E x p e r i m e n t 5 DC Motor Speed Control
|
|
|
- Peregrine Caldwell
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 E x p e r i m e n t 5 DC Motor Speed Control IT IS PREFERED that students ANSWER THE QUESTION/S BEFORE DOING THE LAB BECAUSE THAT provides THE BACKGROUND information needed for THIS LAB. (0% of the grade of the lab) Q: Explain two advantages of the Electric Drive System of the Electric motors? Q2: Two very important power electronic devices are the Power Mosfet and the power IGBT Give explain the construction, the function and the characteristics of both 5. Introduction In experiment-3 and 4, the speed of the DC-motor was controlled by using an open-loop voltage control. The purpose of this experiment is to design and implement a close-loop speed control of a DC-motor drive. We shall use the same DC-motor for which the parameters were calculated in the previous experiment. At first, the controllers will be designed and tested on a simulation model of the DC-motor. Once the parameters are tuned, the model of the DC-motor will be replaced with the real motor. The tuned controllers will be implemented in real-time on DS04 to perform the close-loop speed control of the DC-motor. 5.2 Simulink Model of the DC-motor The model for a DC-motor in frequency domain is derived in Chapter 8 []. I a Va (s) Ea (s) (s) Ea (s) k Em (s) () R sl a a Tem (s) TL (s) m ( s) Tem (s) ktia (s) kt k E (2) sj eq Equations () and (2) can be easily implemented in Simulink using standard blocks as shown in Fig. 5. Download the Simulink model dc_motor.mdl to the desktop (Fig. 5.). Convince yourself that it is the model for a dc motor.
2 The representation in Fig 5. uses integrators instead of transfer functions. This allows setting the initial conditions for the current and speed state variables. The model also includes the friction coefficient B. However, during simulations, B can be considered zero or its value can be obtained from experiment 4, and the model will be similar to the one described by equations () and (2). Create a subsystem by selecting components shown in Fig 5. and name it as DC Machine. The simulation block of the DC motor parameters is shown in Fig Ia 3 Tem + + /L Ke s Ia Tem - - Va /L Vtg int ke I/J Jeq s Mech int IaRa Ra Ra 2 TL B 0 Ke Gain 5 (a) Simulink Model (b) Waveform for m (c) Waveform for I a (d) Waveform for T em Figure 5.: Simulink model of DC-motor and waveforms for m, I a and T em
3 20 Va Scope 2 Va Ia 0. TL Tem Scope Load Torque DC Motor Figure 5.2: Simulation block of DC Motor Parameters Scope 3 Now enter the values of DC-motor parameters, which were evaluated in experiment 3 and 4 in file dc_motor_parameters.m. Ia_initial, _initial are the initial values for the integrator. To observe the zero initial condition response, set these values to zero. Run this file. Make sure your units are all consistent. Run the simulation (with default configuration parameters) for the following two cases. Compare the observed values with calculated values. Save the plots and include them in your report. a) Va = 20V, Load_Torque = 0.3 Nm b) Va = 20V, Load_Torque = 0 Nm 5.3 Controller Design Once the DC-motor model is built, the controllers can be added and tuned. Start with the current loop for which a PI controller is required. Download the file components.mdl. All the necessary blocks can be copied from here. For the more adventurous, follow the instructions as specified in points a, b, and c to build it! a) Build the model for a PI controller see Fig.5.3. Double click the integrator block and enable limit output. Then set the Upper and Lower saturation limits to +lim/-lim. The lim value should be set to (in the.m file) as the absolute maximum value of control voltage is,
4 which is the input to Kp block. The resultant maximum value of voltage applied to the DC motor will be ±42, which is the rating of the DC motor. b) The armature current is fed back to the controller input. + - Kp_i + + Ia_ref Kp_i Saturation Vc 2 Ia Ki_i Ki_i s Integration Figure 5.3: PI controller model c) The Saturation block sets the maximum and minimum limits for the control voltage (in our case ±). Design current controller for a bandwidth of 00 Hz (628.3 rad/sec) (phase margin 90 deg). The parameters of the PI controller (namely Kp_i and Ki_i) are computed using the motor parameters, which were evaluated in the earlier experiment. This procedure is described in section 8-7- [] (Explained at the End after the Report because we don t have the book). Create the file for a current controlled DC motor as shown in Fig 5.4(a). Running the Simulink model for the current controller with reference current as 2A, results similar to the Fig.5.4 (b) and Fig. 5.4(c) will be obtained. Set the value of Kp_i and Ki_i in Matlab prompt (or in the m file dc_motor_parameters ). Also set the values of lim =, Kp = 42, Ia_ref=. Run the m-file before running the simulation, which will load the values of all the variables. Run this simulation for a reference current of A (for sec, variable step, time step e-4). Save the plots for the report.
5 Once the response in current is considered optimal (low overshoot, fast rise-time, zero steady state error), the speed controller can be designed. For designing the speed controller you can assume B=0 but while building the Simulink block, include B. A similar PI controller for the speed loop ( PI_Speed ) will be added to the Simulink model. Design the speed controller for a bandwidth of 0Hz (62.83 rad/sec) (Phase margin 60 deg). Follow the procedure described in [] to design the speed control loop, using the motor parameters determined in earlier experiment. (Explained at the End after the Report because we don t have the book).
6 Ia, Ia_ref Ia_ref Ia_ref Ia_ref Vc Ia PI_Current Kp Gain V_motor 0 Load Torque Va TL Ia Tem DC Motor Terminator (a) Simulink model for current controller For example the current & speed waveform for a reference current of 2A are as given in Fig 5.4 below (b) Current waveform for 2A current reference (c) Speed waveform for 2A current reference Figure 5.4: Simulink model and result for current control loop The Simulink model for the cascade control and the waveforms for speed and current are shown in Fig.5.5 (a). The Speed PI controller has a current limit output of ±5A, necessary to limit the current during transients (both in simulation and real-time systems). To check the controller design, we will give a step change in the speed reference. This is implemented using a constant and step source blocks (Fig 5.5(a)). The results of cascade control are shown in Fig. 5.5(b) and Fig. 5.5(c). If the controller parameters were correctly tuned, then it s time to go on for the next step, and implement the controllers in a real-time system. Set the simulation output of speed response for a step input varying from 00 to 300 rad/s. (run the simulation for 2 sec variable-step, and time step e-4).
