Deafness Glossary 2.1.
|
|
|
- Griffin Stevens
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Deafness Glossary 2.1.
2 Glossary: The Ear / earing Acoustic feedback Squeal produced by a hearing aid when amplified sound escapes and is reamplified. Acoustic nerve The auditory nerve. Acoustic neuroma A benign tumour of the acoustic nerve that grown in the ear canal. Acoustic otoscope A medical instrument used for examining the ear that reflects sound waves off the eardrum. Acoustics Pertaining to sound, the sense of hearing or the science of sound. Often used to refer to the quality of the sound environment Acoustic reflex response G Measurement of the change in transmission of sound through the middle ear by activation of the stapedial reflex with presentation of loud sound. Acoustic trauma Loss of hearing caused by exposure to loud noise over a long period of time, an explosion, blow to the head or another accident. Acquired hearing loss earing loss, which is not present at birth. Sometimes referred to as adventitious loss. Age Induced earing Loss C* Common name for presbycusis. Presbycusis is caused by a gradual deterioration of hair cells, which is part of the normal ageing process. Air Conduction G Measurements of hearing made through earphones. Therefore, the entire auditory system is evaluated. Ambient noise ackground noise, which competes with the main speech signal. American Sign Language A form of sign language with its own grammar, vocabulary and syntax, used primarily by deaf Americans. Amplification The use of hearing aids and other electronic devices to increase the loudness of a sound so that it may be more easily received and understood. Amplifier C* Electronic circuit elements of the hearing instrument. Amplitude C* The magnitude of a signal Analogue Type of hearing-aid circuitry which converts sound into electronic signals. Analysis of variance A A statistical test of the effects of several variables and their interactions. Assistive alerting device Assistive communication device A device which alerts a hearing-impaired individual to sound through a louder sound, such as a bell, whistle or horn. Devices and systems which are available to help deaf and hard of hearing people improve communication, adapt to their environment, and function in society more effectively. Assistive listening Any device which helps a hearing-impaired individual hear; this includes devices which alert, signal, amplify or direct sound or represent sound
3 device visually. Atonal Refers to voice quality that lacks traditional musical tonality or harmonics. Attack/release times C* The speed in which a compression circuit works detecting the beginning and end of a sound. Audiogram G * A graph, made by an audiometer, on which a person's ability to hear different pitches (frequencies) at different volumes (intensities) of sound is recorded. The frequency is plotted on the horizontal axis (250z to 8000 z). The vertical axis shows the degree of hearing loss in d. See: ow to read an Audiogram. Audiological Assessment * A hearing test comprised of identifying pure-tone thresholds, impedance testing, speech recognition, and speech discrimination measurements, which shows the type and degree of hearing loss. The test can also assess how well a person is hearing with amplification. Audiologist A professional trained in the identification, evaluation and nonmedical rehabilitation of hearing loss. Audiometer A/* An electronic instrument used for testing the acuity of hearing and for measuring the conduction of sound through bone and air. Auditory brainstem response (AR) Auditory nerve (VIII Nerve) A/ /E* A non-invasive test that measures responses in the brain waves to auditory stimulus. This test can indicate whether or not sound is being detected, even in an infant. This test may also be referred to as AER, SEP, and SER. The eighth cranial nerve linking the cochlea to higher centres of the brain; it transmits information from the cochlea to the brain. Essentially, it is the transmission line from the sense organs to the central processor of the brain. Auditory training * The process of training a person's residual hearing in the awareness, identification, and interpretation of sound. Done with the help of speech language therapists or audiologists. Aural habilitation Training designed to help a person with hearing loss to make productive use of residual hearing. Sometimes includes training in speech reading. Aural rehabilitation Training and rehabilitation to teach a hearing-impaired individual to cope with limited hearing or adjust to a hearing aid. Auricle The external part of the ear; the pinna. AA C* one Anchored earing Aids used in the treatment of severe, conductive hearing loss. Atitanium bolt is placed in the mastoid bone. As soon as it sits tightly, the bolt is able to conduct sound to the bone and on to the inner ear. A small vibrating hearing aid is then attached to the bolt. arotrauma Injury in the ear caused by a sudden change in air pressure. asilar membrane / E The membrane in the cochlea, where the hair cells are located. A ribbon like structure upon which rests the organ of Corti. The basilar membrane is less wide but stiffer at its basal end toward the oval window, but is wider and more compliant toward its apical end away from the oval window. ecause of these two gradients of size and stiffness, high frequencies are coded at the basal end with low frequencies progressively coded toward the apical end.
4 ehavioural observation audiometry ehind-the-ear (TE) * Assessment of a young child's behavioural response to sound by observation. earing device. Microphone, amplifier and receiver are housed in a small case that sits behind the ear. el A The ratio of two measures of sound power expressed as a logarithm to the base 10. A decibel (d) is one-tenth of a bel. eing a ratio, the bel has no dimensions, and in air the sound-pressure level in decibels is equal to 20 log 10 (p/p 0 ), where p is the sound-pressure level of a given sound and p 0 is an arbitrary sound-pressure level usually taken to be dynes/cm 2 or 1 dyne/cm 2. ilateral Two-sided; referring to both ears. ilateral hearing loss A mild to profound hearing loss in both ears. ilateral presentation A The presentation of stimuli in both sides of a subject s visual field simultaneously. ilingual / icultural eing fluent in two languages and membership in two cultures. Such as hearing (spoken language) and the Deaf culture (sign language). inaural hearing aids earing aids worn on both ears ody-worn hearing aid C* Cigarette packet-sized hearing device worn in a pocket, with a cord attaching it to the earpiece. Provides increased gain (power) and less feedback for individuals with a severe hearing loss. Primarily used only in special situations where ear-level hearing aids cannot be used. one conduction G Measurements of hearing made through a vibrator placed on the mastoid bone behind the ear. Therefore, the cochlea of the inner ear and the VIII nerve are tested. rain stem audiometery Computerized test which measures the response of the brain stem to sound. Cerumen Earwax. Cholesteatoma An abnormal growth of skin, or cyst, in the middle ear. It occurs as a congenital defect or as a complication of otitis media. CIC Completely-inthe-Canal C* earing aid that is placed deep in the ear canal (1-2mm beyond the ear canal opening). Cilia air cells in the cochlea. Claudius Cells E Inert supporting cells. Cochlea E* A spiral-shaped part of the inner ear that is the sensory organ of hearing. It receives sound waves from the middle ear and transmits the information to the auditory nerve. The vibrational patterns that are initiated by vibration of the stapes footplate set up a travelling wave pattern within the cochlea. This wavelike pattern causes a shearing of the cilia of the outer and inner hair cells. This shearing causes harir cell depolarization resulting in all or none neural impulses that the brain interprets as sound.
5 Cochlear implant A device, which, when implanted into the cochlea, enables people with profound hearing loss to hear certain noises. Conductive hearing loss Type of hearing loss caused by something impeding the conduction of sound through the outer and/or middle ear. Confusion method A A way of determining the encoding method used by a subject to store information by assessing the degree of confusion induced by similar stimuli. Congenital hearing loss earing loss present at birth or associated with the birth process, or which develops in the first few days of life. Conservation A In the theory of Piaget, the ability of the child to understand that certain physical properties of matter are conserved despite changes in shape or position, marking a significant stage of cognitive development. Correlation Coefficient (r) A A mathematical expression of the strength of a relationship between two variables, ranging from +1 (perfect correlation) through 0 (no relation evident) to -1 (perfect negative relationship). Cortex A The evolutionarily most advanced outermost position of the brain. Cued speech A technique in which manual signs are used to back up speech reading. Curette A long, thin instrument with a hook at the end; used by doctors to clean earwax from the outer ear canal. Deaf Medically and clinically speaking a hearing loss which is so severe that the child is unable to process linguistic information through hearing alone. Socially when used with a capital letter "D," Deaf refers to the cultural heritage and community of deaf individuals, i.e., the Deaf culture or community. In this context, it applies to those whose primary receptive channel of communication is visual. Deaf community A group of people who share common interests and a common heritage. Their mode of communication is a (national) Sign Language. The Deaf community is comprised of individuals, both deaf and hearing, who respond with varying intensity to particular community goals which derive from Deaf cultural influences. Deaf culture A view of life manifested by the mores, beliefs, artistic expression, understandings and language (SL) particular to Deaf people. A capital "D" is often used in the word Deaf when it refers to community or cultural aspects of Deafness. Deaf blindness Educationally significant combined loss of vision and hearing Decibel (d) A/ A relative measurement of sound intensity or pressure; literally one-tenth of a bel; an increase of one bel is approximately double the loudness of a sound. Decoder An electronic device or computer chip that can display closed captions encoded in television programs or videocassettes. Also called a telecaption adapter. Degree of earing Loss G 0-25d Normal limits d Mild hearing Loss d Moderate hearing loss d Moderately Severe hearing loss d Severe hearing loss.
