Prostate cancer screening. It s YOUR decision!
|
|
|
- Owen Casey
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prostate cancer screening It s YOUR decision!
2 For many years now, a test has been available to screen for. The test is called the prostate-specific antigen blood test (or PSA test). It is used in combination with a digital rectal examination. However, whether or not these tests are actually useful for screening purposes that is, for detecting in men who do not have any signs or symptoms of cancer is still controversial. Given the uncertainties surrounding the use of this test, some men may choose to have the test, while others may not. The Collège des médecins du Québec recommends that doctors discuss the pros and cons of PSA testing combined with a digital rectal exam with patients between 55 and 70 years of age who have a life expectancy of 10 years or more and make sure they clearly understand the issues before making a decision about whether or not to undergo screening. To provide an update on the topic, the Collège des médecins du Québec has prepared this pamphlet in collaboration with the Institut national d excellence en santé et en services sociaux (INESSS) du Québec. The content of this pamphlet is based on the recommendations of a group of experts and on discussions with representatives of the public. The purpose of this leaflet is to provide you with the information you need to discuss screening with your doctor and to help you make your own decision. SCREENING: A DECISION YOU HAVE TO MAKE Prostate cancer is the most common type of cancer found in men. However, for most men who are diagnosed with, usually at an advanced age, it has little effect on duration or quality of life. Unfortunately, for some men, the disease will have serious consequences and they will develop metastases and die. We would like to be able to identify and treat all men who might develop metastases and die from this cancer as quickly as possible and not bother with all the rest. Unfortunately, this isn t possible. The PSA test combined with a digital rectal exam, which is the most accurate method of screening, has advantages, but also limitations and disadvantages. The decision about whether or not to undergo screening depends on how important each of these advantages, limitations and disadvantages is to you. IMPORTANT! If you are worried about changes in your urination habits (difficulty urinating, more frequent urination), this is not screening; talk to your doctor about it. 2
3 KNOW THE PROS AND CONS OF PROSTATE CANCER SCREENING The table below is a summary of what might happen depending on whether or not a man receives screening. In the left-hand column, imagine 100 men who start to have annual screening at age 55, who do so every year until age 70 and who are followed until the end of their life. For comparison, in the right-hand column, imagine another 100 men of the same age who do not have screening and who are also followed until the end of their life. Look carefully at the numbers. They are the most optimistic screening outcomes based on the results of a large study conducted in Europe. By optimistic, we mean the outcomes most in favour of screening. They give a clear picture of the pros and cons of screening. 100 men who 100 men who do not receive screening receive screening Prostate cancer diagnosis 18 are diagnosed with ; 15 as a result of screening and 3 because they developed symptoms, either between screening tests or after the age of are not diagnosed with Prostate cancer metastases 3 develop metastases 4 develop metastases 97 do not develop metastases Deaths from 11 are diagnosed with after developing symptoms (most after the age of 70) 89 are not diagnosed with 96 do not develop metastases THE PROS Being reassured that you don t have You can be reassured that you don t have, which could have serious consequences for your health. The table shows that when cancer is not detected after screening in 100 men who are screened regularly, only 3 are diagnosed with between screening tests or after 70 years of age. But it isn t 0! Sometimes screening does not detect serious cancers. Furthermore, you should know that out of 100 men who are not screened, a minority (11) will be diagnosed with in their lifetime. Not having metastases and not dying of We can see from the table that screening means more s are detected (18 instead of 11). Cancers diagnosed by screening are, on average, detected at an earlier stage than without screening, and treating them at this stage could prevent the spread of metastases and death from. As we can see from the table, according to the most optimistic data, out of 100 men between 55 and 70 years of age who have screening, an average of 1 man will not develop metastases (3 out of 100 will develop metastases compared with 4 out of 100) and 1 will not die from prostate cancer because he received screening (2 out of 100 will die of compared with 3 out of 100). It is estimated that out of the 100 men who have screening, the man who does not die of because he received screening will live an average of 8 years longer than if he had not received screening. However, we don t know if screening prolongs life overall, because most men die of causes other than. 2 die of 16 who are diagnosed 6 would never have known they had prostate cancer without screening (overdiagnosis) 9 would have died of, whether they received screening or not 1 does not die of prostate cancer because he received screening 82 who were not diagnosed 3 die of 8 who are diagnosed 89 who were not diagnosed Screening may be of greater benefit to men who have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer (men whose father or brother had cancer before the age of 65 and men of African American descent) and of less benefit to those who have a lower risk. 3
