LAB MANUAL for Computer Network
|
|
|
- Ernest Ferguson
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LAB MANUAL for Computer Network
2 CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design, troubleshooting, modeling and evaluation of computer networks. In this course, students are going to experiment in a real test-bed networking environment, and learn about network design and troubleshooting topics and tools such as: network addressing, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), basic troubleshooting tools (e.g. ping, ICMP), IP routing (e,g, RIP), route discovery (e.g. traceroute), TCP and UDP, IP fragmentation and many others. Student will also be introduced to the network modeling and simulation, and they will have the opportunity to build some simple networking models using the tool and perform simulations that will help them evaluate their design approaches and expected network performance.
3 S.No Experiment 1 Study of different types of Network cables and Practically implement the cross-wired cable and straight through cable using clamping tool. 2 Study of Network Devices in Detail. 3 Study of network IP. 4 Connect the computers in Local Area Network. 5 Study of basic network command and Network configuration commands. 6 Configure a Network topology using packet tracer software. 7 Configure a Network topology using packet tracer software. 8 Configure a Network using Distance Vector Routing protocol. 9 Configure Network using Link State Vector Routing protocol.
4 Hardware Requirement RJ-45 connector, Climping Tool, Twisted pair Cable Hardware and Software Requirement Software Requirement Command Prompt And Packet Tracer.
5 EXPERIMENT-1 Aim: Study of different types of Network cables and Practically implement the cross-wired cable and straight through cable using clamping tool. Apparatus (Components): RJ-45 connector, Climping Tool, Twisted pair Cable Procedure: To do these practical following steps should be done: 1. Start by stripping off about 2 inches of the plastic jacket off the end of the cable. Be very careful at this point, as to not nick or cut into the wires, which are inside. Doing so could alter the characteristics of your cable, or even worse render is useless. Check the wires, one more time for nicks or cuts. If there are any, just whack the whole end off, and start over. 2. Spread the wires apart, but be sure to hold onto the base of the jacket with your other hand. You do not want the wires to become untwisted down inside the jacket. Category 5 cable must only have 1/2 of an inch of 'untwisted' wire at the end; otherwise it will be 'out of spec'. At this point, you obviously have ALOT more than 1/2 of an inch of un-twisted wire. 3. You have 2 end jacks, which must be installed on your cable. If you are using a pre-made cable, with one of the ends whacked off, you only have one end to install - the crossed over end. Below are two diagrams, which show how you need to arrange the cables for each type of cable end. Decide at this point which end you are making and examine the associated picture below. Diagram shows you how to prepare Cross wired connection
6 Diagram shows you how to prepare straight through wired connection
7 EXPERIMENT-2 Aim: Study of following Network Devices in Detail Repeater Hub Switch Bridge Router Gate Way Apparatus (Software): No software or hardware needed. Procedure: Following should be done to understand this practical. 1. Repeater:Functioning at Physical Layer.A repeater is an electronic device that receives a signal and retransmits it at a higher level and/or higher power, or onto the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances. Repeater have two ports,so cannot be use to connect for more than two devices 2. Hub: An Ethernet hub, active hub, network hub, repeater hub, hub or concentrator is a device for connecting multiple twisted pair or fiber optic Ethernet devices together and making them act as a single network segment. Hubs work at the physical layer (layer 1) of the OSI model. The device is a form of multiport repeater. Repeater hubs also participate in collision detection, forwarding a jam signal to all ports if it detects a collision. 3. Switch:A network switch or switching hub is a computer networking device that connects network segments.the term commonly refers to a network bridge that processes and routes data at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model. Switches that additionally process data at the network layer (layer 3 and above) are often referred to as Layer 3 switches or multilayer switches. 4. Bridge: A network bridge connects multiple network segments at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model. In Ethernet networks, the term bridge formally means a device that behaves according to the IEEE 802.1D standard. A bridge and switch are very much alike; a switch being a bridge with numerous ports. Switch or Layer 2 switch is often used interchangeably with bridge.bridges can analyze incoming data packets to determine if the bridge is able to send the given packet to another segment of the network. 5. Router: A router is an electronic device that interconnects two or more computer networks, and selectively interchanges packets of data between them. Each data packet contains address information that a router can use to determine if the source and destination are on the same network, or if the data packet must be transferred from one network to another. Where multiple routers are used in a large collection of interconnected networks, the routers exchange information about target system addresses, so that each router can build up a table showing the preferred paths between any two systems on the interconnected networks. 6. Gate Way: In a communications network, a network node equipped for interfacing with
8 another network that uses different protocols. A gateway may contain devices such as protocol translators, impedance matching devices, rate converters, fault isolators, or signal translators as necessary to provide system interoperability. It also requires the establishment of mutually acceptable administrative procedures between both networks. A protocol translation/mapping gateway interconnects networks with different network protocol technologies by performing the required protocol conversions.
