Adult Sinusitis Guideline
|
|
|
- Elvin Robertson
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Adult Sinusitis These clinical guidelines are designed to assist clinicians by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation and treatment of patients. They are not intended to replace a clinician s judgment or to establish a protocol for all patients with a particular condition. A guideline will rarely establish the only approach to a problem. GUIDELINE HISTORY and APPROVAL ACTION, Revised and Approved, Revised and Approved Approved, Revised and Approved SEED GUIDELINE and/or MAIN INFORMATION & GROUP SOURCE(S) Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement (ICSI) Sinusitis. December 2002 Version. 1. January 2003 GHP Adult Sinusitis DATE July 2, 2003 March 01-18, 2005 ORGANIZATION Geisinger Health Plan/ Conference Sinusitis Team Sinusitis Team 2. ICSI Adult Sinusitis (May 2004 version) Same as above March 19-22, 2005 Committee Same as above April 27, 2005 Geisinger Health Plan/Quality Improvement Committee Same as above Nov. 1, 2006; Jan 15, 2007 Committee Same as above Apr. 25, 2007 Geisinger Health Plan/Quality Improvement Committee AAOHN Clinical Practice ICSI Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness in Children and Adults. (January 2008 version) Aug. 18, Committee Same as above Apr. 22, 2009 Geisinger Health Plan/Quality Improvement Committee AAOHN Clinical Practice ICSI Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness in Children and Adults. (January 2011 version) Sept Committee Same as above April 27, 2011 Geisinger Health Plan/Quality Improvement Committee AAOHN Clinical Practice ICSI Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness in Children and Adults. (January 2013version) June 2013 Committee Clinical s Page 1
2 Adult Sinusitis Clinical Same as above July 31, 2013 Geisinger Health Plan/Quality Improvement Committee Vice President, Chief Medical Officer OVERVIEW The economic burden of sinusitis in the United States is dramatic. Medical and surgical encounters in which sinusitis was the primary diagnosis were estimated at 5.8 billion for adults in Nearly 90% of all expenditures were associated with ambulatory or emergency department services. More than 1 in 5 antibiotics prescribed in adults are for sinusitis. The indirect cost of sinusitis includes 73 million days of restricted activity per year. Acute bacterial sinusitis usually occurs following an upper respiratory infection that results in obstruction of the osteomeatal complex, impaired mucociliary clearance and overproduction of secretions. The diagnosis is based on the patient s history of a biphasic illness ( double sickening ), purulent rhinorrhea, maxillary toothache, pain on leaning forward, pain with a unilateral prominence and a poor response to decongestant therapy. Radiographs and computed tomographic scans of the sinuses generally are not useful in making the initial diagnosis. Since sinusitis is self-limited in 40 to 50 percent of patients, the expensive, newergeneration antibiotics should not be used as first-line therapy. First-line antibiotics such as amoxicillin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are as effective in the treatment of sinusitis as the more expensive antibiotics. Little evidence supports the use of adjunctive treatments such as nasal corticosteroids and systemic decongestants. Patients with recurrent or chronic sinusitis require referral to an otolaryngology s for consideration of functional Endoscopic sinus surgery. Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology. 103(3 Pt 1):408-14, 1999 Mar. American Family Physician. 58(8): , 805-6, 1998 Nov 15. Clinical Practice : Adult sinusitis. Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery 2007;137:S1-S31. SEED GUIDELINE American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. Clinical Practice : Adult Sinusitis (2007). Clinical s Page 2
3 Adult Sinusitis Clinical Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement (ICSI) Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness in Children and Adults. (Jan.2013 version). GOALS 1. To differentiate between viral upper respiratory infection and acute sinusitis in adults. 2. To appropriately identify patients for phone management. 3. To increase provider understanding of appropriate antibiotic usage for acute sinusitis by ensuring that first line medications are prescribed for patients when indicated. 4. To educate providers about appropriate use of sinus x-rays. 5. To educate providers about appropriate ENT referral. 6. Patient/Provider/Employer Education: a. To provide educational tools and triage guidelines for health care providers, patients and employers. b. To increase patient knowledge of effective home treatment for viral upper respiratory tract infection. c. To change patient expectations regarding treatment with antibiotics for viral upper respiratory infection. FAST FACTS Acute sinusitis is indicated when: URI symptoms have been present for greater than 7 days, AND 2 or more of the following symptoms are present at a point 7 days or more after the onset of the illness during which time an adequate trial of decongestant/analgesic was used: Colored nasal drainage Poor response to decongestant Facial or sinus pain, particularly if aggravated by postural change or valsalva maneuver Headache Initial treatment for acute sinusitis is either Amoxicillin 500 mg tid for days or Trimethoprim/sulfa DS for days 2nd Line treatment is another days of the same antibiotic, or: Amoxicillin-potassium clavulanate (Augmentin) Fluoroquinolone Clinical s Page 3