7 Set the speed reference to be 200 rad/sec and give a step change in the load torque from 0Nm to 0.3 Nm at sec (run for 2 sec). Attach the graph in your lab report. 200 _ref Kp _ref i_ref Ia_ref V0 Kp Va Step PI_Speed Ia PI_Current Kp TL Ia Tem ia, Ia ref Step2 DC Motor Terminator (a) Simulink model for cascade control Following are examples of waveform in Fig 5.5 where a step change of 00 to 350 rad/sec are shown. (b) Current waveform for a step change in speed (c) Speed waveform for a step change in speed Figure 5.5: Simulink model and result for cascade control
8 5.4 Real-time implementation of feedback control For dspace implementation, the dc-motor model will be replaced with the real motor and power converter with 42V dc supply will replace Kp block. The control voltage to duty cycle conversion was already discussed and implemented in experiment 2. All the necessary components to make the model in Fig 5.7 are provided in the file components.mdl. If you would like to build it the instructions as in a to f are given below: a) Add the reset block used in the previous experiment. b) Modify the Speed Control block as shown in Fig Change the integrator block parameters by double clicking on it and changing its external reset to either. Open the Current Controller and change its integrator s reset as was done in the Speed Control. Connect the reset inputs of speed controller and current controller as shown in Fig These changes allow the integrators to start up correctly in the real-time environment. + - Kp_w + + _ref Kp_w Saturation I_ref 2 Ki_w Ki_w s 3 Reset Integration Figure 5.6: Speed Controller
9 boolean Reset Data type Conversion 2 SLAVE BIT OUT DS04 SL_DSP_BIT_OUT_C0 _ref Wref_4quad i_ref Ia_ref reset Ia Vc Duty cycle a PI_Speed_reset reset PI_Current_reset - Gain + + /2 Duty cycle b Gain2 0 Duty cycle c constant dc PWM Stop ADC 20 0 DS04SL_DSP_PWM3 DS04 ADC_C5 motor_current PWM Control Enc position Enc delta position DS04 ENC_POS_CI Encoder Master Setup DS04 ENC_SETUP 2*pi / (Ts*000) Wm_dist Wm Gain 5 Avg Block motor_speed Figure 5.7: Simulink model for real-time implementation of DC motor control dspace I/O Board ADC 5 INC From Encoder Slave I/O PWM 42 V DC GND +42 V CURRA A B To INC DMM ENCODER + DC Motor + MUT Figure 5.8: Connections on the board c) Remove the DC-motor mask model and gain Kp block. d) Copy and paste the duty-cycle calculator from the Simulink model used in previous experiments.
10 e) The current and the speed are to be measured. For measurements use the blocks already designed in previous experiments. f) Replace the speed ref, _ref_step and sum block with a constant block for setting the speed reference. At the Matlab prompt, set the sampling time Ts=0.000 and the dc-bus voltage at Vd=42V. Also set the values of various variables you have defined in the model. Set the Simulation Configuration Parameters Solver Start time=0, Stop time =inf Type: Fixed-step, Solver: ode(euler) Fixed-step size:e-4 Optimization in Simulation and code generation, uncheck everything except Implement logic signals as Boolean data Code Generation System target file rti04.tlc Fig 5.7 is then the simulation block for DC-motor control. Make the connections on the board as shown in Fig The block wref_4quad gives a periodic step change in reference speed from 00 rad/sec to 300 rad/sec. Build (CTRL+B) the model and start dspace Control Desk. Open the variable file (.sdf) and then open the layout file dc_motor_speed_control.lay and add values as shown in Fig.5.9. Run the experiment and compare the real-time results with the simulations.
11 Figure 5.9: Control-desk interface for DC motor control for step from 50 rad/sec to 350 rad/sec
12 Lab Report (0points). Section 5.2: Run the simulation (with default configuration parameters for 0 sec) for the following two cases. Check the observed values with calculated values (show your calculations). Save the plots and include them in your report. (2points) a) Va=20V, Load_Torque = 0.3 Nm b) Va=20V, Load_Torque = 0 Nm 2. Section 5.3: a) Report your calculations for current and speed controller. Note: Design current controller for a bandwidth of 00 Hz (phase margin 90 deg) and speed controller for a bandwidth of 0Hz (Phase margin 60 deg). For designing the speed controller you can assume B=0 but while building the Simulink block, include B. (2 points) b) Attach simulation output of current response for a step input of A. ( point) c) Attach simulation output of speed response for a step input of 200 rad/s from a constant value of 00 rad/s ( point) d) All the responses required for questions 2b) and 2c) are based on step change in reference signals. These are required more for design purposes. In practical applications, it is more important to know how the system responds to disturbances in load torque. In the simulation, give a step load torque of 0.3 N-m while maintaining a constant speed of 200 rad/s. Observe the response in current and speed and attach the plots. ( points) 3. Section 5.4: Attach the speed and current response for a step change in speed reference as observed through control-desk for a step change from 00 rad/sec to 300 rad/sec. (3 points) References [] ELECTRIC DRIVES an integrative approach by Ned Mohan, 2000, MNPERE.
13 Important Calculations : Some Calculation needed in Expierment 5, because we don t have the book Ref [] This is the summary ( procedure) of the sections 8-7- and Desiginig the Torque (Current) Loop That is because the torque equals constant multiplied by the armature current
14 Ki_i and Kp_i is determined as follows : Where electric Time Constant From () Where and is the crossover frequency (Band Width frequency) The procedure is to find Ki_i from equation (4) and then substitute it back in equation () to find Kp_i 8-7- Desiginig the Speed Loop In the PI (proportional Integral ) we need to find Kp_w and Ki_w They can be found using these following equations ( ) (( ) ) Where is the given phase margin.
EE 402 RECITATION #13 REPORT
 MIDDLE EAST TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY EE 402 RECITATION #13 REPORT LEAD-LAG COMPENSATOR DESIGN F. Kağan İPEK Utku KIRAN Ç. Berkan Şahin 5/16/2013 Contents INTRODUCTION... 3 MODELLING... 3 OBTAINING PTF of OPEN
MIDDLE EAST TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY EE 402 RECITATION #13 REPORT LEAD-LAG COMPENSATOR DESIGN F. Kağan İPEK Utku KIRAN Ç. Berkan Şahin 5/16/2013 Contents INTRODUCTION... 3 MODELLING... 3 OBTAINING PTF of OPEN
dspace DSP DS-1104 based State Observer Design for Position Control of DC Servo Motor
 dspace DSP DS-1104 based State Observer Design for Position Control of DC Servo Motor Jaswandi Sawant, Divyesh Ginoya Department of Instrumentation and control, College of Engineering, Pune. ABSTRACT This
dspace DSP DS-1104 based State Observer Design for Position Control of DC Servo Motor Jaswandi Sawant, Divyesh Ginoya Department of Instrumentation and control, College of Engineering, Pune. ABSTRACT This
DCMS DC MOTOR SYSTEM User Manual
 DCMS DC MOTOR SYSTEM User Manual release 1.3 March 3, 2011 Disclaimer The developers of the DC Motor System (hardware and software) have used their best efforts in the development. The developers make
DCMS DC MOTOR SYSTEM User Manual release 1.3 March 3, 2011 Disclaimer The developers of the DC Motor System (hardware and software) have used their best efforts in the development. The developers make
