Why do firms create new products?
|
|
|
- Edgar Warner
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Why do firms create new products? 1. Changing Customer Needs: When they add products, services, and processes to their offerings, firms can create and deliver value more effectively by satisfying the changing needs of their current and new customers by keeping customers from getting bored with the current products or service offering. 2. Market Saturation: The longer a product exists in the marketplace, thee more likely it is that the market will become saturated. 3. Managing Risk through Diversity: Firm often create a broader portfolio of products, which help them diversity their risk and enhance firm value better than a single product can. 4. Fashion Cycles: In industries that rely on fashion trends and experience short product life cycles-including apparel, arts, books, and software markets-most sales come from new products. 5. Improving Business Relationships: Sometimes they function to improve relationship with suppliers. Diffusion of innovation The process by which the use of an innovation-whether a product, a service, or a process-spreads throughout a market group, over time and across various categories of adopters.
2 Truly new product introductions, that is, new-to-theworld products that create new markets, can add tremendous value to firms. Pioneers have the advantage of being first mover; as the first to create the market or product category, they become readily recognizable to consumers and thus establish a commanding and early market share lead. Diffusion of innovation curve 1. Innovators: These buyers enjoy taking risks and are regarded as highly knowledgeable.
3 2. Early Adopters: They generally don t like to take as much risk as innovators do but instead wait and purchase the product after careful review. 3. Early Majority: Its members don t like to take as much risk and therefore tend to wait until the bugs are worked out of a particular product or service. 4. Late Majority: When they do, the product has achieved its full market potential. 5. Laggards: These consumers like to avoid change and rely on traditional products until they are no longer available. Using the Diffusion of Innovation Theory Firms can predict which types of customers will but their new product or service immediately after its introduction, as well as later as the product gets more and more accepted by the market. 1. Relative Advantage: If a product or service is perceived to be better than substitutes, then the diffusion will be relatively quick. 2. Compatibility: A diffusion process may be faster or slower, depending on various consumer features, including international cultural differences. 3. Observability: When products are easily observed, their benefits or uses are easily communicated to others. 4. Complexity and Trialability: Products that are relatively less complex are also relatively easy to try.
4 How Firms Develop New Products Idea Generation Development of viable new product ideas. Concept Testing Testing the new product idea among a set of potential customer Market Testing Testing the actual product in a few test markest. Product Development Development of prototypes and/or the product. Product Launch Full-scale commercialization of the product. Evaluation of results Analysis of the performance of the new product and making appropriate modifications.
5 Sources of New Product Ideas Customer input Competitors Products Internal R&D Source of ideas R&D consortia Licensing Outsourcing Brainstorming The Product Life Cycle
6 Characteristics of Different Stages of the product life cycle The Service-Product Continuum Service Marketing Differs From Product Marketing 1. Intangible: cannot be touched
7 2. Inseparable production and consumption: service are produced and consumed at the same time 3. Heterogeneous: variability 4. Perishable: cannot be store The five Cs of pricing 1. Company Objective Profit orientation: focus on profit Sales orientation: focus on sales Competitor orientation: focus on competitor Customer orientation: focus on customer 2. Customer(skip) 3. Cost Variable costs are those costs, primarily labor and materials, that vary with production volume. Fixed costs are those costs that remain essentially at the same level, regardless of any changes in the volume of production. 4. Competition(skip)
8 5. Channel Members(skip) Considerations for Setting Price Strategies 1. Cost-Based Methods: Determine the final price to charge by starting with the cost. 2. Competition-Based Methods: They may set their prices to reflect the way they want consumers to interpret their own prices, relative to competitors offerings. 3. Value-Based Methods(skip) Pricing Strategies (long term) 1. Everyday Low Pricing(EDLP): ex. Big C, Tesco Lotus 2. High/Low Pricing: ex. The mall, Robinson 3. New Product Pricing Strategies Market Penetration Pricing: encourage consumer to purchase Price skimming: high price, Innovation ex. Mobile Pricing Tactics (short term) Pricing Tactics Aimed at Consumer
9 1. Markdowns are the reductions retailers take on the initial selling price of the product or service. 2. Quantity Discounts: buy more units the price will be cheap 3. Seasonal Discounts price reduction during off-peak season 4. Coupons encourage to repurchase 5. Rebates usually mailed to the consumer at some later date 6. Leasing pay fee for right to use the product 7. Price Bundling selling more than one product for a single and lower price 8. Leader Pricing attempt to build store traffic 9. Price Lining Business Pricing Tactics and Discounts 1. Seasonal Discounts 2. Cash Discounts 3. Allowances 4. Quantity Discounts 5. Uniform Delivered versus Zone Pricing The Importance of Marketing Channel/Supply Chain Management But even if firms execute these activities flawlessly, unless they can secure the placement of products inappropriate outlets in sufficient quantities exactly when customers want them, they are likely to fail.
