Hypospadias Repair with Bilateral Orchiopexy
|
|
|
- Stella Jackson
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Hypospadias Repair with Bilateral Orchiopexy Cindy Rios, cst Hypospadias is a congenital disease that occurs in urethral development during weeks 8 to 20 of gestation. Hypospadias affects the male urethra and phallus. It is thought to be acquired genetically due to the imbalance of hormones. Hypospadias causes the opening of the urethra to be on the ventral side of the penis. A penis affected by this condition often will look as if it is bowing downward because of chordee tension. The malformation will make normal sexual intercourse difficult in the future. Hypospadias is classified into three categories: penile shaft hypospadias, coronal hypospadias and glandular hypospadias. Individuals with hypospadias often experience unsatisfactory erections making intercourse difficult. In some males, hypospadias also makes it difficult to urinate due to the position of the urethra and may require those males to sit while urinating, causing identity issues in children. 2 Cryptorchidism is most often a congenital disease and is usually discovered by the age of one, although it can occur later in life. Cryptorchidism is the absence of the either both or one of the testes in the scrotum. Cryptorchidism usually occurs in children that were born prematurely and most likely is accompanied by an inguinal hernia. The testicles will usually be located in the abdomen or in the groin. Cryptorchidism, if left untreated, can result in cancer and infertility. 2 Case Study The patient is a 3-year-old male who has progressive midshaft hypospadias, which was determined at birth. The child has experienced several medical complications starting during gestation. Several maternal factors affected the pregnancy including polyhydramnios, a condition where excessive accumulation of amniotic fluid causes intrauterine growth restriction of the fetus and premature rupture of the membranes. In this case, this condition led to the mother delivering at only 29 weeks of gestation. The infant spent two and a half months in the LEARNING OBJECTIVES s Review the instruments and equipment necessary for this procedure s Identify the special considerations necessary when conducting a pediatric surgery s Learn about the causes and concerns for patients diagnosed with hypospadias s Examine the role of the surgical technologist in this procedure s Outline the surgical steps for the hypospadias and orchiopexy operations JUNE 2013 The Surgical Technologist 255
3 Chart 1 Instruments/Equipment Needed Basic pediatric lap pack Small basin 4 gowns Nonlatex gloves for all sterile team members Blades safety #15 x 4, V-Lance x 1 Drapes laparotomy sheet, 4 towels Dressings and adhesive strips Liquid adhesive Diapers x 2 Bacitracin ointment (on head of penis after dressings are applied) 10 ml syringe Warming device 25 gauge butterfly needle 250 ml bag of 0.9% normal saline Bag-O-Jet Water soluble lubricant Rubber bands Vessel loops 4-blue Sterile marking pen G-tube Urethral stent Electrosurgical pencil with holster, needle tip, and tip cleaner Bipolar cord for electrosurgical unit Skin antiseptic solution Povidone iodine Specimen cup x 2 Ruler X-ray detectable sponges Sponges x 2 packs 25-gauge needle Sterile towel pack x 2 Suture 5-0 Chromic P-3 (skin) 4-0 Chromic P-3 (tacking) 4-0 Vicryl RB-1 (stet in place) 7-0 Vicryl (flap) 4-0 Prolene RB-1 (glans, retraction) 4-0 Ethibond TF (traction) 7-0 TG (cut in half, used to keep G-tube in place) Medications Sterile water 0.9% normal saline for irrigation In addition to the supplies, the surgical technologist picked the instruments needed for these types of cases, which included: Plastics instrument tray General basic procedures tray Lacrimal 256 duct The Surgical probestechnologist JUNE 2013 newborn intensive care unit (NICU) at the local children s hospital. While in the NICU, the infant developed necrotizing enterocolitis, which was later resolved. He was previously diagnosed with a right inguinal hernia that had been previously repaired and was readmitted to the hospital in 2009 for treatment of meningitis. Most recently, the child was diagnosed with a seizure disorder after experiencing at least one unprovoked seizure. During the patient s last visit with the doctor, human chorionic gonadotropin (hcg) injections began to encourage enlargement of the child s penis. The child s parents have noticed an increase in the size of his penis since the injections where given, although they subsequently noticed that the testes of the child seemed abnormally small and took the child to the pediatrician for assessment. The pediatrician diagnosed the child with a condition called bilateral retractile testes, also known as cryptorchidism and referred him to an urologist. The child seemed to have significant tension in the testicles, with the left testicle suffering more tension than the right. The child s parents were informed that surgery was necessary because undescended testes are associated with an increased risk of genital malignancy as well as decreased sperm and hormone production. The parents understood the risks, benefits and future implications and agreed to proceed with the surgery. 6 Diagnostic Testing For this case, the patient went through several diagnostic tests including medical history, an ultrasound and a physical. Other diagnostic testing done for a hypospadias, although not done for this patient can include retrograde urethrogram, cystourethrogram, intravenous urogram, MRI and CT scans. 2,6 The patient s medical history listed several complications due to the premature birth. The patient previously experienced necrotizing enterocolitis (death of intestinal tissue), apnea (sensation of breathing) and tracheitis (inflammation of the trachea which was caused by a bacterial infection), which progressed to pneumonia. Cholestasis is a condition in which the bile flow of the liver is reduced and total parenteral nutrition (TPN) support is a way of getting nutritional by bypassing the digestive system with an intravenous solution. The patient also had bacterial meningitis, which caused the brain to swell resulting in interference with blood flow. The patient has had a history of seizures and bilateral retractile testes, also known as cryptorchidism. 6 An ultrasound was performed and showed the bilateral lower inguinal testes. The testes were reported to look in normal condition. The patient s liver was also checked with ultrasound. At the time of the viewing, the kidneys appeared