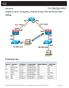
9 Aim: Study of network IP EXPERIMENT- 3 Classification of IP address Sub netting Super netting Apparatus (Software): NA Procedure: Following is required to be study under this practical. Classification of IP address As show in figure we teach how the ip addresses are classified and when they are used. Class Address Range Supports Class A to Supports 16 million hosts on each of 127 networks. Class B to Supports 65,000 hosts on each of 16,000 networks. Class C to Supports 254 hosts on each of 2 million networks. Class D to Reserved for multicast groups. Class E to Reserved. Sub netting Why we Develop sub netting and How to calculate subnet mask and how to identify subnet address. Super netting Why we develop super netting and How to calculate supernet mask and how to identify supernet address.
10 EXPERIMENT-4 Aim: Connect the computers in Local Area Network. Procedure: On the host computer On the host computer, follow these steps to share the Internet connection: 1. Log on to the host computer as Administrator or as Owner. 2. Click Start, and then click Control Panel. 3. Click Network and Internet Connections. 4. Click Network Connections. 5. Right-click the connection that you use to connect to the Internet. For example, if you connect to the Internet by using a modem, right-click the connection that you want under Dial-up / other network available. 6. Click Properties. 7. Click the Advanced tab. 8. Under Internet Connection Sharing, select the Allow other network users to connect through this computer's Internet connection check box. 9. If you are sharing a dial-up Internet connection, select the Establish a dial-up connection whenever a computer on my network attempts to access the Internet check box if you want to permit your computer to automatically connect to the Internet. 10. Click OK. You receive the following message: When Internet Connection Sharing is enabled, your LAN adapter will be set to use IP address Your computer may lose connectivity with other computers on your network. If these other computers have static IP addresses, it is a good idea to set them to obtain their IP addresses automatically. Are you sure you want to enable Internet Connection Sharing? 11. Click Yes. The connection to the Internet is shared to other computers on the local area network (LAN). The network adapter that is connected to the LAN is configured with a static IP address of and a subnet mask of On the client computer To connect to the Internet by using the shared connection, you must confirm the LAN adapter IP configuration, and then configure the client computer. To confirm the LAN adapter IP configuration, follow these steps: 1. Log on to the client computer as Administrator or as Owner. 2. Click Start, and then click Control Panel.
11 3. Click Network and Internet Connections. 4. Click Network Connections. 5. Right-click Local Area Connection and then click Properties. 6. Click the General tab, click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) in the connection uses the following items list, and then click Properties. 7. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click Obtain an IP address automatically (if it is not already selected), and then click OK. Note: You can also assign a unique static IP address in the range of to For example, you can assign the following static IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway: 8. IP Address Subnet mask Default gateway In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, click OK. 12. Quit Control Panel.
12 EXPERIMENT- 5 Aim: Study of basic network command and Network configuration commands. Apparatus (Software): Command Prompt And Packet Tracer. Procedure: To do this EXPERIMENT- follows these steps: In this EXPERIMENT- students have to understand basic networking commands e.g ping, tracert etc. All commands related to Network configuration which includes how to switch to privilege mode and normal mode and how to configure router interface and how to save this configuration to flash memory or permanent memory. This commands includes ping: Configuring the Router commands General Commands to configure network Privileged Mode commands of a router Router Processes & Statistics IP Commands Other IP Commands e.g. show ip route etc. ping(8) sends an ICMP ECHO_REQUEST packet to the specified host. If the host responds, you get an ICMP packet back. Sound strange? Well, you can ping an IP address to see if a machine is alive. If there is no response, you know something is wrong.