4 Adult Sinusitis Clinical Transillumination and plain sinus radiographs add little to the diagnostic process in the primary care setting. BIBLIOGRAPHY 1. Ah-See K (2003). Acute sinusitis. Clinical Evidence (10): American Academy of Otolaryngology--Head and Neck Surgery Snow V, Motter-Pilson C, Hickner JM, et al. Principles of appropriate antibiotic use for acute sinusitis in adults. Ann Intern Med 2001;134(6): (Part 1). 4. Hickner JM, Bartlett JG, Besser RE, Gonzales R, Hoffman JR, Sande MA. Principles of appropriate antibiotic use for acute rhinosinusitis in adults: Background. Ann Intern Med 2001;134(6): (Part 2). 5. Hadley JA, Schaefer SD. Clinical evaluation of rhinosinusitis: History and physical examination. Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. 1997;117(3):S Adelglass, J. DeAbate, CA. McElvaine, P. Fouler, CL. LoCocco, J. Campbell, T. Comparison of the effectiveness of levoflaxacin and amoxicillin-clavulanate for the treatment of acute sinusitis in adults. Otolarygology-Head and Neck Surgery. 1999; 120(3): Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis. Summary, Evidence Report/Technology Assessment: Number 9, March Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, Rockville, MD. 8. The Sanford Guide to Antimicrobial Therapy, 36 th ed, Klossek JM, Federspil P. Update on treatment guidelines for acute bacterial sinusitis. Int J Clin Pract 2005;59(2): Lemiengre MB, van Driel ML, Merenstein D, et al. Antibiotics for clinically diagnosed acute rhinosinusitis in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012; 10:CD Kassel JC, King D, Spurling GK. Saline nasal irrigation for acute upper respiratory tract infections. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010; :CD Spector SL, Bernstein IL, Li JT, et al. Parameters for the diagnosis and management of sinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1998; 102:S Young J, De Sutter A, Merenstein D, et al. Antibiotics for adults with clinically diagnosed acute rhinosinusitis: a meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet 2008; 371: Hwang PH, Getz A. Acute sinusitis and rhinosinusitis in adults: Treatment. UptoDate Jan Clinical s Page 4
5 Adult Sinusitis Clinical Colored Nasal Discharge Facial Pain Headache Poor Response to Decongestants Tobacco Use Temp. > 102 with past Hx sinusitis Upper Tooth Pain Orbital Pain Visual Disturbance Facial Edema or Erythema 2 ENT Hx & PE Sinus X-rays usually not necessary unless frontal or complicated sinusitis suspected 3 Adult Sinusitis URI Symptoms > 7 Days; Suspect Sinusitis Two or More of These Sx YES NO Timely Provider Visit NO Consider (VURI) Viral Upper Respiratory Infection Antibiotics: Amoxicillin 500 mg TID days TMP/SMX DS BID days Doxycycline 100 mg BID days (if allergic to PCN and Sulfa) Decongestants: Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride plus guaifenesin Decongestant nasal spray for no longer than 3 days Other: Saline nasal drops/spray Nasal steroid spray unproven Analgesia Patient Education Sinusitis? YES Treatment YES Complete Response NO NO 7 Consider Alternatives /END Further Treatment Partial Response: Another days same antibiotic then reassess patient No Response Reassess Patient: Consider 2 nd antibiotic for days then reassess patient If no response again, reassess patient, consider sinus X-rays and ENT referral 7 YES END Clinical s Page 5
6 Adult Sinusitis Clinical ANNOTATIONS 1. Phone Triage Indicates Acute Sinusitis Phone Triage Criteria Acute sinusitis is indicated if: Upper respiratory symptoms have been present for at least 7 days, and two or more of the following symptoms are present at a point 7 days or more after the onset of the illness: Colored nasal drainage Poor response to decongestant Facial pain or sinus pain, particularly if aggravated by postural change or Valsalva maneuver Headache Tooth pain with any of the above findings is a more specific indication of sinusitis. Patients with tooth pain could be considered for treatment before 7 days. Fever > 102 degrees and a documented past history of sinusitis in addition to the above symptoms is supportive of a sinusitis diagnosis. Individuals with severe symptoms should be considered for treatment before 7 days. Patients with known anatomical blockage (e.g., chronic nasal polyps, severely deviated septum, (recurrent sinusitis) may need immediate treatment. An individual reporting symptoms meeting the phone triage criteria for acute sinusitis has a reasonably high likelihood of having the disease. Such a patient s symptoms and chart should be presented to the physician or physician extender for further action. Triage for alternative diagnosis Patients not meeting the triage criteria for sinusitis would be triaged for an alternative diagnosis. 2. Needs Visit? Patients who are in generally good health and only mildly ill may be appropriate candidates for phone management of presumed acute sinusitis. Both the patient and the provider should be comfortable with phone management. The following factors are also supportive of phone management: Earlier visit with viral upper respiratory infection that has progressed to probable acute sinusitis Clinical s Page 6
7 Adult Sinusitis Clinical A pattern over time of telephone requests for antibiotics by the same patient should be replaced by a provider visit. Patients on antibiotics for 2 or more days whose sinus symptoms are worsening should be scheduled for a provider visit. 3. Visit Patients with any of the following complicating factors should be seen urgently: Orbital pain Visual disturbances Periorbital swelling or erythema Facial swelling or erythema Patients who meet criteria for phone management should receive the same treatment and instructions outlined in Annotation #5 for visiting patients. Review history Confirm history as in phone triage Regional exam of the head and neck The following physical findings may be found: Presence of purulent nasal drainage Sinus tenderness Decreased transillumination (optional) Review complicating factors Local External facial swelling/erythema over involved sinus Mucoeles Osteomyelitis Orbital Visual changes Extraocular motion abnormal Proptosis Periorbital inflammation/soft tissue edema subperiosteal abscess orbital cellulitis orbital abscess lntracranial, CNS complications Cavernous sinus thrombosis Meningitis Subdural empyema Brain abscess Plain sinus x-rays are usually not necessary in making the diagnosis of acute sinusitis. Maxillary antrum aspiration for culture is indicated only when precise microbial identification is required. 4. Acute Sinusitis? The diagnosis of acute sinusitis is based primarily on the patient s history and is supported by the physical exam. Assess Turbinates. Clinical s Page 7
