Lab Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch
|
|
|
- Loraine Benson
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port S1 CustomerSwitch VLAN N/A R1 CustomerRouter Fa0/ N/A Fa0/5 H1 H1 NIC Fa0/11 H2 H2 NIC Fa0/18 H3 H3 NIC None Objectives Configure initial switch global settings. Configure host PCs and attach them to the switch. Configure a router and attach it to the switch. Configure a switch management VLAN IP address. Verify network connectivity. Configure basic port security. Configure port duplex and speed settings. All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 11
2 Background / Preparation In this lab, you connect multiple hosts and a router to the switch and test connectivity. You will configure port security, speed, and duplex settings for a switch port. This lab focuses on the basic configuration of the Cisco 2960 switch using Cisco IOS commands. The Cisco Catalyst 2960 switch comes preconfigured and only needs to be assigned basic security information before being connected to a network. To use an IP-based management product or Telnet with a Cisco switch, you must configure a management IP address. You will configure VLAN 1 to provide IP access to management functions. The information in this lab applies to other switches, however, command syntax may vary. Required Resources The following resources are required: Cisco 2960 switch or other comparable switch Router with Ethernet interface to connect to switch Three Windows-based PCs, one with a terminal emulation program RJ-45-to-DB-9 connector console cable Three straight-through Ethernet cables Access to the PC command prompt Access to a PC network TCP/IP configuration Note: Perform the instructions in the section Erasing and Reloading the Switch at the end of this lab before continuing. Step 1: Connect the hosts to the switch and configure them. a. Connect host H1 to Fast Ethernet S1 switch port Fa0/11, and connect H2 to port Fa0/18. Configure the hosts to use the same IP subnet for the address and mask as on the switch, as shown in the topology diagram and table above. b. Do not connect host H3 to the switch yet. Step 2: Connect the router to the switch and configure the router. Note: If necessary, see Lab 5.3.5, Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI, for instructions on setting the host name, passwords, and interface addresses. a. Connect the router to switch port Fa0/5. b. Configure the router with the host name CustomerRouter. c. Configure the console access and password, vty access and password, and enable secret password. d. Configure the router Fa0/1 interface as shown in the topology table. Step 3: Configure the switch. a. Configure the switch with the host name CustomerSwitch. Switch>enable Switch#config terminal Switch(config)#hostname CustomerSwitch b. Set the privilege exec mode password to cisco. CustomerSwitch(config)#enable password cisco c. Set the privilege exec mode secret password to cisco123. All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 2 of 11
3 CustomerSwitch(config)#enable secret cisco123 d. Set the console password to cisco123. CustomerSwitch(config)#line console 0 CustomerSwitch(config-line)#password cisco123 e. Configure the console line to require a password at login. CustomerSwitch(config-line)#login f. Set the vty password to cisco123. CustomerSwitch(config-line)#line vty 0 15 CustomerSwitch(config-line)#password cisco123 g. Configure the vty to require a password at login. CustomerSwitch(config-line)#login CustomerSwitch(config-line)#end Step 4: Configure the management interface on VLAN 1. a. Enter global configuration mode. Remember to use the new password. CustomerSwitch>enable CustomerSwitch#configure terminal b. Enter the interface configuration mode for VLAN 1: CustomerSwitch(config)#interface vlan 1 c. Set the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway for the management interface. The IP address must be valid for the local network where the switch is installed. CustomerSwitch(config-if)#ip address CustomerSwitch(config-if)#exit CustomerSwitch(config)#ip default-gateway CustomerSwitch(config)#end Step 5: Verify the configuration of the switch. a. Verify that the IP address of the management interface on the switch VLAN 1 and the IP address of host H1 are on the same local network. Use the show running-configuration command to check the IP address configuration of the switch. CustomerSwitch#show running-configuration Building configuration... Current configuration : 1283 bytes version 12.2 no service pad hostname CustomerSwitch enable secret 5 $1$XUe/$ch4WQ/SpcFCDd2iqd9bda/ enable password cisco interface FastEthernet0/1 interface FastEthernet0/24 interface Vlan1 All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 3 of 11
