Urinary Tract Infections. Objectives. Definitions
|
|
|
- Rosaline Gardner
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Urinary Tract Infections Elizabeth D. Hermsen, Pharm.D. Infectious Diseases Research Fellow University of Minnesota College of Pharmacy Objectives Identify the three factors that determine the progression to a UTI. Differentiate between the characteristic clinical, physical, and laboratory findings associated with UTIs. Identify the most common pathogens associated with the various UTIs. Suggest appropriate Rx and non-rx treatment modalities for UTIs. Spring 2004 PHAR Definitions Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Micro-organisms present in the urine not accounted for by contamination Infection anywhere within the urinary system Cystitis Lower tract infections Pyelonephritis Upper tract infections (kidneys, systemic) Spring 2004 PHAR
2 Definitions (cont.) Uncomplicated Typically in females of childbearing age No structural/neurologic abnormalities interfering with urine flow Complicated Flow impedance secondary to Lesion Congenital abnormality Renal or prostate stones Indwelling catheter Prostatic hypertrophy Physical obstruction Neurologic deficit Spring 2004 PHAR Definitions (cont.) Recurrent Reinfection or relapse with asymptomatic periods Reinfection New organism Relapse Same organism Asymptomatic bacteriuria (ASB) Significant bacteriuria (>10 5 ) without symptoms Always precedes symptoms of UTI Lower tract infection Symptomatic abacteriuria Symptoms without 10 5 CFU/ml Spring 2004 PHAR UTI: Epidemiology Approximately 8 million physician visits annually By age 32, _ of all women have at least 1 UTI 1/5 of men 70 y.o. have experienced a UTI Lead to > 1 million hospitalizations/year Most commonly occurring nosocomial infection Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2003;17: Spring 2004 PHAR
3 Pathogen reservoirs Females (urethra proximal) Rectal Vaginal Males (urethra distal) Rectal Spring 2004 PHAR Pathogenesis Ascending Rectal and/or vaginal reservoirs Colonization of perianal area/ migration to perivaginal area Colonization typically precedes UTI Bacterial adhesive characteristics Host receptor on epithelial surface Surrounding fluids Hematogenous? Lymphatic Spring 2004 PHAR Pathogenesis (cont.) Facilitating issues Females Reservoir(s) and urethra proximity Urethra length Sexual intercourse Spermicide and diaphragm Condoms Pregnancy Biofilm (slime) theory: Bacteria interact microcolonies Small microcolonies coalesce form bacterial biofilms Glycocalyx Spring 2004 PHAR
4 Pathogenesis (cont.) Facilitating issues (cont.) Urinary Catheters Can be traumatic Biofilm adherence Bacterial aggregates can block catheter Catheter can shed bacteria Antibiotics drained immediately Aging Bladder wall collagen content Detrussor muscle thickens Neurologic diseases Vaginal flora Spring 2004 PHAR Predisposing factors Structural abnormalities Obstruction Vesicouretral reflex Miscellaneous Catheterization Pregnancy Diabetes Residual urine Prostatic hypertrophy Tumors Anticholinergic agents Calculi Neurologic disease Spring 2004 PHAR Determining Factors Three factors determine the progression to infection Inoculum size Pathogen virulence Competency of host defenses Spring 2004 PHAR
5 Host defense mechanisms ph (normal range 5-8) Urea concentrations Organic acid concentrations Osmolality Urine flow Vaginal flora Spring 2004 PHAR Clinical presentation Common symptoms of lower UTIs Dysuria Frequency Urgency Hesitancy Nocturia Suprapubic pain/heaviness Spring 2004 PHAR Clinical presentation (cont.) Common symptoms of upper UTIs Flank pain Costovertebral tenderness Abdominal pain Fever N/V Malaise Spring 2004 PHAR
6 Clinical presentation (cont.) Infants and children Typically no specific UTI signs and symptoms fever Elderly Typically no specific UTI symptoms Altered mental status Altered dietary habits Spring 2004 PHAR Laboratory findings Urine analysis Pyuria ( > 10 WBC/mm 3 or leukocyte esterase) Bacteria ( > 10 5 CFU/ml urine) microscopic or dipstick (NO 3 --> NO 2 ) Hematuria (approximately 1/3 gross hematuria) Elevated ph (6.5-8) Proteus, K. pneumoniae, S. saprophyticus produce urease: catalyzes hydrolysis of urea in urine ammonia and CO 2 Leukocyte esterase and nitrite dipsticks Urine culture Gold standard 1, ,000 CFU/ml Spring 2004 PHAR Differential diagnosis Uncomplicated UTI Vaginitis Urethritis STD Odor Itching Pain on intercourse Complicated UTI Depends on contributing underlying diseases Spring 2004 PHAR
