COMPLICATIONS OF PLANTAR FASCIA RELEASE
|
|
|
- Brent Simmons
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C H A P T E R 8 COMPLICATIONS OF PLANTAR FASCIA RELEASE Michelle L. Butterworth, DPM INTRODUCTION Heel pain is one of the most common disorders that foot and ankle surgeons treat. Investigators have stated that of all adult foot complaints, 15% result from heel pain (1). It is important then that the physician know how to properly diagnose and treat this common problem. Although there are many etiologies of plantar heel pain, plantar fasciitis or plantar heel spur syndrome is the most common (2). Fortunately, conservative treatment is successful in roughly 90% of patients seeking treatment with this diagnosis (3, 4). These studies have shown that 6 months of quality conservative treatment should be attempted before surgery is considered. When patients do not respond to conservative therapies, and their plantar heel pain persists, surgical options may be pursued. Surgical treatment for plantar fasciitis has been shown to be very effective with good results routinely reported throughout the literature (5-15). However, complications can be encountered, as with any surgical procedure, so the foot and ankle surgeon must know how to identify complications when they arise and instill a rapid, effective treatment plan. HOW TO AVOID COMPLICATIONS The best way to address complications is to avoid them. Many complications can be avoided by proper patient selection, accurate diagnosis, appropriate procedure selection, good surgical technique, and implementation of an appropriate postoperative regimen. Patient Selection As was stated previously, because of the high rate of success with conservative therapies for plantar heel pain, nonoperative measures should be exhausted prior to surgical intervention. Sometimes patients want a quick fix to their problem and desire to proceed with surgery in an expeditious manner. It is the physician s responsibility to ensure that appropriate conservative therapy is employed and not let the patient control their own treatment protocol. Some patients must also be willing to make certain lifestyle changes to ensure good results. This can be very difficult for many patients and they may view surgery as an easier option. These changes may include shoe modifications, weight reduction, decreased activities, and employment alterations. It needs to be thoroughly discussed with the patient that even when surgery is employed, if some of these changes are not made, persistent pain may ensue. Differential Diagnosis Although plantar fasciitis or heel spur syndrome is the most common reason for plantar heel pain (2), the physician still needs to have a good working differential diagnosis, especially in recalcitrant cases. Other possible sources of plantar heel pain include but are not limited to neuritis or nerve entrapments, stress fractures, bone tumors, and metabolic entities such as systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, reactive arthritis, gout, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and inflammatory bowel disease. When a patient is not responsive to conservative therapy, the surgeon should consider the possibility of these other etiologies prior to surgical intervention or the surgery could be doomed to failure. Surgical Procedures When pursuing surgical intervention for plantar heel pain, the foot and ankle surgeon has several options. A plantar fasciotomy is the most common surgical procedure for plantar fasciitis but there are different techniques that may be employed (7, 9, 12, 13, 16-18). These techniques include open, endoscopic, minimal incision, and in-step plantar fasciotomies. All of these procedures have been shown to have good postoperative results with satisfied patients (8, 11). Regardless of which procedure the surgeon prefers, the proper amount of plantar fascia incised is one of the keys to a successful outcome and can avoid possible complications. Barrett and Day originally advocated complete resection of the plantar fascia (15, 16); however, 2 years later they recommended that only the medial 2/3 of the plantar fascia be released (17). With continued experience and evaluation of postoperative complications, their final recommendation is releasing only the medial 1/3 of the plantar fascia (9). The reason for the change in amount of plantar fascia to be cut is to reduce the common complication of lateral column destabilization. When the lateral fibers of the plantar fascia are left intact it is felt that the locking mechanism for the calcaneocuboid joint will not be disrupted. Cheung
2 32 CHAPTER 8 et al (19) recommend partial release of less than 40% of the fascia to minimize the effect of arch stability and maintain normal foot biomechanics. Brugh et al (20) found that lateral column symptoms were more likely to result when more than 50% of the plantar fascia was released. Surgical Technique Besides releasing the proper amount of plantar fascia, incision placement is another important component to the success of the surgical procedure. For this reason, the medial in-step plantar fasciotomy is the procedure of choice for the author for chronic plantar fasciitis. This technique is easy to perform, has few complications, has a quick recovery and postoperative healing course, and the results are predictable with a high patient satisfaction rate (7,8). Although the open procedure has been popular and still is by many surgeons, it can lead to larger, painful scars, requires significantly more dissection, has a longer postoperative recovery period, and can lead to other complications such as nerve entrapments (12, 