.scotch-whisky.org.uk
|
|
|
- Mervyn Newton
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Questions & Answers
2 H The World of Scotch Whisky ORKNEY Kirkwall S D E Thurso John o'groats R I LEWIS Stornoway E B Lochinver Wick E R Ullapool Brora O U T SOUTH UIST NORTH UIST Portree Torridon Dingwall Bonar Bridge Inverness Tain Invergordon Nairn Speyside Forres Elgin Rothes Lossiemouth Keith Buckie Banff Fraserburgh Macduff SKYE Mallaig Kyle of Lochalsh Beauly Fort Augustus Loch Ness Aviemore Grantownon-Spey Spey Tomintoul Craigellachie Dufftown Huntly Oldmeldrum Inverurie Aberdeen Fort William Ben Nevis 1343 m Loch Ericht Dee Ballater Banchory Stonehaven Tobermory Ballachulish Loch Rannoch Pitlochry MULL Oban Loch Tay Aberfeldy Tay Blairgowrie Arbroath Montrose Loch Awe Perth Dundee Carnoustie Inveraray Crieff Lochgilphead Callander Loch Lomond Dunblane Stirling Auchterarder Kinross St Andrews Glenrothes JURA Helensburgh Falkirk Port Askaig ISLAY Tarbert Greenock Dumbarton GLASGOW EDINBURGH North Berwick Port Ellen East Kilbride Brodick Campbeltown ARRAN Kilmarnock Troon Biggar Tweed Berwickupon-Tweed Prestwick Ayr Melrose Coldstream Moffat Hawick Dumfries Stranraer Wigtown Castle Douglas
3 Contents Introduction 2-3 The World's Leading Drink 4-7 The History of Scotch Whisky 8-10 Making Scotch Whisky The Importance of Blending Scotch Whisky and the World Sale and Distribution Scotch Whisky and the Consumer Definitions Scotch Whisky and the Environment 41 Scotch Whisky and Health Drinks made with Scotch Whisky Information about Scotch Whisky 48 Index Contents - 1
4 Introduction Contents Scotland is the home of Scotch Whisky and host to the greatest concentration of distilleries in the world. There are around 100, making Malt Whisky by the centuries-old Pot Still method or Grain Whisky in the Coffey or Patent Still which has been in use since Few products are so closely linked with the environment, culture and people of their country of origin as Scotch Whisky. Scotch Malt Whisky is usually classified in one of five main categories - Highland, Lowland, Speyside, Islay, and Campbeltown - according to the location of the distillery in which the spirit is made. While many Malt Whisky distilleries bottle some of their production for sale as Single Malt - the product of one distillery, most of the Scotch Whisky consumed today is Blended Scotch Whisky. This means that it is a blend of as many as 50 different Malt and Grain Whiskies, all produced in the distilleries shown on the map and blended skilfully to maintain consistent quality and flavour. Scotch Whisky is Scotland's leading indigenous product, and is of major importance to the economy not only of Scotland, but of the United Kingdom as a whole. Sold around the world for more than 100 years, Scotch Whisky is now established as the leading international spirit drink, making it one of Britain s most important exports. There are, however, many aspects of Scotch Whisky distilling and blending that are not generally understood. The Scotch Whisky Association has therefore produced this handy reference book to provide answers to the many questions which frequently To prepare this book, arise. the Association has had the assistance of many There is often confusion, for example, over people in the Scotch the length of time that Scotch is matured. Most Whisky industry, all expert whiskies mature far longer than the legal minimum in their own fields, to of three years, and the maturation period varies for whom it is indebted. different whiskies. 2 - Introduction
5 Foreword The age statement on a bottle reflects the amount of time the youngest whisky in that bottle has spent maturing in a cask. The distiller, when making whisky, and the blender, when laying it down for maturation, are not aiming to satisfy immediate consumer demand. They must attempt to forecast likely demand ten years or more ahead. It is thus impossible to relate production figures in any one year with consumption figures for that same year. Many distilleries welcome visits by members of the public. It is often necessary to make arrangements in advance, but many distilleries have extensive visitor facilities and do not require prior warning of a visit. A list of distilleries willing to accept visitors is available from: The Scotch Whisky Association 20 Atholl Crescent, Edinburgh EH3 8HF t: e: [email protected] w: scotch-whisky.org.uk or 14 Cork Street, London W1S 3NS t: e: [email protected] Introduction - 3
6 1 The World's Leading Drink The World's Leading Drink 1 What is Scotch Whisky? Scotch Whisky is a distilled spirit drink made in Scotland from cereals, water and yeast. 2 Is Scotch Whisky the world's leading spirit drink? Yes. It is the leading international spirit drink. 3 When consumers ask for a Scotch, what exactly do they mean? They usually mean a Blended Scotch Whisky, that is a blend of as many as 50 individual Scotch Malt and Scotch Grain Whiskies. The wide range of single whiskies available in Scotland ensures the continued high quality and consistency of brands of Blended Scotch Whisky and, year in year out, enables blenders to ensure that all their brands maintain their individual characteristics. Blended Scotch Whiskies accounts for around 90 per cent of all Scotch Whisky sold in world markets. 4 What is a single whisky? It is the product of a single distillery. Most distilleries produce Scotch Whisky primarily for the purpose of blending, but many retain some of their production for sale as single whiskies. A Single Malt Scotch Whisky is the product of one Malt Whisky distillery and a Single Grain Scotch Whisky is the product of one Grain Whisky distillery. 5 What is the legal definition of Scotch Whisky? Scotch Whisky has been defined in United Kingdom (UK) law since 1909 and recognised in European Community legislation since The current UK legislation relating specifically to Scotch Whisky is The Scotch Whisky Act 1988 and the Orders made under it, which came into effect in June 1990 and superseded that part of the Finance Act 1969, as subsequently amended, defining Scotch Whisky. 4 - The World's Leading Drink
7 For the purposes of The Scotch Whisky Act 1988 Scotch Whisky means whisky: (a) which has been produced at a distillery in Scotland from water and malted barley (to which only whole grains of other cereals may be added) all of which have been: (i) processed at that distillery into a mash; (ii) converted to a fermentable substrate only by endogenous enzyme systems; and (iii)fermented only by the addition of yeast; (b) which has been distilled at an alcoholic strength by volume of less than 94.8 per cent so that the distillate has an aroma and taste derived from the raw materials used in, and the method of, its production; (c) which has been matured in an excise warehouse in Scotland in oak casks of a capacity not exceeding 700 litres, the period of that maturation being not less than 3 years; (d) which retains the colour, aroma and taste derived from the raw materials used in, and the method of, its production and maturation; and (e) to which no substance other than water and spirit caramel has been added. The Scotch Whisky Act 1988 prohibits the production in Scotland of whisky other than Scotch Whisky. The Scotch Whisky Act 1988 and The European Spirit Drinks Regulation 1989 both specify a minimum alcoholic strength of 40 per cent by volume, which applies to all Scotch Whisky bottled and/or put up for sale within or exported from the EU. 6 What are the different categories of Scotch Whisky? According to traditional practice, there are five categories of Scotch Whisky: (a) Single Malt Scotch Whisky: A Scotch Whisky distilled at a single distillery (i) from water and malted barley without the addition of any other cereals, and (ii) by batch distillation in pot stills. The World's Leading Drink - 5
8 (b) Single Grain Scotch Whisky: A Scotch Whisky distilled at a single distillery (i) from water and malted barley with or without whole grains of other malted or unmalted cereals, and (ii) which does not comply with the definition of Single Malt Scotch Whisky. (c) Blended Scotch Whisky: A blend of one or more Single Malt Scotch Whiskies with one or more Single Grain Scotch Whiskies. (d) Blended Malt Scotch Whisky: A blend of Single Malt Scotch Whiskies which have been distilled at more than one distillery. (e) Blended Grain Scotch Whisky: A blend of Single Grain Scotch Whiskies which have been distilled at more than one distillery. While these definitions have been governed by convention, the industry is seeking to include them in legislation. 7 What is a Blended Scotch Whisky? It is when a number of distillates each of which separately is entitled to the description Scotch Whisky are combined together. Blended Scotch Whisky (any combination of malt and grain whiskies), Blended Malt Scotch Whisky (a combination of Malt Whiskies from different malt whisky distilleries) and Blended Grain Scotch Whisky (a combination of Grain Whiskies from different grain whisky distilleries) are all available. 8 Which spelling is correct, Whisky or Whiskey? Most well-known dictionaries give both spellings. The Oxford English Dictionary points out that in modern trade usage, Scotch Whisky and Irish Whiskey are thus distinguished in spelling. American-made whiskey is usually spelt with an e, while Canadian and Japanese whisky do not. 9 What is the difference between Scotch, Irish, Rye and Bourbon Whiskies? Scotch Whisky is whisky which has been distilled and matured in Scotland. Irish Whiskey means whiskey distilled and matured in Ireland. Whisky is distilled in Scotland from malted barley in Pot Stills and 6 - The World's Leading Drink
9 from malted and unmalted barley or other cereals in Patent Stills. Irish Whiskey distillers tend to favour three distillations rather than two, as is generally used in Scotland for Malt Whiskies, and the range of cereals used by Irish distillers is wider. As regards Bourbon Whiskey, the United States Regulations provide: (i) that Bourbon Whiskey must be produced from a mash of not less than 51% corn grain; (ii) that the word Bourbon shall not be used to describe any whiskey or whiskey-based distilled spirits not produced in the United States. Rye Whiskey is produced both in the United States and Canada but the name has no geographical significance. In the United States, Rye Whiskey by definition must be produced from a grain mash of which not less than 51% is rye grain. In Canada, there is no similar restriction. The relevant Canadian Regulation states: Canadian Whisky (Canadian Rye Whisky, Rye Whisky) shall be whisky distilled in Canada, and shall possess the aroma, taste and character generally attributed to Canadian Whisky. Canadian Whisky is in fact often referred to simply as Rye Whisky or Rye. 10 What are spirits? The term spirits describes the product of distillation, whatever the raw materials. Generally, the word refers to any volatile inflammable liquid obtained by distillation. Spirits for human consumption, or potable spirits, are the distillates of alcoholic liquids, the alcohol in which has been formed by the fermentation of sugar as contained in grapejuice, sugar cane, etc., or in saccharified materials such as specially prepared cereals, e.g. malted barley. The World's Leading Drink - 7
10 2 The History of Scotch Whisky The History of Scotch Whisky 11 What is the origin of the name 'whisky'? The term whisky comes from the Gaelic uisge beatha, or usquebaugh, meaning water of life. Gaelic is that branch of Celtic spoken in the Highlands of Scotland. 12 When was Scotch Whisky first distilled? Whisky has been distilled in Scotland for hundreds of years. There is some evidence to show that the art of distilling could have been brought to the country by Christian missionary monks, but it has never been proved that Highland farmers did not themselves discover how to distil spirits from their surplus barley. The earliest historical reference to distilling in Scotland appears in the Scottish Exchequer Rolls for 1494, where there is an entry of eight bolls of malt to Friar John Cor wherewith to make aquavitae. A boll was an old Scottish measure of not more than six bushels. (Six busheis is equivalent to kiiograms, enough barley to make around 1500 bottles) When King James IV was in Inverness during September 1506, his Treasurer s Accounts had entries for the 15th and 17th of the month respectively: For aqua vite to the King... and For ane flacat of aqua vite to the King.... lt is probable that the aqua vite in this case was spirit for drinking. The earliest reference to a distillery in the Acts of the Scottish Parliament appears to be in 1690, when mention is made of the famous Ferintosh distillery owned by Duncan Forbes of Culloden. There is also a reference to distilling in a private house in the parish of Gamrie in Banffshire in This occurs in the Register of the Privy Council, where a man accused of the crime of breaking into a private house, combined with assault, was said to have knocked over some aquavitie. 8 - The History of Scotch Whisky
11 One of the earliest references to uiskie occurs in the funeral account of a Highland laird about An unpublished letter of February 1622, written by Sir Duncan Campbell of Glenorchy to the Earl of Mar, reported that certain officers sent to Glenorchy by the King had been given the best entertainment that the season and the country allowed. It stated: For they wantit not wine nor aquavite. This aquavite was no doubt locally distilled whisky. Another writer affirms that aquavitae occasionally formed part of the rent paid for Highland farms, at any rate in Perthshire, but no actual date is given for this practice. 13 What is the history of charging duty on Scotch Whisky? The Scots Parliament in 1644 passed an Excise Act fixing the duty at 2/8d (13p) per pint of aquavitae or other strong liquor - the Scots pint being approximately one third of a gallon. For the remainder of the 17th century various alterations were made to the types and amounts of duty collected. After the Union of the Parliaments in 1707, English revenue staff crossed the border to begin their lengthy attempts to bring whisky production under control. Ninety years later the excise laws were in such a hopeless state of confusion that no two distilleries were taxed at the same rate. Illicit distilling flourished, the smugglers seeing no good reason for paying for the privilege of making their native drink. After a lengthy Royal Commission, the Act of 1823 sanctioned legal distilling at a duty of 2/3d (12p) per gallon for stills with a capacity of more than 40 gallons. There was a licence fee of 10 annually and no stills under the legal limit were allowed. The first distillery came into official existence in the following year and thereafter illicit distilling quickly faded away. The History of Scotch Whisky - 9
12 In 1840, the duty was 5d (2.5p) per bottle and by the beginning of the First World War it had almost quadrupled. In 1939, a typical bottle of Scotch Whisky cost 14/3d (72p) of which 9/71/2d (48p) was duty. In 1995, for the first time in one hundred years, the tax on Scotch Whisky was reduced. Duty fell from 5.77 to 5.54 a bottle (70cl). In 1996, the tax on Scotch Whisky was again reduced. There has only been one duty rise since then, in January This long-term freeze reflects the government's view that the current high level of duty damages Scotch Whisky in a competitive marketplace. Since 1973 the price of a bottle of whisky, including the Excise Duty, has been subject to a Value Added Tax. MOVEMENT OF EXCISE DUTIES The following table gives an indication of how the Excise Duty payable on a typical bottle of Scotch Whisky has increased. Figures for the earlier dates have been converted to decimal currency. Date Duty per bottle / Date Duty per bottle The History of Scotch Whisky
13 Making Scotch Whisky 3 Making Scotch Whisky 14 How is Scotch Whisky made? There are two kinds of Scotch Whisky distilled: Malt Whisky which is made by the Pot Still process and Grain Whisky which is made by the Patent Still (or Coffey Still) process. Malt Whisky is made from malted barley only, while Grain Whisky is made from malted barley together with unmalted barley and other cereals. MALT WHISKY The Pot Still process by which Malt Whisky is made may be divided into four main stages: Malting, Mashing, Fermentation and Distillation. (a) MALTING The barley is first screened to remove any foreign matter and then soaked for two or three days in tanks of water known as steeps. After this it is traditionally spread out on a concrete floor, known as the malting floor, and allowed to germinate. Germination may take from 5 to 8 days depending on the season of the year, the quality of the barley used and other factors. During germination the barley secretes the enzyme diastase which makes the starch in the barley soluble, thus preparing it for conversion into sugar. Throughout this period the barley must be turned at regular intervals to control the temperature and rate of germination. At the appropriate moment germination is stopped by drying the malted barley or 'green malt' in the malt kiln. More usually today malting is carried out in Saladin boxes or in drum maltings, in both of which the process is controlled mechanically. Instead of germinating on the distillery floor, the grain is contained in large rectangular boxes (Saladin) or in large cylindrical drums. Temperature is controlled by blowing air at selected temperatures upwards through the germinating grain, which is turned mechanically. Today, most distilleries obtain their malt, made to their specific requirements, from centralised maltings which supply a number of distilleries, thereby enabling the malting process to be carried out more economically. A very few, Making Scotch Whisky - 11