4 THE CONS Being worried that you might have cancer when you don t If either of the tests (PSA or rectal exam) is abnormal, a third procedure must be performed to confirm whether or not is present: a biopsy. During this test, a needle is inserted into the prostate. You might be worried about having cancer before you have the biopsy. Fortunately, most men who receive a positive screening result do not have. It s a false alarm. In most cases, their prostate is simply enlarged due to age, which is called benign prostatic hypertrophy. Whether or not cancer is detected, all men who have a biopsy may develop complications from this procedure, including pain, fever, temporary urinary difficulties and blood in their semen or urine. Approximately 33% of men believe they developed a moderate to severe complication as a result of the biopsy and up to 3 or 4% will require hospitalization for a complication. Being diagnosed with cancer and having unnecessary treatments We can see from the table that out of the 100 men who receive screening, 18 will be diagnosed with prostate cancer. As we saw earlier, only 1 man will live a longer life and die of a cause other than as a result of having screening. Unfortunately, it s impossible to know which of the men with detected by screening will be that 1. So it could be said that the other 17 men were needlessly diagnosed: 2 die of anyway and 15 die of, irrespective of whether or not they had their cancer detected by a screening test. All men who have and receive treatment feel they owe their survival to screening. It is natural to feel this way, and difficult to think otherwise. But, for the vast majority, screening really only means that they learn that they have on average around 10 years earlier than if they had not had screening, without changing their fate. Furthermore, as the table shows, 6 of these men would never have known that they had prostate cancer in their lifetime if they hadn t had screening. These men are part of what is called overdiagnosis. Overdiagnosis, and the overtreatment it can lead to, are the main disadvantages of screening. Men who are thinking about having screening must understand that when is detected, it s impossible to know if it is a case of overdiagnosis or not. Most men with screening-detected will be treated for it and may develop complications from treatment. Radical prostatectomy, a surgical procedure to remove all of the prostate, is the most common treatment. In men who undergo surgery, around 10 to 20% experience urinary incontinence, while 40 to 50% are unable to get an erection (impotence). These complications are less frequent with radiation therapy, local treatment with radioactive rays that destroy cancer cells, but radiation can cause inflammation of the rectum and bladder. Note that to reduce complications from treatments, doctors are increasingly recommending active surveillance of lowgrade cancers (cancers with a low risk of progressing). This approach involves monitoring the progress of the disease very closely by doing blood tests and prostate biopsies and providing treatment only if the cancer progresses. 4
5 WEIGHING THE PROS AND CONS Deciding whether or not to have screening can be difficult. This is normal. It goes without saying that all men would like to have the advantages of screening without the disadvantages. Unfortunately, it doesn t work that way. If you decide to have screening, you also have to accept that there may be disadvantages, some of which can have harmful health effects, and that screening may be of no benefit at all to you. CONCLUSION There is no right or wrong decision when it comes to screening, only the decision that is best for you. Your doctor is the best trained person to answer all your questions and help you make the decision that is right for you. Don t hesitate to talk to him/her about it. So, before deciding, think about what is most important to you. Read the statements below and see which ones best match what is most important to you. I might consider having screening because: I m worried I might have and would like to know if I do as quickly as possible. I want to be reassured as much as possible that I don t have prostate cancer. side effects of a prostate biopsy if I need to have one. I understand that screening won t necessarily prolong my life, but I think it s more important to do everything I can to reduce the risk of dying of. side effects of treatment or to live with the knowledge that I have cancer. I m willing to accept that the cancer detected by screening would never have caused problems during my life if it hadn t been found. I might consider not having screening because: I m not worried I might have and my chances of having are low. I don t think the screening tests we have are reliable enough. I don t want to take the risk of having side effects from a prostate biopsy. possibility that screening could lower my risk of dying from prostate cancer and to give up this chance if I don t have screening. I don t want to take the risk of having side effects from treatment or live with the knowledge that I have cancer. I m worried my health might get worse if is found without there being any guarantee that I would live longer. TO FIND OUT MORE, visit the Collège des médecins du Québec s Web site at Collège des médecins du Québec September
The PSA Test for Prostate Cancer Screening:
 For more information, please contact your local VA Medical Center or Health Clinic. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration Patient Care Services Health Promotion and Disease
For more information, please contact your local VA Medical Center or Health Clinic. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration Patient Care Services Health Promotion and Disease
Testing for Prostate Cancer. Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me?
 Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Advice to patients about the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test: frequently-asked questions
 Advice to patients about the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test: frequently-asked questions What is the PSA blood test? If you want more information before deciding to have this test, it is important
Advice to patients about the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test: frequently-asked questions What is the PSA blood test? If you want more information before deciding to have this test, it is important
Testing for Prostate Cancer
 Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide for African Americans
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER?
 PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
Talking about Prostate Cancer
 Talking about Prostate Cancer Talking about Prostate Cancer If I can avoid going to a doctor, I will but not when we re talking about prostate cancer. Why take chances with a condition that might be serious?
Talking about Prostate Cancer Talking about Prostate Cancer If I can avoid going to a doctor, I will but not when we re talking about prostate cancer. Why take chances with a condition that might be serious?
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test?
 1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
PSA Testing for Prostate Cancer An information sheet for men considering a PSA Test
 PSA Testing for Prostate Cancer An information sheet for men considering a PSA Test What is the aim of this leaflet? Prostate cancer is a serious condition. The PSA test, which can give an early indication
PSA Testing for Prostate Cancer An information sheet for men considering a PSA Test What is the aim of this leaflet? Prostate cancer is a serious condition. The PSA test, which can give an early indication
PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for Care Providers
 All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
DECISION AID TOOL PROSTATE CANCER SCREENING WITH PSA TESTING
 DECISION AID TOOL PROSTATE CANCER SCREENING WITH PSA TESTING This booklet is what is often called a decision aid. The goals of a decision aid are to help people better understand their medical choices
DECISION AID TOOL PROSTATE CANCER SCREENING WITH PSA TESTING This booklet is what is often called a decision aid. The goals of a decision aid are to help people better understand their medical choices
Screening for Prostate Cancer
 Cancer Expert Working Group on Cancer Prevention and Screening Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for men and their families 1 What is the prostate? 2 What is prostate cancer? prostate The prostate
Cancer Expert Working Group on Cancer Prevention and Screening Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for men and their families 1 What is the prostate? 2 What is prostate cancer? prostate The prostate
Questions to ask my doctor: About prostate cancer
 Questions to ask my doctor: About prostate cancer Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be scary and stressful. You probably have a lot of questions and concerns. Learning about the disease, how it
Questions to ask my doctor: About prostate cancer Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be scary and stressful. You probably have a lot of questions and concerns. Learning about the disease, how it
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE
 HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
Prostate Cancer Screening
 Prostate Cancer Screening The American Cancer Society and Congregational Health Ministry Team June Module To access this module via the Web, visit www.cancer.org and type in congregational health ministry
Prostate Cancer Screening The American Cancer Society and Congregational Health Ministry Team June Module To access this module via the Web, visit www.cancer.org and type in congregational health ministry
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
Oncology Annual Report: Prostate Cancer 2005 Update By: John Konefal, MD, Radiation Oncology
 Oncology Annual Report: Prostate Cancer 25 Update By: John Konefal, MD, Radiation Oncology Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, with 232,9 new cases projected to be diagnosed in the U.S. in
Oncology Annual Report: Prostate Cancer 25 Update By: John Konefal, MD, Radiation Oncology Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, with 232,9 new cases projected to be diagnosed in the U.S. in
CONTENTS: WHAT S IN THIS BOOKLET
 Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment. Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse. Prostate Cancer. An overview of. Treatment. Prolapse. Information and Answers
 Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
Screening for Prostate Cancer
 Screening for Prostate Cancer It is now clear that screening for Prostate Cancer discovers the disease at an earlier and more curable stage. It is not yet clear whether this translates into reduced mortality
Screening for Prostate Cancer It is now clear that screening for Prostate Cancer discovers the disease at an earlier and more curable stage. It is not yet clear whether this translates into reduced mortality
Questions to Ask My Doctor About Prostate Cancer
 Questions to Ask My Doctor Being told you have prostate cancer can be scary and stressful. You probably have a lot of questions and concerns. Learning about the disease, how it s treated, and how this
Questions to Ask My Doctor Being told you have prostate cancer can be scary and stressful. You probably have a lot of questions and concerns. Learning about the disease, how it s treated, and how this
Cancer in Primary Care: Prostate Cancer Screening. How and How often? Should we and in which patients?
