FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent. Tips and tricks on how to improve transfection experiments. Application Note No. 1/September 2006
|
|
|
- Rosaline Simmons
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent Application Note No. 1/September 2006 Tips and tricks on how to improve transfection experiments 1
2 Successful Transfection is based on Choosing the Right Reagent and Using it Appropriately Introduction Under normal conditions, mammalian cells take up and express externally applied DNA with very low efficiency. This is mostly due to the lipid bilayer of the eukaryotic cell membrane, which poses a significant barrier to the entry of charged molecules into a cell. Several transfection methods have been developed to overcome this problem. With these methods, the study of gene expression in cultured cells using DNA or RNA transfection has become routine. Briefly, transfection is the delivery of DNA, RNA, proteins, and macromolecules into eukaryotic cells. Goals for transfection include the study of gene regulation as well as protein expression and function. There exist several different well-established methods for the delivery of molecules, particularly nucleic acids, into eukaryotic cells. These transfection methods are based on three different strategies. (For details, see There Is No Universal Transfection Reagent Not all transfection methods can be applied to all types of cells or experiments. The different methods vary greatly with respect to the level of gene expression that can be achieved. Moreover, no single technique is suitable for the multitude of different cellular systems used for transfection experiments. Each transfer method may have advantages or disadvantages, depending on, for example, the cell type to be transfected (especially true for difficult cell lines), the molecule to be transfected (DNA, RNA, oligonucleotides, proteins), or even the demands of high-throughput applications. In all cases, however, the success of transfection depends on transfection efficiency, low cytotoxicity, and reproducibility. To ensure a highly efficient transfection, you need to choose a reliable transfection technology and the reagents that work optimally under your cell culture conditions. To select the transfection reagent that best meets your needs, check existing references about your special cell type or application, study the characteristics of the various reagents (available on the internet; see and, if possible, test several different reagents using the protocols recommended for that reagent. Considerations for Specific Applications Cell Physiology To study cell physiology, or use cells for target validation, it is important to be sure that the transfection process itself does not alter the pathway of interest, or if it does, does so minimally. If you transfect with reagents that are deleterious to the cells, it can be difficult to differentiate between the effects of transfection itself and the effect of the specific gene being transfected. For this reason, it is critical to always transfect with empty vectors and vectors containing irrelevant genes. Only then can you begin to evaluate the effects of the gene of interest. When performing transfections, one should strive to maximize transfection efficiency and minimize morphologic changes in the cells visible by phase contrast microscopy. We have done studies using two of our reagents, FuGENE 6 and FuGENE HD Transfection Reagents in which we have transfected cells and, using microarray analysis, determined the number of genes that were up or down regulated. These reagents had many fewer off-target effects on test cells compared to a well known competitive reagent (see references). Protein Production using Transient Transfection Previously, to produce high levels of protein, you had to transfect cells, then select stable cell lines for expansion and accumulation of protein. Selection of such cell lines often took weeks or months, due either to the cytotoxicity of the reagent or inefficient transfection. If the transfection reagent was cytotoxic, then fewer cells survived and the protein yield was consequently low. If only a few cells were transfected, then untransfected cells rapidly outgrew the transfected cells, and little protein was produced. 2
3 Now, to produce high levels of protein, you have a better option, i.e. using a gentle reagent that transfects most of the cells. With FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent, you can produce high yields of protein 3-7 days after transfection because it is relatively non-cytotoxic, transfects most of the cells, and results in high yield per cell. However, some proteins are produced at higher levels than other proteins. Thus, critical variables for high levels of protein expression include: Cell line (some cell types are higher producers than others) Plasmid back bone (e.g., enhancers, promoters, transcriptional regulatory elements) Protein produced (some proteins simply are not well produced) cdna sequence of protein (e.g., codon optimization) Medium (nutrition, wastes, inhibitors of transfection) When these factors are optimized and the optimal ratio and amount of complex (Reagent-Plasmid) are added, levels comparable to average levels of stable clones can be obtained. Transient versus Stable Transfection The first step in preparing a stable cell line is choosing a vector that contains both a selectable marker and the gene of interest. The selectable marker is usually one that produces a protein or enzyme that allows cells to grow in the presence of an otherwise toxic chemical. Once the plasmid vector is chosen, the transfection is done the same way for either transient or stable expression. The transfected cells are allowed to grow, at least overnight in standard medium, before the selective agent is added. This gives the cells time to express sufficient quantities of the protein that allows them to overcome the selection agent. The cells are then grown in the presence of the selection agent. Cells that do not have the plasmid are killed; only transfected cells are able to grow. In some instances, the selection agent is continuously added to the culture medium to maintain selective pressure on the cells. Current Transfection Reagents Provided by Roche Applied Science Roche Applied Science offers a variety of reagents for different transfection methods. Below is an overview of the different reagents. Multicomponent reagents Novel multicomponent reagents combine high transfection efficiency with low cytotoxicity, and eliminate the need for extensive optimization. Roche Applied Science offers several multicomponent reagents: FuGENE 6 Transfection Reagent (Cat. Nos , , , and ) FuGENE 6 Transfection Reagent is an optimized blend of lipids and other proprietary compounds. This reagent combines high transfection efficiency with exceptionally low cytotoxicity. In contrast to cationic liposome-based transfection reagents, it can produce successful transfections the first time it is used (without requiring optimization of transfection conditions). The reagent has been used to successfully transfect more than 700 cell types, including many primary cells. Since it is very easy to use, and gentle enough to be used on freshly trypsinized cells, it is ideal for a variety of high-throughput screening applications. FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent. (Cat. Nos , , ) FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent is a next-generation transfection reagent, which is free of animal- or humanderived components, stable at room temperature, and sterile (0.1µm) filtered. FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent is a multipurpose reagent, suitable for diverse applications. For example, it: Has an easily optimizable protocol that allows it to transfect a wide range of eukaryotic cells, including animal and insect cells, with minimal cytotoxicity. Offers excellent transfection efficiency for many cell lines that are not transfected well by other reagents, such as MCF-7, RAW 264.7, PC-3, HeLa, MA-10, HepG2, SH-SY5Y, A7r5, STO, SCC-61, STSAR-90, SQ20B, T98G, A375, A549 and stem cells. Is particularly effective in protein expression experiments over extended periods, since it can transfect many adherent and suspension-adapted cell lines commonly used for protein expression (e.g., CHO-K1, HEK 293, and insect cells). Allows cells to be grown either in serum-containing or serum-free medium, yet still produce high levels of recombinant proteins. FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent even allows high levels of expression in high levels (up to 100%) of serum. Thus, it is the reagent of choice for studies under these conditions. 3
4 X-tremeGENE sirna Transfection Reagent (Cat Nos , ) RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful method for inhibiting the expression of a particular gene. RNAi experiments require a transfection reagent that is specially optimized for sirna delivery into mammalian cells. Such a reagent is X-tremeGENE sirna Transfection Reagent, which forms a complex with sirna and effectively delivers it into eukaryotic cells. The reagent transfects many commonly used cell types very efficiently, including HeLa, NIH 3T3, HEK-293, CHO-K1, COS-7, and several hard-to-transfect cell lines. In co-transfection-based RNAi experiments, X-tremeGENE sirna Transfection Reagent supports both high protein expression and effective gene knockdown. Note: This reagent has low cytotoxicity. It also functions exceptionally well in the presence or absence of serum; it does not require a media change, either before transfection or after addition of transfection complex. Cationic liposomal reagents If a cationic lipid is mixed with a neutral lipid, unilamellar liposome vesicles are formed that carry a net positive charge due to the highly positive amine groups on the cationic molecules. Nucleic acids can adsorb to these vesicles and gain access to the inside of cells, most likely by fusion of the liposome with the plasma membrane to form an endocytic vesicle. Under carefully optimized conditions, liposomemediated transfection methods are highly efficient and are much easier to use than earlier methods. Roche Applied Science offers three liposome-based reagents for transfection of DNA, RNA, and oligonucleotides: DOTAP Liposomal Transfection Reagent (Cat. Nos , ) DOTAP is a