6 >91d Profound hearing loss. Deiter s Cells E Inert supporting cells of the outer hair cells. Digital earing-aid circuitry in which sound is converted into numerically coded signals like those used in computer microchips. Digitally programmable A type of hearing aid with digital circuitry that can be programmed like a computer to tailor it to its user s needs. Dyslexia A Language difficulty associated with problems in perceiving and ordering verbal elements. Ear canal E The opening by which sound enters the ear. The total length of the ear canal in adults is approximately 3400z, an important frequency region for understanding speech. Eardrum Tympanic membrane; a flat membrane which separates the outer ear canal from the middle ear. Ear mould A device that fits in the ear to connect a behind-the-ear hearing aid to the ear. Earmuffs Noise protection devices that cover the ears. Earplugs Noise protection devices that fit in the ear canal. Educational interpreter A person who is able to perform conventional interpreting, together with special skills for working in the educational environment. Electrocochleography A computerised test that provides information about the functioning of the inner ear. Endolymph E* Fluid filling the scala media, one of the three partitions within the cochlea. In contrast to perilymph, endolymph has a high K+ concentration and a low Na+ concentration. The endolymph that is found within the scala media is continuous with the endolymph of the saccule, communicating through the ductus reunions. ENT An ear-and-nose specialist; otolaryngologist Eustachian tube E Tube which connects the ear to the nose-throat cavity. It opens with swallowing or coughing to equalise pressure between the middle ear and ambient pressure that is found in the throat. Exostosis An abnormal growth on the surface of a bone in the ear; also known as surfer s ear. External ear A The pinna and the external auditory canal terminating in the ear drum. Facial Nerve (VII cranial nerve) E The facial nerve is the VII cranial nerve, and travels in parallel with the VIII cranial nerve through the internal acoustic canal. The facial nerve innervates the face and provides both sensory and motor function to the face. Factor analysis A A method determining the factors underlying the correlations between a large number of variables; somewhat controversial but widely used in educational research.
7 Fingerspelling A form of manual communication in which words are spelled out with the hands by means of symbols that represent the letters of the alphabet. FM system An assistive listening device worn by the speaker to amplify his/her voice and transmit it directly to the listener's ears via an electronic receiver and special earphones or the listener's own hearing aids. The device reduces the problem of background noise interference and the problem of distance between speaker and hearing-impaired listener. Frequency A/* The number of vibrations a sound makes per second, conventionally measured in cycles per second hertz (z) or kilohertz (kz) - ; sounds with higher frequencies have higher pitches. Frequency resolution C* The ability to simultaneously distinguish between several sounds of different frequencies. Functional gain test Pure-tone test used to determine hearing abilities when a hearing aid is worn. Fundamental frequency A The pure tone in a complex sound that has the same period as the periodic quantity which is that of sound. Gain * The range that describes how well the amplification is performing mg. For example, a person with unaided hearing at 70 d who, when amplified, hears at 30d, is experiencing a gain of40 d. ard-of-earing A hearing loss, whether permanent or fluctuating, which adversely affects and individual's ability to detect and decipher some sounds. 2) The term preferred over "hearing impaired" by the Deaf and hard-of-hearing community to refer to individuals who have hearing loss, but also have and use residual hearing. armonics A The integral multiples of the fundamental frequency of a complex tone. For example, if the fundamental frequency of a sound is 256c/s, the first harmonic is 2x256(512)c/s and so on. earing screening Audiometric testing of the ability to hear selected frequencies at intensities above normal hearing. The purpose is to identify individuals with hearing loss, with minimal time expenditure, and to refer them for further testing. earing aid An electronic device that conducts and amplifies sound to the ear. earing impaired Applies to those who are acoustically disabled / auditorially deficient for whom the primary receptive channel of communication is, even with deficits, hearing. ensen s Cells E Inert supporting cells. ertz International unit for frequency; equal to one cycle per second. uggies The brand name of a plastic-ringed device designed to "hug" the hearing aid to the ear. Popular for infants and toddlers whose ears may be too small to hold the hearing aid snugly in place. ybrid A type of hearing-aid circuitry in which digital computer chips control the operation of analogue components. ydraulic Advantage E See Stapes. Incus E The anvil; the central of the three small bones in the middle ear. The incus is attached to the malleus, and so vibrates as the malleus vibrates. The long
8 process of the incus is also attached to the head of the stapes. ecause the long process of the incus is slightly shorter than the long process (manubrium) of the malleus, incoming sound is given a slight (2.5d) boost in energy. This is referred to as the lever advantage. Individualised education plan (IEP) * A team-developed, written program, which identifies therapeutic and educational goals and objectives, needed to appropriately address the educational needs of a school-aged student with a disability. An IEP for a child with hearing loss should take into account such factors as 1) communication needs and the child's and family's preferred mode of communication 2) linguistic needs; 3) severity of hearing loss; 4) academic progress; 5) social, emotional needs, including opportunities for peer interactions and communication; and 6) appropriate accommodations to facilitate learning. Infrared system An assistive listening system for a room in which infrared light rays transmit sound to receivers worn by hearing-impaired individuals. Inner ear A/* Consists primarily of the cochlea and its associated structures (labyrinth). It also includes the semi-circular canals that are concerned with balance. Inner air Cell E There is one row of approximately 3500 inner hair cells. These cells receive about 95% of the innervations from the nerve fibers from the acoustic portion of the VIII nerve. These cells have primary responsibility for producing our sensation of hearing. When lost or damaged, a severe to profound hearing loss usually occurs. Inner Sulcus E Inert supporting cells to the inner hair cells. Intensity A A measure of the amount of sound energy that flows through a unit area in a unit interval of time. It is usually measured by recording the pressure of the sound which is related to intensity in the following way: I=p 2 /dxv where I is the intensity of the sound, p is the pressure of the sound, d is the density of the medium, and v is the speed of sound. Interpreter A person who facilitates communication between hearing and deaf or hard of hearing persons through interpretation into a signed language, or transliteration of a language into a visual and/or phonemic code by an oral interpreter, a signed language interpreter or cued speech interpreter. Intonation The aspect of speech made up of changes in stress and pitch in the voice. In-the-ear hearing aid (ITE) C The microphone, amplifier and receiver are mounted in a custom-fitted case that fits in the concha of the auricle. Labyrinth The part of the inner ear, consisting of fluid-filled semicircular canals, which controls balance. Labyrinthectomy Surgery in which the inner ear is removed. Lever advantage E See Incus. Loop system An assistive device for a room, in which a microphone and amplifier are attached to an electrical wire which circles the room and creates a magnetic field; hearing-impaired individuals wearing hearing aids with telecoil circuitry can pick up the magnetised sound. Loudness A The psychological response made by an observer to the physical intensity and
9 which enables sound to be rated on a continuum or louder to softer. Loudness scaling C A procedure to determine at which loudness a certain sound is perceived by an individual. Mainstreaming A An educational philosophy based on the proposition that all handicapped children should be taught together with normal children. Mainstreaming is one point on a continuum of educational options. The term is sometimes used synonymously with "inclusion. Malleus E* The hammer; the first and most lateral (toward the side of the head) of the three small ear bones (ossicles) in the middle ear. The long process of the malleus is attached to the inner layer of tympanic membrane. When the TM vibrates in response to sound, the malleus vibrates in concert. Manual communication Any form of communication in which the hands, rather than the spoken word, are used to communicate; i.e. sign language and fingerspelling. Manual English A form of manual communication in which hand signs are used to represent English words; the grammar and syntax of English are also used. Manually coded English Masking A G* See Manual English In audiometry, masking refers to the noise that is presented to one ear when testing the other ear. The process whereby the presence of one sound (the masking sound) raises the threshold of audibility for a given sound. Mastoid (Air Cells) E A portion of the temporal bone; found behind the ear. Under normal circumstances this honeycombed area cells are filled with air. They can fill with fluid or pus when chronically infected. Mastoidectomy Surgical removal of all or part of the mastoid process. Mastoiditis An inflammation or infection of the mastoid bone or its air cells spaces lined by mucous membrane in the mastoid bone. Ménière s disease An inner-ear disorder of unknown cause that results in periods of vertigo or dizziness, hearing loss, buzzing or ringing in the ear and nausea. Middle ear A Consists of three small bones ( the malleus, the incus, and the stapes) which transmit vibrations from the tympanic membrane (the eardrum) to the oval window in the cochlea. Mixed hearing loss earing loss that is both conductive and sensorial. Monaural amplification Most comfortable range/level (MCL) Multi-disciplinary assessment and evaluation C The use of one hearing aid instead of two. The level at which a person prefers to listen to a particular sound for a long period of time. Qualified persons representing two or more disciplines or professions, i.e.; a speech therapist and an audiologist make this assessment and evaluation of the child The child's development is evaluated to determine if there are any delays or conditions that would indicate the need for special services.
