Overactive bladder (OAB) is a
|
|
|
- Joanna Wilkinson
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Menopause Matters from Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Midlife Women Tyler M. Muffly, MD; Marie Fidela R. Paraiso, MD Overactive bladder is a debilitating health condition that affects 16.6% of the US female population. The inability to control the involuntary loss of urine is one of the most unpleasant and distressing symptoms a woman can experience and may significantly affect her quality of life. Overactive bladder (OAB) is a common and embarrassing problem that affects many women before, during, and beyond menopause. OAB presents with or without incontinence and has a constellation of symptoms including urgency, usually with urinary frequency and nocturia. 1 A diagnosis of OAB is made when a patient presents with urgency in the absence of pathologic or metabolic conditions that might otherwise explain this symptom. OAB is a bladder storage disorder caused by an increase in bladder pressure from an uninhibited contraction of the detrusor muscle. Additionally, many women with OAB have sensory urgency that is not necessarily associated with a bladder contraction. OAB affects 16.6% of the general female population in the United States. 2 OAB prevalence increases with age, and approximately 23% of women ages 55 to 64 years have OAB; hence, this condition will increase in absolute numbers as the demographic of aging women expands. 3 The occurrence of OAB is higher than that of stress incontinence in the aging female population. The inability to control the involuntary loss of urine is one of the most unpleasant and distressing symptoms a woman can experience and may significantly affect her quality of life. Ultimately, these alterations in the physical, occupational, and sexual quality of life may result in depression or loss of self-esteem. Unfortunately, women affected by OAB may attempt to cope with symptoms on their own instead of seeking treatment for a variety of reasons including poor access to health care, embarrassment, and lack of knowledge about OAB treatments. Diagnosis of OAB A presumptive diagnosis of OAB can be made with a careful history and physical examination. Typical symptoms Tyler M. Muffly, MD, is Fellow, Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery, Center of Urogynecology and Pelvic Floor Disorders, Obstetrics, Gynecology & Women s Health Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH. Marie Fidela R. Paraiso, MD, is Professor, Center of Urogynecology and Pelvic Floor Disorders, Obstetrics, Gynecology & Women s Health Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH Follow The Female Patient on and The Female Patient VOL 37 MARCH
2 Menopause Matters include voiding more than 8 times per day (urinary frequency) or more than once at night (nocturia), and a strong and sudden desire to urinate (urinary urgency). One simple question can elicit a response confirming urgency urinary incontinence: Do you feel the need to urinate but cannot get to the toilet fast enough? In addition, validated questionnaires such as the Incontinence Impact Questionnaire measures symptom distress in women with this complaint. A physical should include a focused neurologic examination in which the physician evaluates sacral nerve function by testing the bulbocavernosus reflex and/or an anal wink. Used over a period of 72 hours, a temporal log of urination can gauge progress following treatments and is well correlated with urodynamic FOCUSPOINT Cystometry is the only way to quantitatively diagnose the amplitude of detrusor contractions and thus make the diagnosis of detrusor overactivity. diagnosis. 4 A urinalysis, and possibly a urine culture, should be performed to rule out a urinary tract infection as the etiology of the OAB. Some practitioners feel that a postvoid residual should also be performed to rule out voiding dysfunction, although there are some data to support a less extensive workup. Cystometry is the only way to quantitatively diagnose the amplitude of detrusor contractions and thus make the diagnosis of detrusor overactivity. The most costeffective diagnostic method is office cystometrics in which the bladder is retrograde filled with saline, and the meniscus of fluid in a graduated syringe is observed for fluctuations. Subtracted multichannel urodynamics can be used to make a diagnosis with a history of mixed urinary incontinence or other provocative maneuver defined as stress provoked detrusor overactivity. Cystometry has traditionally been a barrier to treatment since primary care providers do not feel comfortable with the extensive testing. Complicated patients may require cystometry while more clear-cut cases of OAB can be cared for without this step. Conservative Therapy We have recommended noninvasive approaches prior to pursuing invasive approaches for treatment of incontinence. Behavioral modification such as reduction in consumption of bladder irritants, bladder training, and pelvic floor muscle exercises all heavily rely on compliance of the patient. Scheduled voiding (bladder training) is a mainstay of treatment for OAB. Patients are instructed to void every hour while awake then slowly increase the time interval between voids. Pelvic floor muscle rehabilitation focuses on strengthening the levator ani muscles in order to help the patient suppress detrusor contractions. Although anticholinergic medicines, as will be discussed below, may decrease the frequency of urge episodes, medicine will not stop an urge once it starts. When an urge starts, contraction of the levator ani muscles may be the only method to relax the detrusor muscle and prevent urinary incontinence. Many patients will require a concurrent second treatment option, which has been shown to be more effective than a single treatment alone. 