10 Marketing Channels can add value for manufacturer, and produced and distributed in the right quantity, the right location and the right time. Designing Marketing Channels 1. Direct Marketing Channels: There are no intermediaries between the buyer and seller. 2. Indirect Marketing Channels: One or more intermediaries work with manufacturers to provide goods and services to customers. Direct Channels Indirect Channels Indirect Channels 1 intermediary 2 intermediary Manufacturer Manufacturer Manufacturer Customer Retailer Wholesaler Customer Retailer Customer Managing the Marketing Channel and Supply Chain Channel Conflict 1. Vertical Channel Conflict: Supply chain members that buy and sell to one another are not in agreement about their goals, roles, or rewards. 2. Horizontal Channel conflict: It will occur when there is disagreement or discord among members at the same level
11 Vertical Conflict MKT2280 Principles of marketing of marketing channel, such as two competing retailers or two competing manufacturers. Vertical versus Horizontal Channel Conflict Manufacturer Retailer 1 Retailer 2 Retailer 3 Managing the Marketing and Supply Chain through Marketing Systems(VMS) Horizontal conflict Channel Vertical 1. Independent or conventional marketing channel: Several independent members-a manufacturer, a wholesaler, and a retailer-each attempts to satisfy its own objectives and maximize its profits, often at the expense of the other members. 2. Vertical Marketing Channel: a marketing channel in which the members act as a unified system. Administered Vertical Marketing System Contractual Vertical Marketing System Corporate Vertical Marketing System
12 Retailing is defined as the set of business activities that add value to products and services sold to consumers for their personal or family use. A multichannel Strategy involves selling in more than one channel (e.g., store, catalog, and Internet). Factors for Establishing a Relationship with Retailers 1. Choosing Retailing Partners: When choosing retail partners, manufacturers look at the basic channel structure, where their target customers expect to find the products, channel member characteristics, and distribution intensity. Channel Structure Customer Expectations Channel Member Characteristics Distribution Intensity 2. Identify Types of Retailers Food General Merchandise Service Supermarket Full-line discount Specialty Auto rental Supercenter Category specialist Department Health spa Convenience Drug Off-price Vision center Warehouse club Extreme value Bank
13 3. Developing a Retail Strategy Using the Four PS(skip) 4. Managing a multichannel strategy(skip) Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) represents the Promotion P of the four Ps. It encompasses a variety of communication disciplines-advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, public relations, direct marketing, and online marketing including social media-in combination to provide clarity, consistency, and maximum communicative impact. There are three elements n any IMC strategy: the consumer, the channels through which the message is communicated, and the evaluation of the results of the communication. Communicating With Consumers The communication process Noise From the environment Sender (Firm) Transmitter encodes message Communications channel (Media) Receiver (Consumer) decodes message Feedback
14 The AIDA Model Marketing communications move consumers stepwise through a series of mental stages, for which there are several models. The most common is AIDA model, which suggests that Awareness leads to Interest, which leads to Desire, which leads to Action. The AIDA Model Element Marketing Communications Strategy of Integrated 1. Advertising 2. Public relation(pr) 3. Sales promotion 4. Personal selling 5. Direct marketing 6. Online marketing Planning For and Measuring IMC Success (Skip)
15 Advertising is a paid form of communication, delivered through media form an identifiable source, about an organization, product, service, or idea, designed to persuade the receiver to take some action, now or in the future. Steps in Planning and Executing an Ad Campaign Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Step 5 Step 6 Identify target audience Set advertising objectives Determine the advertising budget Convey the message Evaluate and select media Create advertisements Assess impact Step 1 Identify Target Audience Firm conduct research to identify their target audience, then use the information they gain to set the tone for the advertising program and help them select the media they will use to deliver the message to that audience. Step 2 Set Advertising Objectives In advertising to consumers, the objective is a pull strategy and push strategies. Pull strategy: the goal is to get consumers to pull the product into the marketing channel by demanding it. Push strategies: are designed to increase demand by focusing on wholesaler, retailer, or salesperson.
16 Informative Advertising is a communication used to create and build brand awareness. Persuasive Advertising occurs in the growth and early maturity stages of the product life cycle. Reminder Advertising is a communication used to remind or prompt repurchases, especially for product that have gained market acceptance and are in the maturity stage of their life cycle. Step 3 Determine the Advertising Budget (skip) Step 4 Convey the Message Marketers determine what they want to convey about the product or service. First, the firm determines the key message it want to communicate to the target audience. Second, the firm decides what appeal would most effectively convey the message. The message: it provides the target audience with reasons to respond in the desired way. The appeal: 1. Informational appeals help consumer make purchase decisions by offering factual information that encourages consumers to evaluate the brand favorably on the basis of the key benefits it provides. 2. Emotional appeals aims to satisfy consumers emotional desires rather than their utilitarian needs. The key to a successful
17 emotional appeal is the use of emotion to create a bond between the consumer and the brand. Step 5 Evaluate and Select Media Media planning refers to the process of evaluating and selecting the media mix-the combination of the media used and the frequency of advertising in each medium-that will deliver a clear, consistent, compelling message to the intended audience. Media buy is the actual purchase of airtime or print pages, is generally the largest expense in the advertising budget. Step 6 Create Advertisements (skip) Step 7 Assess Impact Using Marketing Metrics (skip)
Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies. Section 17.1 Promotion and Promotional Mix Section 17.2 Types of Promotion
 Unit 6 Promotion Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies Chapter 18 Visual Merchandising and Display Chapter 19 Advertising Chapter 20 Print Advertisements Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies
Unit 6 Promotion Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies Chapter 18 Visual Merchandising and Display Chapter 19 Advertising Chapter 20 Print Advertisements Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies
Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: Promotional Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Promotion. The Traditional Communication Model. Noise.
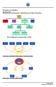 Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: al Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Target Market Product Place Price Personal Selling Mass Selling Sales Advertising Publicity The Traditional Communication Model
Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: al Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Target Market Product Place Price Personal Selling Mass Selling Sales Advertising Publicity The Traditional Communication Model
MKTG301: PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING DEFINITIONS: CHAPTER 18
 MKTG301: PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING DEFINITIONS: CHAPTER 18 Communication (1) The process of conveying a message to others, which requires six elements: a source, a message, a channel of communication, a
MKTG301: PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING DEFINITIONS: CHAPTER 18 Communication (1) The process of conveying a message to others, which requires six elements: a source, a message, a channel of communication, a
Chapter 26 Pricing Strategies. Section 26.1 Basic Pricing Policies Section 26.2 Strategies in the Pricing Process