13 Traceroute: Tracert is a command which can show you the path a packet of information takes from your computer to one you specify. It will list all the routers it passes through until it reaches its destination, or fails to and is discarded. In addition to this, it will tell you how long each 'hop' from router to router takes.
14 nslookup: Displays information from Domain Name System (DNS) name servers. NOTE :If you write the command as above it shows as default your pc's server name firstly. pathping: A better version of tracert that gives you statics about packet lost and latency.
15 Getting Help In any command mode, you can get a list of available commands by entering a question mark (?). Router>? To obtain a list of commands that begin with a particular character sequence, type in those haracters followed immediately by the question mark (?). co? configure connect copy To list keywords or arguments, enter a question mark in place of a keyword or argument. Include a space before the question mark. configure? memory Configure from NV memory network Configure from a TFTP network host terminal Configure from the terminal You can also abbreviate commands and keywords by entering just enough characters to make the command unique from other commands. For example, you can abbreviate the show command to sh. Configuration Files Any time you make changes to the router configuration, you must save the changes to memory because if you do not they will be lost if there is a system reload or power outage. There are two types of configuration files: the running (current operating) configuration and the startup configuration. Use the following privileged mode commands to work with configuration files.
16 configure terminal modify the running configuration manually from the terminal. show running-config display the running configuration. show startup-config display the startup configuration. copy running-config startup-config copy the running configuration to the startup configuration. copy startup-config running-config copy the startup configuration to the running configuration. erase startup-config erase the startup-configuration in NVRAM. copy tftp running-config load a configuration file stored on a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server into the running configuration. copy running-config tftp store the running configuration on a TFTP server. IP Address Configuration Take the following steps to configure the IP address of an interface. Step 1: Enter privileged EXEC mode: Router>enable password Step 2: Enter the configure terminal command to enter global configuration mode. config terminal Step 3: Enter the interface type slot/port (for Cisco 7000 series) or interface type port (for Cisco 2500 series) to enter the interface configuration mode. Example: Router (config)#interface ethernet 0/1 Step 4: Enter the IP address and subnet mask of the interface using the ip address ipaddress subnetmask command. Example, Router (config-if)#ip address Step 5: Exit the configuration mode by pressing Ctrl-Z Router(config-if)#[Ctrl-Z]
17 EXPERIMENT-6 Aim: Configure a Network topology using packet tracer software. Apparatus (Software): Packet tracer Software Procedure: To implement this practical following network topology is required to be configured using the commands learned in previous practical. After configuring the given network a packet should be ping from any one machine to another. Router0 Configuration Command :... Continue with configuration dialog? [yes/no]: no
18 Press RETURN to get started Router> Router>Enable config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#hostname router0 router0(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0 router0(config-if)#ip address router0(config-if)#description router0 fastethernet 0/0 router0(config-if)#no shutdown %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up router0(config-if)#exit router0(config)#interface fastethernet 0/1 router0(config-if)#description router0 fastethernet 0/1 router0(config-if)#no shutdown %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up router0(config-if)#exit router0(config)#exit %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console router0#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 437 bytes
19 version 12.4 no service password-encryption hostname router0 ip ssh version 1 interface FastEthernet0/0 description router0 fastethernet 0/0 ip address duplex auto speed auto interface FastEthernet0/1 description router0 fastethernet 0/1 no ip address duplex auto speed auto interface Vlan1 no ip address
20 shutdown ip classless line con 0 line vty 0 4 login end router0# router0# router0#copy running-config startup-config Destination filename [startup-config]? Building configuration... [OK] router0#
21 EXPERIMENT-7 Aim: Configure a Network topology using packet tracer software. Apparatus (Software): Packet tracer Software Procedure: To implement this practical following network topology is required to be configured using the commands learned in previous practical. After configuring the given network a packet should be ping from any one machine to another. Router0 Configuration Command... Router>enable configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0 Router(config-if)#ip address Router(config-if)#no shutdown %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up Router(config-if)#exit