monocationic reagent. DOSPER Liposomal Transfection Reagent (Cat. Nos , ) DOSPER is a polycationic reagent. X-tremeGENE Q2 Transfection Reagent (Cat. Nos , ) X-tremeGENE Q2 Transfection Reagent was designed and optimized for transfection and high-level protein expression in K-562 and Jurkat cells. Note: This proprietary reagent is supplied as a dried lipid film. For a complete list of cell types successfully transfected with Roche Applied Science Transfection Reagents, see our Transfection Database in the Internet at Keys To Successful Transfection Experiments In this section we explain how key components of the transfection system may influence the efficiency of a cell transfection experiment and, when appropriate, give tips on how to make them work in your favor. Tissue Culture Reagents General tips: Optimize the growth conditions of your cells. Use only fresh media and additives, and minimize variations in the reagents used. Basic Medium Various commercial media are currently used (e.g., RPMI 1640 and DMEM). Medium constituents include nutrients (amino acids, glucose), vitamins, inorganic salts, and buffer substances. Some constituents are quite unstable and thus may cause problems if they are not fresh when used. Always protect medium from light. Some components and buffers, such as HEPES, are broken down into cytotoxic components when exposed to light. Phenol red offers protection from some of the effects of HEPES breakdown, but cytotoxicity could be a problem even in applications where phenol red free medium is used, e.g. luciferase assays. Fetal Bovine Serum Serum is an extremely complex solution of albumins, globulins, growth promoters, and growth inhibitors. The age, nutritional level, and health of the animals from which the serum is obtained affect the quantity and quality of these components. The serum is subject to significant biological variation. Additives Some cells depend on substances that are essential for viability or cell division (e.g., growth factors, trace elements, essential metabolites, and protein). CO 2 incubator Cells are grown at 37 C in a CO 2 incubator at 95% relative humidity. CO 2 is used to control the ph. Cell physiology is highly sensitive to ph variations, so most cell culture media contain a bicarbonate buffer. Some media require a concentration of 5% CO 2 for effective ph control, while other media require 10% CO 2. Check with the supplier of you medium for the appropriate concentration. Inconsistent conditions (temperature, humidity, and CO 2 ) in the incubator can cause plate-to-plate variability in the results. Pollution, chemicals, or fungal/bacterial contamination from the incubator may also affect cell physiology. 4
5 Cells General tips: Keep an eye on your cells; ensure they are in good condition. Before starting transfection, develop a suitable plating protocol for optimal cell density from the beginning to the end of transfection. Increase Success Cells are a key component and can be the greatest variable affecting the consistency and quality of results. To help eliminate these concerns, Roche Applied Science has partnered with ATCC (American Type Culture Collection). To ensure the quality of the cells to be transfected, Roche Applied Science recommends using freshly obtained cell lines from ATCC. Dividing versus Non-dividing Cells Dividing cells tend to be more amenable to uptake and expression of foreign DNA than quiescent cells. Thus for most transfections, cells are plated the day of, or the day prior to transfection. It is also important that the cells are not overgrown at the time they are plated for transfection. Since FuGENE 6 and HD Transfection Reagents are so gentle to the cells, it is possible to simultaneously plate and transfect adherent cells. Furthermore, mitogenic stimuli (e.g., virus transformation, growth factors, conditioned media, and feeder cells) are often used to activate primary cells. Adherent versus Suspension Cells Adherent and suspension cells differ significantly in transfection efficiency. Cells that by nature tend to be in suspension (e.g. HL 60, Jurkat) are very difficult to transfect. In contrast, cells that by nature are adherent (e.g. HEK, CHO) can be adapted to grow in suspension. This is often done in serum-free medium containing special additives that inhibit transfection. With care, the cells can be adapted to grow in suspension without additives. If the suspension-adapted adherent cells are grown without these additives, they can be transfected. The plasma membranes of the two types of cells (those naturally in suspension and those that are adapted to grow in suspension) are different. There is speculation that a limiting step in transfection is uptake of molecules (DNA or RNA complexed to transfection reagent) by endocytosis; however, a plausible mechanistic explanation at the molecular level does not yet exist. The differences in membrane structure among cells may be a partial cause of the inherent difficulty to transfect certain cell types. Therefore, the search for more efficient transfection reagents is mainly empirical, particularly for cells that naturally grow in suspension. Splitting Protocol Before splitting, adherent cells must be trypsinized in order to remove them from the substrate. This routine step causes a severe disruption of normal cellular functions. Therefore, differences in the splitting protocol (e.g., extension of trypsinization, inactivation of trypsin, and time until transfection starts) could affect transfection experiments. If cells are too confluent at the time of transfer, clumps instead of individual cells are plated. For some cell/reagent combinations, it is possible that the altered state of the plasma membrane may affect the optimal amounts and ratio of reagent and DNA. Passage Number The passage number indicates how often a cell line has been split (normally within one lab). In some cases, the exact passage number, since the line was established, is unknown. Some cell lines may be more unstable than others and may change over time in culture depending on the line and culture conditions. Different culture conditions could lead to clonal selection. Thus cell lines with the same name could significantly differ with respect to physiology and morphology (and transfectability). Generally, cells are more difficult to transfect during the first passage or two after cyropreservation or until they have fully recovered. Transfection efficiency varies from cell line to cell line. Some lines exhibit constant transfection efficiencies over many passages while others show differences at much lower passages. Cell Number (Grade of Confluency) Cell lines divide exponentially when there is space on the substrate (tissue culture dish). For normal cells, the growth rate is inhibited by cell density (contact inhibition), however cancer cell lines will continue to grow and may pile up on each other. Depletion of nutrients and build-up of metabolic waste products affect all cells. Cells that have been stressed by lack of nutrients are not suitable for transfection. Rates of reporter gene expression correlate with the cell number and cell health at the beginning of transfection and their subsequent growth prior to cell lysis. Culture Contamination Cultures can be contaminated with bacteria, yeast, fungi, viruses, mycoplasma, even other cell types. All types of contamination lead to erroneous results. 5
6 Mycoplasma contamination Mycoplasma contamination, which is present in 5 35% of all cell cultures, can alter growth characteristics, enzyme patterns, cell membrane composition, chromosomal structure, and transfection efficiency. Specifically, mycoplasma interferes with transfection methods that use lipid, DEAE-dextran, calcium phosphate, or adenovirus mediation, resulting in low or atypical efficiencies. These effects lead to unreliable experimental results as well as loss of time and precious cell lines. Unlike bacteria and fungi, mycoplasma contamination cannot be detected by visual inspection. They are small enough to pass through most sterilization filters; they are resistant to common antibiotics. Therefore, routine screening for mycoplasma contamination is essential. Roche Applied Science offers mycoplasma detection kits to help detect contamination early. Cross-Contamination If different cell types are grown in the same laboratory, it is possible that cross-contamination can occur even when the strictest separation procedures are followed. It is well known that many cell lines are contaminated by HeLa cells. Cross-contamination by other cell lines cannot always be detected by microscopic examination. If a few cells of a faster growing cell type get into the culture, over a matter of months they will take over the culture. The change is gradual; you may not even notice it. Establish identify tests criteria. For example, with human cell lines, STR (Short Tandem Repeats) profiling is a reliable method. Or for the easiest solution when in doubt, and if possible, replace the lines with a fresh, low-passage supply. Vector DNA General tips: Check the quality of your purified vector. Decide whether the sequences that support its normal function are suitable for your cellular system. To test the parameters of your system, always use a control vector that you know is functional. Vector Integrity The function of a vector depends on its structural integrity. Transfection efficiency can be influenced by the ratio of supercoiled form to relaxed form in the plasmid preparation, doublestranded breaks, nuclease degradation, and physical stresses arising from storage and handling. Vector Preparation Vectors are produced in bacterial systems and purified according to various protocols. Contaminants remaining in the vector preparation (e.g., CsCl, endotoxin) may influence transfection efficiency. Vector Architecture (Promoter/Enhancer/ORI) Transfection systems are often optimized and compared using control vectors with strong viral regulatory elements (e.g., RSV, CMV, and SV40). However, the relative efficacy of viral promoter/enhancer systems can differ among cell lines by as much as two orders of magnitude. For example, in some cell lines, the SV40 system expresses the large T antigen (e.g., COS) highly efficiently due to autonomous plasmid amplification; in many other cell lines, the CMV promoter is more efficient. In addition, expression rates of various CMV vectors can differ by more