5 Pharmacologic Therapy Anticholinergics/Antimuscarinics The goal of pharmacotherapy is to limit the frequency and number of leakage episodes by decreasing bladder contractions. Anticholinergic medications block the action of acetylcholine receptors in the bladder smooth muscle to prevent strong bladder contractions at low volumes of urine. The efficacy of various anticholinergics/antimuscarinics has been evaluated by a comprehen- 18 The Female Patient VOL 37 MARCH 2012 All articles are available online at
3 Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Midlife Women FOCUSPOINT We recommend pursuing invasive techniques when behavioral interventions and at least two pharmacologic therapies fail, are contraindicated, or cannot be tolerated. sive Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality meta-analysis. 6 The conclusion of the meta-analysis was that there were mild improvements with anticholinergic medications when compared to placebo, and that long acting agents were more efficacious than short acting medications. In addition, improvements in continence produced by behavior modifications are similar to the impact of antimuscarinics. A 2006 Cochrane review showed at the end of the treatment period, the improvement in leakage episodes in 24 hours was statistically significant favoring medication (RR, 1.39; 95% CI, ). 7 The placebo effect (33% to 56%) is strong in this patient population because patients may be somewhat desperate for a solution. The role of antispasmodic, antidepressant, and calcium channel blocking medications is still under review. Estrogen Therapy Local vaginal estrogen therapy is used by many clinicians in women with urge incontinence and vaginal atrophy, although the evidence of benefit is not clear. Surgery There are several surgical techniques available to treat refractory OAB including detrusor injection of Clostridium botulinum toxin type A (Botox), neuromodulation, and other methods. Surgeons views differ as to when invasive techniques are justified. We recommend pursuing invasive techniques when behavioral interventions and at least two pharmacologic therapies fail, are contraindicated, or cannot be tolerated. Women who fail conservative and pharmacologic management and are diagnosed with refractory undesired bladder contractions may consider surgery. Even in the subset of hard-to-treat women, the decision to treat OAB surgically should not be made lightly. Botulinum toxin type A intra-detrusor injections are not FDA approved and are currently being studied as a chemodenervation agent for temporary paralysis of the muscle. 8 Using a cystoscope, the physician injects 100 to 200 units of botulinum toxin type A within the detrusor muscle or bladder submucosa. Data from two randomized controlled trials (RCTs) illustrated that 200 units decreased urge incontinence in women with idiopathic detrusor overactivity and refractory urge incontinence; however, one trial was halted because of a statistically significant increased risk of urinary retention. 9,10 Women who received these injections were more likely to report improvement on a validated questionnaire, a 3-day urinary diary, and had a median duration of response that was significantly longer than for placebo (P <.0001). However, the clinical significance of the resultant urinary retention is unclear as it was temporary and the majority of patients did not complain of voiding dysfunction. Sacroneuromodulation is another surgical method employed to treat OAB. Several anatomic sites for neuromodulation have included the placement of electrodes adjacent to the dorsal clitoral nerve, sacral nerve roots, and tibial nerve. 11,12 Six months after placement of a sacral nerve stimulator, the number of daily heavy incontinence episodes decreased from 3.4 ± 3.8 to 0.3 ± 0.9 (P <.0001) in one RCT. 13 Sacral nerve stimulation was government approved for use with refractory voiding dysfunction in The exact mechanism of 20 The Female Patient VOL 37 MARCH 2012
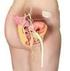