8 Adult Sinusitis Clinical Follow-up for alternative diagnosis Follow-up for an alternative diagnosis should take place if the patient s symptoms, history, and physical exam are not indicative of acute sinusitis. 5. Treatment Note: Pharmaceutical coverage is dependent upon individual pharmacy benefit design and certain drugs may require prior authorization. Providers are encouraged to review the GHP formulary at or contact the GHP Pharmacy Department at Antibiotics Amoxicillin 500 mg TID days or 1000 mg BID x 10 days - or Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX) One double-strength tab BID days For patients allergic to both amoxicillin and TMP/SMX Doxycycline 100 mg BID days can be prescribed. A cephalosporin could be considered but there is approximately a 10% cross-reaction between cephalosporins and amoxicillin. (Refer to Annotation #7) It is important to instruct the patient to complete the course of antibiotics. Decongestants (topically or orally) Pseudoephedrine HCL plus guaifenesin (IE. Duratuss) (e.g., Sudafed) 60 mg q 4-6 hours, not to exceed 4 doses per 24 hours. Oxymetazoline (e.g. Afrin) not to be used more that 3 days. Nonpharmacologic measures for symptomatic relief -Saline nasal drops/spray Commercial (e.g. Ocean, Salinex, Nasal) Homemade (1/4 teaspoon salt and 1/4 teaspoon of baking soda dissolved in 1 cup of water; use bulb syringe or dropper purchased from drug store) Nasal steroid spray Inhaled nasal steroid spray is a rational but unproved adjunctive therapy for acute sinusitis. Provide patient education Although medication will relieve symptoms, the patient should be instructed to implement the following comfort and prevention measures: Comfort measures Maintain adequate hydration Analgesics (Acetaminophen, ibuprofen, ASA as needed) Sleep with head of bed elevated Steamy shower Apply warm facial packs Saline irrigation Maintain adequate hydration Adequate rest Avoid cigarette smoke or extremely cool or dry air Cool mist vaporizer or humidifier Avoid dehydrating agents, caffeine and alcohol. Prevention measures Appropriate treatment of allergies and viral upper respiratory infections can prevent the development of sinusitis. Clinical s Page 8
9 Adult Sinusitis Clinical Environmental factors that affect the sinuses include cigarette smoke, pollution, swimming in contaminated water, use of coal or wood stove or kerosene heaters and barotrauma. Call back instructions The patient should be instructed to call back if symptoms worsen, or if symptoms have not resolved within 48 to 72 hours. 6. Complete response? Complete response Patient is symptomatically normal Partial response Patient is symptomatically improved but not back to normal at the end of the first course of antibiotics. Failure or no response Patient has little or no symptomatic improvement after finishing a day course of first line antibiotic therapy (amoxicillin or TMP/SMX). 7. Further treatment Partial response or no symptomatic improvement: a. Amoxicillin/Clavulanate (Augmentin) 875 mg BID x 14 days b. Cephalosporin 3rd generation ie. Cefuroxime, **Cefpodoxime, Cefprozil, or Cefdinir. For patients allergic to both amoxicillin and TMP/SMX or macrolides can be prescribed. a. Clarithromycin (Biaxin ) 500mg BIDx 14 days b. Azithromycin (Zithromax ) 500 mg every day x 3 days OR quinolones a. Levofloxacin (Levaquin ) 500 mg every day x 14 days b. Moxifloxacin (Avelox ) 400 mg every day x 14 days Failure or No response in 3-4 weeks: Reassess patient for ENT referral. MEASURES Denominator members 18 years and older. No visits in the last three months for acute sinusitis. Primary diagnoses of sinusitis Use Primary ICD9 codes 461 through to identify sinusitis as the primary diagnosis. No claims for the last three months with one of these diagnoses. Clinical s Page 9
10 Adult Sinusitis Clinical Exclude members having chronic sinusitis: exclude codes through Numerator Percent of patients receiving first line antibiotics. (Amoxicillin, Trimethoprim- Sulfa) Percent of patients following initial visit for acute sinusitis had another visit for acute sinusitis within one month. Of the group of people having a second visit the percent of members receiving a second line antibiotic. Percent of patients receiving a sinus x-ray (CPT codes through 70220), CT Scan Sinus (70486 through 70488), MRI (70540, Y7054, Y7055). Break down of pre- and post-60 days. Percent of patient receiving referral to ENT within 60 days of initial episode. Clinical s Page 10
GUIDELINE Sinusitis. David M. Poetker MD, MA Associate Professor. Division of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery
 GUIDELINE Sinusitis David M. Poetker MD, MA Associate Professor Division of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Guideline Fokkens et al. The European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012. Rhinology.
GUIDELINE Sinusitis David M. Poetker MD, MA Associate Professor Division of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Guideline Fokkens et al. The European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012. Rhinology.
Nasal and Sinus Disorders
 Nasal and Sinus Disorders Chronic Nasal Congestion When nasal obstruction occurs without other symptoms (such as sneezing, facial pressure, postnasal drip etc.) then a physical obstruction might be the
Nasal and Sinus Disorders Chronic Nasal Congestion When nasal obstruction occurs without other symptoms (such as sneezing, facial pressure, postnasal drip etc.) then a physical obstruction might be the
Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections
 Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections Format: 1. Case 2. Topic Summary 3. Questions 4. References Case: A 3-year-old boy presents with 2 days of increasing redness, swelling, and pain
Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections Format: 1. Case 2. Topic Summary 3. Questions 4. References Case: A 3-year-old boy presents with 2 days of increasing redness, swelling, and pain
Chapter 10. All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES
 Chapter 10 All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES The sinuses are air filled cavities contained within the bones of
Chapter 10 All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES The sinuses are air filled cavities contained within the bones of
Get Your Head In The Game. Matthew Voorman, MD Hutchinson Clinic March 21, 2016
 Get Your Head In The Game Matthew Voorman, MD Hutchinson Clinic March 21, 2016 About Me Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Geisinger Medical Center General Surgery University of California San Francisco
Get Your Head In The Game Matthew Voorman, MD Hutchinson Clinic March 21, 2016 About Me Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Geisinger Medical Center General Surgery University of California San Francisco
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
 Measure #65 (NQF 0069): Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #65 (NQF 0069): Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Tired of Sinusitis Pain and Pressure?