than an order of magnitude, in part due to the other regulatory elements in the vectors. Transfection Protocol General tips: Establish a suitable transfection protocol; begin with a standard protocol, then optimize it by varying the reagent / DNA ratio and amount of complex. Preparation of the Transfection Complex Variables such as transfection reagent / DNA ratio, ionic strength, buffer ph, and temperature affect the composition and function of the transfection complexes. Plasmid may be diluted in either sterile water or TE buffer. If you are using a commercial transfection reagent, carefully read the instructions that are supplied with the reagent. Trust the supplier; stick to their recommended protocols unless you have very good reasons for changing them. Prepare complex in medium that does not contain serum or other proteins; if the medium used for complex formation contains serum, it will inhibit transfection. The optimal incubation time for complex formation can be quite critical and varies significantly for different transfection reagents. Transfection Reagent / DNA Ratio (Charge Ratio) All transfection reagents are most efficient at a certain reagent / DNA ratio. Sometimes this ratio occurs within a quite narrow range; it must be optimized for each experimental system. The time it takes to find the optimal ratio is well invested. Not only is the ratio important, but the amount of complex added is often critical. Diluent for forming complex For most reagents it is critical to form the complex in plain basal medium or salt solution. FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent is an exception to this, since it allows complex to be formed in water, serum-free medium, or medium containing 10% serum. 6
7 If you are using water or medium containing 10% serum, make sure that it will work with your particular system. Amount of Complex There is an optimum amount of transfection reagent / DNA complex that should be applied to the cells. If you use too little, expression of the transfected DNA is weak; if you use too much, expression may decline due to cytotoxicity or other effects. The optimal amount usually must be determined experimentally. This can be clearly seen with FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent. One exception occurs in transfections involving FuGENE 6 Transfection Reagent, which gives good results over a wide dosage range. In many cases, this property of FuGENE 6 Transfection Reagent makes dose optimization unnecessary. The amount of complex required is related to the number of cells present. Fewer cells require less complex. Application of the Transfection Complex There are two alternative ways to apply the transfection complex to the cells: 1. add the concentrated complex dropwise to the medium, or 2. predilute the transfection complex with the medium, then perform a medium exchange. The first option is more convenient while the latter option provides more consistent application, which avoids localized toxic doses. For gentle reagents such as FuGENE 6 Transfection Reagent and HD Transfection Reagents, you may place the complex in the container, then add freshly trypsinized cells. Transfection Medium The medium present during transfection could affect transfection efficiency either positively or negatively. This is true even for basic medium formulations, particularly when bovine serum is included. With a number of transfection reagents, efficiency is reduced in the presence of fetal bovine serum. Some companies provide optimized serum-free transfection media that may be used in combination with the transfection reagents. The transfection reagents provided by Roche Applied Science are effective in the presence or absence of serum. FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent is unique in that it can transfect tumor cells maintained in 100% serum. Transfection efficiency may be reduced up to 25% if the cells are cultivated in the presence of antibiotics (e.g., penicillin, streptomycin, or fungizone). Thus, for transient transfections, we recommend using medium without antibiotics. Timeline General tips: Ensure a successful end result; set up a suitable timeline for your transfection experiment to ensure optimal expression of your protein of interest. Start of Transfection Twelve hours before transfection, split the cells into culture plates. At the start of transfection, the culture should be approximately 50-80% confluent, so they will be near confluency by the end of the experiment. If serum is taken away during transfection, the cells may arrest for awhile. The uptake of transfection complex by the cells is generally complete within hours. After this time, there is no detectable increase in transfection efficiency. Medium Exchange Some transfection reagents require a medium change after the uptake period. This step is essential if transfection must be performed in the absence of fetal bovine serum. With non-toxic transfection reagents, which work in the presence of serum (e.g., FuGENE 6 Transfection Reagent or FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent), this step can be eliminated if there is enough medium for the subsequent expression period. If the complex is left on the cells until the time of assay, transfection efficiency increases for some cell lines, while in other cells there is no further increase after the first few hours. Although it is not usually necessary to remove the transfection reagent / DNA complex following the transfection step, it is necessary to feed your cells with fresh media during extended growth periods. This is especially important if the transfected cells are allowed to grow for 3-7 days, so they have time to reach maximum protein expression. Time assay Reporter gene expression is usually analyzed hours after the start of transfection. Within this time span, the concentration of the reporter gene product generally increases; this increase depends on the strength of the promoter, cellular reactions involved in expressing the heterologous protein, health of the surviving cells, and nutritional factors. If you are harvesting proteins for purification, it is more common to wait 3-7 days post transfection. At the time of harvest it is a good idea to include Complete Protease Inhibitor (e.g., Cat. Nos ; , available from Roche Applied Science) in the medium to prevent degradation. 7
8 Ordering Information Product Pack Size Cat. No. FuGENE HD 0.4 ml (up to Transfection transfections) Reagent 1.0 ml (up to transfections) 5 x 1 ml (up to ,500 transfections) FuGENE 6 1 ml (up to Transfection transfections) Reagent 0.4 ml (up to transfections) 5 x 1 ml (up to ,500 transfections) Custom-pack (150 ml minimum) X-tremeGENE Q2 1.8 ml ( Transfection Reagent transfections) 0.4 ml ( transfections) X-tremeGENE sirna 1 ml (400 trans Transfection Reagent fections in a 24-well plate) 5 x 1 ml (2, transfections in a 24-well plate) DOTAP Liposomal 0.4 ml Transfection Reagent 2 ml (5 x 0.4 ml, 2 mg) DOSPER Liposomal 0.4 ml Transfection Reagent 2 ml (5 x 0.4 ml, 2 mg) NOTICE TO PURCHASER Purchaser represents and warrants that it will use FuGENE Transfection Reagent purely for research purposes. Transfected cells, materials produced, and any data derived from the use of FuGENE Transfection Reagent, may be used only for the internal research of Purchaser whether Purchaser is a "for-profit" or a "not-for-profit" organization. Under no circumstances may FuGENE Transfection Reagent be used by Purchaser or any third party for a commercial purpose unless Purchaser has negotiated a license for commercial use with Fugent, LLC (contact information: [email protected]). For purposes of the foregoing sentence, "commercial purpose" shall mean use of FuGENE Transfection Reagent for profit or commercial gain. By using FuGENE Transfection Reagent, Purchaser agrees to be bound by the above terms. If Purchaser wishes not to be bound by these terms, Purchaser agrees to return the FuGENE Transfection Reagent to Roche Diagnostics for a full refund. References [1] Linda B. Jacobsen, Susan A. Calvin, Kim E. Colvin and MaryJo Wright. FuGENE 6 Transfection Reagent: the gentle power. Special issue: Transfection of Mammalian Cells - Methods 33 (2004) ; Edited by A. L. Peel; [2] Bindu Raghavan, Guojuan Zhang, Mark Kotur, Jacquelyn Cheatham, and Joanne Trgovcich. Superiority of FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent in Minimizing Non-Specific Cellular Interferon Responses. Biochemica 3 (2006) [3] Vivien Nagy and Manfred Watzele. FuGENE 6 Transfection Reagent: Minimizing Reagent-Dependent Side Effects as Analyzed by Gene-Expression Profiling and Cytotoxicity Assays. Biochemica 4 (2004) [4] Kouichi Hasegawa, Shin-ya Yasuda, and Hirofumi Suemori. Superior Transfection of Human Embryonic Stem Cells with FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent. Biochemica 4 (2006) [5] Susan Calvin, Jay Wang, Jeff Emch, Simone Pitz, and Linda Jacobsen. FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent: Choice of a Transfection Reagent with Minimal Off-Target Effect as Analyzed by Microarray Transcriptional Profiling. Biochemica 4 (2006) For a detailed Troubleshooting please see Application Note 2, Setting up transfection controls For a complete overview of related products and manuals, please visit and bookmark our Special Interest Site To ensure the quality of cells to be transfected, Roche recommends using freshly-obtained, low-passaged cell lines from ATCC. For more information, please visit and bookmark Trademarks The ATCC trademark and trade name and any and all ATCC catalog numbers are trademarks of the American Type Culture Collection. FuGENE is a registered trademark of Fugent, L.L.C., USA. COMPLETE is a trademark of Roche. Other brands or product names are trademarks of their respective holders. Roche Diagnostics GmbH Roche Applied Science Mannheim Germany
TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent
 Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5400 INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent is a high-performance, animal-origin free, broad spectrum reagent
Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5400 INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent is a high-performance, animal-origin free, broad spectrum reagent
Transfection reagent for visualizing lipofection with DNA. For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.