 Cancer in Primary Care: Prostate Cancer Screening How and How often? Should we and in which patients? PLCO trial (Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian) Results In the screening group, rates of compliance
Cancer in Primary Care: Prostate Cancer Screening How and How often? Should we and in which patients? PLCO trial (Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian) Results In the screening group, rates of compliance
PATIENT GUIDE. Localized Prostate Cancer
 PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
CMScript. Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014
 Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
PROSTATE CANCER. Normal-risk men: No family history of prostate cancer No history of prior screening Not African-American
 PROSTATE CANCER 1. Guidelines for Screening Risk Factors Normal-risk men: No family history of prostate cancer No history of prior screening Not African-American High-risk men: Family history of prostate
PROSTATE CANCER 1. Guidelines for Screening Risk Factors Normal-risk men: No family history of prostate cancer No history of prior screening Not African-American High-risk men: Family history of prostate
How prostate cancer is diagnosed
 How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System
 FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate
 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek
Prostate Cancer. There is no known association with an enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
 Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
PSA screening in asymptomatic men the debate continues www.bpac.org.nz keyword: psa
 PSA screening in asymptomatic men the debate continues www.bpac.org.nz keyword: psa Key messages: PSA is present in the benign and malignant prostate There is currently no national screening programme
PSA screening in asymptomatic men the debate continues www.bpac.org.nz keyword: psa Key messages: PSA is present in the benign and malignant prostate There is currently no national screening programme
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER
 An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
Prevention Series. Prostate Cancer. How to reduce your risk. Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 www.cancer.ca
 Prevention Series Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 www.cancer.ca Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in Canadian
Prevention Series Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 www.cancer.ca Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in Canadian
Prostate cancer is the most common cause of death from cancer in men over age 75. Prostate cancer is rarely found in men younger than 40.
 A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
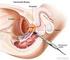 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
to Know About Your Partner s
 What You Need to Know About Your Partner s Prostate Cancer. A Guide for Wives, Partners, and the Men They Love. Providing Support for Your Partner Prostate cancer can be a physical and emotional challenge
What You Need to Know About Your Partner s Prostate Cancer. A Guide for Wives, Partners, and the Men They Love. Providing Support for Your Partner Prostate cancer can be a physical and emotional challenge
Treating Prostate Cancer
 Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment
 A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
BRCA1 and BRCA2 for men
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Regional Genetic Department BRCA1 and BRCA2 for men Information for men from families with a known alteration in the BRCA1/2 gene Introduction BRCA1 and BRCA2
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Regional Genetic Department BRCA1 and BRCA2 for men Information for men from families with a known alteration in the BRCA1/2 gene Introduction BRCA1 and BRCA2
Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER?
 PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
Understanding the PSA test. A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer
 Understanding the PSA test A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer Introduction This booklet is for men who want to know more about having a blood test, called a PSA test, that can help diagnose
Understanding the PSA test A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer Introduction This booklet is for men who want to know more about having a blood test, called a PSA test, that can help diagnose
Prostate Cancer. Patient Information
 Prostate Cancer Patient Information 1 The Prostate & Prostate Cancer The prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive system, approximately the size and shape of a walnut. It is located directly
Prostate Cancer Patient Information 1 The Prostate & Prostate Cancer The prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive system, approximately the size and shape of a walnut. It is located directly
PROSTATE CANCER. Get the facts, know your options. Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology
 PROSTATE CANCER Get the facts, know your options Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology i What is the Prostate? Unfortunately, you have prostate
PROSTATE CANCER Get the facts, know your options Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology i What is the Prostate? Unfortunately, you have prostate
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse
 7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
Locally advanced prostate cancer
 Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Locally advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is locally advanced prostate cancer? How is locally advanced prostate cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Locally advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is locally advanced prostate cancer? How is locally advanced prostate cancer diagnosed?