4 normal and it was noted that the patient had a 5mm gallstone. The patient s physical examination showed the scrotum was well-developed and both testicles were at the level of the pubic bone. When they were brought down to the hemiscrotum level, they experienced significant tension with the left testicle showing more tension than the right. The penis of the child showed a mid-shaft hypospadias with a descent size urethral plate and adequate dorsal hooded foreskin and there was approximately 30 degrees of ventral chordee. 6 Retrograde urethrogram allows the evaluation of abnormalities in the urethra that can include narrowed areas, strictures, contractions and outpouchings. The procedure lasts approximately five minutes and is performed with the patient in the supine position on an X-ray table. The urethral opening is cleaned and the sterile contrast media is inserted into the urethra. X-rays are taken to record the anatomy of patient. 2 Cystourethrogram is performed to examine the bladder and the lower urinary tract using fluoroscopy and contrast media. The genitalia are cleaned and the bladder is catheterized so that it can be filled with a water soluble contrast media. The patient is asked to urinate while X-rays are taken to record the process of urination.intravenous urogram is an X-ray test that takes pictures of the urinary tract. It shows the shape, size, position of the tract and evaluates the kidney s collecting system. Contrast media is injected into a vein in the patient s arm and many X-ray pictures are taken. MRI and CT scans are taken when detailed imaging of the patients organs is needed. A contrast media is used during a CT scan to make the organs easier to identify. 2 Special Considerations When dealing with pediatric patients, special considerations are required. The room temperature must be raised and appropriate heating supplies must be in or near the operating room. Warm blankets and warming devices are generally used as children have low body mass and subcutaneous tissues. Children may need to be shown the equipment that will be used when they are anesthetized to reduce anxiety. Other types of anxiety reducers for a child include: allowing the child to bring in a favorite toy, being brought in on a wagon, medical staff introducing themselves to the child and allowing the child s parents to accompany him or her in the preoperative holding unit. The emotional needs of a child also need to be considered prior to the operation. 2 For a hypospadias repair, it is ideal if the patient has not undergone prior circumcision because the foreskin is often used as a skin graft. The surgical technologist, however, must anticipate the possibility of a free skin graft to be used if there is not enough tissue from the existing foreskin. The surgical technologist also needs to anticipate for a meatoplasty and glanuplasty following a hypospadias surgery and have the applicable instruments and equipment available. Preoperative Procedure The surgical technologist checked the case cart and the surgeon s preference cards to make sure that all the equipment, instruments and supplies needed for the operation were gathered. (See Chart 1 on page 256) Once all of the supplies and instruments were placed in the case cart, the surgical technologist verified that all necessary equipment was in the room. The surgical technologist asked the registered nurse to double check the list which included: Electrosurgical unit with monopolar and bipolar capabilities Suction apparatus x 2 Loupes for the surgeon Warming device The surgical technologist verified that all items were in the room and completed a checklist on the surgeon s preference card. Once the circulator verified that everything on the preference card was available, the patient was visited in the preoperative holding unit by the circulator and anesthesia provider. 2,6 Sterile Field Set-Up Once the case cart was in the room, the surgical technologist and the circulator donned their masks. The surgical technologist positioned the back table, Mayo stand and ring stand at least 12 inches away from the wall. The surgical technologist opened the case cart and took out the basic pack and placed it on the back table. The instrument trays where placed on the ring stands to the left side of the back table. All the supplies that were to be opened for the case were placed on the Mayo. The basic table pack was removed from the plastic covering. After inspecting the pack for damage, the surgical technologist opened the back table pack in a sterile matter. The instrument trays were opened, the filters checked and the lids were placed in the case cart. All the supplies needed for the case were opened and placed onto the back table in a sterile fashion. The sterile gown and gloves for the surgical technologist were opened onto the Mayo table. The surgical technologist walked out of the room and scrubbed in, preforming the counted brush stroke method of scrubbing cleaning the subungual space with the tool provided, 30 counted strokes on nails, 10 back and forth JUNE 2013 The Surgical Technologist 257
5 Anatomy/Pathophysiology The penis is suspended from the front and the sides of the pubic arch. The penis contains the majority of the urethra. The penis s upper surface is called the dorsal portion and the bottom surface is known as the ventral surface. 1 The penile shaft is also known as the middle body. The middle body is made up of three circular masses of cavernous erectile tissues and bound together by a fibrous tunica albuginea. The cavernous erectile tissue is a specialized venous sinus with a variable in diameter and is widely interconnected. 1 Corpus cavernosa Two large columns of the erectile tissue in the penis dorsum. The posterior portion columns are separated by septal fibers. The corpus cavernosum forms the crura of the penis. 1 Tunica albuginea Bands the two columns of the corpus cavernosa together. It is a dense fibrous membrane that encases and separates the dorsal corpora cavernosa and the ventral corpus spongiosum. 1 Corpus spongiosum Located within the ventral side of the penis. The corpus spongiosum does not contribute to penile rigidity and it contains the penile urethra.1 Penile fascia Also called Buck s fascia. The penile fascia consists of loose connective tissue that is located between the dartos layer of the shaft and the tunica albuginea. The penile fascia extends from the root of the penis to the coronal sulcus. The penile fascia contains the penile dorsal veins, small blood vessels, nerve bundles and adipocytes (also known adipose tissue). 1 Dartos layer A discontinuous smooth muscle layer that extends from the homologous scrotal layer and through the entire shaft between the dermis and penile fascia. 1 Urethra Divided into three portions. The length of the urethra ranges from 15 to 29 centimeters. The surface layers of the urethra are columnar and basal stratified epithelium and may be classified as pseudostratified epithelium. The male urethra contains T lymphocytes, macrophages and plasma cells which protect against infections. 1 Prostatic urethra Surrounded by the prostate and contains urothelium. It is the most proximal part of the urethra.1 Membranous urethra Lower pole of the prostate to the bulb of the corpus spongiosum. 1 Penile or distal urethra Passes through the corpus spongiosum.1 Distal penis Glans Distal expansion of the corpus spongiosum and covers the end of the penis shaft. The glans penis forms a bulb-like shape. 1 Glans corona Base of the glans that is elevated circumferentially at the rim. The glans corona may also contain small papillae over the free border. Meatus urethralis Urethral opening that is located at the central ventral glans penis. 1 Fossa navicularis Contains stratified non-keratinized squamous epithelium. The fossa navicularis is the dilated terminal part of the penile urethra. 1 Frenulum Attaches the foreskin of the penis to the ventral glans. It is made up of fibrous bands of tissue. 1 Coronal sulcus Located behind the glans corona. It is a circumferential and narrow cul-de-sac, in uncircumcised males. The coronal sulcus is also known as the area where the dartos and Buck s fascia insert. 