 Chapter 26 Pricing Strategies Section 26.1 Basic Pricing Policies Section 26.2 Strategies in the Pricing Process Basic Pricing Policies Key Terms markup pricing cost-plus pricing one-price policy flexible-price
Chapter 26 Pricing Strategies Section 26.1 Basic Pricing Policies Section 26.2 Strategies in the Pricing Process Basic Pricing Policies Key Terms markup pricing cost-plus pricing one-price policy flexible-price
Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy
 Integrated Marketing Strategy Dr. Richard Sjolander 2003 The Purpose of Integrated Marketing s is to Communicate with a Target Audience Promotion: or Applied marketing communication Attempts to: Inform
Integrated Marketing Strategy Dr. Richard Sjolander 2003 The Purpose of Integrated Marketing s is to Communicate with a Target Audience Promotion: or Applied marketing communication Attempts to: Inform
SplitTarget 2012 Contract Marketing Organization
 SplitTarget 2012 Contract Marketing Organization Split your Target and Conquer the Market. INTERNET MARKETING WEBSITE DEVELOPMENT ECOMMERCE DEVELOPMENT SEARCH ENGINE OPTIMIZATION PAY-PER-CLICK MANAGEMENT
SplitTarget 2012 Contract Marketing Organization Split your Target and Conquer the Market. INTERNET MARKETING WEBSITE DEVELOPMENT ECOMMERCE DEVELOPMENT SEARCH ENGINE OPTIMIZATION PAY-PER-CLICK MANAGEMENT
Principles of Marketing. by Jeff Tanner and Mary Anne Raymond
 Principles of Marketing by Jeff Tanner and Mary Anne Raymond Chapter 8 Using Marketing Channels to Create Value for Customers 2010 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. Marketing Channels and Channel Partners Learning
Principles of Marketing by Jeff Tanner and Mary Anne Raymond Chapter 8 Using Marketing Channels to Create Value for Customers 2010 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. Marketing Channels and Channel Partners Learning
INTEGRATED MARKETING COMMUNICATIONS
 INTEGRATED MARKETING COMMUNICATIONS What is IMC & why IMC? IMC is the concept and practice of designing marketing communications programs that coordinate all promotional activities Ad, PS, SP, PR, publicity,
INTEGRATED MARKETING COMMUNICATIONS What is IMC & why IMC? IMC is the concept and practice of designing marketing communications programs that coordinate all promotional activities Ad, PS, SP, PR, publicity,
Guide to Market Research and Analysis
 The Orangeville & Area Small Business Enterprise Centre (SBEC) 87 Broadway, Orangeville ON L9W 1K1 519-941-0440 Ext. 2286 or 2291 sbec@orangeville.ca www.orangevillebusiness.ca Supported by its Partners:
The Orangeville & Area Small Business Enterprise Centre (SBEC) 87 Broadway, Orangeville ON L9W 1K1 519-941-0440 Ext. 2286 or 2291 sbec@orangeville.ca www.orangevillebusiness.ca Supported by its Partners:
Bingo glossary marketing mix
 Bingo glossary marketing mix The management process which identifies customer wants, anticipates their future wants and then goes about satisfying them profitably. Where the market has been divided up
Bingo glossary marketing mix The management process which identifies customer wants, anticipates their future wants and then goes about satisfying them profitably. Where the market has been divided up
Contents. Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing. Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22. Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38
 Contents Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22 Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38 Part- II: The Customer Experience Chapter 3 Consumer Behavior
Contents Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22 Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38 Part- II: The Customer Experience Chapter 3 Consumer Behavior
Marketing. Joseph F. Hair, Jr. Carl McDaniel. South-Western College Publishing Thomson Learning,.
 Marketing SECOND EDITION C J Charles W. Lamb, Jr. MJ. Neeley Professor of Marketing MJ. Neeley School of Business Texas Christian University Joseph F. Hair, Jr. Alvin C. Copeland Endowed Chair of Franchising
Marketing SECOND EDITION C J Charles W. Lamb, Jr. MJ. Neeley Professor of Marketing MJ. Neeley School of Business Texas Christian University Joseph F. Hair, Jr. Alvin C. Copeland Endowed Chair of Franchising
sixteen retailing and omnichannel marketing Chapter
 Chapter sixteen retailing and omnichannel marketing 1 Retailing and Omnichannel Marketing LO 16-1 Discuss the four factors manufacturers should consider as they develop their strategy for working with
Chapter sixteen retailing and omnichannel marketing 1 Retailing and Omnichannel Marketing LO 16-1 Discuss the four factors manufacturers should consider as they develop their strategy for working with
Marketing Strategy Planning Process
 When we finish this lecture you should CHAPTER FOURTEEN Promotion Introduction to Integrated Marketing Communications 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. For use only with Perreault/Cannon/McCarthy or Perreault/McCarthy texts.
When we finish this lecture you should CHAPTER FOURTEEN Promotion Introduction to Integrated Marketing Communications 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. For use only with Perreault/Cannon/McCarthy or Perreault/McCarthy texts.
Chapter 14: Retailing, Direct Marketing, and Wholesaling
 Chapter 14: Retailing, Direct Marketing, and Wholesaling Pride/Ferrell Foundations of Marketing Fourth Edition Prepared by Milton Pressley University of New Orleans Objectives 1. Understand the purpose
Chapter 14: Retailing, Direct Marketing, and Wholesaling Pride/Ferrell Foundations of Marketing Fourth Edition Prepared by Milton Pressley University of New Orleans Objectives 1. Understand the purpose
Question bank relating to each chapter
 Question bank relating to each chapter Chapter 1 Development of a strategic approach to marketing its culture; internal macro- and external micro-environmental issues 1. What factors have given rise to
Question bank relating to each chapter Chapter 1 Development of a strategic approach to marketing its culture; internal macro- and external micro-environmental issues 1. What factors have given rise to
Marketing s Four P s: First Steps for New Entrepreneurs
 PURDUE EXTENSION EC-730 Marketing s Four P s: First Steps for New Entrepreneurs Cole Ehmke, Joan Fulton, and Jayson Lusk Department of Agricultural Economics Marketing your business is about how you position
PURDUE EXTENSION EC-730 Marketing s Four P s: First Steps for New Entrepreneurs Cole Ehmke, Joan Fulton, and Jayson Lusk Department of Agricultural Economics Marketing your business is about how you position
The Greatest Strategy. For Social Media Marketing
 The Greatest Strategy For Social Media Marketing Table of Contents The Greatest Strategy for Social Media Marketing 03 Introduction: Why Social Media Marketing? 07 Part 1: Attracting Target Audience 12
The Greatest Strategy For Social Media Marketing Table of Contents The Greatest Strategy for Social Media Marketing 03 Introduction: Why Social Media Marketing? 07 Part 1: Attracting Target Audience 12
Marketing communications: integrated marketing communications aspect. Learning outcomes
 Marketing communications: integrated marketing communications aspect Lect. Indre Radaviciene E-mail: indre.radaviciene@gmail.com Vilnius University/Faculty of Economics Marketing Department Learning outcomes
Marketing communications: integrated marketing communications aspect Lect. Indre Radaviciene E-mail: indre.radaviciene@gmail.com Vilnius University/Faculty of Economics Marketing Department Learning outcomes
Unit 4: Marketing Principles
 Unit 4: Marketing Principles Unit code: F/601/0556 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 credits Aim This unit aims to provide learners with understanding and skills relating to the fundamental concepts and principles
Unit 4: Marketing Principles Unit code: F/601/0556 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 credits Aim This unit aims to provide learners with understanding and skills relating to the fundamental concepts and principles
Marketing: Advertising and Sales Promotion
 Marketing: Advertising and Sales Promotion Food Communication II Section G Communication Mix Strategies All of the information has been adapted from: Kotler P. Armstrong, G., 2004. Principles of Marketing.
Marketing: Advertising and Sales Promotion Food Communication II Section G Communication Mix Strategies All of the information has been adapted from: Kotler P. Armstrong, G., 2004. Principles of Marketing.
