Chapter 2 Lower Abdominal Pain/Suprapubic Pain
|
|
|
- Alban Harper
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2 Lower Abdominal Pain/Suprapubic Pain Paolo Gontero and Bruno Frea Abstract The term lower abdomen refers to the portion of abdomen below the umbilicus in which three topographic regions can be identi fi ed: the hypogastrium in the middle and the left and right iliac fossa, both located lateral to the hypogastrium, in the left and right inferior part of the surface of the human abdomen, respectively. The majority of men and women will complain, at least once in their life, of a pain localized in the lower abdomen. For this reason, the number of GP s s because of a lower abdominal pain is expected to be high. A number of different diseases can cause a pain, of variable mode of presentation, intensity, and duration, in the left iliac fossa, the right iliac fossa, and the hypogastrium (this latter also termed suprapubic pain), respectively. These may arise from different organs (bowel, lower urinary tract, and female reproductive system) and thus potentially involve different specialists (general surgeon, urologist, and gynecologist). Importantly, the physician needs to suspect those few cases that need an urgent, i.e., extrauterine pregnancy in fertile females and cecal or sigmoid perforation, more common in elderly patients. The aim of this chapter is to provide general criteria (essentially based on patient s history and examination) that may lead a GP to suspect a urological origin of lower abdominal pain (and the need for a urological ). The main features for the differential diagnosis with diseases belonging to other apparatus will also be provided in order to identify the most appropriate specialist. Keywords Hypogastric pain Suprapubic pain Iliac fossa pain Urine retention Prostatitis Appendicitis Sigmoid diverticulosis Adnexitis P. Gontero, M.D. (*) B. Frea, Ph.D. Dipartimento di Scienze Chirurgiche, Università degli Studi di Torino, C.so Dogliotti, 14, Torino 10121, Italy [email protected] P. Gontero et al. (eds.), Problem Based Urology, DOI / _2, Springer-Verlag London
2 14 P. Gontero and B. Frea Introduction The term lower abdomen refers to the portion of abdomen below the umbilicus. Three topographic regions can be identi fi ed: the hypogastrium in the middle and the left and right iliac fossa, both located lateral to the hypogastrium, in the left and right inferior part of the surface of the human abdomen, respectively. The majority of men and women will complain, at least once in their life, of a pain localized in the lower abdomen. For this reason, the number of GP s s for a lower abdominal pain is expected to be high. A number of different diseases can result in a pain, of variable mode of presentation, intensity, and duration, in the left iliac fossa, the right iliac fossa, and the hypogastrium (this latter also termed suprapubic pain ), respectively. These may arise from different organs (bowel, lower urinary tract, and female reproductive system) and thus potentially involve different specialists (general surgeon, urologist, and gynecologist). The aim of this chapter is to provide general criteria (essentially based on patient s history and examination) that may lead to suspicion of a urological origin for lower abdominal pain (and the need for a urological ). The main features for the differential diagnosis with diseases belonging to other apparatus will also be provided in order to lead GPs to make the most appropriate specialist. Hints to Make a Differential Diagnosis of Lower Abdominal Pain An accurate patient history should focus on the duration and intensity of pain and whether it is a primary presentation or recurrent pain. A thorough examination is crucial to help in localizing the affected organ. It should start with abdominal palpation (looking for palpable masses or signs of peritonism) followed by digital exploration of the inguinal canal in the male and the crural canal in the female. Digital compression of the vertebral spinous processes, the paravertebral muscles, and the pubic tendon of tight adductor muscles may help to identify pain trigger points suggestive of radiculitis. In males, digital rectal examination of the prostate helps to identify a pain of prostatic origin. In females, vaginal examination should preferably be carried out both manually and with the speculum. Digital examination of the vaginal fornices, the cervix, and the trigone (this latter palpable through the anterior vaginal wall) may help to locate the origin of the pain. Tables 2.1 and 2.2 report the main clinical situations that may present with iliac fossa and hypogastric pain, respectively.