21-23). Endoscopic plantar fasciotomy is also a very common procedure employed by foot and ankle surgeons and has been shown to have a high rate of success as well (9, 15-17). The portals however can become painful and nerve entrapment is also possible (24). The in-step plantar fasciotomy is not without reported complications such as scarring as well (7, 8). Fortunately, the author has been able to avoid painful scarring with accurate incision placement. The incision is a small transverse incision, approximately 2 cm in length, in the proximal medial arch distal to the calcaneal fat pad about cm. (Figure 1). This incision is ideal because it is in line with the relaxed skin tension lines and is on a nonweight-bearing surface so scarring is minimized. It can be tempting however, for the surgeon to make the incision too distal where the plantar fascia is more prominent. There is very little subcutaneous tissue in this area and scarring can be problematic at this location. Once the skin incision is made, there is usually minimal dissection needed before the plantar fascia is encountered and ready for release (Figure 2). Once the plantar fascia is incised, the underlying muscle belly should immediately be visualized (Figure 3). The author s preference is to release between 1 /3 to ½ of the medial plantar fascia. The author keeps the digits dorsiflexed and releases the plantar fascia until the tension has resolved. The muscle septum may be encountered in the lateral aspect of the incision. The author does not incise this or cut any of the fibers of the plantar fascia lateral to this landmark. It is important however to ensure that all of the medial fibers of the plantar fascia are released. Since the incision is small, the Figure 1. This displays the incision upon skin closure. The 2 vertical lines mark the medial and lateral aspects of the prominent band of the plantar fascia. The proximal horizontal line marks the distal end of the calcaneal fat pad. The actual skin incision is made about 2 cm (or 2 finger widths) distal to the horizontal line and between the 2 vertical lines. Figure 2. Once the skin incision is made, little dissection is necessary before the plantar fascia can be visualized. This is a major advantage to this incision placement. There is enough subcutaneous tissue still present at this location however to help minimize any scarring or thickening the patient may feel.
3 CHAPTER 8 33 Figure 3. Once the plantar fascia is incised, the underlying muscle belly is easily visualized. This ensures that all of the fibers have been transected. author probes under the skin along the abductor hallucis muscle belly. If any taut fibers are encountered, they are incised with a Metzenbaum scissor (Figure 4). Postoperative Course Fortunately, patients undergoing a plantar facsiotomy, regardless of which surgical technique is employed, typically have a fairly quick healing and recovery time. The author s typical postoperative course following an in-step plantar fasciotomy is immediate weight bearing in a surgical shoe with limited activities. Walking places the plantar fascia under tension and allows the site of the plantar fasciotomy to remain open and avoid re-adherence and fibrosis of the site. Zimmerman et al (25) however, recommend a different postoperative course. They did a retrospective study comparing 3 types of postoperative management for endoscopic plantar fasciotomy. One group was allowed immediate weight bearing. A second group wore a below-the-knee walking cast with a molded medial longitudinal arch for 2 weeks. The third group remained nonweight bearing with crutches for 2 weeks. Their results showed that the patients who wore the below-the-knee walking cast for 2 weeks required less time to obtain 80% pain relief, needed less time to return to full activities, and had fewer complications than those patients who were allowed immediate weight bearing. They were also more satisfied with their postoperative results than the patients who were nonweight bearing for 2 weeks. Figure 4. A metzenbaum scissor is utilized to go under the skin incision to probe and then cut any taut bands that remain along the medial aspect of the plantar fascia. COMPLICATIONS Even when a surgeon has operated on the ideal surgical candidate and has employed the best surgical technique, complications can still result. The physician has to identify the complication so that treatment can be instilled quickly and efficiently. As with any surgical procedure, complications may be encountered with a plantar fasciotomy, but fortunately, they are few in number and when complications are encountered most are usually temporary. Instability The most common complications encountered with a plantar fasciotomy are derived from instability; lateral column pain and instability being most pronounced (5, 9, 15-17, 26). When a plantar fasciotomy is performed, some degree of support to the foot is lost. There are numerous structures involved with this support besides the plantar fascia, including muscles and ligaments. This loss of support is usually temporary while the other structures adapt and accommodate to this loss. During this time patients can experience lateral column instability, sinus tarsitis, medial arch pain and fatigue, metatarsalgia, and strain along the lesser tarsus. With continued strain, stress fractures may also arise. There are many studies that discuss the biomechanical consequences with plantar fasciotomy. Tweed et al (27) found weakness of the medial longitudinal arch and pain