4 Muffl y and Paraiso action of sacral nerve stimulation is not known. Placement of a sacral nerve stimulator is a two-stage process whereby a subcutaneous implantable pulse generator is connected to a lead electrode that lies along the third sacral nerve. The first stage can be performed either as an office percutaneous nerve stimulation or as an outpatient procedure. The neuromodulation device is commonly described to patients as a bladder pacemaker (Figure). Given the high cost associated with sacral neuromodulation, a thorough preoperative evaluation should be performed to ensure the patient is a suitable candidate. Patients should understand that they need to turn off the generator if they are going to undergo a surgical procedure, they cannot have magnetic resonance imaging with the device in place and they cannot undergo a procedure employing diathermy. Unknown durability and operative reversibility are the unique risks of sacral nerve stimulators and should be discussed. 14 Posterior tibial nerve stimulation is a percutaneous therapy. Tibial nerve stimulation is technically simple to perform and is based on the insertion of acupuncture needles. Multiple treatment sessions are scheduled in the office and may be helpful in patients who desire not to take more medications. In extreme cases of OAB with urgency urinary incontinence, bladder augmentation with a loop of bowel establishes an acontractile bladder or bladder-intestine-reservoir. This procedure is rarely performed given the associated morbidity. Prior to any operative procedure, the physician should document that an adequate trial of medical or conservative management has been offered and attempted or refused (informed refusal). Physicians who have a strong understanding of the consent process and the variety of various OAB options will be best prepared to illustrate this risk versus benefit relationship. Conclusions Given the growing number of OAB cases treated annually, it is encouraging to see that during the past 5 years new drugs and procedures have been developed to treat these patients. There remains little data regarding the ideal OAB management that minimizes morbidity while maximizing subjective outcomes for the menopausal patient. Thus, treatment FIGURE. A sacral nerve stimulator with a tined lead placed in the second sacral nerve root. Reprinted with permission, Cleveland Clinic Center for Medical Art & Photography All Rights Reserved. should be individualized, based on provider experience and patient preference, depending on both the patient s and provider s tolerance for risk. The authors report no actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to this article. References 1. Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;187(1): Coyne KS, Payne C, Bhattacharyya SK, et al. The impact of urinary urgency and frequency on health-related qual- The Female Patient VOL 37 MARCH
5 Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Midlife Women ity of life in overactive bladder: results from a national community survey. Value Health. 2004;7(4): Gray M. The importance of screening, assessing, and managing urinary incontinence in primary care. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2003;15(3): Wyman JF, Choi SC, Harkins SW, Wilson MS, Fantl JA. The urinary diary in evaluation of incontinent women: a testretest analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 1988;71(6 Pt 1): Burgio KL, Kraus SR, Menefee S, et al. Behavioral therapy to enable women with urge incontinence to discontinue drug treatment: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149(3): Hartmann KE, McPheeters ML, Biller DH, et al. Treatment of overactive bladder in women. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2009;187:1-120, v. Available at: Accessed January 17, Nabi G, Cody JD, Ellis G, Herbison P, Hay-Smith J. Anticholinergic drugs versus placebo for overactive bladder syndrome in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;(4):CD Mahajan ST, Brubaker L. Botulinum toxin: from lifethreatening disease to novel medical therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007;196(1): Brubaker L, Richter HE, Visco A, et al. Refractory idiopathic urge urinary incontinence and botulinum A injection. J Urol. 2008;180(1): Sahai A, Khan MS, Dasgupta P. Effi cacy of botulinum toxin-a for treating idiopathic detrusor overactivity: results from a single center, randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. J Urol. 2007;177(6): van Balken MR, Vergunst H, Bemelmans BL. The use of electrical devices for the treatment of bladder dysfunction: a review of methods. J Urol. 2004;172(3): Goldman HB, Amundsen CL, Mangel J, et al. Dorsal genital nerve stimulation for the treatment of overactive bladder symptoms. Neurourol Urodyn. 2008;27(6): Schmidt RA, Jonas U, Oleson KA, et al. Sacral nerve stimulation for treatment of refractory urinary urge incontinence. J Urol. 1999;162(2): van Kerrebroeck PE, van Voskuilen AC, Heesakkers JP, et al. Results of sacral neuromodulation therapy for urinary voiding dysfunction: outcomes of a prospective, worldwide clinical study. J Urol. 2007;178(5): For a PATIENT HANDOUT on overactive bladder in midlife women, see page The Female Patient VOL 37 MARCH 2012
Female Urinary Incontinence
 Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives Review the problem Feel confident
Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives Review the problem Feel confident
Normal bladder function requires a coordinated effort between the brain, spinal cord, and the bladder.