22 Router(config)#exit %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0 Router(config-if)# Router(config-if)#exit Router(config)#interface Serial2/0 Router(config-if)#ip address Router(config-if)#no shutdown %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial2/0, changed state to down Router(config-if)#exit Router(config)#exit %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console wr Building configuration... [OK] show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 542 bytes version 12.2 no service password-encryption hostname Router ip ssh version 1 interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address duplex auto speed auto interface FastEthernet1/0 no ip address duplex auto speed auto shutdown interface Serial2/0 ip address
23 interface Serial3/0 no ip address shutdown interface FastEthernet4/0 no ip address shutdown interface FastEthernet5/0 no ip address shutdown ip classless line con 0 line vty 0 4 login end Router1 Configuration Command... Continue with configuration dialog? [yes/no]: no Press RETURN to get started Router>enable configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#interface Serial2/0 Router(config-if)#ip address Router(config-if)#no shutdown %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial2/0, changed state to up Router(config-if)#exit Router(config)#exit %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console config t
24 Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)# Router(config)#interface Serial2/0 Router(config-if)# Router(config-if)#exit Router(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0 Router(config-if)#ip address Router(config-if)#no shutdown %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up Router(config-if)#exit Router(config)#exit %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console wr Building configuration... [OK] show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 542 bytes version 12.2 no service password-encryption hostname Router ip ssh version 1 interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address duplex auto speed auto interface FastEthernet1/0 no ip address duplex auto speed auto shutdown interface Serial2/0 ip address
25 interface Serial3/0 no ip address shutdown interface FastEthernet4/0 no ip address shutdown interface FastEthernet5/0 no ip address shutdown ip classless line con 0 line vty 0 4 login end IP ROUTE Command... config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#ip route Router(config)#exit show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set C /24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 C /24 is directly connected, Serial2/0 S /24 [1/0] via
26 IP ROUTE Command... Router>enable show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set S /24 [1/0] via C /24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 C /24 is directly connected, Serial2/0
27 EXPERIMENT- 8 Aim: Configure a Network using Distance Vector Routing protocol. RIP Apparatus (Software): packet tracer software Procedure: 1. Develop a Topology shown in figure given below. 3. Configure all Routers 4. Implement RIP protocols in Router to configure Network. Router0 configuration... Continue with configuration dialog? [yes/no]: no Press RETURN to get started Router> Router>en config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
28 Router(config)#hostname router0 router0(config)#int lo0 %LINK 5 CHANGED: Interface Loopback0, changed state to up %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback0, changed state to up router0(config if)#ip address router0(config if)#int f0/0 router0(config if)#ip address router0(config if)#no shut %LINK 5 CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up router0(config if)#int f0/1 router0(config if)#ip address router0(config if)#no shut %LINK 5 CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up router0(config if)#end %SYS 5 CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console router0#wr Building configuration... [OK] router0# router0# %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up router0 con0 is now available Press RETURN to get started. router0> router0>en router0#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. router0(config)#router rip router0(config router)#net router0(config router)# router0(config router)#end %SYS 5 CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console router0#show ip route Codes: C connected, S static, I IGRP, R RIP, M mobile, B BGP D EIGRP, EX EIGRP external, O OSPF, IA OSPF inter area N1 OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 OSPF external type 1, E2 OSPF external type 2, E EGP i IS IS, L1 IS IS level 1, L2 IS IS level 2, ia IS IS inter area * candidate default, U per user static route, o ODR P periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set
29 /24 is subnetted, 3 subnets C is directly connected, Loopback0 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 router0# router0# Router1 Configuration... Continue with configuration dialog? [yes/no]: no Press RETURN to get started Router>enable config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#int lo0 %LINK 5 CHANGED: Interface Loopback0, changed state to up %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback0, changed state to up Router(config if)#ip address Router(config if)#no shut Router(config if)#int f0/1 Router(config if)#ip address Router(config if)#no shut %LINK 5 CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up Router(config if)#int f0/0 Router(config if)#ip address Router(config if)#no shut %LINK 5 CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up Router(config if)#end %SYS 5 CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console wr Building configuration... [OK] %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up Router con0 is now available Press RETURN to get started. Router> Router>en con t