4 34 CHAPTER 8 in the lateral midfoot in cadaver specimens with a total release. Sharkey et al (28) also report significant collapse of the arch in the sagittal plane with a complete fasciotomy. In a follow up study Sharkey et al (29) found that cutting only the medial half of the plantar fascia did significantly increase peak pressure under the metatarsal heads but had little effect on pressures in other regions of the forefoot or second metatarsal strain and loading. Dividing the entire plantar fascia however, caused significant shifts in plantar pressure and force from the toes to beneath the metatarsal heads and significantly increased strain and bending in the second metatarsal. What can be concluded then from these biomecachnical studies is the same that has been concluded in the previous studies; cutting 50% or less of the plantar fascia should be performed in order to try to minimize postoperative instability. All of the above are due to instability created by the procedure itself. During the healing process and fibrosis, the arch regains some stability and these entities are typically temporary. Fortunately, when these biomechanical instability problems are encountered they usually resolve with conservative measures. Biomechanical control postoperatively is very important as the foot accommodates to the temporary destabilization. Most patients usually have an orthotic device or arch support as part of their conservative therapy. The author recommends continued use of these devices postoperatively as well, especially when the patient is having symptoms of instability. Balance padding can also be added and can be beneficial particularly along the lateral column. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroid injections can also be utilized for inflammation. If pain from biomechanical instability continues even with these measures incorporated into the treatment plan, immobilization may be necessary. Persistent Pain Continued pain or continued plantar fasciitis is another possible complication. If a patient has persistent pain following a plantar fasciotomy, the physician should look for other possible etiologies for the pain. Neuritis or nerve entrapments, especially Baxter s nerve, are a possible source of continued pain. This nerve can be entrapped as it courses below the abductor hallucis muscle. Although most inferior calcaneal spurs are not the source of heel pain in the majority of patients with plantar fasciitis, (22-24) ones with a large plantar protuberance or patients with a pes planovalgus foot type may have persistent pain requiring resection of the prominence. If a spur was removed during the initial surgery and heel pain persists, the patient should be evaluated for a possible calcaneal fracture. Resection of the spur can produce stress risers, which can develop into a fracture with weight bearing. It is also possible that the patient had a calcaneal stress fracture prior to surgery that was never diagnosed. Metabolic reasons including SLE, rheumatoid arthritis, reactive arthritis, gout, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and inflammatory bowel disease must also be among the differential diagnosis for recalcitrant pain post plantar facsiotomy. Continued inflammation following a plantar fasciotomy may also be a source of continued pain. Once the plantar fascia is allowed to adequately stretch and the tension has been released along the insertion at the calcaneus, the inflammatory process usually starts to subside. This can be a slow process however, and antiinflammatory measures including rest, ice, NSAIDs, and corticosteroid injections can be employed postoperatively if needed. Complications from Surgical Technique and Postoperative Course Besides complications resulting from altered biomechanics, scarring is one of the more common complications with a plantar fasciotomy; regardless of procedure selection. Again, the key to avoid painful, thickened scarring is good surgical execution and incision placement. Scarring can be minimized by making incisions within relaxed skin tension lines, making them parallel to the course of nerves to avoid neuritis or nerve entrapments, and keeping them on nonweight-bearing areas. When painful scars are encountered conservative treatments such as topical medications and massage, gel (Silicon) sheeting, and corticosteroid injections can be employed. Fortunately, many of the painful scars do resolve with time. For persistent pain, excision of the scar can be attempted. Also, if the scar is painful secondary to neuritis or nerve entrapment this must also be addressed. NSAIDs and corticosteroid injections are often helpful for neuritis however; nerve release and/or excision may be needed to relieve the symptoms of nerve entrapment. Persistent pain may also result if not enough of the plantar fascia was released and tight fibers remain. It is also possible that although the plantar fascia was released, if the opening of the fibers are not maintained they can fibrose and reattach. Some surgeons take a small portion of the plantar fascia and perform a plantar fasciectomy to avoid this possible complication. Some surgeons employ immediate weight bearing postoperatively while others utilize splinting and casting to help keep the fibers of the plantar fascia separated. Stretching of the plantar fascia postoperatively may also be helpful to avoid this complication but care should be taken in not being overaggressive causing rupture. Also, if too much of the plantar fascia is released and an