Manufacturing Equipment Modeling
 QUESTION 1 For a linear axis actuated by an electric motor complete the following: a. Derive a differential equation for the linear axis velocity assuming viscous friction acts on the DC motor shaft, leadscrew,
QUESTION 1 For a linear axis actuated by an electric motor complete the following: a. Derive a differential equation for the linear axis velocity assuming viscous friction acts on the DC motor shaft, leadscrew,
Drivetech, Inc. Innovations in Motor Control, Drives, and Power Electronics
 Drivetech, Inc. Innovations in Motor Control, Drives, and Power Electronics Dal Y. Ohm, Ph.D. - President 25492 Carrington Drive, South Riding, Virginia 20152 Ph: (703) 327-2797 Fax: (703) 327-2747 ohm@drivetechinc.com
Drivetech, Inc. Innovations in Motor Control, Drives, and Power Electronics Dal Y. Ohm, Ph.D. - President 25492 Carrington Drive, South Riding, Virginia 20152 Ph: (703) 327-2797 Fax: (703) 327-2747 ohm@drivetechinc.com
HITACHI INVERTER SJ/L100/300 SERIES PID CONTROL USERS GUIDE
 HITACHI INVERTER SJ/L1/3 SERIES PID CONTROL USERS GUIDE After reading this manual, keep it for future reference Hitachi America, Ltd. HAL1PID CONTENTS 1. OVERVIEW 3 2. PID CONTROL ON SJ1/L1 INVERTERS 3
HITACHI INVERTER SJ/L1/3 SERIES PID CONTROL USERS GUIDE After reading this manual, keep it for future reference Hitachi America, Ltd. HAL1PID CONTENTS 1. OVERVIEW 3 2. PID CONTROL ON SJ1/L1 INVERTERS 3
Real-Time Digital Simulator Enabled Hardware-in-the-Loop Electric Machine Drive Lab
 1 Real-Time Digital Simulator Enabled Hardware-in-the-Loop Electric Machine Drive Lab Hossein G. Aghamolki and Zhixin Miao Department of Electrical Engineering University of South Florida, Tampa, FL 3362
1 Real-Time Digital Simulator Enabled Hardware-in-the-Loop Electric Machine Drive Lab Hossein G. Aghamolki and Zhixin Miao Department of Electrical Engineering University of South Florida, Tampa, FL 3362
A Tutorial Introduction to Control Systems Development and Implementation with dspace
 A Tutorial Introduction to Control Systems Development and Implementation with dspace Nicanor Quijano and Kevin Passino Dept. of Electrical Engineering The Ohio State University 2015 Neil Ave. Columbus,
A Tutorial Introduction to Control Systems Development and Implementation with dspace Nicanor Quijano and Kevin Passino Dept. of Electrical Engineering The Ohio State University 2015 Neil Ave. Columbus,
Time Response Analysis of DC Motor using Armature Control Method and Its Performance Improvement using PID Controller
 Available online www.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 5, (6): 56-6 Research Article ISSN: 394-658X Time Response Analysis of DC Motor using Armature Control Method
Available online www.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 5, (6): 56-6 Research Article ISSN: 394-658X Time Response Analysis of DC Motor using Armature Control Method
Work with Arduino Hardware
 1 Work with Arduino Hardware Install Support for Arduino Hardware on page 1-2 Open Block Libraries for Arduino Hardware on page 1-9 Run Model on Arduino Hardware on page 1-12 Tune and Monitor Models Running
1 Work with Arduino Hardware Install Support for Arduino Hardware on page 1-2 Open Block Libraries for Arduino Hardware on page 1-9 Run Model on Arduino Hardware on page 1-12 Tune and Monitor Models Running
Controller Design in Frequency Domain
 ECSE 4440 Control System Engineering Fall 2001 Project 3 Controller Design in Frequency Domain TA 1. Abstract 2. Introduction 3. Controller design in Frequency domain 4. Experiment 5. Colclusion 1. Abstract
ECSE 4440 Control System Engineering Fall 2001 Project 3 Controller Design in Frequency Domain TA 1. Abstract 2. Introduction 3. Controller design in Frequency domain 4. Experiment 5. Colclusion 1. Abstract
EDUMECH Mechatronic Instructional Systems. Ball on Beam System
 EDUMECH Mechatronic Instructional Systems Ball on Beam System Product of Shandor Motion Systems Written by Robert Hirsch Ph.D. 998-9 All Rights Reserved. 999 Shandor Motion Systems, Ball on Beam Instructional
EDUMECH Mechatronic Instructional Systems Ball on Beam System Product of Shandor Motion Systems Written by Robert Hirsch Ph.D. 998-9 All Rights Reserved. 999 Shandor Motion Systems, Ball on Beam Instructional
Laboratory 4: Feedback and Compensation
 Laboratory 4: Feedback and Compensation To be performed during Week 9 (Oct. 20-24) and Week 10 (Oct. 27-31) Due Week 11 (Nov. 3-7) 1 Pre-Lab This Pre-Lab should be completed before attending your regular
Laboratory 4: Feedback and Compensation To be performed during Week 9 (Oct. 20-24) and Week 10 (Oct. 27-31) Due Week 11 (Nov. 3-7) 1 Pre-Lab This Pre-Lab should be completed before attending your regular
Design and Simulation of Soft Switched Converter Fed DC Servo Drive
 International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) ISSN: 2231-237, Volume-1, Issue-5, November 211 Design and Simulation of Soft Switched Converter Fed DC Servo Drive Bal Mukund Sharma, A.
International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) ISSN: 2231-237, Volume-1, Issue-5, November 211 Design and Simulation of Soft Switched Converter Fed DC Servo Drive Bal Mukund Sharma, A.
Design of a TL431-Based Controller for a Flyback Converter
 Design of a TL431-Based Controller for a Flyback Converter Dr. John Schönberger Plexim GmbH Technoparkstrasse 1 8005 Zürich 1 Introduction The TL431 is a reference voltage source that is commonly used
Design of a TL431-Based Controller for a Flyback Converter Dr. John Schönberger Plexim GmbH Technoparkstrasse 1 8005 Zürich 1 Introduction The TL431 is a reference voltage source that is commonly used
Motor Control. Suppose we wish to use a microprocessor to control a motor - (or to control the load attached to the motor!) Power supply.
 Motor Control Suppose we wish to use a microprocessor to control a motor - (or to control the load attached to the motor!) Operator Input CPU digital? D/A, PWM analog voltage Power supply Amplifier linear,
Motor Control Suppose we wish to use a microprocessor to control a motor - (or to control the load attached to the motor!) Operator Input CPU digital? D/A, PWM analog voltage Power supply Amplifier linear,
QNET Experiment #06: HVAC Proportional- Integral (PI) Temperature Control Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Trainer (HVACT)
 Quanser NI-ELVIS Trainer (QNET) Series: QNET Experiment #06: HVAC Proportional- Integral (PI) Temperature Control Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Trainer (HVACT) Student Manual Table of Contents
Quanser NI-ELVIS Trainer (QNET) Series: QNET Experiment #06: HVAC Proportional- Integral (PI) Temperature Control Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Trainer (HVACT) Student Manual Table of Contents
Simulation of VSI-Fed Variable Speed Drive Using PI-Fuzzy based SVM-DTC Technique
 Simulation of VSI-Fed Variable Speed Drive Using PI-Fuzzy based SVM-DTC Technique B.Hemanth Kumar 1, Dr.G.V.Marutheshwar 2 PG Student,EEE S.V. College of Engineering Tirupati Senior Professor,EEE dept.
Simulation of VSI-Fed Variable Speed Drive Using PI-Fuzzy based SVM-DTC Technique B.Hemanth Kumar 1, Dr.G.V.Marutheshwar 2 PG Student,EEE S.V. College of Engineering Tirupati Senior Professor,EEE dept.