10 Myringoplasty Surgical procedure in which a small incision is made in the eardrum to relieve pressure or allow fluid to drain from the middle ear. Native language The language of the home, i.e. the native language of children who are deaf with deaf parents is often Sign Language. Non-linear amplification Non-syndromic hearing loss C D14 A hearing aid compression strategy that varies the amount of amplification according to the specific input level. earing loss with no other organ system abnormalities. Oral An unspecific term that is sometimes used when referring to individuals with hearing loss and deafness who talk but don't necessarily use sign language. Emphasis is placed on use of residual hearing, lip reading and contextual cues to communicate using spoken language. Organ of Corti C E* The sensory organ of hearing. The outer and inner hair cells of the organ of Corti transform vibrational energy into neural energy, which is then transmitted via the VIII nerve to the brain. Osseous Spiral Lamina E A delicate bony plate that extends from the mid portion of the coiled cochlea, helping to separate scala vestibule from scala tympani. Ossicles Three small bones in the middle ear that form a bridge connecting the eardrum with the oval window. Ossicular Chain A See middle ear. Otitis externa An inflammation or infection of the outer ear or outer ear canal; swimmers ear. Otitis media * An inflammation or infection of the middle ear. Children with recurring episodes may experience fluctuating hearing loss and may be at risk for speech language delays. Fluid can be present with or without infection, and may cause temporary hearing loss, which can evolve into permanent loss. Otitis media with effusion Oto-acoustic emissions (OAE) G * An inflammation or infection of the middle ear, in which fluid is present in the middle ear. Measurement of sounds in the outer ear that are produced by outer hair cells in the cochlea. An indirect test of peripheral hearing sensitivity. A probe is placed in the ear canal for this measurement of sensorineural deafness. Otolaryngologist A medical doctor who specialises in disorders of the head and neck, especially those relating to the ear, nose and throat. Otologist An otolaryngologist who subspecialises in disorders of the ear. Otorhinolaryngologist Old term for otolaryngologist. Otosclerosis A congenital condition in which abnormal bone growth forms in the inner ear; it can cause tinnitus and deafness. Otoscope An instrument used to examine the external ear canal, eardrum and ossicles, it consists of a light and a magnifying glass.
11 Ototoxic A substance that has a bad effect on the auditory nerve or inner ear; a substance that is poisonous to the ear. Outer ear That portion of the ear that begins with the pinna and includes the ear canal. Outer hair cells E There are three rows of approximately outer hair cells. Although they are much greater in number than the inner hair cells, they receive only about 5% of the innervations of the nerve fibers from the acoustic portion of the VIII nerve. These cells contain muscle-like filaments that contract upon stimulation and fine tune the response of the basilar membrane to the movement of the travelling wave. ecause of their tuned response, healthy outer hair cells will ring following stimulation. This ringing provides the sound source for Otoacoustic Emissions. Output Refers to how much amplification is being put out by a hearing aid. Oval window Opening in the inner wall of the middle ear through which sound is passed into the inner ear. Perceptive hearing loss C Results from disorders involving sensory cells in the cochlea and/or auditory nerve fibres of the VIII cranial nerves. Peri-lingual deafness Refers to hearing loss acquired while learning a first language. Perilymph E The same as cerebro spinal fluid (CSF). Fluid in the scala media, one of the three partitions within the cochlea. It has a low potassium -K+- concentration and a high -Na+- concentration. Permanent threshold shift A change in the hair cells that permanently changes a person s hearing sensitivity. Pillars of Corti E Supporting cells that bound the tunnel of Corti. The tunnel of Corti runs the entire length of the cochlear partition. Pinna E* Auricle; the external part of the ear, composed of cartilage. Its presence on both sides of the head allows us to localize sound from the front vs. back. Our ability to localize from side to side depends on the relative intensity and relative phase of sound reaching each ear and the analysis of the phase/intensity differences within the brainstem. Pitch A The psychological response made by an observer to the physical frequency and which enables sounds to be rated on a continuum of higher or lower. Post-lingual deafness Refers to hearing loss acquired after learning a first language. Presbycusis Sensorineural hearing loss, usually gradual, caused by aging. Pre-lingual deafness Refers to hearing loss, which is congenital or acquired before acquisition of language. Profound A hearing loss of 90 decibels or more. Prothesis A device which replaces a missing part of the body or makes a part of the body work better. Pure tone A A sound in which the sound pressure changes sinusoidally with the time.
12 Pure-tone audiometry earing tests, using an audiometer, which measure a person s ability to hear pure tones. Pure-tone average (PTA) G The average hearing loss for the best two frequencies or the three frequencies of 500z, 1000z, and 2000 z. Pure-tone threshold The point at which a person is able to hear pure tones from an audiometer. Real ear measurement (REM) An audiological test that measures the actual output of the hearing aid in the ear canal. This test uses a "probe-microphone" that is placed into the ear canal along with the hearing aid and ear mould fitted in place. It assesses how effectively sound is actually being amplified by the hearing aids in the ear. It is considered a very important measurement because everyone's ear canals are shaped differently and this will effect how a hearing aid functions. Regression function A The mathematical relationship between two variables, expressed as the bestfitting straight line function. Reissner s membrane E Separates the endolymph of the scala media from the perilymph of the scala vestibuli. Resonant frequency C* The frequency at which a body will vibrate when set into free vibration. Rinne test Tuning-fork test which determines whether hearing loss is sensorineural or conductive. Round window (niche) E The round window is located within the round window niche. The round window is the most basal end of the scala tympani, and allows release of hydraulic pressure of perilymph that is caused by vibration of the stapes within the oval window. Saccule E See Vestibular Labyrinth Scala Media E One of the three partitions within the cochlea, the scala media is filled with endolymph. Scala Tympani One of the three partitions within the cochlea, filled with perilymph. The scala vestibule and the scala tympani are continuous with each other at the most apical end of the cochlear partition called the helicotrema. Scala Vestibuli E One of the three partitions within the cochlea that is filled with perilymph, which attaches via the cochlear aqueduct to the subarachnoid space. Sensorineural hearing loss The type of hearing loss caused by damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve. Sensory deprivation A The cutting off or reduction of sensory input, in one or more modalities, to the human or animal organism. Short-term memory (STM) A The mechanism presumed to underlie the retention of small amounts of information over short periods. In hearing subjects, STM is auditory in nature. Significance level A The probability that a set of experimental data can be explained as purely random variations. Low probabilities imply high levels of significance. Sign language A form of manual communication in which gestures and signs, in a specific pattern, are used to communicate. Ski-slope hearing loss C* earing for high frequencies is severely impaired, but thresholds remain
13 normal in the low frequencies. Sound pressure A Pressure is defined as the action of a force on something resisting it. In the case of sound waves the force is due to the movement of molecules in the medium of transmission. Spectrum C* A graphic representation of the distribution of frequency components in a given acoustic signal. Speech banana G The speech banana is defined as an area on the audiogram that approximately defines where typical speech sounds occur. Speechdiscrimination tests Speech-language pathologist Oral-aural tests which determine what speech sounds a person can discriminate; the listener must repeat words and sounds spoken to him. An allied health professional who measures and evaluates language and speech production abilities and clinically treats individuals with speech and language disorders. Speech reading A technique in which a hearing-impaired person watches a speaker s lips, face and gestures to determine what the person has said. Speech reception threshold (SRT) G The lowest sound intensity which allows repetition of two syllable words. This measure should be approximately the same as the best two frequency or three frequency PTA. Sperling Paradigm A Method for investigating very short-term visual traces using briefly presented two-dimensional displays. Spiral Ganglia E The cell bodies of nerve fibers that innervate the inner and outer hair cells. Stapedectomy Removal and replacement of the stapes or a portion of the stapes; used to treat otosclerosis. Stapes E The innermost of the three small bones in the middle ear. The stapes has a footplate and a superstructure. Its footplate is seated in the oval window, which separates the middle ear from perilymph of the inner ear. As the long process of the incus vibrates, so does the footplate of the stapes. ecause the vibrating area of the tympanic membrane is larger than the area of the stapes, incoming sound is given a significant boost in energy of over 20d. This is referred to as the hydraulic advantage. Stria Vascularis E A highly vascularized layer of cells that is thought to secrete endolymph. Swimmer s ear Otitis externa; an inflammation or infection of the outer ear. Syndromic earing loss D13 Associated with other organ system abnormalities. Tachistoscope A Device for presenting subjects with very brief visual stimuli. Tactile aids A type of assistive communication device that emits a vibration or "tactile" signal to indicate the presence of sound(s). It is worn on the body and triggers the sense of touch or feeling to draw attention to information that cannot be heard by the individual with hearing loss. Tectorial Membrane E A delicate, flexible, gelatinous membrane overlying the sensory receptive inner and outer hair cells.