 .. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
.. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
OVERACTIVE BLADDER DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS:
 2014 OVERACTIVE BLADDER DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS: AUA/SUFU Guideline (2012); Amended (2014) For Primary Care Providers OVERACTIVE BLADDER Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive
2014 OVERACTIVE BLADDER DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS: AUA/SUFU Guideline (2012); Amended (2014) For Primary Care Providers OVERACTIVE BLADDER Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive
Saint Mary s Hospital. Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit. Overactive Bladder. Information for Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Overactive Bladder Information for Patients What is Overactive Bladder (OAB)? OAB is a condition that causes you to need to pass urine more often
Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Overactive Bladder Information for Patients What is Overactive Bladder (OAB)? OAB is a condition that causes you to need to pass urine more often
TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN
 TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN Scott A Farrell MD Professor Dept of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Dalhousie University Declaration of
TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN Scott A Farrell MD Professor Dept of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Dalhousie University Declaration of
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture
 Overactive bladder (OAB) : Introduction and Medical Management R.J. Opsomer Cliniques St Luc, labo d urodynamique, UCL - Bruxelles Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture The syndrome of Overactive
Overactive bladder (OAB) : Introduction and Medical Management R.J. Opsomer Cliniques St Luc, labo d urodynamique, UCL - Bruxelles Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture The syndrome of Overactive
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or desire to pass
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or desire to pass
It usually presents with a sudden urge to urinate that is very difficult to delay and may be associated with leakage. Other features include:
 visited on Page 1 of 5 View this article online at http://patient.info/doctor/overactive-bladder Overactive Bladder This PatientPlus article is written for healthcare professionals so the language may
visited on Page 1 of 5 View this article online at http://patient.info/doctor/overactive-bladder Overactive Bladder This PatientPlus article is written for healthcare professionals so the language may
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
OAB (Overactive Bladder)
 OAB (Overactive Bladder) PharmCon is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education as a provider of continuing pharmacy education. This webcast has been supported by an educational grant
OAB (Overactive Bladder) PharmCon is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education as a provider of continuing pharmacy education. This webcast has been supported by an educational grant
Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling
 Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling 吳 銘 斌 Ming-Ping Wu, M.D.,Ph.D. Director, Div. Urogynecology & Pelvic Floor Reconstruction, Chi Mei Foundation Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan Assistant Professor,
Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling 吳 銘 斌 Ming-Ping Wu, M.D.,Ph.D. Director, Div. Urogynecology & Pelvic Floor Reconstruction, Chi Mei Foundation Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan Assistant Professor,
Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders Andrea Staack, MD, PhD Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Urinary Incontinence & Female Urology Department of Urology Loma Linda University, CA What will you learn
Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders Andrea Staack, MD, PhD Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Urinary Incontinence & Female Urology Department of Urology Loma Linda University, CA What will you learn
Urinary Incontinence in Women. Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine
 Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
SOGC Recommendations for Urinary Incontinence
 The quality of evidence is rated, and recommendations are made using the criteria described by the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Clinical Practice Guidelines: The Evaluation of Stress
The quality of evidence is rated, and recommendations are made using the criteria described by the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Clinical Practice Guidelines: The Evaluation of Stress
COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
Female Urinary Incontinence
 Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. Objectives Which is most true? Review the problem
Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. Objectives Which is most true? Review the problem
Urinary incontinence during sexual intercourse: a common, but rarely volunteered, symptom
 British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology April 1988, Vol. 95, pp. 77-81 Urinary incontinence during sexual intercourse: a common, but rarely volunteered, symptom PAUL HILTON Summary. A total of 4
British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology April 1988, Vol. 95, pp. 77-81 Urinary incontinence during sexual intercourse: a common, but rarely volunteered, symptom PAUL HILTON Summary. A total of 4
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline
 Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
Case Study on the use of Electro acupuncture for Overactive Bladder. Siu Cheetham Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital
 Case Study on the use of Electro acupuncture for Overactive Bladder Siu Cheetham Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital Overactive bladder Approximately 34 million adults in the United States The International
Case Study on the use of Electro acupuncture for Overactive Bladder Siu Cheetham Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital Overactive bladder Approximately 34 million adults in the United States The International
Case Based Urology Learning Program
 Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 21 CBULP 2011 068 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 21 CBULP 2011 068 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting
 Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide
 Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men
 Prostatic Diseases Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men JMAJ 47(12): 543 548, 2004 Tomonori YAMANISHI Associate Professor, Department of Urology, Dokkyo University School
Prostatic Diseases Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men JMAJ 47(12): 543 548, 2004 Tomonori YAMANISHI Associate Professor, Department of Urology, Dokkyo University School
Urinary Incontinence Dr. Leffler
 Urinary Incontinence Dr. Leffler The involuntary loss of urine at socially unacceptable times occurs in both women and men, but more commonly in women. It has multiple, far-reaching effects on daily activities,
Urinary Incontinence Dr. Leffler The involuntary loss of urine at socially unacceptable times occurs in both women and men, but more commonly in women. It has multiple, far-reaching effects on daily activities,
URINARY INCONTINENCE CASE PRESENTATION #1. Urinary Incontinence - History 2014/10/07. Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract
 Bladder pressure 2014/10/07 Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract Ureter URINARY INCONTINENCE Clinical Clerkship Lecture Series Outer peritoneal coat Detrusor smooth muscle Mucosa Trigone Proximal
Bladder pressure 2014/10/07 Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract Ureter URINARY INCONTINENCE Clinical Clerkship Lecture Series Outer peritoneal coat Detrusor smooth muscle Mucosa Trigone Proximal
Urinary Incontinence: an overview!! Neil Harris Consultant Urological Surgeon, Leeds
 Urinary Incontinence: an overview!! Neil Harris Consultant Urological Surgeon, Leeds Content 1. Epidemiology of pelvic floor dysfunction Urinary incontinence Bowel dysfunction Sexual dysfunction 2. Treatment
Urinary Incontinence: an overview!! Neil Harris Consultant Urological Surgeon, Leeds Content 1. Epidemiology of pelvic floor dysfunction Urinary incontinence Bowel dysfunction Sexual dysfunction 2. Treatment
Question ID: 6 Question type: Intervention Question: Does treatment of overactive bladder symptoms prevent falls in the elderly?