Simulation and Analysis of PWM Inverter Fed Induction Motor Drive
 Simulation and Analysis of PWM Inverter Fed Induction Motor Drive C.S.Sharma, Tali Nagwani Abstract Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation variable speed drives are increasingly applied in many new industrial
Simulation and Analysis of PWM Inverter Fed Induction Motor Drive C.S.Sharma, Tali Nagwani Abstract Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation variable speed drives are increasingly applied in many new industrial
Modelling, Simulation and Performance Analysis of A Variable Frequency Drive in Speed Control Of Induction Motor
 International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 78-7461, p-issn: 319-6491 Volume 3, Issue 5 (December 013) PP: 36-41 Modelling, Simulation and Performance Analysis of A Variable Frequency Drive
International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 78-7461, p-issn: 319-6491 Volume 3, Issue 5 (December 013) PP: 36-41 Modelling, Simulation and Performance Analysis of A Variable Frequency Drive
THE EDUCATIONAL IMPACT OF A GANTRY CRANE PROJECT IN AN UNDERGRADUATE CONTROLS CLASS
 Proceedings of IMECE: International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition Nov. 7-22, 2002, New Orleans, LA. THE EDUCATIONAL IMPACT OF A GANTRY CRANE PROJECT IN AN UNDERGRADUATE CONTROLS CLASS
Proceedings of IMECE: International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition Nov. 7-22, 2002, New Orleans, LA. THE EDUCATIONAL IMPACT OF A GANTRY CRANE PROJECT IN AN UNDERGRADUATE CONTROLS CLASS
Testing a power supply for line and load transients
 Testing a power supply for line and load transients Power-supply specifications for line and load transients describe the response of a power supply to abrupt changes in line voltage and load current.
Testing a power supply for line and load transients Power-supply specifications for line and load transients describe the response of a power supply to abrupt changes in line voltage and load current.
Power Electronics. Prof. K. Gopakumar. Centre for Electronics Design and Technology. Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore.
 Power Electronics Prof. K. Gopakumar Centre for Electronics Design and Technology Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 1 Electric Drive Today, we will start with the topic on industrial drive
Power Electronics Prof. K. Gopakumar Centre for Electronics Design and Technology Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 1 Electric Drive Today, we will start with the topic on industrial drive
ECE 3510 Final given: Spring 11
 ECE 50 Final given: Spring This part of the exam is Closed book, Closed notes, No Calculator.. ( pts) For each of the time-domain signals shown, draw the poles of the signal's Laplace transform on the
ECE 50 Final given: Spring This part of the exam is Closed book, Closed notes, No Calculator.. ( pts) For each of the time-domain signals shown, draw the poles of the signal's Laplace transform on the
Motor Modeling and Position Control Lab Week 3: Closed Loop Control
 Motor Modeling and Position Control Lab Week 3: Closed Loop Control 1. Review In the first week of motor modeling lab, a mathematical model of a DC motor from first principles was derived to obtain a first
Motor Modeling and Position Control Lab Week 3: Closed Loop Control 1. Review In the first week of motor modeling lab, a mathematical model of a DC motor from first principles was derived to obtain a first
TwinCAT NC Configuration
 TwinCAT NC Configuration NC Tasks The NC-System (Numeric Control) has 2 tasks 1 is the SVB task and the SAF task. The SVB task is the setpoint generator and generates the velocity and position control
TwinCAT NC Configuration NC Tasks The NC-System (Numeric Control) has 2 tasks 1 is the SVB task and the SAF task. The SVB task is the setpoint generator and generates the velocity and position control
Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies
 Soonwook Hong, Ph. D. Michael Zuercher Martinson Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies 1. Introduction PV inverters use semiconductor devices to transform the
Soonwook Hong, Ph. D. Michael Zuercher Martinson Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies 1. Introduction PV inverters use semiconductor devices to transform the
Pulse Width Modulated (PWM)
 Control Technologies Manual PWM AC Drives Revision 1.0 Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) Figure 1.8 shows a block diagram of the power conversion unit in a PWM drive. In this type of drive, a diode bridge rectifier
Control Technologies Manual PWM AC Drives Revision 1.0 Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) Figure 1.8 shows a block diagram of the power conversion unit in a PWM drive. In this type of drive, a diode bridge rectifier
2.6. In-Laboratory Session. 2.6.1. QICii Modelling Module. Modelling. 2.6.1.1. Module Description
 2.6. In-Laboratory Session 2.6.1. QICii Modelling Module 2.6.1.1. Module Description The main tool for this lab is the front panel of the module entitled Modelling in the QICii software, which should be
2.6. In-Laboratory Session 2.6.1. QICii Modelling Module 2.6.1.1. Module Description The main tool for this lab is the front panel of the module entitled Modelling in the QICii software, which should be
LOSSELESS STARTING METHOD FOR THE WOUND ROTOR INDUCTION MOTOR
 LOSSELESS STARTING METHOD FOR THE WOUND ROTOR INDUCTION MOTOR Sergiu Ivanov Mihai Rdulescu University of Craiova, Romania INDA Craiova Faculty of Electrical Engineering 30, Mr#e#ti Street 107, Decebal
LOSSELESS STARTING METHOD FOR THE WOUND ROTOR INDUCTION MOTOR Sergiu Ivanov Mihai Rdulescu University of Craiova, Romania INDA Craiova Faculty of Electrical Engineering 30, Mr#e#ti Street 107, Decebal
Interfacing Analog to Digital Data Converters
 Converters In most of the cases, the PIO 8255 is used for interfacing the analog to digital converters with microprocessor. We have already studied 8255 interfacing with 8086 as an I/O port, in previous
Converters In most of the cases, the PIO 8255 is used for interfacing the analog to digital converters with microprocessor. We have already studied 8255 interfacing with 8086 as an I/O port, in previous
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. For a complete data sheet, please also download:
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS
Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) Drives. AC Drives Using PWM Techniques
 Drives AC Drives Using PWM Techniques Power Conversion Unit The block diagram below shows the power conversion unit in Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) drives. In this type of drive, a diode bridge rectifier
Drives AC Drives Using PWM Techniques Power Conversion Unit The block diagram below shows the power conversion unit in Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) drives. In this type of drive, a diode bridge rectifier
Current Loop Tuning Procedure. Servo Drive Current Loop Tuning Procedure (intended for Analog input PWM output servo drives) General Procedure AN-015
 Servo Drive Current Loop Tuning Procedure (intended for Analog input PWM output servo drives) The standard tuning values used in ADVANCED Motion Controls drives are conservative and work well in over 90%
Servo Drive Current Loop Tuning Procedure (intended for Analog input PWM output servo drives) The standard tuning values used in ADVANCED Motion Controls drives are conservative and work well in over 90%
Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ME269 ELECTROMECHANICAL DEVICES AND POWER PROCESSING.