14 Telecommunication devices dor the deaf TDD Telecommunications Device for the Deaf; an assistive device with which the deaf can communicate over the telephone; typewritten messages are sent and received over the phone lines. Telecaptioning A system which allows the deaf and hearing impaired to understand the spoken portion of audiovisual programs; dialogue appears in written form below the picture. Telecoil A circuitry option that can be added to a hearing aid; the telecoil makes the hearing aid circuitry compatible with external electronic devices like the telephone. Temporal bone The large bone on either side of the head; includes the mastoid bone. Temporary threshold shift A temporary change in the hair cells as a response to noise that temporarily changes a person s hearing sensitivity. Threshold C* Threshold is the level at which a stimulus or change in stimulus is just sufficient to produce a sensation or an effect. Timbre A The characteristic quality or distinctiveness which differentiates the perception of sounds with similar acoustic characteristics. Tinnitus A ringing or buzzing in the ear. Total communication An approach to communication for the deaf in which the deaf individual is encouraged to use any form of communication available to him, including sign language, speech, hearing aids, assistive listening devices and speech reading. Tunnel of Corti E A space filled with endolymph that is bordered by the pillars of Corti and basilar membrane. Tympanic membrane E The eardrum; a flat membrane that separates the outer ear canal from the middle ear and carries sound vibrations to the bones of the middle ear. The tympanic membrane actually has three layers, with the outer layer continuous with the skin of the outer ear canal. The upper portion of the TM is called pars flaccida, while the lower portion is called the pars tensa. The central portion of the pars tensa provides the active vibrating area in response to sound. The TM is a continually growing structure, which allows it to close if it has a hole in it and to extrude a ventilation tube. Tympanogram A pressure or "impedance" test that tells how the ear canal, eardrum, eustachian tube, and middle ear bones are working. It is not a hearing test. Tympanometer Machine which tests the function of the eardrum or middle ear. Tymponometry G Measurement of the ability of the eardrum to move when positive and negative pressure are present in the ear canal. Type A: Normal. Type : Flat tympanogram, usually indicating fluid in the middle ear. Type C: Peak at negative pressure, indicating Eustachian tube dysfunction. Tympanoplasty Surgical operation on the eardrum or ossicles to restore or improve hearing; used to repair a broken eardrum. Tympanostomy Surgical implantation of tubes in the eardrum used to prevent a build up of air pressure and fluid in the middle ear and, thus, prevent recurrent middle-ear infections.
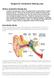
15 Unilateral One-sided; in one ear. Unilateral hearing loss Unilateral presentation A A mild to profound hearing loss in one ear. Presentation of a stimulus to one side only of a subject s visual field. Utricle E See Vestibular Labyrinth Variance A A mathematical estimate of the variation within a given set of experimental data. Vertigo Dizziness Vestibular Labyrinth E The vestibular labyrinth is comprised of the saccule and utricle, sense organs of balance which inform the brain about our linear position in space. The horizontal, anterior, and posterior semi-circular canals are also part of our vestibular labyrinth, and inform our brains about rotational movement in space. VII Nerve E See Facial Nerve. VIII Nerve E See Auditory Nerve. Visual Reinforcement Audiometry (VRA) A method of assessment in which the child is conditioned to look at a toy that lights each time he or she hears a sound; used with young children. Webster s test Tuning-fork test which determines which ear functions better. Word recognition score G In percent correct, the ability to repeat single-syllable words presented at a comfortable loudness level. Usually, 25-word or 50-word lists are used. The words can either be recorded (preferred) or be presented through live voice. Pictures cochlea F
16 Drum F External ear F air cell F Middle Ear F
17 Ossicles F A) Rodda, Michael & Carl Grove Language, Cognition and Deafness. London: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Publishers. p ) ay, Jennifer earing Loss. Questions you have Answers you need. Pennsylvania: People s Medical Society. p C) Oticon Encyclopedia. C_Atlas!Aboutearing/_Index. 28 May D) Swartz, Sue Choices in Deafness. A Parent s Guide to Communication Options. United States: Woodbine ouse. E) Anatomical Tour of the Ear. Atlantic Coast Ear Specialists, P.C May F) ow the Ear Works May G) A Lossary of Some Audiologic Terms July ) ands & Voices de Julho *) Personal adaptation of information
A diagram of the ear s structure. The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal.
 A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
So, how do we hear? outer middle ear inner ear
 The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine
 Physiological Basis of Hearing Tests By Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Introduction Def: Hearing is the ability to perceive certain pressure vibrations in the
Physiological Basis of Hearing Tests By Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Introduction Def: Hearing is the ability to perceive certain pressure vibrations in the
Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884. www.childrensent.com
 Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com You just found out your child has a hearing loss. You know what the Audiologist explained to you, but it is hard to keep track of all the new
Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com You just found out your child has a hearing loss. You know what the Audiologist explained to you, but it is hard to keep track of all the new
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06)
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06) 1. Briefly review the anatomy of the cochlea. What is the cochlear blood supply? SW 2. Discuss the effects of the pinna, head and ear canal on the transmission
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06) 1. Briefly review the anatomy of the cochlea. What is the cochlear blood supply? SW 2. Discuss the effects of the pinna, head and ear canal on the transmission
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary
 X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
Your Hearing ILLUMINATED
 Your Hearing ILLUMINATED INFORMATION FROM YOUR HEARING CARE PROFESSIONAL REDISCOVER your hearing and reconnect 1 with the important things you might have been missing. Your sense of hearing is a vital
Your Hearing ILLUMINATED INFORMATION FROM YOUR HEARING CARE PROFESSIONAL REDISCOVER your hearing and reconnect 1 with the important things you might have been missing. Your sense of hearing is a vital
Hearing Aids. What Is a Hearing Aid? How Common Is Hearing Loss and What Causes It? How Do We Hear?
 Hearing Aids What Is a Hearing Aid? A hearing aid is an electronic, battery-operated device that amplifies and changes sound to allow for improved communication. Hearing aids receive sound through a microphone,
Hearing Aids What Is a Hearing Aid? A hearing aid is an electronic, battery-operated device that amplifies and changes sound to allow for improved communication. Hearing aids receive sound through a microphone,
SEMI-IMPLANTABLE AND FULLY IMPLANTABLE MIDDLE EAR HEARING AIDS
 Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be read in its
Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be read in its
Hearing Tests And Your Child
 HOW EARLY CAN A CHILD S HEARING BE TESTED? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
HOW EARLY CAN A CHILD S HEARING BE TESTED? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
Diseases of the middle ear
 Diseases of the middle ear Acute Suppurative Otitis Media: Acute suppurative otitis media may be viral or bacterial and is accompanied by signs of pain, pressure sensation, diminished hearing and occasional
Diseases of the middle ear Acute Suppurative Otitis Media: Acute suppurative otitis media may be viral or bacterial and is accompanied by signs of pain, pressure sensation, diminished hearing and occasional
Getting Started Kei Te Timata
 Getting Started Kei Te Timata AN INTRODUCTION FOR THE FAMILIES AND WHANAU OF CHILDREN DIAGNOSED WITH A HEARING LOSS. THIS IS A JOINT PROJECT BY DEAF EDUCATION AOTEAROA NEW ZEALAND AND THE NATIONAL AUDIOLOGY
Getting Started Kei Te Timata AN INTRODUCTION FOR THE FAMILIES AND WHANAU OF CHILDREN DIAGNOSED WITH A HEARING LOSS. THIS IS A JOINT PROJECT BY DEAF EDUCATION AOTEAROA NEW ZEALAND AND THE NATIONAL AUDIOLOGY
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology
 Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
Hearing Tests And Your Child
 How Early Can A Child s Hearing Be Tested? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
How Early Can A Child s Hearing Be Tested? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan
 Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan Definition Deaf A deaf person is one whose hearing disability precludes successful processing of linguistic information
Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan Definition Deaf A deaf person is one whose hearing disability precludes successful processing of linguistic information
Presbycusis. What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis?