14 however, continue to use traditional floor maltings for some of their requirements. (b) MASHING The dried malt is ground in a mill and the grist, as it is now called, is mixed with hot water in a large circular vessel called a mash tun. The soluble starch is thus converted into a sugary liquid known as wort. This is drawn off from the mash tun and the solids remaining are removed for use as cattle food. (c) FERMENTATION After cooling, the wort is passed into large vessels (washbacks) holding anything from 9,000 to 45,000 litres of liquid where it is fermented by the addition of yeast. The living yeast attacks the sugar in the wort and converts it into crude alcohol. Fermentation MALTINGS BARLEY STORAGE STEEPS STEEPS MALT HOUSE MASH HOUSE WATER HEATING TANKS MALT GRIST HOPPER TUN ROOM MALT KILN WEIGHING MACHINE GRINDING MILL MASH TUN WASHBACK 12 - Making Scotch Whisky
15 SCOTCH WHISKY SCOTCH WHISKY SCOTCH WHISKY SCOTCH WHISKY takes about 48 hours and produces a liquid known as wash, containing alcohol of low strength, some unfermentable matter and certain byproducts of fermentation. (d) DISTILLATION Malt Whisky is distilled twice in large copper Pot Stills. The liquid wash is heated to a point at which the alcohol becomes vapour. This rises up the still and is passed into the cooling plant where it is condensed back into liquid. The cooling plant frequently takes the form of a coiled copper tube or worm that is kept in continuously running cold water. The first distillation separates the alcohol from the fermented liquid and eliminates the residue of the yeast and unfermentable matter. This distillate, known as low wines, is then passed into another still where it is distilled a second time. The first runnings (foreshots) from this second distillation are not considered potable and it is only when the spirit reaches an acceptable standard that it is collected in the Spirit Receiver. Again, towards the end of the distillation, the spirit begins to fall off in strength and quality. It is then no longer collected as spirit but drawn off and kept, together with the foreshots, for redistillation with the next low wines. Pot Still distillation is a batch process. STILL HOUSE WAREHOUSE CONDENSER SCOTCH WHISKY SCOTCH WHISKY CONDENSER SCOTCH WHISKY SCOTCH WHISKY WASH STILL SPIRIT STILL SPIRIT RECEIVER SPIRIT STORE SCOTCH WHISKY SCOTCH WHISKY SCOTCH WHISKY Making Scotch Whisky - 13
16 GRAIN WHISKY The Patent Still process by which Grain Whisky is made is continuous in operation and differs from the Pot Still process in five other ways. (a) The mash consists of a proportion of malted barley together with unmalted cereals. (b) Any unmalted cereals used are cooked under steam pressure in Converters for about 3 1/ 2 hours. During this time the mixture of grain and water is agitated by stirrers inside the cooker. (c) The starch cells in the grain burst and when this liquid is transferred to the mash tun, with the malted barley, the diastase in the latter converts the starch into sugar. (d) The wort is collected at a specific gravity lower than in the case of the Pot Still process. (e) Distillation is carried out in a Patent or Coffey Still and the spirit collected at a much higher strength. FEINTS INLET ANALYSER VAPOUR PIPE WASH PIPE VAPOUR VENT RECTIFIER WASH INLET SPIRIT TO RECEIVER STEAM INLET SPENT WASH OUTLET HOT FEINTS TO RECEIVER 14 - Making Scotch Whisky
17 MATURATION Both Malt and Grain Whisky must be matured after distillation has been completed. The new spirit is filled into casks of oak wood which, being permeable, allows air to pass in and evaporation takes place. By this means the harsher constituents in the new spirit are removed and it becomes in due course a mellow whisky. Malt Whisky which contains more flavour constituents takes longer to mature than Grain Whisky and is often left in the cask for 10 years or even longer. The period of maturation for both Malt and Grain Whisky is also affected by the size of casks used, the strength at which the spirit is stored, and the temperature and humidity of the warehouse. Newly distilled spirit is a colourless liquid. Scotch Whisky derives much of its colour from the casks in which it matures. The degree of colour will vary from one whisky to another. Whisky matured in former fresh oak sherry casks will usually be a darker colour than that which has been matured in refilled whisky casks. The blender aims at uniformity in his product and he may ensure consistency of colour between batches of mature spirit by adding, if necessary, a small amount of tasteless colouring caramel, which in the small quantities used has no effect on the taste or aroma of the whisky. BLENDING After maturation the different whiskies are blended together. (See Question 22 for a description of the blending process). The blend is then reduced to the strength required for bottling by the addition of soft water. BOTTLING The final stage in the production of Scotch Whisky is bottling and despatch. Most Scotch Whiskies are marketed at home and abroad in branded bottles. Making Scotch Whisky - 15
18 In some instances, for commercial reasons, Scotch Whisky may be shipped overseas in bulk. When Blended Scotch Whisky is shipped abroad in bulk, either at original strength or suitably reduced, it is exported in glass lined stainless steel tanks. The bottling is then carried out by distributors or agents overseas. 15 What are the regions associated with Scotch Whisky making? Malt Whiskies are divided into five groups according to the geographical location of the distilleries in which they are made. In line with traditional practice, the right to bear these names is limited to Scotch Whiskies wholly distilled in the region in question. The recognised regions are: (1) LOWLAND MALT WHISKIES, made south of an imaginary line drawn from Dundee in the east to Greenock in the west. (2) HIGHLAND MALT WHISKIES, made north of that line. (3) SPEYSIDE MALT WHISKIES, from the valley of the River Spey. Although these whiskies come from within the area designated as Highland Malt Whiskies, the concentration of distilleries and the specific climatic conditions produce a whisky of an identifiable character and require a separate classification. (4) ISLAY MALT WHISKIES, from the island of Islay. (5) CAMPBELTOWN MALT WHISKIES, made within the town boundaries of Campbeltown in Argyll. Each group has its own clearly defined characteristics, ranging from the lighter Lowland Malt Whiskies to those distilled on Islay which are generally regarded as the heaviest Malt Whiskies. Malt Whiskies, which differ considerably in flavour according to the distillery from which they come, have a more pronounced bouquet and flavour than Grain Whiskies. The production of Grain Whisky has not been so influenced by geographical factors and it may be distilled anywhere in Scotland Making Scotch Whisky
19 16 What gives Scotch Whisky its distinctive flavour and aroma? This is one of the mysteries of the industry and a secret which many imitators of Scotch Whisky have tried in vain to discover. Many theories and explanations have been put forward, but there is no universally accepted solution. The distilling process itself is one factor. Scotch Whisky, after it has been distilled, contains not only ethyl alcohol and water but certain secondary constituents. The exact nature of these is not fully understood, but it is believed they include some of the essential oils from the malted barley and other cereals and substances that derive from peat. The amount of these secondary constituents retained in the spirit depends upon the shape of the still and the way it is operated, and also on the strength at which the spirit is drawn off. Grain Whisky, because of the process by which it is made, contains fewer secondary constituents than Malt Whisky and is accordingly milder in flavour and aroma. The natural elements of water, peat and the Scottish climate all certainly have a profound effect on the flavour of Scotch Whisky. Water is probably the most important single factor and a source of good, soft water is essential to a distillery. Peat, which is used in the kiln or oven in which the malt is dried, also has an influence that can be detected in the peaty or smoky flavour of many Scotch Whiskies. The Scottish climate is extremely important, particularly when the whisky is maturing. At this stage the soft air permeates the casks and works on the whisky, eliminating harsher constituents to produce a mellow whisky. 17 Why do whiskies produced in different distilleries vary in flavour? This again is a question which it is very difficult to answer with certainty. While some believe water to be a decisive factor, adjoining distilleries which draw their water from different sources are known to produce whiskies that are quite dissimilar in flavour. The size and shape of the stills are important, as are the skill and experience of the Making Scotch Whisky - 17
20 men who manage them. It is the objective of the distiller to produce a whisky whose flavour and character remain consistent at all times and in all circumstances. This is the true art of distilling, acquired only after many years and often handed down from one generation to the next. 18 How many distilleries are there? There are around 100 Pot Still Malt distilleries and Grain or Patent Still distilleries in Scotland; but the number working can vary from year to year. 19 Is it possible to visit a whisky distillery? Around 40 Scotch Whisky distilleries are open to the public. Some distilleries cater specifically for visitors, with custom-built visitor centres, museums or cafes. Others are lower key, but will be delighted to show you around if you make an appointment first. Some do charge a small entrance fee, but this can often be redeemed in the distillery shop at the end of the tour. A Distilleries to Visit guide is published annually and is available from The Scotch Whisky Association. In addition, visit for more information on a range of Scotch Whisky embassies hotels, restaurants and bars across Scotland, and how to visit Scotland and a Scotch Whisky distillery. 20 Can Scotch Whisky be made only in Scotland? Yes. Many products which were originally manufactured only in a particular locality have lost their geographical significance and can now be manufactured anywhere. The word Scotch, however, as applied to whisky, has retained its geographical significance. This is widely recognised in law throughout the world. Thus, whisky may be described as Scotch Whisky only if it has been wholly distilled and matured in Scotland Making Scotch Whisky
21 21 If you could duplicate exactly a Scotch Whisky distillery in, say, Brazil or Spain, could you produce Scotch? No. For the reason given in the preceding answer, whisky can be called Scotch only if it is distilled and matured in Scotland. Whisky produced in Brazil is Brazilian Whisky or in Spain Spanish Whisky. Attempts have been made to copy the unique flavour of Scotch Whisky in many parts of the world, but with no success whatsoever. Making Scotch Whisky - 19
22 4 The Importance of Blending The Importance of Blending 22 What is blending? What is its purpose? A number of distilleries bottle and sell some of the whisky they distil for consumption as single or unblended whiskies. By far the greater part of their production, however, is used for the well-known Blended Scotch Whiskies that are sold all over the world. Blending whisky is a considerable art acquired only after years of experience. A blend will consist of anything from 15 to 50 different single whiskies, combined in the proportions of a formula that is the secret of the blending company concerned. Whiskies from different distilleries have a character of their own and, just as people of different temperaments are often incompatible, so some whiskies will not blend happily with certain others. The Malts and Grains in a blend must therefore, be chosen to complement and enhance their respective flavours. The blender's task is to combine different single whiskies, to produce a blend which brings out the best qualities of each of its constituent parts. The aim of the blender is first to produce a whisky of a definite and recognisable character. It is of the greatest importance that his blend should never vary from this standard, which his customers all over the world will have come to expect. His second aim is, therefore, to achieve consistency. The blender must also decide when the different single whiskies are ready to be used in his blend. They are brought from the warehouse where they have been maturing to the blending hall, where they are mixed together in a blending vat. They are usually returned to cask and left to marry for a period of months, before bottling. Some companies prefer to blend their Malts and Grains separately and only bring the two together before bottling The Importance of Blending
23 Blended Scotch Whisky is a blend of Malt and Grain whiskies. Combining Malt Whisky with other malts is known as Blended Malt Scotch Whisky, and Grain with Grain is known as Blended Grain Scotch Whisky. 23 When was blending introduced? Blending was pioneered by Andrew Usher in Edinburgh in the early 1860 s. In the 19th century Malt Whisky was rarely left to mature for an adequate length of time. As a consequence, it was often a fiery drink, often regarded as too pungent for many palates. Grain Whisky had a much milder flavour, but was too light for many tastes. By combining Malt Whisky with Grain Whisky, a light, yet flavoursome whisky was created. This proved a turning point for the fortunes of Scotch Whisky. The introduction of Blended Scotch Whisky saw demand spread outside of Scotland, first to England and then throughout the world. 24 What is the percentage of Malt and Grain Whiskies in blended Scotch Whisky? There is no fixed percentage and the proportion differs from one blender to another. No brand owner is willing to reveal the proportions of the different whiskies used, but the blender determines the proportion according to the character he is seeking for his blend. This character is determined not only by the proportions of Malt and Grain Whisky which the blend contains, but also by factors such as the ages of the individual whiskies and the manner in which they combine to bring out the finest qualities in each other. 25 What are premium and de luxe Blended Scotch Whiskies? The terms 'premium' and 'de luxe' are not formally defined. A premium or de luxe Blended Scotch Whisky would normally contain a higher proportion of carefully selected older and, therefore, more expensive whiskies. The Importance of Blending - 21
24 26 When there is an age label on a bottle of Blended Scotch Whisky, does it refer to the average age of the whiskies in that blend? No. The law requires that when the age is declared on a label, it must refer to the youngest whisky in the blend. For example, if a blend is described as an eight year old, the youngest whisky in that blend must have been matured for at least eight years. 27 Is it legal to sell whisky which is less than three years old for consumption in this country? No. Although the spirit is distilled under the strict conditions applied to the production of Scotch Whisky, it is not entitled to be described as Scotch Whisky until it has matured for at least three years The Importance of Blending
25 Scotch Whisky and the World 5 Scotch Whisky and the World 28 What is the proportion of home sales to exports? Scotch Whisky is one of Britain s principal export products, contributing 2billion a year to the balance of trade. Exporting is nothing new to the industry and even at the end of the 19th century Scotch Whisky companies were marketing overseas. Today exports represent around 90 per cent of all Scotch Whisky sales. 29 How does consumption of Scotch Whisky in Scotland compare with that in the rest of Britain? Customs and Excise monthly figures of releases from bond give no guide as to the amount of whisky consumed in Scotland itself, but trade sources report that between 15 and 20 per cent of Scotch Whisky sold in Britain is consumed in Scotland. 30 How important is Scotch Whisky as an export earner? Scotch Whisky is one of the United Kingdom s top five export earners, and accounts for almost 25% of UK food and drink exports. 31 To how many countries is Scotch exported? In recent years Scotch has been exported to about 200 different markets all over the world. The major markets are the European Union, USA, and Asia. 32 Is the European Union an important market for Scotch Whisky? Sales to Member States other than the United Kingdom are worth almost 40 per cent of exports. If the United Kingdom is included, the EU accounts for over 50 per cent of the total sales of Scotch Whisky. 33 What are the total stocks of Scotch Whisky? In 1939, the stocks of Scotch were 374 million litres of pure alcohol, but by 1945 they had fallen to less than 247 million litres. Since then they have risen in response to demand and by 2005 had risen to 2,900 million litres. Stocks of mature and maturing whisky are now sufficient to cover projected sales for around nine years. Scotch Whisky and the World - 23
