about 5 days. β-human chorionic gonadotrophin (β-hcg) is produced by trophoblastic elements in the tumour. It is raised in 40 to 60% of NSGCTs and in up to 30% of pure seminomas. It has a half-life of 1 day. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is less specific, but is more common in seminoma. Overall, 90% of NSGCTs elaborate at least one tumour marker, while markers are elevated in <40% of seminomas. Rise of α-fetoprotien in our patent was again due to presence of non-seminoma component. Staging American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage groupings uses both TNM and Serum tumor marker for staging of the disease. 5,6 Risk Classification Good- Risk Non-Seminoma Testicular or retroperitoneal primary tumor, and No non-pulmonary visceral metastases, and Good markers-s1 Intermediate- Risk Non-seminoma Testicular or retroperitoneal primary tumor, and No non-pulmonary visceral metastases, Intermediate marker-s2 Poor risk non-seminoma Mediastinal primary, or Non-pulmonary visceral metastases, or Poor markers-s3: Good-risk Seminoma Any primary site, and No non-pulmonary visceral metastases, and Marker-S1 Intermediate-Risk Seminoma Any primary site, and Nonpulmonary visceral metastases, and Marker-S1 Poor-risk Seminoma No Patients are Classified as Poor Prognosis According to this risk classification our case falls under good risk non-seminomas. So final diagnosis becomes Stage IIIA mixed germ cell tumor and prognosis will be like good risk non seminomas.
4 53 AKMMC J 2015 : 6(1) Treatment Initial therapy is selected according to AJCC stage group; risk stratification (good, intermediate, or poor risk), as per the guidelines of the International Germ Cell Cancer Collaborative Group7 and histology (seminoma versus non-seminoma). Modalities of treatment for testicular cancer are surgery, adjuvent therapy. Adjuvent therapy includes radiotherapy, chemotherapy and surgery for residual disease. Initial therapy consists of radical orchiectomy. Radical orchiectomy means removal of testis and spermatic cord through inguinal approach. Our patient is in advanced stage of mixed germ cell tumour and needs multimodalities treatment. Mixed germ cell tumour behaves like non-seminoma. Current guidelines recommend treatment approach according to AJCC staging. Our patient should be managed as stage IIIA nonseminoma -good risk. Before we go to the management of this particular case we look into the various modalities of testicular cancer and their efficacy and indication. Radical Orciectomy- Cure Clinical stage I seminoma can sometimes be achieved by radical inguinal orchiectomy alone. Options after orchiectomy include active surveillance, adjuvant chemotherapy, and adjuvant radiation therapy. Active surveillance- consists of a history and physical exam and measurement of AFP and hcg every 3 to 4 months for the first 3 years, every 6 months for years 4 to 7, then annually up to year 10. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis is recommended at each visit and a chest x-ray at alternate visits. It is essential that patients maintain strict adherence to the surveillance program for at least 10 years. Adjuvant radiation therapy- consists of delivery of Gy to the infradiaphragmatic area, including th paraaortic lymph nodes and in some cases the ipsilateral ileoinguinal nodes. According to surveillance data, the overall incidence of disease failure without radiation therapy is 15% to 25%. With radiation therapy, failure rates were 2% to 5%. Adjuvant chemotherapy- with a single dose of carboplatin is currently recommended as an alternative to radiation therapy in stage I seminoma. Nonseminoma stage IIIA good risk: Standard treatment is with three cycles of bleomycin, cisplatin and etoposide (BEP) given over 5 days at intervals of 22 days. The overall cure rate using this regimen is 90%. Bleomycine has pulmonary toxicity and side effects must be monitored closely. Surgery for residual disease R Islam, Z Boksh, S Rahman et al Surgical resection is recommended for patients with residual disease after chemotherapy 10. Laparoscopic LN dissection is recommended for stage I and II disease 11. Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) should clear the region of residual disease. Open nerve-sparing RPLND is preferred over laparoscopic RPLND. Patients in whom RPLND reveals viable cancer, postchemotherapy residual masses are treated with subsequent chemotherapy 12. We feel that our patient should receive chemotherapy as mentioned. He should be on active surveillance. Open RPLND may be needed if chemotherapy fails to control the residual disease in the abdomen. Pneumonectomy is also sometimes done for selected cases of pulmonary metastasis 13. Prognosis 14 Good-prognosis nonseminoma: 5 year survival is 90%. Good-prognosis seminoma: 5-year survival is 85% Intermediate-prognosis nonseminoma: 5-year survival is 80% Intermediate-prognosis seminoma: 5-year survival is 70% Poor-prognosis nonseminoma: 5-year survival is 70% Poor-prognosis s eminoma: No seminoma patients are classified as poor prognosis. 