dlsoft Barcodes for Office By dlsoft
|
|
|
- Tyrone Cameron
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 dlsoft Barcodes for Office By dlsoft
2 This manual was produced using ComponentOne Doc-To-Help.
3 Contents Barcodes for Office 1 Introduction... 1 Font or Picture or Object... 2 Licensing of Barcodes & Labels for Office components... 4 Using with CreateObject D Barcodes... 6 Embedded Objects... 6 Inserting a dbarcode image into a document... 6 The Active-X controls Active barcodes in Word Active Barcodes in Excel Active Barcodes in Access Barcode Macros Initialising the Macros Barcode Macros for Word Installation for Word 2007/2010/ Using the macros in Word Customisation of the Word macros Mail-merge Barcode Macros for Excel Installation for Excel Copying to another workbook for Excel 2007/2010/ Making the macros available to all new workbooks Using the macros in Excel Customisation of the Excel macros In-cell Barcode() formula for Excel Barcode macros for Access Installation in your own database Using the macros in Access Customisation of the Access macros Advanced barcode options Barcode Pictures and PBarcodeSetup Barcode Fonts and FBarcodeSetup Programming properties Data Structure Sample coding Function calls Structure members Barcode Types Table D Barcodes Embedded 2D barcode objects Active-X 2D controls D Barcode Macros Barcode 2D Macros for Word Installation for Word 2007/2010/ Using the 2D macros in Word dlsoft Barcodes for Office Contents iii
4 Customisation of the Word macros Mail-merge Barcode 2D Macros for Excel Installation for Excel Copying to another workbook for Excel Making the macros available to all new workbooks Using the macros in Excel Customisation of the Excel macros In-cell Barcode2D() formula for Excel Barcode 2D Macros for Access Installation in Access Copying to another database Using the 2D macros in Access Customisation of the Access macros Advanced barcode options Barcode Pictures and PBarcode2DSetup Barcode Fonts and FBarcode2DSetup Programming D Barcode Types Table Index 81 iv Contents dlsoft Barcodes for Office
5 Barcodes for Office Introduction Barcodes for Office is designed to enable the user to create barcodes easily within the Office products Word, Excel and Access. Barcodes for Office provides three basic methods for placing barcodes on Office documents: 1. Inserting an Object a barcode image 2. Placing an barcode Active-X control on the document 3. Using a macro to generate either a barcode image or a font-based barcode (a string of text which must be displayed in the appropriate barcode font to appear as a barcode). The Active-X control and the macros function by calling a library, known as the dbarcode DLL. The Barcodes for Office Setup program copies the dbarcode DLL to your Windows System32 directory, and places the macro containing files and templates in a samples directory of your choice. Setup also installs the standard versions of the barcode fonts in the fonts subdirectory of your installation directory. The product also includes OLE server which enables barcode images to be embedded in any Office document using the Insert Object method. Barcodes for Office is available in three versions. The full version includes both 1D and 2D barcodes, so two dbarcode DLLs and two OLE servers are installed. The OLE servers provide objects identified as dbarcode Image - for 1D barcodes dbarcode2d Image for 2D barcodes and the Active-X controls are Active Barcode Control for 1D barcodes Active-2D Barcode Control for 2D barcodes. Barcodes for Office 1D version includes only the components for 1D barcodes, while Barcodes for Office 2D version includes only the components for 2D barcodes. The barcode macros are provided in source code form within sample documents to allow for easy customisation. Consequently they are not signed macros and we recommend that the macros you wish to use are copied to your own templates or projects to avoid prompting for permission to enable macros. The macros permit the creation of either barcode images or font-based barcodes. The product also includes an in-cell formula module for Excel, allowing font-based barcode to be created using an in-cell formula. The barcode fonts for 1D barcodes are UNA, UNB, UNC, UND and UNE, which are for common barcode types (such as Code 128, Code 39, etc.), and UNF which is for certain postal barcodes (such as RM4SCC and 4-State). The Wide variants (eg. UNAW) should be used in most cases, although Reduced, Narrow and Thin variants (UNAR, UNAN and UNAT) are provided for printing technologies that result in ink spread. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 1
6 For 2D barcodes the fonts are AZT (for Aztec, Datamatrix and QR Code symbols) and PD2, PD3, PD4, and PD5 (for PDF471 symbols, the number referring to the height;width ratio of each element in the symbol). Again these are provided in W, R, N and T variants. This release includes samples for Office 2007/2010/2013 for Word, Excel and Access. The samples are installed into your chosen Samples directory. Samples in the Office 2007 subdirectory are suitable for 32 bit versions of Office , while those in the Office subdirectory are for 64 bit versions of Office 2010 and Font or Picture or Object Barcodes for Office can generate barcodes either as objects, pictures, or as strings of text which are then displayed/printed in a special font made up of bars and spaces. It is recommended that you give some consideration to the technique that most suits your needs by studying the following section. Embedded Objects (eg. dbarcode.image objects) have the advantage that they are easy to create and the Office document may be sent to another Office user who does not have the dlsoft product and they can still see/print the barcode. On the other hand you may not want to create thousands of barcodes that way. Barcode pictures created using the Active-X control are ideal for dynamically changing data, the images can be viewed or printed by any Office user, but can only be edited by a user who has the dlsoft product. The Macros provide efficient methods of creating either picture barcodes or font-based barcodes, and pictures can be embedded in say a spreadsheet or database so can be passed to others, although at the price of a larger file size. Documents created using Office 2007 or later may have font-based barcodes embedded for transmission to another Office user without requiring that user to have the barcode fonts installed. Separate macros are provided for generating barcodes in these different forms: FBarcode and FBarcode2D macros generate font-based barcodes PBarcode and PBarcode2D macros generate picture barcodes. Active Barcode Control Object macros and the control objects themselves generate pictures that can be changed dynamically. These three types are provided because each has advantages and disadvantages. It is essential for the user to understand which type is most appropriate for a particular application. Picture barcodes provide barcode symbols that are the cosmetically appealing and can include within the picture the "human-readable text" that often appears under common barcodes. Also the pictures once created within a document, spreadsheet or database are part of the document and may be easily passed to another computer where they can be viewed or printed. On the other hand pictures use memory, so a large spreadsheet containing thousands of barcode pictures will have a much larger file size than the spreadsheet without pictures. Finally the mail-merge facility provided by Word is a text-based system and cannot use barcode pictures. Font-based barcodes on the other hand take up no more file space than text and are suitable for use with mail-merge. However, font-based barcodes are not always as cosmetically appealing as pictures (for example, the characteristic elongated outer bars of retail barcodes are not reproduced by the font-based system), and the human-readable text is not included, so you may need to include it. Finally font-based barcodes require the presence of the font on the system that displays or prints the barcode so documents with barcodes created on one system and sent to another system can only be viewed and printed if the receiving system has Barcodes for Office installed. Active Control barcodes allow the barcode data to be modified dynamically and so are ideal for placing on an Access form or report and have all the cosmetic advantages of picture barcodes, but the disadvantage that the control must be present on the system that displays or prints the reports. Users should note that different barcode types require different text as the source of the barcode. Thus EAN/UPC barcodes can only be used for numbers - and a specific number of digits at that. Code 39 supports only numbers and upper case letters, while extended Code 39 supports both upper and lower case letters. (See the Barcodes Help for 2 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
7 details). So just selecting text at random will often result in a message box informing you that there is an illegal character in the barcode source. Note that, when using font-based barcodes, clocked barcodes (eg. Postnet or RM4SCC) must be created using the UNF font and using the recommended font heights which are: Australia Post point Korean PA point PostNet/Planet 18 point RM4SCC point dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 3
8 Licensing of Barcodes & Labels for Office components The Barcodes for Office and the associated barcode libraries are supplied licensed for use on a specific number of computers. You must ensure that you have the required number of licences for the computers onto which you are installing the product. Licences for Barcodes & Labels for Office are available as a single computer product or as a multi-user version for installation on up to 10 PCs. The following licence types are available: Barcodes & Labels for Office - Full version (supports 1D & 2D barcodes) Barcodes & Labels for Office - 1D version (supports only 1D barcodes) Barcodes & Labels for Office - 2D version (supports only 2D barcodes) Barcode pictures (and documents containing the pictures) created with the macros may be distributed without restriction and do not require the presence of any Barcodes for Office component to be viewed or printed. Font-based barcodes require the presence of the font on the PC that will display or view the barcodes. However, multiuser versions of the barcode fonts contain embedding licences and so the fonts may be embedded into Word documents and Acrobat pdf files, so that the document may be viewed or printed on a PC that does not have the font installed. If you intend to redistribute any of the Barcodes for Office components, or their associated library files or fonts then you must obtain a royalty-free redistribution licence version of the Barcode library and associated fonts. These are available within the developer s version of the dlsoft dbarcode 1D Developer Kit or dbarcode 2D Developer Kit. Users and developers may freely edit the macros, but the required licences still apply to the use of the dbarcode library files which the macros call and the associated fonts. Using with CreateObject While the components can be embedded or added to applications at design-time (as described in the sections that follow) they may also be created at run-time using CreateObject. A simple example of code is shown here for a VB6 application consisting of a form containing a PictureBox: Public abc As Object Private Sub Form_Load() Set abc = CreateObject("DLS2D4.A2barcodeCtrl.7") abc.codetype = 4 abc.xunit = 20 abc.caption = "Hello World" Picture1.Picture = abc.picture End Sub When the form loads the abc object is created, some of its properties are specified, then the resulting barcode picture is placed in the PictureBox Picture1. The string in the CreateObject function is the Class name of the component. For the 1D component the class name is abcdl7.control While for the 2D component it is 4 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
9 DLS2D4.A2barcodeCtrl.7 Objects created this way may have their properties set in code or by providing a call to one of the components methods, such as Abc.ShowProps dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 5
10 1D Barcodes Barcodes for Office (2D) does NOT include 1D barcodes. The 1D and full versions of Barcodes for Office product include facilities to create 1D barcodes easily within the Office products Word, Excel and Access. The remainder of this section details the methods available for incorporating 1D barcodes into Office documents. Many of the methods have close parallels when 2D barcodes are used. Embedded Objects One of the simplest ways of placing a barcode in an Office document is to embed an object which is an image of the barcode. This has the advantage that the document can be passed to another Office user and the barcode image will be available to that user without requiring any additional software. Barcodes for Office includes the dbarcode OLE server that can embed such objects. A 1D barcode object created by dbarcode is known as a dbarcode.image, while a 2D one is known as a dbarcode2d.image. The discussion below will use the 1D image as an example. Inserting a dbarcode image into a document To insert a dbarcode image into any OLE application, simply position the cursor at the point where the barcode is required, select the Insert ribbon and click on Object in the ribbon. The Object type dialog appears, showing a list of the types of object available for insertion. Select dbarcode Image from the list of available type by clicking on it with the mouse pointer, and then push the OK button. 6 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
11 An image of dbarcode's default barcode appears within the document at the insertion point and surrounded by an outline frame. At the same time application's menu and Toolbar (if visible) change to reflect the editing facilities provided by dbarcode. [Note some installations will immediately open a full dbarcode editing window.] The actual menus displayed by a client application will depend on the application, but in all cases a replacement EDIT menu becomes available containing only the items: Copy - which copies the image to the clipboard Barcode Properties - which summons the Barcode settings dialog Barcode Font - which summons the Font properties dialog Load barcode which summons dbarcode's File Open dialog to load a barcode configuration from a named file Save defaults - which saves the current configuration as the default configuration (used when a new image is created). The Toolbar contains dbarcode's Code Style and Font buttons just as in the stand-alone application. Once editing (described below) is completed, simply clicking on the document anywhere outside the barcode image will return the standard application display with the dbarcode image no longer surrounded by a frame. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 7
12 Editing of the dbarcode image may be accomplished by either double clicking on the image - whereupon the application s menus and Toolbar are replaced by dbarcode's as described above, or by selecting the barcode, then rightclicking on it and choosing the Edit option from the dbarcode Image Object menu that pops up. Selecting Barcode Properties from the Edit menu opens the Barcode options dialog: 8 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
13 The dbarcode options dialog allows all properties of the barcode to be specified, and pushing the OK button results in the display of the edited barcode. Again clicking anywhere on the document outside the barcode image will return the standard application display with the dbarcode image no longer surrounded by a frame. As mentioned above the Embedded Object is the simplest way to place a barcode into any Office application; but there are many other ways, including macros and Active-X controls, so read on. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 9
14 The Active-X controls. Active-X controls in Word and Excel require the use of the Developer Ribbon which is hidden by default. In Word 2007 or Excel 2007 you can make the Developer ribbon visible by selecting the Office icon, choosing Word Options/Excel Options, and in the Popular pane checking the checkbox labelled Show Developer tab in the Ribbon. For Office 2010/2013 choose Options from the File menu, select Customise ribbon, and check the Developer checkbox in the right-hand pane. Active barcodes in Word An Active Barcode Control may be placed on a Word document by selecting the Controls toolbox on the Developer ribbon. When the Control toolbox is displayed select More controls from the Active-X Controls section (the bottom-right icon). This opens the More Controls dialog which lists the available Active-X controls. Select Active Barcode Control and push the OK button [or double-click on the Active Barcode Control entry]. 10 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
15 A default barcode image is placed on the document. The properties of the barcode may be modified in either of two ways, both of which involve selecting the barcode and this can only be done in Design Mode, so if clicking on it once does not result in the image being selected, select the Design Mode icon on the Developer ribbon and try again. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 11
16 Once selected, right click on the selected barcode and choose Active Barcode Control Object from the pop-up menu displayed. A submenu appears. Select Properties from this menu and the Active Barcode Control Properties dialog is displayed; this allows all features of the barcode to be specified. Alternatively you can use Word s Properties box by right-clicking on the image and selecting Properties from the pop-up menu. This results in the display of Word s Properties dialog for the control where, again, all properties may be specified. 12 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
17 The sample Word document ActiveDemo2007.doc also contains two demonstration macros that enable the content of the barcode to be set. The axbar1 macro pops-up a dialog request the barcode data, while the axbar2 macro takes data from the current selection text in the document. Active Barcodes in Excel An Active Barcode Control may be placed on an Excel spreadsheet by selecting the Insert on the Developer ribbon. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 13
18 When the Control toolbox is displayed select More controls from the Active-X Controls section (the bottom-right icon). This opens the More Controls dialog which lists the available Active-X controls. 14 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
19 Select Active Barcode Control and push the OK button [or double-click on the Active Barcode Control entry]. A default barcode image is placed on the document. The properties of the barcode may be modified in either of two ways, both of which involve selecting the barcode and this can only be done in Design Mode, so if clicking on it once does not result in the image being selected, select the Design Mode icon on the Developer ribbon and try again. Once selected, right click on the selected barcode and choose Active Barcode Control Object from the pop-up menu displayed. A submenu appears. Select Properties from this menu and the Active Barcode Control Properties dialog is displayed; this allows all features of the barcode to be specified. Alternatively you can use Excel s Properties box by right-clicking on the image and selecting Properties from the pop-up menu. This results in the display of Excel s Properties dialog for the control where, again, all properties may be specified, including the Linked Cell property which allows the barcode data to be taken directly from the contents of a cell on the worksheet. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 15
20 . The sample spreadsheet ActiveDemo2007.xls also contains two demonstration macros. DoBarcodes copies pictures from the Active Control to positions on the spreadsheet overlaying colun B. DoLabels prints 3 labels from Sheet2, where an Image is replaced by a barcode for each label. These may be copied to your own spreadsheets using the method described in the Macros section under Copying to another workbook. Active Barcodes in Access An Active Barcode Control may be placed on an Access form or report by selecting the Design mode for the form or report. For Access 2007, select Active-X controls from the Controls section of the ribbon and choose Active Barcode Control from the list displayed. 16 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
21 For Access 2010 or 2013 drop-down the list of controls by selecting the drop-down icon (highlighted below). Now select the ActiveX Controls item displayed. The Insert ActiveX Control dialog is displayed, so you can select Active Barcode Control from the list and push the OK button. A default barcode image appears on the report. Right-clicking on the barcode and selecting Properties from the pop-up menu causes the Access Property Sheet to be displayed. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 17