 Presbycusis What is presbycusis? Presbycusis is the loss of hearing that gradually occurs in most individuals as they grow older. Hearing loss is a common disorder associated with aging. About 30-35 percent
Presbycusis What is presbycusis? Presbycusis is the loss of hearing that gradually occurs in most individuals as they grow older. Hearing loss is a common disorder associated with aging. About 30-35 percent
What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who has a hearing loss? How does hearing work?
 This e-book will answer the following questions: What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis? What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who
This e-book will answer the following questions: What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis? What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice
 AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005
 EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY Andrew P. McGrath, AuD
 PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY Andrew P. McGrath, AuD Pure tone audiometry is the standard behavioral assessment of an individual s hearing. The results of pure tone audiometry are recorded on a chart or form called
PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY Andrew P. McGrath, AuD Pure tone audiometry is the standard behavioral assessment of an individual s hearing. The results of pure tone audiometry are recorded on a chart or form called
Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video. IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
 Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video (Notes are also available for Video segments: Common Mistakes and FAQs) IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video (Notes are also available for Video segments: Common Mistakes and FAQs) IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
Section 4. Hearing loss and hearing tests
 Section 4 Hearing loss and hearing tests How we hear Outer Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear 4. 7. 8. 1. 3. 6. 2. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Ear canal Ear drum Middle ear cavity Middle ear bones the malleus, incus,
Section 4 Hearing loss and hearing tests How we hear Outer Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear 4. 7. 8. 1. 3. 6. 2. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Ear canal Ear drum Middle ear cavity Middle ear bones the malleus, incus,
Middle ear conditions
 Middle ear conditions Middle ear conditions This factsheet is part of our Ears and ear problems range. It is written for people who have been diagnosed with a condition that affects the middle ear. Read
Middle ear conditions Middle ear conditions This factsheet is part of our Ears and ear problems range. It is written for people who have been diagnosed with a condition that affects the middle ear. Read
Hearing Conservation Procedures
 Hearing Conservation Procedures Purpose The University of Regina is committed to providing a safe and healthy work and educational environment for all members of the University community by ensuring that
Hearing Conservation Procedures Purpose The University of Regina is committed to providing a safe and healthy work and educational environment for all members of the University community by ensuring that
Hearcentres Guide to Hearing Aid Terminology
 Hearcentres Guide to Hearing Aid Terminology Sophisticated modern hearing aids use a number of complicated technologies and techniques to ensure great improvements in hearing. Not only are the terms used
Hearcentres Guide to Hearing Aid Terminology Sophisticated modern hearing aids use a number of complicated technologies and techniques to ensure great improvements in hearing. Not only are the terms used
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss
 Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss What is conductive hearing loss Conductive hearing loss is a form of hearing loss due to abnormalities in mobile portions of the ear. Theses are the movable parts (including
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss What is conductive hearing loss Conductive hearing loss is a form of hearing loss due to abnormalities in mobile portions of the ear. Theses are the movable parts (including
Sound Perception. Sensitivity to Sound. Sensitivity to Sound 1/9/11. Not physically sensitive to all possible sound frequencies Range
 Sound Perception Similarities between sound and light perception Characteristics of sound waves Wavelength = Pitch Purity = Timbre Amplitude = loudness Sensitivity to Sound Not physically sensitive to
Sound Perception Similarities between sound and light perception Characteristics of sound waves Wavelength = Pitch Purity = Timbre Amplitude = loudness Sensitivity to Sound Not physically sensitive to
Questions and Answers for Parents
 Questions and Answers for Parents There are simple, inexpensive tests available to detect hearing impairment in infants during the first days of life. In the past, most hearing deficits in children were
Questions and Answers for Parents There are simple, inexpensive tests available to detect hearing impairment in infants during the first days of life. In the past, most hearing deficits in children were
Audiology Services. Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS
 Audiology Services Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS What are we going to cover today? General overview of the ear Hearing loss Hearing assessments, results Hearing aids Paediatric
Audiology Services Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS What are we going to cover today? General overview of the ear Hearing loss Hearing assessments, results Hearing aids Paediatric
Ear Disorders and Problems
 Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
TOOLS for DEVELOPING Communication PLANS
 TOOLS for DEVELOPING Communication PLANS Students with disabilities, like all students, must have the opportunity to fully participate in all aspects of their education. Being able to effectively communicate
TOOLS for DEVELOPING Communication PLANS Students with disabilities, like all students, must have the opportunity to fully participate in all aspects of their education. Being able to effectively communicate
8.Audiological Evaluation
 8. A U D I O L O G I C A L E V A L U A T I O N 8.Audiological Evaluation The external ear of the child with Progeria Behavioral testing for assessing hearing thresholds Objective electrophysiologic tests
8. A U D I O L O G I C A L E V A L U A T I O N 8.Audiological Evaluation The external ear of the child with Progeria Behavioral testing for assessing hearing thresholds Objective electrophysiologic tests
CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS
 CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
1/26/2011. 50% of deafness and hearing impairment is avoidable through prevention, early diagnosis, and management.
 Hearing Impairment Roseann Mulligan, DDS, MS Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry of the University of Southern California 1 JAMA, July 4, 2007 Vol 298, No. 1 2 278 million - moderate to profound bilateral
Hearing Impairment Roseann Mulligan, DDS, MS Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry of the University of Southern California 1 JAMA, July 4, 2007 Vol 298, No. 1 2 278 million - moderate to profound bilateral
- Review ear anatomy. Evaluation of Hearing. - Specific causes of hearing loss
 Hearing Loss in Primary Care Aaron C. Moberly, MD Otolaryngologist Department of Otorhinolaryngology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Overview - Review ear anatomy - Evaluation of hearing
Hearing Loss in Primary Care Aaron C. Moberly, MD Otolaryngologist Department of Otorhinolaryngology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Overview - Review ear anatomy - Evaluation of hearing
A Hearing Aid Primer
 A Hearing Aid Primer Includes: Definitions Photographs Hearing Aid Styles, Types, and Arrangements WROCC Outreach Site at Western Oregon University This hearing aid primer is designed to define the differences
A Hearing Aid Primer Includes: Definitions Photographs Hearing Aid Styles, Types, and Arrangements WROCC Outreach Site at Western Oregon University This hearing aid primer is designed to define the differences
My child has a hearing loss
 My child has a hearing loss A guide for parents Content You are not alone 3 Hearing impairment 5 Methods of testing hearing 6 Audiogram 7 Types and causes of hearing loss 8 Degree of hearing loss 10 Where
My child has a hearing loss A guide for parents Content You are not alone 3 Hearing impairment 5 Methods of testing hearing 6 Audiogram 7 Types and causes of hearing loss 8 Degree of hearing loss 10 Where
Management of Deafness in the Elderly
 Management of Deafness in the Elderly Mrs R Kayarkar Consultant ENT Surgeon Mid Yorks NHS Trust British Geriatric Society Meeting 18.9.2013 Effects of hearing loss Embarrassment, loss of confidence, anger
Management of Deafness in the Elderly Mrs R Kayarkar Consultant ENT Surgeon Mid Yorks NHS Trust British Geriatric Society Meeting 18.9.2013 Effects of hearing loss Embarrassment, loss of confidence, anger
Unilateral (Hearing Loss in One Ear) Hearing Loss Guidance
 Unilateral (Hearing Loss in One Ear) Hearing Loss Guidance Indiana s Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Program Before universal newborn hearing screening, most children with unilateral hearing loss
Unilateral (Hearing Loss in One Ear) Hearing Loss Guidance Indiana s Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Program Before universal newborn hearing screening, most children with unilateral hearing loss
EARLY INTERVENTION: COMMUNICATION AND LANGUAGE SERVICES FOR FAMILIES OF DEAF AND HARD-OF-HEARING CHILDREN