 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ME269 ELECTROMECHANICAL DEVICES AND POWER PROCESSING. Group # First Name Last Name UserID @uwaterloo.ca Experiment #3: DIRECT CURRENT
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ME269 ELECTROMECHANICAL DEVICES AND POWER PROCESSING. Group # First Name Last Name UserID @uwaterloo.ca Experiment #3: DIRECT CURRENT
Matlab and Simulink. Matlab and Simulink for Control
 Matlab and Simulink for Control Automatica I (Laboratorio) 1/78 Matlab and Simulink CACSD 2/78 Matlab and Simulink for Control Matlab introduction Simulink introduction Control Issues Recall Matlab design
Matlab and Simulink for Control Automatica I (Laboratorio) 1/78 Matlab and Simulink CACSD 2/78 Matlab and Simulink for Control Matlab introduction Simulink introduction Control Issues Recall Matlab design
ETEC 421 - Digital Controls PIC Lab 10 Pulse Width Modulation
 ETEC 421 - Digital Controls PIC Lab 10 Pulse Width Modulation Program Definition: Write a program to control the speed of a dc motor using pulse width modulation. Discussion: The speed of a dc motor is
ETEC 421 - Digital Controls PIC Lab 10 Pulse Width Modulation Program Definition: Write a program to control the speed of a dc motor using pulse width modulation. Discussion: The speed of a dc motor is
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. For a complete data sheet, please also download:
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS Logic Family Specifications The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS Logic Package Information The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS Logic Family Specifications The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS Logic Package Information The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS
Lab 3: Introduction to Data Acquisition Cards
 Lab 3: Introduction to Data Acquisition Cards INTRODUCTION: In this lab, you will be building a VI to display the input measured on a channel. However, within your own VI you will use LabVIEW supplied
Lab 3: Introduction to Data Acquisition Cards INTRODUCTION: In this lab, you will be building a VI to display the input measured on a channel. However, within your own VI you will use LabVIEW supplied
Setting up a Local Interconnect Network (LIN) using dspace MicroAutoBox 1401/1501 Simulink Blocks
 Setting up a Local Interconnect Network (LIN) using dspace MicroAutoBox 1401/1501 Simulink Blocks Guiseppe Ferro Design Team 4 3/22/13 Executive Summary Learn how to setup and properly use the Real- Time
Setting up a Local Interconnect Network (LIN) using dspace MicroAutoBox 1401/1501 Simulink Blocks Guiseppe Ferro Design Team 4 3/22/13 Executive Summary Learn how to setup and properly use the Real- Time
PID Control. Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) Control. Matrix Multimedia 2011 MX009 - PID Control. by Ben Rowland, April 2011
 PID Control by Ben Rowland, April 2011 Abstract PID control is used extensively in industry to control machinery and maintain working environments etc. The fundamentals of PID control are fairly straightforward
PID Control by Ben Rowland, April 2011 Abstract PID control is used extensively in industry to control machinery and maintain working environments etc. The fundamentals of PID control are fairly straightforward
Control System Definition
 Control System Definition A control system consist of subsytems and processes (or plants) assembled for the purpose of controlling the outputs of the process. For example, a furnace produces heat as a
Control System Definition A control system consist of subsytems and processes (or plants) assembled for the purpose of controlling the outputs of the process. For example, a furnace produces heat as a
Closed Loop PWM Control for Induction Motor Drive Using Dual Output Three Phase Inverter
 Closed Loop PWM Control for Induction Motor Drive Using Dual Output Three Phase Inverter Archana.P 1, Karthick.R 2 Pg Scholar [PED], Department of EEE, CSI College of Engineering, Ketti, Tamilnadu, India
Closed Loop PWM Control for Induction Motor Drive Using Dual Output Three Phase Inverter Archana.P 1, Karthick.R 2 Pg Scholar [PED], Department of EEE, CSI College of Engineering, Ketti, Tamilnadu, India
Application Information
 Moog Components Group manufactures a comprehensive line of brush-type and brushless motors, as well as brushless controllers. The purpose of this document is to provide a guide for the selection and application
Moog Components Group manufactures a comprehensive line of brush-type and brushless motors, as well as brushless controllers. The purpose of this document is to provide a guide for the selection and application
Switch Mode Power Supply Topologies
 Switch Mode Power Supply Topologies The Buck Converter 2008 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. WebSeminar Title Slide 1 Welcome to this Web seminar on Switch Mode Power Supply Topologies.
Switch Mode Power Supply Topologies The Buck Converter 2008 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. WebSeminar Title Slide 1 Welcome to this Web seminar on Switch Mode Power Supply Topologies.
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 EE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING See beginning of Section H for abbreviations, course numbers and coding. The * denotes labs which are held on alternate weeks. A minimum grade of C is required for all prerequisite
EE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING See beginning of Section H for abbreviations, course numbers and coding. The * denotes labs which are held on alternate weeks. A minimum grade of C is required for all prerequisite
MICRO HYDRO POWER PLANT WITH INDUCTION GENERATOR SUPPLYING SINGLE PHASE LOADS
 MICRO HYDRO POWER PLANT WITH INDUCTION GENERATOR SUPPLYING SINGLE PHASE LOADS C.P. ION 1 C. MARINESCU 1 Abstract: This paper presents a new method to supply single-phase loads using a three-phase induction
MICRO HYDRO POWER PLANT WITH INDUCTION GENERATOR SUPPLYING SINGLE PHASE LOADS C.P. ION 1 C. MARINESCU 1 Abstract: This paper presents a new method to supply single-phase loads using a three-phase induction
MODELLING AND SIMULATION OF SVPWM INVERTER FED PERMANENT MAGNET BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR DRIVE
 MODELLING AND SIMULATION OF SVPWM INVERTER FED PERMANENT MAGNET BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR DRIVE Devisree Sasi 1, Jisha Kuruvilla P Final Year M.Tech, Dept. of EEE, Mar Athanasius College of Engineering, Kothamangalam,
MODELLING AND SIMULATION OF SVPWM INVERTER FED PERMANENT MAGNET BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR DRIVE Devisree Sasi 1, Jisha Kuruvilla P Final Year M.Tech, Dept. of EEE, Mar Athanasius College of Engineering, Kothamangalam,
DRV8312-C2-KIT How to Run Guide
 DRV8312-C2-KIT How to Run Guide Version 1.1 October 2011 C2000 Systems and Applications Team This Guide explains the steps needed to run the DRV8312-C2-KIT with the software supplied through controlsuite.
DRV8312-C2-KIT How to Run Guide Version 1.1 October 2011 C2000 Systems and Applications Team This Guide explains the steps needed to run the DRV8312-C2-KIT with the software supplied through controlsuite.
AC Kinetics Variable Frequency Drive Comparative Transient Inertial Testing. This document was prepared by Advanced Energy.