Things to Know Before Starting an e- Commerce Business
 Things to Know Before Starting an e- Commerce Business By Atul Jain Copyright 2013 Atul Jain All rights reserved Table of Contents About the Author Introduction 1. Understand Your Product Well 2. Calculate
Things to Know Before Starting an e- Commerce Business By Atul Jain Copyright 2013 Atul Jain All rights reserved Table of Contents About the Author Introduction 1. Understand Your Product Well 2. Calculate
PROMOTION TRHOUGH THE MARKETING CHANNEL
 Chapter 12 PROMOTION TRHOUGH THE MARKETING CHANNEL Chapter Objectives One of the major tools the manufacturer uses for implementing an integrated promotional program is selling support by channel members.
Chapter 12 PROMOTION TRHOUGH THE MARKETING CHANNEL Chapter Objectives One of the major tools the manufacturer uses for implementing an integrated promotional program is selling support by channel members.
Chapter3: Literature Review: Marketing and Marketing Mix
 Chapter3: Literature Review: Marketing and Marketing Mix 3.1: Marketing 3.2: Promotion 3.3: Sales Promotion 17 Chapter 3.1: Marketing 1. Introduction 2. Elements of Marketing Mix 3. Promotion or Marketing
Chapter3: Literature Review: Marketing and Marketing Mix 3.1: Marketing 3.2: Promotion 3.3: Sales Promotion 17 Chapter 3.1: Marketing 1. Introduction 2. Elements of Marketing Mix 3. Promotion or Marketing
SALES PROMOTION, EVENTS, AND SPONSORSHIPS
 PART FIVE: INTEGRATION AND EVALUATION Chapter 16 Wells, Moriarty, Burnett & Lwin ADVERTISING Principles and Effective IMC Practice Koekemoer L. (2004)., Marketing Communications, Juta and Company Ltd.
PART FIVE: INTEGRATION AND EVALUATION Chapter 16 Wells, Moriarty, Burnett & Lwin ADVERTISING Principles and Effective IMC Practice Koekemoer L. (2004)., Marketing Communications, Juta and Company Ltd.
for BSNL internal circulation only
 E4-E5 E5 (MANAGEMENT) Marketing of Services AGENDA Define marketing Describe service and its difference from product List the services marketing mix Apply the marketing mix to BSNL services Understand
E4-E5 E5 (MANAGEMENT) Marketing of Services AGENDA Define marketing Describe service and its difference from product List the services marketing mix Apply the marketing mix to BSNL services Understand
Diploma in Marketing
 Brentwood Open Learning College Diploma in Marketing (Level 4) Course Structure & Contents Diploma in Marketing Course Structure Contents Page 1 Unit 1 to Marketing The unit 1 covers the following topics:
Brentwood Open Learning College Diploma in Marketing (Level 4) Course Structure & Contents Diploma in Marketing Course Structure Contents Page 1 Unit 1 to Marketing The unit 1 covers the following topics:
How To Use Big Data To Help A Retailer
 IBM Software Big Data Retail Capitalizing on the power of big data for retail Adopt new approaches to keep customers engaged, maintain a competitive edge and maximize profitability 2 Capitalizing on the
IBM Software Big Data Retail Capitalizing on the power of big data for retail Adopt new approaches to keep customers engaged, maintain a competitive edge and maximize profitability 2 Capitalizing on the
Assessment Vocabulary Strategies. Advertiser. Describe three types of positions typically found in an advertising agency.
 What is Advertising (1-2 days) (1) The student knows business concepts and explains how business satisfies economic needs. The student is expected to: (A) Categorize business activities as production,
What is Advertising (1-2 days) (1) The student knows business concepts and explains how business satisfies economic needs. The student is expected to: (A) Categorize business activities as production,
Because of inherent tradeoffs between marketing mix elements, pricing will depend on other product, distribution, and promotion decisions.
 10. Pricing Strategy One of the four major elements of the marketing mix is price. Pricing is an important strategic issue because it is related to product positioning. Furthermore, pricing affects other
10. Pricing Strategy One of the four major elements of the marketing mix is price. Pricing is an important strategic issue because it is related to product positioning. Furthermore, pricing affects other
Master Agent Value Proposition. Master Agent Value Proposition
 Master Agent Value Proposition Master Agent Value Proposition Overview It is not about what the MFSP s master agents and retail agents can do for them, it is about what the MFSP can do for its channel
Master Agent Value Proposition Master Agent Value Proposition Overview It is not about what the MFSP s master agents and retail agents can do for them, it is about what the MFSP can do for its channel
LECTURE 1 Introduction To Integrated Marketing Communications. Marketing satisfying needs and wants through the exchange process.
 LECTURE 1 Introduction To Integrated Marketing Communications Marketing satisfying needs and wants through the exchange process. The Marketing Management Process 1. Situation analysis (PESTL). 2. Objectives.
LECTURE 1 Introduction To Integrated Marketing Communications Marketing satisfying needs and wants through the exchange process. The Marketing Management Process 1. Situation analysis (PESTL). 2. Objectives.
Six Secrets to Simply Sell More Wine. Texas Wine & Grape Growers Association 2013 Annual Conference & Trade Show
 Six Secrets to Simply Sell More Wine Texas Wine & Grape Growers Association 2013 Annual Conference & Trade Show Case Study: WHY SELL MORE WINE? Facts Winery X was selling 3,000 cases per year, virtually
Six Secrets to Simply Sell More Wine Texas Wine & Grape Growers Association 2013 Annual Conference & Trade Show Case Study: WHY SELL MORE WINE? Facts Winery X was selling 3,000 cases per year, virtually
2 Most producers use to bring their products to market. A detailers B intermediaries C expediters D agents
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1.Caterpillar (famous for earth moving equipment) has a powerful partnership with its dealers. Which of the following is one of the basic principles upon which this successful
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1.Caterpillar (famous for earth moving equipment) has a powerful partnership with its dealers. Which of the following is one of the basic principles upon which this successful
Push & Pull Marketing
 Push & Pull Marketing As we face the new year, foremost in the minds of business owners are how they will increase revenues in the current economic environment. This paper discusses two specific types
Push & Pull Marketing As we face the new year, foremost in the minds of business owners are how they will increase revenues in the current economic environment. This paper discusses two specific types
Chapter 15 Product Development and Supply Chain Management
 CHAPTER OUTLINE Spotlight: Lighting the Way to Product Development (http://www.dinealight.com and http://www.readycheckglo.com) 1 To Grow or Not to Grow Understand the challenges associated with the growth
CHAPTER OUTLINE Spotlight: Lighting the Way to Product Development (http://www.dinealight.com and http://www.readycheckglo.com) 1 To Grow or Not to Grow Understand the challenges associated with the growth
The Marketing Plan. The business must make decisions on how to apply its resources to the target market(s).