5 CHAPTER 8 35 active postoperative course is employed with weight bearing and stretching, one should be cautious of complete rupture. If it is felt that not enough of the plantar fascia has been released or there is scarring along the plantar fasciotomy site, revisional surgery with possible plantar fasciectomy may be warranted for relief of pain. ALTERNATIVE TREATMENT Although plantar fasciotomy has been shown to be a successful technique with few complications, extracorporeal shock wave therapy is a non-invasive alternative for the treatment of chronic plantar fascitiis and has been shown to have good results (30, 31). The surgeon should be aware of this technique and familiarize themselves with the risks and benefits compared to a plantar facsiotomy. SUMMARY Plantar fasciotomy has been shown to be a successful technique for recalcitrant heel pain. Few complications have been reported and fortunately, typically result with conservative therapies. Most complications are due to temporary instability produced in the foot from altered biomechanics resulting from the release of the plantar fascia. With proper patient selection, accurate diagnosis, and good surgical technique, complications can be minimized resulting in high patient satisfaction. For persistent pain revisional surgery may be needed and the patient may need to make lifestyle changes including possible weight loss, change in athletic routines, or even changes in employment. REFERENCES 1. Michetti ML, Jacobs SA. Calcaneal heel spurs: etiology, treatment, and a new surgical approach. J Foot Surg 1983;22: Contompasis JP. Surgical treatment of calcaneal spurs: a three year post surgical study. J Am Podiatry Assoc 1974;69: Davis PF, Severud E, Baxter DE. Painful heel syndrome: results of non-operative treatment. Foot Ankle Int 1994;15: Malay DS. Plantar fasciitis and heel spur syndrome: a retrospective analysis. In Vickers NS, et al. eds. Reconstructive Surgery of the Foot and Leg: Update 96. Tucker (GA): Podiatry Institute Publishing; p Baxter DE, Thigpen SV. Heel pain: operative results. Foot Ankle 1984;5: Anderson RB, Foster MD: Operative treatment of calcaneal pain. Foot Ankle 1989;9: Perelman GK, Figura MA, et al. The medial instep plantar fasciotomy. J Foot Ankle Surg 1995;34: Boberg JS. Heel pain. In: Reconstructive Surgery of the Foot and Leg: Update 95. Tucker (GA): The Podiatry Institute; Barrett SL, Day AV, et al. Endoscopic plantar fasciotomy: a multisurgeon prospective analysis of 652 cases. J Foot Ankle Surg 1995;34: Sammarco GJ. Surgical treatment of recalcitrant plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int 1996;17: Brekke MK, Green DG. Retrospective analysis of minimal-incision, endoscopic, and open procedures for heel spur syndrome. J Am Podiatry Med Assoc 1998;88: Benton-Weil W, Borrelli AH, et al. Percutaneous plantar fasciotomy: a minimally invasive procedure for recalcitrant plantar fasciitis. J Foot Ankle Surg 1998;37: Stone PA, McClure LP. Retrospective review of endoscopic plantar fasciotomy-1994 through J Am Podiatry Med Assoc 1999;89: Lundeen OL, Aziz S et al. Endoscopic plantar fasciotomy: a retrospective analysis of results in 53 patients. J Foot Ankle Surg 2000;39: Barrett SL, Day SV, Brown MG. Endoscopic plantar fasciotomy: preliminary study with cadaveric specimens. J Foot Surg 1991;30: Barrett SL, Day SV. Endoscopic plantar fasciotomy for chronic plantar fasciitis/heel spur syndrome: surgical technique early clinical results. J Foot Surg 1991;30: Barrett SL, Day SV. Endoscopic plantar fasciotomy: Two portal endoscopic surgical techniques clinical results of 65 procedures. J Foot Ankle Surg 1993;32: Ward WG, Clippinger FW. Proximal medial longitudinal arch incision for plantar fascia release. Foot Ankle 1987;8: Cheung JT, An KN, Zhang M. Consequences of partial and total plantar fascia release: a finite element study. Foot Ankle Int 2006;27: Brugh AM, Fallat LM, Savoy-Moore RT. Lateral column symptomatology following plantar fascial release: a prospective study. J Foot Ankle Surg 2002;41: Graves RH 3rd, Levin DR, Giacopelli J, et al. Fluoroscopy-assisted plantar fasciotomy and calcaneal exostectomy: a retrospective study and comparison of surgical techniques. J Foot Ankle Surg 1994;33: Tomczak RL, Haverstock BD. A retrospective comparison of endoscopic plantar fasciotomy to open plantar fasciotomy with heel spur resection for chronic plantar fasciitis/heel spur syndrome. J Foot Ankle Surg 1995;34: Kinley S, Frascone S, Calderone D, et al. Endoscopic plantar fasciotomy versus traditional heel spur surgery: a prospective study. J Foot Ankle Surg 1993;32: O Malley MJ, Page A, et al. Endoscopic plantar fasciotomy for chronic heel pain. Foot Ankle 2000;21: Zimmerman BJ, Cardinal MD, et al. Comparison of three types of postoperative management for endoscopic plantar fasciotomy. A retrospective study. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2000;90: Fishco WD, Goecker RM, et al. The instep plantar fasciotomy for chronic plantar fasciitis. J Am Podiatry Med Assoc 2000;90: Tweed JL, Barnes MR, et al. Biomechanical consequences of total plantar fasciotomy: a review of the literature. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2009;99: Sharkey NA, Ferris L, Donahue SW. Biomechanical consequences of plantar fascial release or rupture during gait: part I-disruptions in longitudinal arch conformation. Foot Ankle Int 1998;19: Sharkey NA, Donahue SW, Ferris L. Biomechanical consequences of plantar fascial release or rupture during gait: part II-alterations in forefoot loading. Foot Ankle Int 1999;20: Weil LS Jr, Roukis TS, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis: indications,protocol, intermediate results, and a comparison to results to fasciotomy. J Foot Ankle Surg 2002;41: Othman AM, Ragab EM. Endoscopic plantar fasciotomy versus extracorporeal shock wave therapy for treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2009; December 24.
ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY
 C H A P T E R 3 3 ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY James L. Bouchard, DPM Andrea Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION It has been estimated that 90% of patients with plantar fasciitis and heel spur syndrome get
C H A P T E R 3 3 ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY James L. Bouchard, DPM Andrea Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION It has been estimated that 90% of patients with plantar fasciitis and heel spur syndrome get
.org. Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs. Anatomy. Cause
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Page 2 of 6 plantar fascia. This is called the windlass mechanism. Later, we'll discuss how this mechanism is used to treat plantar fasciitis with str
 Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Predislocation syndrome
 Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933
 Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Plantar Fascia Release
 Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fascia
 Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People
 The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People Perry Julien, D.P.M. Past President, American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine Podiatry Coordinator, 1996 Summer Olympic Games Atlanta Georgia
The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People Perry Julien, D.P.M. Past President, American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine Podiatry Coordinator, 1996 Summer Olympic Games Atlanta Georgia
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy
 Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Plantar fascia. Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot)
 ! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
Heel Pain Syndromes DELLON INSTITUTES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE SURGERY
 Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
How To Treat Heel Pain
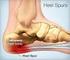 Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis
 A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN
 PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel and arch area of the foot. The plantar fascia is a strong
PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel and arch area of the foot. The plantar fascia is a strong
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10%
 Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome)
 PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understa
 Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Understanding. Heel Pain
 Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Outline. The Agony of the Foot: Disclosure. Plantar Fasciitis. Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care. Daniel Thuillier, M.D.
 The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE
 GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
Lower Back Spinal Fusion & Exercise
 & Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
& Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
.org. Achilles Tendinitis. Description. Cause. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel.
 Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies
 Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study
 Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study Christopher F. Hyer, DPM,' Lynette R. Mehl, DPM,2 Alan J. Block, DPM, MS, FACFAS,3 and Robert B. Vancourt,
Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study Christopher F. Hyer, DPM,' Lynette R. Mehl, DPM,2 Alan J. Block, DPM, MS, FACFAS,3 and Robert B. Vancourt,
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries
 Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Osteoarthritis progresses slowly and the pain and stiffness it causes worsens over time.
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems
 Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Plantar Heel Pain. By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine
 Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
MODIFIED STRAYER GASTROCNEMIUS RECESSION: A Technique Guide for the Supine Positioned Patient
 C H A P T E R 4 5 MODIFIED STRAYER GASTROCNEMIUS RECESSION: A Technique Guide for the Supine Positioned Patient M. Jay Groves, IV, DPM Gastrosoleal equinus is a common deforming force on the foot and ankle.
C H A P T E R 4 5 MODIFIED STRAYER GASTROCNEMIUS RECESSION: A Technique Guide for the Supine Positioned Patient M. Jay Groves, IV, DPM Gastrosoleal equinus is a common deforming force on the foot and ankle.
A Guide to Heel Pain
 The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
FORGET ME NOT: The Triple Arthrodesis
 C H A P T E R 1 5 FORGET ME NOT: The Triple Arthrodesis Andrea D. Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION The triple arthrodesis is a procedure that is performed much less commonly for the same conditions as it was 20
C H A P T E R 1 5 FORGET ME NOT: The Triple Arthrodesis Andrea D. Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION The triple arthrodesis is a procedure that is performed much less commonly for the same conditions as it was 20
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Joint Pain: Wrist, Knee, Shoulder, Ankle, Elbow, TMJ
 Joint Pain: Wrist, Knee, Shoulder, Ankle, Elbow, TMJ 6 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Your wrist hurts when you bend
Joint Pain: Wrist, Knee, Shoulder, Ankle, Elbow, TMJ 6 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Your wrist hurts when you bend
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet. Maneesh Bhatia. Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
.org. Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury. Anatomy. Description
 Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
A Patient s Guide to Arthritis of the Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus) With Discussion on Cheilectomy and Fusion
 A Patient s Guide to Arthritis of the Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus) With Discussion on Cheilectomy and Fusion The foot and ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary
A Patient s Guide to Arthritis of the Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus) With Discussion on Cheilectomy and Fusion The foot and ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary
Chapter 140 Heel Pain
 Chapter 140 Heel Pain David R. Richardson, MD E. Greer Richardson, MD I. Overview and Epidemiology A. General characteristics Heel pain (subcalcaneal pain syndrome) is the most common foot-related symptom
Chapter 140 Heel Pain David R. Richardson, MD E. Greer Richardson, MD I. Overview and Epidemiology A. General characteristics Heel pain (subcalcaneal pain syndrome) is the most common foot-related symptom
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
 Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fasciitis
 Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
HEEL PAIN. Differential diagnosis. 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis. 2. Enthesis. 3. Heel pad atrophy. 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome
 HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
Chamnanni Rungprai, M.D.