1 Foreskin Segment of skin that is folded on itself and covers the glans of the penis. The foreskin also covers the meatus of the penis so that the glans is not seen. It is made up of squamous epithelium, lamina propria, dartos layer and preputial skin. 1 Muscles of the penis Bulbospongiosus muscle Covers the bulb of the penis. It is located in the perineum in front of the anus. The bulbospongiosus muscle runs along the perineum and from the median raphe. This muscle contributes to the feeling of orgasm, ejaculation, and erection. The bulbospongiosus muscle serves to empty the urethra and expel bladder contents. The fibers of the bulbospongiosus generally relaxed and only go contract at the final stage of ejaculation. 1 Ischiocavernosus muscle Helps the anus flex and stabilize the erect penis. The ischiocavernosus muscle compresses the crus penis and slows down the return of blood throughout the veins helping to maintain the penis erect. 1 Superficial transverse perineal muscle Passes across the perineal space anterior to the anus. The superficial transverse perineal muscle comes from the tuberosity of the ischium, runs medially and inserts in the central tendinous point of the perineal body. The bands of the muscle join with the opposite side with the sphincter, ani externus muscle, and bulbospongiosus muscle and function to fix the perineal body in the center of the perineum. 1 Blood supply The blood supply of the penis comes from branches of the internal pudendal artery. Cavernous artery Usually a single artery that comes from each side and enters the corpus cavernosum at the crus and runs through the whole length of penile shaft. The artery gives off helicine arteries that are integral components of the erectile process. 4 Dorsal artery Runs along the dorsum of the penis between the dorsal vein and the dorsal nerve. The dorsal artery branches off circumferentially and is accompanied by the circumflex veins. The terminal branches of the dorsal artery are in the glans penis The Surgical Technologist JUNE 2013
6 Bulbourethral artery Passes through the deep penile Buck s fascia and supplies the bulb of the penis and the spongy urethra. 1 Urethral artery Originates from the internal pudendal artery which is a small distance in anterior to the artery of the urethral bulb. In males, the urethral artery runs medially and forward piercing through the fascia of the urogenital diaphragm and into the corpus cavernosum of the urethra, then continues forward to the glans penis. 1 Venous supply Superficial veins Located in the dartos fascia on the dorsal lateral surface of the penis and combine at the base to form a single superficial dorsal vein. The vein drains into the great saphenous veins via the superficial external pudendal veins. 4 Intermediate veins Contain the deep dorsal and circumflex veins. The veins lie within and beneath the deep penile Buck s fascia. The emissary veins begin within the erectile tissue of the corpora cavernosa and run through the tunica albuginea which drain into the circumflex or deep dorsal veins. 4 Deep veins These drain into the crural and cavernosal veins. The crural veins come from the midline and the space between the crura. The cavernosal veins are between the emissary veins. The emissary veins join to form the large venous channel which drains at the internal pudendal vein. There are about three or four small cavernosal veins that run laterally between the corpus spongiosum and the crus of the penis before draining into the internal pudendal veins. 4 Lymphatic and nerve supply of the penis Lymphatic drainage The lymphatic drainage of the penis drains into the large trunks of the frenulum. The lymphatic vessels go around the dorsum of corona and then come together. They primarily go beneath the Buck s fascia and terminate at the deep inguinal nodes of the femoral triangle. 4 Nerve supply The nerve supply of the penis comes from the pudendal and cavernous nerves. The cavernous nerve is a combination of the visceral afferent fiber and the parasympathetic. The cavernous nerve is the erectile tissue nerve and is in the crus and corpora of the penis. The cavernous nerve is mostly dorsomedial to the deep penile arteries. 4 Anatomy of the testes Testes Two glandular organs that are located on the outside of the body that are suspended between the thighs by the spermatic cords and are contained within the scrotum. In early embryonic life the testes are contained in the abdominal cavity located behind the peritoneum. Around two months before fetus is born the testes descend into the inguinal canal including the pass of the spermatic cord and emerge at the subcutaneous inguinal ring. The cord contains lymphatic vessels, blood vessels, nerves and ductus deferens. The testes descend into the scrotum where they become covered by serous, muscular, fibrous layers and the scrotum. The coverings of the testes are the skin, Dartos fascia, external spermatic fascia, cremaster muscle fascia, internal spermatic fascia, parietal layer of tunica vaginalis, epididymis and the tunica vaginalis. The testes main function is to produce spermatozoa and produce the hormone testosterone. 1,7 Ductus deferens Also known as the vas deferens, is a tube that is contained in the spermatic cord and goes through the inguinal canal into the abdominal cavity. After entering the abdominal cavity, the ductus deferens separates from the remainder of the spermatic cord and curves behind the bladder. The ductus deferens functions in ejaculation by making the walls of the contract reflexively forcing the sperm move forward. As it is propelled, the sperm is transferred from the vas deferens to the urethra. 1,7 Seminal vesicle The seminal vesicle is curled inside the gland and forms an outpocket of the ampulla of each ductus deferens. The excretory duct of the seminal gland opens into the ductus deferens as it inters into the prostate gland. The main function of the seminal vesicle is to secrete significant amounts of fluid that will ultimately become semen. The ph level of the fluid is mildly alkaline which allows the semen to neutralize the acidity of the vagina. 1,7 Ejaculatory ducts The ejaculatory ducts are paired and formed by the union of the ductus deferens with the seminal vesicle. The ducts pass through the prostate and open into the urethra and the colliculus seminalis. The main function of the ejaculatory ducts is to expel the semen for reproduction. 1,7 Epididymis The epididymis is a tube that is twisted and tightly compressed to the point where it looks solid. The epididymis is located at the posterior border of the testis and is composed of three main parts which include the head (caput), body (corpora), and the tail (cauda). The head of the epididymis hangs over the upper poles of the testis and receives seminal fluid from the ducts of the testis that pierce the top portion of the mediastinum. The head allows the passage of the sperm into the distal portion of epididymis. This part of the epididymis allows for storage and maturation of the sperm due to its length. 1,7 Spermatic cord The spermatic cord runs from the abdomen to each side of the testicles. The spermatic cord contains all of the structures that go through the deep inguinal ring and the fascia coverings from the abdominal wall. The spermatic cords main function is to suspend the testis in the scrotum and contain all the structures that run to and from the testis including, blood supply, nerves, lymphatic vessels and the ductus deferens. 1,7 Blood supply The blood supply for the testis includes the testicular artery, artery to ductus deferens and the pampiniform venous plexus. 7 Nerve and lymphatic supply The nerve supply for the testis is the spermatic plexus. The lymph supply is the lumbar lymph nodes. 7 JUNE 2013 The Surgical Technologist 259