3 2 Lower Abdominal Pain/Suprapubic Pain 15 Table 2.1 Most common urological and non-urological diseases that may cause pain in the right or left iliac fossa Disease Patient s history and/or symptoms Examination findings Ureteric calculia History of urinary calculi, recent episode of renal colic, dysuria Acute appendicitis (right iliac fossa) Nausea, low-grade fever, history of pain beginning in the periumbilical region and migrating to the right lower quadrant Severe pain triggered by compression of a localized point of the iliac fossa, b microscopic hematuria Right lower quadrant tender during palpation; rebound tenderness, Rovsing s sign (pain in right lower quadrant with palpation of left lower quadrant) Inguinal hernia Male, pain exacerbated with standing position, strain, or heavy lifting Herniation of bowel detectable by digital exploration of the inguinal canal Sigmoid diverticulosis (left iliac fossa) Elderly, irregular bowel habits, recurrent colicky Localized tenderness in either the left or right iliac Cecal perforation (right iliac fossa) pain fossa, palpable mass, abdominal guarding, fever Extrauterine pregnancy Absence of period or known pregnancy Peritonism, signs of shock, positive pregnancy test Vertebral ovarian pain (ovulation, bleeding, torsion, or rupture of ovarian cyst) Ovulation, known ovarian cystic disease Painful palpation of vaginal fornices Pain referable to a vertebral radiculitis Pain occurred after an abrupt movement, known vertebral disease Pain exacerbated by digital compression of the spinous vertebral processes a Occasionally, a calculus that has migrated to the distal portion of the ureter can lead to a severe pain exclusively radiated to the corresponding iliac fossa (in the absence of an accompanying loin/ fl ank pain) b A worsening of the pain following digital compression in the area of the iliac fossa where the ureter crosses the iliac vessels (usually corresponding to the midpoint of a line between the umbilicus and the anterior superior iliac spine) may suggest a ureteral stone
4 16 P. Gontero and B. Frea Table 2.2 Most common urological and non-urological diseases that may present with a suprapubic pain Disease Patient s history and/or symptoms Examination findings Acute or chronic urine retention a Acute or chronic prostatitis Long-standing lower urinary tract symptoms, severe pain, oliguria, or anuria Dysuria, urinary frequency, fever in the acute phase. Urinary symptoms can be mild or absent in the chronic phase Palpable suprapubic mass Painful, swollen, and hot prostate in the acute phase. Digital rectal examination can be unremarkable in chronic prostatitis Acute cystitis Dysuria, urinary frequency Examination of the anterior vaginal wall can be painful, leukocytes and/or nitrates on urine dipstick Pelvic inflammatory Young women, unprotected sexual Cervical pain on palpation disease intercourse Endometriosis Young women, pain exacerbated during Cervical pain on palpation period Osteitis pubis History of inguinal hernia repair or pelvic surgery, athletes, pregnancy Pressure on the pubic tubercle exacerbates the pain Irritable bowel disease Long-term history of intermittent, migrating abdominal pain, anxious temperament, irregular bowel habits Abdomen thoroughly tender upon examination a Acute urine retention may occasionally occur in totally asymptomatic patients as a result of a sudden blockage of the urine output due to blood clots or acute prostatitis, although in the majority of cases it represents a complication of an obstructive prostate in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms. Acute urinary retention usually presents in patients with normal or reduced bladder compliance; hence, the patient usually experiences severe hypogastric pain for urine volumes minimally exceeding the normal bladder capacity of ml. On the contrary, chronic urinary retention occurs in bladders that have lost their compliance because of a long-standing history of voiding symptoms with high urine residual volumes. The patient usually presents with an enlarged bladder with high urine volume (even 2,000 ml) in spite of only low or moderate discomfort. Over fl ow incontinence is a frequently associated symptom that describes severe urinary urgency and frequency followed by the emission of only a small amount of urine without resolution of the chronic retention Algorithm for Managing Hypogastric and Iliac Fossa Pain in the GP s Of fi ce These fl owcharts aim to provide the GP with simple suggestions to guide the sometimes dif fi cult decision-making in choosing the most appropriate specialist for referring a patient with hypogastric pain, also referred as suprapubic pain (Flowchart 2.1 ), and iliac fossa pain (Flowchart 2.2 ).