14 Our patient as good risk non seminoma has chance of survival of about 90% 5 year survival if he can receive all modalities of treatment discussed above. Anatomical Diagnosis Mixed germ cell tumour with combination of seminoma and embryonal carcinoma. Conflict of interest: No conflict of interest. Reference 1. Huyghe E, Matsuda T, Thonneau P. Increasing incidence of testicular cancer worldwide: a review. J Urol. Jul 2003;170(1): Iffat Kamal, Stewart fleming, Testicular tumour, Surgery international,26:5, p Kush Sachdeva, Mansoor Javeed, Brendan Curti, Testicular cancer, e-medicine, July, Baily &Love-Short practice-26th Edition 5. American Joint Committee on Cancer. Testis. In: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 6th edition. New York: Springer Science Business Media LCC; Bosl GJ, Chaganti RS. The use of tumor markers in germ cell malignancies. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. Jun 1994;8(3):
5 A Rare Combination of Mixed Germ Cell Tumour of Testis- A Case Report 7. International Germ Cell Cancer Collaborative Group. International Germ Cell Consensus Classification: a prognostic factor- based staging system for metastatic germ cell cancers. J Clin Oncol. Feb 1997;15(2):p Oliver RT, Mason MD, Mead GM, et al. Radiotherapy versus single-dose carboplatin in adjuvant treatment of stage I seminoma: a randomised trial. Lancet. Jul ;366(9482): Einhorn LH, Williams SD, Chamness A, et al. High-dose chemotherapy and stem-cell rescue for metastatic germ-cell tumors. N Engl J Med. Jul ;357(4):p Albers P. Surgery is an essential part of salvage treatment in refractory germ cell tumors. Eur Urol. Nov 2006;50(5): Albqami N, Janetschek G. Laparoscopic retroperitoneal lymphnode dissection in the management of clinical stage I and II testicular cancer. J Endourol. Jul-Aug 2005;19(6):683-92; 12. van Dijk MR, Steyerberg EW, Habbema JD. Survival of non-seminomatous germ cell cancer patients according to the IGCC classification: An update based on meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. May 2006;42(7): Robert S. Davidson, Chukwumere E. Nwogu,, Mathijs J. Brentjens, Timothy M. Anderson, Surgical Oncology 10 (2001) Van Dijk MR, Steyerberg EW, Habbema JD. Survival of non-seminomatous germ cell cancer patients according to the IGCC classification: An update based on meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. May 2006;42(7):820-6.
Testicular Cancer. Page 1 of 17 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Testicular Cancer te: Consider Clinical Trials as treatment options for eligible patients. Page 1 of 17 TABLE OF CONTENTS Suspicious Testicular Cancer Page 2 nseminomatous Germ Cell Tumor (NSGCT): workup
Testicular Cancer te: Consider Clinical Trials as treatment options for eligible patients. Page 1 of 17 TABLE OF CONTENTS Suspicious Testicular Cancer Page 2 nseminomatous Germ Cell Tumor (NSGCT): workup
Guidelines on Testicular Cancer
 Guidelines on Testicular Cancer P. Albers (Chair), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi, A. Horwich, M.P. Laguna, N. Nicolai, J. Oldenburg European Association of Urology
Guidelines on Testicular Cancer P. Albers (Chair), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi, A. Horwich, M.P. Laguna, N. Nicolai, J. Oldenburg European Association of Urology
Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Types of Lung Cancer Non-small cell carcinoma (NSCC) (87%) Adenocarcinoma (38%) Squamous cell (20%) Large cell (5%) Small cell carcinoma (13%) Small cell lung cancer is virtually
Small Cell Lung Cancer Types of Lung Cancer Non-small cell carcinoma (NSCC) (87%) Adenocarcinoma (38%) Squamous cell (20%) Large cell (5%) Small cell carcinoma (13%) Small cell lung cancer is virtually
Tumour Markers. What are Tumour Markers? How Are Tumour Markers Used?
 Dr. Anthony C.H. YING What are? Tumour markers are substances that can be found in the body when cancer is present. They are usually found in the blood or urine. They can be products of cancer cells or
Dr. Anthony C.H. YING What are? Tumour markers are substances that can be found in the body when cancer is present. They are usually found in the blood or urine. They can be products of cancer cells or
Testicular Cancer. What is cancer?