7 Treatment Algorithms available Complicating factors Appropriate antimicrobial consideration factors Duration - Adverse Events Spectrum - Resistance Pharmacokinetics Spring 2004 PHAR Non-Rx treatment/prevention Acute uncomplicated UTIs spontaneously resolve in 50-70% of cases Behavior modification Personal toilet hygiene Patient s choice of fabric and clothes Frequent voiding Voiding after intercourse Method of contraception? Vaccines Spring 2004 PHAR Non-Rx treatment/prevention (cont.) Cranberry juice Believed to have preventative/treatment effects Increases fluid intake and urine output Acidifies urine (study ph = 6 vs. CTN ph = 5.5) May interfere with bacterial attachment (fructose or polymeric cpd acts as lectin inhibitor) Benzoic acid hippuric acid which may have intrinsic antibacterial properties Database review of literature conclusion Small number/poor quality trials : no reliable evidence Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. (2):CD and CD001322, Spring 2004 PHAR
8 Non-Rx treatment/prevention (cont.) Lactobacilli Limited data Restoration of normal vaginal flora Prevent colonization by virulent pathogens Acidic ph Direct killing due to H 2 O 2 Interference with bacterial attachment Must select appropriate probiotic strain L. crispatus Intravaginal administration Infect Dis Clin N Am. 2003;17: Spring 2004 PHAR ASB Controversy about clinical importance? Lead to complications of UTIs? Protective effects Diagnosis 2 consecutive urine specimens with >10 5 CFU/ml without symptoms Pathogenesis Urethral ascension of bacteria into urinary tract/introduction by instrumentation persistence without host response Persistence may be facilitated by host genetic predisposition, incomplete bladder emptying, or presence of a foreign body Spring 2004 PHAR ASB (cont.) Etiology Predominantly E. coli Others Structural/functional abnormalities Enterobacteriaceae, P. aeruginosa Enterococcus spp., CoNS other than S. saprophyticus Spring 2004 PHAR
9 Screening/Treatment beneficial Pregnant women Prior to traumatic GU procedure? Renal transplant recipient (1 st 6 mos.)? Females with persistent catheteracquired bacteriuria after catheter removal ASB (cont.) Screening/Treatment not beneficial Healthy individuals Elderly men and women in community and LTCFs Women with diabetes Pts. with HIV Pts. with catheters Pts. with neurologic impairment of bladder emptying Pts. with chronic urologic devices Infect Dis Clin N Am. 2003;17: Spring 2004 PHAR Uncomplicated UTI: Etiology Young women Women >65 years E. coli 80% S. saprophyticus 10-15% Others 5-10% (Klebsiella/Proteus) E. coli 70% P. mirabilis 10% Other Gram (-) 20% (Pseudomonas) Spring 2004 PHAR Uncomplicated UTI: Treatment Current standard of therapy TMP/SMX PO x 3 days 3-Day therapy Superior to single-dose Optimal regimen for TMP/SMX Resistance Spring 2004 PHAR
10 JAMA 1999;281:763-8 Spring 2004 PHAR TMP/SMX Resistance E. coli ~20% resistant Geographic variation Risk factors Recent antibiotic use, especially TMP/SMX Diabetes Recent hospitalization Current use of antibiotics Infect Dis Clin N Am. 2003;17: Spring 2004 PHAR Recommendation Locations with resistance rates > 20% Alternatives 3-day fluoroquinolone 7-day nitrofurantoin Associated with lower cure rates than 1 st line agents (85% vs. 95%) Macrocrystals better GI SE profile Single dose fosfomycin Phosphoric acid bactericidal agent Can be used in pregnancy 3 gm single dose Comparable microbiologic cure as 5-day TMP (alone), but likely less effective than 3-day regimens of TMP/SMX or fluoroquinolones Spring 2004 PHAR
11 Uncomplicated UTI: Treatment (cont.) 3 day treatment options Drug Ciprofloxacin Ciprofloxacin XR Levofloxacin Gatifloxacin Trimethoprim (Proloprim, Trimpex) Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Cotrim, Septra, etc.) Dosage 250 mg q12h 500 mg q24h 250 mg q24h 200 mg q24h 100 mg q12h 160 mg TMP/ 800 mg SMX q12h Spring 2004 PHAR Uncomplicated UTI: Treatment (cont.) Single-dose therapy (SDT) Gatifloxacin 400 mg TMP/SMX 2 DS tablets? Fosfomycin 3 gm NOT to be used in Pregnant women Males Upper UTI infections Renal failure Indwelling catheter Spring 2004 PHAR Uncomplicated UTI: Treatment (cont.) Other therapy options Nitrofurantoin/ Macrobid 100mg BID X 7 days Amoxicillin 250 mg TID x 7 days or 500 mg BID x 7 days Amoxicillin/clavulanate 500/125 mg BID x 7 days Cefixime 400 mg QD x 7 days Cefpodoxime 100 mg BID x 7 days Spring 2004 PHAR