 Outcomes of single versus multi-level Gastrosoleus or Achilles tendon lengthening Techniques: A Comparative Study 1,2 Chamnanni Rungprai, M.D. Co-authors 1 Christopher Cyclosz, M.D. 1 Phinit Phisitkul,
Outcomes of single versus multi-level Gastrosoleus or Achilles tendon lengthening Techniques: A Comparative Study 1,2 Chamnanni Rungprai, M.D. Co-authors 1 Christopher Cyclosz, M.D. 1 Phinit Phisitkul,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. EXCISION OF RETROCALCANEAL SPUR BY A LATERAL APPROACH FOR RELIEF OF HEEL PAIN. Nandivada V.S. Kiran Kumar
 EXCISION OF RETROCALCANEAL SPUR BY A LATERAL APPROACH FOR RELIEF OF HEEL PAIN. Nandivada V.S. Kiran Kumar 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Orthopaedics, King George Hospital. Visakhapatnam. CORRESPONDING
EXCISION OF RETROCALCANEAL SPUR BY A LATERAL APPROACH FOR RELIEF OF HEEL PAIN. Nandivada V.S. Kiran Kumar 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Orthopaedics, King George Hospital. Visakhapatnam. CORRESPONDING
Ankle Arthritis Treatment in Worker Compensation The New Gold Standard ~ Total Ankle Replacement
 Ankle Arthritis Treatment in Worker Compensation The New Gold Standard ~ Total Ankle Replacement Aprajita Nakra, DPM, FACFAS Board Certified, Reconstructive Foot & Ankle Surgery Past President, Arizona
Ankle Arthritis Treatment in Worker Compensation The New Gold Standard ~ Total Ankle Replacement Aprajita Nakra, DPM, FACFAS Board Certified, Reconstructive Foot & Ankle Surgery Past President, Arizona
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION
 RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 C H A P T E R 3 LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE William D. Fishco, DPM The majority of patient encounters with the podiatrist are secondary to pain in the foot and/or ankle. If we draw an
C H A P T E R 3 LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE William D. Fishco, DPM The majority of patient encounters with the podiatrist are secondary to pain in the foot and/or ankle. If we draw an
Integra. Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 Integra Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Introduction Description... 2 Indications... 2 Contraindications... 2 Surgical Technique Step 1: Incision and Dissection...3
Integra Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Introduction Description... 2 Indications... 2 Contraindications... 2 Surgical Technique Step 1: Incision and Dissection...3
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus)
 The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus) Pathomechanical foot types usually refer to structural deformities that
The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus) Pathomechanical foot types usually refer to structural deformities that
June 2010 Case Study: 33-year-old Male with Pudendal Pain Tuesday, 01 June 2010 13:44
 Welcome to the June 2010 Neurography Institute Case Study. In this issue, we learn how MR Neurography (MRN) and Interventional MR (IMR) helped a thirtysomething male regain his active lifestyle without
Welcome to the June 2010 Neurography Institute Case Study. In this issue, we learn how MR Neurography (MRN) and Interventional MR (IMR) helped a thirtysomething male regain his active lifestyle without
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma. Magee, 2008. pg.
 PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide
 Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction The ankle is a very complex joint. There are actually three joints that make up the ankle complex: the tibiotalar
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction The ankle is a very complex joint. There are actually three joints that make up the ankle complex: the tibiotalar
MAKOplasty MAKOplasty MAKOplasty MAKOplasty MAKOplasty MAKOplasty MAKOplasty MAKOplasty MAKOplasty
 Pre-op Patient Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Your Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Page I 1 Partial Knee Resurfacing...2 Benefits Possible with the Procedure...4 Your Guide to Surgery...5 Frequently
Pre-op Patient Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Your Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Page I 1 Partial Knee Resurfacing...2 Benefits Possible with the Procedure...4 Your Guide to Surgery...5 Frequently
CAPPAGH NATIONAL ORTHOPAEDIC HOSPITAL, FINGLAS, DUBLIN 11. The Sisters of Mercy. Plantar Fascitis
 1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 2 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Assessment... 3 7.2 Treatment...
1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 2 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Assessment... 3 7.2 Treatment...