5 2 Lower Abdominal Pain/Suprapubic Pain 17 Hypogastric pain/ suprapubic pain Male (1) No urinary symptom (2) Presence of dysuria and voiding dysfunction (3) Dysuria and voiding dysfunction (5) Bowel disease Vascular disease Prostatitis Cystitis Urine retention Cystitis Extrinsic bladde compression (urine retention) General surgeon Urine culture Suprapubic USS Catheterization Urine culture Pelvic ultrasound Catheterization Consider urological Consider urological Flowchart 2.1 Hypogastric pain/suprapubic pain Female (4) No urinary symptoms (6) Pain at the cervix or vaginal fornices (7) Vaginal examination unremarkable + tender abdomen (8) Consider gynecological Consider general surgeon/ gastroenterological
6 18 P. Gontero and B. Frea Iliac fossa pain Right side (9) Left side (13) Young women (10) Young/adult men (11) Elderly of both sexes (12) Young/adult of both sexes Elderly of both sexes Rule out extrauterine pregnancy Adnexitis Appendicitis Ureteric colic Appendicitis Ureteric colic Constipation Cecal perforation Appendicitis (ureteric colic) Ureteric colic Extrauterine Sigmoid diverticulosis Constipation Flowchart 2.2 Iliac fossa pain Comments About Flowchart Diseases causing hypogastric pain/suprapubic pain in a male patient differ in type and frequency of presentation from those affecting a female patient. 2. Absence of associated urinary symptoms should prompt the GP to consider a bowel disease as the most likely explanation of the symptom. In young patients, a history of recurrent and migrating abdominal discomfort, bloating, and modi fi cation of bowel habits with alternation of diarrhea and constipation can suggest an irritable bowel syndrome. In patients with vascular risk factors and/or comorbidity, acute hypogastric pain may be the result of dissection of an arterial iliac aneurysm or bowel infarction. If any of these latter conditions are suspected, an to an emergency department is mandatory. 3. When hypogastric pain is associated with urinary symptoms, urinary retention must always be ruled out, particularly in elderly patients whose frail mental condition sometimes makes it dif fi cult to interpret their symptoms. The fi nding of a suprapubic mass during examination of the hypogastrium warrants catheterization to rule out urine retention even if urinary symptoms are mild. When available, suprapubic ultrasound is a simple and noninvasive method to rule out the presence of urine retention. A distended bladder due to chronic urine retention may contain up to 2 3l of urine. In this case, it is mandatory to monitor the patient s urine output for at least 24 hours following catheterization because of the risk of severe polyuria. Cystitis or bladder stones are usually accompanied by burning while urinating and urinary frequency. However, the most common cause of suprapubic/hypogastric pain in young and adult males is prostatitis. Urinary symptoms (dysuria and/or frequency and/or urgency), while common, can also be absent. 4. The spectrum of diseases causing hypogastric pain in females differs substantially from that of males.
7 2 Lower Abdominal Pain/Suprapubic Pain The presence of urinary symptoms such as dysuria, frequency, and urgency is highly suggestive of cystitis. In the case of bacterial cystitis, the urine dipstick is usually positive for leukocytes and/or nitrates, whilst urine culture shows signi fi cant growth of a bacterial strain. Antibiotics are usually effective in relieving symptoms and clearing urine. Failure to respond to antibiotic course and/or negative urine culture may indicate so-called abacterial cystitis or urethral syndrome. It is important in such cases to rule out the possibility of an extrinsic bladder compression from a pelvic mass or a bladder tumor. Urine retention is far less frequent in females and should prompt the suspicion of a pelvic prolapse or a neoplastic mass (e.g., carcinoma of the cervix). 6. When hypogastric pain is not accompanied by urinary symptoms, the patient s history and examination should aim to look for hints that may help in the differential diagnosis between gynecological and gastroenterological disorders. 7. A careful vaginal exploration may help to suspect a pelvic in fl ammatory disease in case of tenderness localized at the level of vaginal fornices. An in fl ammatory process localized to the womb (endometriosis, cervicitis, etc.) has to be suspected when the uterine cervix is painful upon palpation. 