 AC Kinetics Variable Frequency Drive Comparative Transient Inertial Testing This document was prepared by Advanced Energy. December 12 th, 2014 Introduction In June of this year, AC Kinetics contacted
AC Kinetics Variable Frequency Drive Comparative Transient Inertial Testing This document was prepared by Advanced Energy. December 12 th, 2014 Introduction In June of this year, AC Kinetics contacted
DS1104 R&D Controller Board
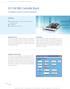 DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
How to program a Zumo Robot with Simulink
 How to program a Zumo Robot with Simulink Created by Anuja Apte Last updated on 2015-03-13 11:15:06 AM EDT Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview Hardware Software List of Software components: Simulink
How to program a Zumo Robot with Simulink Created by Anuja Apte Last updated on 2015-03-13 11:15:06 AM EDT Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview Hardware Software List of Software components: Simulink
Advance Electronic Load Controller for Micro Hydro Power Plant
 Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 8 (2014) 1802-1810 D DAVID PUBLISHING Advance Electronic Load Controller for Micro Hydro Power Plant Dipesh Shrestha, Ankit Babu Rajbanshi, Kushal Shrestha and Indraman
Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 8 (2014) 1802-1810 D DAVID PUBLISHING Advance Electronic Load Controller for Micro Hydro Power Plant Dipesh Shrestha, Ankit Babu Rajbanshi, Kushal Shrestha and Indraman
CONVENTIONALLY reduced order models are being
 Co-Simulation of an Electric Traction Drive Christoph Schulte and Joachim Böcker Abstract For the simulation of electrical drives, reducedorder models or simple look-up tables are often used in order to
Co-Simulation of an Electric Traction Drive Christoph Schulte and Joachim Böcker Abstract For the simulation of electrical drives, reducedorder models or simple look-up tables are often used in order to
INDUCTION MOTOR PERFORMANCE TESTING WITH AN INVERTER POWER SUPPLY, PART 2
 INDUCTION MOTOR PERFORMANCE TESTING WITH AN INVERTER POWER SUPPLY, PART 2 By: R.C. Zowarka T.J. Hotz J.R. Uglum H.E. Jordan 13th Electromagnetic Launch Technology Symposium, Potsdam (Berlin), Germany,
INDUCTION MOTOR PERFORMANCE TESTING WITH AN INVERTER POWER SUPPLY, PART 2 By: R.C. Zowarka T.J. Hotz J.R. Uglum H.E. Jordan 13th Electromagnetic Launch Technology Symposium, Potsdam (Berlin), Germany,
Technical Guide No. 100. High Performance Drives -- speed and torque regulation
 Technical Guide No. 100 High Performance Drives -- speed and torque regulation Process Regulator Speed Regulator Torque Regulator Process Technical Guide: The illustrations, charts and examples given in
Technical Guide No. 100 High Performance Drives -- speed and torque regulation Process Regulator Speed Regulator Torque Regulator Process Technical Guide: The illustrations, charts and examples given in
Motor Control Application Tuning (MCAT) Tool for 3-Phase PMSM
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4642 Application Note Rev. 1, 01/2013 Motor Control Application Tuning (MCAT) Tool for 3-Phase PMSM by: Marek Stulrajter, Pavel Sustek 1 Introduction This application
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4642 Application Note Rev. 1, 01/2013 Motor Control Application Tuning (MCAT) Tool for 3-Phase PMSM by: Marek Stulrajter, Pavel Sustek 1 Introduction This application
Tamura Closed Loop Hall Effect Current Sensors
 Tamura Closed Loop Hall Effect Current Sensors AC, DC, & Complex Currents Galvanic Isolation Fast Response Wide Frequency Bandwidth Quality & Reliability RoHs Compliance Closed Loop Hall Effect Sensors
Tamura Closed Loop Hall Effect Current Sensors AC, DC, & Complex Currents Galvanic Isolation Fast Response Wide Frequency Bandwidth Quality & Reliability RoHs Compliance Closed Loop Hall Effect Sensors
PC BASED PID TEMPERATURE CONTROLLER
 PC BASED PID TEMPERATURE CONTROLLER R. Nisha * and K.N. Madhusoodanan Dept. of Instrumentation, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin 22, India ABSTRACT: A simple and versatile PC based Programmable
PC BASED PID TEMPERATURE CONTROLLER R. Nisha * and K.N. Madhusoodanan Dept. of Instrumentation, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin 22, India ABSTRACT: A simple and versatile PC based Programmable
Reactive Power Control of an Alternator with Static Excitation System Connected to a Network
 Reactive Power Control of an Alternator with Static Excitation System Connected to a Network Dr. Dhiya Ali Al-Nimma Assist. Prof. Mosul Unoversity Dr. Majid Salim Matti lecturer Mosul University Abstract
Reactive Power Control of an Alternator with Static Excitation System Connected to a Network Dr. Dhiya Ali Al-Nimma Assist. Prof. Mosul Unoversity Dr. Majid Salim Matti lecturer Mosul University Abstract
Chapter 9: Controller design
 Chapter 9. Controller Design 9.1. Introduction 9.2. Effect of negative feedback on the network transfer functions 9.2.1. Feedback reduces the transfer function from disturbances to the output 9.2.2. Feedback
Chapter 9. Controller Design 9.1. Introduction 9.2. Effect of negative feedback on the network transfer functions 9.2.1. Feedback reduces the transfer function from disturbances to the output 9.2.2. Feedback
CPW Current Programmed Winder. Application Handbook. Copyright 2002 by Eurotherm Drives, Inc.
 CPW Current Programmed Winder Application Handbook Copyright 2002 by Eurotherm Drives, Inc. All rights strictly reserved. No part of this document may be stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in
CPW Current Programmed Winder Application Handbook Copyright 2002 by Eurotherm Drives, Inc. All rights strictly reserved. No part of this document may be stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in
DIGITAL-TO-ANALOGUE AND ANALOGUE-TO-DIGITAL CONVERSION
 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOGUE AND ANALOGUE-TO-DIGITAL CONVERSION Introduction The outputs from sensors and communications receivers are analogue signals that have continuously varying amplitudes. In many systems
DIGITAL-TO-ANALOGUE AND ANALOGUE-TO-DIGITAL CONVERSION Introduction The outputs from sensors and communications receivers are analogue signals that have continuously varying amplitudes. In many systems
New Pulse Width Modulation Technique for Three Phase Induction Motor Drive Umesha K L, Sri Harsha J, Capt. L. Sanjeev Kumar
 New Pulse Width Modulation Technique for Three Phase Induction Motor Drive Umesha K L, Sri Harsha J, Capt. L. Sanjeev Kumar Abstract In this paper, various types of speed control methods for the three
New Pulse Width Modulation Technique for Three Phase Induction Motor Drive Umesha K L, Sri Harsha J, Capt. L. Sanjeev Kumar Abstract In this paper, various types of speed control methods for the three
LEVERAGING FPGA AND CPLD DIGITAL LOGIC TO IMPLEMENT ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS
 LEVERAGING FPGA AND CPLD DIGITAL LOGIC TO IMPLEMENT ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS March 2010 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503) 268-8000 www.latticesemi.com
LEVERAGING FPGA AND CPLD DIGITAL LOGIC TO IMPLEMENT ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS March 2010 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503) 268-8000 www.latticesemi.com
ACS800. Master/Follower Application Guide Supplement to Firmware Manual for ACS800 Standard Application Program
 ACS800 Master/Follower Application Guide Supplement to Firmware Manual for ACS800 Standard Application Program Master/Follower Application Guide Supplement to Firmware Manual ACS800 Standard Application
ACS800 Master/Follower Application Guide Supplement to Firmware Manual for ACS800 Standard Application Program Master/Follower Application Guide Supplement to Firmware Manual ACS800 Standard Application
SPW3 Speed Programmed Winder. Application Handbook. Copyright 2000 by SSD Drives, Inc. Printed in the United States of America HA355297 Issue 3
 SPW3 Speed Programmed Winder Application Handbook Copyright 2000 by SSD Drives, Inc. All rights strictly reserved. No part of this document may be stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form