 PRIORITY BRIEFING The purpose of this briefing paper is to aid Stakeholders in prioritising topics to be taken further by PenCLAHRC as the basis for a specific evaluation or implementation projects. QUESTION
PRIORITY BRIEFING The purpose of this briefing paper is to aid Stakeholders in prioritising topics to be taken further by PenCLAHRC as the basis for a specific evaluation or implementation projects. QUESTION
Postoperative. Voiding Dysfunction
 Postoperative Voiding Trial Voiding Dysfunction Stephanie Pickett, MD Fellow Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery Objectives Define postoperative voiding dysfunction Describe how to evaluate
Postoperative Voiding Trial Voiding Dysfunction Stephanie Pickett, MD Fellow Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery Objectives Define postoperative voiding dysfunction Describe how to evaluate
Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly. Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012
 1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
PROCEEDINGS INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE * Ananias C. Diokno, MD ABSTRACT
 INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE * Ananias C. Diokno, MD ABSTRACT Urinary incontinence is a worldwide problem that affects millions of women, although the magnitude of the problem
INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE * Ananias C. Diokno, MD ABSTRACT Urinary incontinence is a worldwide problem that affects millions of women, although the magnitude of the problem
Regain Control of Your Active Life Treatment Options for Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Regain Control of Your Active Life Treatment Options for Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Nearly one quarter of all women in the United States have some sort of pelvic floor disorder such as urinary
Regain Control of Your Active Life Treatment Options for Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Nearly one quarter of all women in the United States have some sort of pelvic floor disorder such as urinary
Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence. Overview of Lecture
 Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence Professor Don Wilson Department of Women s and Children s Health Dunedin School of Medicine University of Otago GP Teaching for Roy Morris,
Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence Professor Don Wilson Department of Women s and Children s Health Dunedin School of Medicine University of Otago GP Teaching for Roy Morris,
FEMALE INCONTINENCE REVIEW
 200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence
 Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing
Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing
URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN
 URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Definition Urinary incontinence (UI) is defined as involuntary loss of urine that is a social or hygienic problem (International Continence Society, 1973) Magnitude of the
URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Definition Urinary incontinence (UI) is defined as involuntary loss of urine that is a social or hygienic problem (International Continence Society, 1973) Magnitude of the
Women suffer in silence
 Women suffer in silence Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine resulting from increased intra-abdominal pressure. In people who suffer with this condition, forms of exertion such
Women suffer in silence Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine resulting from increased intra-abdominal pressure. In people who suffer with this condition, forms of exertion such
Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation for the Long-Term Treatment of Overactive Bladder: 3-Year Results of the STEP Study
 Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation for the Long-Term Treatment of Overactive Bladder: 3-Year Results of the STEP Study Kenneth M. Peters,*, Donna J. Carrico, Leslie S. Wooldridge, Christopher J. Miller
Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation for the Long-Term Treatment of Overactive Bladder: 3-Year Results of the STEP Study Kenneth M. Peters,*, Donna J. Carrico, Leslie S. Wooldridge, Christopher J. Miller
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust
 Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction. Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.86 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013
MP 7.01.86 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013
Classification of Mixed Incontinence
 european urology supplements 5 (2006) 837 841 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Classification of Mixed Incontinence Christopher Chapple * Sheffield Hallam University,
european urology supplements 5 (2006) 837 841 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Classification of Mixed Incontinence Christopher Chapple * Sheffield Hallam University,
Botox treatment for an overactive bladder in women. Information for patients Gynaecology
 Botox treatment for an overactive bladder in women Information for patients Gynaecology What is bladder overactivity (OAB)? Bladder overactivity is a common condition, affecting around one in five people.