7 strokes on each finger, followed by 10 circular scrubbing movements of the hands, wrists and arms to two inches above the elbow. Staying sterile, the surgical technologist reentered the operating room and secured the towel ensuring that no water was transferred to the sterile field. After drying off, the sterile gown was secured and donned, followed by the sterile gloves. The surgical technologist then approached the back table, donned the outer pair of gloves and proceeded to dress the Mayo stand. The back table was lined with towels, organized and the instrument trays were retrieved, placed on the back table and organized. Following the facility s policy, the circulator and the surgical technologist worked together to transfer all necessary solutions (including medication) to the sterile field and label them and the initial count was completed. The circulator and anesthesia provider brought the patient into the operating room, positioned him in the supine position on the operating table, and applied the safety strap. Everyone in the room introduced themselves to the child and made the child as comfortable as possible. General anesthesia was induced and an IV was initiated. When dealing with pediatric patients, special considerations are required. The room temperature must be raised and appropriate heating supplies must be in or near the operating room. Warm blankets and Bair Huggers are generally used as children have low body mass and subcutaneous tissues. Pre-Op After the child was under, the circulator applied the warming device and made minor adjustments to the patient s position including tucking the arms at the patient s side and ensuring that all bony prominences and nerves were protected with foam padding. Once the patient was positioned, the circulator prepped the patient with povidone iodine followed by a skin antiseptic solution. The prep began at the child s umbilicus and was continued circumferentially down to the thighs, including the scrotum and the uncircumcised penis. The foreskin was retracted and the glans was also prepped and scrubbed. Following the prep, the dispersive electrode for the electrosurgical unit was placed on the left buttock. The surgeon and the assistant entered the room, verified the presence of all needed instruments, equipment and supplies and the timeout was completed according to facility policy. After the surgeon and assistant scrubbed, entered the operating room, dried their hands and arms and were gowned and gloved, the drapes were applied. A towel was placed under the scrotum and additional towels were used to outline the planned surgical site. A fenestrated drape sheet was applied leaving an opening from the inguinal area to the scrotum. The light handles were applied, the suction and electrosurgical pencil were secured to the drapes using nonperforating instruments, and the ends were passed to the circulator to be connected to the corresponding devices. Operative Steps The skin of the urethra was peeled down using a curved mosquito and the marking pen was used to identify the planned incision site. The penile incision was made circumferentially approximately 8-9 mm proximal to the meatus and corona using a #15 safety knife on a #3 safety knife handle. X-ray detectable sponges were provided and the electrosurgical pencil was used to stop any bleeding. The skin was elevated from the phallus to the sides by using a curved iris scissors to dissect, and the 0.5 tissue forceps were used, as needed. The skin was dissected and cut into a triangular shape using the V-Lance blade and the 0.5 tissue forceps. Weck sponges were used to remove blood and bleeding was controlled by coagulation. The 4-0 Prolene RB-1 was loaded on a plastic needle holder and used to attach the upper metal edges to the distal glandular groove. The 4-0 Prolene was used as a traction suture and was secured with two curved mosquitos. The tip of the stent was lubricated with the water soluble lubricant and inserted in the urethra. The straight Mayo scissors was passed to shorten the stent. The 4-0 Ethibond TF was passed on a plastic needle holder for traction of the lateral gland tissue of the foreskin at the top of the ventral meatus and clamped using curved mosquitos. The 0.5 tissue pickups were passed to assist in suture handling. A green sterile rubber band was placed to serve as a tourniquet line of the penis. A butterfly 25-gauge needle was passed into the erectile bodies to allow inflation with sterile saline for the erection test. The test was done to determine the extent of the chordee. The 4-0 Prolene RB-1 was passed to hold the stent into place for the duration of the surgery. The 7-0 TG double armed was loaded onto a plastic needle holder and cut in half with the suture scissors. The 7-0 TG was used for additional assistance in holding the stent. Further dissection of the tissue of the prepuce was accomplished with the Westcott scissors. The stent was 260 The Surgical Technologist JUNE 2013
8 stitched with a 7-0 PDS II to be used as a back stop. The back stop went all the way up to the head of the penis. The suture was loaded on a needle holder followed by suture scissors and 0.5 fine tissue forceps. The edges of the glands are closed in two layers making a V-shape on the ventral side of the penis, while the third layer of the tissue is placed superiorly as a seal. The first layer seals the urethra while the second layer provides a sealing by taking the tension of the first layer, which allows the blood supply to heal. A towel was placed underneath the penis to catch urine. The Dartos skin was cut with a #15 safety blade and dissected out with the Westcott scissors. The flap was used to cover the third layer. The 7-0 Vicryl was passed for the suturing of the Dartos flap. The suture was loaded on needle holder and a fine 0.5 tissue forceps was also used. The traction suture was cut with suture scissors and all mosquito clamps where retrieved. The 5-0 PDS II was passed for the suturing of the head orifice. The suture was loaded on a needle holder followed by 0.5 tissue forceps. The skin was thin-sutured with a 5-0 Chromic P-3. The suture was loaded on plastic needle holders accompanied by Adson tissue forceps with teeth. The first count was performed as the skin was being sutured. The 4-0 Vicryl RB-1 was loaded and passed followed by Adson tissue forceps with teeth to sew the stent in place. The stent will remain in place until the urethroplasty is healed. Orchiopexy The marking pen was passed to mark inguinal incision and the scrotal incision. The transverse inguinal incision was made approximately two to three inches in length using a #15 safety blade on a safety blade handle cutting through the fascia, external oblique aponeurosis and internal oblique muscle. The external oblique aponeurosis was opened to expose the inguinal canal using the Tenotomy scissors. Adson tissue forceps with teeth where passed to help with the retraction of the skin. The electrosurgical pencil was passed to aid in achieving hemostasis. The gubernacular attachments of the undescended testicle was dissected and brought out into the abdominal cavity using a DeBakey forceps. The inguinal hernia sac was freed and the cord was lengthened so the testis could reach the scrotum. Gerald tissue forceps