26 34 Is there a large amount of money tied up in whisky stocks? Financing stocks of maturing whisky is the most significant capital investment which Scotch Whisky companies have to undertake. The long period of maturation which Scotch Whisky must undergo poses a number of commercial problems. Not the least among these is the difficulty of forecasting accurately the demand for whisky several years ahead which blenders must do when deciding how much new whisky to buy and lay down in any one year Scotch Whisky and the World
27 Sale and Distribution 6 Sale and Distribution 35 How is the alcoholic strength of Scotch Whisky measured? In common with other EU countries, on 1 January 1980 Britain adopted the system of measurement recommended by the International Organisation of Legal Metrology, a body with most major nations among its members. The OIML system measures alcoholic strength as a percentage of alcohol by volume at a temperature of 20 C. It replaced the Sikes system of measuring the proof strength of spirits, which had been used in Britain for over 160 years. 36 What was meant by proof spirit? The Customs and Excise Act of 1952 defined spirits of proof strength as follows: Spirits shall be deemed to be at proof if the volume of the ethyl alcohol contained therein made up to the volume of the spirits with distilled water has a weight equal to that of twelve-thirteenths of a volume of distilled water equal to the volume of the spirits, the volume of each liquid being computed as at fifty-one degrees Fahrenheit. In other words, proof spirit meant that the spirit at a temperature of 51 F, weighed exactly twelve-thirteenths of a volume of distilled water equal to the volume of the spirit. It was, in fact, a mixture of spirit and water of a strength of 57.1% of spirit by volume and 42.9% of water. 37 How was whisky tested for proof strength? Spirit of proof strength was the technical standard by which strength was measured until 1 January l980. Hundreds of years ago, spirit of this strength was proved when whisky and gunpowder were mixed and ignited. If the gunpowder flashed, then there was enough whisky in the mixture to permit ignition. Such whisky was held to have been 'proved'. If the spirit was weaker than this proof strength ignition did not take place. In the 1740s, the Customs and Excise and the London distillers began to use Clark s hydrometer, an instrument devised to measure Sale and Distribution - 25
28 spirit strength. A more accurate version by Bartholomew Sikes was universally adopted under the Hydrometer Act 1818, and remained in standard use until At what strength is Scotch Whisky sold? By law Scotch Whisky must be bottled, sold in and exported from the EU at a minimum 40% alc vol. A strength of 43% alc vol is found in some export markets. 39 How does U.S. proof strength compare with British and European strengths? Some U.S. proofs and their British and European equivalents are: AMERICAN BRITISH AND EUROPEAN 100 Proof 50% Alc. vol. 86 Proof 43% Alc. vol. 80 Proof 40% Alc. vol. 40 What sizes of casks are used for bulk whisky and what are their respective capacities? TYPE APPROXIMATE CONTENT IN LITRES Butt 500 Hogshead American Barrel Quarter Octave What is the liquid content of the bottles most commonly used for Scotch Whisky sales in the home market? TYPE Litre 100cl Bottle 70cl Half-bottle 35cl Miniature 5cl 26 - Sale and Distribution
29 42 How soon after it is distilled is whisky usually sold? The normal practice is for the blender to buy the whisky as soon as it is distilled. It is then kept under bond in warehouses at the distillery to mature until the blender requires it. By law whisky must mature for a minimum of three years, although in practice the minimum age is much greater. After blending, Scotch Whisky is usually returned to cask and left for a further period of several months to allow the constituent whiskies to marry. It is then bottled for sale. Sale and Distribution - 27
30 7 Scotch Whisky and the Consumer Scotch Whisky and the Consumer 43 Why is Scotch Whisky so expensive in Britain? Taxation in the UK is extremely high, accounting for as much as 70% of the retail price of a typical bottle of standard Blended Scotch Whisky. This includes Value Added Tax which is levied on the total retail price, including Excise Duty - a tax on a tax. The remainder of the retail price goes towards production and storage costs, transport, advertising, selling, administration expenses and wholesale and retail margins. The Government is thus by far the biggest beneficiary. 44 How does the rate of duty on Scotch Whisky compare with that on other alcoholic drinks? The Excise Duty paid on mature spirits is the same, whether they are produced in this country or abroad. Scotch Whisky is not protected in any way against competition from spirits produced overseas, even those from countries which themselves discriminate against imports of Scotch Whisky. At the same time, Scotch Whisky is now much more heavily taxed than most competing drinks. Scotch Whisky therefore faces discrimination when competing in the UK market against other alcoholic drinks. UK Excise Duty has only been reduced on three occasions since the 19th century. The first cut was made in On that occasion, however, the rate was lowered only to compensate for the extra taxation which resulted from the introduction of Value Added Tax, and made no difference to the overall impost. However, in 1995 there was the first true cut in the tax on Scotch Whisky for one hundred years. There was a further cut in In the following ten years with one exception UK duty on Scotch Whisky has been unchanged. Although this action has reduced the discrimination against Scotch Whisky slightly, it still carries a much greater tax burden than many of the drinks with which it competes Scotch Whisky and the Consumer
31 45 Why are some whisky sales duty-free? Whisky for consumption on board ships at sea has traditionally been treated as ship s stores. Ship s stores means goods of any kind (whether dutiable or non-dutiable, and whether of British manufacture or imported) taken on board an outward-bound ship for officers, crew and passengers during the voyage. Outward-bound means bound for an eventual destination outside the United Kingdom. Ship s stores have from time immemorial been free of duty, just as goods exported as cargo to countries overseas are. The theory is that the stores are in effect exports, in that they are consumed outside United Kingdom territory, and that the Government cannot expect to collect the duty they would bear if consumed at home. Whisky after distillation is stored (without paying duty) in a bonded warehouse to mature, and whisky shipped as stores or exported goes direct from the bonded warehouse to the ship. HM ships are included in these regulations. Coasting ships which ply from port to port round the coast, and vessels which ply on rivers or other inland waters are not outward-bound and do not get whisky or any other stores duty-free. Since 1 July 1999 duty-free sales are not permitted for passengers travelling between EU Member States. However, an important duty-free market exists for travellers leaving the EU, and in other parts of the world. 46 How many brands of Scotch Whisky are there? More than 2500 brands of Scotch Whisky are sold all over the world, of which as many as 200 are available in the home market. Many of them are sold only locally or to private clubs and individuals. 47 What are the best blends? This is entirely a matter of taste. All the well-known brands on the market are blended by experts with many years experience, and consumers can be confident that in choosing their favourite they are drinking a whisky consistently blended to bring out the best characteristics of the Malt and Grain Whiskies of which it is composed. Scotch Whisky and the Consumer - 29
32 48 Some Scotch Whisky has a smoky flavour. What causes this? The smoky flavour of certain Scotch Whiskies originates from the peat fire over which the green malt is dried, prior to grinding and mashing. 49 Is it possible to tell the difference between one brand of Scotch Whisky and another by smell alone? Yes, it is possible to differentiate between different well-known established brands of Scotch Whisky by smell alone if one is sufficiently experienced. The blenders employed by the blending and bottling firms, who blend the different whiskies which go to make the familiar brands, are guided by smell alone in producing a uniform product over the years. For the drinker who is not a professional blender, the only thing is to go on experimenting until practice makes perfect! 50 How do I find out more information on a particular brand of Scotch Whisky? Full contact details of Scotch Whisky companies and their brands are available on The Scotch Whisky Association website at 51 How old should the best Scotch Whisky be? It is not possible to lay down any precise age as being the best for a particular whisky. Generally speaking, Malt Whiskies require longer to mature fully than Grain Whiskies. UK and EU law insist that Scotch Whisky should be at least three years old. However, it is the practice of the trade to mature for substantially longer than the legal minimum. Malt Whiskies are normally matured for up to 10 years and sometimes even longer. When an age is quoted on a label, it is the age of the youngest whisky in the bottle that determines the age of the whisky, no matter how small the amount. It is never an average. 52 Does Scotch Whisky in a bottle lose its strength with age? Once bottled, whisky does not lose its strength Scotch Whisky and the Consumer
33 53 Does Scotch Whisky improve in a bottle which is kept sealed? No. There is no change in a whisky once it has been bottled and securely sealed. As oxygen in the air cannot get to the whisky, there is no further maturing. 54 How should I store my Scotch Whisky? Unlike wine, Whisky does not mature in the bottle. So even if you keep a 12 year old bottle for 100 years, it will always remain a 12 year old whisky. As long as the bottle is kept out of direct sunlight, the Scotch will neither improve nor deteriorate, even if it is opened. Whisky that is stored at very low temperatures can become cloudy, but the cloudiness should disappear when the whisky is returned to room temperature. 55 At what temperature is whisky best served? This is entirely a matter of personal choice and no rules, such as chilling for certain wines, can be laid down. In the United Kingdom it is usually served at room temperature, but in some overseas countries it is the convention to put ice in the glass. 56 Is the bouquet of Scotch Whisky improved by warming slightly? The bouquet of Scotch Whisky cannot be improved by warming. The effect of such warming would only be to increase the rate of evaporation of the spirit, thus speeding up the release of the aroma. 57 What is the best shape of a whisky glass? A tumbler-shaped glass or goblet is probably the most popular, particularly for drinking Scotch Whisky with ice and a mixer. Scotch Whisky does not require any specific shape to enhance its delights and no rigid convention has grown up in this connection. Many Scotch Whisky lovers believe that a malt whisky is better enjoyed in a balloon shaped glass where the neck is narrower than the base, allowing the drinker to nose and enjoy the bouquet and character, before sipping his dram. Scotch Whisky and the Consumer - 31
34 58 What is the measure at which Scotch Whisky is generally sold across the counter? Since 1 January 1995 Scotch Whisky in the UK, together with gin, vodka and rum, has been sold in licensed premises in measures of either 25ml or 35ml. A notice in the bar must display which of these quantities is being served. Previously, The Weights and Measures Act of 1963 allowed for three standard Imperial measures: one-quarter, one-fifth and one-sixth of a gill, equal respectively to one-and-a-quarter fluid ounces, one fluid ounce and five-sixths fluid ounce. 59 What information must by law be given on the label of a bottle of Scotch Whisky sold in the home market? The liquid measure of the contents, e.g. 70cl, and the strength, e.g. 40% vol, must be stated on the label, together with the name and address of the bottler. From 1 January 2007 spirits must also carry a UK tax mark. 60 Is it injurious to drink whisky with oysters or other shellfish? No. This is an ancient superstition for which there is no foundation. A personal experiment will furnish the proof. 61 What is the difference between Scotch Whisky and gin? Both are potable spirits, but differ in their methods of manufacture and the ingredients used. Their characters, flavour and content of secondary constituents are very different. The spirit base of gin is flavourless. It is first distilled in a Patent Still from a mash of cereals and is then rectified and the juniper and other flavouring materials are added. The rectified spirit may be redistilled with the flavouring materials or these materials may be distilled separately and added to the spirit afterwards. The aroma and flavour of Scotch Whisky are inherent within the spirit itself and depend chiefly on the cereals, water and method of 32 - Scotch Whisky and the Consumer
35 distillation used. The secondary constituents are subsidiary, though important, products of the manufacturing process itself. They are native to the whisky and inseparable from it. Unlike whisky, rectified spirits such as gin and vodka are not matured. They can be consumed immediately and usually reach the consumer in the form in which they left the still and without colour. 62 What is the alcoholic strength of Scotch Whisky? When distilled it is usually reduced for filling into casks at a strength of 63.5 per cent of alcohol by volume. By law the minimum bottling strength is 40 per cent alcohol by volume. In export markets some Scotch Whisky is sold at 43 per cent. 63 What are the usual bottling strengths of other alcoholic drinks? Percentage of aicohol content by volume Cognac, Rum 40 Vodka, Gin 37.5 Fortified wine 20 Champagne 13.1 Table Wines 9 to 13 Beer 3.13 to How should Scotch Whisky be drunk? This depends entirely on your individual taste and on the occasion. Scotch Whisky is a versatile drink, superb in its own right, or as a long mixed drink. Served on its own, or with a little water, it can also be a refreshing drink with ice and a mixer. Scotch Whisky presents a whole range of flavours which can be extended by the addition of soda or mineral water, lemonade, ginger ale or other mixers. Many cocktails contain Scotch Whisky and Section 11 details several examples. Blended Scotch is appreciated as a drink which can be served during a meal in place of wines, while Single Malt Scotch Whisky is popular as an after dinner drink. Scotch Whisky and the Consumer - 33
36 65 Can Scotch Whisky casks be purchased as an investment? The Scotch Whisky Association is unable to offer advice on the purchase or sale of Scotch Whisky, but it is important that potential investors understand the nature and risk of the whisky market before making decisions. While new fillings and matured whisky are sometimes purchased as a form of speculation with the intention of reselling them at a profit, it should be emphasised that only an extremely small proportion of the whisky distilled in Scotland is bought and sold in this way. All the principal blending companies finance their own stocks of whisky, and buy mature whisky only on rare occasions when they happen to find themselves short of a particular type or make. There is no organised Whisky Exchange as exists for other commodities, nor is there any officially recognised list of buying and selling prices for whisky of different types and ages. It should be remembered that, whilst the cask matures in a warehouse, there will be annual storage and insurance charges, and evaporation will reduce the spirit in the cask. Bottling small quantities of whisky can be expensive, and of course there will also be Excise Duty and VAT to pay. Investment for resale is expensive and highly speculateive and should not be entered into lightly. 66 Is there a collectors market for Scotch? Renowned for its quality, and with a wonderful range of whiskies available, it is not surprising that some people have become collectors of bottles of Scotch Whiskies. The Scotch Whisky Association is not in a position to offer advice on the value, purchase or sale of a particular Scotch Whisky. However, one of the best known firms conducting auctions of unusual bottles and other artefacts is McTears t: Scotch Whisky and the Consumer