 What is cancer? Testicular Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person s life,
What is cancer? Testicular Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person s life,
Testicular Cancer. What is cancer?
 What is cancer? Testicular Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person s life,
What is cancer? Testicular Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person s life,
J Clin Oncol 23:6149-6156. 2005 by American Society of Clinical Oncology INTRODUCTION
 VOLUME 23 NUMBER 25 SEPTEMBER 1 2005 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Outcome Analysis for Patients With Elevated Serum Tumor Markers at Postchemotherapy Retroperitoneal Lymph Node
VOLUME 23 NUMBER 25 SEPTEMBER 1 2005 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Outcome Analysis for Patients With Elevated Serum Tumor Markers at Postchemotherapy Retroperitoneal Lymph Node
SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER
 Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient information given at each stage following agreed information pathway 1. DIAGNOSIS New
Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient information given at each stage following agreed information pathway 1. DIAGNOSIS New
Testicular Cancer Overview
 Testicular Cancer Overview This overview is based on the more detailed information in Testicular Cancer. You can get this document and other information by calling 1-800-227-2345 or you can read it on
Testicular Cancer Overview This overview is based on the more detailed information in Testicular Cancer. You can get this document and other information by calling 1-800-227-2345 or you can read it on
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Updates in Mesothelioma By Samieh Amer, MD Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University History Wagner and his colleagues (1960) 33 cases of mesothelioma
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Updates in Mesothelioma By Samieh Amer, MD Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University History Wagner and his colleagues (1960) 33 cases of mesothelioma
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
Carcinoma of the vagina is a relatively uncommon disease, affecting only about 2,000 women in
 EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition, 2001 Vagina Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Carcinoma of the vagina is
EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition, 2001 Vagina Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Carcinoma of the vagina is
TESTICULAR CANCER LUMPS AND SELF-EXAMINATION A BOOKLET IN THE SERIES OF CONSUMER GUIDES ON MALE REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH FROM
 TESTICULAR CANCER LUMPS AND SELF-EXAMINATION A BOOKLET IN THE SERIES OF CONSUMER GUIDES ON MALE REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH FROM First published in October 2003 by Andrology Australia 4th Edition May 2014 Copyright
TESTICULAR CANCER LUMPS AND SELF-EXAMINATION A BOOKLET IN THE SERIES OF CONSUMER GUIDES ON MALE REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH FROM First published in October 2003 by Andrology Australia 4th Edition May 2014 Copyright
Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease Specific Biology and Treatment Options. John Kuruvilla
 Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease Specific Biology and Treatment Options John Kuruvilla My Disclaimer This is where I work Objectives Pathobiology what makes HL different Diagnosis Staging Treatment Philosophy
Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease Specific Biology and Treatment Options John Kuruvilla My Disclaimer This is where I work Objectives Pathobiology what makes HL different Diagnosis Staging Treatment Philosophy
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma
 A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
Objectives. Mylene T. Truong, MD. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Background
 Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
This testicular cancer management guide covers the diagnosis, staging, and treatment of germ-cell tumors and seminoma.
 November 01, 2015 Cancer Management [1] By Nasser H. Hanna, MD [2], Costantine Albany, MD [3], Patrick J. Loehrer, Sr, MD [4], Atreya Dash, MD [5], Jenny Shaffer, MD [6], Mark K. Buyyounouski, MD, MS [7],
November 01, 2015 Cancer Management [1] By Nasser H. Hanna, MD [2], Costantine Albany, MD [3], Patrick J. Loehrer, Sr, MD [4], Atreya Dash, MD [5], Jenny Shaffer, MD [6], Mark K. Buyyounouski, MD, MS [7],
These rare variants often act aggressively and may respond differently to therapy than the more common prostate adenocarcinoma.
 Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
THYROID CANCER. I. Introduction
 THYROID CANCER I. Introduction There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the US. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer than men by a ratio of 3:1, and it is more common in
THYROID CANCER I. Introduction There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the US. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer than men by a ratio of 3:1, and it is more common in
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases.
 Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
6.4 Testicular and scrotal problems
 Página 1 de 7 6.4 Testicular and scrotal problems Joseph L. Chin Overview Excluding dermatological conditions, testicular and scrotal lesions include hydrocele, hernia, spermatocele, varicocele, tumours,
Página 1 de 7 6.4 Testicular and scrotal problems Joseph L. Chin Overview Excluding dermatological conditions, testicular and scrotal lesions include hydrocele, hernia, spermatocele, varicocele, tumours,
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Analysis of Prostate Cancer at Easter Connecticut Health Network Using Cancer Registry Data
 The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer
 Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer Dr Raj Hegde. MD. FRANZCR Consultant Radiation Oncologist. William Buckland Radiotherapy Centre. Latrobe Regional Hospital. Locally advanced
Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer Dr Raj Hegde. MD. FRANZCR Consultant Radiation Oncologist. William Buckland Radiotherapy Centre. Latrobe Regional Hospital. Locally advanced
Aggressive lymphomas. Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital
 Aggressive lymphomas Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital What are the aggressive lymphomas? Diffuse large B cell Mediastinal large B cell Anaplastic large cell Burkitt lymphoma (transformed lymphoma:
Aggressive lymphomas Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital What are the aggressive lymphomas? Diffuse large B cell Mediastinal large B cell Anaplastic large cell Burkitt lymphoma (transformed lymphoma:
How To Treat A Uterine Sarcoma
 EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
95% of childhood kidney cancer cases are Wilms tumours. Childhood kidney cancer is extremely rare, with only 90 cases a year in
 James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
Extrapleural Pneumonectomy for Malignant Mesothelioma: Pro. Joon H. Lee 9/17/2012
 Extrapleural Pneumonectomy for Malignant Mesothelioma: Pro Joon H. Lee 9/17/2012 Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (Epidemiology) Incidence: 7/mil (Japan) to 40/mil (Australia) Attributed secondary to asbestos
Extrapleural Pneumonectomy for Malignant Mesothelioma: Pro Joon H. Lee 9/17/2012 Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (Epidemiology) Incidence: 7/mil (Japan) to 40/mil (Australia) Attributed secondary to asbestos
Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation in the Treatment of Germ-Cell Tumors
 Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation in the Treatment of Germ-Cell Tumors Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.07.020 04/01/2008 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 06/22/2012
Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation in the Treatment of Germ-Cell Tumors Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.07.020 04/01/2008 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 06/22/2012
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS
 LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
Understanding Metastatic Disease
 Supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer Understanding Metastatic Disease Metastatic disease or metastases are phrases that mean the same as Secondary cancer. This means that the cancer
Supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer Understanding Metastatic Disease Metastatic disease or metastases are phrases that mean the same as Secondary cancer. This means that the cancer
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
www.downstatesurgery.org
 Male Breast Cancer Rabih Nemr MD Kings County Hospital August 2008 ACGME Core Competencies 1 Patient t Care Medical Knowledge 2 g 3 4 Practice Based Learning/Improvement Interpersonal Communication Skills
Male Breast Cancer Rabih Nemr MD Kings County Hospital August 2008 ACGME Core Competencies 1 Patient t Care Medical Knowledge 2 g 3 4 Practice Based Learning/Improvement Interpersonal Communication Skills
NEOPLASMS OF KIDNEY (RENAL CELL CARCINOMA) And RENAL PELVIS (TRANSITIONAL CELL CARCINOMA)
 NEOPLASMS OF KIDNEY (RENAL CELL CARCINOMA) And RENAL PELVIS (TRANSITIONAL CELL CARCINOMA) Merat Esfahani, MD Medical Oncologist, Hematologist Cancer Liaison Physician SwedishAmerican Regional Cancer Center
NEOPLASMS OF KIDNEY (RENAL CELL CARCINOMA) And RENAL PELVIS (TRANSITIONAL CELL CARCINOMA) Merat Esfahani, MD Medical Oncologist, Hematologist Cancer Liaison Physician SwedishAmerican Regional Cancer Center
Oncology. Objectives. Cancer Nomenclature. Cancer is a disease of the cell Cancer develops when certain cells begin to grow out of control