 The Marketing Plan The most important part of a business plan is the Marketing Plan. To keep one s business on course this plan must be geared toward the business s mission its product and service lines,
The Marketing Plan The most important part of a business plan is the Marketing Plan. To keep one s business on course this plan must be geared toward the business s mission its product and service lines,
Integrated Communication
 Integrated Communication Integrated Communication is a 15-credit mandatory module which sits within the suite of Level 4 modules. To gain the CIM Level 4 Certificate in Professional Marketing a pass in
Integrated Communication Integrated Communication is a 15-credit mandatory module which sits within the suite of Level 4 modules. To gain the CIM Level 4 Certificate in Professional Marketing a pass in
Management Commentary. Second Quarter 2015 Results
 Management Commentary Second Quarter 2015 Results The RetailMeNot, Inc. ( RetailMeNot ) earnings call will begin on August 5, 2015 at 7:00am central time (8:00am eastern time) and will include prepared
Management Commentary Second Quarter 2015 Results The RetailMeNot, Inc. ( RetailMeNot ) earnings call will begin on August 5, 2015 at 7:00am central time (8:00am eastern time) and will include prepared
Competitive Advantage
 Competitive Advantage When a firm sustains profits that exceed the average for its industry, the firm is said to possess a competitive advantage over its rivals. The goal of much of business strategy is
Competitive Advantage When a firm sustains profits that exceed the average for its industry, the firm is said to possess a competitive advantage over its rivals. The goal of much of business strategy is
HOLIDAY HOT SHEET O C T O B E R 2 3, 2 0 1 4
 HOLIDAY HOT SHEET OCTOBER 23, 2014 2014 Holiday Hot Sheet: Weekly insights for the holiday marketer As marketers seek to connect with their customers during the largest consumer spending season of the
HOLIDAY HOT SHEET OCTOBER 23, 2014 2014 Holiday Hot Sheet: Weekly insights for the holiday marketer As marketers seek to connect with their customers during the largest consumer spending season of the
Boost Your Direct Marketing Success with Prepaid Incentive Cards
 Boost Your Direct Marketing Success with Prepaid Incentive Cards By: Jeannie Stinnett Director, Sales Solutions Consultant First Data 2013 First Data Corporation. All trademarks, service marks and trade
Boost Your Direct Marketing Success with Prepaid Incentive Cards By: Jeannie Stinnett Director, Sales Solutions Consultant First Data 2013 First Data Corporation. All trademarks, service marks and trade
Preliminary Certificate in Marketing
 Preliminary Certificate in Marketing April 5 th, 2015 Examination PCM I 2015 85 th Intake, 25 th Year Candidate s Registration Number (As per in the examination admission form / Student ID) 0 0 0 0 0 For
Preliminary Certificate in Marketing April 5 th, 2015 Examination PCM I 2015 85 th Intake, 25 th Year Candidate s Registration Number (As per in the examination admission form / Student ID) 0 0 0 0 0 For
Marketing (Marketing Principles)
 Marketing (Marketing Principles) Main Aim(s) of the Unit: To provide students with a foundation for the analysis of marketing within organizations including decision making processes, segmentation, the
Marketing (Marketing Principles) Main Aim(s) of the Unit: To provide students with a foundation for the analysis of marketing within organizations including decision making processes, segmentation, the
Chapter 15: Integrated Marketing Communications
 Chapter 15: Integrated Marketing Communications Pride/Ferrell Foundations of Marketing Fourth Edition Prepared by Milton Pressley University of New Orleans Objectives 1. Discuss the nature of integrated
Chapter 15: Integrated Marketing Communications Pride/Ferrell Foundations of Marketing Fourth Edition Prepared by Milton Pressley University of New Orleans Objectives 1. Discuss the nature of integrated
Marketing: Promotion Basics
 Name: Class: Date Taken: Total Possible Marks: 39 Marketing: Promotion Basics Complete the following questions in the time allowed by your teacher Write a short, accurate definition for each of the following
Name: Class: Date Taken: Total Possible Marks: 39 Marketing: Promotion Basics Complete the following questions in the time allowed by your teacher Write a short, accurate definition for each of the following
Chapter 10 Sample Questions on Advertising, PR and Promotion
 Chapter 10 Sample Questions on Advertising, PR and Promotion 1. One issue facing advertisers is that consumers screen out messages that are not relevant to them. 2. Glenn is using a push strategy to promote
Chapter 10 Sample Questions on Advertising, PR and Promotion 1. One issue facing advertisers is that consumers screen out messages that are not relevant to them. 2. Glenn is using a push strategy to promote
Promotions: Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy
 1 Marketing Communication Mix or Promotion Mix Promotions: Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy Design Stores that Sell the Product Price Package 2 The Changing Communications Environment The Need
1 Marketing Communication Mix or Promotion Mix Promotions: Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy Design Stores that Sell the Product Price Package 2 The Changing Communications Environment The Need
MARKETING 26 THE ROAD TO THE CONSUMER
 26 THE ROAD TO THE CONSUMER Insurance. In setting up any kind of business you will need to consider several types of insurance coverage, including 8 : General business liability, including product liability
26 THE ROAD TO THE CONSUMER Insurance. In setting up any kind of business you will need to consider several types of insurance coverage, including 8 : General business liability, including product liability
Making business simple...