 Tired of Sinusitis Pain and Pressure? Instant relief that lasts Quick recovery Sinusitis, Balloon Sinus Dilation, and You 1 What are the Sinuses? How do Healthy Sinuses Work? Paranasal sinuses are air
Tired of Sinusitis Pain and Pressure? Instant relief that lasts Quick recovery Sinusitis, Balloon Sinus Dilation, and You 1 What are the Sinuses? How do Healthy Sinuses Work? Paranasal sinuses are air
Corporate Medical Policy Septoplasty
 Corporate Medical Policy Septoplasty File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: septoplasty 4/1999 8/2015 8/2016 8/2015 Description of Procedure or Service There are many potential
Corporate Medical Policy Septoplasty File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: septoplasty 4/1999 8/2015 8/2016 8/2015 Description of Procedure or Service There are many potential
YALE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE: SECTION OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY PATIENT INFORMATION FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY
 YALE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE: SECTION OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY PATIENT INFORMATION FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY What is functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS)? Functional endoscopic sinus surgery
YALE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE: SECTION OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY PATIENT INFORMATION FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY What is functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS)? Functional endoscopic sinus surgery
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
Sinusitis. Health Promotion and Education Program. Rev. 2014 MP-HEP-PPT-766-01-050514-E
 Sinusitis Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-766-01-050514-E M&P-PRD-TEM-030-032511-S
Sinusitis Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-766-01-050514-E M&P-PRD-TEM-030-032511-S
Headache: Differential diagnosis and Evaluation. Raymond Rios PGY-1 Pediatrics
 Headache: Differential diagnosis and Evaluation Raymond Rios PGY-1 Pediatrics You are evaluating a 9 year old male patient at the ED brought by his mother, who says that her son has had a fever, cough,
Headache: Differential diagnosis and Evaluation Raymond Rios PGY-1 Pediatrics You are evaluating a 9 year old male patient at the ED brought by his mother, who says that her son has had a fever, cough,
Pulsating Aerosol. The New Wave in SINUSitis Therapy. For the precise, effective and gentle treatment of sinusitis
 The New Wave in SINUSitis Therapy Pulsating Aerosol For the precise, effective and gentle treatment of sinusitis PARI SINUS Inhalation treatment for acute and chronic diseases of the upper airways www.parimedical.co.uk
The New Wave in SINUSitis Therapy Pulsating Aerosol For the precise, effective and gentle treatment of sinusitis PARI SINUS Inhalation treatment for acute and chronic diseases of the upper airways www.parimedical.co.uk
Evidence for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Sinusitis in Children: A Systematic Review
 TECHNICAL REPORT Evidence for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Sinusitis in Children: A Systematic Review abstract In 2001, the American Academy of Pediatrics published clinical practice
TECHNICAL REPORT Evidence for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Sinusitis in Children: A Systematic Review abstract In 2001, the American Academy of Pediatrics published clinical practice
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF NASAL CONGESTION AND RHINORRHEA
 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF NASAL CONGESTION AND RHINORRHEA 2010 Allergy Symposium November 6, 2010 David Keschner, MD, JD HNS Orange County General Introduction Overview of material Anatomy and Clinical Features
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF NASAL CONGESTION AND RHINORRHEA 2010 Allergy Symposium November 6, 2010 David Keschner, MD, JD HNS Orange County General Introduction Overview of material Anatomy and Clinical Features
Symptoms of allergic rhinitis can include:
 Rhinitis Rhinitis is an irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane inside the nose. There are two types of rhinitis, allergic rhinitis (hay fever) and nonallergic (such as vasomotor) rhinitis.
Rhinitis Rhinitis is an irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane inside the nose. There are two types of rhinitis, allergic rhinitis (hay fever) and nonallergic (such as vasomotor) rhinitis.
Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection
 BCBS ACO Measure Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection HEDIS Measure CPT II coding required: YES Click here to go to Table of Contents BCBS Measure: Page 50 of 234 Dated:
BCBS ACO Measure Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection HEDIS Measure CPT II coding required: YES Click here to go to Table of Contents BCBS Measure: Page 50 of 234 Dated:
Sinus Headache vs. Migraine
 Sinus Headache vs. Migraine John M. DelGaudio, MD, FACS Professor and Vice Chair Chief of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Department of Otolaryngology Emory University School of Medicine 1 Sinus Headache Problems
Sinus Headache vs. Migraine John M. DelGaudio, MD, FACS Professor and Vice Chair Chief of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Department of Otolaryngology Emory University School of Medicine 1 Sinus Headache Problems
Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis: The Latest Recommendations
 Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis: The Latest Recommendations Shannon Hunter, MD Board-Certified Otolaryngologist Thank you for joining us today We are recording this webinar and will be sending
Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis: The Latest Recommendations Shannon Hunter, MD Board-Certified Otolaryngologist Thank you for joining us today We are recording this webinar and will be sending
Management of exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Primary Care
 Management of exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Primary Care Acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are associated with significant morbidity and mortality.
Management of exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Primary Care Acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are associated with significant morbidity and mortality.