37 Definitions 8 Definitions 67 What is a single whisky? A single whisky is the product of one particular distillery. 68 What is meant by saccharify? To saccharify means to convert to sugar. In whisky distilling it refers to the process which takes place during the malting and mash tun stages by which enzymes in the malt, referred to as diastase, turn the starch in the cereals into sugar ready for the fermenting action of the yeast. 69 What is diastase? When conditions of temperature and moisture favour germination, the embryo and associated parts of the barley grain secrete a mixture of enzymes commonly known as diastase. These act to modify and make soluble the starch in the barley, thus preparing it for conversion at a later stage to maltose. 70 What is wort? Wort is the liquid drawn off the mash tun in which the malted and unmalted cereals have been mashed with warm water. Wort contains all the sugars of the malt and certain secondary constituents. After cooling, it is passed to the fermenting vats. In Malt distilleries the cereals are all malted; in Grain distilleries a proportion only is malted, the remainder being unmalted. In some cases, Grain distilleries do not separate off wort, passing the complete mash to the fermentation vessels. 71 What is Wash? The wort or mash technically becomes wash as soon as yeast is added to start fermentation. However, the term is usually used to refer to the liquid at the end of the fermentation. It is the wash which forms the raw material of the first distillation in the Pot Still process and of the only distillation in the Patent Still process. Definitions - 35
38 72 What is the Pot Still distillation? Malt Whisky is distilled twice - although a few distilleries may undertake a third distillation - in Pot Stills which resemble huge copper kettles. The spirit is driven off from the fermented liquid as a vapour and then condensed back to a liquid. In the first distillation the fermented liquid, or wash, is put into the Wash Still, which is heated either directly by fire or by steam-heated coils. At this stage the wash contains yeast, crude alcohol, some unfermentable matter and the by-products of fermentation. During the process of boiling the wash, changes take place in its constituents which are vital to the flavour and character of the whisky. As the wash boils, vapours pass up the neck of the still and then pass through a water-cooled condenser or a worm, a coiled copper pipe of decreasing diameter enclosed in a water jacket through which cold water circulates. This condenses the vapours and the resulting distillate, known as low wines, is collected for re-distilling. The liquor remaining in the Wash Still is known as pot ale or burnt ale and is usually treated and converted into distillers solubles for animal feed. The low wines are distilled again in the Spirit Still, similar in appearance and construction to the Wash Still but smaller because the bulk of liquid to be dealt with is less. Three fractions are obtained from the distillation in the Spirit Still. The first is termed foreshots, the second constitutes the potable spirit saved for maturation, and the third is called feints. The foreshots and feints are returned to the process and redistilled in the Spirit Still with the succeeding charge of low wines. The residue in the still, called spent lees, is run to waste. In the case of the Spirit Still, the design of the still, the height of the head (or top) of the still and the angle of the wide-diameter pipe or Iyne arm, connecting the head to the condensing unit, are all very important and have an effect on the distillate. The Pot Still has changed little in general design over the centuries Definitions
39 73 What is Patent Still distillation? Unlike Malt Whisky, Grain Whisky is distilled in a continuous operation in a Patent Still. This is sometimes known as the Coffey Still, after Aeneas Coffey, who developed it in Steam is fed into the base of the analyser and hot wash into the top. As the two meet on the surface of the perforated plates, the wash boils and a mixture of alcohol vapours and uncondensed steam rises to the top of the column. The spent wash runs down and is led off from the base. The hot vapours enter the rectifier at the base and as they rise through the chambers they partially condense on the sections of a long coil through which wash is flowing. The spirit vapour condenses at the top of the rectifier and is run off through a water-cooled condenser to the spirit safe and on to the spirit receiver. Once the spirit begins to be collected it runs continuously until the end of distillation. Because of the rectifying element present in this process the distillate is generally lighter in aroma than most Malt Whiskies. It consequently has a milder character and requires less time to mature. 74 What is the worm? The worm and its surrounding bath of cold running water, or wormtub, form together the condenser unit of the Pot Still process of manufacture. The worm itself is a coiled copper tube of decreasing diameter attached by the Iyne arm to the head of the Pot Still and kept continuously cold by running water. In it the vapours from the still condense. Fed by the still, it in turn feeds the receiving vessel with the condensed distillate. In a number of distilleries the worm has been replaced by the more modern tubular condenser. Definitions - 37
40 75 What are low wines? This is the name given to the product of the first distillation in the Pot Still process of manufacture. It is the distillate derived from the wash and contains all the alcohol and secondary constituents and some water. It forms the raw material of the second distillation, which is carried out in the Spirit Still. The feints and foreshots are added to the low wines when the Spirit Still is charged. 76 What is pot ale? Pot ale, alternatively burnt ale, is the liquor left in the Wash Still after the first distillation in the Pot Still process i.e. it is the residue of the wash after the extraction by distillation of the low wines. 77 What are foreshots? Foreshots is the term applied to the first fraction of the distillate received during the distillation of the low wines in the Spirit Still used in the Pot Still process of manufacture. They form the first raw runnings of this second distillation and their collection is terminated by the judgment of the stillman. The following fraction of the distillate is the potable spirit. The foreshots are returned to the still, together with the feints. 78 What are feints? Feints is the name given to the third fraction of the distillate received from the second distillation in the Pot Still process. They form the undesirable last runnings of the distillation. As noted above, they are returned with the foreshots to the Spirit Still when it is recharged with low wines. The term is also applied to the first and last runnings from the Patent Still, in which process they are returned to the wash for re-distillation. The feints and foreshots from the last distillation of the season are kept for adding to the first low wines of the succeeding season Definitions
41 79 What are spent lees? Spent lees are the residue in the Spirit Still after the distillation of the foreshots, potable spirits, and feints. They are usually treated and run to waste. 80 What is draff? Draff is the spent grain left in the mash tun after the liquor, wort, has been drawn off. It represents, as a rule, about 25 per cent of the malt and unmalted cereals, if any, put into the mash tun. Draff enjoys a large market as cattle food. 81 What are the principal by-products of Scotch Whisky? The liquids and solids remaining after distillation are not wasted, nor are they allowed to pollute rivers or coastlines. In recent years the Scotch Whisky industry has invested heavily in developing methods of treating the residue of distillation so that it now makes an important contribution to the animal foodstuffs industry. Most distilleries now possess by-products plants or, in the case of smaller distilleries in remote areas, send their waste material to the area plants which process it into dark grains. These are extremely rich in protein and are sold in pelletised form to farmers who use them to enrich cattle food. Grain Whisky distilleries usually recover the carbon dioxide produced during the fermentation stage. This has several applications in industry and in the production of soft drinks. 82 What is meant by the term finishing? Scotch Whisky must be matured in oak casks for a minimum of three years. Finishing is an extension of the maturation process, when the spirit is subsequently filled into empty casks that previously held other wines or spirits for a further relatively short period at the end of maturation. Definitions - 39
42 The cask used for finishing must have been drained of any liquid prior to its use and any change in the spirit will therefore result from its interaction over time with the wood of the cask. 83 What is chill filtration? Most consumers around the world want their Scotch Whisky to be clear and bright. However, whisky can become cloudy when cold water or ice is added. Chill filtering - a process which has been used in the industry for many years is used in some brands to remove the solid particles that cause this effect in the whisky and which may lead to unnecessary consumer concern. 84 What is cask-strength whisky? Water is normally added to Scotch Whisky to reduce the alcoholic strength of the spirit to no less than the minimum 40 per cent alcohol by volume before bottling. If the whisky is bottled at the alcoholic strength at which it comes from the cask, without the addition of water, it is known as cask-strength whisky. 85 What is a mothballed distillery? From time to time, companies may decide to temporarily cease production at a specific distillery. The dormant distillery is said to be placed in mothballs and is kept in a condition that would allow production to re-start in the future should it be required. 86 What is meant by Under Bond and Duty Paid sales, respectively? (a) Sales Under Bond are sales on which the Excise Duty has not been paid. The goods are consigned to a bonded duty-free warehouse. (b) Sales Duty Paid are sales on which the Excise Duty has already been paid Definitions
43 Scotch Whisky and the Environment 9 Scotch Whisky and the Environment 87 Can Scotch Whisky be described as a drink from nature? Scotch Whisky is recognised as Scotland s national drink. It is also Scotland s natural drink. The making of Scotch Whisky requires only materials which are provided by nature. Water, yeast and peat, plus barley for Malt Whisky and barley, maize and wheat for making Grain Whisky. The starch extracted from the cereals is mixed with clear pure water, water which has often run through ground made up of granite and peat. Peat also plays its part in the drying of the germinating barley - its smoke imparts flavour to the whisky. The yeast is added to bring about the fermentation. Thus it can be seen that distillers and blenders of Scotch Whisky use their skill to combine materials, which nature has provided, into the world s noblest drink. Scotch Whisky producers jealously guard the quality of their product and the environment which produces the essential ingredients. Most of the water used by the industry is returned to the river system, and the cereal is recycled as animal feed. Innovation has resulted in the industry being able to adopt the use of lightweight glass bottles, and to reduce its packaging needs. A brochure detailing some of the industry's environmental initiatives is available from The Scotch Whisky Association. 88 Are there organic Scotch Whiskies? Scotch Whisky is defined in law and produced from simple natural raw materials - cereals, water and yeast - in accordance with traditional practice. While it is possible to use organic-certified cereals in whisky production, provided the legal definition of Scotch Whisky is complied with, it should be remembered that no protein would carry over the distillation process. Scotch Whisky and the Environment - 41
44 10 Scotch Whisky and Health Scotch Whisky and Health 89 Is alcohol good for health? Scotch Whisky is a craft product made by longstanding traditional processes that have come to underpin its quality reputation. As a drink created only after years of maturation, Scotch is a drink to be sipped and savoured; to be enjoyed responsibly. Enjoyed responsibly, alcohol encourages social interaction and relaxation. Research has also shown moderate alcohol consumption may confer health benefits for some people, for example protection from cardiovascular heart disease and against certain forms of stroke. Conversely, the industry recognises misuse of alcohol can damage health in a number of ways, including increased risk of liver disease and heart problems, and may cause domestic and financial problems. Some people for health reasons should not drink at all. In addition, alcohol should be avoided before driving a car or operating machinery. Anyone with questions or concerns about the health implications of consuming alcoholic drinks should contact their doctor. 90 Can whisky be consumed as part of a gluten-free diet? Since malted barley and other cereals are used to make Scotch Whisky, it is not surprising those who suffer from Coeliac disease query whether whisky can be safely included in a gluten-free diet. Proteins (including gluten), however, do not carry over the distillation process and are not present in the final product. Scotch can therefore be safely consumed as part of a gluten free diet. Those wishing further information should consult the Coeliac Society ( 91 A standard measure of Scotch Whisky contains 55 calories. Scotch contains no fat and no added carbohydrates (although there may be a very small carbohydrate level depending on the type of cask used and length of maturation) Scotch Whisky and Health
45 92 What can be done to prevent the misuse of alcohol? Everyone has a role to play in making responsible drinking choices. Better awareness of what is safe to drink on a daily basis assists consumers make informed responsible decisions. The industry believes the best way of preventing misuse of alcohol is by education in sensible and moderate drinking and that this education should start at an early age. Attempts to reduce alcohol related problems by imposing massive taxes on drink or introducing restrictions on its sale and availability only penalise the great majority who drink sensibly, without reaching the problem drinker, and create additional problems. 93 How does the Scotch Whisky industry help in prevention? Scotch Whisky distillers are involved in a wide range of initiatives to encourage responsible enjoyment of their brands, including the use of unit labelling, responsibility messages on bottles and in adverts, and server training. The industry has also developed its own Code of Practice setting out minimum standards for the marketing and promotion of Scotch Whisky brands in the UK. Covering all commercial communications, including advertising, promotional materials, sponsorship, and websites, the Code also has international reach setting out best practice for Scotch Whisky producers in export markets, where stricter national codes do not exist. A brochure highlighting industry efforts to promote responsible alcohol consumption, and the Code of Practice for the Responsible Marketing and Promotion of Scotch Whisky, is available from The Scotch Whisky Association. Scotch Whisky and Health - 43
46 11 Drinks made with Scotch Whisky Atholl Brose Mix an equal quantity of honey (preferably heather honey) and fine oatmeal in a little cold water. Add the Scotch and stir until frothy. Bottle and keep for two days before serving. 50cl of whisky will be needed for 200g of honey and 200g of oatmeal. Auld Alliance Shake together: 25ml measure of Scotch Whisky juice of half a lemon 15ml of Cointreau a dash of sugar syrup ice Pour into a highball glass, top with lemonade Bitter n Twisted In a chilled cocktail glass mix: 25ml measure of Scotch Whisky a few drops of lemon juice 4 drops of Angostura bitters ginger ale to top up Bobby Burns 25ml measure of Scotch Whisky 25ml Sweet Vermouth 1 1 / 4 tsp Benedictine twist of Lemon Peel ice Stir all the ingredients with ice and strain into a cocktail glass. Add a twist of lemon peel Drinks made with Scotch Whisky
47 In a cocktail shaker combine, shake and serve: 25ml measure of Scotch Whisky juice of half a lemon juice of one orange ice Citrus Twist 25ml measure of Scotch Whisky dash of Sambucca black coffee whipped cream Clansman's Coffee Wipe the rim of a goblet with a piece of lemon and dip it in brown sugar. Pour the spirits and coffee into the glass, add sugar to taste and float the whipped cream on top. Decorate with grated chocolate. 25ml measure of Scotch Whisky 1 measure of Creme de Menthe juice of a quarter of a lemon Green Mist Shake to ingredients, strain into a cocktail glass. Decorate with a slice of kiwi fruit and a sprig of mint. 25ml measure of Scotch Whisky 5-6 dashes lemon juice sugar syrup soda Pour into a large glass and fill with soda. Jock Collins Drinks made with Scotch Whisky - 45