 Making business simple... Introduction 2 Contents Every business needs a Marketing Plan. This guide has been created to assist you in putting your Marketing Plan together. This guide will help you to indicate
Making business simple... Introduction 2 Contents Every business needs a Marketing Plan. This guide has been created to assist you in putting your Marketing Plan together. This guide will help you to indicate
Media Today, 5 th Edition. Chapter Recaps & Study Guide
 1 Media Today, 5 th Edition Chapter Recaps & Study Guide Chapter 4: Financing and Shaping the Media: Advertising, Public Relations, and Marketing Communications This chapter explores how advertising, public
1 Media Today, 5 th Edition Chapter Recaps & Study Guide Chapter 4: Financing and Shaping the Media: Advertising, Public Relations, and Marketing Communications This chapter explores how advertising, public
Marketing Demand Push or Demand Pull or Both? The Need for Creating New Plant Awareness
 Marketing Demand Push or Demand Pull or Both? The Need for Creating New Plant Awareness Dr. Forrest E. Stegelin Department of Agricultural and Applied Economics The University of Georgia Nature of Work:
Marketing Demand Push or Demand Pull or Both? The Need for Creating New Plant Awareness Dr. Forrest E. Stegelin Department of Agricultural and Applied Economics The University of Georgia Nature of Work:
Power Struggles and Sales Promotion
 Chapter 18 Sales Promotion Power Struggles and Sales Promotion Sales promotion plays a key strategic role in the channel of distribution Big name brands need to supported with sales promotion and POP in
Chapter 18 Sales Promotion Power Struggles and Sales Promotion Sales promotion plays a key strategic role in the channel of distribution Big name brands need to supported with sales promotion and POP in
Management and Marketing Course Descriptions
 Management and Marketing Course Descriptions Management Course Descriptions HRM 301 Human Resources Management (3-0-3) Covers all activities and processes of the human resources function that include recruitment,
Management and Marketing Course Descriptions Management Course Descriptions HRM 301 Human Resources Management (3-0-3) Covers all activities and processes of the human resources function that include recruitment,
Mobile Marketing for the Restaurant & Retail Industries
 Mobile Marketing for the Restaurant & Retail Industries The restaurant and retail industries require frequent consumer engagement in the forms of advertisements, promotions, direct mail, email marketing
Mobile Marketing for the Restaurant & Retail Industries The restaurant and retail industries require frequent consumer engagement in the forms of advertisements, promotions, direct mail, email marketing
Marketin. Global Edition 14
 Marketin Global Edition 14 PHILIP Kotler Northwestern University GARY Armstrong University of North Carolina Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco Upper Saddle River Amsterdam Cape Town Dubai
Marketin Global Edition 14 PHILIP Kotler Northwestern University GARY Armstrong University of North Carolina Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco Upper Saddle River Amsterdam Cape Town Dubai
Convenience. Product Selection. Fairness in Dealings. Helpful Information. Prices. Social Image. Shopping
 MGMT 120 Principles of Marketing Lecture 23: Place: Retailing and Wholesale Planning a Retailer s Strategy Convenience Key Economic Factors Affecting Consumers Retail Choice Product Selection Fairness
MGMT 120 Principles of Marketing Lecture 23: Place: Retailing and Wholesale Planning a Retailer s Strategy Convenience Key Economic Factors Affecting Consumers Retail Choice Product Selection Fairness
Strategic Framework to Analyze Supply Chains
 Strategic Framework to Analyze Supply Chains 1 Andy Guo A Strategic Framework for Supply Chain Design, Planning, and Operation Part I: Understand the supply chain Part II: Supply chain performance Part
Strategic Framework to Analyze Supply Chains 1 Andy Guo A Strategic Framework for Supply Chain Design, Planning, and Operation Part I: Understand the supply chain Part II: Supply chain performance Part
WHAT WE DO. Account Management Project Management Research & Analytics Strategic Planning Media Creative Services Technical Services
 WHAT WE DO Account Management Project Management Research & Analytics Strategic Planning Media Creative Services Technical Services SOLUTION bk conducted a detailed assessment of the Making Home Affordable
WHAT WE DO Account Management Project Management Research & Analytics Strategic Planning Media Creative Services Technical Services SOLUTION bk conducted a detailed assessment of the Making Home Affordable
7/31/2014. International Distribution Decisions Factors Influencing Distribution Decisions Internal External
 We are striving to achieve noticeable improvements for our customers and distribution systems. ( ) The various sales formats in all major markets will be adapted to new customer requirements. ( ) Every
We are striving to achieve noticeable improvements for our customers and distribution systems. ( ) The various sales formats in all major markets will be adapted to new customer requirements. ( ) Every
What is Market Research? Why Conduct Market Research?
 What is Market Research? Successful businesses have extensive knowledge of their customers and their competitors. Market research is the process of gathering information which will make you more aware
What is Market Research? Successful businesses have extensive knowledge of their customers and their competitors. Market research is the process of gathering information which will make you more aware
over-the-counter selling personal selling field selling network marketing telemarketing outbound telemarketing inbound telemarketing inside selling
 personal selling over-the-counter selling field selling network marketing outbound telemarketing telemarketing inbound telemarketing inside selling relationship selling consultative selling cross-selling
personal selling over-the-counter selling field selling network marketing outbound telemarketing telemarketing inbound telemarketing inside selling relationship selling consultative selling cross-selling
Pricing and Credit Decisions
 CHAPTER OUTLINE Spotlight: Dynamic Network Services (http://www.dyn.com) 1 Setting a Price Discuss the role of cost and demand factors in setting a price. Cost Determination for Pricing Total cost includes
CHAPTER OUTLINE Spotlight: Dynamic Network Services (http://www.dyn.com) 1 Setting a Price Discuss the role of cost and demand factors in setting a price. Cost Determination for Pricing Total cost includes
Between December 2009 and January 2010, Aberdeen surveyed
 Fast-Track Cross-Channel Gains: The Final Frontier for Customer Share of Wallet Sahir Anand, RESEARCH DIRECTOR, RETAIL, HOSPITALITY, & BANKING, ABERDEEN GROUP Chris Cunnane, SENIOR RESEARCH ASSOCIATE,
Fast-Track Cross-Channel Gains: The Final Frontier for Customer Share of Wallet Sahir Anand, RESEARCH DIRECTOR, RETAIL, HOSPITALITY, & BANKING, ABERDEEN GROUP Chris Cunnane, SENIOR RESEARCH ASSOCIATE,
OMNI CHANNEL RETAILING
 OMNI CHANNEL RETAILING Omni Channel Retailing By ERP Omni-channel retailing is more than a trend it s what consumers are demanding. Thus truly, Omnichannel as a means of improving service for customers
OMNI CHANNEL RETAILING Omni Channel Retailing By ERP Omni-channel retailing is more than a trend it s what consumers are demanding. Thus truly, Omnichannel as a means of improving service for customers
An Introduction. Global Edition. "University of North Carolina. Northwestern University
 An Introduction Global Edition "University of North Carolina Northwestern University Boston Columbus Indianapolis NewYork San Francisco Upper Saddle River Amsterdam CapeTown Dubai London Madrid Milan Munich
An Introduction Global Edition "University of North Carolina Northwestern University Boston Columbus Indianapolis NewYork San Francisco Upper Saddle River Amsterdam CapeTown Dubai London Madrid Milan Munich
Collaborative CRM Workshop. 02 Partner Alignment & Project Objectives
 Collaborative CRM Workshop 02 Partner Alignment & Project Objectives 1 Collaborative CRM 2005 02 Partner Alignment & Project Objectives Copyright ECR Europe 2005. All rights reserved. Version 7.0 June
Collaborative CRM Workshop 02 Partner Alignment & Project Objectives 1 Collaborative CRM 2005 02 Partner Alignment & Project Objectives Copyright ECR Europe 2005. All rights reserved. Version 7.0 June
E-FULFILLMENT - A NEW CHALLENGE FOR ELECTRONIC BUSINESS
 Annals of the University of Petroşani, Economics, 14(1), 2014, 121-128 121 E-FULFILLMENT - A NEW CHALLENGE FOR ELECTRONIC BUSINESS CLAUDIA ISAC ABSTRACT: Currently, we are witnessing a uniform interconnect
Annals of the University of Petroşani, Economics, 14(1), 2014, 121-128 121 E-FULFILLMENT - A NEW CHALLENGE FOR ELECTRONIC BUSINESS CLAUDIA ISAC ABSTRACT: Currently, we are witnessing a uniform interconnect
Marketing Management. 1 Many people are surprised when they realize how may different ideas and activities are included in the term.