Sore Throat. Definition. Causes. (Pharyngitis; Tonsillopharyngitis; Throat Infection) Pronounced: Fare-en-JY-tis /TAHN-sill-oh-fare-en-JY-tis
 Sore Throat (Pharyngitis; Tonsillopharyngitis; Throat Infection) Pronounced: Fare-en-JY-tis /TAHN-sill-oh-fare-en-JY-tis by Jennifer Lewy, MSW En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A sore throat is the
Sore Throat (Pharyngitis; Tonsillopharyngitis; Throat Infection) Pronounced: Fare-en-JY-tis /TAHN-sill-oh-fare-en-JY-tis by Jennifer Lewy, MSW En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A sore throat is the
IDSA Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis in Children and Adults
 Clinical Infectious Diseases Advance Access published March 20, 2012 IDSA GUIDELINES IDSA Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis in Children and Adults Anthony W. Chow, 1 Michael
Clinical Infectious Diseases Advance Access published March 20, 2012 IDSA GUIDELINES IDSA Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis in Children and Adults Anthony W. Chow, 1 Michael
New treatment options for chronic sinusitis
 New treatment options for chronic sinusitis Balloon Sinuplasty Technology Vishram Jalukar, MD Mason City Clinic ENT & Allergy MKT01014 Rev. D Sinusitis Overview Inflammation of the sinus lining caused
New treatment options for chronic sinusitis Balloon Sinuplasty Technology Vishram Jalukar, MD Mason City Clinic ENT & Allergy MKT01014 Rev. D Sinusitis Overview Inflammation of the sinus lining caused
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Contents
 Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
PLAN OF ACTION FOR. Physician Name Signature License Date
 PLAN OF ACTION FOR Patient s copy (patient s name) I Feel Well Lignes I feel short directrices of breath: I cough up sputum daily. No Yes, colour: I cough regularly. No Yes I Feel Worse I have changes
PLAN OF ACTION FOR Patient s copy (patient s name) I Feel Well Lignes I feel short directrices of breath: I cough up sputum daily. No Yes, colour: I cough regularly. No Yes I Feel Worse I have changes
Test Request Tip Sheet
 With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
Unilateral Nasal Polyps
 Unilateral Nasal Polyps This tutorial follows on from the rhinosinusitis tutorial but only concerns itself with the unilateral nasal polyp. The majority of unilateral nasal polyps form in the same way
Unilateral Nasal Polyps This tutorial follows on from the rhinosinusitis tutorial but only concerns itself with the unilateral nasal polyp. The majority of unilateral nasal polyps form in the same way
Nasal polyps differ in terms of origin, as well
 Focus on CME at the University of Saskatchewan Clearing the Air on Nasal Polyps By Gordon Franke, MD, BSc, FRCS(C) Presented at the University of Saskatchewan Practical Otolaryngology Conference 2003,
Focus on CME at the University of Saskatchewan Clearing the Air on Nasal Polyps By Gordon Franke, MD, BSc, FRCS(C) Presented at the University of Saskatchewan Practical Otolaryngology Conference 2003,
Evaluation of Headache Syndromes and Migraine
 Evaluation of Headache Syndromes and Migraine Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Department of Neurology Los Angeles Kaiser Objectives 1) Identify the diagnostic features of migraine Differentiate from sinusitis 2)
Evaluation of Headache Syndromes and Migraine Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Department of Neurology Los Angeles Kaiser Objectives 1) Identify the diagnostic features of migraine Differentiate from sinusitis 2)
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
Pulsating Aerosol. The New Wave in SINUSitis Therapy. Cystic Fibrosis. Focus on. For the precise, effective and gentle treatment of sinusitis
 The New Wave in SINUSitis Therapy Focus on Cystic Fibrosis Pulsating Aerosol For the precise, effective and gentle treatment of sinusitis PARI SINUS Inhalation treatment for acute and chronic diseases
The New Wave in SINUSitis Therapy Focus on Cystic Fibrosis Pulsating Aerosol For the precise, effective and gentle treatment of sinusitis PARI SINUS Inhalation treatment for acute and chronic diseases
Surgical Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in. Children
 Surgical Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Children Fuad M. Baroody, M.D., F.A.C.S. Professor of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery and Pediatrics The University of Chicago Medicine and Biological
Surgical Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Children Fuad M. Baroody, M.D., F.A.C.S. Professor of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery and Pediatrics The University of Chicago Medicine and Biological
Headaches. This chapter will discuss:
 C H A P T E R Headaches 1 1 Almost everyone gets an occasional headache at some time or another. Some people get frequent headaches. Most people do not worry about headaches and learn to live with them
C H A P T E R Headaches 1 1 Almost everyone gets an occasional headache at some time or another. Some people get frequent headaches. Most people do not worry about headaches and learn to live with them
What is Balloon Sinuplasty?
 What is Balloon Sinuplasty? The painful symptoms associated with chronic sinusitis can be overwhelming. If symptoms are difficult to control with medications alone, your primary doctor may refer you to
What is Balloon Sinuplasty? The painful symptoms associated with chronic sinusitis can be overwhelming. If symptoms are difficult to control with medications alone, your primary doctor may refer you to
HEADACHES IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS. Brian D. Ryals, M.D.
 HEADACHES IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS Brian D. Ryals, M.D. Frequency and Type of Headaches in Schoolchildren 8993 children age 7-15 in Sweden Migraine in 4% Frequent Nonmigrainous in 7% Infrequent Nonmigrainous
HEADACHES IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS Brian D. Ryals, M.D. Frequency and Type of Headaches in Schoolchildren 8993 children age 7-15 in Sweden Migraine in 4% Frequent Nonmigrainous in 7% Infrequent Nonmigrainous
fig.1: CT scan of sinuses: Right isolated sphenoid sinus opacification
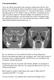 Case presentation: An 8 year old boy presented to the emergency department with few days history of severe headache. Pain is described as fronto-occipital, continuous and not relieved by pain medications.