were used for maneuvering of testis into scrotum. The scrotal incision was made in a transverse manner along the scrotal fold. The tunica albuginea was attached to the Dartos muscle using a 4-0 Chromic P-3 for tacking laterally and inferiorly to prevent herniation. A scrotal pocket was created to anchor the testicles into a normal anatomical position with 4-0 Chromic suture on a plastic s needle holder followed by Adson tissue forceps with teeth and suture scissors. The orchiopexy was performed bilaterally with more emphasis on the left testicle. The incision was closed with 5-0 Chromic P-3 passed on a plastic needle holder and Adson tissue forceps with teeth. The final count was performed when the final skin At the completion of the procedure, the surgical technologist moved the back table and the Mayo stand to its original position, removed and discarded the drapes and waited until the child was put onto the gurney and taken to the postanesthesia care unit (PACU) before breaking down the sterile field. sutures were being placed. All sharps and sponges were accounted for and then the incisions made for both the hypospadias and orchiopexy where cleaned using a wet sponge followed by a dry sponge. The patient may receive a penile block to decrease immediate postoperative pain. Dressings where applied by applying a liquid adhesive on the on penis, inguinal incision and scrotal incision. Two dressings were applied on the penis and one on the inguinal incision on top of small nonstick pad. Then an elastic wrap was wrapped around the penis. A diaper was placed to catch the urine draining from the stent. Postoperative Care At the completion of the procedure, the surgical technologist moved the back table and the Mayo stand to its original position, removed and discarded the drapes and waited until the child was put onto the gurney and taken to the postanesthesia care unit (PACU) before breaking down the sterile field. The child was sent intubated and asleep to the PACU where vital signs were observed and charted until the patient regained consciousness. Once the child regained consciousness, he was transferred to the outpatient area where he was reunited with his family. The patient stayed in the outpatient area for four hours until his vital signs were normal and stable and then he was discharged. The patient was required to return four to six weeks after the surgery for a follow-up with his surgeon. 6 JUNE 2013 The Surgical Technologist 261
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Urinary Catheter Care
 For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Urinary Catheter Care Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather, and prepare
For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Urinary Catheter Care Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather, and prepare
Vasectomy What happens under normal conditions? What is a vasectomy? How is a vasectomy performed?
 Vasectomy The decision to proceed with a vasectomy is a very personal one. It is important that you have a clear understanding of what a vasectomy is and what it is not. Most patients can expect to recover
Vasectomy The decision to proceed with a vasectomy is a very personal one. It is important that you have a clear understanding of what a vasectomy is and what it is not. Most patients can expect to recover
URINARY CATHETER INSERTION - STRAIGHT OR INDWELLING CATHETER
 URINARY CATHETER INSERTION - STRAIGHT OR INDWELLING CATHETER PURPOSE To obtain a sterile urine specimen. To facilitate emptying bladder. To relieve bladder distention. To irrigate bladder. To measure residual
URINARY CATHETER INSERTION - STRAIGHT OR INDWELLING CATHETER PURPOSE To obtain a sterile urine specimen. To facilitate emptying bladder. To relieve bladder distention. To irrigate bladder. To measure residual
2. Does the patient have one of the following appropriate indications for placing indwelling urinary catheters?
 A. Decision to Insert a Urinary Catheter: 1. Before placing an indwelling catheter, please consider if these alternatives would be more appropriate: Bladder scanner: to assess and confirm urinary retention,
A. Decision to Insert a Urinary Catheter: 1. Before placing an indwelling catheter, please consider if these alternatives would be more appropriate: Bladder scanner: to assess and confirm urinary retention,
Foley Catheter Placement
 Foley Catheter Placement Indications for a Foley Catheter Retention of urine leading to urinary hesitancy, straining to urinate, decrease in size and force of the urinary stream, interruption of urinary
Foley Catheter Placement Indications for a Foley Catheter Retention of urine leading to urinary hesitancy, straining to urinate, decrease in size and force of the urinary stream, interruption of urinary
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I
 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Vasectomy: Patient Information. Andrew L. Siegel, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon
 Vasectomy: Patient Information by Andrew L. Siegel, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon An educational service provided by: bergen Urological associates Stuart H. Levey, M.D. Andrew L.
Vasectomy: Patient Information by Andrew L. Siegel, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon An educational service provided by: bergen Urological associates Stuart H. Levey, M.D. Andrew L.
Male Infertility. Penis. Epididymis
 Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
How to Find Out What s Wrong A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE. A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc.
 A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
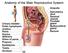 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
EVERY LIVING THING has a number of
 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary
 X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
Urinary tract and perineum
 9 Urinary tract and perineum Key Points 9.1 9.1 THE URINARY BLADDER URINARY RETENTION Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder The common causes of acute retention
9 Urinary tract and perineum Key Points 9.1 9.1 THE URINARY BLADDER URINARY RETENTION Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder The common causes of acute retention
Placement of an indwelling urinary catheter in female dogs
 Female Dog Urinary Catheterization 1 of 6 Placement of an indwelling urinary catheter in female dogs Bernie Hansen DVM MS North Carolina State University College of Veterinary Medicine Materials Needed
Female Dog Urinary Catheterization 1 of 6 Placement of an indwelling urinary catheter in female dogs Bernie Hansen DVM MS North Carolina State University College of Veterinary Medicine Materials Needed
UROLOGY GROUP of PRINCETON
 UROLOGY GROUP of PRINCETON 134 STANHOPE STREET, PRINCETON, NJ 08540 PHONE 609-924-6487 FAX 609-921-7020 BARRY ROSSMAN, M.D. ALEX VUKASIN, M.D. KAREN LATZKO, D.O. ALEXEI WEDMID, M.D. VASECTOMY, THE NO SCALPEL
UROLOGY GROUP of PRINCETON 134 STANHOPE STREET, PRINCETON, NJ 08540 PHONE 609-924-6487 FAX 609-921-7020 BARRY ROSSMAN, M.D. ALEX VUKASIN, M.D. KAREN LATZKO, D.O. ALEXEI WEDMID, M.D. VASECTOMY, THE NO SCALPEL
Men s Health: Testicular & Breast. September 2012
 Men s Health: Testicular & Breast September 2012 Objectives: You will learn: How to perform a testicular self-exam and breast self-exam. You will know when to perform testicular and breast self-exams.