 Oncology Objectives Describe the etiology and pathophysiological mechanisms of cancer Discuss medical and family history findings relevant to cancer Identify general signs and symptoms associated with
Oncology Objectives Describe the etiology and pathophysiological mechanisms of cancer Discuss medical and family history findings relevant to cancer Identify general signs and symptoms associated with
Medullary Renal Cell Carcinoma Case Report
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 4, December 2005 Medullary Renal Cell Carcinoma Case Report Mohammed Abdulla Al-Tantawi MBBCH, CABS* Abdul Amir Issa MBBCH, CABS*** Mohammed Abdulla MBBCH, CABS**
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 4, December 2005 Medullary Renal Cell Carcinoma Case Report Mohammed Abdulla Al-Tantawi MBBCH, CABS* Abdul Amir Issa MBBCH, CABS*** Mohammed Abdulla MBBCH, CABS**
A Practical Guide to Advances in Staging and Treatment of NSCLC
 A Practical Guide to Advances in Staging and Treatment of NSCLC Robert J. Korst, M.D. Director, Thoracic Surgery Medical Director, The Blumenthal Cancer Center The Valley Hospital Objectives Revised staging
A Practical Guide to Advances in Staging and Treatment of NSCLC Robert J. Korst, M.D. Director, Thoracic Surgery Medical Director, The Blumenthal Cancer Center The Valley Hospital Objectives Revised staging
Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Lung Practice Guideline Dr. Brian Dingle MSc, MD, FRCPC Approval Date: April 2007 Revised: November 2008 This guideline is a statement of consensus of the Thoracic Disease Site Team
Small Cell Lung Cancer Lung Practice Guideline Dr. Brian Dingle MSc, MD, FRCPC Approval Date: April 2007 Revised: November 2008 This guideline is a statement of consensus of the Thoracic Disease Site Team
Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA
 Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA 2015-2016 FCDS Educational Webcast Series Steven Peace, BS, CTR September 19, 2015 2015 Focus o Anatomy o SSS 2000 o MPH Rules o AJCC TNM 1 Case 1 Case Vignette HISTORY:
Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA 2015-2016 FCDS Educational Webcast Series Steven Peace, BS, CTR September 19, 2015 2015 Focus o Anatomy o SSS 2000 o MPH Rules o AJCC TNM 1 Case 1 Case Vignette HISTORY:
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
 Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
Male. Female. Death rates from lung cancer in USA
 Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond. Adriana Corben, M.D.
 Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse
 7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
A Review in Management of Testicular Cancer: Single Center Review
 Elmer Original Article ress A Review in Management of Testicular Cancer: Single Center Review Ammar Hameed a, e, Bob White b, Frank Chinegwundoh c, Ali Thwaini d, Ajay Pahuja e Abstract Background: Testicular
Elmer Original Article ress A Review in Management of Testicular Cancer: Single Center Review Ammar Hameed a, e, Bob White b, Frank Chinegwundoh c, Ali Thwaini d, Ajay Pahuja e Abstract Background: Testicular
Mesothelioma: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of
 Lung Cancer Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Lung Cancer JMAJ 46(12): 537 541, 2003 Kazushige HAYAKAWA Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiology, Kitasato University School of Medicine Abstract:
Lung Cancer Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Lung Cancer JMAJ 46(12): 537 541, 2003 Kazushige HAYAKAWA Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiology, Kitasato University School of Medicine Abstract:
Case Number: RT2009-124(M) Potential Audiences: Intent Doctor, Oncology Special Nurse, Resident Doctor
 Renal Cell Carcinoma of the Left Kidney Post Radical Surgery with pt4 Classification with Multiple Lung and Single Brain Metastases: the Role and Treatment Consideration of Radiotherapy Case Number: RT2009-124(M)
Renal Cell Carcinoma of the Left Kidney Post Radical Surgery with pt4 Classification with Multiple Lung and Single Brain Metastases: the Role and Treatment Consideration of Radiotherapy Case Number: RT2009-124(M)
Men s Health: Testicular & Breast. September 2012
 Men s Health: Testicular & Breast September 2012 Objectives: You will learn: How to perform a testicular self-exam and breast self-exam. You will know when to perform testicular and breast self-exams.
Men s Health: Testicular & Breast September 2012 Objectives: You will learn: How to perform a testicular self-exam and breast self-exam. You will know when to perform testicular and breast self-exams.
