Prostate Cancer. Patient Information
|
|
|
- Stephanie Chandler
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prostate Cancer Patient Information 1
2 The Prostate & Prostate Cancer The prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive system, approximately the size and shape of a walnut. It is located directly below the bladder and surrounds the urethra. The prostate produces the seminal fluid, which transports semen during ejaculation. Sagittal plane of the male pelvis seminal vesicles rectum bladder prostate urethra Cancer is a disease that is characterised by uncontrolled growth and division of cells. In some cases, these cells may accumulate into a mass called a tumour. Tumours can be either benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous). During normal aging and in many men around the age of 45, the prostate starts to enlarge. This is generally a non-cancerous condition known as benign prostatic hyperplasia and is rarely life-threatening but can cause problems such as frequent urination or a weak urine stream. 2
3 However, in some cases tumours can be malignant, i.e. become invasive and destroy healthy tissues. Late onset symptoms which do not automatically indicate prostate cancer are a weak urinary stream, interrupted urination, pain or burning while urinating, blood in the urine or inability to urinate. Prostate cancer is the second most frequent cancer in men worldwide but can be treated very effectively when detected at an early stage. Prostate cancer often grows at a very slow pace and sometimes causes no symptoms for years. Early detection of prostate cancer is the key factor in initiating proper treatment that will result in cure of the disease. As long as the cancer is limited to the prostate gland, there is a good chance of eliminating it. Once it passes the border of the gland, it becomes more difficult to treat. Generally, it is recommended that men of a specified age should receive regular cancer prevention check-ups from a urologist. In the UK and in Spain, it is recommended that men 50 years or older may undergo annual screening should there be no positive history of prostate cancer. In France and Germany, annual checkups are recommended beginning with the age of 45. For screening recommendations in your specific country, please contact your physician. 3
4 Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer In general, various diagnostic tools are used in combination to achieve high diagnostic reliability. Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) PSA is a protein that is produced by the prostate. Its concentration in human blood is measured by the PSA test. While men normally have a relatively low level of PSA in their blood, an elevated PSA level indicates an abnormal situation in the prostate, but does not automatically mean that prostate cancer is present. It also may be the result of benign enlargement or other conditions. However, if the PSA level is elevated, further clinical evaluation should be performed. Digital Rectal Examination (DRE) When performing a DRE a urologist examines the prostate by inserting a lubricated and gloved finger inside the rectum and palpates the prostate through the rectal wall. Due to the close proximity of the rectum to the prostate, abnormalities of the gland can be felt. A DRE is very useful in detecting prostate cancer, but only if the tumour has a palpable size and location. Otherwise false negatives can be recorded. It is therefore recommended to conduct this examination in combination with a PSA test. Transrectal Ultrasound (TRUS) The prostate can be visualised on an ultrasound screen using a transrectal ultrasound probe inserted into the rectum. In this way, the physician obtains a precise picture of the gland. The image can then be examined. Biopsy and Gleason Score Small samples of prostate tissue are removed in biopsy form with a special needle. The tissue is examined microscopically and the result graded according to the Gleason pattern (ranging from 2 to 10). The score is a measure of the histologic difference between cancer cells and normal cells and describes how aggressive the tumour cells are. Biopsy is the only definitive confirmation of prostate cancer. 4
5 Classification of Prostate Cancer Based on the results of the examinations, tumours are classified into different stages. Staging is an assessment of the size and location of the cancer. The actual TNM staging (tumour- nodesmetastasis) is as follows: T1 Tumours are very small and cannot be detected by DRE or TRUS T2 Tumours are large enough to be detected by DRE T3/T4 Tumours have already expanded beyond the prostate N N specifies the number of affected lymph nodes (0-3) M M specifies the presence of metastases T1 and T2 tumours are designated as locally confined prostate carcinoma that can be classified as low-, intermediate- or highrisk tumours. bladder ureter seminal vesicle prostate urethra Prostate Cancer T1 Prostate Cancer T2 Prostate Cancer T3 Prostate Cancer T4 5