Men s Health: Testicular & Breast September 2012 Objectives: You will learn: How to perform a testicular self-exam and breast self-exam. You will know when to perform testicular and breast self-exams.
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
The Abdominal Wall And Hernias. Stanley Kurek, DO, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery UTMCK
 The Abdominal Wall And Hernias Stanley Kurek, DO, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery UTMCK The Abdominal Wall The structure of the abdominal wall is similar in principle to the thoracic wall. There are
The Abdominal Wall And Hernias Stanley Kurek, DO, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery UTMCK The Abdominal Wall The structure of the abdominal wall is similar in principle to the thoracic wall. There are
Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis
 2 Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis Intra-Abdominal Anatomy of the Male Pelvic Region Bladder Medial Umbilical Ligaments Lateral Umbilical Ligaments Spermatic Cords Iliac Vessels Ureters Seminal Vesicular
2 Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis Intra-Abdominal Anatomy of the Male Pelvic Region Bladder Medial Umbilical Ligaments Lateral Umbilical Ligaments Spermatic Cords Iliac Vessels Ureters Seminal Vesicular
male sexual dysfunction
 male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
If Your Child has an Inguinal Hernia, Hydrocele or Undescended Testicles. A Guide for Parents
 Introduction Urology Clinic If Your Child has an Inguinal Hernia, Hydrocele or Undescended Testicles A Guide for Parents Three of the most common birth defects in males are an inguinal hernia, hydrocele,
Introduction Urology Clinic If Your Child has an Inguinal Hernia, Hydrocele or Undescended Testicles A Guide for Parents Three of the most common birth defects in males are an inguinal hernia, hydrocele,
URINARY CATHETER CARE
 URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome
 Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Ilioinguinal dissection (removal of lymph nodes in the groin and pelvis)
 Ilioinguinal dissection (removal of lymph nodes in the groin and pelvis) This sheet answers common questions about ilio-inguinal dissection. If you would like further information, or have any particular
Ilioinguinal dissection (removal of lymph nodes in the groin and pelvis) This sheet answers common questions about ilio-inguinal dissection. If you would like further information, or have any particular
Vasectomy Services Patient Information
 Vasectomy Services Patient Information Vasectomy Vasectomy Please read this information leaflet and consent form carefully, and bring it with you to your appointment. Please ask the doctor any questions
Vasectomy Services Patient Information Vasectomy Vasectomy Please read this information leaflet and consent form carefully, and bring it with you to your appointment. Please ask the doctor any questions
Lymph Node Dissection for Penile Cancer
 Lymph Node Dissection for Penile Cancer Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Removal of Lymph Nodes Why are the Lymph Nodes so important when I have penile cancer? Lymph nodes are small bean shaped
Lymph Node Dissection for Penile Cancer Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Removal of Lymph Nodes Why are the Lymph Nodes so important when I have penile cancer? Lymph nodes are small bean shaped
Bladder Catheterization
 Approved by: Bladder Catheterization Gail Cameron Senior Director, Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Ensenat Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Nursery Policy & Procedures
Approved by: Bladder Catheterization Gail Cameron Senior Director, Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Ensenat Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Nursery Policy & Procedures
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Revised Spring 2006 1
 It is important that you know the anatomy and the histology BEFORE the physiology can be covered in lecture. Study the anatomy of the reproductive system using this handout in conjunction with Text Chapter
It is important that you know the anatomy and the histology BEFORE the physiology can be covered in lecture. Study the anatomy of the reproductive system using this handout in conjunction with Text Chapter
PROCEDURE FOR CLEAN INTERMITTENT CATHETERIZATION MALE
 PROCEDURE FOR CLEAN INTERMITTENT CATHETERIZATION MALE 1. Wash hands. PROCEDURE POINTS TO REMEMBER 2. Assemble equipment. Water-soluble lubricant, such as K-Y Jelly, Lubrifax, Surgel Catheter, plastic or
PROCEDURE FOR CLEAN INTERMITTENT CATHETERIZATION MALE 1. Wash hands. PROCEDURE POINTS TO REMEMBER 2. Assemble equipment. Water-soluble lubricant, such as K-Y Jelly, Lubrifax, Surgel Catheter, plastic or
Preparation for your vasectomy
 Preparation for your vasectomy You have been scheduled for a vasectomy with the SIU Division of Urology. Please read through this information carefully. Vasectomies are performed in the REI clinic, 751
Preparation for your vasectomy You have been scheduled for a vasectomy with the SIU Division of Urology. Please read through this information carefully. Vasectomies are performed in the REI clinic, 751
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Location: Clinical Practice Manual
 Subject: Area: Classification: Relevant to: Bladder Management Clinical Practice All Clinical Staff Implementation Date: March 2001 Review Date: March 2004 Responsible for Review: Approved by: Distribution:
Subject: Area: Classification: Relevant to: Bladder Management Clinical Practice All Clinical Staff Implementation Date: March 2001 Review Date: March 2004 Responsible for Review: Approved by: Distribution:
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Inguinal (Groin) Hernia Repair
 Information for patients Inguinal (Groin) Hernia Repair General Surgery Tel: 01473 712233 DMI ref: 11582-09.indd(RP) Issue 1: February 2010 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2010. All rights reserved. Not
Information for patients Inguinal (Groin) Hernia Repair General Surgery Tel: 01473 712233 DMI ref: 11582-09.indd(RP) Issue 1: February 2010 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2010. All rights reserved. Not
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY
 ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
Surgical scissors and forceps Product List
 Surgical scissors and forceps Product List Sr. No Items Picture of Product Product specification 1 Grasping forceps-- 5 MM Grasping forceps are used to remove stones and retrieve foreign objects under
Surgical scissors and forceps Product List Sr. No Items Picture of Product Product specification 1 Grasping forceps-- 5 MM Grasping forceps are used to remove stones and retrieve foreign objects under
41 Assisting with Minor Surgery
 Learning Outcomes 41.1 Define the medical assistant s role in minor surgical procedures. 41-2 CHAPTER 41 Assisting with Minor Surgery 41.2 Describe types of wounds and explain how they heal. 41.3 Describe
Learning Outcomes 41.1 Define the medical assistant s role in minor surgical procedures. 41-2 CHAPTER 41 Assisting with Minor Surgery 41.2 Describe types of wounds and explain how they heal. 41.3 Describe
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft)
 Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Lesions, and Masses, and Tumors Oh My!!