12 Complicated UTI: Etiology E. coli P. mirabilis Other Gram (-) Gram (+) 40% 10% 40% 10% Gram stain of urine culture should be performed Spring 2004 PHAR Complicated UTI: Management Depending on status, may need to admit Severely ill Direct therapy towards bacteremia/sepsis Hospitalize + IV abx. Prompt initiation of broad-spectrum antibiotics Immediate urinary tract decompression in pts. with evidence of obstruction Spring 2004 PHAR Complicated UTI: Treatment Empiric Fluoroquinolones (PO or IV) Gentamicin + Ampicillin IV Preferred when suspect Enterococcus spp. Alternatives to ampicillin Amp/sulbactam Piperacillin 3 rd generation cephalosporins (cefotaxime, ceftriaxone) Nursing home resident or indwelling catheter (suspect Pseudomonas spp.) Ceftazidime or piperacillin + gentamicin Spring 2004 PHAR
13 Complicated UTI: Treatment (cont.) Duration PO Single dose therapy not effective Patients should be treated 10 to 14 days Patients failing 10 to 14 day antibiotic course should then be treated for 4-6 weeks IV IV treatment maintained until afebrile for 24 hours PO treatment continued for days post IV Spring 2004 PHAR Case #1 TJ 28 y.o. female CC: three days of nocturnal frequency, dysuria, urgency U/A (per ml): >50 WBC, 35 RBC, > 10 5 bacteria UC: G- bacilli, lactose fermenting Spring 2004 PHAR Case #1 Discussion What is the most likely diagnosis? What is the most likely organism? Suggest appropriate treatment. Spring 2004 PHAR
14 Case #2 MR 72 y.o. female, nursing home resident; normally active and healthy U/A (per ml): (-) leukocyte esterase, 0 RBCs, (-) bacteria UC: >10 5 E. coli Spring 2004 PHAR Case #2 Discussion What is your assessment? Should we treat? Spring 2004 PHAR Catheter-related UTIs Etiology Most caused by E. coli Nearly any organism is possible, especially in nosocomial infections Usually polymicrobial with rapid and constant changes Spring 2004 PHAR
15 Catheter-related UTIs (cont.) Treatment Asymptomatic + bacteriuria REMOVE CATHETER withhold systemic antibiotics Symptomatic REMOVE CATHETER Start antibiotics complicated UTI Spring 2004 PHAR Recurrent UTI Classification <2-3 episodes/year >3 episodes/year Risk higher with E. coli vs. non-e. coli pathogens Spring 2004 PHAR Recurrent UTI: Management Post-coital single dose antibiotic (SMX/TMP SS) Continuous low-dose therapy (SMX/TMP _ SS qd x 6 mos., Nitrofurantoin 50 mg qd x 6 mos.) Self-initiated antibiotics Vaginal estradiol cream in post-menopausal women Cranberry juice Spring 2004 PHAR
16 Case #3 JS 25 y.o. female, paraplegic, nursing home resident Hx: indwelling catheter CC: spiking fever, cough Chest X-ray: (+) pulmonary process Sputum culture: G- bacilli UC: >10 5 CFU/ml Spring 2004 PHAR Case #3 Discussion What is a predisposing factor to the development of a UTI? What is your assessment? What organism should we suspect due to this patient s situation? Suggest appropriate action. Spring 2004 PHAR UTI in pregnancy 4-7% pregnant patients Most common medical complication Pathogenesis Decreased ureteral peristalsis Urinary stasis Reduced bladder tone Hormonal changes Monitor Quantitative urine Cx Management Treat any significant bacteriuria, including ASB Upper UTI hospitalization + IV antibiotics Spring 2004 PHAR
17 UTI in Pregnancy (cont.) Etiology > 90% E. coli, Klebsiella spp., Enterobacter spp.) Others Proteus, Pseudomonas, Citrobacter, Staphylococcus, S. agalactiae Spring 2004 PHAR UTI in Pregnancy: ASB When left untreated Associated with pyelonephritis and hyptertension in mother Prematurity, low birth weight, mental retardation, and cerebral palsy in infants Thus, treat all pregnant women with ASB Spring 2004 PHAR UTI in Pregnancy: ASB (cont.) Treatment of ASB Amoxicillin 500 mg TID x 3 days Ampicillin 250 mg BID x 3 days Cephalexin 250 mg BID x 3 days Nitrofurantoin* 100 mg BID x 7 days TMP/SMX* 1 DS BID x 3 days * Not during 3 rd trimester Spring 2004 PHAR
18 UTI in Pregnancy: Treatment Treatment Uncomplicated cystitis Same as ASB Pyelonephritis days 2 nd or 3 rd gen. cephalosporin IV Gentamicin IV Aztreonam IV TMP/SMX IV (not in 3 rd trimester) Avoid Tetracyclines (teratogenic) Quinolones (cartilage development) Nitrofurantoin in G6PD deficiency Spring 2004 PHAR UTI in Infants and Children Epidemiology Underestimated in the past Prevalence ranging from % febrile children Newborns More prevalent in premature infants More common in males High recurrence rate Children More common in females Infect Dis Clin N Am. 2003;17: Spring 2004 PHAR UTI in Infants and Children (cont.) Pathogenesis Migration of bacteria from GI tract to periurethral mucosa ascend to bladder Etiology E. coli 70-90% Others P. aeruginosa, Enterococcus spp., P. mirabilis Rarely S. agalactiae, S. aureus, Candida spp. Spring 2004 PHAR