22 In addition to allowing all the barcode properties to be set, the properties dialog also allows the control s source to be selected Field2 in the example above. Barcode properties may also be specified by right-clicking on the barcode image and selecting Active Barcode Control Object, then Properties from the pop-up menu displayed. This results in the display of the Active Barcode Control Properties dialog which allows all properties of the barcode (apart from the source field) to be specified. 18 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
23 The sample database ActiveDemo2007.accdb illustrates the use of the Active Barcode Control on a form and a report, in both case the barcode data is taken from field2 of Table1. Barcode Macros Using and editing the Barcode macros in Word and Excel require the use of the Developer Ribbon which is hidden by default. In Word 2007 or Excel 2007 you can make the Developer ribbon visible by selecting the Office icon, choosing Word Options/Excel Options, and in the Popular pane checking the checkbox labelled Show Developer tab in the Ribbon. For Office 2010/2013 choose Options from the File menu, select Customise ribbon, and check the Developer checkbox in the right-hand pane. The Developer ribbon includes icons for Macros (which allow macros to be run) and Visual Basic (which allows to be edited). For Access the Run Macro and Visual Basic icons are on the Database Tools ribbon. Macros are provided in source form so that they can be easily edited. Consequently they are not sealed and digitally signed and should be copied to your own templates to avoid constant security prompts. Initialising the Macros Barcodes for Office support a wide range of barcode types, so two initialisation macros are provided to allow the barcode type and other parameters to be set. For barcode pictures the initialisation macro is PBarcodeSetup for 1D barcodes, or PBarcode2DSetup for 2D barcodes. In either case running the macro displays a dialog box allowing the barcode type to be selected, and other relevant features such as the human-readable text, check-digits, bearer bars and margin indicators to be turned on or off. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 19
24 Once the parameters have been set the PBarcodeSetup macro need only be called again to change the settings. For further details of the barcode options available see the Advanced Barcode Options section. For font-based barcodes the initialisation macro is FBarcodeSetup for 1D barcodes, and FBarcode2DSetup for 2D barcodes. Again a dialog box is displayed allowing the barcode type to be selected, the font used to create the barcode to be selected, and other features to be selected. Once the parameters have been set the FBarcodeSetup macro need only be called again to change the settings. Active Control barcodes do not have an initialising macro the barcode image is initially placed on the document by Inserting an Active Barcode Control object on the document and then setting the object s properties using a Properties dialog summoned by right-clicking on the object and choosing Properties from the pop-up menu displayed. For further details of the barcode options available see the Advanced Barcode Options section. Barcode Macros for Word The document BMACSn.docm (where n is the Word version, eg. bmacs2007.docm) contains the four macros called PBarcode and FBarcode (which create a barcode from the text selected when the macro is called) and PBarcodeSetup and FbarcodeSetup (which initialise or change the barcode properties). The description that follows uses Word 2007 as an example, but the document describes any minor differences for the various versions of Word. Installation for Word 2007/2010/ Open bmacs2007.docm and using the Options button alongside the security warning (if prompted) ensure that "Allow this content" is selected. For Word 2010 just push the button labelled Enable content 2. On the Developer tab, in the Code group, click Visual Basic. This starts the Project explorer. 20 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
25 3. To make the barcode macros available to any new documents, expand the Project(Bmac2007) item and drag the module Barmacs (or Module1 for the 64 bit version) and drop it on the Normal project at the top of the list or any other template you wish to use. If you prefer not to make the macros available for all new documents then follow the instruction in Word s Help to create a new template and copy the macros to that template instead of the Normal template. 4. Close the target template then close the dialog and close the bmacs2007 document. The barcode macros is now ready for use in any document you create based on this template. Selecting the Macros icon on the Developer Ribbon will show that the four macros are present. Note To help prevent potentially dangerous code from running, we recommend that you return to any of the settings that disable all macros after you finish working with macros. Using the macros in Word PBarcodeSetup or FBarcodeSetup must be run at least once before the PBarcode and FBarcode macros can be used. Whenever you wish to create a barcode simply select the text you need to turn into a barcode then run either the PBarcode macro (if you want a barcode picture) or FBarcode (if you want a font-based barcode) from the list of macros in the Macros dialog. If you use a macro frequently you may wish to create a key shortcut for the macros concerned. For Office 2007 choose Word Options from the Office button, select Customize and scroll down the left-hand list of categories to select Macros. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 21
26 For Office 2010/2013 choose Options from the File menu, select Customise Ribbon, and push the Keyboard shortcuts Customise button, then scroll down to Macros. Select one of the macros. Place the cursor into the Press New Shortcut Key box and press the key you would like to use as a shortcut for this macro (e.g. the F11 key). Then push the Assign button. Finally push the Close button. Now whenever you select some text and push the appropriate shortcut key, the selected text will be replaced by a barcode. Customisation of the Word macros The PBarcode macro replaces selected text with a barcode picture generated from that text using the code. St$ = Selection.Text If Len(St$) < 1 Then MsgBox ("Please select text required for barcode") GoTo done End If pa = 0 er1 = BarCodew(St$, pa) If er1 = 0 Then Selection.PasteSpecial DataType:=wdPasteMetafilePicture Else If er1 = 1 Then x$ = "Wrong number of characters in barcode" ElseIf er1 = 4 Then 22 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
27 x$ = "Illegal character in barcode data" Else x$ = "Error in barcode data" End If MsgBox (x$) End If This code pastes the barcode picture into the existing selected text thus replacing the text. The macro can easily be edited to paste the picture elsewhere if required, just generating another Selection or cursor point before the Selection.PasteSpecial DataType:=wdPasteMetafilePicture line. The Fbarcode macro replaces selected text with other text returned by the DLL and then selects the new text and changes its font to the current barcode font settings: St$ = Selection.Text If Len(St$) < 1 Then MsgBox ("Please select text required for barcode") GoTo done End If pa = 0 so$ = String(200, " ") fo$ = String(36, " ") er1 = BarCodewF(ByVal St$, pa, ByVal so$, ByVal fo$, fht) If er1 > 0 Then Selection.Text = Left(so$, er1) Selection.Font.Name = fo$ Selection.Font.Size = fht Else If er1 = 1 Then x$ = "Wrong number of characters in barcode" ElseIf er1 = 4 Then x$ = "Illegal character in barcode data" Else x$ = "Error in barcode data" End If MsgBox (x$) End If done: Again the barcode text returned in Left(so$,er1) can be inserted elsewhere if required. Mail-merge Word's mail-merge is suitable only for font-based barcodes. The merge data must already exist contain the correct characters to form the barcode when displayed in the barcode font. While the data can come from any source this description assume that the data is in an Excel spreadsheet and that the font-based barcodes within the spreadsheet have already been created using the FBarcode macro within Excel or by using the in-line barcode() function. A sample mail-merge group of files is provided in the mailmerge subdirectory of the installation directory. If you are not already familiar with mail-merge techniques the description below outlines the steps needed to include barcodes on mailmerge documents. [Mail-merge instructions for other versions of Word will be found in the readmemm.txt file in the directory provided for the specific version of Microsoft Office.] To demonstrate the mailmerge facility create new document, select Letters and Mailings from the Tools menu and choose Mail Merge Wizard from the pop-up menu displayed. The following steps are required - at least the first time you create a mailmerge document. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 23
28 1. Choose the type of document to be created (eg. Labels) 2. Select the labels sizes (eg Avery Mini address) 3. When selecting recipients, choose Browse and locate the merge2k.xls spreadsheet, then choose Sheet1$ from the list of tables. Note that the first row of data in this spreadsheet does NOT contain column headers - so ensure that the "First row contains column headers" checkbox is NOT checked. All the records will be selected by default 4. Layout the first label by selecting "More items", then double-click on the database fields shown as F1 and UJEfbZVYZeBfP (this is the barcode but displayed in a normal font!). Select the <UJEfbZVYZeBfP> shown on the top label (INCLUDING THE << AND >> CHARACTERS) and change the font to one of the barcode fonts (eg. UNBW at 28 point). A barcode should now be visible. Now push the "Update all labels" button. 5. Selecting "Preview your labels" will display the number of labels you selected in step Selecting "Complete the merge" create the complete document ready for saving or printing If you enable the Mail Merge toolbar (by checking the Show Mail Merge Toolbar item on the Letters and Mailings menu) you can check the contents of each label by using the navigation items on the toolbar. Barcode Macros for Excel The Excel Workbook BMACS2003.XLS contains the Barcode macros which creates a barcode from the text in each cell selected when the macro is called, and positions either the barcode image (Pbarcode) over the adjacent cell while deleting the cell s previous content, or replacing the adjacent cells contents with a font based barcode (Fbarcode). In each case the cell height is resized to accommodate the barcode. An entire column may be selected on a worksheet by pushing the column letter button at the top of the column. When a macro is called, the barcode will be copied onto the worksheet at the position of the adjacent column. For alternative arrangements the macros can be customised (see below). If you use the macro frequently you may wish to create a shortcut for it. Installation for Excel To install these macros in Excel you should follow these instructions: Open the supplied BMACS20xx.XLS workbook, eg. bmacs2007 for 32 bit versions of Excel 2007/2010/2013. Save it with a different name (e.g. Barcodes.xls) With this newly saved workbook open, open the Macros dialog from the Tools menu and confirm that the following macros are visible: FBarcode FBarcodeSetup PBarcode PBarcodeSetup SelectPictures DeletePictures Copying to another workbook for Excel 2007/2010/ Open Excel Options from the Office icon (Excel 2007) or the File menu (Excel 2010/2013). 2. Open bmacs2007.xlsm and using the Options button alongside the security warning ensure that "Allow this content" is selected. For Excel 2010/2013 just push the button labelled Enable content 24 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
29 3. Open a new blank workbook or one in which you wish to use the barcode macros. 4. Select the Developer tab above the Ribbon and select the Visual Basic icon. 5. In the Project section (top left) expand the topics for both the bmacs2007 and the other workbook as shown above. 6. Select BarmacsExcel module in the bmacs2007 section, then, holding down the control key, drag it to the main heading of the other book VBAProject (Book1) in the sample above. A Modules section will appear in the list under the second workbook. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 25
30 7. Now from the File menu choose Close and Return to Microsoft Excel ; Save your workbook. The barcode macros are now present in your workbook and ready for use. Note To help prevent potentially dangerous code from running, we recommend that you return to any of the settings that disable all macros after you finish working with macros. Making the macros available to all new workbooks Follow the steps given above for copying the barcode macros to another workbook ensuring that the other workbook is a new one. Then close the bmac200x workbook and save the new workbook (Book1) as follows: For Excel From the Office button menu choose Save AS and drop down the file types to select Excel Macro-enabled Templates (*.xltm) 2. Navigate to C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office12\XLStart. Save the template as Book.xltm For Excel 2010/ Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
31 Choose Save As from the File menu and save the template as a Macro-enabled template with a name of your choice (eg barcodes.xltm Excel will recommend the location), so that when creating a new workbook you can choose to use the template by selecting it from My templates From now on when you start Excel each new workbook can have the macros installed. Using the macros in Excel PBarcodeSetup or FBarcodeSetup must be run at least once before the PBarcode and FBarcode macros can be used. Whenever you wish to create a single barcode simply click the cursor in the cell containing the text you need to turn into a barcode, then run one of the barcode macros from the list of macros in the Macros dialog. If you wish to make barcode images from the data in several cells or an entire column, select the cells required or push the column button at the top of the column, then choose the required barcode macro. After the PBarcode macro has run the spreadsheet contains pictures super-imposed over cells. The pictures cannot be selected by clicking on a column header. However, the macro SelectPictures allows all pictures on the spreadsheet to be selected simultaneously, and the macro DeletePictures allows them all to be deleted. Note that these two macros affect all pictures on the spreadsheet so if there are images other than barcodes created with PBarcode those image will be selected or deleted as well. If you use the barcode macros frequently you may wish to create a key shortcut for the macros concerned. To do this select the required macro in the Macros dialog, then push the Options button. Enter the required shortcut key in the dialog box presented and push the OK button. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 27
32 Now whenever you select a cell and push the appropriate shortcut key the text in that cell will be replaced by a barcode. Customisation of the Excel macros By default the PBarcode macro centres each barcode image over the cell adjacent to its data source cell using the cellcolumn1 value as shown below (where cellcolumn is the column that contains the source data). The height of the row is adjusted to be 120% of the barcode image height. By editing the code the barcode position can be customised. cellcolumn1 = cellcolumn + 1 St$ = (Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn).text) If Len(St$) = 0 Then ' skip empty cells Barcode = -1 GoTo done End If ' i = 0 er1 = BarCodew(ByVal St$, i) If er1 = 0 Then Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn1).clearcontents Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn1).select Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn1).interior.colorindex = xlnone Set px = ActiveSheet.Pictures.Paste Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn1).rowheight = px.height * 1.2 ' cell heights are in points; this is 20% larger than barcode height px.border.linestyle = xlnone ' centre barcode image in the cell ih = (Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn1).height - px.height) / 2 iw = (Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn1).width - px.width) / 2 px.left = Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn1).left + iw px.top = Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn1).top + ih Barcode = -1 Else If er1 = 1 Then x$ = "Wrong number of characters in barcode" ElseIf er1 = 4 Then x$ = "Illegal character in barcode data" Else x$ = "Error in barcode data" End If MsgBox x$ 28 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
33 Barcode = 0 End If done: The FBarcode macro places the font-based barcode text into the cell adjacent to the data, using the column identifier cellcolumn1% in the code below. The font used for the cell is set to the fontname and height returned from the BarCodewF() call (where it had been stored by the FBarcodeSetup macro) Out$ = String(120, " ") Barcode2 = 1 cellcolumn1% = cellcolumn% + 1 ' edit this line if you want the barcode elsewhere St$ = (Cells(cellrow%, cellcolumn%).text) Cells(cellrow%, cellcolumn1%).clearcontents If Len(St$) = 0 Then ' skip empty cells Barcode2 = -1 GoTo done End If fonname$ = String(48, " ") fonht& = 24 j& = BarCodewF(ByVal St$, nn&, ByVal Out$, ByVal fonname$, fonht&) If (j& > 0) Then Cells(cellrow%, cellcolumn1%) = Out$ Cells(cellrow%, cellcolumn1%).font.name = fonname$ Cells(cellrow%, cellcolumn1%).font.size = fonht& Rows(cellrow%).RowHeight = fonht& * 1.2 Else If j& = 1 Then x$ = "Wrong number of characters in barcode" ElseIf j& = 4 Then x$ = "Illegal character in barcode data" Else x$ = "Error in barcode data" End If MsgBox x$ Barcode2 = 0 End If done: The destination cell for the barcode may be changed by editing the cellcolumn1% variable in the code above. In-cell Barcode() formula for Excel The function barcode(cell,code,flags) enables the contents of a cell to show a font-based barcode based on the data in another cell simply by placing the formula =Barcode(cell,code,flags) into the cell. eg =barcode(a1,9,0) produces a Code 128 barcode in the cell using data from the cell A1. Similarly the function barcodeh(cell,code,flags) returns the human readable version of the barcode (including any checkdigit character calculated automatically is flags=1). The code for these functions is included in the BarMacsExcel module. However, if these are the only functions required the code below may be pasted in a module by: 1. Open the workbook 2. Open the Visual Basic editor 3. Right-click on the VBAProject and choose Insert Module from the pop-up menu displayed dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 29
34 4. Copy the code shown below and paste it into the empty module 5. Select "Close and return to Microsoft Excel" from the Visual Basic File menu. Rem Rem code for simple Barcode() inline formula for Excel Rem Declare Function Barcodeudf Lib "dlsbar34" (ByVal szin As String, ByRef cd As Long, ByRef fl As Long, ByRef szout As String, ByRef szhuman As String) As Long Function barcode(dat As Range, code As Integer, flags As Integer) As String cd& = code fl& = flags Out$ = String(120, " ") Human$ = String(84, " ") St$ = dat.text If Len(St$) = 0 Then barcode = "" Else j& = Barcodeudf(ByVal St$, cd&, fl&, ByVal Out$, ByVal Human$) If (j& > 0) Then barcode = Out$ Else barcode = "" End If End If End Function Function barcodeh(dat As Range, code As Integer, flags As Integer) As String cd& = code fl& = flags Out$ = String(120, " ") Human$ = String(84, " ") St$ = dat.text If Len(St$) = 0 Then barcodeh = "" Else j& = Barcodeudf(ByVal St$, cd&, fl&, ByVal Out$, ByVal Human$) If (j& > 0) Then barcodeh = Human$ Else barcodeh = "" End If End If End Function Rem Rem Rem The code parameter is a number that determines the barcode type required (see the Barcode Types Table for complete list), and the flags parameter specifies all other options available. Generally this will be 0, but if automatic check digit calculation is required it should be 1. For additional options available through the flags parameter see the Barcodes Help file for a specified barcode type. Note that, by default, formulae in Excel are normally recalculated when Excel recognises that the data for the formula changes. However, we recommend forcing a recalculation of all formulae in the spreadsheet before assuming that all barcodes have been updated. The way of forcing recalculation depends on the version of Excel, so see you Excel Help for details. In most case SHIFT+F9 recalculates the current worksheet. 30 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