 Marketing Management 1 Many people are surprised when they realize how may different ideas and activities are included in the term. 1. Marketing 2. Manufacturing 3. Labeling 2 One of the most important
Marketing Management 1 Many people are surprised when they realize how may different ideas and activities are included in the term. 1. Marketing 2. Manufacturing 3. Labeling 2 One of the most important
Marketing channels exist to create utility for. Customers
 Channel Objectives Global Marketing Channels and Physical Distribution Global Marketing Chapter 12 1 Marketing channels exist to create utility for customers Place utility availability of a product or
Channel Objectives Global Marketing Channels and Physical Distribution Global Marketing Chapter 12 1 Marketing channels exist to create utility for customers Place utility availability of a product or
ICSC European Retail Property School RETAILING PRINCIPLES TENANT RETENTION
 ICSC European Retail Property School RETAILING PRINCIPLES TENANT RETENTION Introduction and Overview I. Retailing defined II. Retailer Classifications III. The Retailer s Organizational Structure IV. Understanding
ICSC European Retail Property School RETAILING PRINCIPLES TENANT RETENTION Introduction and Overview I. Retailing defined II. Retailer Classifications III. The Retailer s Organizational Structure IV. Understanding
Digital Marketing Budgets Increase, Reflecting Focus on Customer Experience
 G00255396 Digital Marketing Budgets Increase, Reflecting Focus on Customer Experience Published: 9 January 2014 Analyst(s): Laura McLellan Gartner's Digital Marketing Spending Survey shows that digital
G00255396 Digital Marketing Budgets Increase, Reflecting Focus on Customer Experience Published: 9 January 2014 Analyst(s): Laura McLellan Gartner's Digital Marketing Spending Survey shows that digital
Distributor/Reseller Marketing A Riddle Wrapped in a Mystery Inside an Enigma
 Distributor/Reseller Marketing A Riddle Wrapped in a Mystery Inside an Enigma 2006 Frank Lynn & Associates, Inc. All Rights Reserved 0 Distributor/Reseller Marketing Over the last 50 years, changes in
Distributor/Reseller Marketing A Riddle Wrapped in a Mystery Inside an Enigma 2006 Frank Lynn & Associates, Inc. All Rights Reserved 0 Distributor/Reseller Marketing Over the last 50 years, changes in
This involves making goods or services available for those who want to buy them
 Place This involves making goods or services available for those who want to buy them There are 2 main issues: Distribution Channels How goods are actually moved from manufacturer to consumer and where
Place This involves making goods or services available for those who want to buy them There are 2 main issues: Distribution Channels How goods are actually moved from manufacturer to consumer and where
2. A service company earns net income by buying and selling merchandise. Ans: False
 Chapter 6: Accounting For Merchandising Activities True/False 1. Merchandise consists of products that a company acquires for the purpose of reselling them to customers. 2. A service company earns net
Chapter 6: Accounting For Merchandising Activities True/False 1. Merchandise consists of products that a company acquires for the purpose of reselling them to customers. 2. A service company earns net
Chapter 15: Pricing and the Revenue Management
 Chapter 15: Pricing and the Revenue Management 1 Outline The Role of RM (Revenue Management) in the SCs RM for Multiple Customer Segments RM for Perishable Assets RM for Seasonable Demand RM for Bulk and
Chapter 15: Pricing and the Revenue Management 1 Outline The Role of RM (Revenue Management) in the SCs RM for Multiple Customer Segments RM for Perishable Assets RM for Seasonable Demand RM for Bulk and
Course Outline. BUSN 5050/1-3 Marketing Management (3,0,0)
 Course Outline Department of Marketing, International Business, Entrepreneurship School of Business and Economics BUSN 5050/1-3 Marketing Management (3,0,0) Calendar Description Students examine the key
Course Outline Department of Marketing, International Business, Entrepreneurship School of Business and Economics BUSN 5050/1-3 Marketing Management (3,0,0) Calendar Description Students examine the key
WSTiE. Marketing in Tourism
 WSTiE Marketing in Tourism dr Anna Sobczyk-Kolbuch AGENDA 1. Marketing the essence and features. Clasical and modern concepts of marketing 2. Evolution of enterprises` activities on the market the origin
WSTiE Marketing in Tourism dr Anna Sobczyk-Kolbuch AGENDA 1. Marketing the essence and features. Clasical and modern concepts of marketing 2. Evolution of enterprises` activities on the market the origin
An intoduction to Multichannel. www.brightpearl.com
 An intoduction to Multichannel Whats inside Read our best practice tips for keeping stock control in check. Even the best inventory managers sometimes trip up, but using our experience we've complied some
An intoduction to Multichannel Whats inside Read our best practice tips for keeping stock control in check. Even the best inventory managers sometimes trip up, but using our experience we've complied some
Global Supply Chain Management. Ecosystem Aware. ZARA-Fast Fashion (HBS 9-703-497) N. Viswanadham
 ZARA-Fast Fashion N. Viswanadham (HBS 9-703-497) Contents l Apparel Supply Chain l Zara s Business System l Zara s internationalization strategy l IT at Zara l The risks of failure of the Zara business
ZARA-Fast Fashion N. Viswanadham (HBS 9-703-497) Contents l Apparel Supply Chain l Zara s Business System l Zara s internationalization strategy l IT at Zara l The risks of failure of the Zara business
MARKETING INTERMEDIATE LEVEL
 Syllabus MARKETING INTERMEDIATE LEVEL Proposed for examinations sessions starting May 2017 INTERMEDIATE Level, Marketing, MATSEC 1 Syllabus objectives The syllabus is intended to encourage candidates to:
Syllabus MARKETING INTERMEDIATE LEVEL Proposed for examinations sessions starting May 2017 INTERMEDIATE Level, Marketing, MATSEC 1 Syllabus objectives The syllabus is intended to encourage candidates to:
Chapter 11: Campaign Management
 Chapter 11: Campaign Management Overview Topics discussed: Campaign Management Process Campaign Planning and Development Campaign Execution Analysis & Control Campaign Feedback 2 Campaign A series of interconnected
Chapter 11: Campaign Management Overview Topics discussed: Campaign Management Process Campaign Planning and Development Campaign Execution Analysis & Control Campaign Feedback 2 Campaign A series of interconnected
The Global E-Commerce Gold Rush How Retailers Can Find Riches Overseas
 The Global E-Commerce Gold Rush How Retailers Can Find Riches Overseas By Joanne Bethlahmy, Bharat Popat, and Paul Schottmiller E-commerce is going global as retailers from around the world take advantage
The Global E-Commerce Gold Rush How Retailers Can Find Riches Overseas By Joanne Bethlahmy, Bharat Popat, and Paul Schottmiller E-commerce is going global as retailers from around the world take advantage
GENERATE REVENUES WITH AN EFFECTIVE PARTS WHOLESALE STRATEGY.