Case presentation: An 8 year old boy presented to the emergency department with few days history of severe headache. Pain is described as fronto-occipital, continuous and not relieved by pain medications.
COPD and Asthma Differential Diagnosis
 COPD and Asthma Differential Diagnosis Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death in America. Learning Objectives Use tools to effectively diagnose chronic obstructive
COPD and Asthma Differential Diagnosis Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death in America. Learning Objectives Use tools to effectively diagnose chronic obstructive
Headaches in Children
 Children s s Hospital Headaches in Children Manikum Moodley, MD, FRCP Section of Pediatric Neurology The Cleveland Clinic Foundation Introduction Headaches are common in children Most headaches are benign
Children s s Hospital Headaches in Children Manikum Moodley, MD, FRCP Section of Pediatric Neurology The Cleveland Clinic Foundation Introduction Headaches are common in children Most headaches are benign
Sample Treatment Protocol
 Sample Treatment Protocol 1 Adults with acute episode of LBP Definition: Acute episode Back pain lasting
Sample Treatment Protocol 1 Adults with acute episode of LBP Definition: Acute episode Back pain lasting
Neuroimaging of Headache. Kenneth D. Williams, MD
 Neuroimaging of Headache Kenneth D. Williams, MD Disclosures Financial: None Off Label Usage: None Key Points Headache is an extremely common symptom. Structural abnormalities (Primary HA) are rare. Clinical
Neuroimaging of Headache Kenneth D. Williams, MD Disclosures Financial: None Off Label Usage: None Key Points Headache is an extremely common symptom. Structural abnormalities (Primary HA) are rare. Clinical
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
PRESEPTAL AND ORBITAL CELLULITIS IN CHILDREN- CLINICAL GUIDELINE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline
 PRESEPTAL AND ORBITAL CELLULITIS IN CHILDREN- CLINICAL GUIDELINE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to medical and nursing staff caring for a child with Preseptal and Orbital
PRESEPTAL AND ORBITAL CELLULITIS IN CHILDREN- CLINICAL GUIDELINE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to medical and nursing staff caring for a child with Preseptal and Orbital
Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology
 Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease) PROGRAM Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for STDs Guidance for Medical Providers in
Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease) PROGRAM Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for STDs Guidance for Medical Providers in
By James D. Gould, MD FACS
 By James D. Gould, MD FACS BACKGROUND Balloon devices enlarge narrowed sinus ostia and outflow tracts by remodeling the surrounding bone and paranasal sinus structures. Multiple studies have demonstrated
By James D. Gould, MD FACS BACKGROUND Balloon devices enlarge narrowed sinus ostia and outflow tracts by remodeling the surrounding bone and paranasal sinus structures. Multiple studies have demonstrated
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
Clinical guidance for MRI referral
 MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
Sinus and Nasal Surgery
 D E C A T U R M E M O R I A L H O S P I T A L Sinus and Nasal Surgery Introduction You are scheduled for sinus and nasal surgery. This helps open your sinuses and restore normal sinus functioning. Usually,
D E C A T U R M E M O R I A L H O S P I T A L Sinus and Nasal Surgery Introduction You are scheduled for sinus and nasal surgery. This helps open your sinuses and restore normal sinus functioning. Usually,
Common Breast Complaints:
 : Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
: Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
BALLOON SINUS OSTIAL DILATION
 BALLOON SINUS OSTIAL DILATION Effective Date: March 11, 2014 Review Dates: 12/11, 12/12, 2/13, 2/14, 2/15 Date Of Origin: December 14, 2011 Status: Current I. POLICY/CRITERIA A. The use of balloon sinus
BALLOON SINUS OSTIAL DILATION Effective Date: March 11, 2014 Review Dates: 12/11, 12/12, 2/13, 2/14, 2/15 Date Of Origin: December 14, 2011 Status: Current I. POLICY/CRITERIA A. The use of balloon sinus
Coding Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 Coding Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Audio Seminar/Webinar July 31, 2008 Practical Tools for Seminar Learning Copyright 2008 American Health Information Management Association. All rights reserved. Disclaimer
Coding Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Audio Seminar/Webinar July 31, 2008 Practical Tools for Seminar Learning Copyright 2008 American Health Information Management Association. All rights reserved. Disclaimer
Guidelines for the Use of Antibiotics in Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
 Guidelines for the Use of Antibiotics in Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections DAVID M. WONG, D.O., Arrowhead Regional Medical Center, Colton, California DEAN A. BLUMBERG, M.D., University of California
Guidelines for the Use of Antibiotics in Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections DAVID M. WONG, D.O., Arrowhead Regional Medical Center, Colton, California DEAN A. BLUMBERG, M.D., University of California
Toothaches of Non-dental Origin
 Toothaches of Non-dental Origin This brochure is produced by the American Academy of Orofacial Pain The American Academy of Orofacial Pain is an organization of health care professionals dedicated to alleviating
Toothaches of Non-dental Origin This brochure is produced by the American Academy of Orofacial Pain The American Academy of Orofacial Pain is an organization of health care professionals dedicated to alleviating
Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon
 Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon Oregon Health Authority Center for Public Health Practice HIV/STD/TB Section Principles of
Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon Oregon Health Authority Center for Public Health Practice HIV/STD/TB Section Principles of
An Overview of Asthma - Diagnosis and Treatment
 An Overview of Asthma - Diagnosis and Treatment Asthma is a common chronic disorder of the airways that is complex and characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness,
An Overview of Asthma - Diagnosis and Treatment Asthma is a common chronic disorder of the airways that is complex and characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness,
Antibiotic use in the management of uncomplicated URTIs and bronchitis
 Antibiotic use in the management of uncomplicated URTIs and bronchitis Aims of clinical audit To review your prescribing of antibiotics for uncomplicated upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) and
Antibiotic use in the management of uncomplicated URTIs and bronchitis Aims of clinical audit To review your prescribing of antibiotics for uncomplicated upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) and