35 Barcodes created using the In-cell formula cannot be distributed to other Excel users who do not have the Barcodes for Office product installed. Developers wishing to use in-line barcode formulae in spreadsheets for distribution should use the dbarcode 1D Developers Kit. Barcode macros for Access The Access database BMACS2003.MDB contains the barcode macros which creates a barcode from the text in each cell selected when the macro is called, and either places a barcode picture in an OLEObject table field or places a font-based barcode into a text field. The PBarcode macro must be run while the target Table is in DataSheet view. The FBarcode macro may be run in any view. Installation in your own database To copy the Barcode Macros to another Access 2007/2010/2013 database: 1. Open both the bmacs2007 database (bmacs2010_64 for 64 bit version) and your target database. 2. Select the Modules group in the bmacs2007 database. You will see the modules named BarcodeMacs; right-click on it and choose copy. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 31
36 3. In the "All Access Objects" windows of the target database right-click on an empty part of the window and choose Paste. (the BarcodeMacs module will appear in the list). 4. Select the Macros group in the bmacs2007 database. You will see the 4 macros (FBarcode, FBarcodeSetup, PBarcode and PBarcodeSetup). Select all 4, right-click and choose Copy. 32 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
37 5. In the "All Access Objects" windows of the target database right-click on an empty part of the window and choose Paste. (the four macros will appear in the list). Finally, if you will be using the PBarcode macro to create barcode pictures, open your table in design view and ensure that the field that will receive the barcode image (which as the macro is written is adjacent to the data source) is set to the type "OLE Object". The FBarcode macro takes data from the field named BarcodeSource and places the barcode into the field named BarcodeFont. All these features may be modified by editing the macros. Using the macros in Access PBarcodeSetup or FBarcodeSetup must be run at least once before the PBarcode and FBarcode macros can be used. Barcode pictures To create barcode images within the currently displayed table simply select the table cell or cells containing the barcode data and run the PBarcode macro from the list of macros in the Macro dialog. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 33
38 The barcode picture will be pasted into the cell on the right. Note that the picture will not be visible while in datasheet view; the word Picture will be displayed instead. It would probably be more usual to create an entire column of barcodes in a datasheet, rather than just one. Select an entire column by pushing the column title button at the top of the column, and then run the macro to generate the barcode pictures. The barcode pictures may be displayed in a form or report by inserting a bound control onto the form, with its control source specified as the table column containing the barcode pictures. 34 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
39 Font-based barcodes To create font barcode within a table simply select the table cell or cells containing the barcode data and run the FBarcode macro from the list of macros in the Macro dialog. By default the FBarcode macro takes its data source from a field named BarcodeSource in Table1 and placed the barcode into a field called BarcodeFont in the same table. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 35
40 The font barcodes will appear in datasheet view as a meaningless jumble of characters. To view the barcodes a form or report containing a text box is required, with the box s font set to the appropriate barcode font. If you use the barcode macros frequently you may wish to create a key shortcut for it. The Access Help system describes how to do this. NOTE: You must obtain a royalty-free redistribution licence version of the dbarcode library if you distribute the barcode macros and the associated library with an application/template you have created. Developers wishing to distribute these components should use the dbarcode 1D Developers Kit. Customisation of the Access macros The PBarcode macro operates when a table is displayed in datasheet view, takes the barcode data from selected cells (which must be Text cells) and pastes the barcode images into the adjacent cells (which must be OLEObect cells). Navigation and pasting are controlled by sending keystrokes to the table. TAB keys move the cursor around and the ^v (Control + V) initiates the pasting of the image. Set tbl = Screen.ActiveDatasheet i = tbl.seltop j = tbl.selleft k = tbl.selheight If k > 1 Then n = k - 1 Else n = 1 SendKeys "{TAB}", True SendKeys "+{TAB}", True For i = 1 To n Set CurrentControl = Screen.ActiveControl If (IsEmpty(CurrentControl.Text) Or IsNull(CurrentControl.Text) Or CurrentControl.Text = "") Then errorcode = 9 GoTo done End If BarcodeString = CurrentControl.Text k = 0 errorcode = BarCodew(ByVal BarcodeString, k) If (errorcode = 0) Then ' these keys paste the barcode image into the adjacent cell SendKeys "{TAB}", True SendKeys "{DEL}", True SendKeys "^v", True ElseIf errorcode = 1 Then MsgBox "Wrong number of characters in barcode" ElseIf errorcode = 4 Then MsgBox "Illegal character in barcode data" Else MsgBox "Error in barcode data" End If ' these keys move to the cell below for the next source SendKeys "+{TAB}", True SendKeys "{DOWN}", True Next i done: It is generally not necessary to edit this macro because there is no significance in the order of columns in datasheet view. 36 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
41 The FBarcode macro uses named fields in a named table, by default taking the barcode data from a field named BarcodeSource in Table1 and placing the font-based barcode into a field named BarcodeFont. Any of these names may be changed simply by editing the macro code: Set MyDB = CurrentDb() Set dset = MyDB.OpenRecordset("Table1") ' ' The rest just cycles down the table taking the source text from a field called BarcodeSource ' and placing the output in a field called BarcodeFont ' ' Edit as required to change fieldnames ' dset.movefirst Do Until dset.eof dset.edit St$ = dset!barcodesource n = Len(St$) Out$ = String(255, " ") x = BarCodewF(ByVal St$, n, ByVal Out$, ByVal foname$, foht) If (x > 0) Then dset!barcodefont = Out$ dset.update End If dset.movenext Loop dset.close Advanced barcode options Barcode Pictures and PBarcodeSetup In each Office application the PBarcodeSetup macro causes the display of the Barcode Image Options dialog which is used to specify the barcode type and other details of barcode images to be created next time the PBarcode macro is to run. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 37
42 The Barcode Image dialog contains the following: Code type combo box This drop-down combo box lists the code types supported by dbarcode. Clicking on the arrow alongside the box causes the list to drop down. A specific code type may be selected by clicking on the name within the list. Code box The code edit box provides the entry point for the user to enter the code that is to be converted into the barcode. Not used by the macros. Units combo box Measurement units may be millimetres or inches and the drop down list premits one of these to be selected. Target Size box The Target Size box contains two edit boxes that allow the user to enter height and width values (in millimetres or inches depending on the selection of the Units combo box) for the final image. Note that the metafile image produced by dbarcode may be resized independently of the target size, but that when resized any font size will also change. Note that those barcodes which have a nominal size (e.g. the EAN-13 and EAN-8 codes) may have the nominal size entered into the height and width edit boxes automatically, by checking the Use Nominal Size checkbox. Barcodes may be scaled to a percentage of the nominal size by entering the required value in the nominal size multiplier edit box. Allowed values are %. Note, however, that the acceptable size range for most barcodes types that have nominal sizes is %. The width of the image may be overridden by specifying a value for the X unit (the width of the smallest bar element). Note that this value is in the standard unit of mils (0.001 inches), and should not normally be less than 10. It must not be less than 8 or the barcode images may not scan. When not required X should be specified as Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
43 Show Text checkbox When this option is checked dbarcode will include the text form of the barcode under the barcode image - using the currently selected font properties to render the text. Justify Text checkbox This is a 3 state checkbox which set the justification for text under the barcode. When unchecked to text is centred; when checked with a white background the text is left justified to the outside of the light margin; when checked with a grey background the text is right justified. Auto Checkdigit check box When this option is checked dbarcode automatically calculates the checksum digits of the code. Consequently checksum digits should not be entered by the user when this item is checked. dbarcode will modify the number that appears as Characters Required when the Auto Checkdigit option is checked. Note that for Code 128 and EAN-128 the checksum calculation is always automatic and the resulting characters are not displayed in human readable form. These features are specified by the EAN-128 standard. Show Checkdigit check box When this option is checked dbarcode will include checkdigits that it calculates automatically with the text version of the code displayed below the bars. When the option is not checked, such check digits will not be displayed. Note that the display of check digits is NOT optional for EAN and UPC codes. Note also that some codes (e.g.. Code 39) may generate alphabetic check digits from numeric codes. No Background checkbox When this option is checked the background is set to Transparent and no background (or border) colour is applied to the image. Note however, that this facility should be used with caution. Images showing through a barcode can disrupt the scanning process. Horizontal bearers checkbox When this option is checked horizontal bearer bars are included on many barcode types as specified by the Bearer Size value. When this item is unchecked the behaviour depends on the value in the Bearer Size box. When the checkbox is checked the standard bearer bars are included on ITF barcodes. The ITF specification does indicate that the horizontal bearer bars should be printed wherever possible. Extend Bearers checkbox When checked any bearer bars are extended into the light margins. When uncheck bearer bars extend only over the bars. Bearer Size edit box A value in this box specifies that bearer bars are to be produced with the specified thickness in the current units (if positive) or X units (if negative). If a value is entered and the horizontal bearer checkbox is not checked, then a single bearer bar is produced at the top of the bars. If the horizontal bearers check box is checked, then bearer are produced at both the top and bottom of the bars. This value is ignored for EAN/UPC retail barcodes and for ITF packing case barcodes. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 39
44 Margin indicators checkbox When this item is checked margin indicators are included for many barcode types in the space allowed by the Margin Size value. There is special treatment for EAN and ITF barcodes, and for these types the setting of the Margin Size value is ignored. For EAN codes the light margin indicators are < and > symbols, while for ITF codes the margin indicators are thick bars connecting the ends of the horizontal bearer bars. In both cases the specifications recommend the use of margin indicators, but their use is not mandatory. Margin Size edit box For most barcode types except EAN/UPC and ITF the value in the Margin Size edit box specifies the left and right margin size in the current units (if positive) or X units (if negative). This property is used in conjunction with the bearer bar settings to specify the amount by which the bearer bars extend outside the barcode. This is effectively the size of the light margin. Border edit box The Border edit box allows the choice of a thickness of a border between the barcode image and the edge of the image area. Any border is displayed using the current background colour. The permitted value of the border thickness is in the range 0 25 mm or 0-1 inch. Bar reduction edit box The user may enter into this box a percentage reduction that is used to reduce the thickness of all lines in the barcode. Any value between 0 and 50 may be entered. This facility may be used to compensate for ink spread following wet ink printing. Lift Text by edit box The user may enter into this box a percentage amount (of the font height) by which text may be moved up. This provides a correction for some older applications that do not correctly align text in metafiles Character spacing edit box The value in the Character spacing edit box determines how characters are spaced out under a barcode. A value of 0% results in the characters being centered under the barcode with their normal default spacing. A value in the range % causes dbarcode to separate the characters from one another so that the length of the text occupies the specified percentage of the barcode length. Note that some applications do not correctly support alignment of characters within metafiles. Wide/Narrow ratio The value in this box may be used to specify the wide to narrow bar ratio to be used for those barcode types which permit this adjustment (Code 39, Interleaved 2/5, 2 of 5 and Codabar). The allowed range is A value of 0 causes the default value of 2.5 to be used. Background colour button When pushed, the Colours dialog box is displayed and allows the choice of a colour with which the image background will be rendered when the barcode image is redrawn. Bar colour button When selected, the Colours dialog box is displayed and allows the choice of a colour with which the image bars and text font will be rendered when the barcode image is redrawn. 40 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
45 Other options Two additional option checkboxes have been added to the dialog, Extra1 and Extra2. These will normally be left unchecked. They do, however, provide for extra functions that are specific to particular barcode types. For details see the Barcodes HELP system. The 128 Options button may be pushed to display the Code 128 Control Codes dialog which allows the user to specify characters in the data used to represent Code 128 control characters such as FNC1. The default values are those defined in the Barcodes Help file. The dialog also contains OK and Cancel buttons. Pushing the OK button causes the macro to close the dialog and use the settings of the dialog as defaults for barcode creation. Pushing the Cancel button causes the dialog to be closed without affecting the current default settings. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 41
46 Barcode Fonts and FBarcodeSetup In each Office application the FBarcodeSetup macro causes the display of the Barcode Font Options dialog which is used to specify the barcode type and other details of font-based barcodes to be created next time the FBarcode macro is to run. The Barcode Font dialog contains the following: Code type combo box This drop-down combo box lists the code types supported by dbarcode. Clicking on the arrow alongside the box causes the list to drop down. A specific code type may be selected by clicking on the name within the list. Code box The code edit box provides the entry point for the user to enter the code that is to be converted into the barcode. Not used by the macros. Auto Checkdigit check box When this option is checked dbarcode automatically calculates the checksum digits of the code. Consequently checksum digits should not be entered by the user when this item is checked. dbarcode will modify the number that appears as Characters Required when the Auto Checkdigit option is checked. Note that for Code 128 and EAN-128 the checksum calculation is always automatic and the resulting characters are not displayed in human readable form. These features are specified by the EAN-128 standard. Wide Bars checkbox When check the wide to narrow bar ratio to be used for those barcode types which permit adjustment (Code 39, Interleaved 2/5, 2 of 5 and Codabar) is set to 3. When unchecked the ratio is set to Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
47 Barcode font properties The font used to generate the barcode and either the font height (in points) are displayed here and may be changed by pushing the Change button and selecting the required options. Alternatively the equivalent X unit value (the thickness of the thinnest bar in mils) may be entered (the font height will then be set automatically). The barcode font must be one of UNAx, UNBx, UNCx, UNDx or UNEx, where x will normally be W (for the wide font), but may be R (reduced width) or N (narrow width) to suit specific printer technologies. Note that Clocked barcodes (eg. Postnet or RM4SCC) must be created using the UNF font and using the recommended font heights which are: Australia Post point Korean PA point PostNet/Planet 18 point RM4SCC point Other options Two additional option checkboxes have been added to the dialog, Extra1 and Extra2. These will normally be left unchecked. They do, however, provide for extra functions that are specific to particular barcode types. For details see the Barcodes HELP system. The dialog also contains OK and Cancel buttons. Pushing the OK button causes the macro to close the dialog and use the settings of the dialog as defaults for font-based barcode creation. Pushing the Cancel button causes the dialog to be closed without affecting the current default settings. Programming properties Programmers may prefer to set barcode properties programmatically rather than face the end-user with a dialog box for setting the properties. This may be achieved by modifying the contents of the BARCODE structure held within the DLL. Data Structure The dbarcode DLL uses a single data structure for holding barcode data within the library, BARCODE, and to use the structure in VBA code the structure must be defined as shown below Private Type BARCODE code As Long name1(12) As Byte show_text As Long auto_parity As Long orient As Long show_checkdigit As Long nominal_size As Long line_reduction As Long border_thickness As Long fore_color As Long back_color As Long ierror As Long string1(80) As Byte req_number As Long parity As Long alphabetic As Long length As Long Height As Long dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 43
48 subscript As Long flags As Long textgap As Long string2(80) As Byte bearer_size As Long spare As Long xunit As Long bxx As Long margin_size As Long barratio As Long charspacing As Long justification As Long End Type A BARCODE structure must exist before any barcode-creating library routines are called, so your program requires a declaration such as Dim bc as BARCODE to appear in the program before any calls are made to the library routines. For picture barcodes the human readable text that may appear under barcodes is generated in a font that may be specified to the DLL using a LOGFONT structure: Private Type LogFnt lfheight As Long lfwidth As Long lfescapement As Long lforientation As Long lfweight As Long lfitalic As Byte lfunderline As Byte lfstrikeout As Byte lfcharset As Byte lfoutprecision As Byte lfclipprecision As Byte lfquality As Byte lfpitchandfamily As Byte lffacename(32) As Byte End Type A LogFnt structure must exist before being used in a library call, so your program requires a declaration such as Dim lf as LogFnt to appear in the program before any calls are made to the library routines. Sample coding While it is possible to fill all input members of the BARCODE and LogFnt structures directly it is more efficient to retrieve from the DLL the current values (the defaults if no filling has been done either programmatically or by using the PbarcodeSetup or FbarcodeSetup macros), and then changing just the values you need to change. The structure may then be returned to the DLL. The current structure, along with the current font structure used for the human readable font used for picture barcodes may be retrieved by calling BarCdrd() and the modified structures returned by calling BarCdin() as shown in the sample code below, which changes only the barcode type by setting the code value to 9, the human readable font to Arial, and the image height and width to 15 and 35 mm respectively. 44 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