8. A lower abdominal pain that is worsened by palpation along with a negative pelvic examination suggests in fl ammatory bowel diseases. Referral to a general surgeon or gastroenterologist may be appropriate. Comments About Flowchart In the differential diagnosis of a right-sided iliac fossa pain, it is important to consider the patient s age and sex. 10. In a fertile female, pregnancy should always be ruled out, particularly in the presence of delayed period, by carrying out a pregnancy test (easily feasible in the of fi ce using pregnancy test strips). It should always be kept in mind that a pain in either the two iliac fossae can be the presenting symptom of an extrauterine pregnancy. After pregnancy has been excluded, the following clinical conditions should be considered as the most likely: appendicitis (signs of peritonism helps in the diagnosis), adnexitis (an in fl ammatory disease affecting the fallopian tubes and ovaries: vaginal exploration is usually painful), and ureteric colic. 11. In young or adult men, ureteric colic and appendicitis are the most likely clinical conditions to included the differential diagnosis. 12. In elderly patients, while appendicitis is always possible, a cecal perforation secondary to a tumor needs to be taken into consideration. A differential diagnosis among these two diseases may be extremely dif fi cult due to overlapping signs. Often, mild symptoms with a palpable mass may simply be due to constipation. Ureteral stones are always possible but less probable than in younger men. 13. When assessing a left-sided iliac fossa pain, it is important to exclude the possibility of sigmoid diverticulitis, not an uncommon situation in elderly patients of both sexes. Sigmoid diverticula are highly prevalent in the elderly and can occasionally undergo in fl ammation or even perforation resulting in left lower quadrant pain, fever, and the feeling of a palpable mass. Younger adult diseases causing left iliac fossa pain include adnexitis and ectopic pregnancy in females and ureteric colic in both sexes.
8 20 P. Gontero and B. Frea Bibliography Ackermann D. Lower abdominal quadrants pain. In: Urologische differntialdiagnose. Stuttgart: Georg Thieme Verlag; Singh I, Collins RE. Right iliac fossa pain. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2005;66(11):M76 8. Hochreiter WW, Z Brun S. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome and voiding dysfunction. Curr Urol Rep. 2004;5(4):300 4.
9
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Problems in Early Pregnancy
 Problems in Early Pregnancy Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered This information answers queries about issues that may arise in early pregnancy. Not all of these issues will apply to you. It provides
Problems in Early Pregnancy Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered This information answers queries about issues that may arise in early pregnancy. Not all of these issues will apply to you. It provides
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
The Acute Abdomen. Dr. Ed Snyder Dr. Melanie Walker Huntington Memorial Hospital
 The Acute Abdomen Dr. Ed Snyder Dr. Melanie Walker Huntington Memorial Hospital Causes of the Acute Abdomen Hemorrhage in the GI tract Blood vessel GU tract Perforation of the GI tract Ulcer Infection
The Acute Abdomen Dr. Ed Snyder Dr. Melanie Walker Huntington Memorial Hospital Causes of the Acute Abdomen Hemorrhage in the GI tract Blood vessel GU tract Perforation of the GI tract Ulcer Infection
Acute abdominal conditions Key Points
 7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Hysterectomy. What is a hysterectomy? Why is hysterectomy done? Are there alternatives to hysterectomy?
 ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page
 A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Acute Abdominal Pain: Other causes
 Acute Abdominal Pain: Other causes Vishal Gupta, MCh Associate Professor Deptt Surg. Gastroenterology KGMU Definition Acute abdominal pain: Presentation of previously undiagnosed abdominal pain Lasting
Acute Abdominal Pain: Other causes Vishal Gupta, MCh Associate Professor Deptt Surg. Gastroenterology KGMU Definition Acute abdominal pain: Presentation of previously undiagnosed abdominal pain Lasting
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
190.12 - Urine Culture, Bacterial Summary Information Highlighted items indicate most frequently used codes.
 Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE
 LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
Differential diagnosis of abdominal pain. Lakatos Péter László
 Differential diagnosis of abdominal pain Lakatos Péter László Precise anamnesis Physical examination are prognosticated to the cause of the pain Anamnesis Sudden pain Perforation Mesenteric infarction
Differential diagnosis of abdominal pain Lakatos Péter László Precise anamnesis Physical examination are prognosticated to the cause of the pain Anamnesis Sudden pain Perforation Mesenteric infarction
Summa Health System. A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy
 Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Have a shower, rather than a bath to avoid exposing your genitals to the chemicals in your cleaning products for too long. Always empty your bladder
 Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer
 Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
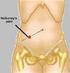 Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
Guide to Claims against General Practitioners (GPs)
 Patients often build up a relationship of trust with their GP over a number of years. It can be devastating when a GP fails in his or her duty to a patient. Our medical negligence solicitors understand
Patients often build up a relationship of trust with their GP over a number of years. It can be devastating when a GP fails in his or her duty to a patient. Our medical negligence solicitors understand
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Inguinal Hernia (Female)
 Inguinal Hernia (Female) WHAT IS AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT CAUSES AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT / MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Inguinal Hernia (Female) WHAT IS AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT CAUSES AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT / MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Abdominal Pain. Charles Henley, DO, MPH Department of Family Medicine. OSU College of Osteopathic Medicine (Revised 9/2002)
 Abdominal Pain Charles Henley, DO, MPH Department of Family Medicine OSU College of Osteopathic Medicine (Revised 9/2002) Common Causes of Abdominal Pain Infants - colic, gastroenteritis, constipation,
Abdominal Pain Charles Henley, DO, MPH Department of Family Medicine OSU College of Osteopathic Medicine (Revised 9/2002) Common Causes of Abdominal Pain Infants - colic, gastroenteritis, constipation,
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome
 Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
FEMALE ANATOMY. the Functions of the Female Organs
 FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Urinary tract and perineum
 9 Urinary tract and perineum Key Points 9.1 9.1 THE URINARY BLADDER URINARY RETENTION Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder The common causes of acute retention
9 Urinary tract and perineum Key Points 9.1 9.1 THE URINARY BLADDER URINARY RETENTION Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder The common causes of acute retention
Considering a Hysterectomy?
 Considering a Hysterectomy? Learn more about virtually scarless surgery using da Vinci Single-Site technology { {Symptoms & Conditions: Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis, Pelvic Prolapse
Considering a Hysterectomy? Learn more about virtually scarless surgery using da Vinci Single-Site technology { {Symptoms & Conditions: Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis, Pelvic Prolapse
3 Lower Abdominal Pain in the First Trimester of Pregnancy
 3 Lower Abdominal Pain in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Sisty J. Moshi INTRODUCTION Abdominal pain in pregnancy is very common. Many of the complications of early pregnancy present with some form of
3 Lower Abdominal Pain in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Sisty J. Moshi INTRODUCTION Abdominal pain in pregnancy is very common. Many of the complications of early pregnancy present with some form of
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Patient. Frequently Asked Questions. Transvaginal Surgical Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Patient Frequently Asked Questions Transvaginal Surgical Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse Frequently Asked Questions WHAT IS PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE AND HOW IS IT TREATED? Q: What is pelvic organ prolapse
Patient Frequently Asked Questions Transvaginal Surgical Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse Frequently Asked Questions WHAT IS PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE AND HOW IS IT TREATED? Q: What is pelvic organ prolapse
RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL
 RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL Introduction Ultrasound can be very useful as a first line investigation; it is typically non-invasive and does not involve ionising radiation. However, a significant
RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL Introduction Ultrasound can be very useful as a first line investigation; it is typically non-invasive and does not involve ionising radiation. However, a significant
International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine
 International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 340925, 18 minipages. DOI:10.5171/2013.340925 www.ibimapublishing.com Copyright 2013. Massinde Anthony. Distributed under
International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 340925, 18 minipages. DOI:10.5171/2013.340925 www.ibimapublishing.com Copyright 2013. Massinde Anthony. Distributed under
Endometriosis: An Overview
 Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA
 Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
CHOC CHILDREN SUROLOGY CENTER. Constipation
 Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is a condition in which a person has uncomfortable or infrequent bowel movements. Generally, a person is considered to be constipated when bowel movements
Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is a condition in which a person has uncomfortable or infrequent bowel movements. Generally, a person is considered to be constipated when bowel movements
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients
 Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
URINARY CATHETER CARE
 URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place.