 Lesions, and Masses, and Tumors Oh My!! Presented by: Susan Ward, CPC, CPC-H, CPC-I, CPCD, CEMC, CPRC 1 1 CPT GUIDELINES Agenda CPT DEFINITIONS OP REPORT CASES 2 Definitions Cyst - a closed sac having
Lesions, and Masses, and Tumors Oh My!! Presented by: Susan Ward, CPC, CPC-H, CPC-I, CPCD, CEMC, CPRC 1 1 CPT GUIDELINES Agenda CPT DEFINITIONS OP REPORT CASES 2 Definitions Cyst - a closed sac having
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to cardiac catheterization. In the following pages, we will
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to cardiac catheterization. In the following pages, we will
Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2013 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Integumentary...1 Arteries and Veins...15 Lymph
Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2013 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Integumentary...1 Arteries and Veins...15 Lymph
Posterior Cervical Decompression
 Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary Ballooning of the aorta, also known as an "abdominal aortic aneurysm," can lead to life threatening bleeding. Doctors may recommend
X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary Ballooning of the aorta, also known as an "abdominal aortic aneurysm," can lead to life threatening bleeding. Doctors may recommend
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida. Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions
 Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Male Catheterisation
 1 Prepare your equipment, put what you need on to the trolley, choose catheter appropriate for urethral size and check the volume of water needed to inflate the balloon. All this information is written
1 Prepare your equipment, put what you need on to the trolley, choose catheter appropriate for urethral size and check the volume of water needed to inflate the balloon. All this information is written
How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver
 Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives stepby-step instructions for changing a Foley catheter, a tube in the bladder to drain urine.
Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives stepby-step instructions for changing a Foley catheter, a tube in the bladder to drain urine.
Urinary System Lab Guide
 Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
How To Become A Surgical Technologist
 JOB DESCRIPTION: SURGICAL TECHNOLOGIST. The Standards and Guidelines for the Accreditation of Educational Programs in Surgical Technology have been approved by the Association of Surgical Technologists
JOB DESCRIPTION: SURGICAL TECHNOLOGIST. The Standards and Guidelines for the Accreditation of Educational Programs in Surgical Technology have been approved by the Association of Surgical Technologists
Obstetrical Emergencies
 Date: July 18, 2014 Page 1 of 5 Obstetrical Emergencies Purpose: To provide the process for the assessment and management of the patient with an obstetrical related emergency. Pre-Medical Control 1. Follow
Date: July 18, 2014 Page 1 of 5 Obstetrical Emergencies Purpose: To provide the process for the assessment and management of the patient with an obstetrical related emergency. Pre-Medical Control 1. Follow
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE
 LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
The Children s Hospital Treatment for Hypospadias Information for parents
 The Children s Hospital Treatment for Hypospadias Information for parents What is hypospadias and what is the cause? Hypospadias is a congenital (since birth) abnormality of a boy s penis. Hypospadias
The Children s Hospital Treatment for Hypospadias Information for parents What is hypospadias and what is the cause? Hypospadias is a congenital (since birth) abnormality of a boy s penis. Hypospadias
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2. Patient Information. Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate
 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
An Overview of Transradial Patient Set-up. Susan R. Cooney RN,BSN,CCRN Durham VAMC Cardiac Catheterization Lab Duke University School of Nursing
 An Overview of Transradial Patient Set-up Susan R. Cooney RN,BSN,CCRN Durham VAMC Cardiac Catheterization Lab Duke University School of Nursing Advantages of the Transradial Approach from a Nursing Perspective!!
An Overview of Transradial Patient Set-up Susan R. Cooney RN,BSN,CCRN Durham VAMC Cardiac Catheterization Lab Duke University School of Nursing Advantages of the Transradial Approach from a Nursing Perspective!!
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 4 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 4 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of the
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 4 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 4 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of the
TREATMENT 1. Control bleeding by applying pressure over wound with Gauze Pads (Surgical Supply-4). 2. Contact Surgeon for laceration repair options.
 Page 1 of 8 pages NOTE Contact Surgeon before giving any medication marked with an asterisk. In an emergency or during Loss of Signal, begin appropriate treatment; then call Surgeon as soon as possible.
Page 1 of 8 pages NOTE Contact Surgeon before giving any medication marked with an asterisk. In an emergency or during Loss of Signal, begin appropriate treatment; then call Surgeon as soon as possible.
Fact Sheet. Caring for and Changing your Supra-Pubic Catheter (SPC) Queensland Spinal Cord Injuries Service
 and Caring for and Changing your Supra-Pubic Catheter (SPC) What is a Suprapubic Catheter? A supra-pubic catheter is a tube that goes into your bladder through your abdominal wall which continuously drains
and Caring for and Changing your Supra-Pubic Catheter (SPC) What is a Suprapubic Catheter? A supra-pubic catheter is a tube that goes into your bladder through your abdominal wall which continuously drains
CATHETERISATION. East Lancashire Hospitals NHS Trust Eileen Whitehead 2010
 CATHETERISATION East Lancashire Hospitals NHS Trust Eileen Whitehead 2010 1 Indications for catheterisation: A person is unable to void naturally due to injury or a disease process Diagnostic or therapeutic
CATHETERISATION East Lancashire Hospitals NHS Trust Eileen Whitehead 2010 1 Indications for catheterisation: A person is unable to void naturally due to injury or a disease process Diagnostic or therapeutic
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3
 Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3 Time Needed One class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Locate and spell at least 75% of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems,
Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3 Time Needed One class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Locate and spell at least 75% of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems,
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner
 Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
CONSENT TO STERILIZATION OPERATION (SURGICAL VASECTOMY)
 CONSENT TO STERILIZATION OPERATION (SURGICAL VASECTOMY) I (Patient s Name) have been given the following information: Explanation of Sterilization: Vasectomy is a minor surgical procedure that can be performed
CONSENT TO STERILIZATION OPERATION (SURGICAL VASECTOMY) I (Patient s Name) have been given the following information: Explanation of Sterilization: Vasectomy is a minor surgical procedure that can be performed
VASECTOMY What is Vasectomy? How is the procedure performed? What is the no-scalpel method of doing vasectomy? When can I go back to work?