Lung Cancer Treatment Guidelines
 Updated June 2014 Derived and updated by consensus of members of the Providence Thoracic Oncology Program with the aid of evidence-based National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) national guidelines,
Updated June 2014 Derived and updated by consensus of members of the Providence Thoracic Oncology Program with the aid of evidence-based National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) national guidelines,
Clinical Management Guideline Management of locally advanced or recurrent Renal cell carcinoma. Protocol for Planning and Treatment
 Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: LOCALLY ADVANCED OR METASTATIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Patient information given at each stage following agreed information
Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: LOCALLY ADVANCED OR METASTATIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Patient information given at each stage following agreed information
Guidelines for Management of Renal Cancer
 Guidelines for Management of Renal Cancer Date Approved by Network Governance July 2012 Date for Review July 2015 Changes Between Versions 2 and 3 Section 5 updated bullets 5.3 and 5.4 Section 6 updated
Guidelines for Management of Renal Cancer Date Approved by Network Governance July 2012 Date for Review July 2015 Changes Between Versions 2 and 3 Section 5 updated bullets 5.3 and 5.4 Section 6 updated
Pediatric Oncology for Otolaryngologists
 Pediatric Oncology for Otolaryngologists Frederick S. Huang, M.D. Division of Hematology/Oncology Department of Pediatrics The University of Texas Medical Branch Grand Rounds Presentation to Department
Pediatric Oncology for Otolaryngologists Frederick S. Huang, M.D. Division of Hematology/Oncology Department of Pediatrics The University of Texas Medical Branch Grand Rounds Presentation to Department
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Survival analysis of 220 patients with completely resected stage II non small cell lung cancer
 窑 Original Article 窑 Chinese Journal of Cancer Survival analysis of 22 patients with completely resected stage II non small cell lung cancer Yun Dai,2,3, Xiao Dong Su,2,3, Hao Long,2,3, Peng Lin,2,3, Jian
窑 Original Article 窑 Chinese Journal of Cancer Survival analysis of 22 patients with completely resected stage II non small cell lung cancer Yun Dai,2,3, Xiao Dong Su,2,3, Hao Long,2,3, Peng Lin,2,3, Jian
Summary of treatment benefits
 Risk Management Plan PEMETREXED Powder for concentrate for Solution for infusion Pemetrexed is also indicated as monotherapy for the maintenance treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non small cell
Risk Management Plan PEMETREXED Powder for concentrate for Solution for infusion Pemetrexed is also indicated as monotherapy for the maintenance treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non small cell
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Diagnosis and Prognosis of Pancreatic Cancer
 Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Post-recurrence survival in completely resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer with local recurrence
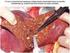 Post- survival in completely resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer with local J-J Hung, 1,2,3 W-H Hsu, 3 C-C Hsieh, 3 B-S Huang, 3 M-H Huang, 3 J-S Liu, 2 Y-C Wu 3 See Editorial, p 185 c A supplementary
Post- survival in completely resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer with local J-J Hung, 1,2,3 W-H Hsu, 3 C-C Hsieh, 3 B-S Huang, 3 M-H Huang, 3 J-S Liu, 2 Y-C Wu 3 See Editorial, p 185 c A supplementary
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary
 TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
Lymph Nodes and Cancer What is the lymph system?
 Lymph Nodes and Cancer What is the lymph system? Our bodies have a network of lymph vessels and lymph nodes. (Lymph is pronounced limf.) This network is a part of the body s immune system. It collects
Lymph Nodes and Cancer What is the lymph system? Our bodies have a network of lymph vessels and lymph nodes. (Lymph is pronounced limf.) This network is a part of the body s immune system. It collects
SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD
 SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD Case Presentation 35 year old male referred from PMD with an asymptomatic palpable right neck mass PMH/PSH:
SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD Case Presentation 35 year old male referred from PMD with an asymptomatic palpable right neck mass PMH/PSH:
New strategies in anticancer therapy
 癌 症 診 療 指 引 簡 介 及 臨 床 應 用 New strategies in anticancer therapy 中 山 醫 學 大 學 附 設 醫 院 腫 瘤 內 科 蔡 明 宏 醫 師 2014/3/29 Anti-Cancer Therapy Surgical Treatment Radiotherapy Chemotherapy Target Therapy Supportive
癌 症 診 療 指 引 簡 介 及 臨 床 應 用 New strategies in anticancer therapy 中 山 醫 學 大 學 附 設 醫 院 腫 瘤 內 科 蔡 明 宏 醫 師 2014/3/29 Anti-Cancer Therapy Surgical Treatment Radiotherapy Chemotherapy Target Therapy Supportive
Report series: General cancer information
 Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Surgery. Wedge resection only part of the lung, not. not a lobe, is removed. Cancer Council NSW