 What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
Urinary Incontinence. Anatomy and Terminology Overview. Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS
 Urinary Incontinence Anatomy and Terminology Overview Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS Purpose Locate and describe the anatomy of the Female Urinary System Define terminology related to Incontinence Describe
Urinary Incontinence Anatomy and Terminology Overview Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS Purpose Locate and describe the anatomy of the Female Urinary System Define terminology related to Incontinence Describe
Night frequency None 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10. Not enough warning before needing to urinate. none mild moderate severe
 {Patient Label} SYMPTOMS SURVEY: FREQUENCY: How many times do you urinate during the day and get up from sleep to urinate at night? Day frequency 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 More Night frequency None
{Patient Label} SYMPTOMS SURVEY: FREQUENCY: How many times do you urinate during the day and get up from sleep to urinate at night? Day frequency 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 More Night frequency None
Get the Facts, Be Informed, Make YOUR Best Decision. Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Pelvic Organ Prolapse ETHICON Women s Health & Urology, a division of ETHICON, INC., a Johnson & Johnson company, is dedicated to providing innovative solutions for common women s health problems and to
Pelvic Organ Prolapse ETHICON Women s Health & Urology, a division of ETHICON, INC., a Johnson & Johnson company, is dedicated to providing innovative solutions for common women s health problems and to
Femoral Hernia Repair
 Femoral Hernia Repair WHAT IS A FEMORAL HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES A FEMORAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/ MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Femoral Hernia Repair WHAT IS A FEMORAL HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES A FEMORAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/ MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
 Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon
 Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model
 Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S.
 Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
2 of 6 10/17/2014 9:51 AM
 1 of 6 10/17/2014 9:51 AM 010101 Free 14-Day Trial Tutorial Help Search by keyword or medical code User Name: Password: Directory Print Email Advanced Search Medical Disability Advisor > Cystocele Or Rectocele
1 of 6 10/17/2014 9:51 AM 010101 Free 14-Day Trial Tutorial Help Search by keyword or medical code User Name: Password: Directory Print Email Advanced Search Medical Disability Advisor > Cystocele Or Rectocele
Leader's Resource. Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms.
 Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Why would you need a hysterectomy?
 Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Are You at Risk for Ovarian Cancer?
 Are You at Risk for Ovarian Cancer? A Woman s Guide Read this brochure to learn more about ovarian cancer symptoms, risk factors and what you can do to reduce your risk. ALL WOMEN HAVE SOME RISK OF OVARIAN
Are You at Risk for Ovarian Cancer? A Woman s Guide Read this brochure to learn more about ovarian cancer symptoms, risk factors and what you can do to reduce your risk. ALL WOMEN HAVE SOME RISK OF OVARIAN
Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
 Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY
 LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 About this information This leaflet is for you if you have a cyst on one or both ovaries and are considering surgery.
LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 About this information This leaflet is for you if you have a cyst on one or both ovaries and are considering surgery.
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 [email protected] Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 [email protected] Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Treating your enlarged prostate gland HoLEP (holmium laser enucleation of the prostate)
 Treating your enlarged prostate gland HoLEP (holmium laser enucleation of the prostate) This leaflet is designed to answer any questions you may have about having holmium laser treatment for your enlarged
Treating your enlarged prostate gland HoLEP (holmium laser enucleation of the prostate) This leaflet is designed to answer any questions you may have about having holmium laser treatment for your enlarged
GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision
 RADIATION THERAPY FOR GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Gynecologic cancers
RADIATION THERAPY FOR GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Gynecologic cancers
Hysterosalpingography
 Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Introduction. Physiology of the Abdomen. Anatomy & Physiology. Abdominal Pain Introduction (2 of 2) Gastrointestional and Urologic Emergencies
 Gastrointestional and Urologic Emergencies Introduction Abdominal pain is a common complaint. Cause of abdominal pain is often difficult to determine. As an EMT: You do not need to determine exact cause.
Gastrointestional and Urologic Emergencies Introduction Abdominal pain is a common complaint. Cause of abdominal pain is often difficult to determine. As an EMT: You do not need to determine exact cause.
Normal bladder function requires a coordinated effort between the brain, spinal cord, and the bladder.