48 Red Scotch Shake together: 25ml measure of Scotch Whisky tomato juice juice of half a lemon dash of Worcester sauce dash of Tabasco sauce pinch of salt Fill a glass with ice and pour the mixture over and decorate with freshly ground black pepper Rob Roy 25ml measure of Scotch Whisky small measure (5-10ml) Sweet Vermouth dash of Angostura Bitters garnish with cherry Mix all ingredients with ice. Stir and strain into a chilled cocktail glass. Scotch Paradise Moisten the edge of a highball glass with sugar syrup. Roll the glass in desiccated coconut to coat the outer edge. Fill a cocktail shaker with ice and add: a large (50ml) measure of Scotch Whisky a dash of coconut syrup top with milk (enough to fill the glass) Shake well and pour into the glass 46 - Drinks made with Scotch Whisky
49 Scotch Whisky Toddy Place a spoonful of sugar in a warm glass and add enough boiling water to dissolve the sugar and hot lemon juice. Add a generous measure of Scotch and stir with a silver spoon; pour in more boiling water and top up with more whisky. Stir well. Whisky Mac Scotch and green-ginger wine to taste. They may be in equal proportions or two-thirds whisky and one-third green ginger wine. Whisky Royale 25ml measure of Scotch Whisky dash of Apple Schnapps (or clear apple juice) ginger ale sliced green apple crushed ice Half fill a chilled champagne flute with crushed ice. Pour in the Scotch Whisky and then the Apple Schnapps. Top up with Ginger Ale. Place a slice of green apple into the drink. Whisky Sour To a double Scotch add the juice of half a lemon and half a teaspoonful of sugar. Shake with ice and serve with a squirt of soda water. Drinks made with Scotch Whisky - 47
50 12 Information about Scotch Whisky Information About Scotch Whisky Publications Scotch Whisky - Questions and Answers - Also available in French, German, Italian and Spanish. (Mandarin being considered) The World of Scotch Whisky - A coloured map of Scotland showing the location of distilleries and with information on the different categories of Scotch Whisky. Distilleries to Visit - Identifying distilleries which welcome visitors. Forbidden Fruits - Scotch Whisky Cocktails that dare to be different. Mix Scotch and fruit juice or milk, the results are delicious. Statistical Review - A digest of industry statistics. Factsheets - Giving information on industry issues. Scotch at a Glance - A leaflet showing top export markets and quirky facts. Matured to be Enjoyed Responsibily - A summary of industry initiatives that encourage responsible drinking, and discourage misuse of alcohol. Code of Practice for the Responsible Marketing and Promotion of Scotch Whisky - Code governing the activities of SWA members. Scotch Whisky - the original sustainable industry - Detailing some of the industry's environmental initiatives. Films Available on short loan or for sale. Spirit of Scotland - Selected video or CD (10 minutes). A documentary film of the Scotch Whisky industry, available in English, French, Japanese and Spanish. Colour Slide Sets Twenty two 35 mm colour slides illustrating the distilling and blending process. Also available on CD. Available on short loan or for sale. The above can be obtained from The Scotch Whisky Association 48 - Information about Scotch Whisky
51 Unless stated, references are to question numbers not to pages Index 13 Index A Age of whisky, minimum required for consumer sale in UK... 5, 27, 42 - best label on blended whisky...26, 51 Alcohol - good for health in moderation...89 Alcoholism - can damage health education to prevent SWA initiatives to prevent...93 Alcoholic strengths of various liquors...63 Analyser (Patent Still)...73 Aqua vitae early references...12 Aroma... 5, 16, 49, 61 B Barley - effect on whisky making malting use in distilling...14 Bar measure of Scotch Whisky...58 Beer strength...63 Blend 'best'...47 Blended Scotch Whisky, see whiskies Blended Blending - individual character introduction malt/grain whisky ratio in number of whiskies in blend process...14, 22 - purpose sense of smeli in...49 Bond meaning...86 Bonded Warehouse...45, 86 Bottle common size (home) storing whisky unchanged in...52, 53 Bottling - process strength of Scotch Whisky at...62 Bouquet and warming...56 Bourbon Whiskey, different from Scotch Whisky...9 Brands, best differentiation by nose number...46 Brazil, whisky produced in...21 Brightness of Scotch Whisky...83 Butt...40 By-products...14, 81 C Calories...91 Campbelltown Malt Whisky...15 Canadian Whisky, different from Scotch spelling...8 Casks, effect on maturation impart colour to Scotch Whisky sizes...40 Cask strength...84 Cereals...14 Champagne, strength...63 Chill filtration, description...83 Climate, Scottish, importance in maturing...16 Code of Practice for Responsible Marketing...93 Coeliac disease...90 Coffey Still...14, 73 See also Patent Still Cognac, strength...63 Collectors' Market...66 Colour of Scotch Whisky, cause...14 Consumption of Scotch Whisky - comparison with exports in Scotland, compared with rest of UK...29 Cor, Friar John...12 Customs Duty See Duty D Dark grains...81 Definitions of Scotch Whisky...1, 5 De luxe blended whisky...25 Diastase... 14, 68, 69 Distillation description by Patent Still...14, 73 - by Pot Still...14, 72 - strength of Scotch Whisky at...62 Distilleries, number visiting...19 Distillery, mothballed...85 Draff...80 Index - 49
52 Unless stated, references are to question numbers not to pages Drinks made with Scotch Whisky...p44-47 Drying of green-malt...14 Duty, comparison between rate on Scotch Whisky and on other alcoholic drinks history of charging...13, 44 - per bottle of Scotch Whisky...13 Duty-free...45 Duty Paid sales E Environment...87 Enzyme, diastase... 14, 68, 69 European Spirit Drinks Regulation...5 Exchequer Rolls Excise Duty, See 'Duty' Exports importance of Scotch Whisky proportion to home sales markets strength of Scotch Whisky to EU Member States...32 F Feints...75, 78 Ferintosh distillery...12 Fermentation, description...14 Finishing, description...82 Flavour of Scotch Whisky, etc , 16, 48, 61 Foreshots... 14, 75, 77 Fortified wine, strength...63 G Gaelic...11 Gill...58 Gin, contrasted with Scotch Whisky strength...63 Glass, best shape for Scotch Whisky...57 Gluten-free...90 Grain Whisky, See Whisky, Grain Green-malt...14 Grinding of dried malt...14 Grist...14 H Health, Scotch Whisky and...89 Highland Malt Whisky, See also 'Whisky, Malt'...15 Hogshead...40 Home market - compared with exports Scotland compared to UK...29 Hydrometer...37 I Ice in whisky...55, 64 International Organisation of Legal Metrology (OIML)...35 Inverness, James IV buys aqua-vitae at...12 Investment...65 Irish Whiskey, different from Scotch Whisky spelling...8 Islay Malt Whisky...15 J James IV, King, buys aqua-vitae at Inverness...12 K Kiln for drying green-malt...14 L Label, age...26, 51 - information...59 Legal definition...5 Low Wines definition...75 Lowland Malt Whisky...15 Lyne Arm...74 M Maize...81 Malt Whisky, See whiskies, Malt Malting, description...14 Manufacture of Scotch Whisky - description earliest reference...12 Marrying of whiskies...22 Mash tun...14, 68, 70, 80 Mashing of ground malt (grist)...14 Materials for manufacture...14, 81 Maturation, beyond legal minimum... 14, 42, Index
53 Unless stated, references are to question numbers not to pages - climatic factor description legal requirements... 5, 26, 27, 42 - strength of Scotch Whisky after...62 McTears...66 Measure of whisky, in bar in bottle (UK)...41, 59 Minimum age of Scotch Whisky... 5, 27, 42, 51 Mothballed distillery...85 N Nature...87 Nip, See 'Measure' O Octave...40 Organic Scotch Whisky...88 Oysters and Whisky...60 P Parliament, Scottish, Act of Patent Still... 9, 15, 73 Patent Still Whisky, See 'whiskies, Grain' Peat, imparts flavour... 14, 16, 81 - use...14, 81 Pot Ale, definition...76 Pot Still...14, 72 Pot Still Whisky, See 'whiskies, Malt' Potable spirit production...14 Price, high retail, reason for...43 Proof Spirit, definition methods of testing for proof strength...37 Proof, US, compared with British and European strengths...39 Publications...p48 Q Quarter Casks...40 R Recipes of Scotch Whisky drinks...p44-47 Rectification...61, 73 Responsible Marketing - Code of Practice...93 Rum, strength...63 Rye Whiskey, different from Scotch Whisky...9 S Saccharify, definition...10, 68 Sales, see Consumption - Duty Paid, definition 'Under Bond definition...86 Scotch, blended see whiskies Blended Scotch, geographical significance... 5, 16, 20, 21 Scotch Whisky, See Whisky, Scotch Scotch Whisky Act...5 Scotch Whisky Association, The...19, 50, 65, 66, 87, 93, p3, p48 Scotlandwhisky.com...19 Secondary constituents in whisky...16, 61 Shellfish and whisky...60 Ship s Stores, duty-free...45 Sikes, Bartholomew and hydrometer...35, 37 Single Whiskies... 4, 6, 22, 67 Smoky flavour of Scotch Whisky...48 Spain, Whisky made in...21 Spent Lees, definition...79 Speyside Malt Whisky...15 Spirit, Proof, definition...36 Spirits, definition...10 Spirit Still...14, 72 Starch, modified in malting...14 Steeps...14 Stocks of Scotch Whisky...33, 34 Strength of Scotch Whisky at different stages of manufacture cask strength comparison with US proof comparison with other alcoholic liquors for export method for measurement...35, 36 - minimum strength in UK...5, 38 - regulations and stated strength unchanged in bottle...52, 53 Sugar, produced in malting and mashing... 14, 68 T Tax see 'Duty' Temperature for serving Scotch Whisky...55 Types of Scotch Whisky...15 Index - 51
54 Unless stated, references are to question numbers not to pages U Uisge beatha or usquebaugh...11 Under Bond sales, meaning...86 USA - Rye and Bourbon made in...9 Usher, Andrew ways of drinking world s leading drink...2 Wines, strengths...63 Worm, description...14, 74 Wort, definition production...14 V Value Added Tax...13, 43, 44, 65 Visiting a Distillery...19 Vodka, strength...63 Y Yeast...14, 87 W Wash, changes in...14, 72 - definition production...14 Wash Still...14, 72 See also 'Pot Still Washback...14 Water, importance of quality in distilling... 14, 16, 17 Whiskey, Irish...8, 9 See also Irish - spelling...8 Whisky origin of name aroma... 5, 16, 61 - by-products characteristic flavour... 15, 48, 61 - difference between Scotch Whisky and other whiskies Blended... 3, 6, 7, 13, 22 - Grain (or Patent Still)... 4, 6, 14, 73 - Malt (or Pot Still)... 4, 6, 14, 72 - manufacture described...72, 73 - percentage in blends range of variety of flavours, etc... 15, 16, 17 - single...4, 67 - spelling...8 Whisky, Scotch categories definition...1, 5 - differences from gin different from other whiskies...9, 15 - does not change in bottle...52, 53 - first distilled main types organic Index
55 Did you know? Scotch Whisky accounts for more than 23% of UK food and drink exports. Scotch Whisky is sold in 200 markets worldwide. Scotch Whisky sells nearly four times its nearest rival whisky. Scotch Whisky uses some 410,000 tonnes of barley and about 510,000 tonnes of other cereals each year. 10% of Scottish agriculture jobs depend upon the industry. 1 in 50 Scottish jobs rely on the Scotch Whisky industry. Some 18.5 million casks lie maturing in warehouses in Scotland. To be Scotch Whisky, the spirit must mature in oak casks in Scotland for at least 3 years. Greeks drink more Scotch Whisky per person than any other country. More Scotch is sold in one month in France than Cognac in a year. There are five categories of Scotch Whisky: Single Malt Scotch Whisky, Single Grain Scotch Whisky, Blended Scotch Whisky (a mix of malt and grain whiskies), Blended Malt Scotch Whisky and Blended Grain Scotch Whisky. Drinkers in the UK often choose to enjoy it with just a little water, but in Spain they mix it with cola, in Japan Scotch is enjoyed with lots of water and ice, and in China with cold green tea. Scotch Whisky also goes well with food, including smoked salmon, beef and especially chocolate desserts. 20 Atholl Crescent, Edinburgh EH3 8HF t: f: e: [email protected] w: scotch-whisky.org.uk 14 Cork Street, London W1S 3NS t: f: e: [email protected]
Questions & Answers. www.scotch-whisky.org.uk
 Questions & Answers www.scotch-whisky.org.uk The World of Scotch Whisky Contents Introduction 2-3 The World s Leading Drink 4-7 The History of Scotch Whisky 8-9 Making Scotch Whisky 10-15 The Importance
Questions & Answers www.scotch-whisky.org.uk The World of Scotch Whisky Contents Introduction 2-3 The World s Leading Drink 4-7 The History of Scotch Whisky 8-9 Making Scotch Whisky 10-15 The Importance
An Introduction to Whisky English (B1 B2)
 An Introduction to Whisky English (B1 B2) www.celangue.com Barley, water & a whole lot of goodness The words highlighted in red are very important for your whisky vocabulary. If you look at any bottle
An Introduction to Whisky English (B1 B2) www.celangue.com Barley, water & a whole lot of goodness The words highlighted in red are very important for your whisky vocabulary. If you look at any bottle
Questions & Answers. www.scotch-whisky.org.uk
 Questions & Answers www.scotch-whisky.org.uk SWA Q+A Booklet.indd 1 30/09/2013 10:05 The World of Scotch Whisky SPEYSIDE HIGHLAND ISLAY LOWLAND CAMPBELTOWN SWA Q+A Booklet.indd 2 30/09/2013 10:05 Contents
Questions & Answers www.scotch-whisky.org.uk SWA Q+A Booklet.indd 1 30/09/2013 10:05 The World of Scotch Whisky SPEYSIDE HIGHLAND ISLAY LOWLAND CAMPBELTOWN SWA Q+A Booklet.indd 2 30/09/2013 10:05 Contents
History of Whisky Production. By: Lyric Kilpatrick
 History of Whisky Production By: Lyric Kilpatrick Whiskey and Whisky Whisky is known to be called the water of life because they believed it was a cure and medicine from the herbs it had been made out
History of Whisky Production By: Lyric Kilpatrick Whiskey and Whisky Whisky is known to be called the water of life because they believed it was a cure and medicine from the herbs it had been made out
Scotch Whisky Training Seminar
 Scotch Whisky Training Seminar Legal Definition of Scotch Distilled and aged in Scotland for a minimum of three years, in oak barrels and bottled at a minimum of 40% alcohol Single Malt must also be bottled
Scotch Whisky Training Seminar Legal Definition of Scotch Distilled and aged in Scotland for a minimum of three years, in oak barrels and bottled at a minimum of 40% alcohol Single Malt must also be bottled
Contents. 03 Who we are 04 What we do 07 Product 10 Quality 13 Innovation 14 Global reach
 Private Label Contents 03 Who we are 04 What we do 07 Product 10 Quality 13 Innovation 14 Global reach Who we are Welcome to the Private Label division of the Whyte & Mackay Group. The Whyte & Mackay Group,
Private Label Contents 03 Who we are 04 What we do 07 Product 10 Quality 13 Innovation 14 Global reach Who we are Welcome to the Private Label division of the Whyte & Mackay Group. The Whyte & Mackay Group,
David Wishart Research Fellow School of Management University of St Andrews
 The New Scotch Whisky Regulations Case Study for Feni Thursday September 24 th, 2009 David Wishart Research Fellow School of Management University of St Andrews The Scotch Whisky Association sends Warmest
The New Scotch Whisky Regulations Case Study for Feni Thursday September 24 th, 2009 David Wishart Research Fellow School of Management University of St Andrews The Scotch Whisky Association sends Warmest
SOME NOTES ON WHISKEY FLAVOUR by Dave Quinn, Master of Whiskey Science at Midleton Distillery
 SOME NOTES ON WHISKEY FLAVOUR by Dave Quinn, Master of Whiskey Science at Midleton Distillery Ultimately, it s the wonderful flavour of Single Pot Still whiskey from Midleton Distillery that makes it all
SOME NOTES ON WHISKEY FLAVOUR by Dave Quinn, Master of Whiskey Science at Midleton Distillery Ultimately, it s the wonderful flavour of Single Pot Still whiskey from Midleton Distillery that makes it all
Cask Type Approximate Capacity Price
 Cask Offer 2015 The Distillery The Isle of Arran Distillery opened in 1995 at Lochranza, on the north-west tip of the island, where the perfect elements for making single malt were discovered. Although
Cask Offer 2015 The Distillery The Isle of Arran Distillery opened in 1995 at Lochranza, on the north-west tip of the island, where the perfect elements for making single malt were discovered. Although
A guide to Scotch Whisky
 A guide to Scotch Whisky Legal Definition of Scotch Distilled and aged in Scotland for a minimum of three years, in oak barrels and bottled at a minimum of 40% alcohol Single Malt must also be bottled
A guide to Scotch Whisky Legal Definition of Scotch Distilled and aged in Scotland for a minimum of three years, in oak barrels and bottled at a minimum of 40% alcohol Single Malt must also be bottled
Waldviertler Roggenhof is Austria's First Whisky Distillery (established in 1995).