SPW3 Speed Programmed Winder Application Handbook Copyright 2000 by SSD Drives, Inc. All rights strictly reserved. No part of this document may be stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form
Frequency Response of Filters
 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:224 Principles of Electrical Engineering II Laboratory Experiment 2 Frequency Response of Filters 1 Introduction Objectives To
School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:224 Principles of Electrical Engineering II Laboratory Experiment 2 Frequency Response of Filters 1 Introduction Objectives To
(!' ) "' # "*# "!(!' +,
 ( Controls Signal Processing Telecommunications Network and processor modeling and simulation http://www.mathworks.com/academia/classroom-resources/departments/electrical-computerengineering.html ( MATLAB
( Controls Signal Processing Telecommunications Network and processor modeling and simulation http://www.mathworks.com/academia/classroom-resources/departments/electrical-computerengineering.html ( MATLAB
IEC 1000-4-2 ESD Immunity and Transient Current Capability for the SP72X Series Protection Arrays
 IEC 00-4-2 ESD Immunity and Transient Current Capability for the SP72X Series Protection Arrays Application Note July 1999 AN9612.2 Author: Wayne Austin The SP720, SP721, SP723, and SP724 are protection
IEC 00-4-2 ESD Immunity and Transient Current Capability for the SP72X Series Protection Arrays Application Note July 1999 AN9612.2 Author: Wayne Austin The SP720, SP721, SP723, and SP724 are protection
Micro-Step Driving for Stepper Motors: A Case Study
 Micro-Step Driving for Stepper Motors: A Case Study N. Sedaghati-Mokhtari Graduate Student, School of ECE, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran n.sedaghati @ece.ut.ac.ir Abstract: In this paper, a case study
Micro-Step Driving for Stepper Motors: A Case Study N. Sedaghati-Mokhtari Graduate Student, School of ECE, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran n.sedaghati @ece.ut.ac.ir Abstract: In this paper, a case study
Introduction to LabVIEW for Control Design & Simulation Ricardo Dunia (NI), Eric Dean (NI), and Dr. Thomas Edgar (UT)
 Introduction to LabVIEW for Control Design & Simulation Ricardo Dunia (NI), Eric Dean (NI), and Dr. Thomas Edgar (UT) Reference Text : Process Dynamics and Control 2 nd edition, by Seborg, Edgar, Mellichamp,
Introduction to LabVIEW for Control Design & Simulation Ricardo Dunia (NI), Eric Dean (NI), and Dr. Thomas Edgar (UT) Reference Text : Process Dynamics and Control 2 nd edition, by Seborg, Edgar, Mellichamp,
Module 2 Introduction to SIMULINK
 Module 2 Introduction to SIMULINK Although the standard MATLAB package is useful for linear systems analysis, SIMULINK is far more useful for control system simulation. SIMULINK enables the rapid construction
Module 2 Introduction to SIMULINK Although the standard MATLAB package is useful for linear systems analysis, SIMULINK is far more useful for control system simulation. SIMULINK enables the rapid construction
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. LAB 1 - Introduction to USRP
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev LAB 1 - Introduction to USRP - 1-1 Introduction In this lab you will use software reconfigurable RF hardware from National
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev LAB 1 - Introduction to USRP - 1-1 Introduction In this lab you will use software reconfigurable RF hardware from National
MODELING FIRST AND SECOND ORDER SYSTEMS IN SIMULINK
 MODELING FIRST AND SECOND ORDER SYSTEMS IN SIMULINK First and second order differential equations are commonly studied in Dynamic courses, as they occur frequently in practice. Because of this, we will
MODELING FIRST AND SECOND ORDER SYSTEMS IN SIMULINK First and second order differential equations are commonly studied in Dynamic courses, as they occur frequently in practice. Because of this, we will
U-102 APPLICATION NOTE UC1637/2637/3637 SWITCHED MODE CONTROLLER FOR DC MOTOR DRIVE
 U-102 APPLICATION NOTE UC1637/2637/3637 SWITCHED MODE CONTROLLER FOR DC MOTOR DRIVE INTRODUCTION There is an increasing demand today for motor control circuits, as a result of the incredible proliferation
U-102 APPLICATION NOTE UC1637/2637/3637 SWITCHED MODE CONTROLLER FOR DC MOTOR DRIVE INTRODUCTION There is an increasing demand today for motor control circuits, as a result of the incredible proliferation
Iowa State University Electrical and Computer Engineering. E E 452. Electric Machines and Power Electronic Drives. Laboratory #3 Figures of Merit
 Electrical and Computer Engineering E E 452. Electric Machines and Power Electronic Drives Laboratory #3 Figures of Merit Summary Simple experiments will be conducted. Experimental waveforms will be measured,
Electrical and Computer Engineering E E 452. Electric Machines and Power Electronic Drives Laboratory #3 Figures of Merit Summary Simple experiments will be conducted. Experimental waveforms will be measured,
A MULTILEVEL INVERTER FOR SYNCHRONIZING THE GRID WITH RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES BY IMPLEMENTING BATTERY CUM DC-DC CONERTER
 A MULTILEVEL INVERTER FOR SYNCHRONIZING THE GRID WITH RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES BY IMPLEMENTING BATTERY CUM DC-DC CONERTER 1 KARUNYA CHRISTOBAL LYDIA. S, 2 SHANMUGASUNDARI. A, 3 ANANDHI.Y 1,2,3 Electrical
A MULTILEVEL INVERTER FOR SYNCHRONIZING THE GRID WITH RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES BY IMPLEMENTING BATTERY CUM DC-DC CONERTER 1 KARUNYA CHRISTOBAL LYDIA. S, 2 SHANMUGASUNDARI. A, 3 ANANDHI.Y 1,2,3 Electrical
Fully Differential CMOS Amplifier
 ECE 511 Analog Electronics Term Project Fully Differential CMOS Amplifier Saket Vora 6 December 2006 Dr. Kevin Gard NC State University 1 Introduction In this project, a fully differential CMOS operational
ECE 511 Analog Electronics Term Project Fully Differential CMOS Amplifier Saket Vora 6 December 2006 Dr. Kevin Gard NC State University 1 Introduction In this project, a fully differential CMOS operational
Simulation and Analysis of Parameter Identification Techniques for Induction Motor Drive
 International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174 Volume 7, Number 10 (2014), pp. 1027-1035 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Simulation and
International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174 Volume 7, Number 10 (2014), pp. 1027-1035 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Simulation and
METHODOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS OF DRIVE SYSTEM SIMULATION, WHEN COUPLING FINITE ELEMENT MACHINE MODELS WITH THE CIRCUIT SIMULATOR MODELS OF CONVERTERS.
 SEDM 24 June 16th - 18th, CPRI (Italy) METHODOLOGICL CONSIDERTIONS OF DRIVE SYSTEM SIMULTION, WHEN COUPLING FINITE ELEMENT MCHINE MODELS WITH THE CIRCUIT SIMULTOR MODELS OF CONVERTERS. Áron Szûcs BB Electrical
SEDM 24 June 16th - 18th, CPRI (Italy) METHODOLOGICL CONSIDERTIONS OF DRIVE SYSTEM SIMULTION, WHEN COUPLING FINITE ELEMENT MCHINE MODELS WITH THE CIRCUIT SIMULTOR MODELS OF CONVERTERS. Áron Szûcs BB Electrical
Lab Session 4 Introduction to the DC Motor
 Lab Session 4 Introduction to the DC Motor By: Professor Dan Block Control Systems Lab Mgr. University of Illinois Equipment Agilent 54600B 100 MHz Ditizing Oscilloscope (Replacement model: Agilent DSO5012A
Lab Session 4 Introduction to the DC Motor By: Professor Dan Block Control Systems Lab Mgr. University of Illinois Equipment Agilent 54600B 100 MHz Ditizing Oscilloscope (Replacement model: Agilent DSO5012A
See Horenstein 4.3 and 4.4
 EE 462: Laboratory # 4 DC Power Supply Circuits Using Diodes by Drs. A.V. Radun and K.D. Donohue (2/14/07) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Updated
EE 462: Laboratory # 4 DC Power Supply Circuits Using Diodes by Drs. A.V. Radun and K.D. Donohue (2/14/07) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Updated
Inrush Current. Although the concepts stated are universal, this application note was written specifically for Interpoint products.