Documentation Guidelines for Physicians Interventional Pain Services
 Documentation Guidelines for Physicians Interventional Pain Services Pamela Gibson, CPC Assistant Director, VMG Coding Anesthesia and Surgical Divisions 343.8791 1 General Principles of Medical Record
Documentation Guidelines for Physicians Interventional Pain Services Pamela Gibson, CPC Assistant Director, VMG Coding Anesthesia and Surgical Divisions 343.8791 1 General Principles of Medical Record
Septoplasty and Turbinate Reduction Surgical Information
 Septoplasty and Turbinate Reduction Surgical Information PREOPERATIVE DISCUSSION FOR SEPTOPLASTY and TURBINATE REDUCTION Septoplasty The nasal septum is made of cartilage and bone covered with a lining
Septoplasty and Turbinate Reduction Surgical Information PREOPERATIVE DISCUSSION FOR SEPTOPLASTY and TURBINATE REDUCTION Septoplasty The nasal septum is made of cartilage and bone covered with a lining
OTITIS MEDIA AND SINUSITIS
 Page 1 OTITIS MEDIA AND SINUSITIS I. OTITIS MEDIA A. Definition: 1. Inflammatory reaction to foreign antigens in the middle ear that cannot adequately drain via the eustachian tube. 2. Three major divisions
Page 1 OTITIS MEDIA AND SINUSITIS I. OTITIS MEDIA A. Definition: 1. Inflammatory reaction to foreign antigens in the middle ear that cannot adequately drain via the eustachian tube. 2. Three major divisions
Herniated Cervical Disc
 Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Headaches in Children How to Manage Difficult Headaches
 Headaches in Children How to Manage Difficult Headaches Peter Procopis Childhood headaches Differential diagnosis Migraine Psychological Raised Pressure Childhood headaches Other causes: Constitutional
Headaches in Children How to Manage Difficult Headaches Peter Procopis Childhood headaches Differential diagnosis Migraine Psychological Raised Pressure Childhood headaches Other causes: Constitutional
Acute Dental Problems in the School Setting
 Acute Dental Problems in the School Setting Keri Discepolo, D.D.S., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, Yale Pediatric Dentistry Residency Program Associate, Yale School of Medicine Objectives Brief Description of
Acute Dental Problems in the School Setting Keri Discepolo, D.D.S., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, Yale Pediatric Dentistry Residency Program Associate, Yale School of Medicine Objectives Brief Description of
Nasal Polyps B. Todd Schaeffer, MD, FACS Lake Success, Long Island, NY
 Advanced Sinus /Skull Base Center ENT & Allergy Associates, LLP Fall 2014 Nasal Polyps B. Todd Schaeffer, MD, FACS Lake Success, Long Island, NY www.schaeffermd.com New Treatments for Nasal Polyps Dr Schaeffer
Advanced Sinus /Skull Base Center ENT & Allergy Associates, LLP Fall 2014 Nasal Polyps B. Todd Schaeffer, MD, FACS Lake Success, Long Island, NY www.schaeffermd.com New Treatments for Nasal Polyps Dr Schaeffer
The Lewin Group undertook the following steps to identify the guidelines relevant to the 11 targeted procedures:
 Guidelines The following is a list of proposed medical specialty guidelines that have been found for the 11 targeted procedures to be included in the Medicare Imaging Demonstration. The list includes only
Guidelines The following is a list of proposed medical specialty guidelines that have been found for the 11 targeted procedures to be included in the Medicare Imaging Demonstration. The list includes only
A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO CHRONIC COUGH IN CHILDREN
 A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO CHRONIC COUGH IN CHILDREN Chng Seo Yi Chronic cough is defined as a persistent cough of more than three weeks duration which is not getting better. It is a common symptom in childhood.
A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO CHRONIC COUGH IN CHILDREN Chng Seo Yi Chronic cough is defined as a persistent cough of more than three weeks duration which is not getting better. It is a common symptom in childhood.
Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients.
 Dec QMJ VOL.5 No.8 Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients. Radhi F.Alshaibani* الخلاصھ لا زالت حمى التایفوید سببا مھما من اسباب الامراض وفقدان ساعات العمل
Dec QMJ VOL.5 No.8 Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients. Radhi F.Alshaibani* الخلاصھ لا زالت حمى التایفوید سببا مھما من اسباب الامراض وفقدان ساعات العمل
Use of Packing for Surgical Wounds. Maggie Benson Clinical Problem Solving II
 Use of Packing for Surgical Wounds Maggie Benson Clinical Problem Solving II Purpose Present patient management s/p Incision and Drainage in an outpatient setting Examine evidence for the use of wound
Use of Packing for Surgical Wounds Maggie Benson Clinical Problem Solving II Purpose Present patient management s/p Incision and Drainage in an outpatient setting Examine evidence for the use of wound
Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions
 Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Definition: Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs. Many different organisms can cause it, including bacteria,
Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Definition: Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs. Many different organisms can cause it, including bacteria,
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of. Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care
 A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
CT scans and IV contrast (radiographic iodinated contrast) utilization in adults
 CT scans and IV contrast (radiographic iodinated contrast) utilization in adults At United Radiology Group, a majority of CT exams are performed either with IV contrast or without while just a few exams
CT scans and IV contrast (radiographic iodinated contrast) utilization in adults At United Radiology Group, a majority of CT exams are performed either with IV contrast or without while just a few exams
ORAL MAXILLO FACIAL SURGERY REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS
 ORAL MAXILLO FACIAL SURGERY REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines General problems include: Soft tissue conditions of the face and oral cavity
ORAL MAXILLO FACIAL SURGERY REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines General problems include: Soft tissue conditions of the face and oral cavity
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History
 Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative treatment
 STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative Pregnancy Chlamydia Chancroid Epdidymitis Gonorrhea: Uncomplicated (cx, urethra, and rectum):
STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative Pregnancy Chlamydia Chancroid Epdidymitis Gonorrhea: Uncomplicated (cx, urethra, and rectum):
Cough, as a leading symptom, would certainly be in the top 10 of reasons for seeing a GP.