6 Treatment Options for locally confined Prostate Cancer Modern medicine offers various treatment methods that can be applied as monotherapy or in combination if neccessary. The appropriate treatment should be carefully selected, considering the stage of the disease, the patient s condition and the patient s and physician s concerns. Based on your examination results, your physician will discuss with you the appropriate and applicable treatment method. Active Surveillance Since prostate cancer often grows at a slow pace, physicians may not necessarily offer immediate treatment, instead the cancer is monitored at regular intervals. This treatment form may be preferable for low risk tumour patients as well as for elderly patients with relatively feeble health, in order to avoid surgical or hormonal treatment. If there are any changes in tumour characteristics, the physician is able to react instantly. Radical Prostatectomy The prostate gland, the seminal vesicles and the organ-specific lymph nodes are surgically removed (open, laparoscopic or robotic-assisted). Radical prostatectomy can be performed on low, intermediate and high risk prostate cancer and is an inpatient treatment. Hormone Treatment This non-surgical treatment method involves decelerating the growth of the prostate cancer by depriving the body of testosterone (the male sex hormone). It is not a curative procedure and is sometimes combined with percutaneous radiation therapy or brachytherapy. Percutaneous Radiation Therapy In radiation therapy, the cancer cells are exposed to high doses of radiation. Cancer cells are much more susceptible to radiation than healthy tissue. There are two main types of percutaneous radiation therapy available: 1. During External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) a so-called linear accelerator emits a high energy X-ray beam onto the targeted tumorous tissue. External beam radiation is delivered in daily fractions five days a week for approximately six to seven weeks which requires frequent visits to the hospital. 6
7 2. During Proton Beam Therapy accelerated protons enter the body and deposit the prescribed dose inside the tumour. This treatment method requires more than 20 fractions. Brachytherapy Brachytherapy applies radioactive sources directly to or into the tumour, allowing a high dose to the tumour while sparing the surrounding healthy tissue. Brachytherapy, which is also called radiation from the inside, can be performed in different ways. 1. During high dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy, which is also known as afterloading, tiny radioactive sources containing iridium-192 or cobalt-60 are temporarily placed into the prostate via transperineally inserted needles. Usually two sessions are required which are then followed by EBRT (3 4 weeks). 2. Performing low dose rate (LDR) brachytherapy, tiny metal pellets containing radioactive iodine-125 or palladium-103 are permanently implanted into the prostate via transperineally inserted needles. LDR brachytherapy is also called Prostate Seed Implantation or Permanent Brachytherapy Treatment effectiveness and side effects There is no consensus on what is the best way to treat prostate cancer, as many approaches have comparable outcomes. All treatment options have different hospitalisation and recovery times and come along with side effects, which in quantity and grade depend on the chosen treatment option, the patient s pre-treatment status and his individual reaction on the treatment. Prostate cancer treatment side effects may comprise: erectile dysfunction, genitourinary bothers like urge, incontinence, urethritis, dysuria or urinary retention, as well as fatigue and gastrointestinal irritations (proctitis, diarrhoea, rectal bleeding). There is evidence that LDR brachytherapy has a better side effect profile than other treatment options for localised prostate cancer. Anyway, the decision for one of the treatment options is highly individual and should be taken in close cooperation with your physician. 7