19 UTI in Infants and Children (cont.) Clinical findings Typically no specific urinary tract symptoms Limited value of physical examination Less than 2 y.o. Failure to thrive, feeding problems, vomiting, and fever 2 5 y.o. Fever, abdominal pain > 5 y.o. Classic UTI symptoms more common Spring 2004 PHAR UTI in Infants and Children (cont.) Management Hospitalization Infants <2 mos. Consider for any child < 5 y.o. Not necessary for children who are not severely ill, can tolerate oral fluids and oral abx, and follow-up is guaranteed Imaging studies Any child < 5 y.o. with a positive urine culture Consider for older girls with recurrent UTIs Renal ultrasound and cystography Spring 2004 PHAR UTI in Infants and Children (cont.) Treatment Need coverage for S. agalactiae and Enterobacteriaceae during first 8 weeks of life pending blood and CSF cultures Oral therapy for well-appearing children TMP/SMX, cephalosporins, nitrofurantoin Failure of oral therapy IV antibiotics IM ceftriaxone or gentamicin Spring 2004 PHAR
20 Prostatitis Spring 2004 PHAR Definitions and classification Prostatitis Inflammation of the prostate & surrounding tissues Bacterial prostatitis Inflammation in presence of bacteria and significant inflammatory cells Acute: severe illness, sudden onset, fever Chronic: recurrent infection with same organism Nonbacterial prostatitis S+S in presence of inflammatory cells WITHOUT bacteria Prostatodynia S+S with bacteria WITHOUT leukocytosis Spring 2004 PHAR Pathogenesis Reflux Ascending Hematogenous Lymphatic Other Catheter, urethral instrumentation, transurethral prostatectomy Spring 2004 PHAR
21 Host defense mechanisms Prostatic fluid Antibacterial factor (PAF) High concentrations of zinc Note: concentrations of Zn decreased in elderly ph Normal: Inflamed: 7-9 Spring 2004 PHAR Etiology Acute Bacterial E. coli K. pneumoniae P. mirabilis P. aeruginosa Serratia Enterobacter Chronic bacterial E. coli K. pneumoniae P. mirabilis E. faecalis S. aureus S. epidermidis Chronic nonbacterial Chlamydia Trichomonas Ureaplasma Spring 2004 PHAR Clinical presentation Acute Local Uncomplicated UTI symptoms Systemic High fever Malaise Chills Myalgia Prostate Swollen Tender Warm Chronic Commonly asymptomatic Vague symptoms Recurrent UTIs Frequency Urgency Dysuria Lower back pain Suprapubic discomfort Prostate May appear normal Spring 2004 PHAR
22 Treatment Empiric Acute Severely ill: AG + b-lactam IV Patient able to take PO TMP/SMX Fluoroquinolone Duration Chronic Fluoroquinolone X 4-6 weeks TMP/SMX X 4-6 weeks Duration May need to extend to 12 weeks IV therapy until patient is afebrile for 48h (or 3 5 days of IV therapy) Continue PO for 4 weeks total Spring 2004 PHAR Questions??? Spring 2004 PHAR
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
 A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
Urinary Tract Infections. Clinical Scenario #1. Urinary Tract Infections. Clinical Scenario #1 : Labs
 Clinical Scenario #1 : Labs Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD Urinalysis: pyuria (WBC too numerous to count), RBC and bacteria present Urine dipstick: positive leukocyte esterase and nitrite
Clinical Scenario #1 : Labs Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD Urinalysis: pyuria (WBC too numerous to count), RBC and bacteria present Urine dipstick: positive leukocyte esterase and nitrite
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Columbia University Clinical Scenario #1 23 y.o woman presents to her doctor complaining of 1 day of increased urinary
Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Columbia University Clinical Scenario #1 23 y.o woman presents to her doctor complaining of 1 day of increased urinary
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of. Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care
 A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
Age in years Females (% prevalence) Males (% prevalence) 6-15 Vesicoureteral reflux (4.4%) Vesicoureteral reflux (0.5%)
 Magdalena E. Sobieszczyk Urinary Tract Infections AIMS: 1. Understand epidemiology and microbiology of urinary tract infections 2. Understand pathogenesis of lower and upper urinary tract infections 3.
Magdalena E. Sobieszczyk Urinary Tract Infections AIMS: 1. Understand epidemiology and microbiology of urinary tract infections 2. Understand pathogenesis of lower and upper urinary tract infections 3.