49 Declare Function BarCdrd Lib Dlsbar34 (bc As Barcode, lf As LogFont) As Long Declare Function BarCdin Lib Dlsbar34 (bc As Barcode, lf As LogFont) As Long Declare Function SetBarCdsz Lib Dlsbar34 (ht As Long, wd As Long) Dim bc as BARCODE Dim lf as LogFnt Private Sub Cchange() Dim i As Long Dim ht As Long Dim wd As Long Dim tfnt As String i = BarCdrd(bc, lf) bc.code = 9 tfnt = "Arial" n = Len(tfnt) For i = 0 To n 1 lf.lffacename(i) = Asc(Mid$(tfnt, i + 1, 1)) Next i lf.lffacename(n) = 0 ht=1500 wd=3500 i=setbarcdsz(ht,wd) i = BarCdin(bc, lf) End Sub Function calls The following functions may be called using VBA within Office applications to assist in programmatically setting barcode properties. BarInit A call to BarInit(bc) initialises the members of the barcode structure to default values (code=8 Code 39). Declare Function BarInit Lib Dlsbar34 (bc As BARCODE) Where bc is a BARCODE structure. The function always returns 0. BarCdrd - copies the current default barcode properties into a BARCODE structure and a LogFnt structure. Declare Function BarCdrd Lib Dlsbar34 (bc As BARCODE, lf As LogFont) As Long where bc is a BARCODE structure and lf is a LogFnt structure. The function always returns 0. BarCdin sets the default barcode properties to the values passed as a BARCODE structure and a Logfnt structure and saves the defaults for future use. Declare Function BarCdin Lib Dlsbar34 (bc As BARCODE, lf As LogFont) As Long where bc is a BARCODE structure and lf is a LogFnt structure. The function always returns 0. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 45
50 Barcodeudf Calls to Barocdeudf() generate the characters for a font-based barcode from parameters providing the data, barcode type and a flags parameter. Int WINAPI Barcodeudf(LPSTR szin, LPINT ptrcode, LPINT ptrflags, LPSTR szout, LPSTR szhuman) szin is a pointer to a string holding the barcode data ptrcode is a pointer to an integer holding the barcode type value (as defined in the Barcode Type Table) ptrflags is a pointer to an integer holding a bitwise collection of flag values. The flag values for this function are: 1 automatically calculate check digit (default 0 = non automatic calculation) 2 use 3:1 bar width ratio for variable ratio barcode types (default 0 = 2:1 ratio used) 16 the Extra1 flag (see Barcode help) 32 the Extra2 flag. sszout is a pointer to a string that receives the font version of the barcode. This string needs to be displayed/printed in one of the UN** fonts included with the kit. We recommend that szout is char[120]. If szout is NULL then no string is produced. szhuman is a pointer to a string that receives the human-readable version of the barcode data, including any automatically generated check digit. We recommend that szhuman is char[96]. If szhuman is NULL then no string is produced. This function is provided primarily to allow the easy use of in-cell formulae within Microsoft Excel. See In-cell Barcode function for Excel. BarCodew Calls to BarCodew create a picture barcode, leaving the image on the Windows clipboard from where it may be pasted into the location required. Declare Function BarCodew Lib dlsbar34 (ByVal sin as String, n as Long) As Long Where sin is the barcode data. n is unused in this release and should be set to 0. The function returns 0 if successful, or an error number that may be passed to ErrorMess() to obtain an error message.. SetBarCdsz() must should be used to specify a barcode size before calling BarCodew(). BarCodewF Calls to BarCodewF create a Font barcode, returning the barcode character in the sout string.. Declare Function BarCodewF Lib dlsbar34 (ByVal sin as String, n as Long, sout As String, fname As String, fht As Long) As Long Where sin is the barcode data. and n is length of the data string. The sout string must exist and be long enough to contain the barcode characters returned. The string may be space filled using, for example, sout=string(255, ) prior to the call. The fname and fht parameters return the name and height of the barcode font specified in the FbarcodeSetup macro. These parameters must exist and the fname string must be large enough to receive 24 characters. However, as the results do not have to be used!! The function returns the number of characters in sout, or a negative value if an error has occurred. If a negative value is returned changing the sign provides an error number that may be passed to ErrorMess() to obtain an error message. ErrorMess Calls to ErrorMess fill a string with a text version of the error code. 46 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
51 Declare Function ErrorMess Lib "Dlsbar34" (er as Long, msg As String) As Long where error is a pointer to an integer containing the error code from the barcode structure, and msg is a pointer to a string that receives the text. The buffer msg must be large enough to receive 24 characters. The function always returns 0. GetBarCdsz Calls to GetBarCdsz provide the setting for the current target height and width of the barcode picture in HIMETRIC units (1 unit = 0.01 mm) Declare Function GetBarCdsz Lib "Dlsbar34" (ht as Long, wd As Long) As Long Where ht receives the target height and wd receives the target width. Note that the Width value is not used if an Xunit value has been specified as the width of the picture is then determined by the number and width of the bar elements. The function always returns 0. SetBarCdsz Calls to SetBarCdsz set the current target height and width of the barcode picture in HIMETRIC units (1 unit = 0.01 mm) Declare Function GetBarCdsz Lib "Dlsbar34" (ht as Long, wd As Long) As Long Where ht specifies the target height and wd specifies the target width. Note that the Width value is not used if an Xunit value has been specified as the width of the picture is then determined by the number and width of the bar elements. A positive wd value should be specified even if an Xunit value is being provided because a barcode image is created before being adjusted for the Xunit value. The function always returns 0. Structure members The properties of the BARCODE structure members are described below. Note that the members belong to a C structure and are described using C variable types. The int type corresponds to VB s Integer type. The char arrays which would not normally be accessed using VB can be retrieved or filled using the character by character method used to change the font in the example given above. Some structure members are not intended for use from VB and are omitted from the descriptions below. int auto_parity Default value 0 This variable specifies whether a checkdigit should be automatically generated when a call to BarCodem generates the barcode image. Allowed values: 0 - no automatic calculation 1 - checkdigit is automatically calculated Note that for barcode types which do not have check digits this parameter is ignored. COLORREF back_color Default: &H00FFFFFF& Sets the colour of the image background. Allowed values: 0 (black) dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 47
52 to &H00FFFFFF& (white) int barratio Default value 0 This parameter is used to set the thick/thin bar ratio for those barcode types which allow the value to vary (such as Code 39). The actual ratio use is one tenth of the value of this parameter. When a value of 0 is specified the default bar width ratio of 2.5 : 1 is used Allowed values: int bearer_size Default value 0 This variable is used to set the thickness of bearer bars in HIMETRIC units. If the bearer thickness is a non-zero value then a bearer bar is produced above and below the bars IF the DL_FLAG_BEARERS flag is set (see flags), or only above the bars if the DL_FLAG_BEARERS flag is not set. To have no bearer bars the bearer thickness must be 0. The light margin value is applied whether or not bearer bars are produced. Note that if bearer bars have been specified and the DL_FLAG_EXBEARERS flag has been set, then the bearer bars extend over the light margins. If the DL_FLAG_EXBEARERS flag has not been set then the bearers do not extend into the light margins. This parameter is ignored for EAN/UPC barcodes and for ITF and ITF-6 barcodes, which have their own standards for these items. int border_thickness Default value 0 This variable specifies the thickness (in points) of any border required around the barcode image. Any border is created using the colour specified as the background colour. Allowed values: 0 (no border) to 1/3 * ImageHeight int charspacing Default value: 0 This parameter may be used to adjust the space under the barcode occupied by the human readable text. The value is a percentage of the width of the barcode. When set to zero the text under the barcode is produced at its normal intercharacter spacing. Allowed values: int code Default value 0 The value of this variable specifies the code type as defined as code # in the barcodes table shown in the Barcodes Help file int error Returns a value representing the error code if a valid barcode image cannot be created on a call to BarCodem. The error codes are shown below. code meaning 48 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
53 0 No error 1 Wrong code length 2 Unrecognised code type 3 Wrong add-on code length 4 Illegal character in code 5 Error in embedded code 6 Generated line width less than 1 unit 7 font error 8 unable to create metafile 9 no code provided 10 error writing disk file The text versions of the error codes may be obtained by calling ErrorMess() int flags; The flags variable holds a number of bit flags that determine aspects of the formatting for some barcode types. The variable may be filled by ORing with the available codes defined in DLSBARn.H: #define DL_FLAG_MARGINS 1 specifies that barcodes should show margin indicators (ie. < and > marks), and that UPC-A and UPC-E codes should have the Country Prefix code and the checkdigit printed in the light margin regions. Also used to show the end bars for ITF-6 and ITF-14 codes although in this case the flag is only applied if the Bearers flag is also set. #define DL_FLAG_BEARERS 2 specifies how Bearer bars should be shown (see bearer_size). For ITF-6 and ITF-14 codes the flag specifies standard ITF bearer bars and bearer_size is ignored. #define DL_FLAG_TRANSPARENT 4 specifies that the barcode image is generated with no background (i.e. any background colour is ignored). However, this flag should be used with caution as a background image showing through a barcode can disrupt the scanning process. #define DL_FLAG_EXBEARERS 8 margins. specifies that any bearer bars are extended beyond the bars into the light Two additional flags have been added, DL_FLAG_EXTRA1 (16) and DL_FLAG_EXTRA2 (32). These will normally be unused. They do, however, provide for extra functions that are specific to particular barcode types. For details see the Barcodes HELP system. COLORREF fore_color Default: 0 Set the colour of the image foreground, i.e. the bars and text colour. Allowed values: 0 (black) to &H00FFFFFF& (white) dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 49
54 int line_reduction Default: 0 the line thickness of each line drawn on the barcode image is reduced by this percentage amount. This property may be used to compensate for ink spreading during wet-ink printing. A negative value applies a reduction equal to the percentage of the thinnest bar. Allowed values: 0-50 (%) int justification Default value: 0 Sets the alignment of human readable text under the barcode. Allowed values: 0 = text centred 1 = Left aligned 2 = Right aligned Note that only 0 should be used when margin indicators have been enabled with the DL_FLAG_MARGINS flag. int margin_size Default value: 0 The light margin size in HIMETRIC units. Allowed values: 0 to half the width of the barcode Note that if bearer bars have been specified and the DL_FLAG_EXBEARERS flag has been set, then the bearer bars extend over the light margins. If the DL_FLAG_EXBEARERS flag has not been set then the bearers do not extend into the light margins. int nominal_size Default value 0 Some barcodes are specified by their designers to be reproduced at a nominal size (EAN and UPC codes are examples). This variable may be used to generate a barcode image that is at the nominal size rather than the size specified by the lprectin parameter in calls to BarCodem Allowed values: 0 - Size specified in lprectin is used 1 - Nominal size is used and lprectin is ignored Note that for barcode types that do not have a nominal size this parameter is ignored. int orientation Default value 0 This variable specifies whether the barcode image should be generated normally or with clockwise or anticlockwise rotation through 90 degrees. Allowed values 0 - Normal orientation 1 - clockwise rotation by 90 degrees 2 anti-clockwise rotation by 90 degrees -1 inverted (ie rotated by 180 degrees Note that only TrueType or compatible fonts may be rotated 50 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
55 int show_checkdigit Default value 0 This variable specifies whether any checkdigit should be included with the code text when a call to BarCodem generates the barcode image. Allowed values: 0 - checkdigit is not included 1 - checkdigit is included Note that for barcode types that do not have check digits this parameter is ignored. It is also ignored if text inclusion has not been requested. int show_text Default value 0 This variable specifies whether a text version of the barcode should appear (usually underneath the bar image) when a call to BarCodem generates an image. Allowed values: 0 - no text appears 1 - text appears, using the font specified in the lplogfontin structure. char string[84] This variable contains the code string from which the barcode is to be created. In the present context this data is passed as the sin parameter to either BarCodew() or BarCodewF() and so should NOT be passed directly to the BARCODE structure. Note that in barcodes the difference between upper and lower case letters is significant. Few coding schemes support lower case letters. Also note that when calling from Visual Basic this item is dimensioned in Basic as an array of 80 bytes - not a Basic string. int textgap; This variable specifies a distance (as a percentage of the Text Font Height) by which the text form of the code is raised before displaying. This variable has been included because some applications do not correctly align text when displaying metafiles. int xunit Default value: 0 (the xunit value is not used when set = 0) Allowed values: mils This may be used to specify the X unit dimension (ie. The width of the narrowest bar) in standard mil units (NOT mm. 1 mil = inches). Barcode should not normally be produced with an X value smaller than 10, and MUST NOT be produced with an X value smaller than 8 - or the barcode will not meet the standard specification. This provides an alternative way of specifying the barcode size - rather than using the lprect parameter. When xunit is specified the length of the barcode is calculated within the DLL and the length implied by other parameters is ignored. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 51
56 Other variables char string2[84]; string2 is returned with the barcode text plus any checkdigit calculated automatically. This is useful for collecting strings from auto-check digit produced barcodes for use in systems in which a scanned barcode must be matched with the complete barcode text. Note that the standard checkdigit for Code 128 and EAN 128 barcodes is never provided in human readable form and so is NOT returned is string2. Also note that when calling from Visual Basic the string2 item is dimensioned in Basic as an array of 80 bytes - not a Basic string. 52 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
57 Barcode Types Table code# Code type no. of characters check digit 0 EAN13 13 numbers 1 1 EAN-8 8 numbers 2 EAN numbers 1 3 EAN numbers 1 4 UPC-A 12 numbers 1 5 UPC-E 7 numbers 1 6 ITF numbers 1 (EAN optional) 7 ITF-6 6 numbers 8 Code 39 any 1 optional 9 Code 128 any* automatic 10 EAN/UCC-128 any* automatic 11 2 of 5 any numbers 12 Interleaved-2 of 5 number pairs 1 optional 13 3 of 9 any 14 Code B any numbers 15 Code 11 any 1 or 2 16 Codabar any 17 MSI any numbers 1 or 2 18 Ext. Code 39 any (full ASCII) 1 optional 19 UPCA+2 14 numbers 1 20 UPCA+5 17 numbers 1 21 EAN numbers 1 22 EAN numbers 1 23 UPCE+2 9 numbers 1 24 UPCE+5 12 numbers 1 25 Telepen standard any 1 optional 26 Telepen ASCII any 1 optional 27 Telepen numeric any 1 optional 28 PostNet type A 5 numbers 1 29 PostNet type C 9 numbers 1 30 PostNet type C' 11 numbers 1 31 FIM A fixed code 0 32 FIM B fixed code 0 33 FIM C fixed code 0 34 RM4SCC any State any 1 optional 36 Code 93 any 2 optional dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 53
58 37 Ex Code 93 any (full ASCII) 2 optional 38 ISBN 10/13 digit ISBN 1 automatic 39 Matrix 2/5 numeric 1 optional 40 Plessey numeric/some alpha 2 41 Australia Post numeric automatic 42 Swiss Post fixed code 0 43 Deutsche Post numeric 44 SISAC SICI codes 1 45 EAN/UCC Planet automatic 47 Planet automatic 48 ISSN 9/10 digit ISSN 1 automatic 49 ISMN 8/9 digit ISMN 1 automatic 50 SSCC Korean Postal Authority Italian Postal 3/9 2+8+c Italian Postal 2/ automatic 54 ISBN+2 digit any / 2 1 automatic 55 ISBN+5 digit any / 5 1 automatic 56 ISSN+2 digit any / 2 1 automatic 57 ISSN+5 digit any / 5 1 automatic 58 Japan Post any automatic 59 IATA 2 of 5 numeric 60 China Post numeric 1 optional 61 Intelligent Mail numeric 62 Code 128 Type A 1 automatic 63 Code 128 Type B 1 automatic 64 UPC-E0 12 reduced to UPC-E1 12 reduced to InfoMail Barcode A 21 numeric 67 PZN 6 numbers 1 automatic 68 Databar Omnidirectional 14 digits + AI 1 automatic 69 Databar Trucated 14 digits + AI 1 automatic 70 Databar Limited 14 digits + AI 1 automatic 71 Databar Expanded 72 HIBC Code 39 various 1 73 HIBC Code 128 various 1 74 IM Package Barcode numeric 1 optional 75 FIM D Fixed code 0 54 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
59 dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 55
60
61 2D Barcodes Barcodes for Office (1D) does NOT include 2D barcodes. The 2D and full versions of Barcodes for Office product include facilities to create 2D barcodes easily within the Office products Word, Excel and Access. Incorporating 2D barcodes in Office documents is achieved using the same procedures as described above (with one exception ). The remainder of this document discusses points to bear in mind when using 2D barcodes. The one exception refers to 2D font barcodes on an Excel spreadsheet. Excel does not provide a method for adjusting the line spacing within a cell. As a result 2D font barcodes will appear with gaps between the lines making them unsuitable for scanning. Fortunately the cells containing such barcode can be made the source for printing from other applications such as Word using mailmerge, because Word does permit the line spacing to be specified. It should be noted that for 2D picture barcodes the size of the barcode is specified primarily through the X dimension the width in Mils (1/1000 inches) of the barcode s elements. Typically this will be a value of between 8 and 30. The number of elements within the barcode may be determined by the amount of data, but beyond that it may be increased by specifying properties such as the security level (the amount of error correction included in the barcode) or the number of columns elements. See the Barcode Help file for details for different barcode types. Embedded 2D barcode objects A 2D barcode may be embedded into an Office document in the same way as described above, except that dbarcode2d Image is the object type. The Barcode Properties dialog for 2D barcodes is rather different. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 57
62 This allows the barcode type and mode to be selected as well as all other features which will vary slightly from one barcode type to another. Active-X 2D controls The 2D Active-X control may be inserted into documents in the same way as the 1D control, but selecting Active 2DdBarcode Control from the list of available controls. 58 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
63 And right-clicking on the barcode image and selecting Active 2D-dBarcode Control Object.Properties displays the Control Properties tabbed dialog which allows the barcode properties to be specified. In Excel right-clicking on the barcode image and choosing Propeties allows the data source to be taken from a LinkedCell on the spreadsheet. In Access right-clicking on the barcode image and choosing Propeties allows the data source to be taken from a ControlSource (ie a table field). The sample Word document a2bc2007.doc also contains two demonstration macros that enable the content of the barcode to be set. The axbar1 macro pops-up a dialog request the barcode data, while the axbar2 macro takes data from the current selection text on the document. 2D Barcode Macros It is important to note that 2D macros supports font barcodes only for Aztec, Datamatrix, PDF417 and QR Code symbols; it does not support all the types available using the picture barcode components. The macros provide efficient methods of creating either picture barcodes or font-based barcodes, and pictures can be embedded in say a spreadsheet or database so can be passed to others, although at the price of a larger file size. Documents created using Office 2007 or later may also have font-based barcodes embedded for transmission to another Office user without requiring that user to have the barcode fonts installed. Initialising the Macros The 2D barcode macros support a range of barcode types, and an initialisation macro is provided to allow the barcode type and other parameters to be set. The initialisation macros are FBarcode2DSetup for font barcodes, and PBarcode2DSetup for picture barcodes dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 59
64 These macros display a dialog box allowing the barcode type and mode to be selected, and for picture barcodes the width of the thinnest bar (the X dimension in Mils thousandths of an inch) and the height of the elements as a multiple of X (the Y multiplier). For font based barcodes the font and the font size may be specified. The Font barcode properties dialog for the macro FBarcode2DSetup 60 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
65 The Picture barcode properties dialog for the macro PBarcode2DSetup Once the parameters have been set the barcode setup macro need only be called again to change the settings. Barcode 2D Macros for Word Using and editing the Barcode macros in Word and Excel require the use of the Developer Ribbon which is hidden by default. In Word 2007 or Excel 2007 you can make the Developer ribbon visible by selecting the Office icon, choosing Word Options/Excel Options, and in the Popular pane checking the checkbox labelled Show Developer tab in the Ribbon. For Office 2010/2013 choose Options from the File menu, select Customise ribbon, and check the Developer checkbox in the right-hand pane. The Developer ribbon includes icons for Macros (which allow macros to be run) and Visual Basic (which allows to be edited). For Access the Run Macro and Visual Basic icons are on the Database Tools ribbon. Macros are provided in source form so that they can be easily edited. Consequently they are not sealed and digitally signed and should be copied to your own templates to avoid constant security prompts. Installation for Word 2007/2010/ Open b2dmacs2007.docm and using the Options button alongside the security warning ensure that "Allow this content" is selected. For Word 2010 just push the button labelled Enable content 2. On the Developer tab, in the Code group, click Visual Basic. This starts the Project explorer. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 61
66 3. To make the barcode macros available to any new documents, expand the Project(B2dmacs2007) item and drag the module Module1 (or the four separate macro modules for the B2Dmacs2010_64 version) and drop it on the Normal project at the top of the list or any other template you wish to use. 4. Close the target template then close the dialog and close the b2dmacs2007 document. The 2D macros are now ready for use in any document you create based on this template. Selecting the Macros icon on the Developer Ribbon will show that the four macros are present. Note To help prevent potentially dangerous code from running, we recommend that you return to any of the settings that disable all macros after you finish working with macros. Using the 2D macros in Word PBarcode2DSetup or FBarcode2DSetup must be run at least once before the PBarcode2D and FBarcode2D macros can be used. Whenever you wish to create a barcode simply select the text you need to turn into a barcode then run either the PBarcode2D macro (if you want a barcode picture) or FBarcode2D (if you want a font-based barcode) from the list of macros in the Macros dialog. 62 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
67 If you use a macro frequently you may wish to create a key shortcut for the macros concerned as described earlier. Customisation of the Word macros The PBarcode2D macro replaces selected text with a barcode picture generated from that text using the co2de. St$ = Selection.Text If Len(St$) < 1 Then MsgBox ("Please select text required for barcode") GoTo done End If j = Bar2Drd(bc) i = setdata(bc, ByVal St$) er1 = Bar2D2vba(bc) ' or Bar2D2vb(ByVal St$) If er1 = 0 Then Selection.PasteSpecial DataType:=wdPasteMetafilePicture Else x$ = "Error in barcode data" MsgBox (x$) End If This code pastes the barcode picture into the existing selected text thus replacing the text. The macro can easily be edited to paste the picture elsewhere if required, just generating another Selection or cursor point before the Selection.PasteSpecial DataType:=wdPasteMetafilePicture line. The Fbarcode2D macro replaces selected text with other text returned by the DLL and then selects the new text and changes its font to the current barcode font settings: St$ = Selection.Text If Len(St$) < 1 Then MsgBox ("Please select text required for barcode") GoTo done End If j& = Bar2Drd(bc) Out$ = String(1024, " ") fo$ = String(24, vbnullchar) fht& = 8 j& = GetFnt2DDetail(ByVal fo$, fht&) j& = setdata(bc, ByVal St$) er1 = Bar2D2fnt(bc, ByVal Out$) If er1 > 0 Then Selection.Text = Left(StrConv(Out$, vbfromunicode), er1) Selection.Font.Bold = False Selection.Font.Italic = False Selection.Font.Name = fo$ Selection.Font.Size = fht& Selection.ParagraphFormat.SpaceAfter = 0 Selection.ParagraphFormat.LineSpacingRule = wdlinespacesingle Else x$ = "Error in barcode data" MsgBox (x$) dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 63
68 End If done: Again the barcode text returned in Left(StrConv(Out$, vbfromunicode), er1) can be inserted elsewhere if required. Mail-merge Word's mail-merge is suitable only for font-based barcodes. The merge data must already exist contain the correct characters to form the barcode when displayed in the barcode font. While the data can come from any source this description assume that the data is in an Excel spreadsheet and that the font-based barcodes within the spreadsheet have already been created using the FBarcode2D macro within Excel or by using the in-line barcode() function. A sample mail-merge group of files is provided in the mailmerge subdirectory of the installation directory. If you are not already familiar with mail-merge techniques the description below outlines the steps needed to include barcodes on mailmerge documents. [Mail-merge instructions for other versions of Word will be found in the readmemm.txt file in the directory provided for the specific version of Microsoft Office.] To demonstrate the mailmerge facility create new document, select Letters and Mailings from the Tools menu and choose Mail Merge Wizard from the pop-up menu displayed. The following steps are required - at lease the first time you create a mailmerge document. 1. Choose the type of document to be created (eg. Labels) 2. Select the labels sizes (eg Avery Mini address) 3. When selecting recipients, choose Browse and locate the merge2k.xls spreadsheet, then choose Sheet1$ from the list of tables. Note that the first row of data in this spreadsheet contains column headers - so ensure that the "First row contains column headers" checkbox is checked. All the records will be selected by default 4. Layout the first label by selecting "More items", then double-click on the database fields shown as data and barcode. Select the <barcode> shown on the top label (INCLUDING THE << AND >> CHARACTERS) and change the font to one of the barcode fonts (eg. AZTW at 8 point). Now push the "Update all labels" button. 5. Selecting "Preview your labels" will display the number of labels you selected in step Selecting "Complete the merge" create the complete document ready for saving or printing If you enable the Mail Merge toolbar (by checking the Show Mail Merge Toolbar item on the Letters and Mailings menu) you can check the contents of each label by using the navigation items on the toolbar. Barcode 2D Macros for Excel The Excel Workbook B2DMACS2007.XLS contains the 2D barcode macros which creates a barcode from the text in each cell selected when the macro is called, and positions either the barcode image (Pbarcode2D) over the adjacent cell while deleting the cell s previous content, or replacing the adjacent cells contents with a font based barcode (Fbarcode2D). When PBarcode2D is run the cell height is resized to accommodate the barcode. An entire column may be selected on a worksheet by pushing the column letter button at the top of the column. When a macro is called, the barcode will be copied onto the worksheet at the position of the adjacent column. For alternative arrangements the macros can be customised (see below). If you use the macro frequently you may wish to create a shortcut for it. Installation for Excel To install these macros in Excel you should follow these instructions: 64 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
69 Open the supplied B2DMACS20xx.XLS workbook, eg. b2dmacs2007 for Excel 2007/2010/2013. Save it with a different name (e.g. Barcodes.xls) With this newly saved workbook open, open the Macros dialog from the Tools menu and confirm that the following macros are visible: FBarcode2D FBarcode2DSetup PBarcode2D PBarcode2DSetup SelectPictures DeletePictures Copying to another workbook for Excel To copy the macros to another workbook in Excel do the following: 1. Open b2dmacs2007.xlsm and using the Options button alongside the security warning ensure that "Allow this content" is selected. For Excel 2010/2013 just push the button labelled Enable content 2. Open a new blank workbook or one in which you wish to use 2D macros. 3. Select the Developer tab above the Ribbon and select the Visual Basic icon. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 65
70 4. In the Project section (top left) expand the topics for both the b2dmacs2007 and the other workbook as shown above. 5. Select Module Bar2Dmacs in the b2dmacs2007 section, then, holding down the control key, drag it to the main heading of the other book VBAProject (Book1) in the sample above. A Modules section will appear in the list under the second workbook. 66 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
71 6. Now from the File menu choose Close and Return to Microsoft Excel ; Save your workbook. The 2D macros is now present in your workbook and ready for use. Note To help prevent potentially dangerous code from running, we recommend that you return to any of the settings that disable all macros after you finish working with macros. Making the macros available to all new workbooks Follow the steps given above for copying the 2D macros to another workbook ensuring that the other workbook is a new one. Then close the b2dmac200x workbook and save the new workbook (Book1) as follows: For Excel From the Office button menu choose Save AS and drop down the file types to select Excel Macro-enabled Templates (*.xltm) dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 67
72 2. Navigate to C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office12\XLStart. Save the template as Book.xltm For Excel 2010/2013 Choose Save As from the File menu and save the template as a Macro-enabled template with a name of your choice (eg barcodes.xltm Excel will recommend the location), so that when creating a new workbook you can choose to use the template by selecting it from My templates From now on when you start Excel each new workbook can have the macros installed. Using the macros in Excel PBarcode2DSetup or FBarcode2DSetup must be run at least once before the PBarcode2D and FBarcode2D macros can be used. Whenever you wish to create a single barcode simply click the cursor in the cell containing the text you need to turn into a barcode, then run one of the Barcode macros from the list of macros in the Macros dialog. If you wish to make barcode images from the data in several cells or an entire column, select the cells required or push the column button at the top of the column, then choose the required Barcode macro. After the PBarcode2D macro has run the spreadsheet contains pictures super-imposed over cells. The pictures cannot be selected by clicking on a column header. However, the macro SelectPictures allows all pictures on the spreadsheet to be selected simultaneously, and the macro DeletePictures allows them all to be deleted. Note that these two macros affect all pictures on the spreadsheet so if there are images other than barcodes created with PBarcode2D then those image will be selected or deleted as well. If you use the Barcode macros frequently you may wish to create a key shortcut for the macros concerned. To do this select the required macro in the Macros dialog, then push the Options button. Enter the required shortcut key in the dialog box presented and push the OK button. Customisation of the Excel macros By default the PBarcode2D macro centres each barcode image over the cell adjacent+1 to its data source cell using the cellcolumn2 value as shown below (where cellcolumn is the column that contains the source data). The height of the row is adjusted to be 120% of the barcode image height. By editing the code the barcode position can be customised. Function barcodepic(cellrow, cellcolumn) ' ' cellrow and cellcolumn are the row and column numbers ' of the cell containing the text for the barcode ' this procedure positions the barcode image over the next but one cell cellcolumn2 = cellcolumn + 2 St$ = (Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn).text) If Len(St$) = 0 Then ' skip empty cells barcodepic = -1 GoTo done End If ' i = 0 i = setdata(bc, ByVal St$) er1 = Bar2D2vba(bc) ' or Bar2D2vb(ByVal St$) If er1 = 0 Then Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn2).clearcontents Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn2).select Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn2).interior.colorindex = xlnone 68 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
73 Set px = ActiveSheet.Pictures.Paste Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn2).rowheight = px.height * 1.5 px.border.linestyle = xlnone ih = (Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn2).height - px.height) / 2 iw = (Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn2).width - px.width) / 2 px.left = Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn2).left + iw px.top = Cells(cellrow, cellcolumn2).top + ih barcodepic = -1 Else x$ = "Error in barcode data" MsgBox x$ barcodepic = 0 End If done: End Function The FBarcode2D macro places the font-based barcode text into the cell adjacent to the data, using the column identifier cellcolumn1% in the code below. The font used for the cell may be set to the fontname and height returned from the GetFnt2DDetail() call (where it had been stored by the FBarcode2DSetup macro) Out$ = String(512, " ") Barcode2 = 1 cellcolumn1% = cellcolumn% + 1 ' edit this line if you want the barcode elsewhere St$ = (Cells(cellrow%, cellcolumn%).text) Cells(cellrow%, cellcolumn1%).clearcontents If Len(St$) = 0 Then ' skip empty cells Barcode2 = -1 GoTo done End If j& = setdata(bc, ByVal St$) j& = Bar2D2fnt(bc, ByVal Out$) If (j& > 0) Then Cells(cellrow%, cellcolumn1%) = StrConv(Out$, vbfromunicode) Else x$ = "Error in barcode data" MsgBox x$ Barcode2 = 0 End If done: The destination cell for the barcode may be changed by editing the cellcolumn1% variable in the code above. In-cell Barcode2D() formula for Excel The function barcode2d() enables the contents of a cell to show a font-based barcode based on the data in another cell simply by placing a formula such as =barcode2d(cell,code,mode,columns,level,flags) into the cell. eg =barcode2d(a1,4,0,0,0,0) produces a Datamatrix barcode in the cell using data from the cell A1. The code for this function is included in the macros module. However, if this is the only function required the code for the function barcode2d() and the Declaration of the Bar2DfntO() function may be pasted into any other module. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 69
74 The code parameter is a number that determines the barcode type required (see the Barcode Types Table for complete list), and the mode, columns, level and flags parameter specifies all other options available. Generally these will be 0, but may be set to appropriate values see the Barcodes Help file for details for specific barcode types. Note that, by default, formulae in Excel are normally recalculated when Excel recognises that the data for the formula changes. However, we recommend forcing a recalculation of all formulae in the spreadsheet before assuming that all barcodes have been updated. The way of forcing recalculation depends on the version of Excel, so see you Excel Help for details. In most case SHIFT+F9 recalculates the current worksheet. Barcodes created using the In-cell formula cannot be distributed to other Excel users who do not have the Barcode 2D Macros product installed. Developers wishing to use in-line barcode formulae in spreadsheets for distribution should use the dbarcode 2D Developers Kit. 70 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
75 Barcode 2D Macros for Access The Access database B2DMACS2007.MDB contains the 2D Barcode macros which creates a barcode from the text in each cell selected in a column when the macro is called, and either places a barcode picture in an OLEObject table field or places a font-based barcode into a text field. As supplied the PBarcode2D macro must be run while the target Table is in DataSheet view. The FBarcode2D macro may be run in any view. The behaviour Installation in Access To install these macros you should follow these instructions: Open the supplied B2DMACS2007.ACCDB database. Save it with a different name (e.g. Barcodes.accdb) Copying to another database To copy Barcode 2D Macros to another Access 2007/2010/2013 database: 1. Open both the bmacs2007 database and your target database 2. Expand the Modules group in b2dmacs2007 and select the module named Barcode2DMacs; right-click on it and choose copy. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 71
76 3. In the "All Access Objects" windows of the target database right-click on an empty part of the window and choose Paste. (the Barcode2DMacs module will appear in the list). 4. Select the Macros group in the bmacs2007 database. You will see the four macros (FBarcode2D, FBarcode2DSetup, PBarcode2D and PBarcode2DSetup). Select all four, right-click and choose Copy. 5. In the "All Access Objects" windows of the target database right-click on an empty part of the window and choose Paste. (the four macros will appear in the list). 6. Finally, if you will be using the PBarcode2D macro to create barcode pictures, open your table in design view and ensure that the field that will receive the barcode image is set to the type "OLE Object" Using the 2D macros in Access PBarcode2DSetup or FBarcode2DSetup must be run at least once before the PBarcode2D and FBarcode2D macros can be used. Barcode pictures and font barcodes may be created in fields in the table in the same way as described for the 1D macros above. 72 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
77 Note that the pictures created using the P2DBarcode macro will not be visible while in datasheet view; the word Picture will be displayed instead. To view the barcode pictures a form or report containing a Bound Object Frame control is required, with its data Control Source set to the relevant field. Also the font barcodes created using the F2DBarcode macro will appear in datasheet view as a meaningless jumble of characters. To view the barcodes a form or report containing a text box is required, with the box s font set to the appropriate barcode font. Customisation of the Access macros The PBarcode2D macro operates when a table is displayed in datasheet view, takes the barcode data from selected cells (which must be Text cells) and pastes the barcode images into the adjacent cells (which must be OLEObect cells). Navigation and pasting are controlled by sending keystrokes to the table. TAB keys move the cursor around and the ^v (Control + V) initiates the pasting of the image. It is generally not necessary to edit this macro because there is no significance in the order of columns in datasheet view. The FBarcode2D macro uses named fields in a named table, by default taking the barcode data from a field named BarcodeSource in Table1 and placing the font-based barcode into a field named BarcodeFont. Any of these names may be changed simply by editing the macro code: Advanced barcode options Barcode Pictures and PBarcode2DSetup In each Office application the PBarcode2DSetup macro causes the display of the Barcode Image Options dialog which is used to specify the barcode type and other details of barcode images to be created next time the PBarcode2D macro is to run. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 73
78 The Barcode Image dialog contains the following: Code type combo box This drop-down combo box lists the code types supported by the library. Clicking on the arrow alongside the box causes the list to drop down. A specific code type may be selected by clicking on the name within the list. Start Mode combo box The Start Mode combo box provides a drop-down list of the modes supported by the currently selected code type. A specific code type may be selected by clicking on the name within the list. Security Level combo box The Security Level combo box provides a drop-down list of the levels supported by the currently selected code type and start mode. A specific Security Level may be selected by clicking on the name within the list. X dimension The size of barcode symbols generated by the library is specified by the X dimension (which is the width of the thinnest element in the symbol) specified in Mils (thousandths of an inch. Values between 10 and 40 are typical. Y multiplier He height of each element in the symbol given in multiples of the X dimension. For PDF417 symbols the value should be in the range 2 5, while for GS1-Databar symbols the value should be For Aztec, Datamatrix and QR Code symbols the value is ignored. 74 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
79 Border thickness The Border thickness edit box allows the choice of a thickness in mm of a border between the barcode image and the edge of the image area. Any border is displayed using the current background colour. The permitted value of the border thickness is in the range 0 25 mm. Bar reduction The user may enter into this box a percentage reduction that is used to reduce the thickness of all lines in the barcode. Any value between 0 and 50 may be entered. This facility may be used to compensate for ink spread following wet ink printing. Background colour button When pushed, the Colours dialog box is displayed and allows the choice of a colour with which the image background will be rendered when the barcode image is redrawn. Bar colour button When selected, the Colours dialog box is displayed and allows the choice of a colour with which the image bars and text font will be rendered when the barcode image is redrawn. Columns edit box The Columns edit box allows the user to specify the size of some barcode types. For Aztec, Datamatrix and QR Code the number specifies the number of elements across the symbol, while for PDF417 and GS1-Databar Expanded Stacked symbols the number specifies the number of codewords per row. Other options A number of additional option checkboxes will appear in the dialog for certain barcode types. The Postmatrix and DeutschePost boxes allow these variants of Datamatrix to be encoded. The dialog also contains OK and Cancel buttons. Pushing the OK button causes the macro to close the dialog and use the settings of the dialog as defaults for barcode creation. Pushing the Cancel button causes the dialog to be closed without affecting the current default settings. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 75
80 Barcode Fonts and FBarcode2DSetup In each Office application the FBarcode2DSetup macro causes the display of the Barcode Properties dialog which is used to specify the barcode type and other details of font-based barcodes to be created next time the FBarcode2D macro is to run. The Barcode Font dialog contains the following: Code type combo box This drop-down combo box lists the code types supported by the library. Clicking on the arrow alongside the box causes the list to drop down. A specific code type may be selected by clicking on the name within the list. Start Mode combo box The Start Mode combo box provides a drop-down list of the modes supported by the currently selected code type. A specific code type may be selected by clicking on the name within the list. Security Level combo box The Security Level combo box provides a drop-down list of the levels supported by the currently selected code type and start mode. A specific Security Level may be selected by clicking on the name within the list. 76 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
81 Barcode font properties The font used to generate the barcode may be selected from the two combo boxes. The font height (in points) is displayed here and may be changed. Typically values between 4 and 12 point are used. The barcode font must be one of AZTx, PD2x, PD3x, PD4x or PD5x, where x will normally be W (for the wide font), but may be R (reduced width) or N (narrow width) to suit specific printer technologies that produce ink spread. Other options A number of additional option checkboxes will appear in the dialog for certain barcode types. The Postmatrix and DeutschePost boxes allow these variants of Datamatrix to be encoded. The dialog also contains OK and Cancel buttons. Pushing the OK button causes the macro to close the dialog and use the settings of the dialog as defaults for barcode creation. Pushing the Cancel button causes the dialog to be closed without affecting the current default settings. Programming Programmers may prefer to set barcode properties programmatically rather than face the end-user with a dialog box for setting the properties. This may be achieved by modifying the contents of the BARCODE2D structure held within the DLL. Details of the BARCODE2 structure and the library API may be found in the documentation for the dbarcode 2D Developer Kit available for download from our web site at The following section outlines the function calls used by the macros within VBS and Office applications. Bar2Drd Declare Function Bar2Drd Lib "dls2d4u" (ByRef bc As barcode2d) As Long This function fills a BARCODE2D structure with the members created during the most recent use of the barcode properties dialog. Bar2DAsk3 Declare Function Bar2DAsk3 Lib "dls2d4u" (ByRef bc As barcode2d, i As Long) As Long This function displays the barcode properties dialog for picture barcodes and, if the OK button is pushed in the dialog, returns the settings in the barcode2d structure bc. The return value is negative if the OK button was pressed or 0 if the user cancelled the dialog. Bar2D2vba Declare Function Bar2D2vba Lib "dls2d4u" (ByRef bc As barcode2d) As Long This function creates a picture barcode using the barcode2d structure bc, and places the picture on the clipboard. The return value is 0 if successful or an error code. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 77
82 Bar2DAskF Declare Function Bar2DAskF Lib "dls2d4u" (ByRef bc As barcode2d, ByVal fname As String, ByRef fnth As Long, ByRef k As Long) As Long This function displays the barcode properties dialog for font barcodes and, if the OK button is pushed in the dialog, returns the settings in the barcode2d structure bc, and the font name and font height in the fname and fnth parameters. The final parameter should be 1 on calling Bar2DAskF, as this causes the data to be retained by the library. The return value is negative if the OK button was pressed or 0 if the user cancelled the dialog. Bar2D2fnt Declare Function Bar2D2fnt Lib "dls2d4u" (ByRef bc As barcode2d, ByVal szout As String) As Long This function returns a font based barcode (in szout) created using the barcode2d structure bc. Note that when the Unicode library is used the result in szout must be converted for VBA using: StrConv(szOut$, vbfromunicode) The return value is the length of the Szo string if successful or a negative error value. Bar2DfntO Declare Function Bar2DfntO Lib "dls2d4u" (ByVal Szi As String, ByRef Ic As Long, ByRef Im As Long, ByRef Icl As Long, ByRef Ilv As Long, ByRef Ifl As Long, ByVal Szo As String) As Long This function creates a font barcode using the following parameters: Szi: Barcode data Ic: code type value (eg 4 for Datamatrix) Im: start mode Icl: columns Ilv: secutiry level Ifl: flag settings The output string Szo contains the font barcode on return. The return value is the length of the Szo string if successful or a negative error value. This function is used for the in-line barcode2d() function for Excel. GetFnt2DDetail Declare Function GetFnt2DDetail Lib "dls2d4u" (ByVal fname As String, ByRef fnth As Long) As Long This function retrieves the font name (fname) and font height (fnth) created during the most recent use of the font barcode properties dialog. setdata Declare Function setdata Lib "dls2d4u" (ByRef bc As barcode2d, ByVal szdat As String) As Long This function passes the data string szdat to the string1 member of the BARCODE2D structure. 78 Barcodes for Office dlsoft Barcodes for Office
83 2D Barcode Types Table Barcode Code value Code 16k 0 * Code 49 1 * PDF417 2 Aztec 3 DataMatrix 4 MaxiCode 5 * MicroPDF 6 Databar (formerly RSS) 7 * Codablock F 8 * QR Code 9 Micro QR Code 10 * Code values marked * are NOT available as font barcodes. dlsoft Barcodes for Office Barcodes for Office 79
84
85 Index 1 1D Barcodes 6 2 2D Barcode Macros 59 2D Barcode Types Table 79 2D Barcodes 57 A Active Barcodes in Access 16 Active Barcodes in Excel 13 Active barcodes in Word 10 Active-X 2D controls 58 Advanced barcode options 37, 73 Auto Checkdigit check box 39, 42 B Background colour button 40, 75 Bar colour button 40, 75 Bar reduction 75 Bar reduction edit box 40 Bar2D2fnt 78 Bar2D2vba 77 Bar2DAsk3 77 Bar2DAskF 78 Bar2DfntO 78 Bar2Drd 77 BarCdin 45 BarCdrd 45 Barcode 2D Macros for Access 71 Barcode 2D Macros for Excel 64 Barcode 2D Macros for Word 61 Barcode font properties 43, 77 Barcode Fonts and FBarcode2DSetup 76 Barcode Fonts and FBarcodeSetup 42 Barcode Macros 19 Barcode Macros for Access 31 Barcode Macros for Excel 24 Barcode Macros for Word 20 Barcode pictures 33 Barcode Pictures and PBarcode2DSetup 73 Barcode Pictures and PBarcodeSetup 37 Barcode Types Table 53 Barcodes for Office 1 Barcodeudf 46 BarCodew 46 BarCodewF 46 BarInit 45 Bearer Size edit box 39 Border edit box 40 Border thickness 75 C char string[84] 51 Character spacing edit box 40 Code box 38, 42 Code type combo box 38, 42, 74, 76 COLORREF back_color 47 COLORREF fore_color 49 Columns edit box 75 Copying to another database 71 Copying to another workbook for Excel 65 Copying to another workbook for Excel 2007/2010/ Customisation of the Access macros 36, 73 Customisation of the Excel macros 28, 68 Customisation of the Word macros 22, 63 D Data Structure 43 E Embedded 2D barcode objects 57 Embedded Objects 6 ErrorMess 46 Extend Bearers checkbox 39 F Font or Picture or Object 2 Font-based barcodes 35 Function calls 45 G GetBarCdsz 47 GetFnt2DDetail 78 H Horizontal bearers checkbox 39 dlsoft Barcodes for Office Index 81
86 I In-cell Barcode() formula for Excel 29 In-cell Barcode2D() formula for Excel 69 Initialising the Macros 19, 59 Inserting a dbarcode image into a document 6 Installation for Excel 24, 64 Installation for Word 2007/2010/ , 61 Installation in Access 71 Installation in your own database 31 int auto_parity 47 int border_thickness 48 int code 48 int error 48 int line_reduction 50 int nominal_size 50 int orientation 50 int show_checkdigit 51 int show_text 51 int textgap; 51 int barratio 48 int bearer_size 48 int charspacing 48 int flags; 49 int justification 50 int margin_size 50 int xunit 51 Introduction 1 J Justify Text checkbox 39 L Licensing of Barcodes & Labels for Office components 4 Lift Text by edit box 40 M Mail-merge 23, 64 Making the macros available to all new workbooks 26, 67 Margin indicators checkbox 40 Margin Size edit box 40 P Programming 77 Programming properties 43 S Sample coding 44 Security Level combo box 74, 76 SetBarCdsz 47 setdata 78 Show Checkdigit check box 39 Show Text checkbox 39 Start Mode combo box 74, 76 Structure members 47 T Target Size box 38 The Active-X controls. 10 U Units combo box 38 Using the 2D macros in Access 72 Using the 2D macros in Word 62 Using the macros in Access 33 Using the macros in Excel 27, 68 Using the macros in Word 21 Using with CreateObject 4 W Wide Bars checkbox 42 Wide/Narrow ratio 40 X X dimension 74 Y Y multiplier 74 N No Background checkbox 39 O Other options 41, 43, 75, 77 Other variables Index dlsoft Barcodes for Office
Introduction to Microsoft Access 2003
 Introduction to Microsoft Access 2003 Zhi Liu School of Information Fall/2006 Introduction and Objectives Microsoft Access 2003 is a powerful, yet easy to learn, relational database application for Microsoft
Introduction to Microsoft Access 2003 Zhi Liu School of Information Fall/2006 Introduction and Objectives Microsoft Access 2003 is a powerful, yet easy to learn, relational database application for Microsoft
Microsoft Access 2010 Part 1: Introduction to Access
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Microsoft Access 2010 Part 1: Introduction to Access Fall 2014, Version 1.2 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Starting Access...3
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Microsoft Access 2010 Part 1: Introduction to Access Fall 2014, Version 1.2 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Starting Access...3
Excel 2003 Tutorial I
 This tutorial was adapted from a tutorial by see its complete version at http://www.fgcu.edu/support/office2000/excel/index.html Excel 2003 Tutorial I Spreadsheet Basics Screen Layout Title bar Menu bar
This tutorial was adapted from a tutorial by see its complete version at http://www.fgcu.edu/support/office2000/excel/index.html Excel 2003 Tutorial I Spreadsheet Basics Screen Layout Title bar Menu bar
Word 2010: Mail Merge to Email with Attachments
 Word 2010: Mail Merge to Email with Attachments Table of Contents TO SEE THE SECTION FOR MACROS, YOU MUST TURN ON THE DEVELOPER TAB:... 2 SET REFERENCE IN VISUAL BASIC:... 2 CREATE THE MACRO TO USE WITHIN
Word 2010: Mail Merge to Email with Attachments Table of Contents TO SEE THE SECTION FOR MACROS, YOU MUST TURN ON THE DEVELOPER TAB:... 2 SET REFERENCE IN VISUAL BASIC:... 2 CREATE THE MACRO TO USE WITHIN
Microsoft Office Access 2007 Basics
 Access(ing) A Database Project PRESENTED BY THE TECHNOLOGY TRAINERS OF THE MONROE COUNTY LIBRARY SYSTEM EMAIL: [email protected] MONROE COUNTY LIBRARY SYSTEM 734-241-5770 1 840 SOUTH ROESSLER
Access(ing) A Database Project PRESENTED BY THE TECHNOLOGY TRAINERS OF THE MONROE COUNTY LIBRARY SYSTEM EMAIL: [email protected] MONROE COUNTY LIBRARY SYSTEM 734-241-5770 1 840 SOUTH ROESSLER
Microsoft Access Basics
 Microsoft Access Basics 2006 ipic Development Group, LLC Authored by James D Ballotti Microsoft, Access, Excel, Word, and Office are registered trademarks of the Microsoft Corporation Version 1 - Revision
Microsoft Access Basics 2006 ipic Development Group, LLC Authored by James D Ballotti Microsoft, Access, Excel, Word, and Office are registered trademarks of the Microsoft Corporation Version 1 - Revision
Instructions for Creating an Outlook E-mail Distribution List from an Excel File
 Instructions for Creating an Outlook E-mail Distribution List from an Excel File 1.0 Importing Excel Data to an Outlook Distribution List 1.1 Create an Outlook Personal Folders File (.pst) Notes: 1) If
Instructions for Creating an Outlook E-mail Distribution List from an Excel File 1.0 Importing Excel Data to an Outlook Distribution List 1.1 Create an Outlook Personal Folders File (.pst) Notes: 1) If
Microsoft Access 2010 handout
 Microsoft Access 2010 handout Access 2010 is a relational database program you can use to create and manage large quantities of data. You can use Access to manage anything from a home inventory to a giant
Microsoft Access 2010 handout Access 2010 is a relational database program you can use to create and manage large quantities of data. You can use Access to manage anything from a home inventory to a giant
Basic Excel Handbook
 2 5 2 7 1 1 0 4 3 9 8 1 Basic Excel Handbook Version 3.6 May 6, 2008 Contents Contents... 1 Part I: Background Information...3 About This Handbook... 4 Excel Terminology... 5 Excel Terminology (cont.)...
2 5 2 7 1 1 0 4 3 9 8 1 Basic Excel Handbook Version 3.6 May 6, 2008 Contents Contents... 1 Part I: Background Information...3 About This Handbook... 4 Excel Terminology... 5 Excel Terminology (cont.)...
Create Mailing Labels from an Electronic File
 Create Mailing Labels from an Electronic File Microsoft Word 2002 (XP) Electronic data requests for mailing labels will be filled by providing the requester with a commadelimited text file. When you receive
Create Mailing Labels from an Electronic File Microsoft Word 2002 (XP) Electronic data requests for mailing labels will be filled by providing the requester with a commadelimited text file. When you receive
A Quick Tour of F9 1
 A Quick Tour of F9 1 Table of Contents I. A Quick Tour of F9... 3 1. Getting Started... 3 2. Quick Trial Balance... 7 3. A More Dynamic Table Report... 10 II. The Fundamental F9 Formula... 14 The GL Formula...
A Quick Tour of F9 1 Table of Contents I. A Quick Tour of F9... 3 1. Getting Started... 3 2. Quick Trial Balance... 7 3. A More Dynamic Table Report... 10 II. The Fundamental F9 Formula... 14 The GL Formula...
Microsoft Access 2010 Overview of Basics
 Opening Screen Access 2010 launches with a window allowing you to: create a new database from a template; create a new template from scratch; or open an existing database. Open existing Templates Create
Opening Screen Access 2010 launches with a window allowing you to: create a new database from a template; create a new template from scratch; or open an existing database. Open existing Templates Create
Getting Started with Excel 2008. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Elements of An Excel Document... 2 Resizing and Hiding Columns and Rows... 3 Using Panes to Create Spreadsheet Headers... 3 Using the AutoFill Command... 4 Using AutoFill for Sequences...
Table of Contents Elements of An Excel Document... 2 Resizing and Hiding Columns and Rows... 3 Using Panes to Create Spreadsheet Headers... 3 Using the AutoFill Command... 4 Using AutoFill for Sequences...
Outlook Email. User Guide IS TRAINING CENTER. 833 Chestnut St, Suite 600. Philadelphia, PA 19107 215-503-7500
 Outlook Email User Guide IS TRAINING CENTER 833 Chestnut St, Suite 600 Philadelphia, PA 19107 215-503-7500 This page intentionally left blank. TABLE OF CONTENTS Getting Started... 3 Opening Outlook...
Outlook Email User Guide IS TRAINING CENTER 833 Chestnut St, Suite 600 Philadelphia, PA 19107 215-503-7500 This page intentionally left blank. TABLE OF CONTENTS Getting Started... 3 Opening Outlook...
MICROSOFT OFFICE ACCESS 2007 - NEW FEATURES
 MICROSOFT OFFICE 2007 MICROSOFT OFFICE ACCESS 2007 - NEW FEATURES Exploring Access Creating and Working with Tables Finding and Filtering Data Working with Queries and Recordsets Working with Forms Working
MICROSOFT OFFICE 2007 MICROSOFT OFFICE ACCESS 2007 - NEW FEATURES Exploring Access Creating and Working with Tables Finding and Filtering Data Working with Queries and Recordsets Working with Forms Working
Microsoft Office. Mail Merge in Microsoft Word
 Microsoft Office Mail Merge in Microsoft Word TABLE OF CONTENTS Microsoft Office... 1 Mail Merge in Microsoft Word... 1 CREATE THE SMS DATAFILE FOR EXPORT... 3 Add A Label Row To The Excel File... 3 Backup
Microsoft Office Mail Merge in Microsoft Word TABLE OF CONTENTS Microsoft Office... 1 Mail Merge in Microsoft Word... 1 CREATE THE SMS DATAFILE FOR EXPORT... 3 Add A Label Row To The Excel File... 3 Backup
Task Force on Technology / EXCEL
 Task Force on Technology EXCEL Basic terminology Spreadsheet A spreadsheet is an electronic document that stores various types of data. There are vertical columns and horizontal rows. A cell is where the
Task Force on Technology EXCEL Basic terminology Spreadsheet A spreadsheet is an electronic document that stores various types of data. There are vertical columns and horizontal rows. A cell is where the
Microsoft PowerPoint 2008
 Microsoft PowerPoint 2008 Starting PowerPoint... 2 Creating Slides in Your Presentation... 3 Beginning with the Title Slide... 3 Inserting a New Slide... 3 Slide Layouts... 3 Adding an Image to a Slide...
Microsoft PowerPoint 2008 Starting PowerPoint... 2 Creating Slides in Your Presentation... 3 Beginning with the Title Slide... 3 Inserting a New Slide... 3 Slide Layouts... 3 Adding an Image to a Slide...
Module One: Getting Started... 6. Opening Outlook... 6. Setting Up Outlook for the First Time... 7. Understanding the Interface...
 2 CONTENTS Module One: Getting Started... 6 Opening Outlook... 6 Setting Up Outlook for the First Time... 7 Understanding the Interface...12 Using Backstage View...14 Viewing Your Inbox...15 Closing Outlook...17
2 CONTENTS Module One: Getting Started... 6 Opening Outlook... 6 Setting Up Outlook for the First Time... 7 Understanding the Interface...12 Using Backstage View...14 Viewing Your Inbox...15 Closing Outlook...17
Excel 2007 Basic knowledge
 Ribbon menu The Ribbon menu system with tabs for various Excel commands. This Ribbon system replaces the traditional menus used with Excel 2003. Above the Ribbon in the upper-left corner is the Microsoft
Ribbon menu The Ribbon menu system with tabs for various Excel commands. This Ribbon system replaces the traditional menus used with Excel 2003. Above the Ribbon in the upper-left corner is the Microsoft
Microsoft PowerPoint 2010
 Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 Starting PowerPoint... 2 PowerPoint Window Properties... 2 The Ribbon... 3 Default Tabs... 3 Contextual Tabs... 3 Minimizing and Restoring the Ribbon... 4 The Backstage View...
Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 Starting PowerPoint... 2 PowerPoint Window Properties... 2 The Ribbon... 3 Default Tabs... 3 Contextual Tabs... 3 Minimizing and Restoring the Ribbon... 4 The Backstage View...
Microsoft Excel 2013: Macro to apply Custom Margins, Titles, Gridlines, Autofit Width & Add Macro to Quick Access Toolbar & How to Delete a Macro.
 Microsoft Excel 2013: Macro to apply Custom Margins, Titles, Gridlines, Autofit Width & Add Macro to Quick Access Toolbar & How to Delete a Macro. Do you need to always add gridlines, bold the heading
Microsoft Excel 2013: Macro to apply Custom Margins, Titles, Gridlines, Autofit Width & Add Macro to Quick Access Toolbar & How to Delete a Macro. Do you need to always add gridlines, bold the heading
Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2013
 Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2013 Navigating the PowerPoint 2013 Environment The Ribbon: The ribbon is where you will access a majority of the commands you will use to create and develop your presentation.
Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2013 Navigating the PowerPoint 2013 Environment The Ribbon: The ribbon is where you will access a majority of the commands you will use to create and develop your presentation.
Results CRM 2012 User Manual
 Results CRM 2012 User Manual A Guide to Using Results CRM Standard, Results CRM Plus, & Results CRM Business Suite Table of Contents Installation Instructions... 1 Single User & Evaluation Installation
Results CRM 2012 User Manual A Guide to Using Results CRM Standard, Results CRM Plus, & Results CRM Business Suite Table of Contents Installation Instructions... 1 Single User & Evaluation Installation
Advanced Presentation Features and Animation
 There are three features that you should remember as you work within PowerPoint 2007: the Microsoft Office Button, the Quick Access Toolbar, and the Ribbon. The function of these features will be more
There are three features that you should remember as you work within PowerPoint 2007: the Microsoft Office Button, the Quick Access Toolbar, and the Ribbon. The function of these features will be more
Excel 2003 A Beginners Guide
 Excel 2003 A Beginners Guide Beginner Introduction The aim of this document is to introduce some basic techniques for using Excel to enter data, perform calculations and produce simple charts based on
Excel 2003 A Beginners Guide Beginner Introduction The aim of this document is to introduce some basic techniques for using Excel to enter data, perform calculations and produce simple charts based on
Access 2007 Creating Forms Table of Contents
 Access 2007 Creating Forms Table of Contents CREATING FORMS IN ACCESS 2007... 3 UNDERSTAND LAYOUT VIEW AND DESIGN VIEW... 3 LAYOUT VIEW... 3 DESIGN VIEW... 3 UNDERSTAND CONTROLS... 4 BOUND CONTROL... 4
Access 2007 Creating Forms Table of Contents CREATING FORMS IN ACCESS 2007... 3 UNDERSTAND LAYOUT VIEW AND DESIGN VIEW... 3 LAYOUT VIEW... 3 DESIGN VIEW... 3 UNDERSTAND CONTROLS... 4 BOUND CONTROL... 4
SECTION 5: Finalizing Your Workbook
 SECTION 5: Finalizing Your Workbook In this section you will learn how to: Protect a workbook Protect a sheet Protect Excel files Unlock cells Use the document inspector Use the compatibility checker Mark
SECTION 5: Finalizing Your Workbook In this section you will learn how to: Protect a workbook Protect a sheet Protect Excel files Unlock cells Use the document inspector Use the compatibility checker Mark
Using an Access Database
 A Few Terms Using an Access Database These words are used often in Access so you will want to become familiar with them before using the program and this tutorial. A database is a collection of related
A Few Terms Using an Access Database These words are used often in Access so you will want to become familiar with them before using the program and this tutorial. A database is a collection of related
Table and field properties Tables and fields also have properties that you can set to control their characteristics or behavior.
 Create a table When you create a database, you store your data in tables subject-based lists that contain rows and columns. For instance, you can create a Contacts table to store a list of names, addresses,
Create a table When you create a database, you store your data in tables subject-based lists that contain rows and columns. For instance, you can create a Contacts table to store a list of names, addresses,
Excel 2007 A Beginners Guide
 Excel 2007 A Beginners Guide Beginner Introduction The aim of this document is to introduce some basic techniques for using Excel to enter data, perform calculations and produce simple charts based on
Excel 2007 A Beginners Guide Beginner Introduction The aim of this document is to introduce some basic techniques for using Excel to enter data, perform calculations and produce simple charts based on
MICROSOFT ACCESS 2007 BOOK 2
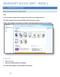 MICROSOFT ACCESS 2007 BOOK 2 4.1 INTRODUCTION TO ACCESS FIRST ENCOUNTER WITH ACCESS 2007 P 205 Access is activated by means of Start, Programs, Microsoft Access or clicking on the icon. The window opened
MICROSOFT ACCESS 2007 BOOK 2 4.1 INTRODUCTION TO ACCESS FIRST ENCOUNTER WITH ACCESS 2007 P 205 Access is activated by means of Start, Programs, Microsoft Access or clicking on the icon. The window opened
Quickstart Tutorial. Bradford Technologies, Inc. 302 Piercy Road, San Jose, California 95138 800-622-8727 fax 408-360-8529 www.bradfordsoftware.
 Quickstart Tutorial A ClickFORMS Tutorial Page 2 Bradford Technologies. All Rights Reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced in any form or by any means without the written permission of Bradford
Quickstart Tutorial A ClickFORMS Tutorial Page 2 Bradford Technologies. All Rights Reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced in any form or by any means without the written permission of Bradford
Introduction to MS WINDOWS XP
 Introduction to MS WINDOWS XP Mouse Desktop Windows Applications File handling Introduction to MS Windows XP 2 Table of Contents What is Windows XP?... 3 Windows within Windows... 3 The Desktop... 3 The
Introduction to MS WINDOWS XP Mouse Desktop Windows Applications File handling Introduction to MS Windows XP 2 Table of Contents What is Windows XP?... 3 Windows within Windows... 3 The Desktop... 3 The
FileMaker Pro and Microsoft Office Integration
 FileMaker Pro and Microsoft Office Integration page Table of Contents Executive Summary...3 Introduction...3 Top Reasons to Read This Guide...3 Before You Get Started...4 Downloading the FileMaker Trial
FileMaker Pro and Microsoft Office Integration page Table of Contents Executive Summary...3 Introduction...3 Top Reasons to Read This Guide...3 Before You Get Started...4 Downloading the FileMaker Trial
Create a New Database in Access 2010
 Create a New Database in Access 2010 Table of Contents OVERVIEW... 1 CREATING A DATABASE... 1 ADDING TO A DATABASE... 2 CREATE A DATABASE BY USING A TEMPLATE... 2 CREATE A DATABASE WITHOUT USING A TEMPLATE...
Create a New Database in Access 2010 Table of Contents OVERVIEW... 1 CREATING A DATABASE... 1 ADDING TO A DATABASE... 2 CREATE A DATABASE BY USING A TEMPLATE... 2 CREATE A DATABASE WITHOUT USING A TEMPLATE...
Mitigation Planning Portal MPP Reporting System
 Mitigation Planning Portal MPP Reporting System Updated: 7/13/2015 Introduction Access the MPP Reporting System by clicking on the Reports tab and clicking the Launch button. Within the system, you can
Mitigation Planning Portal MPP Reporting System Updated: 7/13/2015 Introduction Access the MPP Reporting System by clicking on the Reports tab and clicking the Launch button. Within the system, you can
EMAIL QUICK START GUIDE
 IT Services Microsoft Outlook 2010 EMAIL QUICK START GUIDE Contents What is Outlook?...2 Quick Guide to Email...2 Create a new e-mail message...2 Forward or reply to an e-mail message...2 Creating new
IT Services Microsoft Outlook 2010 EMAIL QUICK START GUIDE Contents What is Outlook?...2 Quick Guide to Email...2 Create a new e-mail message...2 Forward or reply to an e-mail message...2 Creating new
EXCEL PIVOT TABLE David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA Dean s Office Oct 2002
 EXCEL PIVOT TABLE David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA Dean s Office Oct 2002 Table of Contents Part I Creating a Pivot Table Excel Database......3 What is a Pivot Table...... 3 Creating Pivot Tables
EXCEL PIVOT TABLE David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA Dean s Office Oct 2002 Table of Contents Part I Creating a Pivot Table Excel Database......3 What is a Pivot Table...... 3 Creating Pivot Tables
Word 2007: Basics Learning Guide
 Word 2007: Basics Learning Guide Exploring Word At first glance, the new Word 2007 interface may seem a bit unsettling, with fat bands called Ribbons replacing cascading text menus and task bars. This
Word 2007: Basics Learning Guide Exploring Word At first glance, the new Word 2007 interface may seem a bit unsettling, with fat bands called Ribbons replacing cascading text menus and task bars. This
How to Edit an Email. Here are some of the things you can do to customize your email:
 How to Edit an Email Editing a new email created during the Create an Email wizard or editing an existing email in the Edit Email section of the Manage Emails tab is easy, using editing tools you re probably
How to Edit an Email Editing a new email created during the Create an Email wizard or editing an existing email in the Edit Email section of the Manage Emails tab is easy, using editing tools you re probably
BID2WIN Workshop. Advanced Report Writing
 BID2WIN Workshop Advanced Report Writing Please Note: Please feel free to take this workbook home with you! Electronic copies of all lab documentation are available for download at http://www.bid2win.com/userconf/2011/labs/
BID2WIN Workshop Advanced Report Writing Please Note: Please feel free to take this workbook home with you! Electronic copies of all lab documentation are available for download at http://www.bid2win.com/userconf/2011/labs/
MICROSOFT OUTLOOK 2010 WORK WITH CONTACTS
 MICROSOFT OUTLOOK 2010 WORK WITH CONTACTS Last Edited: 2012-07-09 1 Access to Outlook contacts area... 4 Manage Outlook contacts view... 5 Change the view of Contacts area... 5 Business Cards view... 6
MICROSOFT OUTLOOK 2010 WORK WITH CONTACTS Last Edited: 2012-07-09 1 Access to Outlook contacts area... 4 Manage Outlook contacts view... 5 Change the view of Contacts area... 5 Business Cards view... 6
Q&As: Microsoft Excel 2013: Chapter 2
 Q&As: Microsoft Excel 2013: Chapter 2 In Step 5, why did the date that was entered change from 4/5/10 to 4/5/2010? When Excel recognizes that you entered a date in mm/dd/yy format, it automatically formats
Q&As: Microsoft Excel 2013: Chapter 2 In Step 5, why did the date that was entered change from 4/5/10 to 4/5/2010? When Excel recognizes that you entered a date in mm/dd/yy format, it automatically formats
Microsoft Access 2007
 How to Use: Microsoft Access 2007 Microsoft Office Access is a powerful tool used to create and format databases. Databases allow information to be organized in rows and tables, where queries can be formed
How to Use: Microsoft Access 2007 Microsoft Office Access is a powerful tool used to create and format databases. Databases allow information to be organized in rows and tables, where queries can be formed
Working together with Word, Excel and PowerPoint
 Working together with Word, Excel and PowerPoint Have you ever wanted your Word document to include data from an Excel spreadsheet, or diagrams you ve created in PowerPoint? This note shows you how to
Working together with Word, Excel and PowerPoint Have you ever wanted your Word document to include data from an Excel spreadsheet, or diagrams you ve created in PowerPoint? This note shows you how to
Google Docs Basics Website: http://etc.usf.edu/te/
 Website: http://etc.usf.edu/te/ Google Docs is a free web-based office suite that allows you to store documents online so you can access them from any computer with an internet connection. With Google
Website: http://etc.usf.edu/te/ Google Docs is a free web-based office suite that allows you to store documents online so you can access them from any computer with an internet connection. With Google
Simply Accounting Intelligence Tips and Tricks Booklet Vol. 1
 Simply Accounting Intelligence Tips and Tricks Booklet Vol. 1 1 Contents Accessing the SAI reports... 3 Running, Copying and Pasting reports... 4 Creating and linking a report... 5 Auto e-mailing reports...
Simply Accounting Intelligence Tips and Tricks Booklet Vol. 1 1 Contents Accessing the SAI reports... 3 Running, Copying and Pasting reports... 4 Creating and linking a report... 5 Auto e-mailing reports...
MS Access Lab 2. Topic: Tables
 MS Access Lab 2 Topic: Tables Summary Introduction: Tables, Start to build a new database Creating Tables: Datasheet View, Design View Working with Data: Sorting, Filtering Help on Tables Introduction
MS Access Lab 2 Topic: Tables Summary Introduction: Tables, Start to build a new database Creating Tables: Datasheet View, Design View Working with Data: Sorting, Filtering Help on Tables Introduction
Basic Microsoft Excel 2007
 Basic Microsoft Excel 2007 The biggest difference between Excel 2007 and its predecessors is the new layout. All of the old functions are still there (with some new additions), but they are now located
Basic Microsoft Excel 2007 The biggest difference between Excel 2007 and its predecessors is the new layout. All of the old functions are still there (with some new additions), but they are now located
-SoftChalk LessonBuilder-
 -SoftChalk LessonBuilder- SoftChalk is a powerful web lesson editor that lets you easily create engaging, interactive web lessons for your e-learning classroom. It allows you to create and edit content
-SoftChalk LessonBuilder- SoftChalk is a powerful web lesson editor that lets you easily create engaging, interactive web lessons for your e-learning classroom. It allows you to create and edit content
Section 4. Mastering Folders
 Section 4 Mastering Folders About This Section Section 3: Working with Receipts introduced you to the Receipts Grid area of the Receipt Organizer window (the lower of the two grids). In the Receipts Grid,
Section 4 Mastering Folders About This Section Section 3: Working with Receipts introduced you to the Receipts Grid area of the Receipt Organizer window (the lower of the two grids). In the Receipts Grid,
BIGPOND ONLINE STORAGE USER GUIDE Issue 1.1.0-18 August 2005
 BIGPOND ONLINE STORAGE USER GUIDE Issue 1.1.0-18 August 2005 PLEASE NOTE: The contents of this publication, and any associated documentation provided to you, must not be disclosed to any third party without
BIGPOND ONLINE STORAGE USER GUIDE Issue 1.1.0-18 August 2005 PLEASE NOTE: The contents of this publication, and any associated documentation provided to you, must not be disclosed to any third party without
Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2010
 Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2010 Screen Elements Quick Access Toolbar The Ribbon Formula Bar Expand Formula Bar Button File Menu Vertical Scroll Worksheet Navigation Tabs Horizontal Scroll Bar Zoom
Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2010 Screen Elements Quick Access Toolbar The Ribbon Formula Bar Expand Formula Bar Button File Menu Vertical Scroll Worksheet Navigation Tabs Horizontal Scroll Bar Zoom
Excel 2007: Basics Learning Guide
 Excel 2007: Basics Learning Guide Exploring Excel At first glance, the new Excel 2007 interface may seem a bit unsettling, with fat bands called Ribbons replacing cascading text menus and task bars. This
Excel 2007: Basics Learning Guide Exploring Excel At first glance, the new Excel 2007 interface may seem a bit unsettling, with fat bands called Ribbons replacing cascading text menus and task bars. This
ECDL. European Computer Driving Licence. Database Software BCS ITQ Level 1. Syllabus Version 1.0
 ECDL European Computer Driving Licence Database Software BCS ITQ Level 1 Using Microsoft Access 2013 Syllabus Version 1.0 This training, which has been approved by BCS, includes exercise items intended
ECDL European Computer Driving Licence Database Software BCS ITQ Level 1 Using Microsoft Access 2013 Syllabus Version 1.0 This training, which has been approved by BCS, includes exercise items intended
Microsoft Office System Tip Sheet
 Experience the 2007 Microsoft Office System The 2007 Microsoft Office system includes programs, servers, services, and solutions designed to work together to help you succeed. New features in the 2007
Experience the 2007 Microsoft Office System The 2007 Microsoft Office system includes programs, servers, services, and solutions designed to work together to help you succeed. New features in the 2007
Advanced Excel 10/20/2011 1
 Advanced Excel Data Validation Excel has a feature called Data Validation, which will allow you to control what kind of information is typed into cells. 1. Select the cell(s) you wish to control. 2. Click
Advanced Excel Data Validation Excel has a feature called Data Validation, which will allow you to control what kind of information is typed into cells. 1. Select the cell(s) you wish to control. 2. Click
EXCEL 2007. Using Excel for Data Query & Management. Information Technology. MS Office Excel 2007 Users Guide. IT Training & Development
 Information Technology MS Office Excel 2007 Users Guide EXCEL 2007 Using Excel for Data Query & Management IT Training & Development (818) 677-1700 [email protected] http://www.csun.edu/training TABLE
Information Technology MS Office Excel 2007 Users Guide EXCEL 2007 Using Excel for Data Query & Management IT Training & Development (818) 677-1700 [email protected] http://www.csun.edu/training TABLE
Excel 2002. What you will do:
 What you will do: Explore the features of Excel 2002 Create a blank workbook and a workbook from a template Format a workbook Apply formulas to a workbook Create a chart Import data to a workbook Share
What you will do: Explore the features of Excel 2002 Create a blank workbook and a workbook from a template Format a workbook Apply formulas to a workbook Create a chart Import data to a workbook Share
Programming in Access VBA
 PART I Programming in Access VBA In this part, you will learn all about how Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) works for Access 2010. A number of new VBA features have been incorporated into the 2010
PART I Programming in Access VBA In this part, you will learn all about how Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) works for Access 2010. A number of new VBA features have been incorporated into the 2010
Learning Services IT Guide. Access 2013
 Learning Services IT Guide Access 2013 Microsoft Access is a programme which allows you to store a lot of information easily in the form of a database. For example you could create a database which stored
Learning Services IT Guide Access 2013 Microsoft Access is a programme which allows you to store a lot of information easily in the form of a database. For example you could create a database which stored
Software User's Guide
 BROTHER QL-500/550/650TD/1050/1050N Software User's Guide QL-500 QL-650TD QL-550 QL-1050/1050N 1 Contents Contents....................................................................................2................................................................................4
BROTHER QL-500/550/650TD/1050/1050N Software User's Guide QL-500 QL-650TD QL-550 QL-1050/1050N 1 Contents Contents....................................................................................2................................................................................4
Microsoft Excel Basics
 COMMUNITY TECHNICAL SUPPORT Microsoft Excel Basics Introduction to Excel Click on the program icon in Launcher or the Microsoft Office Shortcut Bar. A worksheet is a grid, made up of columns, which are
COMMUNITY TECHNICAL SUPPORT Microsoft Excel Basics Introduction to Excel Click on the program icon in Launcher or the Microsoft Office Shortcut Bar. A worksheet is a grid, made up of columns, which are
Ohio University Computer Services Center August, 2002 Crystal Reports Introduction Quick Reference Guide
 Open Crystal Reports From the Windows Start menu choose Programs and then Crystal Reports. Creating a Blank Report Ohio University Computer Services Center August, 2002 Crystal Reports Introduction Quick
Open Crystal Reports From the Windows Start menu choose Programs and then Crystal Reports. Creating a Blank Report Ohio University Computer Services Center August, 2002 Crystal Reports Introduction Quick
Introduction to dobe Acrobat XI Pro
 Introduction to dobe Acrobat XI Pro Introduction to Adobe Acrobat XI Pro is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this
Introduction to dobe Acrobat XI Pro Introduction to Adobe Acrobat XI Pro is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this
User Services. Intermediate Microsoft Access. Use the new Microsoft Access. Getting Help. Instructors OBJECTIVES. July 2009
 User Services July 2009 OBJECTIVES Develop Field Properties Import Data from an Excel Spreadsheet & MS Access database Create Relationships Create a Form with a Subform Create Action Queries Create Command
User Services July 2009 OBJECTIVES Develop Field Properties Import Data from an Excel Spreadsheet & MS Access database Create Relationships Create a Form with a Subform Create Action Queries Create Command
Introduction To Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007. Bob Booth July 2008 AP-PPT5
 Introduction To Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007. Bob Booth July 2008 AP-PPT5 University of Sheffield Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. GETTING STARTED... 4 2.1 STARTING POWERPOINT... 4 3. THE USER INTERFACE...
Introduction To Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007. Bob Booth July 2008 AP-PPT5 University of Sheffield Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. GETTING STARTED... 4 2.1 STARTING POWERPOINT... 4 3. THE USER INTERFACE...
Handout: Word 2010 Tips and Shortcuts
 Word 2010: Tips and Shortcuts Table of Contents EXPORT A CUSTOMIZED QUICK ACCESS TOOLBAR... 2 IMPORT A CUSTOMIZED QUICK ACCESS TOOLBAR... 2 USE THE FORMAT PAINTER... 3 REPEAT THE LAST ACTION... 3 SHOW
Word 2010: Tips and Shortcuts Table of Contents EXPORT A CUSTOMIZED QUICK ACCESS TOOLBAR... 2 IMPORT A CUSTOMIZED QUICK ACCESS TOOLBAR... 2 USE THE FORMAT PAINTER... 3 REPEAT THE LAST ACTION... 3 SHOW
WHAT S NEW IN OUTLOOK 2010 & HOW TO CUSTOMIZE IT
 WHAT S NEW IN OUTLOOK 2010 & HOW TO CUSTOMIZE IT THE RIBBON... 2 CONTEXTUAL TABS... 4 THE FILE TAB... 4 DIALOG BOXES... 5 MINIMIZING THE RIBBON... 5 CUSTOMIZING THE RIBBON... 6 CUSTOMIZING THE QUICK ACCESS
WHAT S NEW IN OUTLOOK 2010 & HOW TO CUSTOMIZE IT THE RIBBON... 2 CONTEXTUAL TABS... 4 THE FILE TAB... 4 DIALOG BOXES... 5 MINIMIZING THE RIBBON... 5 CUSTOMIZING THE RIBBON... 6 CUSTOMIZING THE QUICK ACCESS
Microsoft Excel 2010 Tutorial
 1 Microsoft Excel 2010 Tutorial Excel is a spreadsheet program in the Microsoft Office system. You can use Excel to create and format workbooks (a collection of spreadsheets) in order to analyze data and
1 Microsoft Excel 2010 Tutorial Excel is a spreadsheet program in the Microsoft Office system. You can use Excel to create and format workbooks (a collection of spreadsheets) in order to analyze data and
Excel basics. Before you begin. What you'll learn. Requirements. Estimated time to complete:
 Excel basics Excel is a powerful spreadsheet and data analysis application, but to use it most effectively, you first have to understand the basics. This tutorial introduces some of the tasks and features
Excel basics Excel is a powerful spreadsheet and data analysis application, but to use it most effectively, you first have to understand the basics. This tutorial introduces some of the tasks and features
Easy Scan Complete. Administrator User Guide. HealthStream Competency Cent. HealthStream, Inc. 209 10th Ave. South Suite 450 Nashville, TN 37203
 Easy Scan Complete Administrator User Guide HealthStream, Inc. 209 10th Ave. South Suite 450 Nashville, TN 37203 HealthStream Competency Cent Table of Contents Easy Scan Overview... 3 Gathering Data for
Easy Scan Complete Administrator User Guide HealthStream, Inc. 209 10th Ave. South Suite 450 Nashville, TN 37203 HealthStream Competency Cent Table of Contents Easy Scan Overview... 3 Gathering Data for
Using Excel for Business Analysis: A Guide to Financial Modelling Fundamentals
 Excel 2003 Instructions Using Excel for Business Analysis: A Guide to Financial Modelling Fundamentals contains extensive instructions for using Excel 2010 and Excel for Mac 2011. There are a few instances
Excel 2003 Instructions Using Excel for Business Analysis: A Guide to Financial Modelling Fundamentals contains extensive instructions for using Excel 2010 and Excel for Mac 2011. There are a few instances
Migrating to Excel 2010 from Excel 2003 - Excel - Microsoft Office 1 of 1
 Migrating to Excel 2010 - Excel - Microsoft Office 1 of 1 In This Guide Microsoft Excel 2010 looks very different, so we created this guide to help you minimize the learning curve. Read on to learn key
Migrating to Excel 2010 - Excel - Microsoft Office 1 of 1 In This Guide Microsoft Excel 2010 looks very different, so we created this guide to help you minimize the learning curve. Read on to learn key
MICROSOFT ACCESS STEP BY STEP GUIDE
 IGCSE ICT SECTION 11 DATA MANIPULATION MICROSOFT ACCESS STEP BY STEP GUIDE Mark Nicholls ICT Lounge P a g e 1 Contents Task 35 details Page 3 Opening a new Database. Page 4 Importing.csv file into the
IGCSE ICT SECTION 11 DATA MANIPULATION MICROSOFT ACCESS STEP BY STEP GUIDE Mark Nicholls ICT Lounge P a g e 1 Contents Task 35 details Page 3 Opening a new Database. Page 4 Importing.csv file into the
MICROSOFT ACCESS 2003 TUTORIAL
 MICROSOFT ACCESS 2003 TUTORIAL M I C R O S O F T A C C E S S 2 0 0 3 Microsoft Access is powerful software designed for PC. It allows you to create and manage databases. A database is an organized body
MICROSOFT ACCESS 2003 TUTORIAL M I C R O S O F T A C C E S S 2 0 0 3 Microsoft Access is powerful software designed for PC. It allows you to create and manage databases. A database is an organized body
Working together with Word, Excel and PowerPoint 2013
 Working together with Word, Excel and PowerPoint 2013 Information Services Working together with Word, Excel and PowerPoint 2013 Have you ever needed to include data from Excel or a slide from PowerPoint
Working together with Word, Excel and PowerPoint 2013 Information Services Working together with Word, Excel and PowerPoint 2013 Have you ever needed to include data from Excel or a slide from PowerPoint
Lab 2: MS ACCESS Tables
 Lab 2: MS ACCESS Tables Summary Introduction to Tables and How to Build a New Database Creating Tables in Datasheet View and Design View Working with Data on Sorting and Filtering 1. Introduction Creating
Lab 2: MS ACCESS Tables Summary Introduction to Tables and How to Build a New Database Creating Tables in Datasheet View and Design View Working with Data on Sorting and Filtering 1. Introduction Creating
Importing Contacts to Outlook
 Importing Contacts to Outlook 1. The first step is to create a file of your contacts from the National Chapter Database. 2. You create this file under Reporting, Multiple. You will follow steps 1 and 2
Importing Contacts to Outlook 1. The first step is to create a file of your contacts from the National Chapter Database. 2. You create this file under Reporting, Multiple. You will follow steps 1 and 2
MS Excel. Handout: Level 2. elearning Department. Copyright 2016 CMS e-learning Department. All Rights Reserved. Page 1 of 11
 MS Excel Handout: Level 2 elearning Department 2016 Page 1 of 11 Contents Excel Environment:... 3 To create a new blank workbook:...3 To insert text:...4 Cell addresses:...4 To save the workbook:... 5
MS Excel Handout: Level 2 elearning Department 2016 Page 1 of 11 Contents Excel Environment:... 3 To create a new blank workbook:...3 To insert text:...4 Cell addresses:...4 To save the workbook:... 5
Creating and Editing Workbooks. STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES (SLOs) After completing this chapter, you will be able to:
 CHAPTER 1 Creating and Editing Workbooks CHAPTER OVERVIEW Microsoft Excel (Excel) is a spreadsheet program you can use to create electronic workbooks to organize numerical data, perform calculations, and
CHAPTER 1 Creating and Editing Workbooks CHAPTER OVERVIEW Microsoft Excel (Excel) is a spreadsheet program you can use to create electronic workbooks to organize numerical data, perform calculations, and
Microsoft Word 2010 Prepared by Computing Services at the Eastman School of Music July 2010
 Microsoft Word 2010 Prepared by Computing Services at the Eastman School of Music July 2010 Contents Microsoft Office Interface... 4 File Ribbon Tab... 5 Microsoft Office Quick Access Toolbar... 6 Appearance
Microsoft Word 2010 Prepared by Computing Services at the Eastman School of Music July 2010 Contents Microsoft Office Interface... 4 File Ribbon Tab... 5 Microsoft Office Quick Access Toolbar... 6 Appearance
Microsoft PowerPoint 2011
 Microsoft PowerPoint 2011 Starting PowerPoint... 2 Creating Slides in Your Presentation... 3 Beginning with the Title Slide... 3 Inserting a New Slide... 3 Adding an Image to a Slide... 4 Downloading Images
Microsoft PowerPoint 2011 Starting PowerPoint... 2 Creating Slides in Your Presentation... 3 Beginning with the Title Slide... 3 Inserting a New Slide... 3 Adding an Image to a Slide... 4 Downloading Images
BulkSMS Text Messenger Product Manual
 BulkSMS Text Messenger Product Manual 1. Installing the software 1.1. Download the BulkSMS Text Messenger Go to www.bulksms.com and choose your country. process. Click on products on the top menu and select
BulkSMS Text Messenger Product Manual 1. Installing the software 1.1. Download the BulkSMS Text Messenger Go to www.bulksms.com and choose your country. process. Click on products on the top menu and select
Writer Guide. Chapter 15 Using Forms in Writer
 Writer Guide Chapter 15 Using Forms in Writer Copyright This document is Copyright 2005 2008 by its contributors as listed in the section titled Authors. You may distribute it and/or modify it under the
Writer Guide Chapter 15 Using Forms in Writer Copyright This document is Copyright 2005 2008 by its contributors as listed in the section titled Authors. You may distribute it and/or modify it under the
WHAT S NEW IN WORD 2010 & HOW TO CUSTOMIZE IT
 WHAT S NEW IN WORD 2010 & HOW TO CUSTOMIZE IT The Ribbon... 2 Default Tabs... 2 Contextual Tabs... 2 Minimizing and Restoring the Ribbon... 3 Customizing the Ribbon... 3 A New Graphic Interface... 5 Live
WHAT S NEW IN WORD 2010 & HOW TO CUSTOMIZE IT The Ribbon... 2 Default Tabs... 2 Contextual Tabs... 2 Minimizing and Restoring the Ribbon... 3 Customizing the Ribbon... 3 A New Graphic Interface... 5 Live
Microsoft Office Access 2007 which I refer to as Access throughout this book
 Chapter 1 Getting Started with Access In This Chapter What is a database? Opening Access Checking out the Access interface Exploring Office Online Finding help on Access topics Microsoft Office Access
Chapter 1 Getting Started with Access In This Chapter What is a database? Opening Access Checking out the Access interface Exploring Office Online Finding help on Access topics Microsoft Office Access
Microsoft Excel 2013 Tutorial
 Microsoft Excel 2013 Tutorial TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Getting Started Pg. 3 2. Creating A New Document Pg. 3 3. Saving Your Document Pg. 4 4. Toolbars Pg. 4 5. Formatting Pg. 6 Working With Cells Pg. 6 Changing
Microsoft Excel 2013 Tutorial TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Getting Started Pg. 3 2. Creating A New Document Pg. 3 3. Saving Your Document Pg. 4 4. Toolbars Pg. 4 5. Formatting Pg. 6 Working With Cells Pg. 6 Changing
CONTENTM WEBSITE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM. Getting Started Guide
 CONTENTM WEBSITE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Getting Started Guide Table of Contents CONTENTM WEBSITE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM... 1 GETTING TO KNOW YOUR SITE...5 PAGE STRUCTURE...5 Templates...5 Menus...5 Content Areas...5
CONTENTM WEBSITE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Getting Started Guide Table of Contents CONTENTM WEBSITE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM... 1 GETTING TO KNOW YOUR SITE...5 PAGE STRUCTURE...5 Templates...5 Menus...5 Content Areas...5
Creating Interactive PDF Forms
 Creating Interactive PDF Forms Using Adobe Acrobat X Pro Information Technology Services Outreach and Distance Learning Technologies Copyright 2012 KSU Department of Information Technology Services This
Creating Interactive PDF Forms Using Adobe Acrobat X Pro Information Technology Services Outreach and Distance Learning Technologies Copyright 2012 KSU Department of Information Technology Services This
PowerPoint 2007: Basics Learning Guide
 PowerPoint 2007: Basics Learning Guide What s a PowerPoint Slide? PowerPoint presentations are composed of slides, just like conventional presentations. Like a 35mm film-based slide, each PowerPoint slide
PowerPoint 2007: Basics Learning Guide What s a PowerPoint Slide? PowerPoint presentations are composed of slides, just like conventional presentations. Like a 35mm film-based slide, each PowerPoint slide
Chapter 15 Using Forms in Writer
 Writer Guide Chapter 15 Using Forms in Writer OpenOffice.org Copyright This document is Copyright 2005 2006 by its contributors as listed in the section titled Authors. You can distribute it and/or modify
Writer Guide Chapter 15 Using Forms in Writer OpenOffice.org Copyright This document is Copyright 2005 2006 by its contributors as listed in the section titled Authors. You can distribute it and/or modify
Business Objects Version 5 : Introduction
 Business Objects Version 5 : Introduction Page 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction About Business Objects Changing Your Password Retrieving Pre-Defined Reports Formatting Your Report Using the Slice and Dice
Business Objects Version 5 : Introduction Page 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction About Business Objects Changing Your Password Retrieving Pre-Defined Reports Formatting Your Report Using the Slice and Dice
2. Building Cross-Tabs in Your Reports Create a Cross-Tab Create a Specified Group Order Filter Cross-Tab by Group Keep Groups Together
 Crystal Reports Level 2 Computer Training Solutions Course Outline 1. Creating Running Totals Create a Running Total Field Modify a Running Total Field Create a Manual Running Total on Either Detail Data
Crystal Reports Level 2 Computer Training Solutions Course Outline 1. Creating Running Totals Create a Running Total Field Modify a Running Total Field Create a Manual Running Total on Either Detail Data
Excel macros made easy
 IT Training Excel macros made easy Jane Barrett, IT Training & Engagement Team Information System Services Version 1.1 Scope Learning outcomes Understand the concept of what a macro is and what it does.
IT Training Excel macros made easy Jane Barrett, IT Training & Engagement Team Information System Services Version 1.1 Scope Learning outcomes Understand the concept of what a macro is and what it does.
ECDL. European Computer Driving Licence. Spreadsheet Software BCS ITQ Level 2. Syllabus Version 5.0
 European Computer Driving Licence Spreadsheet Software BCS ITQ Level 2 Using Microsoft Excel 2010 Syllabus Version 5.0 This training, which has been approved by BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT, includes
European Computer Driving Licence Spreadsheet Software BCS ITQ Level 2 Using Microsoft Excel 2010 Syllabus Version 5.0 This training, which has been approved by BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT, includes
Microsoft Excel 2010. Understanding the Basics
 Microsoft Excel 2010 Understanding the Basics Table of Contents Opening Excel 2010 2 Components of Excel 2 The Ribbon 3 o Contextual Tabs 3 o Dialog Box Launcher 4 o Quick Access Toolbar 4 Key Tips 5 The
Microsoft Excel 2010 Understanding the Basics Table of Contents Opening Excel 2010 2 Components of Excel 2 The Ribbon 3 o Contextual Tabs 3 o Dialog Box Launcher 4 o Quick Access Toolbar 4 Key Tips 5 The