 GENERATE REVENUES WITH AN EFFECTIVE PARTS WHOLESALE STRATEGY. fueled by challenge. powering success. sm 1,500 dealer programs in 27 markets Parts wholesale has the potential to significantly contribute
GENERATE REVENUES WITH AN EFFECTIVE PARTS WHOLESALE STRATEGY. fueled by challenge. powering success. sm 1,500 dealer programs in 27 markets Parts wholesale has the potential to significantly contribute
Chapter One Integrated Marketing Communications
 1 Chapter One Integrated Marketing Communications 1-1 1 Virgin Atlantic Still Red Hot 25 th Anniversary campaign Bold, distinctive imagery Global campaign Integrated across many platforms and channels
1 Chapter One Integrated Marketing Communications 1-1 1 Virgin Atlantic Still Red Hot 25 th Anniversary campaign Bold, distinctive imagery Global campaign Integrated across many platforms and channels
MARKETING CHANNELS AND WHOLESALING
 C H A P T E R S I XT E E N MARKETING CHANNELS AND WHOLESALING 16-1 AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Explain what is meant by a marketing channel of distribution and why intermediaries
C H A P T E R S I XT E E N MARKETING CHANNELS AND WHOLESALING 16-1 AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Explain what is meant by a marketing channel of distribution and why intermediaries
Methods to Price Your Product
 Agriculture Business Strategies February 1999 Agdex 845-2 Methods to Price Your Product The purpose of this factsheet series is to help producers and processors understand the key elements needed to manage
Agriculture Business Strategies February 1999 Agdex 845-2 Methods to Price Your Product The purpose of this factsheet series is to help producers and processors understand the key elements needed to manage
27. Which of the following is not a typical element of the promotion section of the 4-Ps? A. Personal selling B. Sales promotions C.
 1 Student: 1. Which answer best describes the? A. Companies maximize sales by promoting their products and services B. Company profits relate directly to the sales of their products C. Companies achieve
1 Student: 1. Which answer best describes the? A. Companies maximize sales by promoting their products and services B. Company profits relate directly to the sales of their products C. Companies achieve
DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS
 Distribution channels Factors influencing the method of distribution Activity 27 : ASOS and Place Distribution channels The place element of the marketing mix refers to where products are made available
Distribution channels Factors influencing the method of distribution Activity 27 : ASOS and Place Distribution channels The place element of the marketing mix refers to where products are made available
Merchandise Accounts. Chapter 7 - Unit 14
 Merchandise Accounts Chapter 7 - Unit 14 Merchandising... Merchandising... There are many types of companies out there Merchandising... There are many types of companies out there Service company - sells
Merchandise Accounts Chapter 7 - Unit 14 Merchandising... Merchandising... There are many types of companies out there Merchandising... There are many types of companies out there Service company - sells
Sales Promotion. The Marketers Dilemma. Sales Promotion Defined:
 Sales Promotion The Marketers Dilemma Sales Promotion Defined: A direct inducement that offers extra value or incentive for the product to the salesforce, distributors, or the ultimate consumer with the
Sales Promotion The Marketers Dilemma Sales Promotion Defined: A direct inducement that offers extra value or incentive for the product to the salesforce, distributors, or the ultimate consumer with the
How To Start A Home Performance Contractor
 2.4.3 Home Performance Contractor Business Model The home performance contractor model walks through the one-stop-shop model for home energy upgrades. It illustrates both the opportunities and barriers
2.4.3 Home Performance Contractor Business Model The home performance contractor model walks through the one-stop-shop model for home energy upgrades. It illustrates both the opportunities and barriers
Course Outcome Summary
 Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 3.00 This course focuses on the marketing process as it relates
Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 3.00 This course focuses on the marketing process as it relates
Strategic Elements of Competitive Advantage. PPT 6 (First ppt slides after the mid-term) Assist. Prof. Dr. Ayşen Akyüz
 Strategic Elements of Competitive Advantage PPT 6 (First ppt slides after the mid-term) Assist. Prof. Dr. Ayşen Akyüz Industry Analysis: Forces Influencing Competition Industry group of firms that produce
Strategic Elements of Competitive Advantage PPT 6 (First ppt slides after the mid-term) Assist. Prof. Dr. Ayşen Akyüz Industry Analysis: Forces Influencing Competition Industry group of firms that produce
Chapter 19 Advertising. Section 19.1 Advertising Media Section 19.2 Media Measurement and Rates
 Chapter 19 Advertising Section 19.1 Advertising Media Section 19.2 Media Measurement and Rates Advertising Media Key Terms promotional advertising institutional advertising media print media transit advertising
Chapter 19 Advertising Section 19.1 Advertising Media Section 19.2 Media Measurement and Rates Advertising Media Key Terms promotional advertising institutional advertising media print media transit advertising
Marketing at McDonald s
 at McDonald s Careers McDonald s is one of the best known brands worldwide. This case study shows how McDonald s aims to continually build its brand by listening to its customers. It also identifies the
at McDonald s Careers McDonald s is one of the best known brands worldwide. This case study shows how McDonald s aims to continually build its brand by listening to its customers. It also identifies the