8 LDR-Brachytherapy Prostate Seed Implantation Permanent Brachytherapy Seed Implantation Permanent brachytherapy is the most conservative treatment method for early stage prostate cancer. Its international popularity has continuously increased since the early 1990s and it is now generally accepted as a state-of-the art therapy. Prostate seed implantation is an effective and well-tolerated method to cure prostate cancer. Its cure rates are comparable to the ones of EBRT and prostatectomy for early stage prostate cancer In this treatment, small radioactive iodine-125 sources, so called seeds, are placed inside the prostate. Each seed has a length of 4.5 mm and a diameter of 0.8 mm and emits a specific low dose of radiation to its surrounding tissue inside the prostate. By placing the seeds homogeneously throughout the organ, the prostate is covered with the designated dose required to destroy the cancerous cells. Since irradiation is mainly localised around the radioactive source, neighbouring tissues are spared unnecessary damage. Patient Selection Criteria Prostate seed implantation is especially suitable for patients with early stage prostate cancer. The cancerous tissue should be limited to the prostate gland, with the following diagnostic features: Gleason score < 7 PSA < 10 Staging T2a or lower, N = 0, M = 0 Prostate volume < 50 cm 3 Urine flow test: maximum flow rate >15 ml/s The individual indication may vary from the above values, due to other characteristics of the patient s condition. 8
9 Advantages of Permanent Brachytherapy Compared to other treatment methods, prostate seed implantation may offer the following advantages: Quicker physical recovery after the medical intervention, including mobility the day after implantation and fast return to daily activities Shorter hospital stay (often performed as outpatient treatment) Minimal treatment time (only one session) duration of seed implantation: minutes Better preservation of urinary continence, erectile and rectal function in comparison to other treatment options, resulting in enhanced quality of life Sagittal view of the male pelvis Implantation of seeds with LDR brachytherapy Grid Guide for the needles Stylet Used to push the seeds Needle Transport channel for the seeds Seeds Cure cancer by emitting radiation Transrectal ultrasound Visualisation of the prostate 9
10 Prostate Seed Implantation Procedure The procedure is as follows: The patient is anaesthetised and an ultrasound probe is inserted into the rectum. A treatment planning system calculates the number of seeds as well as their exact location based on the ultrasound prostate image. It guarantees an optimal dose distribution, with minimal exposure of surrounding tissue and organs at risk to radiation. The physician inserts the implantation needles into the prostate and implants the seeds. The optimal placement is continuously monitored by ultrasound and fluoroscopy. The complete procedure takes approximately minutes. After the treatment is completed, the patient may leave the clinic on the same day and resume his normal activities a few days later. As Iodine-125 has a short half-life, the seeds emit radiation only for a certain period of time. Since the rate of emitted energy is low, there is limited risk of irradiation outside of the body. Safety Measures after Prostate Seed Implants Patients do not need to worry about the radiation from the implanted seeds. By the time it reaches the outside of the body, the amount of radiation is so small that there is no danger to surrounding people. Nevertheless, up to 8 weeks after the implantation, extended close physical contact with the patient should be avoided. Pregnant women and children under 18 years should prevent direct physical contact with the patient during this period, however a short hug or a salutation is harmless. During two months following the implantation, it is recommended to use a condom for intercourse. After one year, almost 100% of the radiation has been delivered. Two years after implantation, no special safety measures need to be taken anymore, i.e. in case a removal of the prostate should be required. For any question or concern, please contact your physician. 10
11 An Iodine-125 seed has a length of 4.5 mm and a diameter of 0.8 mm Fluoroscopic image after successful seed implantation A treatment planning system calculates the number of seeds as well as their exact location based on the ultrasound prostate image 11
12 P13D101/Rev. 03/ This information was provided by: Eckert & Ziegler BEBIG s.a. Zone Industrielle C 7180 Seneffe Belgium Telephone Telefax [email protected] Eckert & Ziegler BEBIG GmbH Robert-Rössle-Str Berlin Germany Telephone Telefax
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment
 A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
PATIENT GUIDE. Localized Prostate Cancer
 PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment. Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse. Prostate Cancer. An overview of. Treatment. Prolapse. Information and Answers
 Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER
 An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for Care Providers
 All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
These rare variants often act aggressively and may respond differently to therapy than the more common prostate adenocarcinoma.
 Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
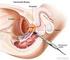 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
PROSTATE CANCER. Get the facts, know your options. Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology
 PROSTATE CANCER Get the facts, know your options Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology i What is the Prostate? Unfortunately, you have prostate
PROSTATE CANCER Get the facts, know your options Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology i What is the Prostate? Unfortunately, you have prostate
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide for African Americans
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
CMScript. Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014
 Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you
 Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE
 HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
Prostate Cancer. There is no known association with an enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
 Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Treating Prostate Cancer
 Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
BRACHYTHERAPY OR RADIOACTIVE SEED IMPLANTATION CANCER OF THE PROSTATE
 BRACHYTHERAPY OR RADIOACTIVE SEED IMPLANTATION CANCER OF THE PROSTATE Prostate cancer, like other cancers, is a disease of the body's cells. Normal cells reproduce themselves by dividing--facilitating
BRACHYTHERAPY OR RADIOACTIVE SEED IMPLANTATION CANCER OF THE PROSTATE Prostate cancer, like other cancers, is a disease of the body's cells. Normal cells reproduce themselves by dividing--facilitating
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System
 FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
Prostate Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER
 DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER Determining the presence of prostate cancer generally involves a series of tests and exams. Before starting the testing process, the physician will ask questions about the
DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER Determining the presence of prostate cancer generally involves a series of tests and exams. Before starting the testing process, the physician will ask questions about the
CONTENTS: WHAT S IN THIS BOOKLET
 Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment options and future directions
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment options and future directions David Weksberg, M.D., Ph.D. PinnacleHealth Cancer Institute September 12, 2015 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment options and future directions David Weksberg, M.D., Ph.D. PinnacleHealth Cancer Institute September 12, 2015 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment
Understanding Prostate Cancer. The Urology Group Guide for Newly Diagnosed Patients. Advanced Care. Improving Lives.
 Understanding Prostate Cancer The Urology Group Guide for Newly Diagnosed Patients Advanced Care. Improving Lives. UNDERSTANDING PROSTATE CANCER The Urology Group has created this publication to provide
Understanding Prostate Cancer The Urology Group Guide for Newly Diagnosed Patients Advanced Care. Improving Lives. UNDERSTANDING PROSTATE CANCER The Urology Group has created this publication to provide
LIvING WITH Prostate Cancer
 Living with Prostate Cancer A Common Cancer in Men If you ve been diagnosed with prostate cancer, it s normal to be concerned about your future. It may help you to know that this disease can often be cured
Living with Prostate Cancer A Common Cancer in Men If you ve been diagnosed with prostate cancer, it s normal to be concerned about your future. It may help you to know that this disease can often be cured
Prostate Cancer Guide. A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
For further information on screening and early detection of prostate cancer, see the Section entitled Screening for Prostate Cancer.
 Prostate Cancer For many older men, prostate cancer may be present but never cause symptoms or problems and many men will die with their prostate cancer rather than of their prostate cancer. Yet it remains
Prostate Cancer For many older men, prostate cancer may be present but never cause symptoms or problems and many men will die with their prostate cancer rather than of their prostate cancer. Yet it remains
to Know About Your Partner s
 What You Need to Know About Your Partner s Prostate Cancer. A Guide for Wives, Partners, and the Men They Love. Providing Support for Your Partner Prostate cancer can be a physical and emotional challenge
What You Need to Know About Your Partner s Prostate Cancer. A Guide for Wives, Partners, and the Men They Love. Providing Support for Your Partner Prostate cancer can be a physical and emotional challenge
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER?
 PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
A918: Prostate: adenocarcinoma
 A918: Prostate: adenocarcinoma General facts of prostate cancer The prostate is about the size of a walnut. It is just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The tube that carries urine (the urethra)
A918: Prostate: adenocarcinoma General facts of prostate cancer The prostate is about the size of a walnut. It is just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The tube that carries urine (the urethra)
Talking about Prostate Cancer
 Talking about Prostate Cancer Talking about Prostate Cancer If I can avoid going to a doctor, I will but not when we re talking about prostate cancer. Why take chances with a condition that might be serious?