There are many different types of cancer and sometimes cancer is diagnosed when in fact you are not suffering from the disease at all.
 About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
Prostate Cancer Screening. Dr. J. McCracken, Urologist
 Prostate Cancer Screening Dr. J. McCracken, Urologist USPSTF Lifetime risk for diagnosis currently estimated at 15.9% Llifetime risk of dying of prostate cancer is 2.8% Seventy percent of deaths due to
Prostate Cancer Screening Dr. J. McCracken, Urologist USPSTF Lifetime risk for diagnosis currently estimated at 15.9% Llifetime risk of dying of prostate cancer is 2.8% Seventy percent of deaths due to
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you
 Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet
 Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 What is the purpose of my appointment? Your doctor has informed us that you have an elevated Prostate Specific
Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 What is the purpose of my appointment? Your doctor has informed us that you have an elevated Prostate Specific
These rare variants often act aggressively and may respond differently to therapy than the more common prostate adenocarcinoma.
 Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Prostate Cancer Screening: Are We There Yet? March 2010 Andrew M.D. Wolf, MD University of Virginia School of Medicine
 Prostate Cancer Screening: Are We There Yet? March 2010 Andrew M.D. Wolf, MD University of Virginia School of Medicine Case #1 A 55 yo white man with well-controlled hypertension presents for his annual
Prostate Cancer Screening: Are We There Yet? March 2010 Andrew M.D. Wolf, MD University of Virginia School of Medicine Case #1 A 55 yo white man with well-controlled hypertension presents for his annual
Prostate Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Localised prostate cancer
 Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Localised prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is localised prostate cancer? How is localised prostate cancer diagnosed? What do my
Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Localised prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is localised prostate cancer? How is localised prostate cancer diagnosed? What do my
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems
 Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Thomas A. Kollmorgen, M.D. Oregon Urology Institute
 Thomas A. Kollmorgen, M.D. Oregon Urology Institute None 240,000 new diagnosis per year, and an estimated 28,100 deaths (2012) 2 nd leading cause of death from cancer in U.S.A. Approximately 1 in 6 men
Thomas A. Kollmorgen, M.D. Oregon Urology Institute None 240,000 new diagnosis per year, and an estimated 28,100 deaths (2012) 2 nd leading cause of death from cancer in U.S.A. Approximately 1 in 6 men
Cryosurgery in Cancer Treatment: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Cryosurgery in Cancer
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Cryosurgery in Cancer
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome
 Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Analysis of Prostate Cancer at Easter Connecticut Health Network Using Cancer Registry Data
 The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
LIvING WITH Prostate Cancer
 Living with Prostate Cancer A Common Cancer in Men If you ve been diagnosed with prostate cancer, it s normal to be concerned about your future. It may help you to know that this disease can often be cured
Living with Prostate Cancer A Common Cancer in Men If you ve been diagnosed with prostate cancer, it s normal to be concerned about your future. It may help you to know that this disease can often be cured
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing
 Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner
 Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer: Understanding Your Risk
 Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer: Understanding Your Risk When the urologist calls with the life-changing news that your prostate biopsy is positive for prostate cancer, an office appointment is made to
Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer: Understanding Your Risk When the urologist calls with the life-changing news that your prostate biopsy is positive for prostate cancer, an office appointment is made to
TO SCREEN OR NOT TO SCREEN: THE PROSTATE CANCER
 TO SCREEN OR NOT TO SCREEN: THE PROSTATE CANCER DILEMMA Thomas J Stormont MD January 2012 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8jd 7bAHVp0A&feature=related related INTRODUCTION A government health panel (the
TO SCREEN OR NOT TO SCREEN: THE PROSTATE CANCER DILEMMA Thomas J Stormont MD January 2012 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8jd 7bAHVp0A&feature=related related INTRODUCTION A government health panel (the
Beyond the PSA: Genomic Testing in Localized Prostate Cancer
 Beyond the PSA: Genomic Testing in Localized Prostate Cancer Kelvin A. Moses, MD, PhD Vanderbilt University Medical Center Wednesday, December 2, 2015 5:00 p.m. ET/2:00 p.m. PT About ZERO ZERO s mission