Botox treatment for an overactive bladder in women Information for patients Gynaecology What is bladder overactivity (OAB)? Bladder overactivity is a common condition, affecting around one in five people.
Bladder and Bowel Control
 Bladder and Bowel Control Dr Sue Woodward Lecturer, Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery 2 Why do we need to understand anatomy? Normal physiology Normal adult bladder capacity = 450-500mls
Bladder and Bowel Control Dr Sue Woodward Lecturer, Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery 2 Why do we need to understand anatomy? Normal physiology Normal adult bladder capacity = 450-500mls
Should SUI Surgery be Combined with Pelvic Organ Prolapse Surgery?
 Should SUI Surgery be Combined with Pelvic Organ Prolapse Surgery? Geoffrey W. Cundiff, M.D. 36 th National Congress of the South African Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists SASOG 2014 Learning
Should SUI Surgery be Combined with Pelvic Organ Prolapse Surgery? Geoffrey W. Cundiff, M.D. 36 th National Congress of the South African Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists SASOG 2014 Learning
GENUINE STRESS AND URGE INCONTINENCE PROTOCOL
 GENUINE STRESS AND URGE INCONTINENCE PROTOCOL Using the NeuroTrac ETSTM in combination of electrostimulation and EMG Biofeedback in the treatment of female urinary incontinence. Anna Pawlaczyk Specialist
GENUINE STRESS AND URGE INCONTINENCE PROTOCOL Using the NeuroTrac ETSTM in combination of electrostimulation and EMG Biofeedback in the treatment of female urinary incontinence. Anna Pawlaczyk Specialist
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in MS. Tracy Walker, WOCN, MSCN, FNP C Nurse Practitioner MS Institute at Shepherd Center. Bladder Dysfunction
 Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in MS Tracy Walker, WOCN, MSCN, FNP C Nurse Practitioner MS Institute at Shepherd Center Bladder Dysfunction Approximately 75% of people with MS experience bladder problems
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in MS Tracy Walker, WOCN, MSCN, FNP C Nurse Practitioner MS Institute at Shepherd Center Bladder Dysfunction Approximately 75% of people with MS experience bladder problems
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary Urinary (YOOR-in-air-ee) incontinence (in-kahn-tih-nens) is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have urinary incontinence, you re not alone.
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary Urinary (YOOR-in-air-ee) incontinence (in-kahn-tih-nens) is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have urinary incontinence, you re not alone.
THE ROLE OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER TREATMENT
 THE ROLE OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER TREATMENT Prof. Junizaf, SpOG(K) Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology School of Medicine, University of Indonesia/ Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital
THE ROLE OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER TREATMENT Prof. Junizaf, SpOG(K) Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology School of Medicine, University of Indonesia/ Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital
Urinary Incontinence Definitions
 (AADL) Program Urge Stress Overflow Functional Mixed DHIC (Detrussor hyperreflexia with impaired contractility) Reflex Incontinence Leakage of urine (usually larger volumes) because of inability to delay
(AADL) Program Urge Stress Overflow Functional Mixed DHIC (Detrussor hyperreflexia with impaired contractility) Reflex Incontinence Leakage of urine (usually larger volumes) because of inability to delay
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Botulinum toxin injections for the bladder Department of Uro-Neurology If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Botulinum toxin injections for the bladder Department of Uro-Neurology If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services
9/24/2015. Incontinence and Prolapse 2015 Primary Care Update CME Symposium. Objectives. Mark Memo, DO, FACS NEO Urology September 25-27
 Incontinence and Prolapse 2015 Primary Care Update CME Symposium Mark Memo, DO, FACS NEO Urology September 25-27 Objectives Incontinence Pelvic Organ Prolapse Vaginal Mesh Litigation 1 Urinary Incontinence
Incontinence and Prolapse 2015 Primary Care Update CME Symposium Mark Memo, DO, FACS NEO Urology September 25-27 Objectives Incontinence Pelvic Organ Prolapse Vaginal Mesh Litigation 1 Urinary Incontinence
symptoms of Incontinence
 Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Managing Overactive Bladder
 Patient Educational Material Managing Overactive Bladder The bladder s job is pretty simple: hold urine until full, then empty when we get to a restroom. When you have an overactive bladder, the bladder
Patient Educational Material Managing Overactive Bladder The bladder s job is pretty simple: hold urine until full, then empty when we get to a restroom. When you have an overactive bladder, the bladder
Stress Urinary Incontinence & Sexual Function
 Stress Urinary Incontinence & Sexual Function Lior Lowenstein, MD, MS Associate Professor Deputy Chairman of Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Rambam Health Care Campus Haifa Israel No Disclosures Disclosures