30 % Ambiguous command: "con t" co t % Ambiguous command: "co t" conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#router rip Router(config router)#net Router(config router)# Router(config router)# Router(config router)#end %SYS 5 CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console Router2 Configuration... Continue with configuration dialog? [yes/no]: no Press RETURN to get started Router>en config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#int lo0 %LINK 5 CHANGED: Interface Loopback0, changed state to up %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback0, changed state to up Router(config if)#ip address Router(config if)#no shut Router(config if)#int f0/0 Router(config if)#ip address Router(config if)#no shut %LINK 5 CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up Router(config if)#int f0/1 Router(config if)#ip address Router(config if)#no shut %LINK 5 CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up Router(config if)#end %SYS 5 CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console wr Building configuration... [OK] %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up
31 Router con0 is now available Press RETURN to get started. Router> Router> Router>en show ip route Codes: C connected, S static, I IGRP, R RIP, M mobile, B BGP D EIGRP, EX EIGRP external, O OSPF, IA OSPF inter area N1 OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 OSPF external type 1, E2 OSPF external type 2, E EGP i IS IS, L1 IS IS level 1, L2 IS IS level 2, ia IS IS inter area * candidate default, U per user static route, o ODR P periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set /24 is subnetted, 3 subnets C is directly connected, Loopback0 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#router rip Router(config router)#net Router(config router)#end %SYS 5 CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console show ip route Codes: C connected, S static, I IGRP, R RIP, M mobile, B BGP D EIGRP, EX EIGRP external, O OSPF, IA OSPF inter area N1 OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 OSPF external type 1, E2 OSPF external type 2, E EGP i IS IS, L1 IS IS level 1, L2 IS IS level 2, ia IS IS inter area * candidate default, U per user static route, o ODR P periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set R R C R R C /24 is subnetted, 7 subnets [120/2] via , 00:00:19, FastEthernet0/ [120/1] via , 00:00:19, FastEthernet0/ is directly connected, Loopback [120/1] via , 00:00:19, FastEthernet0/ [120/2] via , 00:00:19, FastEthernet0/ is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
32 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 Router3 Configuration... Continue with configuration dialog? [yes/no]: no Press RETURN to get started Router> Router>en config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#int lo0 %LINK 5 CHANGED: Interface Loopback0, changed state to up %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback0, changed state to up Router(config if)#int f0/0 Router(config if)#ip address Router(config if)#no shut %LINK 5 CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up Router(config if)# Router(config if)#int f0/1 Router(config if)#ip address Router(config if)#no shut %LINK 5 CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up Router(config if)#end %SYS 5 CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console wr Building configuration... [OK] show ip route Codes: C connected, S static, I IGRP, R RIP, M mobile, B BGP D EIGRP, EX EIGRP external, O OSPF, IA OSPF inter area N1 OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 OSPF external type 1, E2 OSPF external type 2, E EGP i IS IS, L1 IS IS level 1, L2 IS IS level 2, ia IS IS inter area * candidate default, U per user static route, o ODR P periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set
33 /24 is subnetted, 2 subnets C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#router rip Router(config router)#net Router(config router)# Router(config router)#end %SYS 5 CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console show ip route Codes: C connected, S static, I IGRP, R RIP, M mobile, B BGP D EIGRP, EX EIGRP external, O OSPF, IA OSPF inter area N1 OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 OSPF external type 1, E2 OSPF external type 2, E EGP i IS IS, L1 IS IS level 1, L2 IS IS level 2, ia IS IS inter area * candidate default, U per user static route, o ODR P periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set /24 is subnetted, 7 subnets R [120/1] via , 00:00:09, FastEthernet0/1 R [120/2] via , 00:00:14, FastEthernet0/0 [120/2] via , 00:00:09, FastEthernet0/1 R [120/1] via , 00:00:14, FastEthernet0/0 R [120/1] via , 00:00:09, FastEthernet0/1 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 R [120/1] via , 00:00:14, FastEthernet0/0 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
34 EXPERIMENT- 9 Aim: Configure Network using Link State Vector Routing protocol. OSPF Apparatus (Software): Packet Tracer Software Procedure: 1. Develop a Topology shown in figure given below. 2. Configure all the workstations 3. Configure all switches 4. Configure all Routers 5. Implement OSPF protocols in Router to configure Network.