Beyond the PSA: Genomic Testing in Localized Prostate Cancer Kelvin A. Moses, MD, PhD Vanderbilt University Medical Center Wednesday, December 2, 2015 5:00 p.m. ET/2:00 p.m. PT About ZERO ZERO s mission
Cancer research in the Midland Region the prostate and bowel cancer projects
 Cancer research in the Midland Region the prostate and bowel cancer projects Ross Lawrenson Waikato Clinical School University of Auckland MoH/HRC Cancer Research agenda Lung cancer Palliative care Prostate
Cancer research in the Midland Region the prostate and bowel cancer projects Ross Lawrenson Waikato Clinical School University of Auckland MoH/HRC Cancer Research agenda Lung cancer Palliative care Prostate
DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER
 DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER Determining the presence of prostate cancer generally involves a series of tests and exams. Before starting the testing process, the physician will ask questions about the
DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER Determining the presence of prostate cancer generally involves a series of tests and exams. Before starting the testing process, the physician will ask questions about the
Science Highlights. To PSA or not to PSA: That is the Question.
 Science Highlights June 2012 by Ann A. Kiessling, PhD at the To PSA or not to PSA: That is the Question. The current raucous debate over the commonly used PSA blood test to screen for prostate cancer,
Science Highlights June 2012 by Ann A. Kiessling, PhD at the To PSA or not to PSA: That is the Question. The current raucous debate over the commonly used PSA blood test to screen for prostate cancer,
Bowel cancer: should I be screened?
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Bowel cancer: should I be screened? Bowel cancer is a serious condition, but there are good treatments. Treatment works best if it's started early.to pick up early
Patient information from the BMJ Group Bowel cancer: should I be screened? Bowel cancer is a serious condition, but there are good treatments. Treatment works best if it's started early.to pick up early
After Diagnosis: Prostate Cancer. Understanding Your Treatment Options
 After Diagnosis: Prostate Cancer Understanding Your Treatment Options What s inside How will this booklet help me?... 3 What is the prostate?... 4 What is prostate cancer?... 4 Who gets prostate cancer?...
After Diagnosis: Prostate Cancer Understanding Your Treatment Options What s inside How will this booklet help me?... 3 What is the prostate?... 4 What is prostate cancer?... 4 Who gets prostate cancer?...
Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Your Questions, Our Answers.
 Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Your Questions, Our Answers. When you re looking for the right treatment for your prostate cancer, nothing s more important than accurate information. Read on, and learn
Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Your Questions, Our Answers. When you re looking for the right treatment for your prostate cancer, nothing s more important than accurate information. Read on, and learn
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
co-sponsored by the Health & Physical Education Department, the Health Services Office, and the Student Development Center
 Cancer is a group of more than 100 related diseases. Normally, cells grow and divide to produce more cells to keep the body healthy. Sometimes, this process goes wrong. New cells form when the body doesn
Cancer is a group of more than 100 related diseases. Normally, cells grow and divide to produce more cells to keep the body healthy. Sometimes, this process goes wrong. New cells form when the body doesn
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
BRCA Genes and Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer. Patient information leaflet
 BRCA Genes and Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer Patient information leaflet This booklet has been written for people who have a personal or family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer that could
BRCA Genes and Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer Patient information leaflet This booklet has been written for people who have a personal or family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer that could
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 [email protected] Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 [email protected] Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Prostate Cancer & Its Treatment
 Your Health Matters Prostate Cancer & Its Treatment By the UCSF Medical Center Prostate Cancer Advocates Greetings! From our personal experience in dealing with our own prostate cancers, we UCSF Patient
Your Health Matters Prostate Cancer & Its Treatment By the UCSF Medical Center Prostate Cancer Advocates Greetings! From our personal experience in dealing with our own prostate cancers, we UCSF Patient
Prostate Cancer Guide. A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