4 ip address no ip route-cache ip default-gateway ip http server line con 0 password cisco123 login line vty 0 4 password cisco123 login line vty 5 15 password cisco123 login end b. Save the configuration. CustomerSwitch#copy running-config startup-config Step 6: Verify connectivity using ping and Telnet. a. To verify that the switch and router are correctly configured, ping the router Fa0/1 interface (default gateway) IP address from the switch CLI. b. Are the pings successful? c. To verify that the hosts and switch are correctly configured, ping the switch IP address from host H1. d. Are the pings successful? e. If the ping is not successful, verify the connections and configurations again. Check to ensure that all cables are correct and that connections are seated. Check the host, switch, and router configurations. f. Open a command prompt on host H1, and telnet the IP address assigned to switch management VLAN 1. g. Enter the vty password configured in Step 3. What is the result? At the switch prompt, issue the show version command. CustomerSwitch>show version Cisco IOS Software, C2960 Software (C2960-LANBASE-M), Version 12.2(0.0.16)FX, CISCO DEVELOPMENT TEST VERSION Copyright (c) by Cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Tue 17-May-05 01:43 by yenanh ROM: Bootstrap program is C2960 boot loader BOOTLDR: C2960 Boot Loader (C2960-HBOOT-M), Version 12.2 [lqianflo_pilsner 100] Switch uptime is 3 days, 20 hours, 8 minutes System returned to ROM by power-on System image file is "flash:c2960-lanbase-mz fx.bin" cisco WS-C TC-L (PowerPC405) processor with 61440K/4088K bytes of memory. Processor board ID FHH J Last reset from power-on Target IOS Version 12.2(25)FX All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 4 of 11
5 1 Virtual Ethernet interface 24 FastEthernet interfaces 2 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces The password-recovery mechanism is enabled. 64K bytes of flash-simulated non-volatile configuration memory. Base ethernet MAC Address : 00:0B:FC:FF:E8:80 Motherboard assembly number : Motherboard serial number : FHH J Motherboard revision number : 01 System serial number : FHH J Hardware Board Revision Number : 0x01 Switch Ports Model SW Version SW Image * 1 26 WS-C TC-L 12.2(0.0.16)FX C2960- LANBASE-M Configuration register is 0xF h. What is the Cisco IOS version of this switch? i. Type quit at the switch command prompt to terminate the Telnet session. Step 7: Determine which MAC addresses that the switch has learned. a. From the Windows command prompt, get the Layer 2 addresses of the PC network interface card for each host by using the ipconfig /all command. Host H1: Host H2: Host H3: b. Determine which MAC addresses the switch has learned by using the show mac-address-table command at the privileged exec mode prompt. CustomerSwitch#show mac-address-table Mac Address Table Vlan Mac Address Type Ports All 000b.be7f.ed40 STATIC CPU All ccc.cccc STATIC CPU All ccc.cccd STATIC CPU All cdd.dddd STATIC CPU 1 000b.db04.a5cd DYNAMIC Fa0/ c DYNAMIC Fa0/ d ad DYNAMIC Fa0/18 Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 7 c. How many dynamic addresses are there? d. Do the MAC addresses match the host MAC addresses? e. Review the options that the mac-address-table command has by using the? help feature. CustomerSwitch(config)#mac-address-table? address address keyword aging-time aging-time keyword count count keyword All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 5 of 11
6 dynamic dynamic entry type interface interface keyword multicast multicast info for selected wildcard notification MAC notification parameters and history table static static entry type vlan VLAN keyword Output modifiers <cr> f. Set up a static MAC address on the Fast Ethernet interface 0/18. Use the address that was recorded for H1 in Step 7. The MAC address XXXX.YYYY.ZZZZ is used in the example statement only. CustomerSwitch(config)#mac-address-table static XXXX.YYYY.ZZZZ interface fastethernet 0/18 vlan 1 g. Verify the MAC address table entries. CustomerSwitch#show mac-address-table Mac Address Table Vlan Mac Address Type Ports All 000b.be7f.ed40 STATIC CPU All ccc.cccc STATIC CPU All ccc.cccd STATIC CPU All cdd.dddd STATIC CPU 1 000b.db04.a5cd DYNAMIC Fa0/ c DYNAMIC Fa0/ d ad STATIC Fa0/18 h. How many total MAC addresses are there now? i. What type are they? Step 8: Configure basic port security. a. Determine the options for setting port security on Fast Ethernet interface 0/4. CustomerSwitch#configure terminal CustomerSwitch(config)#interface fastethernet 0/18 CustomerSwitch(config-if)#switchport port-security? aging Port-security aging commands mac-address Secure mac address maximum Max secure addrs violation Security Violation Mode b. To allow the switch port FastEthernet 0/4 to accept only one device, configure port security. CustomerSwitch(config-if)#switchport mode access CustomerSwitch(config-if)#switchport port-security CustomerSwitch(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address sticky CustomerSwitch(config-if)#end c. Check the port security settings. CustomerSwitch#show port-security Secure Port MaxSecureAddr CurrentAddr SecurityViolation Security Action (Count) (Count) (Count) Fa0/ Shutdown All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 6 of 11