Talking about Prostate Cancer Talking about Prostate Cancer If I can avoid going to a doctor, I will but not when we re talking about prostate cancer. Why take chances with a condition that might be serious?
PROSTATE CANCER. Diagnosis and Treatment
 Diagnosis and Treatment Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Patient and Coach Information... 1 About Your Prostate... 1 What You Should Know About Prostate Cancer... 2 Screening and Diagnosis... 2 Digital
Diagnosis and Treatment Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Patient and Coach Information... 1 About Your Prostate... 1 What You Should Know About Prostate Cancer... 2 Screening and Diagnosis... 2 Digital
Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer: Understanding Your Risk
 Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer: Understanding Your Risk When the urologist calls with the life-changing news that your prostate biopsy is positive for prostate cancer, an office appointment is made to
Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer: Understanding Your Risk When the urologist calls with the life-changing news that your prostate biopsy is positive for prostate cancer, an office appointment is made to
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test?
 1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
The PSA Test for Prostate Cancer Screening:
 For more information, please contact your local VA Medical Center or Health Clinic. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration Patient Care Services Health Promotion and Disease
For more information, please contact your local VA Medical Center or Health Clinic. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration Patient Care Services Health Promotion and Disease
Prostate Cancer & Its Treatment
 Your Health Matters Prostate Cancer & Its Treatment By the UCSF Medical Center Prostate Cancer Advocates Greetings! From our personal experience in dealing with our own prostate cancers, we UCSF Patient
Your Health Matters Prostate Cancer & Its Treatment By the UCSF Medical Center Prostate Cancer Advocates Greetings! From our personal experience in dealing with our own prostate cancers, we UCSF Patient
Prostate cancer screening. It s YOUR decision!
 Prostate cancer screening It s YOUR decision! For many years now, a test has been available to screen for. The test is called the prostate-specific antigen blood test (or PSA test). It is used in combination
Prostate cancer screening It s YOUR decision! For many years now, a test has been available to screen for. The test is called the prostate-specific antigen blood test (or PSA test). It is used in combination
Screening for Prostate Cancer
 Cancer Expert Working Group on Cancer Prevention and Screening Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for men and their families 1 What is the prostate? 2 What is prostate cancer? prostate The prostate
Cancer Expert Working Group on Cancer Prevention and Screening Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for men and their families 1 What is the prostate? 2 What is prostate cancer? prostate The prostate
Advice to patients about the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test: frequently-asked questions
 Advice to patients about the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test: frequently-asked questions What is the PSA blood test? If you want more information before deciding to have this test, it is important
Advice to patients about the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test: frequently-asked questions What is the PSA blood test? If you want more information before deciding to have this test, it is important
Prostate Cancer Screening
 Prostate Cancer Screening The American Cancer Society and Congregational Health Ministry Team June Module To access this module via the Web, visit www.cancer.org and type in congregational health ministry
Prostate Cancer Screening The American Cancer Society and Congregational Health Ministry Team June Module To access this module via the Web, visit www.cancer.org and type in congregational health ministry
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER?
 PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
Prevention Series. Prostate Cancer. How to reduce your risk. Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 www.cancer.ca
 Prevention Series Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 www.cancer.ca Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in Canadian
Prevention Series Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 www.cancer.ca Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in Canadian
Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men
 Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men 2 Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men About this booklet This booklet is for men who have recently been diagnosed with prostate cancer. It is
Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men 2 Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men About this booklet This booklet is for men who have recently been diagnosed with prostate cancer. It is
Prostate Cancer In-Depth
 Prostate Cancer In-Depth Introduction Prostate cancer is the most common visceral malignancy among American men. In the year 2003, there are expected to be 220,000 new cases and nearly 29,000 deaths in
Prostate Cancer In-Depth Introduction Prostate cancer is the most common visceral malignancy among American men. In the year 2003, there are expected to be 220,000 new cases and nearly 29,000 deaths in
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing
 Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Locally advanced prostate cancer
 Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Locally advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is locally advanced prostate cancer? How is locally advanced prostate cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Locally advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is locally advanced prostate cancer? How is locally advanced prostate cancer diagnosed?