 Whisky-Erlebniswelt 1. Austrian whiskydistillery Waldviertler Roggenhof is Austria's First Whisky Distillery (established in 1995). In 1990, Johann Haider III took over farming operations from his parents.
Whisky-Erlebniswelt 1. Austrian whiskydistillery Waldviertler Roggenhof is Austria's First Whisky Distillery (established in 1995). In 1990, Johann Haider III took over farming operations from his parents.
NATIONAL AGENCY FOR FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION AND CONTROL ACT 1993 (AS AMENDED) Spirit Drinks Regulations 2005. Commencement:
 S. I. of 2005 NATIONAL AGENCY FOR FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION AND CONTROL ACT 1993 (AS AMENDED) Spirit Drinks Regulations 2005 Commencement: In exercise of the powers conferred on the Governing Council
S. I. of 2005 NATIONAL AGENCY FOR FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION AND CONTROL ACT 1993 (AS AMENDED) Spirit Drinks Regulations 2005 Commencement: In exercise of the powers conferred on the Governing Council
TECHNICAL FILE SETTING OUT THE SPECIFICATIONS WITH WHICH IRISH WHISKEY/UISCE BEATHA EIREANNACH/IRISH WHISKY MUST COMPLY
 TECHNICAL FILE SETTING OUT THE SPECIFICATIONS WITH WHICH IRISH WHISKEY/UISCE BEATHA EIREANNACH/IRISH WHISKY MUST COMPLY Food Industry Development Division Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine
TECHNICAL FILE SETTING OUT THE SPECIFICATIONS WITH WHICH IRISH WHISKEY/UISCE BEATHA EIREANNACH/IRISH WHISKY MUST COMPLY Food Industry Development Division Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine
A guide to one of life s little joys: Scotch whisky
 A guide to one of life s little joys: Scotch whisky Picture the scene: a few months ago I m at Soho House eating a sandwich with the crusts expertly sliced off, wearing an ill-fitting and un-ironed shirt,
A guide to one of life s little joys: Scotch whisky Picture the scene: a few months ago I m at Soho House eating a sandwich with the crusts expertly sliced off, wearing an ill-fitting and un-ironed shirt,
Resource efficiency in the UK whisky sector
 Case Study: UK Drinks Sector Resource efficiency in the UK whisky sector Reducing water, material and packaging use in the whisky sector. Resource efficiency in the UK whisky sector 2 WRAP s vision is
Case Study: UK Drinks Sector Resource efficiency in the UK whisky sector Reducing water, material and packaging use in the whisky sector. Resource efficiency in the UK whisky sector 2 WRAP s vision is
The Bushmills distillery was gutted in 1885 in a fire, BuT was rebuilt soon.
 Did you know that Irish monks were known to have brought distilling to the country as far back as 1000 AD! Step into the Bushmills distillery, Northern Ireland, the oldest distillery in the world. Text
Did you know that Irish monks were known to have brought distilling to the country as far back as 1000 AD! Step into the Bushmills distillery, Northern Ireland, the oldest distillery in the world. Text
HAZARDS AND RELATED ISSUES IN THE WHISKY DISTILLATION INDUSTRY
 HAZARDS AND RELATED ISSUES IN THE WHISKY DISTILLATION INDUSTRY Clive Timms Strathayr, Rhu-Na-Haven Road, Aboyne, Aberdeenshire, AB34 5JB; e-mail: [email protected] The very traditional methods
HAZARDS AND RELATED ISSUES IN THE WHISKY DISTILLATION INDUSTRY Clive Timms Strathayr, Rhu-Na-Haven Road, Aboyne, Aberdeenshire, AB34 5JB; e-mail: [email protected] The very traditional methods
Adding water to Single Malt Whisky
 Adding water to Single Malt Whisky Single Malt Scotch Whisky is a truly unique spirit. Its infinite complexity of flavours and aromas deserve to be appreciated. Speyside Professional tasters and whisky
Adding water to Single Malt Whisky Single Malt Scotch Whisky is a truly unique spirit. Its infinite complexity of flavours and aromas deserve to be appreciated. Speyside Professional tasters and whisky
BOX DISTILLERY ÅDALEN SWEDEN NORDIC PASSION FOR THE ART OF WHISKY
 BOX DISTILLERY ÅDALEN SWEDEN NORDIC PASSION FOR THE ART OF WHISKY A POETIC MEETING IN THE WORLD OF WHISKY OUR STORY BEGINS HERE LIKE EVERY GOOD STORY, ours begins in a place far, far away. More precisely
BOX DISTILLERY ÅDALEN SWEDEN NORDIC PASSION FOR THE ART OF WHISKY A POETIC MEETING IN THE WORLD OF WHISKY OUR STORY BEGINS HERE LIKE EVERY GOOD STORY, ours begins in a place far, far away. More precisely
Session of 2015. HOUSE BILL No. 2332. By Committee on Federal and State Affairs 2-12
 Session of 0 HOUSE BILL No. By Committee on Federal and State Affairs - 0 0 AN ACT concerning alcoholic beverages; relating to microbreweries; permitting the manufacture and sale of hard cider and mead;
Session of 0 HOUSE BILL No. By Committee on Federal and State Affairs - 0 0 AN ACT concerning alcoholic beverages; relating to microbreweries; permitting the manufacture and sale of hard cider and mead;
3/97 Food And Agricultural Industry 9.12.3-1
 9.12.3 Distilled Spirits 9.12.3.1 General 1-2 The distilled spirits industry includes the production of whisky, gin, vodka, rum, and brandy. The production of brandy is discussed in AP-42 Section 9.12.2,
9.12.3 Distilled Spirits 9.12.3.1 General 1-2 The distilled spirits industry includes the production of whisky, gin, vodka, rum, and brandy. The production of brandy is discussed in AP-42 Section 9.12.2,
(Refill Bourbon Hogshead)
 Aberlour (Bourbon- / Sherry-casks) Brennerei 10 y 40,0 % 0,05 l 4,50 Speyside 90,00 Amrut peated Amrut o.a. 46,0 % 0,05 l 5,00 Indien 100,00 Amrut peated & cask strength Amrut o.a. 62,8 % 0,05 l 6,50 Indien
Aberlour (Bourbon- / Sherry-casks) Brennerei 10 y 40,0 % 0,05 l 4,50 Speyside 90,00 Amrut peated Amrut o.a. 46,0 % 0,05 l 5,00 Indien 100,00 Amrut peated & cask strength Amrut o.a. 62,8 % 0,05 l 6,50 Indien
WHISKY, WHISKEY & BOURBON. whisky. noun noun: whiskey 1.a spirit distilled from malted grain, especially barley or rye.
 WHISKY, WHISKEY & BOURBON whisky noun noun: whiskey 1.a spirit distilled from malted grain, especially barley or rye. 1 Page 3- Scotland- History Page 4- Scotland- History Continued & Selection Page 5-
WHISKY, WHISKEY & BOURBON whisky noun noun: whiskey 1.a spirit distilled from malted grain, especially barley or rye. 1 Page 3- Scotland- History Page 4- Scotland- History Continued & Selection Page 5-
Making Scotch: Engineering, Chemistry, and Education JR Collier 1, SA Morton III 1, 2, TB Rogers 1, 4, BJ Collier 3, J McEwan 5, M.
 1 Making Scotch: Engineering, Chemistry, and Education JR Collier 1, SA Morton III 1, 2, TB Rogers 1, 4, BJ Collier 3, J McEwan 5, M. Reynier 5 1 Chemical Engineering Department 3 Materials Science and
1 Making Scotch: Engineering, Chemistry, and Education JR Collier 1, SA Morton III 1, 2, TB Rogers 1, 4, BJ Collier 3, J McEwan 5, M. Reynier 5 1 Chemical Engineering Department 3 Materials Science and
Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs TECHNICAL FILE FOR SCOTCH WHISKY
 Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs TECHNICAL FILE FOR SCOTCH WHISKY Date of receipt (DD/MM/YYYY): [to be completed by the Commission] Number of pages (including this page): 26 Language
Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs TECHNICAL FILE FOR SCOTCH WHISKY Date of receipt (DD/MM/YYYY): [to be completed by the Commission] Number of pages (including this page): 26 Language
The Scotch Whisky Regulations 2009
 Scotch Whisky Association The Scotch Whisky Regulations 2009 2/12/2009 Guidance for Producers and Bottlers The Scotch Whisky Regulations 2009 (SWR) came into force on 23 November 2009*. They replaced the
Scotch Whisky Association The Scotch Whisky Regulations 2009 2/12/2009 Guidance for Producers and Bottlers The Scotch Whisky Regulations 2009 (SWR) came into force on 23 November 2009*. They replaced the
Single Malt Scotch. Single Malt Scotch is made in Scotland and
 Single Malt Scotch Single Malt Scotch is made in Scotland and sometimes s in America, c, Canada and Ireland. It is produced only from 100% malted barley, which has been aged a minimum of three years. Single
Single Malt Scotch Single Malt Scotch is made in Scotland and sometimes s in America, c, Canada and Ireland. It is produced only from 100% malted barley, which has been aged a minimum of three years. Single
The Alcoholic Beverage Menu continued
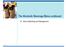 The Alcoholic Beverage Menu continued Menu Marketing and Management OH 5-1 Alcoholic Beverages Are Part of the Dining Experience Many customers enjoy an alcoholic beverage with their food. Food and alcoholic
The Alcoholic Beverage Menu continued Menu Marketing and Management OH 5-1 Alcoholic Beverages Are Part of the Dining Experience Many customers enjoy an alcoholic beverage with their food. Food and alcoholic
Top tips for running the perfect Single Malt Whisky evening
 Top tips for running the perfect Single Malt Whisky evening Share your whisky passion Here at the Classic Malts, we believe that Single Malt Scotch Whisky is something to be shared amongst Friends. Whether
Top tips for running the perfect Single Malt Whisky evening Share your whisky passion Here at the Classic Malts, we believe that Single Malt Scotch Whisky is something to be shared amongst Friends. Whether
Alcoholic Drinks, Measures & Units. United Kingdom
 Alcoholic Drinks, Measures & Units in the United Kingdom Frank Tapson An account of the different sorts and sizes of measures used in connection with alcoholic drinks and the relationships between them
Alcoholic Drinks, Measures & Units in the United Kingdom Frank Tapson An account of the different sorts and sizes of measures used in connection with alcoholic drinks and the relationships between them
Whiskey from Moldova. Too much of anything is bad, but too much good whiskey is barely enough. Mark Twain
 Whiskey from Moldova Too much of anything is bad, but too much good whiskey is barely enough. Mark Twain About us Joint Stock Company "ENTEH" formed in 1994, but on the market of alcoholic beverages it
Whiskey from Moldova Too much of anything is bad, but too much good whiskey is barely enough. Mark Twain About us Joint Stock Company "ENTEH" formed in 1994, but on the market of alcoholic beverages it
MATURED IN OAK BEER CASKS THAT ARE UP TO 120 YEARS OLD
 MATURED IN OAK BEER CASKS THAT ARE UP TO 120 YEARS OLD Special products have a unique history. Whisky from over 120-year-old oak casks. The Locher brewery is steeped in history and tradition, and has been
MATURED IN OAK BEER CASKS THAT ARE UP TO 120 YEARS OLD Special products have a unique history. Whisky from over 120-year-old oak casks. The Locher brewery is steeped in history and tradition, and has been
Maturation casks where up to 16 years of chemistry takes place. Chemistry World December 2008 41. www.chemistryworld.org MACDUFF EVERTON / CORBIS
 A whisky tour Is this the most chemically complicated drink in the world? Victoria Gill attempts to unlock some of the mysteries of Scotch malt whisky JUPITER IMAGES 40 Chemistry World December 2008 When
A whisky tour Is this the most chemically complicated drink in the world? Victoria Gill attempts to unlock some of the mysteries of Scotch malt whisky JUPITER IMAGES 40 Chemistry World December 2008 When
GILLMAN PROFESSIONAL CORPORATION
 GILLMAN PROFESSIONAL CORPORATION Canadian Barristers & Solicitors Special Regulatory Report: Canadian Whisky, Its History, Taste, Legal Regulation Introduction Gary M. Gillman* What is Canadian whisky?