 VASECTOMY What is Vasectomy? Every man has a basic right to a vasectomy, a valuable medical procedure. Before you actually have a vasectomy, you should think about it carefully, because a vasectomy is
VASECTOMY What is Vasectomy? Every man has a basic right to a vasectomy, a valuable medical procedure. Before you actually have a vasectomy, you should think about it carefully, because a vasectomy is
Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias. A simple guide to help answer your questions
 Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias A simple guide to help answer your questions What is a hernia? A hernia is defined as a hole or defect in the abdominal (belly) wall. A hernia can either be congenital (a
Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias A simple guide to help answer your questions What is a hernia? A hernia is defined as a hole or defect in the abdominal (belly) wall. A hernia can either be congenital (a
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary
 X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
Patient Information. Posterior Cervical Surgery. Here to help. Respond Deliver & Enable
 Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Percutaneous No-Scalpel Vasectomy
 Percutaneous No-Scalpel Vasectomy Cleveland Clinic Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute Your Personal Guide To This Safe and Innovative Procedure Vasectomy is a simple, safe operation that involves blocking
Percutaneous No-Scalpel Vasectomy Cleveland Clinic Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute Your Personal Guide To This Safe and Innovative Procedure Vasectomy is a simple, safe operation that involves blocking
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Understand nurse aide skills needed to promote skin integrity.
 Unit B Resident Care Skills Essential Standard NA5.00 Understand nurse aide s role in providing residents hygiene, grooming, and skin care. Indicator Understand nurse aide skills needed to promote skin
Unit B Resident Care Skills Essential Standard NA5.00 Understand nurse aide s role in providing residents hygiene, grooming, and skin care. Indicator Understand nurse aide skills needed to promote skin
KEYHOLE HERNIA SURGERY
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage a hernia or abdominal pain. All decisions about the management of a hernia must be made in conjunction with your Physician
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage a hernia or abdominal pain. All decisions about the management of a hernia must be made in conjunction with your Physician
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Final Exam Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Final Exam Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Chapter 28: Reproductive System
 I. Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System A. Scrotum 1. What does the scrotum contain? 2. An incomplete connective tissue septum divides the scrotum into 3. Externally the scrotum has an irregular ridge
I. Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System A. Scrotum 1. What does the scrotum contain? 2. An incomplete connective tissue septum divides the scrotum into 3. Externally the scrotum has an irregular ridge
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
That being said, consider the following as you decide whether or not a vasectomy is your best option for birth control.
 Since you re reading this, you are probably strongly considering a vasectomy as a way to enjoy sex without the risk of pregnancy. You may feel nervous or hesitant to get one or have questions and concerns
Since you re reading this, you are probably strongly considering a vasectomy as a way to enjoy sex without the risk of pregnancy. You may feel nervous or hesitant to get one or have questions and concerns
Gastroschisis and My Baby
 Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY IN ROBOTIC SURGERY
 RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY IN ROBOTIC SURGERY FLORENCE BOCHU CENTRE OSCAR LAMBRET LILLE PATRICIA VARUMBEKE CENTRE OSCAR LAMBRET LILLE MELANIE FLAMENT CENTRE OSCAR LAMBRET LILLE More and more centers across the
RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY IN ROBOTIC SURGERY FLORENCE BOCHU CENTRE OSCAR LAMBRET LILLE PATRICIA VARUMBEKE CENTRE OSCAR LAMBRET LILLE MELANIE FLAMENT CENTRE OSCAR LAMBRET LILLE More and more centers across the
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy)
 Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
FREEDOM INGUINAL Hernia Repair System TECHNIQUE GUIDE
 FREEDOM INGUINAL Hernia Repair System TECHNIQUE GUIDE The following describes the open surgical preparation and implantation technique for the Freedom Inguinal Hernia Repair System. 1) Anesthesia can be
FREEDOM INGUINAL Hernia Repair System TECHNIQUE GUIDE The following describes the open surgical preparation and implantation technique for the Freedom Inguinal Hernia Repair System. 1) Anesthesia can be
PHaSES: Practical Hands-on Surgical Education System
 U.S. Toll Free 866-GOLIMBS PHaSES Range PHaSES: Practical Hands-on Surgical Education System Limbs & Things is pleased to introduce the PHaSES Range. The range is based upon our well known basic & general
U.S. Toll Free 866-GOLIMBS PHaSES Range PHaSES: Practical Hands-on Surgical Education System Limbs & Things is pleased to introduce the PHaSES Range. The range is based upon our well known basic & general
Anatomy and Physiology of the Boar. W.L. Flowers Department of Animal Science North Carolina State University Raleigh, N.C.
 Anatomy and Physiology of the Boar W.L. Flowers Department of Animal Science North Carolina State University Raleigh, N.C. 27695-7621 Introduction The boar has a tremendous impact on the reproductive efficiency
Anatomy and Physiology of the Boar W.L. Flowers Department of Animal Science North Carolina State University Raleigh, N.C. 27695-7621 Introduction The boar has a tremendous impact on the reproductive efficiency
da Vinci Prostatectomy Information Guide (Robotically-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy)
 da Vinci Prostatectomy Information Guide (Robotically-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy) Prostate Cancer Overview Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the
da Vinci Prostatectomy Information Guide (Robotically-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy) Prostate Cancer Overview Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the
PATIENT GUIDE. Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL
 PATIENT GUIDE Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL Introduction The following information is presented as a guideline for your reference. The best
PATIENT GUIDE Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL Introduction The following information is presented as a guideline for your reference. The best
Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
9.Pediatric Procedures
 9.Pediatric Procedures A. Introduction 1. Pediatric blood collection may be by skin puncture or venipuncture. 2. Skill in pediatric phlebotomy is gained by knowledge of special collection equipment, observation
9.Pediatric Procedures A. Introduction 1. Pediatric blood collection may be by skin puncture or venipuncture. 2. Skill in pediatric phlebotomy is gained by knowledge of special collection equipment, observation
A Child s guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization. Boys
 A Child s guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization Boys Introduction Probably you have just heard that you have to learn to catheterize your bladder. Most children are worried, frightened or scared
A Child s guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization Boys Introduction Probably you have just heard that you have to learn to catheterize your bladder. Most children are worried, frightened or scared
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery
 Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop
 Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