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2. Patient Information. Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate
 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
Oncology Annual Report: Prostate Cancer 2005 Update By: John Konefal, MD, Radiation Oncology
 Oncology Annual Report: Prostate Cancer 25 Update By: John Konefal, MD, Radiation Oncology Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, with 232,9 new cases projected to be diagnosed in the U.S. in
Oncology Annual Report: Prostate Cancer 25 Update By: John Konefal, MD, Radiation Oncology Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, with 232,9 new cases projected to be diagnosed in the U.S. in
male sexual dysfunction
 male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
Prostate Cancer Treatment: What s Best for You?
 Prostate Cancer Treatment: What s Best for You? Prostate Cancer: Radiation Therapy Approaches I. Choices There is really a variety of options in prostate cancer management overall and in radiation therapy.
Prostate Cancer Treatment: What s Best for You? Prostate Cancer: Radiation Therapy Approaches I. Choices There is really a variety of options in prostate cancer management overall and in radiation therapy.
Understanding the PSA test. A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer
 Understanding the PSA test A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer Introduction This booklet is for men who want to know more about having a blood test, called a PSA test, that can help diagnose
Understanding the PSA test A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer Introduction This booklet is for men who want to know more about having a blood test, called a PSA test, that can help diagnose
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse
 7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
Clinical Trials and Radiation Treatment. Gerard Morton Odette Cancer Centre Sunnybrook Research Institute University of Toronto
 Clinical Trials and Radiation Treatment Gerard Morton Odette Cancer Centre Sunnybrook Research Institute University of Toronto What I will cover.. A little about radiation treatment The clinical trials
Clinical Trials and Radiation Treatment Gerard Morton Odette Cancer Centre Sunnybrook Research Institute University of Toronto What I will cover.. A little about radiation treatment The clinical trials
PROSTATE CANCER. Normal-risk men: No family history of prostate cancer No history of prior screening Not African-American
 PROSTATE CANCER 1. Guidelines for Screening Risk Factors Normal-risk men: No family history of prostate cancer No history of prior screening Not African-American High-risk men: Family history of prostate
PROSTATE CANCER 1. Guidelines for Screening Risk Factors Normal-risk men: No family history of prostate cancer No history of prior screening Not African-American High-risk men: Family history of prostate
da Vinci Prostatectomy Information Guide (Robotically-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy)
 da Vinci Prostatectomy Information Guide (Robotically-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy) Prostate Cancer Overview Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the
da Vinci Prostatectomy Information Guide (Robotically-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy) Prostate Cancer Overview Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the
Analysis of Prostate Cancer at Easter Connecticut Health Network Using Cancer Registry Data
 The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
Localised prostate cancer
 Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Localised prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is localised prostate cancer? How is localised prostate cancer diagnosed? What do my
Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Localised prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is localised prostate cancer? How is localised prostate cancer diagnosed? What do my
Dynamic prostate brachytherapy
 Dynamic prostate brachytherapy a single visit treatment for prostate cancer This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having brachytherapy to treat your prostate cancer. It explains the benefits,
Dynamic prostate brachytherapy a single visit treatment for prostate cancer This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having brachytherapy to treat your prostate cancer. It explains the benefits,
After Diagnosis: Prostate Cancer. Understanding Your Treatment Options
 After Diagnosis: Prostate Cancer Understanding Your Treatment Options What s inside How will this booklet help me?... 3 What is the prostate?... 4 What is prostate cancer?... 4 Who gets prostate cancer?...