Ankle Injury/Sprains in Youth Soccer Players Elite Soccer Community Organization (ESCO) November 14, 2013
 Ankle Injury/Sprains in Youth Soccer Players Elite Soccer Community Organization (ESCO) November 14, 2013 Jeffrey R. Baker, DPM, FACFAS Weil Foot and Ankle Institute Des Plaines, IL Ankle Injury/Sprains
Ankle Injury/Sprains in Youth Soccer Players Elite Soccer Community Organization (ESCO) November 14, 2013 Jeffrey R. Baker, DPM, FACFAS Weil Foot and Ankle Institute Des Plaines, IL Ankle Injury/Sprains
Position Statement: The Use of Total Ankle Replacement for the Treatment of Arthritic Conditions of the Ankle
 Position Statement: The Use of Total Ankle Replacement for the Treatment of Arthritic Conditions of the Ankle Position Statement The (AOFAS) endorses the use of total ankle replacement surgery for treatment
Position Statement: The Use of Total Ankle Replacement for the Treatment of Arthritic Conditions of the Ankle Position Statement The (AOFAS) endorses the use of total ankle replacement surgery for treatment
Herniated Lumbar Disc
 Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Posterior Tibial Tendon Tear/Insufficiency/Rupture PTTD Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Flatfeet Deformity, Pes Planus, Fallen Arches
 Jonathan Deland, MD Chief Foot and Ankle Service 535 East 70 th Street New York, NY 10021 212-606-1665 Posterior Tibial Tendon Tear/Insufficiency/Rupture PTTD Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Flatfeet
Jonathan Deland, MD Chief Foot and Ankle Service 535 East 70 th Street New York, NY 10021 212-606-1665 Posterior Tibial Tendon Tear/Insufficiency/Rupture PTTD Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Flatfeet
Imaging of Lisfranc Injury
 November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
Mary LaBarre, PT, DPT,ATRIC
 Aquatic Therapy and the ACL Current Concepts on Prevention and Rehab Mary LaBarre, PT, DPT,ATRIC Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) tears are a common knee injury in athletic rehab. Each year, approximately
Aquatic Therapy and the ACL Current Concepts on Prevention and Rehab Mary LaBarre, PT, DPT,ATRIC Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) tears are a common knee injury in athletic rehab. Each year, approximately
Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion
 Surgical Technique Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion Prepared in consultation with: Phinit Phisitkul, MD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation University of Iowa
Surgical Technique Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion Prepared in consultation with: Phinit Phisitkul, MD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation University of Iowa
CPME Memorandum Proper Logging of Surgical Procedures November 15, 2012
 For the procedure codes listed below, the program director must review each entry to determine proper usage. 1.13 other osseous digital procedure not listed above 2.3.10 other first ray procedure not listed
For the procedure codes listed below, the program director must review each entry to determine proper usage. 1.13 other osseous digital procedure not listed above 2.3.10 other first ray procedure not listed
Arthritis www.patientedu.org
 written by Harvard Medical School Arthritis www.patientedu.org Arthritis is the most common chronic disease in the world, and it s the leading cause of disability in the United States. There are more than
written by Harvard Medical School Arthritis www.patientedu.org Arthritis is the most common chronic disease in the world, and it s the leading cause of disability in the United States. There are more than
Foot and Ankle Complaints
 Foot and Ankle Complaints INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals phalanges Midfoot 5 tarsals
Foot and Ankle Complaints INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals phalanges Midfoot 5 tarsals
Integra. Subtalar MBA Implant
 Integra Subtalar MBA Implant Patient EDUCATION Overview: What is Flatfoot? Flatfoot is a physical deformity where there is an absence of the arch that runs from the heel of the foot to the toes. A common
Integra Subtalar MBA Implant Patient EDUCATION Overview: What is Flatfoot? Flatfoot is a physical deformity where there is an absence of the arch that runs from the heel of the foot to the toes. A common
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability
 Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Common Foot Pathologies
 Common Foot Pathologies Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) What is it? Chondromalacia (of Greek origin meaning softening of the
Common Foot Pathologies Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) What is it? Chondromalacia (of Greek origin meaning softening of the
Effective Plantar Fasciitis Exercises
 Effective Plantar Fasciitis Exercises Effective Plantar Fasciitis Exercises - 12 Week Plantar Fasciitis Exercise Solution - 1 3 Month Plantar Fasciitis Exercise Program Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Structure
Effective Plantar Fasciitis Exercises Effective Plantar Fasciitis Exercises - 12 Week Plantar Fasciitis Exercise Solution - 1 3 Month Plantar Fasciitis Exercise Program Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Structure
Get Rid of Elbow Pain
 Get Rid of Elbow Pain Self Regional Healthcare Optimum Life Center 115 Academy Avenue Greenwood, SC 29646 Office: (864) 725-7088 Self Regional Healthcare Physical Therapy Savannah Lakes 207 Holiday Road
Get Rid of Elbow Pain Self Regional Healthcare Optimum Life Center 115 Academy Avenue Greenwood, SC 29646 Office: (864) 725-7088 Self Regional Healthcare Physical Therapy Savannah Lakes 207 Holiday Road
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
Therapeutic shoes (for individuals with diabetes) and foot (in-shoe) orthotics are reimbursable under Plans administered by QualCare, Inc.