 METAFECTENE FluoR Transfection reagent for visualizing lipofection with DNA For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
METAFECTENE FluoR Transfection reagent for visualizing lipofection with DNA For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
Instructions. Torpedo sirna. Material. Important Guidelines. Specifications. Quality Control
 is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent
 For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. FOR IN VITRO USE ONLY. FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent For the transient and stable transfection of animal and insect cells Cat. No.
For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. FOR IN VITRO USE ONLY. FuGENE HD Transfection Reagent For the transient and stable transfection of animal and insect cells Cat. No.
Fast, easy and effective transfection reagent for mammalian cells
 METAFECTENE EASY + Fast, easy and effective transfection reagent for mammalian cells For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
METAFECTENE EASY + Fast, easy and effective transfection reagent for mammalian cells For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
Manual for: sirna-trans Maximo Reagent
 Manual for: sirna-trans Maximo Reagent Contact: [email protected]; www.geneon.net GeneON GmbH Germany GeneON GmbH / Protocol sirna-trans reagent vs. 1.3 / www.geneon.net / - 0 - sirna-trans reagent Instruction
Manual for: sirna-trans Maximo Reagent Contact: [email protected]; www.geneon.net GeneON GmbH Germany GeneON GmbH / Protocol sirna-trans reagent vs. 1.3 / www.geneon.net / - 0 - sirna-trans reagent Instruction
PRODUCT INFORMATION...
 VIROMER RED In vitro plasmid DNA and mrna Standard Transfection PRODUCT INFORMATION... 2 GENERAL... 2 RED OR YELLOW?... 3 PROTOCOL GUIDELINES... 4 GENERAL REMARKS... 4 CELL CULTURE AND PLATING... 4 FORWARD/REVERSE
VIROMER RED In vitro plasmid DNA and mrna Standard Transfection PRODUCT INFORMATION... 2 GENERAL... 2 RED OR YELLOW?... 3 PROTOCOL GUIDELINES... 4 GENERAL REMARKS... 4 CELL CULTURE AND PLATING... 4 FORWARD/REVERSE
MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit
 page 1 of 7 MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the mice they are isolated
page 1 of 7 MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the mice they are isolated
Especially developed for the transfection of mammalian cells with sirna or mirna
 METAFECTENE SI Especially developed for the transfection of mammalian cells with sirna or mirna For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No.
METAFECTENE SI Especially developed for the transfection of mammalian cells with sirna or mirna For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No.
MEF Nucleofector Kit 1 and 2
 page 1 of 7 MEF Nucleofector Kit 1 and 2 for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the they are isolated
page 1 of 7 MEF Nucleofector Kit 1 and 2 for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the they are isolated
HiPerFect Transfection Reagent Handbook
 Fifth Edition October 2010 HiPerFect Transfection Reagent Handbook For transfection of eukaryotic cells with sirna and mirna Sample & Assay Technologies QIAGEN Sample and Assay Technologies QIAGEN is the
Fifth Edition October 2010 HiPerFect Transfection Reagent Handbook For transfection of eukaryotic cells with sirna and mirna Sample & Assay Technologies QIAGEN Sample and Assay Technologies QIAGEN is the
MTT Cell Proliferation Assay
 ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
TOOLS sirna and mirna. User guide
 TOOLS sirna and mirna User guide Introduction RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful tool for suppression gene expression by causing the destruction of specific mrna molecules. Small Interfering RNAs (sirnas)
TOOLS sirna and mirna User guide Introduction RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful tool for suppression gene expression by causing the destruction of specific mrna molecules. Small Interfering RNAs (sirnas)
Classic Immunoprecipitation
 292PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 [email protected] A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Classic Immunoprecipitation Utilizes Protein A/G Agarose for Antibody Binding (Cat.
292PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 [email protected] A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Classic Immunoprecipitation Utilizes Protein A/G Agarose for Antibody Binding (Cat.
Amaxa 4D-Nucleofector Protocol for Mouse Embryonic Stem [ES] Cells For 4D-Nucleofector X Unit Transfection in suspension
![Amaxa 4D-Nucleofector Protocol for Mouse Embryonic Stem [ES] Cells For 4D-Nucleofector X Unit Transfection in suspension Amaxa 4D-Nucleofector Protocol for Mouse Embryonic Stem [ES] Cells For 4D-Nucleofector X Unit Transfection in suspension](/thumbs/30/14702458.jpg) For 4D-Nucleofector X Unit Transfection in suspension Cells derived from mouse blastocysts; round cells, growing in clumps s 1. This protocol is meant to provide an outline for the handling and the Nucleofection
For 4D-Nucleofector X Unit Transfection in suspension Cells derived from mouse blastocysts; round cells, growing in clumps s 1. This protocol is meant to provide an outline for the handling and the Nucleofection
SmartFlare RNA Detection Probes: Principles, protocols and troubleshooting
 Technical Guide SmartFlare RNA Detection Probes: Principles, protocols and troubleshooting Principles of SmartFlare technology RNA detection traditionally requires transfection, laborious sample prep,
Technical Guide SmartFlare RNA Detection Probes: Principles, protocols and troubleshooting Principles of SmartFlare technology RNA detection traditionally requires transfection, laborious sample prep,
Mouse ES Cell Nucleofector Kit
 page 1 of 7 Mouse ES Cell Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells Cell type Origin Cells derived from mouse blastocysts. Morphology Round cells growing in clumps. Important remarks! 1. This protocol
page 1 of 7 Mouse ES Cell Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells Cell type Origin Cells derived from mouse blastocysts. Morphology Round cells growing in clumps. Important remarks! 1. This protocol
Proto col. GoClone Repor ter Construc ts: Sample Protocol for Adherent Cells. Tech support: 877-994-8240. Luciferase Assay System
 Luciferase Assay System Proto col GoClone Repor ter Construc ts: Sample Protocol for Adherent Cells LightSwitch Luciferase Assay System GoClone Reporter Assay Workflow Step 1: Seed cells in plate format.
Luciferase Assay System Proto col GoClone Repor ter Construc ts: Sample Protocol for Adherent Cells LightSwitch Luciferase Assay System GoClone Reporter Assay Workflow Step 1: Seed cells in plate format.
Transfection-Transfer of non-viral genetic material into eukaryotic cells. Infection/ Transduction- Transfer of viral genetic material into cells.