 The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Information for Men Diagnosed with Testicular Cancer
 Patient Information Service Information for Men Diagnosed with Testicular Cancer Bristol Haematology and Oncology Centre Bristol Testicular Cancer Service Patient Information is supported by September
Patient Information Service Information for Men Diagnosed with Testicular Cancer Bristol Haematology and Oncology Centre Bristol Testicular Cancer Service Patient Information is supported by September
Lung cancer is not just one disease. There are two main types of lung cancer:
 1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
Lung Cancer. Public Outcomes Report. Submitted by Omar A. Majid, MD
 Public Outcomes Report Lung Cancer Submitted by Omar A. Majid, MD Lung cancer is the most common cancer-related cause of death among men and women. It has been estimated that there will be 226,1 new cases
Public Outcomes Report Lung Cancer Submitted by Omar A. Majid, MD Lung cancer is the most common cancer-related cause of death among men and women. It has been estimated that there will be 226,1 new cases
Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines
 Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines DCIS Stage 0 TisN0M0 Tamoxifen for 5 years for patients with ER positive tumors treated with: -Breast conservative therapy (lumpectomy) and radiation therapy -Excision
Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines DCIS Stage 0 TisN0M0 Tamoxifen for 5 years for patients with ER positive tumors treated with: -Breast conservative therapy (lumpectomy) and radiation therapy -Excision
RT for Recurrent, Bulky, and Chemotherapy-Refractory Follicular Lymphoma: A Treatment Modality for Both Alleviating Symptoms and Potential Cure
 RT for Recurrent, Bulky, and Chemotherapy-Refractory Follicular Lymphoma: A Treatment Modality for Both Alleviating Symptoms and Potential Cure Case Number: RT2009-04(M) Potential Audiences: Intent Doctor,
RT for Recurrent, Bulky, and Chemotherapy-Refractory Follicular Lymphoma: A Treatment Modality for Both Alleviating Symptoms and Potential Cure Case Number: RT2009-04(M) Potential Audiences: Intent Doctor,
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Introduction. Case History
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Case Report of Renal Cell Carcino Shimajiri, Shouhei; Shingaki, Yoshi Masaya; Tamamoto, Tooru; Toda, Taka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Case Report of Renal Cell Carcino Shimajiri, Shouhei; Shingaki, Yoshi Masaya; Tamamoto, Tooru; Toda, Taka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
Avastin: Glossary of key terms
 Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer
 Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
People Living with Cancer
 Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer ADVANCED LUNG CANCER TREATMENT Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical Oncology
Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer ADVANCED LUNG CANCER TREATMENT Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical Oncology
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma
 Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Treatment Algorithms for the Management of Lung Cancer in NSW Guide for Clinicians
 Treatment Algorithms for the Management of Lung Cancer in NSW Guide for Clinicians Background The Cancer Institute New South Wales Oncology Group Lung (NSWOG Lung) identified the need for the development
Treatment Algorithms for the Management of Lung Cancer in NSW Guide for Clinicians Background The Cancer Institute New South Wales Oncology Group Lung (NSWOG Lung) identified the need for the development
Guide to Understanding Breast Cancer
 An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML),
 1 ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML), ALSO KNOWN AS ACUTE MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA WHAT IS CANCER? The body is made up of hundreds of millions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly
1 ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML), ALSO KNOWN AS ACUTE MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA WHAT IS CANCER? The body is made up of hundreds of millions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly
Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer
 Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer What is the appendix? The appendix is a pouch-like tube attached to the first part of the large intestine (cecum). The appendix is about 10 centimetres long and has no
Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer What is the appendix? The appendix is a pouch-like tube attached to the first part of the large intestine (cecum). The appendix is about 10 centimetres long and has no
The TV Series. www.healthybodyhealthymind.com INFORMATION TELEVISION NETWORK
 The TV Series www.healthybodyhealthymind.com Produced By: INFORMATION TELEVISION NETWORK ONE PARK PLACE 621 NW 53RD ST BOCA RATON, FL 33428 1-800-INFO-ITV www.itvisus.com 2005 Information Television Network.
The TV Series www.healthybodyhealthymind.com Produced By: INFORMATION TELEVISION NETWORK ONE PARK PLACE 621 NW 53RD ST BOCA RATON, FL 33428 1-800-INFO-ITV www.itvisus.com 2005 Information Television Network.