7 d. What is the security action for port Fa0/18 if a security violation occurs? e. What is the maximum secure address count? f. Display the running configuration. Note: Some output is omitted in the following display. CustomerSwitch#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 1452 bytes version 12.2 hostname CustomerSwitch interface FastEthernet0/1 interface FastEthernet0/2 interface FastEthernet0/3 interface FastEthernet0/18 switchport mode access switchport port-security switchport port-security mac-address sticky interface FastEthernet0/5 mac-address-table static 000b.db04.a5cd vlan 1 interface FastEthernet0/18 end g. Are there statements that directly reflect the security implementation in the listing of the running configuration? Step 9: Connect a different PC to the secure switch port. a. If you do not have another PC available (H3) or you cannot disconnect the PC, go to alternative Step 9. b. Disconnect host H2 from Fast Ethernet 0/18, and connect host H3 to the port. H3 has not yet been attached to the switch. From H3, ping the switch address to generate some traffic. c. Record any observations at the PC and the switch terminal session. 01:11:12: %PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: psecure-violation error detected on Fa0/18, putting Fa0/18 in err-disable state 01:11:12: %PORT_SECURITY-2-PSECURE_VIOLATION: Security violation occurred, cause d by MAC address 000c on port FastEthernet0/18. 01:11:13: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/18, chang ed state to down 01:11:14: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/18, changed state to down d. View the configuration information for just Fast Ethernet port 0/18. CustomerSwitch#show interface fastethernet 0/18 e. What is the state of this interface? Fast Ethernet 0/18 is and the line protocol is All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 7 of 11
8 Alternative Step 9: (Optional) If you do not have a third PC (host H3) and you are working with a remote lab setup and cannot physically disconnect H2, you may be able to use the following procedure to change the MAC address of the H2. The following procedure works for a wide variety of NICs. a. Choose Start > Settings > Control Panel, and double-click Network Connections. b. Right-click on the NIC for which you want to change the MAC address, and click Properties. c. In the General tab, click the Configure button. d. In the Advanced tab, under the Property section, click on Network Address or Locally Administered Address. e. On the right side, under Value, type in the new MAC address. Use the original MAC address, but change only the last value. For example, if the original MAC is 000C29C1510A, change it to 000C29C1510B. f. Type c:\>ipconfig /all to verify the changes. g. From H2, ping the switch VLAN 1 address at c:\>ping h. Record any observations from the PC and switch terminal session. 01:11:12: %PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: psecure-violation error detected on Fa0/18, putting Fa0/18 in err-disable state 01:11:12: %PORT_SECURITY-2-PSECURE_VIOLATION: Security violation occurred, cause d by MAC address 000c on port FastEthernet0/18. 01:11:13: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/18, chang ed state to down 01:11:14: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/18, changed state to down i. View the configuration information for just Fast Ethernet port 0/18. CustomerSwitch#show interface fastethernet 0/18 j. What is the state of this interface? Fast Ethernet 0/18 is, and the line protocol is. Step 10: Reactivate the port. a. Clear the sticky address entry for port Fa0/18 using the clear port-security command. S1#clear port-security sticky interface fa0/18 access b. To return the interface from error disable to administratively up, enter the shutdown command followed by the no shutdown command. S1(config)#interface fa0/18 S1(config-if)#shutdown S1(config-if)#no shutdown c. Enter the original host or change the MAC address to its original value. Ping from the command prompt. You can ping multiple times or use the ping n 100 command, which sets the number of ping packets to 100, instead of 4. Step 11: Set speed and duplex options for the ports. a. Switch port settings default to auto-duplex and auto-speed. If a computer with a 100 Mbps NIC is attached to the port, it automatically goes into full-duplex 100 Mbps mode. If a hub is attached to the switch port, it normally goes into half-duplex 10 Mbps mode. All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 8 of 11
9 b. Issue the show interfaces command to see the setting for ports Fa0/5, Fa0/11, and Fa0/18. This command generates a large amount of output. Press the spacebar until you can see all the information for these ports. What are the duplex and speed settings for these ports? Port Fa0/5 Port Fa0/11 Port Fa0/18 c. It is sometimes necessary to set the speed and duplex of a port to ensure that it operates in a particular mode. You can set the speed and duplex with the duplex and speed commands while in interface configuration mode. To force Fast Ethernet port 5 to operate at half duplex and 10 Mbps, issue the following commands: CustomerSwitch>enable CustomerSwitch#Config Terminal CustomerSwitch(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/10 CustomerSwitch(config-if)#speed 10 CustomerSwitch(config-if)#duplex half CustomerSwitch(config-if)#end CustomerSwitch# d. Issue the show interfaces command again. What is the duplex and speed setting for Fa0/5 now? Step 12: Exit the switch. a. Type exit to leave the switch and return to the welcome screen. Switch#exit b. When the steps are completed, turn off all the devices. Remove and store the cables and adapter. Step 13: Reflection. a. Which password needs to be entered to switch from user mode to privilege exec mode on the Cisco switch, and why? b. Which symbol is used to show a successful ping in the Cisco IOS software? c. What is the benefit of using port security? d. What other port-related security steps could be taken to further improve switch security? All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 9 of 11
10 Erasing and Reloading the Switch For the majority of the labs in CCNA Discovery, it is necessary to start with an unconfigured switch. Using a switch with an existing configuration may produce unpredictable results. The following instructions prepare the switch prior to performing the lab so that previous configuration options do not interfere. Instructions are provided for the 2900 and 2950 series switches. a. Enter privileged EXEC mode by typing enable. If prompted for a password, enter class (if that does not work, ask the instructor). Switch>enable b. Remove the VLAN database information file. Switch#delete flash:vlan.dat Delete filename [vlan.dat]?[enter] Delete flash:vlan.dat? [confirm] [Enter] If there was no VLAN file, this message is displayed: %Error deleting flash:vlan.dat (No such file or directory) c. Remove the switch startup configuration file from NVRAM. Switch#erase startup-config Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files Continue? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. The response should be: Erase of nvram: complete d. Check that the VLAN information was deleted in Step b by using the show vlan command. If the VLAN information was deleted, go to Step e and restart the switch using the reload command. If previous VLAN configuration information (other than the default management VLAN 1) is still present, you must power cycle the switch (hardware restart) instead of issuing the reload command. To power cycle the switch, remove the power cord from the back of the switch or unplug it, and then plug it back in. e. Restart the software using the reload command in privileged EXEC mode. Note: This step is not necessary if the switch was restarted using the power cycle method. 1) At the privileged EXEC mode, enter the reload command: Switch(config)#reload System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: Type n, and then press Enter. Proceed with reload? [confirm] [Enter] The first line of the response is: Reload requested by console. After the switch has reloaded, the line prompt is: Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 10 of 11
11 Type n, and then press Enter. Press RETURN to get started [Enter] Erasing and reloading the router a. Enter privileged EXEC mode by typing enable. Router>enable b. In privileged EXEC mode, enter the erase startup-config command. Router#erase startup-config Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files Continue? [confirm] c. Press Enter to confirm. The response is: Erase of nvram: complete d. In privileged EXEC mode, enter the reload command. Router(config)#reload System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: e. Type n, and then press Enter. Proceed with reload? [confirm] f. Press Enter to confirm. In the first line of the response is: Reload requested by console. After the router has reloaded the line prompt is: Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: g. Type n, and then press Enter. Press RETURN to get started h. Press Enter. The router is ready for the assigned lab to be performed. All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 11 of 11
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table
 Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. The configuration
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. The configuration
Connect the Host to attach to Fast Ethernet switch port Fa0/2. Configure the host as shown in the topology diagram above.
 Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration
 3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP. Objective. Background / Preparation. General Configuration Tips
 Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Configuring Port Security
 32 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure port security on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. Note For complete syntax and usage information
32 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure port security on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. Note For complete syntax and usage information
Configuring Port Security
 CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP
 Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses
 Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
Lab - Using IOS CLI with Switch MAC Address Tables
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Objectives. Router as a Computer. Router components and their functions. Router components and their functions
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands
 Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. Part 1: Router & Switch
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram
 Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Lab 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
(Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Chapter 2 Reading Organizer
 Chapter 2 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the advantages and disadvantages of static routing Configure initial settings on a Cisco switch Configure switch
Chapter 2 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the advantages and disadvantages of static routing Configure initial settings on a Cisco switch Configure switch
Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program
 APPENDIX D Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI)-based setup procedure for a standalone switch. For product overview information,
APPENDIX D Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI)-based setup procedure for a standalone switch. For product overview information,
Applicazioni Telematiche
 Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide
 Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide April 29, 2011 This document explains how to start using Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) and Cisco Configuration Professional
Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide April 29, 2011 This document explains how to start using Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) and Cisco Configuration Professional
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1
 Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration
 CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
Basic Wireless Configuration
 Basic Wireless Configuration Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Configure options in the Linksys Setup tab. Configure options in the Linksys Wireless tab. Configure options in the Linksys Administration
Basic Wireless Configuration Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Configure options in the Linksys Setup tab. Configure options in the Linksys Wireless tab. Configure options in the Linksys Administration
Router Lab Reference Guide
 Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
Configuring a Cisco 2509-RJ Terminal Router
 created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices)
 Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
 APPENDIXC Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI) setup procedure for a standalone switch. To set up the switch by using Express Setup, see
APPENDIXC Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI) setup procedure for a standalone switch. To set up the switch by using Express Setup, see
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client
 Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows
 Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers Document ID: 22189 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by Step Procedure
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers Document ID: 22189 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by Step Procedure
Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets
 Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 8 Device Interface
Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 8 Device Interface
Lab: Basic Router Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH
 Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH Objectives Use SDM to configure a router to accept SSH connections. Configure SSH client software on a PC. Establish a connection to a Cisco ISR using SSH
Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH Objectives Use SDM to configure a router to accept SSH connections. Configure SSH client software on a PC. Establish a connection to a Cisco ISR using SSH
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations
 PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows
 Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ Settings
 Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ Settings Objectives Log in to a multi-function device and view security settings. Set up Internet access policies based on IP address and application. Set
Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ Settings Objectives Log in to a multi-function device and view security settings. Set up Internet access policies based on IP address and application. Set
Objectives Understand Cisco IOS system architecture components. Work with the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface (CLI) and common commands.
 Objectives Understand Cisco IOS system architecture components. Work with the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface (CLI) and common commands. Learn about Cisco IOS troubleshooting techniques. Understand upgrading
Objectives Understand Cisco IOS system architecture components. Work with the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface (CLI) and common commands. Learn about Cisco IOS troubleshooting techniques. Understand upgrading
Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and Managing the Configuration
 CHAPTER 3 Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Connecting
CHAPTER 3 Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Connecting
Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network
 Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network CMPE 150 Fall 2005 Introduction Today you are going to be thrown into using Cisco s Internetwork Operating System (IOS) to configure
Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network CMPE 150 Fall 2005 Introduction Today you are going to be thrown into using Cisco s Internetwork Operating System (IOS) to configure
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers Document ID: 12065 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers Document ID: 12065 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
CCNA Exploration 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual
 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
Lab 4.2.3 Analyzing Network Traffic
 Lab 4.2.3 Analyzing Network Traffic Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Network Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 4.2.3 Analyzing Network Traffic Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Network Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1 255.255.0.0
Objectives. Background. Required Resources. CCNA Security
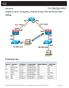 Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab Configuring Syslog and NTP (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Cisco - Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW)
 Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
Configuring Network Load Balancing for vethernet
 Configuring Network Load Balancing for vethernet This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Microsoft Network Load Balancing, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations, page 1 Configuring
Configuring Network Load Balancing for vethernet This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Microsoft Network Load Balancing, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations, page 1 Configuring
Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications
 Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
CS 326e F2002 Lab 1. Basic Network Setup & Ethereal Time: 2 hrs
 CS 326e F2002 Lab 1. Basic Network Setup & Ethereal Time: 2 hrs Tasks: 1 (10 min) Verify that TCP/IP is installed on each of the computers 2 (10 min) Connect the computers together via a switch 3 (10 min)
CS 326e F2002 Lab 1. Basic Network Setup & Ethereal Time: 2 hrs Tasks: 1 (10 min) Verify that TCP/IP is installed on each of the computers 2 (10 min) Connect the computers together via a switch 3 (10 min)
CISCO CATALYST 3550 Series Switches
 CISCO CATALYST 3550 Series Switches The switches that belong to this series are stackable and are multilayer switches that provide QoS, high availability and security that are responsible for enhancing
CISCO CATALYST 3550 Series Switches The switches that belong to this series are stackable and are multilayer switches that provide QoS, high availability and security that are responsible for enhancing
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA
 ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior
 Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab will introduce to the student the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new. This introductory
Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab will introduce to the student the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new. This introductory
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
Deploying Windows Streaming Media Servers NLB Cluster and metasan
 Deploying Windows Streaming Media Servers NLB Cluster and metasan Introduction...................................................... 2 Objectives.......................................................
Deploying Windows Streaming Media Servers NLB Cluster and metasan Introduction...................................................... 2 Objectives.......................................................
LAB Configuring NAT. Objective. Background/Preparation
 LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
USER GUIDE. Ethernet Configuration Guide (Lantronix) P/N: 2900-300321 Rev 6
 KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. USER GUIDE Ethernet Configuration Guide (Lantronix) P/N: 2900-300321 Rev 6 Contents 1 Connecting to the Kramer Device via the Ethernet Port 1 1.1 Connecting the Ethernet Port Directly
KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. USER GUIDE Ethernet Configuration Guide (Lantronix) P/N: 2900-300321 Rev 6 Contents 1 Connecting to the Kramer Device via the Ethernet Port 1 1.1 Connecting the Ethernet Port Directly
CCNA Discovery 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual
 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2900 Series Integrated Services Router
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2900 Series Integrated Services Router Document ID: 112033 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2900 Series Integrated Services Router Document ID: 112033 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by
Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ Settings
 Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ Settings Objectives Log in to a multi-function device and view security settings. Set up Internet access policies based on IP address and application. Set
Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ Settings Objectives Log in to a multi-function device and view security settings. Set up Internet access policies based on IP address and application. Set
- Advanced IOS Functions -
 1 The Configuration Register - Advanced IOS Functions - The configuration register (config-register) is a hexadecimal value that controls various aspects of how a router boots, including: Baud Rate Boot
1 The Configuration Register - Advanced IOS Functions - The configuration register (config-register) is a hexadecimal value that controls various aspects of how a router boots, including: Baud Rate Boot
ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT)
 ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT) Hostname: 2. hostname SW1 SWITCH CONFIGURATION Mgmt IP: 2. interface vlan 1 3. ip address 10.0.0.2 4. no shut Gateway: 2. ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1 Local User/Pwd:
ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT) Hostname: 2. hostname SW1 SWITCH CONFIGURATION Mgmt IP: 2. interface vlan 1 3. ip address 10.0.0.2 4. no shut Gateway: 2. ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1 Local User/Pwd:
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers Document ID: 12738 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Step by Step Procedure
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers Document ID: 12738 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Step by Step Procedure
http://computernetworkingnotes.com/ccna-study-guide/cisco-ios-naming-convention-explainedwith-examples.html
 IOS is the most critical part of any cisco device. We should always keep a backup copy of IOS to deal with any unwanted situation. In this article I will explain the backup and restore process of IOS in
IOS is the most critical part of any cisco device. We should always keep a backup copy of IOS to deal with any unwanted situation. In this article I will explain the backup and restore process of IOS in
1 crossover cable. the PCs. network
 King Abdul-Aziz University Faculty of Computing and Information Technology Department of Information Technology Computer Networks CPIT370 Lab#2: Wired Peer to Peer network and star topology using a switch
King Abdul-Aziz University Faculty of Computing and Information Technology Department of Information Technology Computer Networks CPIT370 Lab#2: Wired Peer to Peer network and star topology using a switch
Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router
 CHAPTER 2 Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router This chapter describes how to boot and configure the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router. It discusses the following subjects: Cisco
CHAPTER 2 Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router This chapter describes how to boot and configure the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router. It discusses the following subjects: Cisco
PT Activity 8.1.2: Network Discovery and Documentation Topology Diagram
 Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet
Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet
Cisco ISE Command-Line Interface
 This chapter provides information on the Cisco Identity Services Engine (Cisco ISE) command-line interface (CLI) that you can use to configure and maintain Cisco ISE. Cisco ISE Administration and Configuration
This chapter provides information on the Cisco Identity Services Engine (Cisco ISE) command-line interface (CLI) that you can use to configure and maintain Cisco ISE. Cisco ISE Administration and Configuration
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version
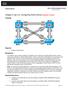 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
School of Information Technology and Engineering (SITE) CEG 4395: Computer Network Management. Lab 4: Remote Monitoring (RMON) Operations
 School of Information Technology and Engineering (SITE) CEG 4395: Computer Network Management Lab 4: Remote Monitoring (RMON) Operations Objective To become familiar with basic RMON operations, alarms,
School of Information Technology and Engineering (SITE) CEG 4395: Computer Network Management Lab 4: Remote Monitoring (RMON) Operations Objective To become familiar with basic RMON operations, alarms,
Configuring DHCP Snooping
 CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples.
CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples.
During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses.
 Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
ICND1 Lab Guide. 640-822 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version: Beta. Labs powered by
 ICND1 Lab Guide 640-822 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version: Beta Labs powered by Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 640-822 Lab Guide 25 Century Blvd. Ste. 500 Nashville,
ICND1 Lab Guide 640-822 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version: Beta Labs powered by Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 640-822 Lab Guide 25 Century Blvd. Ste. 500 Nashville,
Configuring the PIX Firewall with PDM
 Configuring the PIX Firewall with PDM Objectives In this lab exercise you will complete the following tasks: Install PDM Configure inside to outside access through your PIX Firewall using PDM Configure
Configuring the PIX Firewall with PDM Objectives In this lab exercise you will complete the following tasks: Install PDM Configure inside to outside access through your PIX Firewall using PDM Configure
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example
 Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
50-Port 10/100/1000Mbps with 4 Shared SFP. Managed Gigabit Switch WGSW-50040. Quick Installation Guide
 50-Port 10/100/1000Mbps with 4 Shared SFP Managed Gigabit Switch WGSW-50040 Quick Installation Guide Table of Contents 1. Package Content... 3 2. Switch Management... 4 3. Requirements... 5 4. Terminal
50-Port 10/100/1000Mbps with 4 Shared SFP Managed Gigabit Switch WGSW-50040 Quick Installation Guide Table of Contents 1. Package Content... 3 2. Switch Management... 4 3. Requirements... 5 4. Terminal
Configuring PROFINET
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure the PROFINET feature on the Cisco IE 3000 switch. Understanding PROFINET, page 9-1, page 9-4 Displaying the PROFINET Configuration, page 9-5 Troubleshooting
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure the PROFINET feature on the Cisco IE 3000 switch. Understanding PROFINET, page 9-1, page 9-4 Displaying the PROFINET Configuration, page 9-5 Troubleshooting
1 Basic Configuration of Cisco 2600 Router. Basic Configuration Cisco 2600 Router
 1 Basic Configuration of Cisco 2600 Router Basic Configuration Cisco 2600 Router I decided to incorporate the Cisco 2600 into my previously designed network. This would give me two seperate broadcast domains
1 Basic Configuration of Cisco 2600 Router Basic Configuration Cisco 2600 Router I decided to incorporate the Cisco 2600 into my previously designed network. This would give me two seperate broadcast domains
1. Hardware Installation
 4 Port 10/100M Internet Broadband Router with USB Printer server Quick Installation Guide #4824904AXZZ0 1. Hardware Installation A. System Requirement Before you getting started, make sure that you meet
4 Port 10/100M Internet Broadband Router with USB Printer server Quick Installation Guide #4824904AXZZ0 1. Hardware Installation A. System Requirement Before you getting started, make sure that you meet
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI
 Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
Backup and Recovery Procedures
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter provides Content Distribution Manager database backup and ACNS software recovery procedures. This chapter contains the following sections: Performing Backup and Restore Operations
CHAPTER 10 This chapter provides Content Distribution Manager database backup and ACNS software recovery procedures. This chapter contains the following sections: Performing Backup and Restore Operations
Lab 4.5.3 Diagramming Traffic Flows to and from Remote Sites
 Lab 4.5.3 Diagramming Traffic Flows to and from Remote Sites Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2
Lab 4.5.3 Diagramming Traffic Flows to and from Remote Sites Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2
Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface
 Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface This document describes how to use the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) to perform a basic software configuration for your
Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface This document describes how to use the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) to perform a basic software configuration for your
Table of Contents. Cisco Using the Cisco IOS Firewall to Allow Java Applets From Known Sites while Denying Others
 Cisco IOS Firewall to Allow Java Applets From Known Sites w Table of Contents Using the Cisco IOS Firewall to Allow Java Applets From Known Sites while Denying Others...1 Introduction...1 To Deny Java
Cisco IOS Firewall to Allow Java Applets From Known Sites w Table of Contents Using the Cisco IOS Firewall to Allow Java Applets From Known Sites while Denying Others...1 Introduction...1 To Deny Java
Chapter 7 Configuring Trunk Groups and Dynamic Link Aggregation
 Chapter 7 Configuring Trunk Groups and Dynamic Link Aggregation This chapter describes how to configure trunk groups and 802.3ad link aggregation. Trunk groups are manually-configured aggregate links containing
Chapter 7 Configuring Trunk Groups and Dynamic Link Aggregation This chapter describes how to configure trunk groups and 802.3ad link aggregation. Trunk groups are manually-configured aggregate links containing
Felix Rohrer. PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N. Topology Diagram
 Felix Rohrer PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Felix Rohrer PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
EDGE FX Network configuration
 Page 1 of 16 TITLE: Category: EDGE FX Network configuration GERBER EDGE Document Number: 4280 Supplied by: Gerber Service Last Modified: April 14, 2011 Summary: In order to connect an EDGE FX to your PC
Page 1 of 16 TITLE: Category: EDGE FX Network configuration GERBER EDGE Document Number: 4280 Supplied by: Gerber Service Last Modified: April 14, 2011 Summary: In order to connect an EDGE FX to your PC
Router and Routing Basics
 Router and Routing Basics Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts CCNA2 Routing and packet forwarding Static routing Dynamic
Router and Routing Basics Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts CCNA2 Routing and packet forwarding Static routing Dynamic