 EARLY INTERVENTION: COMMUNICATION AND LANGUAGE SERVICES FOR FAMILIES OF DEAF AND HARD-OF-HEARING CHILDREN Our child has a hearing loss. What happens next? What is early intervention? What can we do to
EARLY INTERVENTION: COMMUNICATION AND LANGUAGE SERVICES FOR FAMILIES OF DEAF AND HARD-OF-HEARING CHILDREN Our child has a hearing loss. What happens next? What is early intervention? What can we do to
62 Hearing Impaired MI-SG-FLD062-02
 62 Hearing Impaired MI-SG-FLD062-02 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1: General Information About the MTTC Program and Test Preparation OVERVIEW OF THE TESTING PROGRAM... 1-1 Contact Information Test Development
62 Hearing Impaired MI-SG-FLD062-02 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1: General Information About the MTTC Program and Test Preparation OVERVIEW OF THE TESTING PROGRAM... 1-1 Contact Information Test Development
Paediatric Hearing Assessment
 Information for parents Paediatric Hearing Assessment Hearing assessment of infants is limited by their ability to respond to sounds. This is determined by both the development of the hearing system and
Information for parents Paediatric Hearing Assessment Hearing assessment of infants is limited by their ability to respond to sounds. This is determined by both the development of the hearing system and
Noise: Impact on Hearing; Regulation
 Noise: Impact on Hearing; Regulation EOH 466A Fall 2008 Mechanism of Hearing Sound waves collected, focused by the outer ear. Humans have little control over muscles in outer ear. Many animals have the
Noise: Impact on Hearing; Regulation EOH 466A Fall 2008 Mechanism of Hearing Sound waves collected, focused by the outer ear. Humans have little control over muscles in outer ear. Many animals have the
1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera 10 Choroid
 Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
Light wear for a powerful hearing. Bone Conduction Headset
 Light wear for a powerful hearing Bone Conduction Headset 2 Light wear for a powerful hearing Melody Flex, the new bone conduction headset is AUTEL s solution to improve hearing quality of those affected
Light wear for a powerful hearing Bone Conduction Headset 2 Light wear for a powerful hearing Melody Flex, the new bone conduction headset is AUTEL s solution to improve hearing quality of those affected
Hearing Loss in Geriatric Primary Care Mary Ann Forciea MD Josh Uy MD
 Hearing Loss in Geriatric Primary Care Mary Ann Forciea MD Josh Uy MD Q: In my office practice, I screen for hearing loss with A Level of difficulty in office conversation Questionnaire Hand held hldaudiometer
Hearing Loss in Geriatric Primary Care Mary Ann Forciea MD Josh Uy MD Q: In my office practice, I screen for hearing loss with A Level of difficulty in office conversation Questionnaire Hand held hldaudiometer
A Guide to Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs) for Physicians
 A Guide to Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs) for Physicians Introduction Hearing loss is not uncommon in children and adults. According to recent estimates, 31.5 million people in the United States report difficulty
A Guide to Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs) for Physicians Introduction Hearing loss is not uncommon in children and adults. According to recent estimates, 31.5 million people in the United States report difficulty
REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN AUDIOLOGY (MSc[Audiology])
![REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN AUDIOLOGY (MSc[Audiology]) REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN AUDIOLOGY (MSc[Audiology])](/thumbs/27/10327872.jpg) 224 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN AUDIOLOGY (MSc[Audiology]) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain a reference to
224 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN AUDIOLOGY (MSc[Audiology]) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain a reference to
Hearing Tests for Children with Multiple or Developmental Disabilities by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Hearing Tests for Children with Multiple or Developmental Disabilities by Susan Agrawal Hearing impairment is a common problem in children with developmental disabilities or who have
www.complexchild.com Hearing Tests for Children with Multiple or Developmental Disabilities by Susan Agrawal Hearing impairment is a common problem in children with developmental disabilities or who have
Pediatric Hearing Assessment
 Pediatric Hearing Assessment Stanton Jones Key Points This chapter outlines the methods of hearing assessment that are appropriate for children from birth to adolescence. The importance of timely referral
Pediatric Hearing Assessment Stanton Jones Key Points This chapter outlines the methods of hearing assessment that are appropriate for children from birth to adolescence. The importance of timely referral
The Role of the Educational Audiologist 2014. Introduction:
 The Role of the Educational Audiologist 2014. Introduction: As the current CHAIR of the BAEA I felt that it was time for the Role of the Educational Audiologist to be updated. There has been a period of
The Role of the Educational Audiologist 2014. Introduction: As the current CHAIR of the BAEA I felt that it was time for the Role of the Educational Audiologist to be updated. There has been a period of
5th Congress of Alps-Adria Acoustics Association NOISE-INDUCED HEARING LOSS
 5th Congress of Alps-Adria Acoustics Association 12-14 September 2012, Petrčane, Croatia NOISE-INDUCED HEARING LOSS Davor Šušković, mag. ing. el. techn. inf. davor.suskovic@microton.hr Abstract: One of
5th Congress of Alps-Adria Acoustics Association 12-14 September 2012, Petrčane, Croatia NOISE-INDUCED HEARING LOSS Davor Šušković, mag. ing. el. techn. inf. davor.suskovic@microton.hr Abstract: One of
MODEL SUPERBILL for AUDIOLOGY
 MODEL SUPERBILL for AUDIOLOGY The following is a model of a superbill which could be used by an audiology practice when billing private health plans. This sample is not meant to dictate which services
MODEL SUPERBILL for AUDIOLOGY The following is a model of a superbill which could be used by an audiology practice when billing private health plans. This sample is not meant to dictate which services
Cochlear Implant and Associated Technologies for Hearing
 Cochlear Implant and Associated Technologies for Hearing Mada Assistive Technology Center Tel: 00 974 44594050 Fax: 00 974 44594051 Email: info@mada.org.qa What is a cochlear implant? Cochlear implants
Cochlear Implant and Associated Technologies for Hearing Mada Assistive Technology Center Tel: 00 974 44594050 Fax: 00 974 44594051 Email: info@mada.org.qa What is a cochlear implant? Cochlear implants
Noise. CIH Review PDC March 2012
 Noise CIH Review PDC March 2012 Learning Objectives Understand the concept of the decibel, decibel determination, decibel addition, and weighting Know the characteristics of frequency that are relevant
Noise CIH Review PDC March 2012 Learning Objectives Understand the concept of the decibel, decibel determination, decibel addition, and weighting Know the characteristics of frequency that are relevant
Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians
 Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received for such services is a
Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received for such services is a
Byron's Hudson Valley Hearing Aid Centers Kingston/Lake Katrine 845-336-0108 Poughkeepsie 845-485-0168 Your hearing Journey
 Your hearing Journey Don't miss out on the joys of life, your hearing is our concern. Trust our experts to enhance your quality of life. Ask Yourself: Do you have difficulty following a conversation in
Your hearing Journey Don't miss out on the joys of life, your hearing is our concern. Trust our experts to enhance your quality of life. Ask Yourself: Do you have difficulty following a conversation in
BONE-CONDUCTION HEARING AIDS
 BONE-CONDUCTION HEARING AIDS Introduction Conventional hearing aids fit in the ear canal and amplify sounds, which the hearing aid user then hears in the normal way. However, these hearing aids are not
BONE-CONDUCTION HEARING AIDS Introduction Conventional hearing aids fit in the ear canal and amplify sounds, which the hearing aid user then hears in the normal way. However, these hearing aids are not
Occupational Noise Induced Hearing Loss
 Occupational Noise Induced Hearing Loss M Baxter FRACS SISA Adelaide June 2014 ENT in Personal Injury Claims EAR Hearing Loss -main, Dizziness Nose Injuries ->cosmesis,breathing: Loss of sense of smell:
Occupational Noise Induced Hearing Loss M Baxter FRACS SISA Adelaide June 2014 ENT in Personal Injury Claims EAR Hearing Loss -main, Dizziness Nose Injuries ->cosmesis,breathing: Loss of sense of smell:
Diagnostic Tests for Vestibular Problems By the Vestibular Disorders Association
 PO BOX 13305 PORTLAND, OR 97213 FAX: (503) 229-8064 (800) 837-8428 INFO@VESTIBULAR.ORG WWW.VESTIBULAR.ORG Diagnostic Tests for Vestibular Problems By the Vestibular Disorders Association The inner ear
PO BOX 13305 PORTLAND, OR 97213 FAX: (503) 229-8064 (800) 837-8428 INFO@VESTIBULAR.ORG WWW.VESTIBULAR.ORG Diagnostic Tests for Vestibular Problems By the Vestibular Disorders Association The inner ear
Veterans UK Leaflet 10. Notes about War Pension claims for deafness
 Veterans UK Leaflet 10 Notes about War Pension claims for deafness 1 About this leaflet About this leaflet This leaflet tells you how claims for deafness are decided and gives you some information about
Veterans UK Leaflet 10 Notes about War Pension claims for deafness 1 About this leaflet About this leaflet This leaflet tells you how claims for deafness are decided and gives you some information about
The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software