GILLMAN PROFESSIONAL CORPORATION Canadian Barristers & Solicitors Special Regulatory Report: Canadian Whisky, Its History, Taste, Legal Regulation Introduction Gary M. Gillman* What is Canadian whisky?
Welcome to Lark distillery
 Welcome to Lark distillery W It occurred to Bill and Lyn Lark in the mid 1980s that Tasmania was ideally situated to make malt whisky, and yet no one was doing it. Tasmania grows some of the world s best
Welcome to Lark distillery W It occurred to Bill and Lyn Lark in the mid 1980s that Tasmania was ideally situated to make malt whisky, and yet no one was doing it. Tasmania grows some of the world s best
A Scotch Whisky Primer
 This article was originally published online at www.nicks.com.au ARDBEG Voted World s Best Whisky 2008 & 2009 by Jim Murray s Whisky Bible. A Scotch Whisky Primer What is Scotch Whisky? Today, Scotch whisky
This article was originally published online at www.nicks.com.au ARDBEG Voted World s Best Whisky 2008 & 2009 by Jim Murray s Whisky Bible. A Scotch Whisky Primer What is Scotch Whisky? Today, Scotch whisky
2009 No. 2890 FOOD. The Scotch Whisky Regulations 2009
 STATUTORY INSTRUMENTS 2009 No. 2890 FOOD The Scotch Whisky Regulations 2009 Made - - - - 26th October 2009 Laid before Parliament 30th October 2009 Coming into force - - 23rd November 2009 CONTENTS 1.
STATUTORY INSTRUMENTS 2009 No. 2890 FOOD The Scotch Whisky Regulations 2009 Made - - - - 26th October 2009 Laid before Parliament 30th October 2009 Coming into force - - 23rd November 2009 CONTENTS 1.
Irish Whiskies. Tullamore Dew: Blended to produce 80 proof. Medium amber hue with a fruity nose. Light on the tongue and a medium long finish.
 Irish Whiskies Irish Whisky is made with a mixture of malted and unmalted barley and in some cases oats, wheat and rye may be added. They are distilled 3 times and do not use any peat. The aging is the
Irish Whiskies Irish Whisky is made with a mixture of malted and unmalted barley and in some cases oats, wheat and rye may be added. They are distilled 3 times and do not use any peat. The aging is the
Contribution of the Scotch Whisky Industry to the Scottish Economy
 Contribution of the Scotch Whisky Industry to the Scottish Economy Graeme Blackett November 2012 BiGGAR Economics Graeme Blackett mobile: 07890 998147 Email: [email protected] CONTENTS Page
Contribution of the Scotch Whisky Industry to the Scottish Economy Graeme Blackett November 2012 BiGGAR Economics Graeme Blackett mobile: 07890 998147 Email: [email protected] CONTENTS Page
Founded in 1824, The Macallan was one of the first distilleries in Scotland to be legally licensed. Since then, The Macallan has built a reputation
 Founded in 1824, The Macallan was one of the first distilleries in Scotland to be legally licensed. Since then, The Macallan has built a reputation as one of the world's truly great single malt whiskies.
Founded in 1824, The Macallan was one of the first distilleries in Scotland to be legally licensed. Since then, The Macallan has built a reputation as one of the world's truly great single malt whiskies.
SCOTTISH GOVERNMENT SPENDING REVIEW AND WHITE PAPER ON LEGAL AID REFORM
 CIVIL LEGAL AID EFFICIENCY SAVINGS PROPOSALS INTRODUCTION Following the publication of the Scottish Government Spending Review and the White Paper, A Sustainable Future for Legal Aid, the Society s civil
CIVIL LEGAL AID EFFICIENCY SAVINGS PROPOSALS INTRODUCTION Following the publication of the Scottish Government Spending Review and the White Paper, A Sustainable Future for Legal Aid, the Society s civil
Distilling: How Spirits are Made
 Distilling: How Spirits are Made Aims and learning outcomes This chapter aims to provide the knowledge and skills to understand how distilled spirits are made. On completion the learner should be able
Distilling: How Spirits are Made Aims and learning outcomes This chapter aims to provide the knowledge and skills to understand how distilled spirits are made. On completion the learner should be able
The Vermont Statutes Online
 1 of 5 7/20/2009 4:09 PM The Vermont Statutes Online Title 7: Alcoholic Beverages Chapter 1: General Provisions 2. Definitions 2. Definitions The following words as used in this title, unless a contrary
1 of 5 7/20/2009 4:09 PM The Vermont Statutes Online Title 7: Alcoholic Beverages Chapter 1: General Provisions 2. Definitions 2. Definitions The following words as used in this title, unless a contrary
CHAPTER 1 MANDATORY LABEL INFORMATION
 CHAPTER 1 MANDATORY LABEL INFORMATION 1. BRAND NAME GENERAL FEATURES Usually, the most prominent piece of on the label Name under which a distilled spirits or line of distilled spirits is marketed NOTE:
CHAPTER 1 MANDATORY LABEL INFORMATION 1. BRAND NAME GENERAL FEATURES Usually, the most prominent piece of on the label Name under which a distilled spirits or line of distilled spirits is marketed NOTE:
Wine and drinks lists
 Wine and drinks lists 10 Units covered This chapter covers the following units: Level 1 Prepare and clear areas for drink service (1BS2, 113) Serve drinks (1BS2) Level 2 Principles of beverage product
Wine and drinks lists 10 Units covered This chapter covers the following units: Level 1 Prepare and clear areas for drink service (1BS2, 113) Serve drinks (1BS2) Level 2 Principles of beverage product
Alcohol Units. A brief guide
 Alcohol Units A brief guide 1 2 Alcohol Units A brief guide Units of alcohol explained As typical glass sizes have grown and popular drinks have increased in strength over the years, the old rule of thumb
Alcohol Units A brief guide 1 2 Alcohol Units A brief guide Units of alcohol explained As typical glass sizes have grown and popular drinks have increased in strength over the years, the old rule of thumb
The Wine and Spirits Market in Asia-Pacific and Worldwide with Prospects Until 2017
 The Wine and Spirits Market in Asia-Pacific and Worldwide with Prospects Until 2017 From the VINEXPO* market study For the 12 th consecutive year, VINEXPO the international wine and spirits exhibition
The Wine and Spirits Market in Asia-Pacific and Worldwide with Prospects Until 2017 From the VINEXPO* market study For the 12 th consecutive year, VINEXPO the international wine and spirits exhibition
(1) The following shall not be considered unlawful gifts, loans of money or property, or rebates:
 61A-1.010 Approved Advertising and Promotional Gifts. (1) The following shall not be considered unlawful gifts, loans of money or property, or rebates: DESCRIPTION SPECIAL CONDITIONS RESTRICTIONS Wine
61A-1.010 Approved Advertising and Promotional Gifts. (1) The following shall not be considered unlawful gifts, loans of money or property, or rebates: DESCRIPTION SPECIAL CONDITIONS RESTRICTIONS Wine
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. Anaerobic Digestion and Resource Use within the Scotch Whisky & UK Beer Industries
 Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Anaerobic Digestion and Resource Use within the Scotch Whisky & UK Beer Industries Author: Scott Meadows Supervisor: Paul Strachan A thesis submitted
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Anaerobic Digestion and Resource Use within the Scotch Whisky & UK Beer Industries Author: Scott Meadows Supervisor: Paul Strachan A thesis submitted
Scotland. in the red. A research report prepared by StepChange Debt Charity
 Scotland in the red A research report prepared by StepChange Debt Charity Contents Introduction & key findings 1. Home nation debts 1.1 Debt by volume 2. The debt problem in Scotland 2.1 Average incomes
Scotland in the red A research report prepared by StepChange Debt Charity Contents Introduction & key findings 1. Home nation debts 1.1 Debt by volume 2. The debt problem in Scotland 2.1 Average incomes
Control and sale of alcoholic beverages, for the year ending March 31, 2013 Released at 8:30 a.m. Eastern time in The Daily, Thursday, April 10, 2014
 Control and sale of alcoholic beverages, for the year ending March 31, 2013 Released at 8:30 a.m. Eastern time in The Daily, Thursday, April 10, 2014 Beer and liquor stores and agencies sold $21.4 billion
Control and sale of alcoholic beverages, for the year ending March 31, 2013 Released at 8:30 a.m. Eastern time in The Daily, Thursday, April 10, 2014 Beer and liquor stores and agencies sold $21.4 billion
ALCOHOLIC DRINKS INDUSTRY GUIDE
 ALCOHOLIC DRINKS INDUSTRY GUIDE Updated 10 th July 2012 Directories Harpers Wine & Spirit Directory 2012 (Harper Trade Journals Ltd, 2012) [(B) DIR 663.1029441] Comprehensive listing of wine and spirit
ALCOHOLIC DRINKS INDUSTRY GUIDE Updated 10 th July 2012 Directories Harpers Wine & Spirit Directory 2012 (Harper Trade Journals Ltd, 2012) [(B) DIR 663.1029441] Comprehensive listing of wine and spirit
The Legal Guide To Establishing A Brewery In Massachusetts
 The Legal Guide To Establishing A Brewery In Massachusetts Law Offices of John P. Connell, P.C 112 Water Street, Suite 201 Boston, MA 02109 www.connelllawoffices.com @ConnellLaw The Application Process
The Legal Guide To Establishing A Brewery In Massachusetts Law Offices of John P. Connell, P.C 112 Water Street, Suite 201 Boston, MA 02109 www.connelllawoffices.com @ConnellLaw The Application Process
Control and sale of alcoholic beverages, for the year ending March 31, 2012 Released at 8:30 a.m. Eastern time in The Daily, Thursday, April 11, 2013
 Control and sale of alcoholic beverages, for the year ending March 31, 2012 Released at 8:30 a.m. Eastern time in The Daily, Thursday, April 11, 2013 Beer and liquor stores and agencies sold $20.9 billion
Control and sale of alcoholic beverages, for the year ending March 31, 2012 Released at 8:30 a.m. Eastern time in The Daily, Thursday, April 11, 2013 Beer and liquor stores and agencies sold $20.9 billion
Effective at Retail November 1, 2015
 Prepared by LCBO Financial Planning & Analysis LCBO Pricing Examples Spirits Wine Page Whiskey 1 Brandy 2 Spirits 3 Spirits - Licensee 4 Low Alcohol Spirits 5 Table Wines 6 Table Wines at LCBO versus WRS
Prepared by LCBO Financial Planning & Analysis LCBO Pricing Examples Spirits Wine Page Whiskey 1 Brandy 2 Spirits 3 Spirits - Licensee 4 Low Alcohol Spirits 5 Table Wines 6 Table Wines at LCBO versus WRS
A Beginner's Guide to Beer Making
 A Beginner's Guide to Beer Making By the Staff of Maryland Home Brew, Inc. You may share this document for non-commercial purposes, provided you cite the source as A Beginner s Guide to Beer Making 2010
A Beginner's Guide to Beer Making By the Staff of Maryland Home Brew, Inc. You may share this document for non-commercial purposes, provided you cite the source as A Beginner s Guide to Beer Making 2010
PART III. LICENSES AND PERMITS, GENERAL PROVISIONS 281-31 Licenses, classes. (a) Licenses may be granted by the liquor commission as provided in this
 PART III. LICENSES AND PERMITS, GENERAL PROVISIONS 281-31 Licenses, classes. (a) Licenses may be granted by the liquor commission as provided in this section. (b) Class 1. Manufacturers licenses. A license
PART III. LICENSES AND PERMITS, GENERAL PROVISIONS 281-31 Licenses, classes. (a) Licenses may be granted by the liquor commission as provided in this section. (b) Class 1. Manufacturers licenses. A license
9-1 CASE STUDY. Wine Horizons. Case Study 1
 Case Study 1 CASE STUDY was a medium-sized New York State winery that emphasized sparkling wines. The company was not known to the public as a producer of good-quality domestic champagne because all of
Case Study 1 CASE STUDY was a medium-sized New York State winery that emphasized sparkling wines. The company was not known to the public as a producer of good-quality domestic champagne because all of
Financial Scrutiny Unit Briefing Earnings in Scotland 2014
 The Scottish Parliament and Scottish Parliament Infor mation C entre l ogos. Financial Scrutiny Unit Briefing Earnings in Scotland 2014 Andrew Aiton 15 December 2014 The Office for National Statistics
The Scottish Parliament and Scottish Parliament Infor mation C entre l ogos. Financial Scrutiny Unit Briefing Earnings in Scotland 2014 Andrew Aiton 15 December 2014 The Office for National Statistics
Beer Day Britain Britain's Annual National Beer Day June 15th
 1 Beer Day Britain Britain's Annual National Beer Day June 15th Contents: Background to Beer Day Britain.Page 3 What is the intention of Beer Day Britain?...Page 5 How does Beer Day Britain work?...page
1 Beer Day Britain Britain's Annual National Beer Day June 15th Contents: Background to Beer Day Britain.Page 3 What is the intention of Beer Day Britain?...Page 5 How does Beer Day Britain work?...page
Sales Purchases Stock Prices Cost changes Incorrect stocktake Product sales mix Efficient purchasing Shrinkage/pilferage
 Bar A club s bar is a main source of income and needs to generate profit. It does carry big responsibilities and needs to be well run to ensure maximum benefit to members. Principal Responsibility The
Bar A club s bar is a main source of income and needs to generate profit. It does carry big responsibilities and needs to be well run to ensure maximum benefit to members. Principal Responsibility The
Lagavulin Feis Programme. Lagavulin Feis Open Day - Saturday 21 st May 2016