After Diagnosis: Prostate Cancer Understanding Your Treatment Options What s inside How will this booklet help me?... 3 What is the prostate?... 4 What is prostate cancer?... 4 Who gets prostate cancer?...
Radioactive Seed Implants for Prostate Cancer information for patients and their families
 UROLOGICAL CANCER Radioactive Seed Implants for Prostate Cancer information for patients and their families The Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center 660 South Euclid Avenue, Box 8100 St. Louis, MO 63110-1093
UROLOGICAL CANCER Radioactive Seed Implants for Prostate Cancer information for patients and their families The Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center 660 South Euclid Avenue, Box 8100 St. Louis, MO 63110-1093
Prostate cancer is the most common cause of death from cancer in men over age 75. Prostate cancer is rarely found in men younger than 40.
 A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
There are many different types of cancer and sometimes cancer is diagnosed when in fact you are not suffering from the disease at all.
 About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Your Questions, Our Answers.
 Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Your Questions, Our Answers. When you re looking for the right treatment for your prostate cancer, nothing s more important than accurate information. Read on, and learn
Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Your Questions, Our Answers. When you re looking for the right treatment for your prostate cancer, nothing s more important than accurate information. Read on, and learn
Testing for Prostate Cancer. Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me?
 Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
How To Know If You Should Get A Brachytherapy Or Radioactive Seed Implantation
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: BRACHYTHERAPY OR PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: BRACHYTHERAPY OR PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy
Possible Side Effects of Radiation Therapy on the Prostate Gland
 Possible Side Effects of Radiation Therapy on the Prostate Gland Information compiled by Daniel J. Faber, Coordinator of the Warriors+one, a Breakout Group of the Prostate Cancer Canada Network- Ottawa,
Possible Side Effects of Radiation Therapy on the Prostate Gland Information compiled by Daniel J. Faber, Coordinator of the Warriors+one, a Breakout Group of the Prostate Cancer Canada Network- Ottawa,
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
 Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
How prostate cancer is diagnosed
 How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
Prostate Cancer. Treatments as unique as you are
 Prostate Cancer Treatments as unique as you are UCLA Prostate Cancer Program Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men. The UCLA Prostate Cancer Program brings together the elements essential
Prostate Cancer Treatments as unique as you are UCLA Prostate Cancer Program Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men. The UCLA Prostate Cancer Program brings together the elements essential
Basic Radiation Therapy Terms
 Basic Radiation Therapy Terms accelerated radiation: radiation schedule in which the total dose is given over a shorter period of time. (Compare to hyperfractionated radiation.) adjuvant therapy (add-joo-vunt):
Basic Radiation Therapy Terms accelerated radiation: radiation schedule in which the total dose is given over a shorter period of time. (Compare to hyperfractionated radiation.) adjuvant therapy (add-joo-vunt):
Prostate cancer. A guide for men who ve just been diagnosed
 Prostate cancer A guide for men who ve just been diagnosed 2 Prostate cancer A guide for men who ve just been diagnosed About this booklet This booklet is for men who ve recently been diagnosed with prostate
Prostate cancer A guide for men who ve just been diagnosed 2 Prostate cancer A guide for men who ve just been diagnosed About this booklet This booklet is for men who ve recently been diagnosed with prostate
Understanding brachytherapy
 Understanding brachytherapy Brachytherapy Cancer Treatment Legacy Cancer Institute Your health care provider has requested that you receive a type of radiation treatment called brachytherapy as part of
Understanding brachytherapy Brachytherapy Cancer Treatment Legacy Cancer Institute Your health care provider has requested that you receive a type of radiation treatment called brachytherapy as part of
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems
 Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Prostate Cancer. What is cancer?
 What is cancer? Prostate Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide into new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person s life, normal
What is cancer? Prostate Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide into new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person s life, normal