 Chapter 10 Auditory Content The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software David Bernstein Jones and Bartlett Publishers www.jbpub.com David Bernstein (jbpub.com) Multimedia Software Jones and Bartlett
Chapter 10 Auditory Content The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software David Bernstein Jones and Bartlett Publishers www.jbpub.com David Bernstein (jbpub.com) Multimedia Software Jones and Bartlett
Noice induced hearing loss, Ototoxic drugs, Meniers disease, Rotataory vertigo, Sensorineural hearing loss, Tinnitis, Infections, Acoustic neuroma,
 Disorders of hearing and balance LEARNING OBJECTIVE At the end of lecture student must be able to know, Hearing disorders, Types of hearing disorders, Functional classification, Causes, Middle ear disorders,
Disorders of hearing and balance LEARNING OBJECTIVE At the end of lecture student must be able to know, Hearing disorders, Types of hearing disorders, Functional classification, Causes, Middle ear disorders,
Audiology (0340) Test at a Glance. About this test. Test Guide Available. See Inside Back Cover. Test Code 0340
 Audiology (0340) Test Guide Available See Inside Back Cover Test at a Glance Test Name Audiology Test Code 0340 Time 2 hours Number of Questions 150 Format Multiple-choice questions Approximate Approximate
Audiology (0340) Test Guide Available See Inside Back Cover Test at a Glance Test Name Audiology Test Code 0340 Time 2 hours Number of Questions 150 Format Multiple-choice questions Approximate Approximate
ear health How to look after your ears and cope with tinnitus, dizziness and balance problems
 Ears and ear health How to look after your ears and cope with tinnitus, dizziness and balance problems We re RNID, the charity working to create a world where deafness or hearing loss do not limit or determine
Ears and ear health How to look after your ears and cope with tinnitus, dizziness and balance problems We re RNID, the charity working to create a world where deafness or hearing loss do not limit or determine
More information >>> HERE <<<
 More information >>> HERE http://urlzz.org/hearloss/pdx/dcli864/ Tags: ## best way to get cheapest natural methods to
More information >>> HERE http://urlzz.org/hearloss/pdx/dcli864/ Tags: ## best way to get cheapest natural methods to
Hearing Screenings in Arkansas Schools. Education for School Nurses in Arkansas Updated Summer 2012
 Hearing Screenings in Arkansas Schools Education for School Nurses in Arkansas Updated Summer 2012 The planning committee & faculty attest that NO relevant financial, professional or personal conflict
Hearing Screenings in Arkansas Schools Education for School Nurses in Arkansas Updated Summer 2012 The planning committee & faculty attest that NO relevant financial, professional or personal conflict
Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians
 1/1/2015 Hearing Testing Coding Fact Sheet Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received
1/1/2015 Hearing Testing Coding Fact Sheet Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received
Michigan Ear Institute. Cochlear Implant.
 Michigan Ear Institute Cochlear Implant www.michiganear.com DOCTORS Jack M. Kartush, MD Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Michael J. LaRouere, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS Eric W. Sargent, MD, FACS Seilesh C. Babu,
Michigan Ear Institute Cochlear Implant www.michiganear.com DOCTORS Jack M. Kartush, MD Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Michael J. LaRouere, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS Eric W. Sargent, MD, FACS Seilesh C. Babu,
3030. Eligibility Criteria.
 3030. Eligibility Criteria. 5 CA ADC 3030BARCLAYS OFFICIAL CALIFORNIA CODE OF REGULATIONS Barclays Official California Code of Regulations Currentness Title 5. Education Division 1. California Department
3030. Eligibility Criteria. 5 CA ADC 3030BARCLAYS OFFICIAL CALIFORNIA CODE OF REGULATIONS Barclays Official California Code of Regulations Currentness Title 5. Education Division 1. California Department
Table of Contents SOUND STEPS SOUND STEPS. Hawaii State Resource Guide for Families of Children with Hearing Loss
 Table of Contents SOUND STEPS SOUND STEPS Hawaii State Resource Guide for Families of Children with Hearing Loss Hawaii State Resource Guide for Families of Children with Hearing Loss Hawaii State Department
Table of Contents SOUND STEPS SOUND STEPS Hawaii State Resource Guide for Families of Children with Hearing Loss Hawaii State Resource Guide for Families of Children with Hearing Loss Hawaii State Department
GONCA SENNAROĞLU PhD LEVENT SENNAROĞLU MD. Department of Otolaryngology Hacettepe University ANKARA, TURKEY
 GONCA SENNAROĞLU PhD LEVENT SENNAROĞLU MD Department of Otolaryngology Hacettepe University ANKARA, TURKEY To present the audiological findings and rehabilitative outcomes of CI in children with cochlear
GONCA SENNAROĞLU PhD LEVENT SENNAROĞLU MD Department of Otolaryngology Hacettepe University ANKARA, TURKEY To present the audiological findings and rehabilitative outcomes of CI in children with cochlear
Counseling parents for the use of hearing aids
 Counseling parents for the use of hearing aids AUTHORS NACHIKETA ROUT ANIKET PANDIT (Under Revision) Kindly Post your Suggestions/ comments which can be incorporated for necessary modification at nachiketa_raut@yahoo.com
Counseling parents for the use of hearing aids AUTHORS NACHIKETA ROUT ANIKET PANDIT (Under Revision) Kindly Post your Suggestions/ comments which can be incorporated for necessary modification at nachiketa_raut@yahoo.com
The Effects of Ultrasonic Sound Generated by Ultrasonic Cleaning Systems on Human Hearing and Physiology
 The Effects of Ultrasonic Sound Generated by Ultrasonic Cleaning Systems on Human Hearing and Physiology Questions about the effects of ultrasonic energy on hearing and other human physiology arise from
The Effects of Ultrasonic Sound Generated by Ultrasonic Cleaning Systems on Human Hearing and Physiology Questions about the effects of ultrasonic energy on hearing and other human physiology arise from
Hearing Aids - Adult HEARING AIDS - ADULT HS-159. Policy Number: HS-159. Original Effective Date: 3/18/2010. Revised Date(s): 3/18/2011; 3/1/2012
 Harmony Behavioral Health, Inc. Harmony Behavioral Health of Florida, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. HealthEase of Florida, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance
Harmony Behavioral Health, Inc. Harmony Behavioral Health of Florida, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. HealthEase of Florida, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance
COCHLEAR NERVE APLASIA : THE AUDIOLOGIC PERSPECTIVE A CASE REPORT. Eva Orzan, MD Pediatric Audiology University Hospital of Padova, Italy
 COCHLEAR NERVE APLASIA : THE AUDIOLOGIC PERSPECTIVE A CASE REPORT Eva Orzan, MD Pediatric Audiology University Hospital of Padova, Italy Congenital absence or underdevelopment of the cochlear nerve has
COCHLEAR NERVE APLASIA : THE AUDIOLOGIC PERSPECTIVE A CASE REPORT Eva Orzan, MD Pediatric Audiology University Hospital of Padova, Italy Congenital absence or underdevelopment of the cochlear nerve has
Information for parents. Deafness
 About this publication This is a guide for parents with young children who have recently been told that their child is deaf, or who are in the process of getting a diagnosis. It was developed by the Early
About this publication This is a guide for parents with young children who have recently been told that their child is deaf, or who are in the process of getting a diagnosis. It was developed by the Early
HEARING SCREENING: PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY
 HEARING SCREENING: PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY QUALIFIED SCREENERS 7-005.01 For the purposes of the school officials verifying that a qualified screener is carrying out the required screening activity, the qualified
HEARING SCREENING: PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY QUALIFIED SCREENERS 7-005.01 For the purposes of the school officials verifying that a qualified screener is carrying out the required screening activity, the qualified
Department of Developmental Services Terrence W. Macy, Ph.D., Commissioner Linda Goodman, System Director
 Acknowledgments This guideline was revised and updated in July 2012 to add more current information and resources. The Connecticut Birth to Three System would like to thank the following people who worked
Acknowledgments This guideline was revised and updated in July 2012 to add more current information and resources. The Connecticut Birth to Three System would like to thank the following people who worked
GP Masterclass ENT Hillingdon. Mr Arvind Singh Consultant ENT Surgeon Hillingdon, Mount Vernon, Northwick Park and Central Middlesex Hospitals
 GP Masterclass ENT Hillingdon Mr Arvind Singh Consultant ENT Surgeon Hillingdon, Mount Vernon, Northwick Park and Central Middlesex Hospitals Overview Hearing Loss Otitis Media Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
GP Masterclass ENT Hillingdon Mr Arvind Singh Consultant ENT Surgeon Hillingdon, Mount Vernon, Northwick Park and Central Middlesex Hospitals Overview Hearing Loss Otitis Media Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
Guide for families of infants and children with hearing loss
 With early detection, Early Intervention can begin! Guide for families of infants and children with hearing loss Birth to 3 2008 Cover photograph Geneva Marie Durgin was born January 20, 2007. She lives
With early detection, Early Intervention can begin! Guide for families of infants and children with hearing loss Birth to 3 2008 Cover photograph Geneva Marie Durgin was born January 20, 2007. She lives
Infant hearing screening will not hurt your baby, and will only take between 5 and 20 minutes. Ideally it is done whilst baby is asleep or settled.