Advances in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
 Advances in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Steven A. De Jong, M.D., FACS, FACE Professor and Vice Chair Clinical Affairs Department of Surgery Loyola University Medical Center Thyroid Cancer classification
Advances in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Steven A. De Jong, M.D., FACS, FACE Professor and Vice Chair Clinical Affairs Department of Surgery Loyola University Medical Center Thyroid Cancer classification
Hosts. New Methods for Treating Colorectal Cancer
 Hosts Anees Chagpar MD Associate Professor of Surgical Oncology Francine MD Professor of Medical Oncology New Methods for Treating Colorectal Cancer Guest Expert: Scott, MD Associate Professor in the Department
Hosts Anees Chagpar MD Associate Professor of Surgical Oncology Francine MD Professor of Medical Oncology New Methods for Treating Colorectal Cancer Guest Expert: Scott, MD Associate Professor in the Department
Stomach (Gastric) Cancer. Prof. M K Mahajan ACDT & RC Bathinda
 Stomach (Gastric) Cancer Prof. M K Mahajan ACDT & RC Bathinda Gastric Cancer Role of Radiation Layers of the Stomach Mucosa Submucosa Muscularis Serosa Stomach and Regional Lymph Nodes Stomach and Regional
Stomach (Gastric) Cancer Prof. M K Mahajan ACDT & RC Bathinda Gastric Cancer Role of Radiation Layers of the Stomach Mucosa Submucosa Muscularis Serosa Stomach and Regional Lymph Nodes Stomach and Regional
Update on Mesothelioma
 November 8, 2012 Update on Mesothelioma Intro incidence and nomenclature Update on Classification Diagnostic specimens Morphologic features Epithelioid Histology Biphasic Histology Immunohistochemical
November 8, 2012 Update on Mesothelioma Intro incidence and nomenclature Update on Classification Diagnostic specimens Morphologic features Epithelioid Histology Biphasic Histology Immunohistochemical
Colorectal cancer. A guide for journalists on colorectal cancer and its treatment
 Colorectal cancer A guide for journalists on colorectal cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Colorectal cancer 4 i. What is colorectal cancer? 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 4 iii.
Colorectal cancer A guide for journalists on colorectal cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Colorectal cancer 4 i. What is colorectal cancer? 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 4 iii.
Management of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Guide for General Practitioners
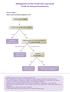 Management of n-small Cell Lung Cancer Guide for General Practitioners Clinical Stage I Cancer only in one lobe of lung and
Management of n-small Cell Lung Cancer Guide for General Practitioners Clinical Stage I Cancer only in one lobe of lung and
Laboratory Medicine Practice Guidelines
 Laboratory Medicine Practice Guidelines Use of Tumor Markers in Testicular, Prostate, Colorectal, Breast, and Ovarian Cancers Edited by Catharine M. Sturgeon and Eleftherios Diamandis NACB_LMPG_Ca1cover.indd
Laboratory Medicine Practice Guidelines Use of Tumor Markers in Testicular, Prostate, Colorectal, Breast, and Ovarian Cancers Edited by Catharine M. Sturgeon and Eleftherios Diamandis NACB_LMPG_Ca1cover.indd
Epidemiology, Staging and Treatment of Lung Cancer. Mark A. Socinski, MD
 Epidemiology, Staging and Treatment of Lung Cancer Mark A. Socinski, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Multidisciplinary Thoracic Oncology Program Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center University of
Epidemiology, Staging and Treatment of Lung Cancer Mark A. Socinski, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Multidisciplinary Thoracic Oncology Program Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center University of
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Therapies
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Therapies Guest Expert: Roy, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Therapeutic Radiology Scott, MD Assistant Professor of Medical Oncology www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Therapies Guest Expert: Roy, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Therapeutic Radiology Scott, MD Assistant Professor of Medical Oncology www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome
Screening, early referral and treatment for asbestos related cancer
 Screening, early referral and treatment for asbestos related cancer Marc de Perrot, MD, MSc, FRCSC Toronto Mesothelioma Research Program University of Toronto Asbestos related diseases Mesothelioma Lung
Screening, early referral and treatment for asbestos related cancer Marc de Perrot, MD, MSc, FRCSC Toronto Mesothelioma Research Program University of Toronto Asbestos related diseases Mesothelioma Lung
Breast Cancer. Presentation by Dr Mafunga
 Breast Cancer Presentation by Dr Mafunga Breast cancer in the UK Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women. Around 1 in 9 women will develop breast cancer It most commonly affects women over
Breast Cancer Presentation by Dr Mafunga Breast cancer in the UK Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women. Around 1 in 9 women will develop breast cancer It most commonly affects women over
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Management of spinal cord compression
 Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