 .. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
.. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use.
 Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias. A simple guide to help answer your questions
 Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias A simple guide to help answer your questions What is a hernia? A hernia is defined as a hole or defect in the abdominal (belly) wall. A hernia can either be congenital (a
Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias A simple guide to help answer your questions What is a hernia? A hernia is defined as a hole or defect in the abdominal (belly) wall. A hernia can either be congenital (a
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Ilioinguinal dissection (removal of lymph nodes in the groin and pelvis)
 Ilioinguinal dissection (removal of lymph nodes in the groin and pelvis) This sheet answers common questions about ilio-inguinal dissection. If you would like further information, or have any particular
Ilioinguinal dissection (removal of lymph nodes in the groin and pelvis) This sheet answers common questions about ilio-inguinal dissection. If you would like further information, or have any particular
Laparoscopic surgery for endometriosis
 Introduction This leaflet covers laparoscopic surgery for endometriosis. It provides information for women who have been offered or are considering laparoscopic surgery for the treatment of endometriosis.
Introduction This leaflet covers laparoscopic surgery for endometriosis. It provides information for women who have been offered or are considering laparoscopic surgery for the treatment of endometriosis.
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
What are the differences between fibroid and ovarian cyst?
 DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
Hernia- Open Inguinal Hernia Repair PROCEDURAL CONSENT FORM. A. Interpreter / cultural needs. B. Condition and treatment
 DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v5.00-04/2011 SW9317 Hernia- Open Inguinal Hernia Repair Facility: A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified
DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v5.00-04/2011 SW9317 Hernia- Open Inguinal Hernia Repair Facility: A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified
The main surgical options for treating early stage cervical cancer are:
 INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
Preparing for your laparoscopic pyeloplasty
 Preparing for your laparoscopic pyeloplasty Welcome We look forward to welcoming you to The Royal London Hospital. You have been referred to us for a laparoscopic pyeloplasty, which is an operation using
Preparing for your laparoscopic pyeloplasty Welcome We look forward to welcoming you to The Royal London Hospital. You have been referred to us for a laparoscopic pyeloplasty, which is an operation using
symptoms of Incontinence
 Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation
 J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy
 What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
Considering a Hysterectomy?
 Considering a Hysterectomy? Learn more about virtually scarless surgery using da Vinci Single-Site technology { {Symptoms & Conditions: Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis, Adenomyosis,
Considering a Hysterectomy? Learn more about virtually scarless surgery using da Vinci Single-Site technology { {Symptoms & Conditions: Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis, Adenomyosis,
Guide to Abdominal or Gastroenterological Surgery Claims
 What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
FEMALE INCONTINENCE REVIEW
 200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Feline Cystitis (Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease)
 Feline Cystitis (Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease) The term "cystitis" literally means inflammation of the urinary bladder. Although this term is rather general, there is a common form of cystitis that
Feline Cystitis (Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease) The term "cystitis" literally means inflammation of the urinary bladder. Although this term is rather general, there is a common form of cystitis that
Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC. OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract
 Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Urinary Tract Infections in Children
 Urinary Tract Infections in Children National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Urinary
Urinary Tract Infections in Children National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Urinary
Vaginal Repair- with Mesh A. Interpreter / cultural needs B. Condition and treatment C. Risks of a vaginal repair- with mesh
 The State of Queensland (Queensland Health), 2011 Permission to reproduce should be sought from [email protected] DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v2.00-03/2011 SW9226 Facility: A. Interpreter
The State of Queensland (Queensland Health), 2011 Permission to reproduce should be sought from [email protected] DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v2.00-03/2011 SW9226 Facility: A. Interpreter
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2. Patient Information. Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate
 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary
 X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
Saint Mary s Hospital. Hysterectomy. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Hysterectomy Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What is a hysterectomy? 4 Why is a hysterectomy necessary? 4 How common is it? 7 Things to consider before having a hysterectomy
Saint Mary s Hospital Hysterectomy Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What is a hysterectomy? 4 Why is a hysterectomy necessary? 4 How common is it? 7 Things to consider before having a hysterectomy

 More details >>> HERE
More details >>> HERE