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page
 A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD
 82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC. OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract
 Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
Case Studies in Urinary Tract Infections
 Case Studies in Urinary Tract Infections Robert L. Holley, MSc, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Case Studies in Urinary Tract Infections Robert L. Holley, MSc, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Guidance
 Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Guidance Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most common indication for antimicrobial use in hospitals and a significant proportion of this use is
Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Guidance Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most common indication for antimicrobial use in hospitals and a significant proportion of this use is
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS
 GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2010) M. Grabe (chairman), T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction Infections
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2010) M. Grabe (chairman), T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction Infections
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS
 GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2014) M. Grabe (chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2014) M. Grabe (chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults. A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013)
 Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women
 Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience
 Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Leading cause of morbidity and health care expenditures in persons of all ages. An estimated 50 % of women report having had a UTI at some point in their lives. 8.3 million office
Urinary Tract Infections Leading cause of morbidity and health care expenditures in persons of all ages. An estimated 50 % of women report having had a UTI at some point in their lives. 8.3 million office
Urinary Tract Infection
 Guidelines for Clinical Care Ambulatory Urinary Tract Infection Guideline Team Team Leader Steven E Gradwohl, MD General Medicine Team Members Catherine M Bettcher, MD Family Medicine Carol E Chenoweth,
Guidelines for Clinical Care Ambulatory Urinary Tract Infection Guideline Team Team Leader Steven E Gradwohl, MD General Medicine Team Members Catherine M Bettcher, MD Family Medicine Carol E Chenoweth,
Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department. 24/06/2013 Beryl Navti, Clinical Pharmacist, SEPT
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department The Genitourinary System The organs system of the reproductive organs and urinary system Grouped dtogether th because of their proximity it
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department The Genitourinary System The organs system of the reproductive organs and urinary system Grouped dtogether th because of their proximity it
CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D.
 ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D. ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION Antibiotic use in the safest
ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D. ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION Antibiotic use in the safest
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Event
 Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are tied with pneumonia as the second most common type of healthcare-associated infection, second only
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are tied with pneumonia as the second most common type of healthcare-associated infection, second only
Patient with: 3 or more UTI in 6 months 4 or more UTI in 12 months
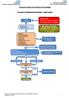 Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
UTI in children. Quick reference guide. Issue date: August 2007. Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management
 Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN ADULTS
 URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN ADULTS Urinary tract infection in adults is common and may be complicated or uncomplicated. Infection of the urinary tract (UTI) is frequently encountered in clinical practice
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN ADULTS Urinary tract infection in adults is common and may be complicated or uncomplicated. Infection of the urinary tract (UTI) is frequently encountered in clinical practice
190.12 - Urine Culture, Bacterial Summary Information Highlighted items indicate most frequently used codes.
 Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings
 Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings Dr. Mary Vearncombe PIDAC-IPC February 2012 Objectives: To provide an overview of the RP/AP Annex
Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings Dr. Mary Vearncombe PIDAC-IPC February 2012 Objectives: To provide an overview of the RP/AP Annex
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail?
 Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC
 Lower Urinary Tract Infections WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September, 2015, Expires September, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG,
Lower Urinary Tract Infections WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September, 2015, Expires September, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG,
STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative treatment
 STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative Pregnancy Chlamydia Chancroid Epdidymitis Gonorrhea: Uncomplicated (cx, urethra, and rectum):
STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative Pregnancy Chlamydia Chancroid Epdidymitis Gonorrhea: Uncomplicated (cx, urethra, and rectum):
RECOMMENDATIONS. MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF URINARY TRACT INFECTION Clinical Practice Guideline November 2013 PRACTICE POINT
 MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF URINARY TRACT INFECTION Clinical Practice Guideline November 2013 GOALS Urgent primary care assessment and management of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in patients
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF URINARY TRACT INFECTION Clinical Practice Guideline November 2013 GOALS Urgent primary care assessment and management of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in patients
COMPASS Therapeutic Notes on the Management of Bacterial Urinary Tract Infections in Primary Care
 COMPASS Therapeutic Notes on the Management of Bacterial Urinary Tract Infections in Primary Care In this issue: Page Introduction, Background & Diagnostic Tests 1 UTI in non-pregnant women 3 UTI in pregnant
COMPASS Therapeutic Notes on the Management of Bacterial Urinary Tract Infections in Primary Care In this issue: Page Introduction, Background & Diagnostic Tests 1 UTI in non-pregnant women 3 UTI in pregnant
CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H.
 CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, CA Prevention Training Center Disclosure Information Sharon Adler MD, MPH I have no financial relationships
CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, CA Prevention Training Center Disclosure Information Sharon Adler MD, MPH I have no financial relationships
Managing the E coli UTI
 C o n s u l t a n t o n C a l l I N F E C T I O U S / Z O O N O T I C D I S E A S E Peer Reviewed Kate S. KuKanich, DVM, PhD, Diplomate ACVIM Kansas State University Managing the E coli UTI PROFILE Definition
C o n s u l t a n t o n C a l l I N F E C T I O U S / Z O O N O T I C D I S E A S E Peer Reviewed Kate S. KuKanich, DVM, PhD, Diplomate ACVIM Kansas State University Managing the E coli UTI PROFILE Definition
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
PATIENT CARE MANUAL PROCEDURE
 PATIENT CARE MANUAL PROCEDURE NUMBER VII-E-5 PAGE 1 OF 7 APPROVED BY: CATEGORY: Tri-site Nursing Policy and Procedures Review Committee Body Systems; Genitourinary 1.0 GOALS To influence patient care providers
PATIENT CARE MANUAL PROCEDURE NUMBER VII-E-5 PAGE 1 OF 7 APPROVED BY: CATEGORY: Tri-site Nursing Policy and Procedures Review Committee Body Systems; Genitourinary 1.0 GOALS To influence patient care providers
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Long-term urinary catheter-associated urinary tract infection (UTI)
 Peer reviewed article Long-term urinary catheter-associated urinary tract infection (UTI) Abstract This paper reviews the literature on the current management of symptomatic urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Peer reviewed article Long-term urinary catheter-associated urinary tract infection (UTI) Abstract This paper reviews the literature on the current management of symptomatic urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Childhood Urinary Tract Infections
 Childhood Urinary Tract Infections What is a UTI? Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections in childhood. It can cause distress to the child, concerns to the parents, and may
Childhood Urinary Tract Infections What is a UTI? Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections in childhood. It can cause distress to the child, concerns to the parents, and may
MODULE 2: ADULT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
 MODULE 2: ADULT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS KEYWORDS: Urinary tract infection (UTI); cystitis; pyelonephritis; uropathogens; antibiotics LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will
MODULE 2: ADULT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS KEYWORDS: Urinary tract infection (UTI); cystitis; pyelonephritis; uropathogens; antibiotics LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention. Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013
 Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS
 GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Limited text update March 2015) M. Grabe (Chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund Johansen, M. Çek, B. Köves (Guidelines Associate), K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke,
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Limited text update March 2015) M. Grabe (Chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund Johansen, M. Çek, B. Köves (Guidelines Associate), K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke,
URINE CULTURES GENERAL PROCEDURE
 University of Nebraska Medical Center Division of Laboratory Science Clinical Laboratory Science Program CLS 418/CLS 419 URINE CULTURES GENERAL PROCEDURE I. Principle Urine cultures are performed to detect
University of Nebraska Medical Center Division of Laboratory Science Clinical Laboratory Science Program CLS 418/CLS 419 URINE CULTURES GENERAL PROCEDURE I. Principle Urine cultures are performed to detect
signs suggesting chlamydia:
 Chlamydia - uncomplicated genital - Management View full scenario When should I suspect and test for chlamydia? Women: o Test for chlamydia if they are sexually active with symptoms and signs suggesting
Chlamydia - uncomplicated genital - Management View full scenario When should I suspect and test for chlamydia? Women: o Test for chlamydia if they are sexually active with symptoms and signs suggesting
Urinary Tract Infections - How to Identify, Treat and Prevent Them
 1 of 12 4/29/2016 1:49 PM Library Home Find A Physician Find A Practice Request An Appointment Search Clinical Studies Classes and Support Groups Ask A Health Librarian Subscribe to enewsletters Bone and
1 of 12 4/29/2016 1:49 PM Library Home Find A Physician Find A Practice Request An Appointment Search Clinical Studies Classes and Support Groups Ask A Health Librarian Subscribe to enewsletters Bone and
Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly. Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012
 1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Definitions and Reporting
 AHRQ Safety Program for Long-term Care: HAIs/CAUTI Learning Objectives Upon completion of the webinar, core team members will be able to: Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Definitions
AHRQ Safety Program for Long-term Care: HAIs/CAUTI Learning Objectives Upon completion of the webinar, core team members will be able to: Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Definitions
Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections
 Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Marnie Peterson, Pharm.D., BCPS Dept. of Pediatric Infectious Diseases Medical School University of Minnesota Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Intra-abdominal abdominal
Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Marnie Peterson, Pharm.D., BCPS Dept. of Pediatric Infectious Diseases Medical School University of Minnesota Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Intra-abdominal abdominal
Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Patients with Urinary Catheters
 Clinical Review Article Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Patients with Urinary Catheters Maria L. Alcaide, MD Daniel M. Lichtstein, MD Urinary tract infections (UTIs) in patients with urinary
Clinical Review Article Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Patients with Urinary Catheters Maria L. Alcaide, MD Daniel M. Lichtstein, MD Urinary tract infections (UTIs) in patients with urinary
Have a shower, rather than a bath to avoid exposing your genitals to the chemicals in your cleaning products for too long. Always empty your bladder
 Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
IDSA GUIDELINES EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 IDSA GUIDELINES International Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in Women: A 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and
IDSA GUIDELINES International Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in Women: A 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT
 THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 13, 2015 1400 EDT (2:00 PM EDT) NH-HAN 20150813 Updated Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 13, 2015 1400 EDT (2:00 PM EDT) NH-HAN 20150813 Updated Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
Frequently Asked Questions
 Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
Kalpana Gupta, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases Boston University School of Medicine
 2010 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases Kalpana Gupta, M.D. Associate Professor Department
2010 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases Kalpana Gupta, M.D. Associate Professor Department
Don t Go With The Flow! Control and Management of UTIs in the Elderly
 Don t Go With The Flow! Control and Management of UTIs in the Elderly Acknowledgements Central West Infection Control Network Toronto Central Infection Control Network Erie St Clair Infection Control Network
Don t Go With The Flow! Control and Management of UTIs in the Elderly Acknowledgements Central West Infection Control Network Toronto Central Infection Control Network Erie St Clair Infection Control Network
Comparison of effectiveness of sterile vs. clean technique for indwelling catheter care in preventing urinary tract infection
 Comparison of effectiveness of sterile vs. clean technique for indwelling catheter care in preventing urinary tract infection Monika Dutta, Prem Verma, A.K. Mandal Abstract : Indwelling urinary catheterization
Comparison of effectiveness of sterile vs. clean technique for indwelling catheter care in preventing urinary tract infection Monika Dutta, Prem Verma, A.K. Mandal Abstract : Indwelling urinary catheterization
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS INTRODUCTION Urinary tract infections are a very common medical problem. The term urinary tract infection is frequently used to refer to an infection of the bladder. However, although
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS INTRODUCTION Urinary tract infections are a very common medical problem. The term urinary tract infection is frequently used to refer to an infection of the bladder. However, although
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis
 Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis ANTIBIOTIC-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Disturbance of the normal colonic microflora Leading to alterations in bacterial degradation
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis ANTIBIOTIC-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Disturbance of the normal colonic microflora Leading to alterations in bacterial degradation
URINARY INCONTINENCE CASE PRESENTATION #1. Urinary Incontinence - History 2014/10/07. Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract
 Bladder pressure 2014/10/07 Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract Ureter URINARY INCONTINENCE Clinical Clerkship Lecture Series Outer peritoneal coat Detrusor smooth muscle Mucosa Trigone Proximal
Bladder pressure 2014/10/07 Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract Ureter URINARY INCONTINENCE Clinical Clerkship Lecture Series Outer peritoneal coat Detrusor smooth muscle Mucosa Trigone Proximal
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE
 in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients.