 Transfection Key words: Transient transfection, Stable transfection, transfection methods, vector, plasmid, origin of replication, reporter gene/ protein, cloning site, promoter and enhancer, signal peptide,
Transfection Key words: Transient transfection, Stable transfection, transfection methods, vector, plasmid, origin of replication, reporter gene/ protein, cloning site, promoter and enhancer, signal peptide,
Measuring Cell Viability/Cytotoxicity: Cell Counting Kit-F
 Introduction The Cell Counting Kit-F is a fluorometic assay for the determination of viable cell numbers. Calcein-AM in this kit passes through the cell membrane and is hydrolized by the esterase in the
Introduction The Cell Counting Kit-F is a fluorometic assay for the determination of viable cell numbers. Calcein-AM in this kit passes through the cell membrane and is hydrolized by the esterase in the
Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Table of Contents Introduction 3 Kit Components 3 Storage Conditions 4 Recommended Equipment and Reagents 4 Introduction to the Protocol 4 General Overview
Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Table of Contents Introduction 3 Kit Components 3 Storage Conditions 4 Recommended Equipment and Reagents 4 Introduction to the Protocol 4 General Overview
Bacterial Transformation with Green Fluorescent Protein. Table of Contents Fall 2012
 Bacterial Transformation with Green Fluorescent Protein pglo Version Table of Contents Bacterial Transformation Introduction..1 Laboratory Exercise...3 Important Laboratory Practices 3 Protocol...... 4
Bacterial Transformation with Green Fluorescent Protein pglo Version Table of Contents Bacterial Transformation Introduction..1 Laboratory Exercise...3 Important Laboratory Practices 3 Protocol...... 4
Human Adult Mesothelial Cell Manual
 Human Adult Mesothelial Cell Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0025.01 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Adult Mesothelial Cells Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier. All US and Canada orders are shipped
Human Adult Mesothelial Cell Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0025.01 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Adult Mesothelial Cells Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier. All US and Canada orders are shipped
Protein Stabilization Reagents. Elevated Protein Protection
 Protein Stabilization Reagents Elevated Protein Protection Protein Stabilization Reagents Naturally occurring proteases and phosphatases can destroy proteins you spent days isolating. Save valuable time
Protein Stabilization Reagents Elevated Protein Protection Protein Stabilization Reagents Naturally occurring proteases and phosphatases can destroy proteins you spent days isolating. Save valuable time
QIAGEN Transfection Technologies
 QIAGEN Transfection Technologies Efficient and robust transfection for all your applications Sample & Assay Technologies Table of contents QIAGEN solutions for efficient transfection Transfection is a
QIAGEN Transfection Technologies Efficient and robust transfection for all your applications Sample & Assay Technologies Table of contents QIAGEN solutions for efficient transfection Transfection is a
MGC premier Expression-Ready cdna clones TCH1103, TCM1104, TCR1105, TCB1106, TCH1203, TCM1204, TCR1205, TCB1206, TCH1303, TCM1304, TCR1305
 MGC premier Expression-Ready cdna clones TCH1103, TCM1104, TCR1105, TCB1106, TCH1203, TCM1204, TCR1205, TCB1206, TCH1303, TCM1304, TCR1305 The MGC premier Expression-Ready collection has the high quality,
MGC premier Expression-Ready cdna clones TCH1103, TCM1104, TCR1105, TCB1106, TCH1203, TCM1204, TCR1205, TCB1206, TCH1303, TCM1304, TCR1305 The MGC premier Expression-Ready collection has the high quality,
HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit
 HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit For purification of high pure plasmid DNA with high yields www.tiangen.com PP120109 HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit Kit Contents Storage Cat.no. DP116 Contents RNaseA (100 mg/ml) Buffer
HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit For purification of high pure plasmid DNA with high yields www.tiangen.com PP120109 HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit Kit Contents Storage Cat.no. DP116 Contents RNaseA (100 mg/ml) Buffer
Luca Romagnoli, Ph.D. Business Development Manager
 Modelli innovativi di produzione per lo sviluppo di un processo altamente qualitativo di farmaci biologici Luca Romagnoli, Ph.D. Business Development Manager BIOLOGICAL DRUGS - SOURCES Monoclonal antibodies
Modelli innovativi di produzione per lo sviluppo di un processo altamente qualitativo di farmaci biologici Luca Romagnoli, Ph.D. Business Development Manager BIOLOGICAL DRUGS - SOURCES Monoclonal antibodies
DP419 RNAsimple Total RNA Kit. RNAprep pure Series. DP501 mircute mirna Isolation Kit. DP438 MagGene Viral DNA / RNA Kit. DP405 TRNzol Reagent
 Overview of TIANGEN Products DP419 RNAsimple Total RNA Kit DP430 RNAprep pure Kit(For Cell/Bacteria) DP315/DP315-R TIANamp Virus DNA/RNA Kit DP431 RNAprep pure Kit (For Tissue) Silica-membrane Technology
Overview of TIANGEN Products DP419 RNAsimple Total RNA Kit DP430 RNAprep pure Kit(For Cell/Bacteria) DP315/DP315-R TIANamp Virus DNA/RNA Kit DP431 RNAprep pure Kit (For Tissue) Silica-membrane Technology
Manufacturing process of biologics
 Manufacturing process of biologics K. Ho Afssaps, France 2011 ICH International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use 2011 ICH 1 Disclaimer:
Manufacturing process of biologics K. Ho Afssaps, France 2011 ICH International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use 2011 ICH 1 Disclaimer:
BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System Free your hands with the BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System
 BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System Free your hands with the BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System The BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System gives you: Unique speed and simplicity High-throughput
BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System Free your hands with the BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System The BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System gives you: Unique speed and simplicity High-throughput
Expression and Purification of Recombinant Protein in bacteria and Yeast. Presented By: Puspa pandey, Mohit sachdeva & Ming yu
 Expression and Purification of Recombinant Protein in bacteria and Yeast Presented By: Puspa pandey, Mohit sachdeva & Ming yu DNA Vectors Molecular carriers which carry fragments of DNA into host cell.
Expression and Purification of Recombinant Protein in bacteria and Yeast Presented By: Puspa pandey, Mohit sachdeva & Ming yu DNA Vectors Molecular carriers which carry fragments of DNA into host cell.
Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual
 User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
Thermo Scientific DharmaFECT Transfection Reagents
 Thermo Scientific Transfection Reagents Maintain cell viability with lipids specially formulated to deliver sirna Achieve robust sirna uptake for dependable gene silencing Expand your RNAi applications
Thermo Scientific Transfection Reagents Maintain cell viability with lipids specially formulated to deliver sirna Achieve robust sirna uptake for dependable gene silencing Expand your RNAi applications
GRS Plasmid Purification Kit Transfection Grade GK73.0002 (2 MaxiPreps)
 1 GRS Plasmid Purification Kit Transfection Grade GK73.0002 (2 MaxiPreps) (FOR RESEARCH ONLY) Sample : Expected Yield : Endotoxin: Format : Operation Time : Elution Volume : 50-400 ml of cultured bacterial
1 GRS Plasmid Purification Kit Transfection Grade GK73.0002 (2 MaxiPreps) (FOR RESEARCH ONLY) Sample : Expected Yield : Endotoxin: Format : Operation Time : Elution Volume : 50-400 ml of cultured bacterial
Optimized Protocol sirna Test Kit for Cell Lines and Adherent Primary Cells
 page 1 of 8 sirna Test Kit for Cell Lines and Adherent Primary Cells Kit principle Co-transfection of pmaxgfp, encoding the green fluorescent protein (GFP) from Pontellina p. with an sirna directed against
page 1 of 8 sirna Test Kit for Cell Lines and Adherent Primary Cells Kit principle Co-transfection of pmaxgfp, encoding the green fluorescent protein (GFP) from Pontellina p. with an sirna directed against
INTERFERin in vitro sirna/mirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL. 1 Standard sirna transfection of adherent cells... 2
 INTERFERin in vitro sirna/mirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION INTERFERin is a powerful sirna/mirna transfection reagent that ensures efficient gene silencing and reproducible transfection in
INTERFERin in vitro sirna/mirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION INTERFERin is a powerful sirna/mirna transfection reagent that ensures efficient gene silencing and reproducible transfection in
Growth and Maintenance of T-REx Cell Lines
 USER GUIDE Growth and Maintenance of T-REx Cell Lines Catalog Numbers R710-07, R714-07, R718-07, R722-07 Document Part Number 25-0272 Publication Number MAN0000106 Revision 3.0 For Research Use Only. Not
USER GUIDE Growth and Maintenance of T-REx Cell Lines Catalog Numbers R710-07, R714-07, R718-07, R722-07 Document Part Number 25-0272 Publication Number MAN0000106 Revision 3.0 For Research Use Only. Not
Annexin V-EGFP Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab14153 Annexin V-EGFP Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab14153 Annexin V-EGFP Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended
Animal Cell Culture. Third Edition. A Practical Approach OXJORD VNIVVRSITY 1'RVSS
 Animal Cell Culture Third Edition A Practical Approach Edited by John R. W. Masters 3rd Floor Research Laboratories, University College London OXJORD VNIVVRSITY 1'RVSS Contents List of protocols page xiii
Animal Cell Culture Third Edition A Practical Approach Edited by John R. W. Masters 3rd Floor Research Laboratories, University College London OXJORD VNIVVRSITY 1'RVSS Contents List of protocols page xiii
Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit
 Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit For T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice Evaluated for murine T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice This protocol is designed for murine lymphocytes or
Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit For T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice Evaluated for murine T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice This protocol is designed for murine lymphocytes or
Methods of Grading S/N Style of grading Percentage Score 1 Attendance, class work and assignment 10 2 Test 20 3 Examination 70 Total 100
 COURSE: MIB 303 Microbial Physiology and Metabolism (3 Units- Compulsory) Course Duration: Three hours per week for 15 weeks (45 hours). Lecturer: Jimoh, S.O. B.Sc., M.Sc, Ph.D Microbiology (ABU, Zaria)
COURSE: MIB 303 Microbial Physiology and Metabolism (3 Units- Compulsory) Course Duration: Three hours per week for 15 weeks (45 hours). Lecturer: Jimoh, S.O. B.Sc., M.Sc, Ph.D Microbiology (ABU, Zaria)
NIH Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)
 USER GUIDE NIH Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC) Catalog number FL1002 Revision date 28 November 2011 Publication Part number 25-0610 MAN0000351 For Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic procedures. ii Table
USER GUIDE NIH Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC) Catalog number FL1002 Revision date 28 November 2011 Publication Part number 25-0610 MAN0000351 For Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic procedures. ii Table
Integrated Protein Services
 Integrated Protein Services Custom protein expression & purification Version DC04-0012 Expression strategy The first step in the recombinant protein generation process is to design an appropriate expression
Integrated Protein Services Custom protein expression & purification Version DC04-0012 Expression strategy The first step in the recombinant protein generation process is to design an appropriate expression
TransformAid Bacterial Transformation Kit
 Home Contacts Order Catalog Support Search Alphabetical Index Numerical Index Restriction Endonucleases Modifying Enzymes PCR Kits Markers Nucleic Acids Nucleotides & Oligonucleotides Media Transfection
Home Contacts Order Catalog Support Search Alphabetical Index Numerical Index Restriction Endonucleases Modifying Enzymes PCR Kits Markers Nucleic Acids Nucleotides & Oligonucleotides Media Transfection
Application Note No. 2 / July 2012. Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation. System
 Application Note No. 2 / July 2012 Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation System Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation Introduction In vitro
Application Note No. 2 / July 2012 Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation System Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation Introduction In vitro
How To Develop A Cell Line
 Advances in The Development of Biopharmaceuticals The application of modern technologies and services to the development of Biopharmaceutical processes Dr Jonathan H Dempsey Process Science Fellow Invitrogen
Advances in The Development of Biopharmaceuticals The application of modern technologies and services to the development of Biopharmaceutical processes Dr Jonathan H Dempsey Process Science Fellow Invitrogen
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes. 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
 Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Workshop 14-16 February 2006
 Theoretical and practical approaches of Hepatocyte primary culture Workshop 14-16 February 2006 Lecture (2) Disaggregation & purification of target cells Coarse organizer Dr. Abo bakr Mohamed Eltayeb General
Theoretical and practical approaches of Hepatocyte primary culture Workshop 14-16 February 2006 Lecture (2) Disaggregation & purification of target cells Coarse organizer Dr. Abo bakr Mohamed Eltayeb General
sirna Duplexes & RNAi Explorer
 P r o d u c t S p e c i f i c a t i o n s Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fl/Dabcyl Molecular Beacon Catalog No.:27-6402-01 Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fluorescein/Tamra TaqMan Catalog No.:27-6402-01
P r o d u c t S p e c i f i c a t i o n s Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fl/Dabcyl Molecular Beacon Catalog No.:27-6402-01 Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fluorescein/Tamra TaqMan Catalog No.:27-6402-01
Enzymes: Practice Questions #1
 Enzymes: Practice Questions #1 1. Compound X increases the rate of the reaction below. Compound X is most likely A. an enzyme B. a lipid molecule C. an indicator D. an ADP molecule 2. The equation below
Enzymes: Practice Questions #1 1. Compound X increases the rate of the reaction below. Compound X is most likely A. an enzyme B. a lipid molecule C. an indicator D. an ADP molecule 2. The equation below
Application Guide... 2
 Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
ADP/ATP Ratio Assay Kit (Bioluminescent)
 ab65313 ADP/ATP Ratio Assay Kit (Bioluminescent) Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of the ratio of ADP/ATP in various samples. This product is for research use only
ab65313 ADP/ATP Ratio Assay Kit (Bioluminescent) Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of the ratio of ADP/ATP in various samples. This product is for research use only
First Strand cdna Synthesis
 380PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 [email protected] A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name First Strand cdna Synthesis (Cat. # 786 812) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
380PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 [email protected] A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name First Strand cdna Synthesis (Cat. # 786 812) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1. Immunity and Disease
 ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit
 Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit Part # 103015-100 User Guide For use with Seahorse XF e and XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers For Research Use Only 1 Table of Contents Product Description... 2 Introduction...
Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit Part # 103015-100 User Guide For use with Seahorse XF e and XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers For Research Use Only 1 Table of Contents Product Description... 2 Introduction...
Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology
 Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology Chapter 18 Lecture Objectives What Is Recombinant DNA? How Are New Genes Inserted into Cells? What Sources of DNA Are Used in Cloning? What Other Tools Are Used to Study
Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology Chapter 18 Lecture Objectives What Is Recombinant DNA? How Are New Genes Inserted into Cells? What Sources of DNA Are Used in Cloning? What Other Tools Are Used to Study
User Manual. CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit. Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube
 User Manual CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Table of contents Introduction 4 Contents 5 Storage 5 Additionally
User Manual CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Table of contents Introduction 4 Contents 5 Storage 5 Additionally
An Introduction to Transfection Methods Technical Reference Guide
 An Introduction to Transfection Methods Transfection Technologies The introduction of nucleic acids into cells is one of the most valuable and frequently used tools of biological science. Transfection
An Introduction to Transfection Methods Transfection Technologies The introduction of nucleic acids into cells is one of the most valuable and frequently used tools of biological science. Transfection
Integrated Protein Services
 Integrated Protein Services Custom protein expression & purification Last date of revision June 2015 Version DC04-0013 www.iba-lifesciences.com Expression strategy The first step in the recombinant protein
Integrated Protein Services Custom protein expression & purification Last date of revision June 2015 Version DC04-0013 www.iba-lifesciences.com Expression strategy The first step in the recombinant protein
Lab 10: Bacterial Transformation, part 2, DNA plasmid preps, Determining DNA Concentration and Purity
 Lab 10: Bacterial Transformation, part 2, DNA plasmid preps, Determining DNA Concentration and Purity Today you analyze the results of your bacterial transformation from last week and determine the efficiency
Lab 10: Bacterial Transformation, part 2, DNA plasmid preps, Determining DNA Concentration and Purity Today you analyze the results of your bacterial transformation from last week and determine the efficiency
GASTRIC ORGANOID CULTURE PROTOCOL
 GASTRIC ORGANOID CULTURE PROTOCOL THIS PROTOCOL PROVIDES THE PROCEDURE FOR SUBCULTURING NORMAL HUMAN GASTRIC ORGANOIDS WHICH WAS DERIVED FROM THE SUBMERGED METHOD AS DESCRIBED IN BARKER N, ET AL. LGR5+VE
GASTRIC ORGANOID CULTURE PROTOCOL THIS PROTOCOL PROVIDES THE PROCEDURE FOR SUBCULTURING NORMAL HUMAN GASTRIC ORGANOIDS WHICH WAS DERIVED FROM THE SUBMERGED METHOD AS DESCRIBED IN BARKER N, ET AL. LGR5+VE
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology
 Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Essentials of Real Time PCR. About Sequence Detection Chemistries
 Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Cell Culture Experiments
 Cell Culture Experiments Cell cultures are another way to observe and analyze biological systems. These in vitro (in glass; outside the living body and in an artificial environment) models allow experimental
Cell Culture Experiments Cell cultures are another way to observe and analyze biological systems. These in vitro (in glass; outside the living body and in an artificial environment) models allow experimental
岑 祥 股 份 有 限 公 司 技 術 專 員 費 軫 尹 20100803
 技 術 專 員 費 軫 尹 20100803 Overview of presentation Basic Biology of RNA interference Application of sirna for gene function? How to study mirna? How to deliver sirna and mirna? New prospects on RNAi research
技 術 專 員 費 軫 尹 20100803 Overview of presentation Basic Biology of RNA interference Application of sirna for gene function? How to study mirna? How to deliver sirna and mirna? New prospects on RNAi research
STOP. Before using this product, please read the Limited Use License statement below:
 STOP Before using this product, please read the Limited Use License statement below: Important Limited Use License information for pdrive5lucia-rgfap The purchase of the pdrive5lucia-rgfap vector conveys
STOP Before using this product, please read the Limited Use License statement below: Important Limited Use License information for pdrive5lucia-rgfap The purchase of the pdrive5lucia-rgfap vector conveys
Supplementary Figure 1.
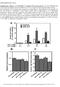 Supplementary Figure 1. (A) MicroRNA 212 enhances IS from pancreatic β-cells. INS-1 832/3 β-cells were transfected with precursors for mirnas 212, 375, or negative control oligonucleotides. 48 hrs after
Supplementary Figure 1. (A) MicroRNA 212 enhances IS from pancreatic β-cells. INS-1 832/3 β-cells were transfected with precursors for mirnas 212, 375, or negative control oligonucleotides. 48 hrs after
Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay
 Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay 6 Vocabulary: In Vitro: studies in biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings
Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay 6 Vocabulary: In Vitro: studies in biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings
Path-ID Multiplex One-Step RT-PCR Kit
 USER GUIDE Path-ID Multiplex One-Step RT-PCR Kit TaqMan probe-based multiplex one-step real-time RT-PCR detection of RNA targets Catalog Numbers 4428206, 4428207, 4440022 Publication Part Number 4440907
USER GUIDE Path-ID Multiplex One-Step RT-PCR Kit TaqMan probe-based multiplex one-step real-time RT-PCR detection of RNA targets Catalog Numbers 4428206, 4428207, 4440022 Publication Part Number 4440907
Zeocin Selection Reagent
 USER GUIDE Zeocin Selection Reagent Catalog nos. R250-01, R250-05 Revision date 19 January 2012 Publication Part number 25-0078 MAN0000019 For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic
USER GUIDE Zeocin Selection Reagent Catalog nos. R250-01, R250-05 Revision date 19 January 2012 Publication Part number 25-0078 MAN0000019 For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic
Genolution Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Life Science and Molecular Diagnostic Products
 Genolution Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Revolution through genes, And Solution through genes. Life Science and Molecular Diagnostic Products www.genolution1.com TEL; 02-3010-8670, 8672 Geno-Serum Hepatitis B
Genolution Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Revolution through genes, And Solution through genes. Life Science and Molecular Diagnostic Products www.genolution1.com TEL; 02-3010-8670, 8672 Geno-Serum Hepatitis B
UltraClean Soil DNA Isolation Kit
 PAGE 1 UltraClean Soil DNA Isolation Kit Catalog # 12800-50 50 preps New improved PCR inhibitor removal solution (IRS) included Instruction Manual (New Alternative Protocol maximizes yields) Introduction
PAGE 1 UltraClean Soil DNA Isolation Kit Catalog # 12800-50 50 preps New improved PCR inhibitor removal solution (IRS) included Instruction Manual (New Alternative Protocol maximizes yields) Introduction
Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC)- conjugated Antibodies
 USER GUIDE Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC)- conjugated Antibodies Catalog Numbers R933-25, R953-25, R963-25 Document Part Number 25-0376 Publication Number MAN0000194 Revision 2.0 For Research Use Only.
USER GUIDE Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC)- conjugated Antibodies Catalog Numbers R933-25, R953-25, R963-25 Document Part Number 25-0376 Publication Number MAN0000194 Revision 2.0 For Research Use Only.
DNA Isolation Kit for Cells and Tissues
 DNA Isolation Kit for Cells and Tissues for 10 isolations of 00 mg each for tissue or 5 x 10 7 cultured cells Cat. No. 11 81 770 001 Principle Starting material Application Time required Results Benefits
DNA Isolation Kit for Cells and Tissues for 10 isolations of 00 mg each for tissue or 5 x 10 7 cultured cells Cat. No. 11 81 770 001 Principle Starting material Application Time required Results Benefits
Protein extraction from Tissues and Cultured Cells using Bioruptor Standard & Plus
 Protein extraction from Tissues and Cultured Cells using Bioruptor Standard & Plus Introduction Protein extraction from tissues and cultured cells is the first step for many biochemical and analytical
Protein extraction from Tissues and Cultured Cells using Bioruptor Standard & Plus Introduction Protein extraction from tissues and cultured cells is the first step for many biochemical and analytical
pcas-guide System Validation in Genome Editing
 pcas-guide System Validation in Genome Editing Tagging HSP60 with HA tag genome editing The latest tool in genome editing CRISPR/Cas9 allows for specific genome disruption and replacement in a flexible
pcas-guide System Validation in Genome Editing Tagging HSP60 with HA tag genome editing The latest tool in genome editing CRISPR/Cas9 allows for specific genome disruption and replacement in a flexible
ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit
 ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit Instructions for Use For the measuring in vivo protein sumoylation in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit Instructions for Use For the measuring in vivo protein sumoylation in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service
 KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service 1. Polyclonal Antibody Development Service KMS offering a variety of Polyclonal Antibody Services to fit your research and production needs. we develop polyclonal
KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service 1. Polyclonal Antibody Development Service KMS offering a variety of Polyclonal Antibody Services to fit your research and production needs. we develop polyclonal
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual
 Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34 + Progenitor Cell Care Manual
 Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34 + Progenitor Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0065.03 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34+ Progenitor Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human umbilical
Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34 + Progenitor Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0065.03 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34+ Progenitor Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human umbilical
Guidance. 2. Definitions. 1. Introduction
 Work with naked DNA or RNA (including oligonucleotides, sirna, mirna, sequences that code for highly biologically active molecules and full length viral genomes) Guidance 1. Introduction The following
Work with naked DNA or RNA (including oligonucleotides, sirna, mirna, sequences that code for highly biologically active molecules and full length viral genomes) Guidance 1. Introduction The following
CHAPTER 2 ANTIGEN/ANTIBODY INTERACTIONS
 CHAPTER 2 ANTIGEN/ANTIBODY INTERACTIONS See APPENDIX (1) THE PRECIPITIN CURVE; (2) LABELING OF ANTIBODIES The defining characteristic of HUMORAL immune responses (which distinguishes them from CELL-MEDIATED
CHAPTER 2 ANTIGEN/ANTIBODY INTERACTIONS See APPENDIX (1) THE PRECIPITIN CURVE; (2) LABELING OF ANTIBODIES The defining characteristic of HUMORAL immune responses (which distinguishes them from CELL-MEDIATED
Viruses. Viral components: Capsid. Chapter 10: Viruses. Viral components: Nucleic Acid. Viral components: Envelope
 Viruses Chapter 10: Viruses Lecture Exam #3 Wednesday, November 22 nd (This lecture WILL be on Exam #3) Dr. Amy Rogers Office Hours: MW 9-10 AM Too small to see with a light microscope Visible with electron
Viruses Chapter 10: Viruses Lecture Exam #3 Wednesday, November 22 nd (This lecture WILL be on Exam #3) Dr. Amy Rogers Office Hours: MW 9-10 AM Too small to see with a light microscope Visible with electron
ZR-96 DNA Sequencing Clean-up Kit Catalog Nos. D4052 & D4053
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZR-96 DNA Sequencing Clean-up Kit Catalog Nos. D4052 & D4053 Highlights Simple 10 Minute Bind, Wash, Elute Procedure Flexible 15-20 µl Elution Volumes Allow for Direct Loading of Samples
INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZR-96 DNA Sequencing Clean-up Kit Catalog Nos. D4052 & D4053 Highlights Simple 10 Minute Bind, Wash, Elute Procedure Flexible 15-20 µl Elution Volumes Allow for Direct Loading of Samples
Quick Guide to AlphaScreen SureFire Assay Optimization
 PPLITION NOT lpha Technology Quick uide to lphascreen Sureire ssay Optimization Introduction Screening kinase activities in cell-based assays offers advantages over the more traditional biochemical approach
PPLITION NOT lpha Technology Quick uide to lphascreen Sureire ssay Optimization Introduction Screening kinase activities in cell-based assays offers advantages over the more traditional biochemical approach
General Properties Protein Nature of Enzymes Folded Shape of Enzymes H-bonds complementary
 Proteins that function as biological catalysts are called enzymes. Enzymes speed up specific metabolic reactions. Low contamination, low temperature and fast metabolism are only possible with enzymes.