 Subject: Foot Orthotics and Diabetic Shoes* Effective Date: October 1, 1999 Department(s): Utilization Management Policy: Objective: Procedure: Therapeutic shoes (for individuals with diabetes) and foot
Subject: Foot Orthotics and Diabetic Shoes* Effective Date: October 1, 1999 Department(s): Utilization Management Policy: Objective: Procedure: Therapeutic shoes (for individuals with diabetes) and foot
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities. John A. Schneider, M.D.
 Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Anatomic Percutaneous Ankle Reconstruction of Lateral Ligaments (A Percutaneous Anti ROLL)
 Anatomic Percutaneous Ankle Reconstruction of Lateral Ligaments (A Percutaneous Anti ROLL) Mark Glazebrook James Stone Masato Takao Stephane Guillo Introduction Ankle stabilization is required when a patient
Anatomic Percutaneous Ankle Reconstruction of Lateral Ligaments (A Percutaneous Anti ROLL) Mark Glazebrook James Stone Masato Takao Stephane Guillo Introduction Ankle stabilization is required when a patient
Physician Labeling. ( Clinical Application of the Duolith SD1 will be added to Operating Manuals upon PMA Approval.)
 Physician Labeling ( Clinical Application of the Duolith SD1 will be added to Operating Manuals upon PMA Approval.) CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
Physician Labeling ( Clinical Application of the Duolith SD1 will be added to Operating Manuals upon PMA Approval.) CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
Once the immune system is triggered, cells migrate from the blood into the joints and produce substances that cause inflammation.
 HealthExchange Points For Your Joints An Arthritis Talk Howard Epstein, MD Orthopaedic & Rheumatologic Institute Rheumatic & Immunologic Disease Cleveland Clinic Beachwood Family Health & Surgery Center
HealthExchange Points For Your Joints An Arthritis Talk Howard Epstein, MD Orthopaedic & Rheumatologic Institute Rheumatic & Immunologic Disease Cleveland Clinic Beachwood Family Health & Surgery Center
Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the ATP in the
 Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the ATP in the JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD Editor s Note: Part Three consists of ankle injury evaluation and taping. Part Two
Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the ATP in the JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD Editor s Note: Part Three consists of ankle injury evaluation and taping. Part Two
Council on Podiatric Medical Education
 CPME MEMORANDUM November 15, 2012 TO: Program Directors and Residents FROM: Council on Podiatric Medical Education SUBJECT: By conference call in October 2012, members of the Council's Residency Review
CPME MEMORANDUM November 15, 2012 TO: Program Directors and Residents FROM: Council on Podiatric Medical Education SUBJECT: By conference call in October 2012, members of the Council's Residency Review
A Patient s Guide to Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of the Ankle
 A Patient s Guide to Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of the Ankle The Foot and Ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of three specialist
A Patient s Guide to Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of the Ankle The Foot and Ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of three specialist
Runner's Injury Prevention
 JEN DAVIS DPT Runner's Injury Prevention Jen Davis DPT Orthopedic Physical Therapy Foot Traffic 7718 SE 13th Ave Portland, OR 97202 (503) 482-7232 [email protected] www.runfastpt.com!1 THE AMAZING RUNNER
JEN DAVIS DPT Runner's Injury Prevention Jen Davis DPT Orthopedic Physical Therapy Foot Traffic 7718 SE 13th Ave Portland, OR 97202 (503) 482-7232 [email protected] www.runfastpt.com!1 THE AMAZING RUNNER
A Simplified Approach to Common Shoulder Problems
 A Simplified Approach to Common Shoulder Problems Objectives: Understand the basic categories of common shoulder problems. Understand the common patient symptoms. Understand the basic exam findings. Understand
A Simplified Approach to Common Shoulder Problems Objectives: Understand the basic categories of common shoulder problems. Understand the common patient symptoms. Understand the basic exam findings. Understand
Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement through the Direct Lateral Approach
 Surgical Technique INNOVATIONS IN MINIMALLY INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement through the Direct Lateral Approach *smith&nephew Introduction Prosthetic replacement of the hip joint
Surgical Technique INNOVATIONS IN MINIMALLY INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement through the Direct Lateral Approach *smith&nephew Introduction Prosthetic replacement of the hip joint
.org. Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Anatomy. Cause
 Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard.
 world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard. Patient Promise: At Adventist Hinsdale Hospital, our Patient Promise means we strive for continued excellence in everything we do. This means you
world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard. Patient Promise: At Adventist Hinsdale Hospital, our Patient Promise means we strive for continued excellence in everything we do. This means you
TMJ DISEASE TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT DISEASE
 TMJ DISEASE TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT DISEASE The temporomandibular joint is the point at which the mandible (lower jaw) hinges on the skull. Frequently, the pain experienced is ear pain, s o patients are
TMJ DISEASE TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT DISEASE The temporomandibular joint is the point at which the mandible (lower jaw) hinges on the skull. Frequently, the pain experienced is ear pain, s o patients are