 Dec QMJ VOL.5 No.8 Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients. Radhi F.Alshaibani* الخلاصھ لا زالت حمى التایفوید سببا مھما من اسباب الامراض وفقدان ساعات العمل
Dec QMJ VOL.5 No.8 Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients. Radhi F.Alshaibani* الخلاصھ لا زالت حمى التایفوید سببا مھما من اسباب الامراض وفقدان ساعات العمل
Case Studies. Case Studies
 Case Studies Case Studies Purpose Training on use of definitions based on the January 2013 NHSN Patient Safety Manual Learn to accurately apply definitions Surveillance Clinical Optimize consistency in
Case Studies Case Studies Purpose Training on use of definitions based on the January 2013 NHSN Patient Safety Manual Learn to accurately apply definitions Surveillance Clinical Optimize consistency in
How To Find Out If A Diabetic Woman Has A Urinary Tract Infection
 Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 12 (2014) 171-178 Difference on the Incidence of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) between Diabetic and Non-diabetic Women Admitted in Metro Cebu, Philippines
Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 12 (2014) 171-178 Difference on the Incidence of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) between Diabetic and Non-diabetic Women Admitted in Metro Cebu, Philippines
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN CHILDREN. Yap Hui Kim, Belinda Murugasu
 URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN CHILDREN Yap Hui Kim, Belinda Murugasu Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common problem in childhood and the primary health care practitioner is usually the frontline in diagnosis
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN CHILDREN Yap Hui Kim, Belinda Murugasu Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common problem in childhood and the primary health care practitioner is usually the frontline in diagnosis
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE
 HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
Protocol for Macroscopic and Microscopic Urinalysis and Investigation of Urinary Tract Infections
 Protocol for Macroscopic and Microscopic Urinalysis and Investigation of Urinary Tract Infections Reprinted 2004 Scope The purpose of this protocol is to avoid unnecessary testing in routine cases while
Protocol for Macroscopic and Microscopic Urinalysis and Investigation of Urinary Tract Infections Reprinted 2004 Scope The purpose of this protocol is to avoid unnecessary testing in routine cases while
Urinary Tract Infection among Clean-Room Workers
 J Occup Health 2002; 44: 329 333 Journal of Occupational Health Urinary Tract Infection among Clean-Room Workers Jian-Nan WANG 1, Shih-Bin SU 2, 3 and How-Ran GUO 3 1 Department of Family Medicine, Chie-Mei
J Occup Health 2002; 44: 329 333 Journal of Occupational Health Urinary Tract Infection among Clean-Room Workers Jian-Nan WANG 1, Shih-Bin SU 2, 3 and How-Ran GUO 3 1 Department of Family Medicine, Chie-Mei
Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services. 18/07/2008 Cardiff and Vale NHS Trust
 Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services Types of continence problems Bladder Stress incontinence Urgency and urge Incontinence Mixed incontinence Obstructive incontinence
Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services Types of continence problems Bladder Stress incontinence Urgency and urge Incontinence Mixed incontinence Obstructive incontinence
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter
 Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections in Children
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections in Children BRETT WHITE, MD, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon Acute urinary tract infections are relatively common in children,
Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections in Children BRETT WHITE, MD, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon Acute urinary tract infections are relatively common in children,
Leader's Resource. Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms.
 Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Treatment of sexually transmitted and other genital infections
 www.bpac.org.nz keyword: sti Treatment of sexually transmitted and other genital infections Key reviewer: Dr Murray Reid, Sexual Health Physician, Auckland Sexual Health Service General points: If one
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: sti Treatment of sexually transmitted and other genital infections Key reviewer: Dr Murray Reid, Sexual Health Physician, Auckland Sexual Health Service General points: If one
Guidelines on Urological Infections
 Guidelines on Urological Infections M. Grabe (Chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund Johansen, T. Cai (Guidelines Associate), M. Çek, B. Köves (Guidelines Associate), K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke,
Guidelines on Urological Infections M. Grabe (Chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund Johansen, T. Cai (Guidelines Associate), M. Çek, B. Köves (Guidelines Associate), K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke,
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2. Patient Information. Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate
 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate. Guidelines for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (SSI)
 State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Guidelines for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (SSI) September 1999 Updated 2007 Surgical Wound: According to 1998 Kuwait National
State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Guidelines for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (SSI) September 1999 Updated 2007 Surgical Wound: According to 1998 Kuwait National
NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital Sites: Columbia University Medical Center Guideline: Medication Use Manual Page 1 of 12
 Page 1 of 12 TITLE: ANTIBIOTICS IN ADULT PATIENTS EMPIRIC USE GUIDELINES, COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER MEDICATION GUIDELINE PURPOSE: These are the 2011 guidelines for the empiric use of antibiotics
Page 1 of 12 TITLE: ANTIBIOTICS IN ADULT PATIENTS EMPIRIC USE GUIDELINES, COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER MEDICATION GUIDELINE PURPOSE: These are the 2011 guidelines for the empiric use of antibiotics
Lecture Outline. Quinolones
 Lecture Outline Quinolones Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole Miscellaneous antimicrobials - Metronidazole Daptomycin Cases Quinolones Bactericidal broad spectrum antibiotics Increasingly used because of their
Lecture Outline Quinolones Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole Miscellaneous antimicrobials - Metronidazole Daptomycin Cases Quinolones Bactericidal broad spectrum antibiotics Increasingly used because of their
Welcome and Instructions
 Welcome and Instructions For audio, join by telephone at 877-594-8353, participant code: 56350822 Your line is OPEN. Please do not use the hold feature on your phone but do mute your line by dialing *6.
Welcome and Instructions For audio, join by telephone at 877-594-8353, participant code: 56350822 Your line is OPEN. Please do not use the hold feature on your phone but do mute your line by dialing *6.
A THREE YEAR REVIEW OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS REPORTED TO THE NATIONAL HEALTHCARE SAFETY NETWORK AT A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL
 A THREE YEAR REVIEW OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS REPORTED TO THE NATIONAL HEALTHCARE SAFETY NETWORK AT A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL by Jessi Marie Bond BS, Clinical Laboratory Science, Idaho
A THREE YEAR REVIEW OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS REPORTED TO THE NATIONAL HEALTHCARE SAFETY NETWORK AT A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL by Jessi Marie Bond BS, Clinical Laboratory Science, Idaho
PREVENTION OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION FOLLOWING GYNAECOLOGIC SURGERY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
 PREVENTION OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION FOLLOWING GYNAECOLOGIC SURGERY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW *Christine M. Chu, Lily A. Arya Division of Urogynecology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
PREVENTION OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION FOLLOWING GYNAECOLOGIC SURGERY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW *Christine M. Chu, Lily A. Arya Division of Urogynecology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Therapeutic protocoles for adults concerning ESBL Enterobacteria infections in health care institutions
 Therapeutic protocoles for adults concerning ESBL Enterobacteria infections in health care institutions CYSTITIS The growing importance of resistance to quinolones, their environmental impact and reduced
Therapeutic protocoles for adults concerning ESBL Enterobacteria infections in health care institutions CYSTITIS The growing importance of resistance to quinolones, their environmental impact and reduced
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Urinary tract infections
 Facts Behind the Fact Card Pharmacist CPE Urinary tract infections by Lynn Gould Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are very common, affecting about 250,000 people in Australia each year. 1 Many people go
Facts Behind the Fact Card Pharmacist CPE Urinary tract infections by Lynn Gould Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are very common, affecting about 250,000 people in Australia each year. 1 Many people go
Diseases that can be spread during sex
 Diseases that can be spread during sex Did you know... over 65 million people in the United States have a chronic, incurable sexually transmitted disease (STD)? and that every year another 19 million persons
Diseases that can be spread during sex Did you know... over 65 million people in the United States have a chronic, incurable sexually transmitted disease (STD)? and that every year another 19 million persons
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies
 C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis RICHARD COLGAN, MD, and MOZELLA WILLIAMS, MD University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltime, Maryland Urinary tract infections are the most common
Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis RICHARD COLGAN, MD, and MOZELLA WILLIAMS, MD University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltime, Maryland Urinary tract infections are the most common
35-40% of GBS disease occurs in the elderly or in adults with chronic medical conditions.
 What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Prevention of catheter associated urinary tract infections
 Prevention of catheter associated urinary tract infections Dr. Suzan Sanavi, Nephrologist, M.D University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Akhavan Physical Spine Center INTRODUCTION Urinary bladder
Prevention of catheter associated urinary tract infections Dr. Suzan Sanavi, Nephrologist, M.D University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Akhavan Physical Spine Center INTRODUCTION Urinary bladder