Stress Urinary Incontinence & Sexual Function Lior Lowenstein, MD, MS Associate Professor Deputy Chairman of Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Rambam Health Care Campus Haifa Israel No Disclosures Disclosures
Position Statement on Mesh Midurethral Slings for Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Position Statement on Mesh Midurethral Slings for Stress Urinary Incontinence The polypropylene mesh midurethral sling is the recognized worldwide standard of care for the surgical treatment of stress
Position Statement on Mesh Midurethral Slings for Stress Urinary Incontinence The polypropylene mesh midurethral sling is the recognized worldwide standard of care for the surgical treatment of stress
A Physical Therapist s Perspective
 You Can Do Something About INCONTINENCE A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association 1 You Can Do Something About Urinary Incontinence Incontinence, involuntary loss of bladder
You Can Do Something About INCONTINENCE A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association 1 You Can Do Something About Urinary Incontinence Incontinence, involuntary loss of bladder
Urinary Incontinence. Anatomy and Terminology Overview. Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS
 Urinary Incontinence Anatomy and Terminology Overview Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS Purpose Locate and describe the anatomy of the Female Urinary System Define terminology related to Incontinence Describe
Urinary Incontinence Anatomy and Terminology Overview Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS Purpose Locate and describe the anatomy of the Female Urinary System Define terminology related to Incontinence Describe
botulinum toxin type A 50, 100, 200 Allergan units/vial (Botox ) SMC No. (916/13) Allergan Ltd
 botulinum toxin type A 50, 100, 200 Allergan units/vial (Botox ) SMC No. (916/13) Allergan Ltd 06 September 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
botulinum toxin type A 50, 100, 200 Allergan units/vial (Botox ) SMC No. (916/13) Allergan Ltd 06 September 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
Botox (Botulinum Toxin) injections into the bladder
 York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Botox (Botulinum Toxin) injections into the bladder Information for patients, relatives and carers Department of Urology York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation
York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Botox (Botulinum Toxin) injections into the bladder Information for patients, relatives and carers Department of Urology York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation
Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation
 MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation Number 7.01.69 Effective
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation Number 7.01.69 Effective
1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE
 in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
Urinary incontinence and Prolapse. Dr Zeelha Abdool Consultant OBGYN Steve Biko Academic Hospital
 Urinary incontinence and Prolapse Dr Zeelha Abdool Consultant OBGYN Steve Biko Academic Hospital Definitions: IUGA/ICS standardized terminology Urinary incontinence (symptom): complaint of involuntary
Urinary incontinence and Prolapse Dr Zeelha Abdool Consultant OBGYN Steve Biko Academic Hospital Definitions: IUGA/ICS standardized terminology Urinary incontinence (symptom): complaint of involuntary
Bard: Continence Therapy. Stress Urinary Incontinence. Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle.
 Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Becoming knowledgeable about urinary incontinence Uterus Normal Pelvic Anatomy
Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Becoming knowledgeable about urinary incontinence Uterus Normal Pelvic Anatomy
Urinary Continence. Second edition FAST FACTS. by Julian Shah and Gary Leach. Anatomy and physiology 7. Investigations and diagnosis 11
 FAST FACTS Urinary Continence Second edition Indispensable Guides to by Julian Shah and Gary Leach Clinical Practice Anatomy and physiology 7 Investigations and diagnosis 11 Detrusor instability 28 Primary
FAST FACTS Urinary Continence Second edition Indispensable Guides to by Julian Shah and Gary Leach Clinical Practice Anatomy and physiology 7 Investigations and diagnosis 11 Detrusor instability 28 Primary
1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. It s time to talk about SUI Get the facts. This Patient s Guide is intended as a public resource on the issue of Stress Urinary Incontinence
A PATIENT S GUIDE 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. It s time to talk about SUI Get the facts. This Patient s Guide is intended as a public resource on the issue of Stress Urinary Incontinence
Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction
 Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction (Text update March 2009) M. Stöhrer (chairman), B. Blok, D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier- Kastler, P. Denys, G. Kramer, J. Pannek, G. del Popolo, P.
Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction (Text update March 2009) M. Stöhrer (chairman), B. Blok, D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier- Kastler, P. Denys, G. Kramer, J. Pannek, G. del Popolo, P.
Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services. 18/07/2008 Cardiff and Vale NHS Trust
 Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services Types of continence problems Bladder Stress incontinence Urgency and urge Incontinence Mixed incontinence Obstructive incontinence
Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services Types of continence problems Bladder Stress incontinence Urgency and urge Incontinence Mixed incontinence Obstructive incontinence
Lifestyle changes. Pelvic floor muscle training
 Incontinence, urinary - Treatment Treating urinary incontinence The treatment you receive for urinary incontinence will depend on the type of incontinence you have and the severity of your symptoms. If
Incontinence, urinary - Treatment Treating urinary incontinence The treatment you receive for urinary incontinence will depend on the type of incontinence you have and the severity of your symptoms. If
Bladder Control Does Matter
 Bladder Control Does Matter Y0028_2726_0 File&Use 04092012 If you suffer from urinary incontinence, you re not alone Don t be afraid to raise your hand if you ve been struggling with the embarrassment
Bladder Control Does Matter Y0028_2726_0 File&Use 04092012 If you suffer from urinary incontinence, you re not alone Don t be afraid to raise your hand if you ve been struggling with the embarrassment
Fecal incontinence (Encopresis) It is the fecal incontinence condition observed in children with chronic constipation over 1-2 years.
 WHAT IS DYSFUNCTIONAL URINATION (URINATION FUNCTION DISORDER)? It stands for the urination phase disorders, which appear due to wrongly acquired urination habits during the toilet training of some neurologically
WHAT IS DYSFUNCTIONAL URINATION (URINATION FUNCTION DISORDER)? It stands for the urination phase disorders, which appear due to wrongly acquired urination habits during the toilet training of some neurologically
CONSENT FORM 12/19/08
 12/19/08 1001 University Place Evanston, Illinois 60201 www.northshore.org CONSENT FORM Phone (224) 364-7100 Fax (847) 570-8011 Intravesical Alkalized Lidocaine for the Treatment of Overactive Bladder
12/19/08 1001 University Place Evanston, Illinois 60201 www.northshore.org CONSENT FORM Phone (224) 364-7100 Fax (847) 570-8011 Intravesical Alkalized Lidocaine for the Treatment of Overactive Bladder
The overactive bladder and bladder retraining
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust The overactive bladder and bladder retraining Information for patients Normal bladder function Your bladder normally stores urine produced by your kidneys. The kidneys
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust The overactive bladder and bladder retraining Information for patients Normal bladder function Your bladder normally stores urine produced by your kidneys. The kidneys
Low Back Pain and Urinary Incontinence. Mary Ka Mei LEUNG Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital Hong Kong SAR, China
 Low Back Pain and Urinary Incontinence Mary Ka Mei LEUNG Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital Hong Kong SAR, China Hong Kong Background Prevalence of LBP in HK 39%: LBP at some time 21%: LBP in the past
Low Back Pain and Urinary Incontinence Mary Ka Mei LEUNG Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital Hong Kong SAR, China Hong Kong Background Prevalence of LBP in HK 39%: LBP at some time 21%: LBP in the past
Michelle H. Cameron, M.D., P.T., M.C.R. Portland VA MS Center of Excellence- West, and Oregon Health & Science University
 Michelle H. Cameron, M.D., P.T., M.C.R. Portland VA MS Center of Excellence- West, and Oregon Health & Science University Ileana Howard, M.D. VA Puget Sound, Seattle, WA and University of Washington PVA
Michelle H. Cameron, M.D., P.T., M.C.R. Portland VA MS Center of Excellence- West, and Oregon Health & Science University Ileana Howard, M.D. VA Puget Sound, Seattle, WA and University of Washington PVA
Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
 Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
Comparison of Fesoterodine, Tolterodine, Oxybutynin and Solifenacin in patients with overactive bladder A systematic review
 Comparison of Fesoterodine, Tolterodine, Oxybutynin and Solifenacin in patients with overactive bladder A systematic review Hamed Kakarª, Bastiaantje M. Kok b, Sahar Mokhles c, Malalay Sarwar d * Supervisors:
Comparison of Fesoterodine, Tolterodine, Oxybutynin and Solifenacin in patients with overactive bladder A systematic review Hamed Kakarª, Bastiaantje M. Kok b, Sahar Mokhles c, Malalay Sarwar d * Supervisors:
Dr Eva Fong. Urologist Auckland
 Dr Eva Fong Urologist Auckland Urinary incontinence: Treatment options GPCME 2013 Eva Fong Urologist Urinary incontinence Is not normal part of aging or childbearing We can make it better Urinary incontinence:
Dr Eva Fong Urologist Auckland Urinary incontinence: Treatment options GPCME 2013 Eva Fong Urologist Urinary incontinence Is not normal part of aging or childbearing We can make it better Urinary incontinence:
