II B.COM [ECOMMERCE] [ ] Semester IV Core: Online Marketing - 404B Multiple Choice Questions.
|
|
|
- Helen Daniels
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM Dr.G.R.Damodaran College of Science (Autonomous, affiliated to the Bharathiar University, recognized by the UGC)Reaccredited at the 'A' Grade Level by the NAAC and ISO 9001:2008 Certified CRISL rated 'A' (TN) for MBA and MIB Programmes 1. modern marketing is A. price oriented B. product oriented C. consumer oriented D. profit oriented 2. marketability utility consists of A. price B. place,price C. product, price, place and profit D. price,place,promotion and product 3. a place for buying and selling activities is called A. market B. marketing C. market research D. market information 4. which one of the following statements is correct? A. selling includes marketing B. marketing includes selling C. selling and marketing are the same D. marketing not including in business 5. marketing research is concerned with A. anticipation of production B. supply position C. financial problems D. solution to specific problems of marketing 6. mercatus means A. buying II B.COM [ECOMMERCE] [ ] Semester IV Core: Online Marketing - 404B Multiple Choice Questions.
2 2 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM B. to sell C. to assemble D. to trade 7. perfect market means A. prices are not uniform B. product are not identical C. free entry and exit into market D. lack of communication 8. the prime object of marketing is A. profit B. service C. sales D. consumer satisfaction 9. markets are created by A. nature B. economic force C. business men D. product 10. zero level channel of distribution is also called as A. direct marketing B. multilevel marketing C. two level marketing D. micro level marketing 11. marketing begins and ends with A. consumer B. transport C. price D. product brings about the changes in the ownership of products A. exchange B. storing C. promotion D. MIS is the most fundamental aspect for any merchandise transactions A. financing B. grading C. insurance
3 3 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM D. packing plays a significant role in under developed countries, as it is a multiplier of activities A. sales B. buying C. marketing D. production 15. in evolution of marketing stage was concerned only with mass production of goods. A. production orientation B. barter system C. sales orientation D. consumer orientation 16. in stage selling activity becomes the dominate factor, without any efforts for the satisfaction of the consumer needs. A. production orientation B. barter system C. sales orientation D. consumer orientation 17. according to whom-"market includes both place and region in which buyers and sellers are in free competition with one another" A. pyle B. kotler C. drucker D. clark and clark 18. marketing emphasizes on A. consumer wants B. sellers need C. manufactures profit D. retailers margin 19. factors influencing marketing concepts A. population growth B. assembling of goods C. physical transfer of goods D. scatter of goods are networks that connect people within a company to each other and to the company network A. internets B. extranets C. bit streams
4 4 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM D. WWW 21. when preparing a website, designers should ensure that the site enables user -to user communication. this design feature is known as A. context B. commerce C. community D. connection 22. when preparing a website, designers should ensure that the site makes effective use of the text, pictures and video. this design feature is known as A. content B. communication C. connection D. context 23. the exchange value of a good/service in terms of money is A. price B. product C. buying D. selling 24. selling the same product at different prices is known as A. price lining B. dual pricing C. geographical pricing D. monopoly pricing 25. the words used to convey the advertisement idea is A. advertisement B. advertisement research C. advertisement copy D. advertisement budget 26. fixing a high price for a new product will be called as A. price skimming B. price segmenetation C. dual pricing D. customary pricing 27. brand loyalty refers to product A. identification B. recognition C. preference
5 5 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM D. insistence 28. pricing based on area is called as A. domestic pricing B. geographical pricing C. skimming pricing D. cost plus pricing 29. sales management deals with A. sales B. product C. profit D. market 30. when a manufacture seller the same product two or more prices, it is called----- A. customary pricing B. dual pricing C. mark up pricing D. sealed pricing 31. consumer purchasing power is determined by A. salary B. disposable income C. total income D. price 32. a group of products that are closely related is called A. product mix B. product line C. product item D. product diversification 33. price and consumption is increasingly servers in A. decline stage B. growth stage C. maturity stage D. introduction stage 34. identify the one which is demand based pricing----- A. target pricing B. mark up pricing C. marginal pricing D. skimming pricing
6 6 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM 35. agmark standardization is given to ---- A. industrial goods B. agricultural goods C. imported goods D. consumer goods 36. product mix is the set of all product---- A. lines and items B. lines C. items D. width is the first step in marketing A. buying B. selling C. assembling D. financing 38. transportation creates utility A. time B. place C. form D. storage 39. warehouse creates -----utility A. place B. time C. form D. storage 40. brand is a means of A. communication B. identification C. packing D. specialization 41. selling is an act of A. persuasion B. illusion C. forcing D. communication 42. price is a -----term
7 7 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM A. absolute B. relative C. composite D. standard creates a particular image in the minds of consumer A. branding B. personal selling C. grading D. product planning 44. the second element to effect the volume of sales is A. price B. product C. promotion D. distribution 45. anything which possess utility is A. product B. finished goods C. raw materials D. stock is a group of products that are closely related A. product line B. product mix C. product development D. product positioning may be defined as the exchange of goods or services in terms of money A. price B. product C. grading D. branding is the high initial of the product at the time of introduction of the product in the market A. skimming price B. penetrating price C. high pricing D. moderate pricing creates a non personal stimulation of demand in advertising A. pricing B. production
8 8 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM C. public relation D. distribution 50. the stage in the product life cycle that focuses on expanding market and creating product awareness and trail is the A. decline stage B. introduction stage C. growth stage D. maturity stage 51. a----- is a promotion strategy that calls for using the sales force and trade promotion to move the product through channels. A. push strategy B. pull strategy C. blocking strategy D. integrated strategy 52. consumer goods with unique characteristics or brand identification often requiring a special purchase effort are called----- A. custom product B. specialty products C. convenience product D. shopping products 53. which of the following is NOT one of the five stages of the buyer decision process? A. need recognition B. brand identification C. information search D. purchase decision 54. 4p 's of marketing A. product, price, promotion,place B. product, price, preference, place C. product, payment, promotion, place D. product, price,promotion, publicity 55. advertisement promotes A. purchase B. production C. sales D. price is a process by which a product is branded A. brand
9 9 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM B. branding C. packaging D. pricing 57. the main principal of cooperative marketing is A. more profit B. increased production C. normal profit with service D. low price is a part of the product, which carries verbal information about the product A. label B. price C. product D. bill 59. a----- is a good offered either free or at low cost as an incentive to buy a product A. patronage reward B. coupon C. price pack D. premium 60. middlemen will increase the----- A. price of the product B. quality of the product C. profit of the product D. time and place utility of the product 61. when advertising is reached to the residential place of the people it is called A. promotional advertising B. outdoor advertising C. indoor advertising D. direct advertising is an element of buying A. financing B. assembling C. risk bearing D. customer services 63. an advertisement copy must have----- A. description B. narration C. exposition
10 10 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM D. report 64. sales promotion tool includes----- A. appeals B. coupons C. vertical marketing D. price 65. standardization includes----- A. estimating demand B. locating sources of supply C. grading D. product line 66. the middlemen who do not take any title to goods A. retailer B. wholesaler C. agent D. commission houses is allowed in the form of deductions from the list price A. trade discount B. quantity decisions C. cash discount D. seasonal discount is price at which a retailer sells the products to his buyers A. retail price B. wholesale price C. FOB price D. administered price 69. a method which aims to capture the market and increase the sales volume in known as A. packing B. purchasing C. sales promotion D. marketing gives a chance to the consumers to compare the products with their substitutes. A. sampling B. contest C. premium offers D. distribution
11 11 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM is a mass communication of information intended to persuade buyers as to maximize profits. A. advertising B. salesmanship C. sales promotion D. personal selling and other forms of promotion are supported by a advertisement. A. personal selling B. branding C. promotion D. publicity are published according to the taste or liking of the public. A. magazines B. journals C. newspaper D. special issues is a group of persons, who are experts on various phases of advertising and related marketing areas. A. advertising agency B. marketing agency C. promotion agency D. marketing research agency influences the buyer to buy a product A. personal selling B. packing C. price D. grading 76. products reach the hands of customers through a number of channels, of that the main channels is A. distributor B. wholesaler C. retailer D. agents is a wide term which includes advertising, sales and personal selling A. distribution B. warehousing C. promotion D. transportation
12 12 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM 78. an example of agent middleman A. broker B. retailer C. wholesaler D. truck jobbers 79. an example of merchant middlemen A. commission agent B. wholesaler C. resident buyers D. factors 80. the wholesaler who don't provide credit and transport facility are called as A. cash and carry wholesaler B. limited function wholesaler C. mail order wholesaler D. full service wholesaler 81. services rendered by wholesaler to manufacturer is A. acting as an intermediary B. advice to retailer C. facilitating small purchase D. to keep varieties of goods 82. a is a promotion strategy that calls for using the sales force and trade promotion to move the product channels. A. push strategy B. pull strategy C. blocking strategy D. integrated strategy 83. promotional mix includes A. advertising, personal selling and sales promotion B. advertising,awareness and sales promotion C. advertising, personal selling and publicity D. segmentation, personal selling and sales promotion 84. distributional activities involve decision regarding A. advertisement B. channels of distribution C. decision making D. promotion strategies 85. assembling of goods means bringing goods to a ----place
13 13 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM A. central B. market C. consumer D. seller's 86. transport involves goods from their place of origin to the place of their consumption. A. distributing B. collecting C. sending D. controlling 87. the social aspect of marketing is to ensure A. price B. demand C. low price with high quality D. service goods 88. the type of sales presentation approach that requires good listening and problem solving skills is the A. canned approach B. formula approach C. need - satisfaction approach D. critical - thinking approach consists of dividing a market into distinct groups of buyers on the basis of needs, characteristics, or behavior who might require separate products. A. product differentiation B. market segmentation C. market targeting D. market positioning 90. market segmentation is A. dividing B. targeting C. positioning D. differentiation 91. the behavior exhibited by people in the course of purchasing is A. seller behavior B. consumer behavior C. government behavior D. purchase behavior 92. the process of subdividing total markets into several sub market is
14 14 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM A. market fluctuating B. market positioning C. market segmentation D. market penetration 93. sound marketing of a product is depended upon A. good product B. better prices C. consumer D. proper distribution goods are meant for final consumption. A. consumer B. convenience C. shopping D. specialty is all psychological, social and physical behavior of potential consumer. A. consumer behaviour B. seller behavior C. manufacturer behavior D. household behavior 96. a buyer makes a purchase of a particular product or a particular brand is termed as A. product buying motives B. patronage motives C. selection motives D. purchase motives 97. a careful study of will facilitate the marketer in determining the size, from, style, colour, package etc. A. consumer behavior B. manufacturers potential C. market D. market segmentation 98. the process whereby individuals decide whether, what, when, how and from whom to purchase goods and services can be termed as A. buyer behavior B. household behavior C. product buying motives D. purchase motives 99. motives refers to strong
15 15 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM A. emotions B. purchase power C. needs D. behavior 100. buying decision of a customer depends on his A. attitude B. promotion C. price D. product 101. a satisfied buyer is a silent A. advertisement B. slaeman C. promotion D. target market 102. a consumer chooses an alternative which gives maximum A. satisfaction B. usage C. utility D. durability 103. the buying process begins when a person has A. a satisfied need B. an unsatisfied need C. an immediate need D. a future need 104. the individual specific behavior in the market place is affected by internal factors A. attitudes B. family C. culture D. economic 105. the external factor of consumer behavior are also called as ---- A. environmental factors B. consumer behavior factors C. product factors D. specific factor 106. economics explains that consumer behavior in relation to factors A. social B. economic
16 16 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM C. product factor D. specific factor 107. a collection of individuals which influences individual's opinion are called as A. reference groups B. advertising agency C. manufactures D. friends 108. culture refers to A. needs, motives, perception B. wants, search, decide C. product preference D. social values, language, customs carry their goods from place to place in hand craft and sell them to the consumers at their door steps. A. hawkers B. pedlars C. cheap jacks D. street traders and are the criteria for market segmentation. A. accessibility, user status B. accessibility, loyal status C. accessibility, attitude D. accessibility, responsiveness 111. the purpose of segmentation is to the changing pattern of consumers. A. measure B. access C. identify D. usage rate 112. in the whole market is divided into different geographic units A. demographic segmentation B. geographic segmentation C. socio-economic segmentation D. psychographic segmentation 113. division of market on the basis of variables like gender, income, occupation, education are called as----- A. demographic segmentation B. geographic segmentation
17 17 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM C. socio - economic segmentation D. psychographic segmentation 114. a market may be segmented by classifying people according to their enthusiasm for a product are termed as A. attitude segmentation B. geographic segmentation C. socio- economic segmentation D. psyshographic segmentation 115. benefits of segmentation A. reduced scale B. shifting loyals C. unknowm markets D. determining marketing strategies 116. when the consumers are classified on the basis of religion, customs, culture are termed as A. demographic segmentation B. geographic segmentation C. socio - economic segmentation D. psychographic segmentation 117. consumers who buy one brand all the time A. hard core loyals B. safe core loyals C. shifting loyals D. switchers 118. consumers who are loyal to two or three brands A. hard core loyals B. safe core loyals C. shifting loyals D. switchers 119. agricultural products are A. perishable B. highly priced C. low quality products D. heterogeneous goods 120. identify the one which comes under service marketing A. insurance B. motor cars C. refrigerators
18 18 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM D. television marketing is identifying and serving the needs of consumers living in villages. A. rural B. agricultural marketing C. retail marketing D. international marketing 122. increasing competition in markets make markets attractive. A. urban, rural B. urban, retail C. urban, agricultural D. urban, wholesale 123. the level of urban consumers is high and hence product features have to be changed often. A. awareness B. educational C. loyalty D. satisfaction marketing is concerned with the floe of goods and services from urban to rural and vice versa. A. urban B. retail C. international D. rural 125. reasons for growing rural markets are A. change in rural consumer behaviour B. marketing strategies C. promotional strategies D. product mix is the final stage of any economic activity. A. retail B. wholeslae C. brokering D. fatoring 127. green marketing A. making environmental friendly productd B. making more products with natural ingredients C. make use of more green colors in packages D. educate marketers about the importance of natural environment
19 19 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM are products bought by individuals and organisations for further processing or use in conducting a business. A. consumer products B. services C. industrial products D. specialty products 129. the increased has enhanced rural demand for several products A. income B. purchase power C. awareness D. population 130. product specifications like desgin, price and durability should be in a accordance with the needs of masses. A. rural B. urban C. producer D. retailer 131. rural india has many fairs and festivals and marketers use these platforms for A. brand promotions B. price strategy C. marketing strategy D. formulating strategies 132. marketing communication in the rural area has to be in A. local language B. press media C. national language D. outdoor media is where goods are sold directly to consumers A. e-commerce B. retail marketing C. product strategy D. pricing decision 134. when a product is sold utility is created A. ownership B. time C. place D. transport
20 20 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM 135. a retailer creates utility by keeping the store open when the consumers prefer to shop A. ownership B. time C. place D. transport 136. a retailer by being avaliable at a convenient location, he creates----- utiltiy A. ownership B. time C. place D. transport is the largest global online auction website A. e-bay B. alibaba.com C. wal-mart D. relience fresh will be attached to most consumer products, turning ordinary items into smart products. A. RFID tags B. barcode C. electronic coded D. electronic tags the limitations of e-marketing is A. th inability to touch and feel B. instant cash payment C. touch and feel D. immediate delivery is the encompassing term that involves the use of electronic platform-intranets, extranet and the internet to conduct a company's business. A. e- procurement B. e-business C. e-commerce D. e-marketing 141. which of the following is not one of the benefits of e-commerce to sellers? A. e-commerce can help to reduce cots B. e-commerce is a powerful tool for customer relationship building C. e-commerce increases the net cost per contact D. e-commerce offers greater flexibility in meeting customer needs.
21 21 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM 142. the e-commerce domain that involves business activity initiated by the consumer and targeted to businesses is known as: A. business to business - B2B B. consumer to consumer - C2C C. business to consumer - B2C D. consumer to business - C2B 143. a is a B2B trading network that link a particular seller with its own trading partners A. web community B. bit stream C. private trading network D. virtual network 144. the type of website that is designed to build customer goodwill and to supplement other sales channels rather than sell the company's products directly is known as a website A. customer service B. click-and mortar C. marketing D. corporate is an online advertisement that pops up between changes on a website A. border B. plunge C. boarder D. interstitial marketing is the internet version of word of mouth marketing A. viral B. visceral C. virile D. virtual 147. websites upon which members can congregate online and exchange views on issues of common interest are known as A. e-marketing B. web communities C. web casts D. virtual communities 148. what does the following definition refer to? "Achieving marketing objectives through the use of any electronic communications technology" A. e-business B. e-commerce C. e-marketing D. internet marketing
22 22 of 22 1/30/ :05 PM 149. using the internet for marketing research to find out customers needs and wants is an example of: A. promotion B. satisfying customer requirements C. anticipating customer requirements D. identifying customer requirements 150. assessing the demand for digital services(the online revenue contribution) is an example of A. awareness creation B. identifying customer requirements C. satisfying customer requirements D. anticipating customer requirements Staff Name Dr Ravi Shankar C.
What this topic is about. The purpose of marketing Different approaches to marketing Segmentation Niche &mass markets B2C & B2B marketing
 Effective Marketing What this topic is about The purpose of marketing Different approaches to marketing Segmentation Niche &mass markets B2C & B2B marketing What is Marketing? The process of identifying,
Effective Marketing What this topic is about The purpose of marketing Different approaches to marketing Segmentation Niche &mass markets B2C & B2B marketing What is Marketing? The process of identifying,
Bingo glossary marketing mix
 Bingo glossary marketing mix The management process which identifies customer wants, anticipates their future wants and then goes about satisfying them profitably. Where the market has been divided up
Bingo glossary marketing mix The management process which identifies customer wants, anticipates their future wants and then goes about satisfying them profitably. Where the market has been divided up
over-the-counter selling personal selling field selling network marketing telemarketing outbound telemarketing inbound telemarketing inside selling
 personal selling over-the-counter selling field selling network marketing outbound telemarketing telemarketing inbound telemarketing inside selling relationship selling consultative selling cross-selling
personal selling over-the-counter selling field selling network marketing outbound telemarketing telemarketing inbound telemarketing inside selling relationship selling consultative selling cross-selling
Preliminary Certificate in Marketing
 Preliminary Certificate in Marketing April 5 th, 2015 Examination PCM I 2015 85 th Intake, 25 th Year Candidate s Registration Number (As per in the examination admission form / Student ID) 0 0 0 0 0 For
Preliminary Certificate in Marketing April 5 th, 2015 Examination PCM I 2015 85 th Intake, 25 th Year Candidate s Registration Number (As per in the examination admission form / Student ID) 0 0 0 0 0 For
A review of Marketing strategy of motorcycle products in Bangladesh.
 A review of Marketing strategy of motorcycle products in Bangladesh. *Farooq Hossan *Issa Ahammad Abstract In Bangladesh extensive road network has been made in the rural areas as part of the infrastructural
A review of Marketing strategy of motorcycle products in Bangladesh. *Farooq Hossan *Issa Ahammad Abstract In Bangladesh extensive road network has been made in the rural areas as part of the infrastructural
Marketing (Marketing Principles)
 Marketing (Marketing Principles) Main Aim(s) of the Unit: To provide students with a foundation for the analysis of marketing within organizations including decision making processes, segmentation, the
Marketing (Marketing Principles) Main Aim(s) of the Unit: To provide students with a foundation for the analysis of marketing within organizations including decision making processes, segmentation, the
Barco Marketing Case Analysis
 Barco Marketing Case Analysis I. Position Statement: Over the past few months, many events have led Barco Projection Systems to be confronted with an important decision: Barco needs to continue its development
Barco Marketing Case Analysis I. Position Statement: Over the past few months, many events have led Barco Projection Systems to be confronted with an important decision: Barco needs to continue its development
Pantene myshampoo Marketing Management Project
 SOCIAL SCIENCES INSTITUTE MBA PROGRAMME Pantene myshampoo Marketing Management Project Mehmet Nuri ÇANKAYA June, 2003 Table of Contents Selection Of The Product... 3 Market Segments and Target Markets...
SOCIAL SCIENCES INSTITUTE MBA PROGRAMME Pantene myshampoo Marketing Management Project Mehmet Nuri ÇANKAYA June, 2003 Table of Contents Selection Of The Product... 3 Market Segments and Target Markets...
Marketing Management. 1 Many people are surprised when they realize how may different ideas and activities are included in the term.
 Marketing Management 1 Many people are surprised when they realize how may different ideas and activities are included in the term. 1. Marketing 2. Manufacturing 3. Labeling 2 One of the most important
Marketing Management 1 Many people are surprised when they realize how may different ideas and activities are included in the term. 1. Marketing 2. Manufacturing 3. Labeling 2 One of the most important
SECTION A Consists of a separate multiple choice paper. Each question is worth one mark. Attempt all 25 questions.
 Foundations of Marketing: B1072: 2012/13 Exam Paper This examination is in TWO sections. SECTION A Consists of a separate multiple choice paper. Each question is worth one mark. Attempt all 25 questions.
Foundations of Marketing: B1072: 2012/13 Exam Paper This examination is in TWO sections. SECTION A Consists of a separate multiple choice paper. Each question is worth one mark. Attempt all 25 questions.
Marketing: Helping Buyers Buy
 Chapter Thirteen Marketing: Helping Buyers Buy McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. CRICKET LEE Fitlogic Developed a system of clothes sizing called
Chapter Thirteen Marketing: Helping Buyers Buy McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. CRICKET LEE Fitlogic Developed a system of clothes sizing called
Marketing s Four P s: First Steps for New Entrepreneurs
 PURDUE EXTENSION EC-730 Marketing s Four P s: First Steps for New Entrepreneurs Cole Ehmke, Joan Fulton, and Jayson Lusk Department of Agricultural Economics Marketing your business is about how you position
PURDUE EXTENSION EC-730 Marketing s Four P s: First Steps for New Entrepreneurs Cole Ehmke, Joan Fulton, and Jayson Lusk Department of Agricultural Economics Marketing your business is about how you position
MARKETING INTERMEDIATE LEVEL
 Syllabus MARKETING INTERMEDIATE LEVEL Proposed for examinations sessions starting May 2017 INTERMEDIATE Level, Marketing, MATSEC 1 Syllabus objectives The syllabus is intended to encourage candidates to:
Syllabus MARKETING INTERMEDIATE LEVEL Proposed for examinations sessions starting May 2017 INTERMEDIATE Level, Marketing, MATSEC 1 Syllabus objectives The syllabus is intended to encourage candidates to:
Why do firms create new products?
 Why do firms create new products? 1. Changing Customer Needs: When they add products, services, and processes to their offerings, firms can create and deliver value more effectively by satisfying the changing
Why do firms create new products? 1. Changing Customer Needs: When they add products, services, and processes to their offerings, firms can create and deliver value more effectively by satisfying the changing
Mkt501 final term subjective Solve Questions By Adnan Awan
 Mkt501 final term subjective Solve Questions By Adnan Awan Question No: ( Marks: 3 ) How public relations are helpful in creating goodwill for organizations? ANSWER Corporations use marketing public relations
Mkt501 final term subjective Solve Questions By Adnan Awan Question No: ( Marks: 3 ) How public relations are helpful in creating goodwill for organizations? ANSWER Corporations use marketing public relations
Chapter 8 Product Concepts
 Marketing Management Chapter 8 Product Concepts Product-Introduction The customer never buys a product buy only a bundle of satisfaction Product represents anticipated and even unanticipated solutions
Marketing Management Chapter 8 Product Concepts Product-Introduction The customer never buys a product buy only a bundle of satisfaction Product represents anticipated and even unanticipated solutions
Principles of Marketing. by Jeff Tanner and Mary Anne Raymond
 Principles of Marketing by Jeff Tanner and Mary Anne Raymond Chapter 8 Using Marketing Channels to Create Value for Customers 2010 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. Marketing Channels and Channel Partners Learning
Principles of Marketing by Jeff Tanner and Mary Anne Raymond Chapter 8 Using Marketing Channels to Create Value for Customers 2010 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. Marketing Channels and Channel Partners Learning
St. Joseph s College of Commerce (Autonomous) Lesson plan 2015-2016 Even Semester M1 15 202: Marketing Management
 St. Joseph s College of Commerce (Autonomous) Lesson plan 2015-2016 Even Semester M1 15 202: Management Prepared by: Tina P Singh & Fr. Roshan Objectives of the subject: To familiarize the student with
St. Joseph s College of Commerce (Autonomous) Lesson plan 2015-2016 Even Semester M1 15 202: Management Prepared by: Tina P Singh & Fr. Roshan Objectives of the subject: To familiarize the student with
MODULE TITLE: Foundations of Marketing
 SCHOOL OF ARTS, SOCIAL SCIENCES AND MANAGEMENT DIVISION OF BUSINESS, ENTERPRISE AND MANAGEMENT LEVEL 1 DIET 1 MODULE CODE: B1072 MODULE TITLE: Foundations of Marketing DATE: 16/12/2014 WRITING TIME: 2
SCHOOL OF ARTS, SOCIAL SCIENCES AND MANAGEMENT DIVISION OF BUSINESS, ENTERPRISE AND MANAGEMENT LEVEL 1 DIET 1 MODULE CODE: B1072 MODULE TITLE: Foundations of Marketing DATE: 16/12/2014 WRITING TIME: 2
Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies. Section 17.1 Promotion and Promotional Mix Section 17.2 Types of Promotion
 Unit 6 Promotion Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies Chapter 18 Visual Merchandising and Display Chapter 19 Advertising Chapter 20 Print Advertisements Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies
Unit 6 Promotion Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies Chapter 18 Visual Merchandising and Display Chapter 19 Advertising Chapter 20 Print Advertisements Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies
ADVERTISING AND SALES PROMOTION
 C.B.C.S.S. B.Com Programme Semester V Complementary Course- 1 ADVERTISING AND SALES PROMOTION 1. Promotion mix includes Sales Promotion, Personal Selling, Advertising and a) Marketing b) Sales c) Publicity
C.B.C.S.S. B.Com Programme Semester V Complementary Course- 1 ADVERTISING AND SALES PROMOTION 1. Promotion mix includes Sales Promotion, Personal Selling, Advertising and a) Marketing b) Sales c) Publicity
Estimating Market Potential. Estimating Market Potential. Elastic and Inelastic Demand Curves Determinants of Demand Elasticity. Estimation by analogy
 Estimating Market Potential Estimation by analogy comparing data from similar countries problems: geography, culture, tradition and historical reasons Income elasticity of demand market s level of development
Estimating Market Potential Estimation by analogy comparing data from similar countries problems: geography, culture, tradition and historical reasons Income elasticity of demand market s level of development
Unit 4: Marketing Principles
 Unit 4: Marketing Principles Unit code: F/601/0556 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 credits Aim This unit aims to provide learners with understanding and skills relating to the fundamental concepts and principles
Unit 4: Marketing Principles Unit code: F/601/0556 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 credits Aim This unit aims to provide learners with understanding and skills relating to the fundamental concepts and principles
Course Outline. BUSN 5050/1-3 Marketing Management (3,0,0)
 Course Outline Department of Marketing, International Business, Entrepreneurship School of Business and Economics BUSN 5050/1-3 Marketing Management (3,0,0) Calendar Description Students examine the key
Course Outline Department of Marketing, International Business, Entrepreneurship School of Business and Economics BUSN 5050/1-3 Marketing Management (3,0,0) Calendar Description Students examine the key
Chapter 2 Market Structure, Types and Segmentation
 Market Structure There are a variety of differing market structures which are separated by the levels of competition that exist within each market and the market conditions in which the businesses operate.
Market Structure There are a variety of differing market structures which are separated by the levels of competition that exist within each market and the market conditions in which the businesses operate.
E-DISTRIBUTION. Dr. Jaume Gené Albesa Universitat Rovira i Virgili Reus (Spain) www.jaumegene.com [email protected]
 E-DISTRIBUTION Dr. Jaume Gené Albesa Universitat Rovira i Virgili Reus (Spain) www.jaumegene.com [email protected] Agenda Overview Place and Internet edistribution and product Intermediary Models Online
E-DISTRIBUTION Dr. Jaume Gené Albesa Universitat Rovira i Virgili Reus (Spain) www.jaumegene.com [email protected] Agenda Overview Place and Internet edistribution and product Intermediary Models Online
Strategies for Marketing, Sales, and Promotion
 Introduction to e-commerce Strategies for Marketing, Sales, and Promotion Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: When to use product-based and customer-based marketing strategies Communicating
Introduction to e-commerce Strategies for Marketing, Sales, and Promotion Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: When to use product-based and customer-based marketing strategies Communicating
the combination of varying methods and strategies to get your into the minds and hands of prospective buyers. Marketing is
 Marketing for Growth Wayne Brass Art Mahoney Bill McKown Heather Bender the combination of varying methods and strategies to get your product or service into the minds and hands of prospective buyers.
Marketing for Growth Wayne Brass Art Mahoney Bill McKown Heather Bender the combination of varying methods and strategies to get your product or service into the minds and hands of prospective buyers.
Chapter 11: E-Commerce
 Chapter 11: E-Commerce What is E-Commerce? E-commerce Act of doing business transactions using communications technology Has existed for years via private networks (electronic funds transfers, etc.) Now
Chapter 11: E-Commerce What is E-Commerce? E-commerce Act of doing business transactions using communications technology Has existed for years via private networks (electronic funds transfers, etc.) Now
Diploma in Marketing
 Brentwood Open Learning College Diploma in Marketing (Level 4) Course Structure & Contents Diploma in Marketing Course Structure Contents Page 1 Unit 1 to Marketing The unit 1 covers the following topics:
Brentwood Open Learning College Diploma in Marketing (Level 4) Course Structure & Contents Diploma in Marketing Course Structure Contents Page 1 Unit 1 to Marketing The unit 1 covers the following topics:
Module 6. e-business and e- Commerce
 Module 6 e-business and e- Commerce 6.1 e-business systems 6.2 e-commerce systems 6.3 Essential e- commerce processes 6.4 Electronic payment processes 6.5 e-commerce application trends 6.6 Web store requirements
Module 6 e-business and e- Commerce 6.1 e-business systems 6.2 e-commerce systems 6.3 Essential e- commerce processes 6.4 Electronic payment processes 6.5 e-commerce application trends 6.6 Web store requirements
1 Compiled by: Deep Banerjee, Marketingpundit.com (Market Segmentation)
 MARKET SEGMENTATION (Compiled by Deep Banerjee, Marketingpundit.com) Definition : The division of a market into different homogenous groups of consumers is known as Market Segmentation. Market segmentation
MARKET SEGMENTATION (Compiled by Deep Banerjee, Marketingpundit.com) Definition : The division of a market into different homogenous groups of consumers is known as Market Segmentation. Market segmentation
We use a large variety of goods and services in our daily life. These include items like
 19 INTRODUCTION TO MARKETING We use a large variety of goods and services in our daily life. These include items like toothpaste, toothbrush, soap, oil, clothes, food items, telephone, electricity and
19 INTRODUCTION TO MARKETING We use a large variety of goods and services in our daily life. These include items like toothpaste, toothbrush, soap, oil, clothes, food items, telephone, electricity and
Effective Marketing Solutions for your Small Business
 COMMUNITY TECHNOLOGY CENTER PASSAIC COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Teacher: Lucia Gheorghiu Effective Marketing Solutions for your Small Business Ideas for Today and Tomorrow Dr. Lucia Gheorghiu 1 Effective
COMMUNITY TECHNOLOGY CENTER PASSAIC COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Teacher: Lucia Gheorghiu Effective Marketing Solutions for your Small Business Ideas for Today and Tomorrow Dr. Lucia Gheorghiu 1 Effective
explain the concept and characteristics of marketing mix;
 22 Marketing Mix 22.1 Introduction The basic task of marketing is the delivery of product(s) to consumers so that their needs are fulfilled and organisational objectives are also achieved. This involves
22 Marketing Mix 22.1 Introduction The basic task of marketing is the delivery of product(s) to consumers so that their needs are fulfilled and organisational objectives are also achieved. This involves
Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy
 Integrated Marketing Strategy Dr. Richard Sjolander 2003 The Purpose of Integrated Marketing s is to Communicate with a Target Audience Promotion: or Applied marketing communication Attempts to: Inform
Integrated Marketing Strategy Dr. Richard Sjolander 2003 The Purpose of Integrated Marketing s is to Communicate with a Target Audience Promotion: or Applied marketing communication Attempts to: Inform
Chapter 6 Marketing services
 Egg marketing 81 Chapter 6 Marketing services Market information, marketing education and training, promotional campaigns to promote egg consumption, marketing research to aid in producer and trader decision
Egg marketing 81 Chapter 6 Marketing services Market information, marketing education and training, promotional campaigns to promote egg consumption, marketing research to aid in producer and trader decision
Agricultural Marketing. Direct Marketing Strategies and Opportunities. Commodity or Niche? MARKETS DEFINED
 Direct Marketing Strategies and Opportunities Mykel Taylor Assistant Professor Dept. of Agricultural Economics NCKS Commercial Enterprises Conference February 25, 2012 Agricultural Marketing Commodity
Direct Marketing Strategies and Opportunities Mykel Taylor Assistant Professor Dept. of Agricultural Economics NCKS Commercial Enterprises Conference February 25, 2012 Agricultural Marketing Commodity
In the previous lesson you learnt that marketing identifies consumers needs and supplies
 MODULE-5 20 MARKETING MIX In the previous lesson you learnt that marketing identifies consumers needs and supplies various goods and services to satisfy those needs most effectively. So the businessman
MODULE-5 20 MARKETING MIX In the previous lesson you learnt that marketing identifies consumers needs and supplies various goods and services to satisfy those needs most effectively. So the businessman
Executive Cover Memo. The Allround brand is in a favorable position, but the cold medicine is also becoming a
 Executive Cover Memo The Allround brand is in a favorable position, but the cold medicine is also becoming a cash cow. I believe that Allround needs to increase its unit sales with both grocery stores
Executive Cover Memo The Allround brand is in a favorable position, but the cold medicine is also becoming a cash cow. I believe that Allround needs to increase its unit sales with both grocery stores
Scaling Up For Regional Markets Grading Standards and Wholesale Glossary of Terms
 Scaling Up For Regional Markets Grading Standards and Wholesale Glossary of Terms Wholesale food markets often use terms and phrases unique to the industry. To understand a market report, communicate with
Scaling Up For Regional Markets Grading Standards and Wholesale Glossary of Terms Wholesale food markets often use terms and phrases unique to the industry. To understand a market report, communicate with
Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: Promotional Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Promotion. The Traditional Communication Model. Noise.
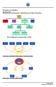 Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: al Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Target Market Product Place Price Personal Selling Mass Selling Sales Advertising Publicity The Traditional Communication Model
Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: al Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Target Market Product Place Price Personal Selling Mass Selling Sales Advertising Publicity The Traditional Communication Model
Non-personal communication
 Week 8: Promotions Integrated Marketing Communications: advertising, Sales Promotion, Public Relations, and Direct Marketing Strategic Goals Of Marketing Communication Create awareness Build positive images
Week 8: Promotions Integrated Marketing Communications: advertising, Sales Promotion, Public Relations, and Direct Marketing Strategic Goals Of Marketing Communication Create awareness Build positive images
Final Examination Semester 1 / Year 2010
 Southern College Kolej Selatan 南 方 学 院 Final Examination Semester 1 / Year 2010 COURSE : MARKETING PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE COURSE CODE : ADAD 2062 TIME : 2 1/2 HOURS DEPARTMENT : ART AND DESIGN LECTURER
Southern College Kolej Selatan 南 方 学 院 Final Examination Semester 1 / Year 2010 COURSE : MARKETING PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE COURSE CODE : ADAD 2062 TIME : 2 1/2 HOURS DEPARTMENT : ART AND DESIGN LECTURER
Table 1: Profile of Consumer Particulars Classification Numbers Percentage Upto 20 25 41.67 Age. 21 to 40 18 30.00 Above 40 17 28.
 2014; 1(7): 280-286 IJMRD 2014; 1(7): 280-286 www.allsubjectjournal.com Received: 04-12-2014 Accepted: 22-12-2014 e-issn: 2349-4182 p-issn: 2349-5979 V. Suganthi Assistant Professor, Department of Commerce,
2014; 1(7): 280-286 IJMRD 2014; 1(7): 280-286 www.allsubjectjournal.com Received: 04-12-2014 Accepted: 22-12-2014 e-issn: 2349-4182 p-issn: 2349-5979 V. Suganthi Assistant Professor, Department of Commerce,
Outline. Introduction to E-commerce. Why is e-commerce? [Awad] What is e-commerce? Session 1. Yan Wang [email protected]. E-commerce.
![Outline. Introduction to E-commerce. Why is e-commerce? [Awad] What is e-commerce? Session 1. Yan Wang yan.wang@mq.edu.au. E-commerce. Outline. Introduction to E-commerce. Why is e-commerce? [Awad] What is e-commerce? Session 1. Yan Wang yan.wang@mq.edu.au. E-commerce.](/thumbs/32/15625297.jpg) Introduction to E-commerce Session 1 Yan Wang [email protected] Outline E-commerce E-business Examples of e-commerce Types of e-commerce 1 2 What is e-commerce? The marketing, buying and selling of products
Introduction to E-commerce Session 1 Yan Wang [email protected] Outline E-commerce E-business Examples of e-commerce Types of e-commerce 1 2 What is e-commerce? The marketing, buying and selling of products
Contents. Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing. Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22. Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38
 Contents Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22 Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38 Part- II: The Customer Experience Chapter 3 Consumer Behavior
Contents Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22 Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38 Part- II: The Customer Experience Chapter 3 Consumer Behavior
Power Struggles and Sales Promotion
 Chapter 18 Sales Promotion Power Struggles and Sales Promotion Sales promotion plays a key strategic role in the channel of distribution Big name brands need to supported with sales promotion and POP in
Chapter 18 Sales Promotion Power Struggles and Sales Promotion Sales promotion plays a key strategic role in the channel of distribution Big name brands need to supported with sales promotion and POP in
Marketing Plan Checklist
 Marketing Plan Checklist Water Street Design, LLC 205 North Cameron Street Winchester, VA 22601 540-667-6646 waterstdesign.com Creating a Marketing Plan You d be surprised how many large brands rely on
Marketing Plan Checklist Water Street Design, LLC 205 North Cameron Street Winchester, VA 22601 540-667-6646 waterstdesign.com Creating a Marketing Plan You d be surprised how many large brands rely on
WORKSHOP #4 CUSTOMER TARGETING (MARKETING) STRATEGY
 WORKSHOP #4 CUSTOMER TARGETING (MARKETING) STRATEGY THE FUNDAMENTAL ELEMENTS OF THE DEFINITION OF A CUSTOMER TARGETING (MARKETING) STRATEGY Corporate Strategy Mission of the firm Strategic thrusts and
WORKSHOP #4 CUSTOMER TARGETING (MARKETING) STRATEGY THE FUNDAMENTAL ELEMENTS OF THE DEFINITION OF A CUSTOMER TARGETING (MARKETING) STRATEGY Corporate Strategy Mission of the firm Strategic thrusts and
Chapter 14: Retailing, Direct Marketing, and Wholesaling
 Chapter 14: Retailing, Direct Marketing, and Wholesaling Pride/Ferrell Foundations of Marketing Fourth Edition Prepared by Milton Pressley University of New Orleans Objectives 1. Understand the purpose
Chapter 14: Retailing, Direct Marketing, and Wholesaling Pride/Ferrell Foundations of Marketing Fourth Edition Prepared by Milton Pressley University of New Orleans Objectives 1. Understand the purpose
Detailed Syllabus of POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN RETAIL MANAGEMENT (SEMESTER SYSTEM)
 Detailed Syllabus of POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN RETAIL MANAGEMENT (SEMESTER SYSTEM) 1 COURSE TITLE: POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN RETAIL MANAGEMENT DURATION : 1 YEAR (Semester System) TOTAL DIPLOMA MARKS : 900
Detailed Syllabus of POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN RETAIL MANAGEMENT (SEMESTER SYSTEM) 1 COURSE TITLE: POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN RETAIL MANAGEMENT DURATION : 1 YEAR (Semester System) TOTAL DIPLOMA MARKS : 900
LOYALTY PROGRAMS: BUILDING CUSTOMER LOYALTY TO BUILD PROFITS
 LOYALTY PROGRAMS: BUILDING CUSTOMER LOYALTY TO BUILD PROFITS Loyalty is one of the great engines of business success. Frederick F. Reicheld, author of The Loyalty Effect Today s successful businesses recognize
LOYALTY PROGRAMS: BUILDING CUSTOMER LOYALTY TO BUILD PROFITS Loyalty is one of the great engines of business success. Frederick F. Reicheld, author of The Loyalty Effect Today s successful businesses recognize
Consumer Behaviour. Customer is profit, all else is overload...
 Consumer Behaviour 1 1 Consumer Behaviour Customer is profit, all else is overload... This chapter provides an introduction to consumer behaviour. Consumer is the most important person. The business revolves
Consumer Behaviour 1 1 Consumer Behaviour Customer is profit, all else is overload... This chapter provides an introduction to consumer behaviour. Consumer is the most important person. The business revolves
Marketing channels exist to create utility for. Customers
 Channel Objectives Global Marketing Channels and Physical Distribution Global Marketing Chapter 12 1 Marketing channels exist to create utility for customers Place utility availability of a product or
Channel Objectives Global Marketing Channels and Physical Distribution Global Marketing Chapter 12 1 Marketing channels exist to create utility for customers Place utility availability of a product or
Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning
 Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning What We Learn? Learn the three steps of target marketing, market segmentation, target marketing, and market positioning Understand the major bases for segmenting
Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning What We Learn? Learn the three steps of target marketing, market segmentation, target marketing, and market positioning Understand the major bases for segmenting
Course Description Applicable to students admitted in 2015-2016
 Course Description Applicable to students admitted in 2015-2016 Required and Elective Courses (from ) COMM 4820 Advertising Creativity and Creation The course mainly consists of four areas: 1) introduction
Course Description Applicable to students admitted in 2015-2016 Required and Elective Courses (from ) COMM 4820 Advertising Creativity and Creation The course mainly consists of four areas: 1) introduction
Introduction to E-Commerce
 Introduction to E-Commerce 1/12/2016 What is E-commerce? Buying and selling of products or services over electronic systems such as the Internet and other computer networks Online purchase of goods or
Introduction to E-Commerce 1/12/2016 What is E-commerce? Buying and selling of products or services over electronic systems such as the Internet and other computer networks Online purchase of goods or
Chapter 26 Pricing Strategies. Section 26.1 Basic Pricing Policies Section 26.2 Strategies in the Pricing Process
 Chapter 26 Pricing Strategies Section 26.1 Basic Pricing Policies Section 26.2 Strategies in the Pricing Process Basic Pricing Policies Key Terms markup pricing cost-plus pricing one-price policy flexible-price
Chapter 26 Pricing Strategies Section 26.1 Basic Pricing Policies Section 26.2 Strategies in the Pricing Process Basic Pricing Policies Key Terms markup pricing cost-plus pricing one-price policy flexible-price
Marketing: Advertising and Sales Promotion
 Marketing: Advertising and Sales Promotion Food Communication II Section G Communication Mix Strategies All of the information has been adapted from: Kotler P. Armstrong, G., 2004. Principles of Marketing.
Marketing: Advertising and Sales Promotion Food Communication II Section G Communication Mix Strategies All of the information has been adapted from: Kotler P. Armstrong, G., 2004. Principles of Marketing.
Alexander Nikov. 7. ecommerce Marketing Concepts. Consumers Online: The Internet Audience and Consumer Behavior. Outline
 INFO 3435 E-Commerce Teaching Objectives 7. ecommerce Marketing Concepts Alexander Nikov Identify the key features of the Internet audience. Discuss the basic concepts of consumer behavior and purchasing
INFO 3435 E-Commerce Teaching Objectives 7. ecommerce Marketing Concepts Alexander Nikov Identify the key features of the Internet audience. Discuss the basic concepts of consumer behavior and purchasing
SALES PROMOTION, EVENTS, AND SPONSORSHIPS
 PART FIVE: INTEGRATION AND EVALUATION Chapter 16 Wells, Moriarty, Burnett & Lwin ADVERTISING Principles and Effective IMC Practice Koekemoer L. (2004)., Marketing Communications, Juta and Company Ltd.
PART FIVE: INTEGRATION AND EVALUATION Chapter 16 Wells, Moriarty, Burnett & Lwin ADVERTISING Principles and Effective IMC Practice Koekemoer L. (2004)., Marketing Communications, Juta and Company Ltd.
7096 TRAVEL AND TOURISM
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 7096 TRAVEL AND TOURISM 7096/23 Paper 2 (Alternative to Coursework), maximum raw mark 100
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 7096 TRAVEL AND TOURISM 7096/23 Paper 2 (Alternative to Coursework), maximum raw mark 100
Sales Promotion. The Marketers Dilemma. Sales Promotion Defined:
 Sales Promotion The Marketers Dilemma Sales Promotion Defined: A direct inducement that offers extra value or incentive for the product to the salesforce, distributors, or the ultimate consumer with the
Sales Promotion The Marketers Dilemma Sales Promotion Defined: A direct inducement that offers extra value or incentive for the product to the salesforce, distributors, or the ultimate consumer with the
LCCI International Qualifications. Level 3 Certificate in Selling and Sales Management. Extended Syllabus. Effective from 2007
 LCCI International Qualifications Level 3 Certificate in Selling and Sales Management Extended Syllabus Effective from 2007 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909 Email. [email protected]
LCCI International Qualifications Level 3 Certificate in Selling and Sales Management Extended Syllabus Effective from 2007 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909 Email. [email protected]
WSTiE. Marketing in Tourism
 WSTiE Marketing in Tourism dr Anna Sobczyk-Kolbuch AGENDA 1. Marketing the essence and features. Clasical and modern concepts of marketing 2. Evolution of enterprises` activities on the market the origin
WSTiE Marketing in Tourism dr Anna Sobczyk-Kolbuch AGENDA 1. Marketing the essence and features. Clasical and modern concepts of marketing 2. Evolution of enterprises` activities on the market the origin
Contents. Chapter 1 Introduction to Sales Management 3-16. Chapter 2 The Sales Organization 17-40. Chapter 3 Sales Functions and Policies 41-54
 Contents Part- I: The Sales Perspective Chapter 1 Introduction to Sales Management 3-16 Chapter 2 The Sales Organization 17-40 Chapter 3 Sales Functions and Policies 41-54 Chapter 4 Personal Selling 55-80
Contents Part- I: The Sales Perspective Chapter 1 Introduction to Sales Management 3-16 Chapter 2 The Sales Organization 17-40 Chapter 3 Sales Functions and Policies 41-54 Chapter 4 Personal Selling 55-80
What is Small Business Marketing?
 What is Small Business Marketing? Small Business Marketing (definition) Business activities that direct the creation, development, and delivery of a bundle of satisfaction from the creator to the targeted
What is Small Business Marketing? Small Business Marketing (definition) Business activities that direct the creation, development, and delivery of a bundle of satisfaction from the creator to the targeted
For example: The market for music could be segmented in various ways, including: Age ie teenagers will have different tastes to 40 year olds
 Market Segmentation Most businesses will not treat a market as a single entity Instead they break the market into small pieces, or segments, where the consumers in each segment have similar characteristics
Market Segmentation Most businesses will not treat a market as a single entity Instead they break the market into small pieces, or segments, where the consumers in each segment have similar characteristics
Marketing Management
 Marketing Management Theocharis Katranis Fall Semester 2014 1 Today s Lecture 1. We will discuss the competitive forces in a market 2. We will identify and analyse competitors 3. We will elaborate different
Marketing Management Theocharis Katranis Fall Semester 2014 1 Today s Lecture 1. We will discuss the competitive forces in a market 2. We will identify and analyse competitors 3. We will elaborate different
Marketing Mix of 4P S for Competitive Advantage
 IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSRJBM) ISSN: 2278-487X Volume 3, Issue 6 (Sep,-Oct. 2012), PP 40-45 Marketing Mix of 4P S for Competitive Advantage Meera Singh 1 1 (Computer Department (H.S.S),
IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSRJBM) ISSN: 2278-487X Volume 3, Issue 6 (Sep,-Oct. 2012), PP 40-45 Marketing Mix of 4P S for Competitive Advantage Meera Singh 1 1 (Computer Department (H.S.S),
MARKET SEGMENTATION: A CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
 Jasmer Singh International Journal of Advanced Research in MARKET SEGMENTATION: A CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK Abstract: The more a marketing paradigm evolves, the more long-term relationship with customers gains
Jasmer Singh International Journal of Advanced Research in MARKET SEGMENTATION: A CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK Abstract: The more a marketing paradigm evolves, the more long-term relationship with customers gains
Marketing: Mastering the Process
 Marketing: Mastering the Process Course Description This course teaches you key components of marketing strategy and tactics including: identification, analysis and selection of target markets; development
Marketing: Mastering the Process Course Description This course teaches you key components of marketing strategy and tactics including: identification, analysis and selection of target markets; development
Factors Influencing Laptop Buying Behavior a Study on Students Pursuing Ug/Pg in Computer Science Department of Assam University
 Commerce Factors Influencing Laptop Buying Behavior a Study on Students Pursuing Ug/Pg in Computer Science Department of Assam University Keywords Laptop, Buying behavior, Students of computer science,
Commerce Factors Influencing Laptop Buying Behavior a Study on Students Pursuing Ug/Pg in Computer Science Department of Assam University Keywords Laptop, Buying behavior, Students of computer science,
BA 7012 Retail Management
 UNIT-1 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT SCIENCE BA7012 RETAILMANAGEMENT 1. What Is Retailing. 2. What are the challenges of retailing 3. What are the opportunities of retailing 4.
UNIT-1 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT SCIENCE BA7012 RETAILMANAGEMENT 1. What Is Retailing. 2. What are the challenges of retailing 3. What are the opportunities of retailing 4.
Marketing: Promotion Basics
 Name: Class: Date Taken: Total Possible Marks: 39 Marketing: Promotion Basics Complete the following questions in the time allowed by your teacher Write a short, accurate definition for each of the following
Name: Class: Date Taken: Total Possible Marks: 39 Marketing: Promotion Basics Complete the following questions in the time allowed by your teacher Write a short, accurate definition for each of the following
E-commerce refers to paperless exchange of business information using following ways.
 E-Commerce E-Commerce or Electronics Commerce is a methodology of modern business which fulfills the need of business organizations, vendors and customers to reduce cost and improve the quality of goods
E-Commerce E-Commerce or Electronics Commerce is a methodology of modern business which fulfills the need of business organizations, vendors and customers to reduce cost and improve the quality of goods
Fundamentals of Marketing Management
 Fundamentals of Management Dr. P.V. (Sundar) Managing World-Class Organizations What is? Process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products
Fundamentals of Management Dr. P.V. (Sundar) Managing World-Class Organizations What is? Process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products
Trier 5. Segmentation and positioning
 Trier 5 Segmentation and positioning Previewing concepts (1) Define the steps in designing a customerdriven marketing strategy: market segmentation, market targeting, differentiation, and positioning (STP)
Trier 5 Segmentation and positioning Previewing concepts (1) Define the steps in designing a customerdriven marketing strategy: market segmentation, market targeting, differentiation, and positioning (STP)
MARKETING CHANNELS AND WHOLESALING
 C H A P T E R S I XT E E N MARKETING CHANNELS AND WHOLESALING 16-1 AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Explain what is meant by a marketing channel of distribution and why intermediaries
C H A P T E R S I XT E E N MARKETING CHANNELS AND WHOLESALING 16-1 AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Explain what is meant by a marketing channel of distribution and why intermediaries
Making business simple...
 Making business simple... Introduction 2 Contents Every business needs a Marketing Plan. This guide has been created to assist you in putting your Marketing Plan together. This guide will help you to indicate
Making business simple... Introduction 2 Contents Every business needs a Marketing Plan. This guide has been created to assist you in putting your Marketing Plan together. This guide will help you to indicate
Product. Promotion. Price. Customer. Place. People. Physical Evidence. Processes
 What is Marketing? Marketing is about customers Marketing for Squash Presented by Elizabeth A Dendle Senior Programme Director HKU SPACE Who are they? Marketing is a cultural approach to management - it
What is Marketing? Marketing is about customers Marketing for Squash Presented by Elizabeth A Dendle Senior Programme Director HKU SPACE Who are they? Marketing is a cultural approach to management - it
1.Because e-commerce is ubiquitous it reduces A. marketspace. B. transaction costs. C. dynamic pricing. D. price discrimination.
 1.Because e-commerce is ubiquitous it reduces A. marketspace. B. transaction costs. C. dynamic pricing. D. price discrimination. 2. The ability of consumers to use the Internet to discover the actual costs
1.Because e-commerce is ubiquitous it reduces A. marketspace. B. transaction costs. C. dynamic pricing. D. price discrimination. 2. The ability of consumers to use the Internet to discover the actual costs
Marketing at McDonald s
 at McDonald s Careers McDonald s is one of the best known brands worldwide. This case study shows how McDonald s aims to continually build its brand by listening to its customers. It also identifies the
at McDonald s Careers McDonald s is one of the best known brands worldwide. This case study shows how McDonald s aims to continually build its brand by listening to its customers. It also identifies the
E-Commerce Business Models and Concepts
 Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 2-1 E-Commerce Business Models and Concepts Created by, David Zolzer, Northwestern State University Louisiana Learning Objectives! Identify the key components
Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 2-1 E-Commerce Business Models and Concepts Created by, David Zolzer, Northwestern State University Louisiana Learning Objectives! Identify the key components
MCQ s Unit-I: Introduction to Sales and Distribution Management
 MCQ s Unit-I: Introduction to Sales and Distribution Management 1. Avon, Amway, and Tupperware use which of the following forms of channel distribution? a. direct marketing channel b. indirect marketing
MCQ s Unit-I: Introduction to Sales and Distribution Management 1. Avon, Amway, and Tupperware use which of the following forms of channel distribution? a. direct marketing channel b. indirect marketing
1. Which segment do ebay, Amazon.com, and LandsEnd.com belong? 2. Which segment focuses on consumers dealing with each other?
 1. Which segment do ebay, Amazon.com, and LandsEnd.com belong? A) B2Bs B) B2Cs C) C2Bs D) C2Cs 2. Which segment focuses on consumers dealing with each other? A) B2B B) B2C C) C2B D) C2C 3. Which segment
1. Which segment do ebay, Amazon.com, and LandsEnd.com belong? A) B2Bs B) B2Cs C) C2Bs D) C2Cs 2. Which segment focuses on consumers dealing with each other? A) B2B B) B2C C) C2B D) C2C 3. Which segment
MBA I Year Examination. MP-106 : Marketing Management. Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 80
 MBA I Year Examination MP-106 : Marketing Management Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 80 Note: The question paper is divided into three sections A, B & C. Write Answers as per the given instructions. Section
MBA I Year Examination MP-106 : Marketing Management Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 80 Note: The question paper is divided into three sections A, B & C. Write Answers as per the given instructions. Section
BUSINESS. Unit 7 Marketing campaign. 2016 Suite. Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3. L/507/8154 Guided learning hours: 60. ocr.org.
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 BUSINESS Unit 7 Marketing campaign L/507/8154 Guided learning hours: 60 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016 ocr.org.uk/business LEVEL 3 UNIT 7: Marketing campaign
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 BUSINESS Unit 7 Marketing campaign L/507/8154 Guided learning hours: 60 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016 ocr.org.uk/business LEVEL 3 UNIT 7: Marketing campaign
MICHIGAN TEST FOR TEACHER CERTIFICATION (MTTC) TEST OBJECTIVES FIELD 036: MARKETING EDUCATION
 MICHIGAN TEST FOR TEACHER CERTIFICATION (MTTC) TEST OBJECTIVES Subarea Marketing Foundations Marketing Functions Technology, Ethics, and Career Development Approximate Percentage of Questions on Test 40%
MICHIGAN TEST FOR TEACHER CERTIFICATION (MTTC) TEST OBJECTIVES Subarea Marketing Foundations Marketing Functions Technology, Ethics, and Career Development Approximate Percentage of Questions on Test 40%
RELEVANT TO FOUNDATION LEVEL PAPER FAB / ACCA QUALIFICATION PAPER F1
 RELEVANT TO FOUNDATION LEVEL PAPER FAB / ACCA QUALIFICATION PAPER F1 The role of marketing Section B2(e) of the Paper FAB Study Guide states that candidates should be able to describe the roles and functions
RELEVANT TO FOUNDATION LEVEL PAPER FAB / ACCA QUALIFICATION PAPER F1 The role of marketing Section B2(e) of the Paper FAB Study Guide states that candidates should be able to describe the roles and functions
Basic Marketing Principles. Author: Mickey Smith, RPh, PhD Director, Center for Pharmaceutical Marketing and Management University of Mississippi
 Basic Marketing Principles Author: Mickey Smith, RPh, PhD Director, Center for Pharmaceutical Marketing and Management University of Mississippi Learning Objectives Define marketing in official and real
Basic Marketing Principles Author: Mickey Smith, RPh, PhD Director, Center for Pharmaceutical Marketing and Management University of Mississippi Learning Objectives Define marketing in official and real