 INTERPOINT Although the concepts stated are universal, this application note was written specifically for Interpoint products. In today s applications, high surge currents coming from the dc bus are a
INTERPOINT Although the concepts stated are universal, this application note was written specifically for Interpoint products. In today s applications, high surge currents coming from the dc bus are a
Fairchild On-Line Design Tool: Power Supply WebDesigner Step-by-Step Guide
 Fairchild On-Line Design Tool: Power Supply WebDesigner Step-by-Step Guide Start Decide what your power supply requirements will be. Design Example: For this step we will design an AC to DC off-line power
Fairchild On-Line Design Tool: Power Supply WebDesigner Step-by-Step Guide Start Decide what your power supply requirements will be. Design Example: For this step we will design an AC to DC off-line power
Lab #9: AC Steady State Analysis
 Theory & Introduction Lab #9: AC Steady State Analysis Goals for Lab #9 The main goal for lab 9 is to make the students familar with AC steady state analysis, db scale and the NI ELVIS frequency analyzer.
Theory & Introduction Lab #9: AC Steady State Analysis Goals for Lab #9 The main goal for lab 9 is to make the students familar with AC steady state analysis, db scale and the NI ELVIS frequency analyzer.
Transient analysis of integrated solar/diesel hybrid power system using MATLAB Simulink
 Transient analysis of integrated solar/diesel hybrid power system using ATLAB Simulink Takyin Taky Chan School of Electrical Engineering Victoria University PO Box 14428 C, elbourne 81, Australia. Taky.Chan@vu.edu.au
Transient analysis of integrated solar/diesel hybrid power system using ATLAB Simulink Takyin Taky Chan School of Electrical Engineering Victoria University PO Box 14428 C, elbourne 81, Australia. Taky.Chan@vu.edu.au
Building a Simulink model for real-time analysis V1.15.00. Copyright g.tec medical engineering GmbH
 g.tec medical engineering GmbH Sierningstrasse 14, A-4521 Schiedlberg Austria - Europe Tel.: (43)-7251-22240-0 Fax: (43)-7251-22240-39 office@gtec.at, http://www.gtec.at Building a Simulink model for real-time
g.tec medical engineering GmbH Sierningstrasse 14, A-4521 Schiedlberg Austria - Europe Tel.: (43)-7251-22240-0 Fax: (43)-7251-22240-39 office@gtec.at, http://www.gtec.at Building a Simulink model for real-time
FlexPak 3000 Digital DC Drive Software Reference Manual Version 4.3
 FlexPak 3000 Digital DC Drive Software Reference Manual Version 4.3 Instruction Manual D2-3405-2 The information in this manual is subject to change without notice. Throughout this manual, the following
FlexPak 3000 Digital DC Drive Software Reference Manual Version 4.3 Instruction Manual D2-3405-2 The information in this manual is subject to change without notice. Throughout this manual, the following
Jump Start: Aspen HYSYS Dynamics V7.3
 A Brief Tutorial (and supplement to training and online documentation) Glenn Dissinger, Product Director, Aspen Technology, Inc. Julie Levine, Associate Product Marketing Professional, Aspen Technology,
A Brief Tutorial (and supplement to training and online documentation) Glenn Dissinger, Product Director, Aspen Technology, Inc. Julie Levine, Associate Product Marketing Professional, Aspen Technology,
Active Vibration Isolation of an Unbalanced Machine Spindle
 UCRL-CONF-206108 Active Vibration Isolation of an Unbalanced Machine Spindle D. J. Hopkins, P. Geraghty August 18, 2004 American Society of Precision Engineering Annual Conference Orlando, FL, United States
UCRL-CONF-206108 Active Vibration Isolation of an Unbalanced Machine Spindle D. J. Hopkins, P. Geraghty August 18, 2004 American Society of Precision Engineering Annual Conference Orlando, FL, United States
TURBOtech srl. SED-635 Digital Excitation System. Industrial Electronics Sector FEATURES
 SED-635 Digital Excitation System SED-635 is a complete excitation system capable of adapting to control synchronous generators of any size. The integration of the TOUCH SCREEN operator interface and a
SED-635 Digital Excitation System SED-635 is a complete excitation system capable of adapting to control synchronous generators of any size. The integration of the TOUCH SCREEN operator interface and a
EE289 Lab Fall 2009. LAB 4. Ambient Noise Reduction. 1 Introduction. 2 Simulation in Matlab Simulink
 EE289 Lab Fall 2009 LAB 4. Ambient Noise Reduction 1 Introduction Noise canceling devices reduce unwanted ambient noise (acoustic noise) by means of active noise control. Among these devices are noise-canceling
EE289 Lab Fall 2009 LAB 4. Ambient Noise Reduction 1 Introduction Noise canceling devices reduce unwanted ambient noise (acoustic noise) by means of active noise control. Among these devices are noise-canceling
Pulse Width Modulation Applications
 Pulse Width Modulation Applications Lecture 21 EE 383 Microcomputers Learning Objectives What is DTMF? How to use PWM to generate DTMF? How to use PWM to control a servo motor? How to use PWM to control
Pulse Width Modulation Applications Lecture 21 EE 383 Microcomputers Learning Objectives What is DTMF? How to use PWM to generate DTMF? How to use PWM to control a servo motor? How to use PWM to control
ω h (t) = Ae t/τ. (3) + 1 = 0 τ =.
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mechanical Engineering 2.004 Dynamics and Control II Fall 2007 Lecture 2 Solving the Equation of Motion Goals for today Modeling of the 2.004 La s rotational
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mechanical Engineering 2.004 Dynamics and Control II Fall 2007 Lecture 2 Solving the Equation of Motion Goals for today Modeling of the 2.004 La s rotational
Hollow Cylinder Apparatus (GDS SS-HCA)
 HCA:1 Options available for SS-HCA Axial Load/Torque 1kN/1Nm 1kN/2Nm 12kN/2Nm 15kN/4Nm Dynamic upgrade frequencies Hollow Cylinder Apparatus (GDS SS-HCA).5Hz 2Hz 1Hz 5Hz Sample Height/Outer Ø/Inner Ø 2/1/6mm
HCA:1 Options available for SS-HCA Axial Load/Torque 1kN/1Nm 1kN/2Nm 12kN/2Nm 15kN/4Nm Dynamic upgrade frequencies Hollow Cylinder Apparatus (GDS SS-HCA).5Hz 2Hz 1Hz 5Hz Sample Height/Outer Ø/Inner Ø 2/1/6mm
Understanding Delta Conversion Online "Power Regulation" - Part 2
 Application Note #40 Understanding Delta Conversion Online "Power Regulation" - Part 2 Introduction This application note is the second in a series on delta conversion theory of operation. For complete
Application Note #40 Understanding Delta Conversion Online "Power Regulation" - Part 2 Introduction This application note is the second in a series on delta conversion theory of operation. For complete
SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS
 Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
DC Link Voltage Control
 Aalborg University Institute of Energy Technology Power Electronics and Drives DC Link Voltage Control PED10-1013a Institute of Energy Technology Aalborg University PED10 Spring 2008 Pontoppidanstræde
Aalborg University Institute of Energy Technology Power Electronics and Drives DC Link Voltage Control PED10-1013a Institute of Energy Technology Aalborg University PED10 Spring 2008 Pontoppidanstræde