 COUGH Cough, as a leading symptom, would certainly be in the top 10 of reasons for seeing a GP. A cough in a child seems to cause more concern, even when it has not been present very long, whereas in adults
COUGH Cough, as a leading symptom, would certainly be in the top 10 of reasons for seeing a GP. A cough in a child seems to cause more concern, even when it has not been present very long, whereas in adults
A Guide to MANAGING. breathe easy
 A Guide to MANAGING Respiratory Infections breathe easy A Guide to MANAGING Respiratory Infections breathe easy Copyright 2008 Conrad & Associates, LLC All Rights Reserved No part of this book may be reproduced
A Guide to MANAGING Respiratory Infections breathe easy A Guide to MANAGING Respiratory Infections breathe easy Copyright 2008 Conrad & Associates, LLC All Rights Reserved No part of this book may be reproduced
Irish Association for Emergency Medicine (IAEM) submission to the National COPD Strategy
 31 st Irish Association for Emergency Medicine (IAEM) submission to the National COPD Strategy 1 Introduction Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is an important disease for patients, the health
31 st Irish Association for Emergency Medicine (IAEM) submission to the National COPD Strategy 1 Introduction Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is an important disease for patients, the health
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck)
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Managing your health care benefits on myuhc.com
 Managing your health care benefits on myuhc.com Managing your health care benefits and communications online is easy and convenient on myuhc.com We ve made it easier for you to manage your health care
Managing your health care benefits on myuhc.com Managing your health care benefits and communications online is easy and convenient on myuhc.com We ve made it easier for you to manage your health care
Double-click the EncounterPRO-OS icon on the desktop. The EncounterPRO-OS login screen appears.
 Test Drive This Test Drive is intended to help you document a simple sick visit. Step-by-step instructions and screen shots are provided so that you can be sure you are on the right track. More information
Test Drive This Test Drive is intended to help you document a simple sick visit. Step-by-step instructions and screen shots are provided so that you can be sure you are on the right track. More information
Other Causes of Fever
 T e c h n i c a l S e m i n a r s Other Causes of Fever Febrile Illness Causes Fever After Seven Days Referral Relapsing Fever - Borreliosis Overview JHR Adaptation Sore Throat Overview Prevention Management
T e c h n i c a l S e m i n a r s Other Causes of Fever Febrile Illness Causes Fever After Seven Days Referral Relapsing Fever - Borreliosis Overview JHR Adaptation Sore Throat Overview Prevention Management
NOSE AND SINUS PROBLEMS. Sinusitis
 NOSE AND SINUS PROBLEMS Sinusitis The sinuses also called paranasal sinuses are 4 pairs of air-containing spaces in the head (maxillary, ethmoid, frontal, and sphenoid). They extend from the nasal passages
NOSE AND SINUS PROBLEMS Sinusitis The sinuses also called paranasal sinuses are 4 pairs of air-containing spaces in the head (maxillary, ethmoid, frontal, and sphenoid). They extend from the nasal passages
Title: Antibiotic Guideline for Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
 Title: Antibiotic Guideline for Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Version 3 Date ratified December 2007 Review date December 2009 Ratified by NUH Antimicrobial Guidelines Committee Gynaecology Directorate
Title: Antibiotic Guideline for Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Version 3 Date ratified December 2007 Review date December 2009 Ratified by NUH Antimicrobial Guidelines Committee Gynaecology Directorate
EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT
 This assessment is effective as of October 2014. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, e-mail [email protected] EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT
This assessment is effective as of October 2014. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, e-mail [email protected] EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT
Item 90 : Nose and sinus infections in children and adults Collège Français d'orl et de Chirurgie Cervico-faciale
 Item 90 : Nose and sinus infections in children and adults Collège Français d'orl et de Chirurgie Cervico-faciale 2013 1 Table des matières 1. Pathology of acuite nose and sinus infections...3 1.1. Acute
Item 90 : Nose and sinus infections in children and adults Collège Français d'orl et de Chirurgie Cervico-faciale 2013 1 Table des matières 1. Pathology of acuite nose and sinus infections...3 1.1. Acute
Interventional Radiology
 Nationwide Children s Hospital Department of Radiology is recognized as a pioneering center for research and innovation, and a renowned leader in diagnostic and interventional pediatric radiology. Our
Nationwide Children s Hospital Department of Radiology is recognized as a pioneering center for research and innovation, and a renowned leader in diagnostic and interventional pediatric radiology. Our
PRESCRIBING FOR SMOKING CESSATION. (Adapted from the Self-Limiting Conditions Independent Study Program for Manitoba Pharmacists)
 PRESCRIBING FOR SMOKING CESSATION (Adapted from the Self-Limiting Conditions Independent Study Program for Manitoba Pharmacists) Acknowledgements The Self-Limiting Conditions Independent Study Program
PRESCRIBING FOR SMOKING CESSATION (Adapted from the Self-Limiting Conditions Independent Study Program for Manitoba Pharmacists) Acknowledgements The Self-Limiting Conditions Independent Study Program