 Early diagnosis of hearing loss will make a difference to your baby s life. Significant hearing loss is the most common condition present at birth. In the private sector, 3 in every 1000 babies are born
Early diagnosis of hearing loss will make a difference to your baby s life. Significant hearing loss is the most common condition present at birth. In the private sector, 3 in every 1000 babies are born
The essentials of managing. an important role at all stages of life. In. early childhood, near-normal hearing in
 MedicineToday 2015; 16(2): 31-42 PEER REVIEWED FEATURE 2 CPD POINTS The essentials of managing Hearing loss RICH LEGG/ISTOCKPHOTO Key points Hearing loss is very MELVILLE DA CRUZ FRACS, MSc, MD Hearing
MedicineToday 2015; 16(2): 31-42 PEER REVIEWED FEATURE 2 CPD POINTS The essentials of managing Hearing loss RICH LEGG/ISTOCKPHOTO Key points Hearing loss is very MELVILLE DA CRUZ FRACS, MSc, MD Hearing
Noise and Hearing Protection
 Noise and Hearing Protection Noise and Hearing Safety Training This training module is designed to teach you about the purpose and benefits of a hearing conservation program. After completing the training,
Noise and Hearing Protection Noise and Hearing Safety Training This training module is designed to teach you about the purpose and benefits of a hearing conservation program. After completing the training,
A PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE PROFILE
 A PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE PROFILE FOR HEARING HEALTH PROFESSIONALS The International Hearing Society has adopted the following practice profile as a comprehensive declaration of dispensing characteristics
A PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE PROFILE FOR HEARING HEALTH PROFESSIONALS The International Hearing Society has adopted the following practice profile as a comprehensive declaration of dispensing characteristics
Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control
 EVERYONE'S RESPONSIBILITY Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control February 2007 Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control Workplace Safety & Health Division 200 401 York Avenue
EVERYONE'S RESPONSIBILITY Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control February 2007 Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control Workplace Safety & Health Division 200 401 York Avenue
NIHL - understanding audiograms and medical causation
 NIHL - understanding audiograms and medical causation Darrell Smith Partner, BLM Manchester Birmingham Cardiff Leeds Liverpool London Manchester Southampton Stockton-on-Tees How the ear works The human
NIHL - understanding audiograms and medical causation Darrell Smith Partner, BLM Manchester Birmingham Cardiff Leeds Liverpool London Manchester Southampton Stockton-on-Tees How the ear works The human
Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing.
 The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
HEARING LOSS AND LANGUAGE DELAY IN LITTLE CHILDREN. Prepared by Jane H. LeBlanc, M.S., M.S.P. Audiologist, CCC-A Speech Language Pathologist, CCC-SLP
 HEARING LOSS AND LANGUAGE DELAY IN LITTLE CHILDREN Prepared by Jane H. LeBlanc, M.S., M.S.P. Audiologist, CCC-A Speech Language Pathologist, CCC-SLP This is being written to provide information to concerned
HEARING LOSS AND LANGUAGE DELAY IN LITTLE CHILDREN Prepared by Jane H. LeBlanc, M.S., M.S.P. Audiologist, CCC-A Speech Language Pathologist, CCC-SLP This is being written to provide information to concerned
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES PROCEDURE CODES
 NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES PROCEDURE CODES Table of Contents WHAT S NEW FOR THE 2016 MANUAL? --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES PROCEDURE CODES Table of Contents WHAT S NEW FOR THE 2016 MANUAL? --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
My child has a hearing loss. A guide for parents
 My child has a hearing loss A guide for parents 2 Donna S. Wayner, Ph.D., author of Hearing and Learning: A Guide for Helping Children, prepared the material in this booklet. Copies of her various books
My child has a hearing loss A guide for parents 2 Donna S. Wayner, Ph.D., author of Hearing and Learning: A Guide for Helping Children, prepared the material in this booklet. Copies of her various books
PROTECT YOUR HEARING
 PROTECT YOUR HEARING Original idea from David Carlisle Aviation can be a noisy business that can assault tour ears and chip away at your ability to hear clearly. Prevention is your only effective defense.
PROTECT YOUR HEARING Original idea from David Carlisle Aviation can be a noisy business that can assault tour ears and chip away at your ability to hear clearly. Prevention is your only effective defense.
Children s Hearing Aid Clinic
 Children s Hearing Aid Clinic Enclosed are a number of information sheets. Each has a separate heading. Don t feel that you have to read them all at one go. These sheets are not intended to be the answer
Children s Hearing Aid Clinic Enclosed are a number of information sheets. Each has a separate heading. Don t feel that you have to read them all at one go. These sheets are not intended to be the answer
Getting a Cochlear Implant
 Cochlear Implants Getting a Cochlear Implant the journey to better hearing 1 All of life s journeys depend on taking the first step determining how to get from where you are to where you want to go. This
Cochlear Implants Getting a Cochlear Implant the journey to better hearing 1 All of life s journeys depend on taking the first step determining how to get from where you are to where you want to go. This
 THE EARS IN CHARGE FOR THE PHYSICIAN Sandra L.H. Davenport, M.D. SensoryGenetic/Neuro-development, 5801 Southwood Drive, Bloomington MN 55437-1739 952-831-5522 slhdaven@tc.umn.edu Udayan K. Shah, M.D.
THE EARS IN CHARGE FOR THE PHYSICIAN Sandra L.H. Davenport, M.D. SensoryGenetic/Neuro-development, 5801 Southwood Drive, Bloomington MN 55437-1739 952-831-5522 slhdaven@tc.umn.edu Udayan K. Shah, M.D.
Vibrant Soundbridge Implantable Hearing System
 Vibrant Soundbridge Implantable Hearing System Kristin M. Avitabile, MS, CCC-A Clinical Manager, Southeastern U.S. MED-EL Corporation Hearing Technology Hearing Aids Mild to severe HL Problems with feedback
Vibrant Soundbridge Implantable Hearing System Kristin M. Avitabile, MS, CCC-A Clinical Manager, Southeastern U.S. MED-EL Corporation Hearing Technology Hearing Aids Mild to severe HL Problems with feedback
Vision: Receptors. Modes of Perception. Vision: Summary 9/28/2012. How do we perceive our environment? Sensation and Perception Terminology
 How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
GUIDELINES FOR HEARING SCREENING In the School Setting
 GUIDELINES FOR HEARING SCREENING In the School Setting SEPTEMBER 2014 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Contributors This manual was reviewed and revised based on valuable input from the following individuals: Karen Bauer,
GUIDELINES FOR HEARING SCREENING In the School Setting SEPTEMBER 2014 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Contributors This manual was reviewed and revised based on valuable input from the following individuals: Karen Bauer,
S-822. Noise and Hearing Conservation RISK MANAGEMENT
 RISK MANAGEMENT Noise and Hearing Conservation Resources and information for developing Patient handling programs in health care Employers with workplaces that have excessive levels of noise need to implement
RISK MANAGEMENT Noise and Hearing Conservation Resources and information for developing Patient handling programs in health care Employers with workplaces that have excessive levels of noise need to implement
Education Adjustment Program (EAP) Handbook
 Education Adjustment Program (EAP) Handbook Current as at September 2015 The State of Queensland (2015) This document is licensed under CC-BY 4.0, with the exception of the government coat of arms, logos
Education Adjustment Program (EAP) Handbook Current as at September 2015 The State of Queensland (2015) This document is licensed under CC-BY 4.0, with the exception of the government coat of arms, logos