 Lagavulin Feis Programme Please read thoroughly the notes section at the end of the programme before making any Lagavulin Feis Open Day - Saturday 21 st May 2016 Our very special Lagavulin Islay Festival
Lagavulin Feis Programme Please read thoroughly the notes section at the end of the programme before making any Lagavulin Feis Open Day - Saturday 21 st May 2016 Our very special Lagavulin Islay Festival
Distillery Design: Producing Vodka and Other Spirits
 Distillery Design: Producing Vodka and Other Spirits A Major Qualifying Project submitted to the Faculty of Worcester Polytechnic Institute in partial fulfillment of the requirements for a Bachelor of
Distillery Design: Producing Vodka and Other Spirits A Major Qualifying Project submitted to the Faculty of Worcester Polytechnic Institute in partial fulfillment of the requirements for a Bachelor of
Necessary equipment. - Food grade fermenter or bucket with airtight lid - Airlock - Syphon tube - Bottles or a pressure barrel (keg) with S30 valve
 Necessary equipment - Food grade fermenter or bucket with airtight lid - Airlock - Syphon tube - Bottles or a pressure barrel (keg) with S30 valve A fermenter/bucket with lots of headspace is best, 27L
Necessary equipment - Food grade fermenter or bucket with airtight lid - Airlock - Syphon tube - Bottles or a pressure barrel (keg) with S30 valve A fermenter/bucket with lots of headspace is best, 27L
NHS Scotland Accident and Emergency Waiting Times
 NHS Scotland Accident and Emergency Waiting Times The Scottish Government target for Accident and Emergency departments is that 98 % of all attendances are seen within 4 hours. The figures presented here
NHS Scotland Accident and Emergency Waiting Times The Scottish Government target for Accident and Emergency departments is that 98 % of all attendances are seen within 4 hours. The figures presented here
The Water of Life. For queries please contact your Executive Edge Travel & Events consultant (61) 3 9519 7777
 Edinburgh city skyline The Water of Life A luxury chauffeur driven trip, taken over 8 days showcasing the spectacular scenery of Scotland with visits to our Classic Collection of Distilleries. Designed
Edinburgh city skyline The Water of Life A luxury chauffeur driven trip, taken over 8 days showcasing the spectacular scenery of Scotland with visits to our Classic Collection of Distilleries. Designed
Global Supply. 17 November 2011
 Global Supply 17 November 2011 David Gosnell President, Global Supply and Procurement Supply goals: Enhancing margin and enabling growth Competitive advantage in cost will deliver gross margin expansion
Global Supply 17 November 2011 David Gosnell President, Global Supply and Procurement Supply goals: Enhancing margin and enabling growth Competitive advantage in cost will deliver gross margin expansion
The State of Canada s Processed Food Sector: Trade Balance
 Understanding the Processed Food Trade Balance The State of Canada s Processed Food Sector: Trade Balance November 2012 Report prepared by Douglas Hedley, PhD, and the Canadian Agri-Food Policy Institute
Understanding the Processed Food Trade Balance The State of Canada s Processed Food Sector: Trade Balance November 2012 Report prepared by Douglas Hedley, PhD, and the Canadian Agri-Food Policy Institute
2. Definitions Alcohol Alcohol Management Plan Alcohol-related harm - Amenity and good order of the locality Authorised customer Authorised visitor
 MACKENZIE, TIMARU AND WAIMATE DISTRICT COUNCILS JOINT LOCAL ALCOHOL POLICY 1. Background This Local Alcohol Policy (LAP) has been developed jointly by the Mackenzie, Timaru and Waimate District Councils.
MACKENZIE, TIMARU AND WAIMATE DISTRICT COUNCILS JOINT LOCAL ALCOHOL POLICY 1. Background This Local Alcohol Policy (LAP) has been developed jointly by the Mackenzie, Timaru and Waimate District Councils.
EDICT ± OF GOVERNMENT
 EDICT ± OF GOVERNMENT Inordertopromotepubliceducationandpublicsafety,equal justiceforal,abeterinformedcitizenry,theruleoflaw,world tradeandworldpeace,thislegaldocumentisherebymade availableonanoncommercialbasis,asitistherightofal
EDICT ± OF GOVERNMENT Inordertopromotepubliceducationandpublicsafety,equal justiceforal,abeterinformedcitizenry,theruleoflaw,world tradeandworldpeace,thislegaldocumentisherebymade availableonanoncommercialbasis,asitistherightofal
Estimating alcohol consumption from survey data: updated method of converting volumes to units
 National Statistics Methodological Series No. 37 Estimating alcohol consumption from survey data: updated of converting volumes to units Eileen Goddard December 2007 Office for National Statistics Government
National Statistics Methodological Series No. 37 Estimating alcohol consumption from survey data: updated of converting volumes to units Eileen Goddard December 2007 Office for National Statistics Government
SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the properties of water. LAB: Experimenting with different soap mixtures. POST: Analyzing
SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the properties of water. LAB: Experimenting with different soap mixtures. POST: Analyzing
Spirited Returns. How to Invest in Rare and Collectible Scotch Whisky. By Mark S. Smith, Editorial Director
 Spirited Returns How to Invest in Rare and Collectible Scotch Whisky By Mark S. Smith, Editorial Director As a reporter for a national U.K. newspaper in Scotland a few years ago, I was sent on a 200-mile
Spirited Returns How to Invest in Rare and Collectible Scotch Whisky By Mark S. Smith, Editorial Director As a reporter for a national U.K. newspaper in Scotland a few years ago, I was sent on a 200-mile
How To Sell Wine In The Uk
 CBI Market channels and s for wine in the United kingdom Your trade route through the European market Wine trade in the United Kingdom (UK) is dominated by supermarkets, which increasingly sell private
CBI Market channels and s for wine in the United kingdom Your trade route through the European market Wine trade in the United Kingdom (UK) is dominated by supermarkets, which increasingly sell private
EC 691 January 1996 HACCP AND MICROBREWERIES PRACTICAL GUIDELINES OF FOOD SAFETY FOR MICROBREWERIES, BREWPUBS AND THE BEER INDUSTRY
 EC 691 January 1996 HACCP AND MICROBREWERIES PRACTICAL GUIDELINES OF FOOD SAFETY FOR MICROBREWERIES, BREWPUBS AND THE BEER INDUSTRY TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Purpose of this publication... 3 II. Introduction...
EC 691 January 1996 HACCP AND MICROBREWERIES PRACTICAL GUIDELINES OF FOOD SAFETY FOR MICROBREWERIES, BREWPUBS AND THE BEER INDUSTRY TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Purpose of this publication... 3 II. Introduction...
AUSTRALIAN GOVERNMENT PRODUCTIVITY COMMISSION. Economic Structure and Performance of the Australian Retail Industry
 AUSTRALIAN GOVERNMENT PRODUCTIVITY COMMISSION Economic Structure and Performance of the Australian Retail Industry Bicycle Industries Australia Ltd Suite 324, 1 Queens Road Melbourne VIC 3004 Bicycle Industries
AUSTRALIAN GOVERNMENT PRODUCTIVITY COMMISSION Economic Structure and Performance of the Australian Retail Industry Bicycle Industries Australia Ltd Suite 324, 1 Queens Road Melbourne VIC 3004 Bicycle Industries
WINERY RETAIL STORE INFORMATION GUIDE
 Alcohol and Gaming Commission of Ontario Licensing and Registration 90 SHEPPARD AVENUE EAST SUITE 200 TORONTO ON M2N 0A4 416 326-8700 or 1 800 522-2876 toll free in Ontario WINERY RETAIL STORE INFORMATION
Alcohol and Gaming Commission of Ontario Licensing and Registration 90 SHEPPARD AVENUE EAST SUITE 200 TORONTO ON M2N 0A4 416 326-8700 or 1 800 522-2876 toll free in Ontario WINERY RETAIL STORE INFORMATION
Stockholm 2013. www.symposionhot.com
 S O R T I M E N T S L I S T A Stockholm 2013 www.symposionhot.com SORTIMENTSLISTA % Smakprov Artikelnr Pris SB Blended whisky Cadenhead Creations 20 Years Old, Cadenhead 46% 50 kr / 2 cl 87905 875 kr Compass
S O R T I M E N T S L I S T A Stockholm 2013 www.symposionhot.com SORTIMENTSLISTA % Smakprov Artikelnr Pris SB Blended whisky Cadenhead Creations 20 Years Old, Cadenhead 46% 50 kr / 2 cl 87905 875 kr Compass
Food Law and Due Diligence Defence
 The Society of Food Hygiene and Technology INTRODUCTION This document explains the general requirements of food law and covers the main EC and UK legislation on food imports and exports, safety, traceability,
The Society of Food Hygiene and Technology INTRODUCTION This document explains the general requirements of food law and covers the main EC and UK legislation on food imports and exports, safety, traceability,
on Alcohol Doses, Measurements, and Blood Alcohol Levels
 Indiana Prevention Resource Center on Alcohol Doses, Measurements, and Blood Alcohol Levels by William J. Bailey, M.P.H. The punch line to an often told joke suggests that the reason medical journals use
Indiana Prevention Resource Center on Alcohol Doses, Measurements, and Blood Alcohol Levels by William J. Bailey, M.P.H. The punch line to an often told joke suggests that the reason medical journals use
High-performance steam boiler and hot water boiler plants for industry
 High-performance steam boiler and hot water boiler plants for industry Information 2/3 HKB leading manufacturer of industrial boiler plants in Europe and Asia Steam boilers with outputs up to 120 t/h and
High-performance steam boiler and hot water boiler plants for industry Information 2/3 HKB leading manufacturer of industrial boiler plants in Europe and Asia Steam boilers with outputs up to 120 t/h and
Guide to Cereals. in the UK
 Guide to Cereals in the UK 1 WHEAT Wheat is the most widely grown arable crop in the UK. On average, it covers around 2 million hectares of land and produces about 15 million tonnes of wheat each year
Guide to Cereals in the UK 1 WHEAT Wheat is the most widely grown arable crop in the UK. On average, it covers around 2 million hectares of land and produces about 15 million tonnes of wheat each year
A pint sized history of alcohol
 A pint sized history of alcohol Cultures change. How can we be part of it? 1. There is evidence of alcohol use for many thousands of years Going all the way back to ancient China, there are wine jars dating
A pint sized history of alcohol Cultures change. How can we be part of it? 1. There is evidence of alcohol use for many thousands of years Going all the way back to ancient China, there are wine jars dating
Changing Tastes The UK Soft Drinks Annual Report 2015
 Changing Tastes The UK Soft Drinks Annual Report 2015 Changing tastes The number of consumers switching to low, no and mid calorie drinks in 2014 speaks volumes for industry s efforts to meet changing
Changing Tastes The UK Soft Drinks Annual Report 2015 Changing tastes The number of consumers switching to low, no and mid calorie drinks in 2014 speaks volumes for industry s efforts to meet changing
Employee Handbook of the Royal College of Physicians of Ireland. RCPI Policy Group on Alcohol. 2014 Pre Budget Submission
 Employee Handbook of the Royal College of Physicians of Ireland RCPI Policy Group on Alcohol 2014 Pre Budget Submission September 2013 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Recommendations... 5 3. Effect of
Employee Handbook of the Royal College of Physicians of Ireland RCPI Policy Group on Alcohol 2014 Pre Budget Submission September 2013 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Recommendations... 5 3. Effect of
Retail Prices of Whiskies in the USA, European Union and Switzerland
 Retail Prices of Whiskies in the USA, European Union and Switzerland Whisky is one the best selling spirits in the world. During these last years, there has been a change in the attitude of the consumer
Retail Prices of Whiskies in the USA, European Union and Switzerland Whisky is one the best selling spirits in the world. During these last years, there has been a change in the attitude of the consumer
PRISLISTA - Stockholm Beer & Whisky Festival 2007
 PRISLISTA - Stockholm Beer & Whisky Festival 2007 The Grand Bark Reserve "VM-guld 2004-2007" 40% 20 kronor inkl. chokladtryffel The Grand Bark 21 Years Old 40% 80 kronor Avonside 8 Years Old De Luxe 40%
PRISLISTA - Stockholm Beer & Whisky Festival 2007 The Grand Bark Reserve "VM-guld 2004-2007" 40% 20 kronor inkl. chokladtryffel The Grand Bark 21 Years Old 40% 80 kronor Avonside 8 Years Old De Luxe 40%
GOVERNMENT EXPENDITURE & REVENUE SCOTLAND 2013-14 MARCH 2015
 GOVERNMENT EXPENDITURE & REVENUE SCOTLAND 2013-14 MARCH 2015 GOVERNMENT EXPENDITURE & REVENUE SCOTLAND 2013-14 MARCH 2015 The Scottish Government, Edinburgh 2015 Crown copyright 2015 This publication is
GOVERNMENT EXPENDITURE & REVENUE SCOTLAND 2013-14 MARCH 2015 GOVERNMENT EXPENDITURE & REVENUE SCOTLAND 2013-14 MARCH 2015 The Scottish Government, Edinburgh 2015 Crown copyright 2015 This publication is
2.5 Monetary policy: Interest rates
 2.5 Monetary policy: Interest rates Learning Outcomes Describe the role of central banks as regulators of commercial banks and bankers to governments. Explain that central banks are usually made responsible
2.5 Monetary policy: Interest rates Learning Outcomes Describe the role of central banks as regulators of commercial banks and bankers to governments. Explain that central banks are usually made responsible