Proteins that function as biological catalysts are called enzymes. Enzymes speed up specific metabolic reactions. Low contamination, low temperature and fast metabolism are only possible with enzymes.
Human Free Testosterone(F-TESTO) ELISA Kit
 Human Free Testosterone(F-TESTO) ELISA Kit Catalog Number. MBS700040 For the quantitative determination of human free testosterone(f-testo) concentrations in serum, plasma. This package insert must be
Human Free Testosterone(F-TESTO) ELISA Kit Catalog Number. MBS700040 For the quantitative determination of human free testosterone(f-testo) concentrations in serum, plasma. This package insert must be
Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). This product is for research
ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). This product is for research
Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). This product is for research
ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). This product is for research
Biopharmaceutical Process Evaluated for Viral Clearance
 Authored by S. Steve Zhou, Ph.D. Microbac Laboratories, Inc., Microbiotest Division The purpose of Viral Clearance evaluation is to assess the capability of a manufacturing production process to inactivate
Authored by S. Steve Zhou, Ph.D. Microbac Laboratories, Inc., Microbiotest Division The purpose of Viral Clearance evaluation is to assess the capability of a manufacturing production process to inactivate
HiPer Ion Exchange Chromatography Teaching Kit
 HiPer Ion Exchange Chromatography Teaching Kit Product Code: HTC001 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 5-6 hours Storage Instructions: The kit is stable for
HiPer Ion Exchange Chromatography Teaching Kit Product Code: HTC001 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 5-6 hours Storage Instructions: The kit is stable for
The fastest spin-column based procedure for purifying up to 10 mg of ultra-pure endotoxin-free transfection-grade plasmid DNA.
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZymoPURE Plasmid Gigaprep Kit Catalog Nos. D4204 (Patent Pending) Highlights The fastest spin-column based procedure for purifying up to 10 mg of ultra-pure endotoxin-free transfection-grade
INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZymoPURE Plasmid Gigaprep Kit Catalog Nos. D4204 (Patent Pending) Highlights The fastest spin-column based procedure for purifying up to 10 mg of ultra-pure endotoxin-free transfection-grade
Lecture 1 MODULE 3 GENE EXPRESSION AND REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION. Professor Bharat Patel Office: Science 2, 2.36 Email: [email protected].
 Lecture 1 MODULE 3 GENE EXPRESSION AND REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION Professor Bharat Patel Office: Science 2, 2.36 Email: [email protected] What is Gene Expression & Gene Regulation? 1. Gene Expression
Lecture 1 MODULE 3 GENE EXPRESSION AND REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION Professor Bharat Patel Office: Science 2, 2.36 Email: [email protected] What is Gene Expression & Gene Regulation? 1. Gene Expression
ZR DNA Sequencing Clean-up Kit
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZR DNA Sequencing Clean-up Kit Catalog Nos. D40 & D4051 Highlights Simple 2 Minute Bind, Wash, Elute Procedure Flexible 6-20 µl Elution Volumes Allow for Direct Loading of Samples with
INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZR DNA Sequencing Clean-up Kit Catalog Nos. D40 & D4051 Highlights Simple 2 Minute Bind, Wash, Elute Procedure Flexible 6-20 µl Elution Volumes Allow for Direct Loading of Samples with
Taqman TCID50 for AAV Vector Infectious Titer Determination
 Page 1 of 8 Purpose: To determine the concentration of infectious particles in an AAV vector sample. This process involves serial dilution of the vector in a TCID50 format and endpoint determination through
Page 1 of 8 Purpose: To determine the concentration of infectious particles in an AAV vector sample. This process involves serial dilution of the vector in a TCID50 format and endpoint determination through
Frozen-EZ Yeast Transformation II Catalog No. T2001
 INSTRUCTIONS Frozen-EZ Yeast Transformation II Catalog No. T2001 Highlights High transformation efficiency that yields approximately 10 5-10 6 transformants per μg plasmid DNA (circular). Frozen storage
INSTRUCTIONS Frozen-EZ Yeast Transformation II Catalog No. T2001 Highlights High transformation efficiency that yields approximately 10 5-10 6 transformants per μg plasmid DNA (circular). Frozen storage
Guideline for Generation of Stable Cell Lines Technical Reference Guide
 BioResearch Guideline for Generation of Stable Cell Lines Technical Reference Guide 1. Background Stable, long-term expression of a gene of interest can be either achieved by eukaryotic vectors that harbor
BioResearch Guideline for Generation of Stable Cell Lines Technical Reference Guide 1. Background Stable, long-term expression of a gene of interest can be either achieved by eukaryotic vectors that harbor
LightSwitch Dual Assay System DA010 (100 assays)
 LightSwitch Dual Assay System DA010 (100 assays)! Description The LightSwitch Dual Assay System is used to normalize for variation between transfection replicates in cell lines that are particularly difficult
LightSwitch Dual Assay System DA010 (100 assays)! Description The LightSwitch Dual Assay System is used to normalize for variation between transfection replicates in cell lines that are particularly difficult
CHAPTER 6: RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY YEAR III PHARM.D DR. V. CHITRA
 CHAPTER 6: RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY YEAR III PHARM.D DR. V. CHITRA INTRODUCTION DNA : DNA is deoxyribose nucleic acid. It is made up of a base consisting of sugar, phosphate and one nitrogen base.the
CHAPTER 6: RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY YEAR III PHARM.D DR. V. CHITRA INTRODUCTION DNA : DNA is deoxyribose nucleic acid. It is made up of a base consisting of sugar, phosphate and one nitrogen base.the