Lab: Basic Router Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Objectives. Router as a Computer. Router components and their functions. Router components and their functions
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
Configuring a Router
 CHAPTER 3 Configuring a Router This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring a router, specifically: Names Passwords Interfaces MOTD banners IP host tables
CHAPTER 3 Configuring a Router This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring a router, specifically: Names Passwords Interfaces MOTD banners IP host tables
Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial
 Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial Cisco Inter-network Operating System: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation The Cisco IOS software provides access to several different command modes. Each command mode provides
Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial Cisco Inter-network Operating System: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation The Cisco IOS software provides access to several different command modes. Each command mode provides
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration
 3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration
 CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
Connect the Host to attach to Fast Ethernet switch port Fa0/2. Configure the host as shown in the topology diagram above.
 Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP. Objective. Background / Preparation. General Configuration Tips
 Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA
 ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
LAB Configuring NAT. Objective. Background/Preparation
 LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
Applicazioni Telematiche
 Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP
 Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
How to Configure Cisco 2600 Routers
 Helsinki University of Technology Department of Communications and Networking How to Configure Cisco 2600 Routers Juha Järvinen 10.6.2004 [email protected] Modified by Zhong Yunqiu 7.8.2008 Table
Helsinki University of Technology Department of Communications and Networking How to Configure Cisco 2600 Routers Juha Järvinen 10.6.2004 [email protected] Modified by Zhong Yunqiu 7.8.2008 Table
How To Configure A Cisco Router With A Cio Router
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches
 How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
Angelos Stavrou. OF COURSE there is no Magic so lets see show things work in practice...
 Cisco Inter-network Operating System (IOS) A short guide for the NetAdmin Angelos Stavrou Let's start out at the very beginning with the question: "What is a Command?" The most important thing to understand
Cisco Inter-network Operating System (IOS) A short guide for the NetAdmin Angelos Stavrou Let's start out at the very beginning with the question: "What is a Command?" The most important thing to understand
Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network
 Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network CMPE 150 Fall 2005 Introduction Today you are going to be thrown into using Cisco s Internetwork Operating System (IOS) to configure
Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network CMPE 150 Fall 2005 Introduction Today you are going to be thrown into using Cisco s Internetwork Operating System (IOS) to configure
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. Part 1: Router & Switch
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers Document ID: 22189 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by Step Procedure
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers Document ID: 22189 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by Step Procedure
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
SSVP SIP School VoIP Professional Certification
 SSVP SIP School VoIP Professional Certification Exam Objectives The SSVP exam is designed to test your skills and knowledge on the basics of Networking and Voice over IP. Everything that you need to cover
SSVP SIP School VoIP Professional Certification Exam Objectives The SSVP exam is designed to test your skills and knowledge on the basics of Networking and Voice over IP. Everything that you need to cover
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers Document ID: 12065 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers Document ID: 12065 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface
 Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface This document describes how to use the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) to perform a basic software configuration for your
Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface This document describes how to use the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) to perform a basic software configuration for your
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1
 Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Networking Technology Online Course Outline
 Networking Technology Online Course Outline Introduction Networking Technology Introduction Welcome to InfoComm University About InfoComm International About Networking Technology Network Technology Course
Networking Technology Online Course Outline Introduction Networking Technology Introduction Welcome to InfoComm University About InfoComm International About Networking Technology Network Technology Course
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Implementing
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Implementing
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
ICND1 Lab Guide. 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version 2.0. Labs powered by
 ICND1 Lab Guide 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version 2.0 ii Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 100-101 Lab Guide LM20130929/BV2.01 iii 25 Century Blvd. Ste. 500
ICND1 Lab Guide 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version 2.0 ii Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 100-101 Lab Guide LM20130929/BV2.01 iii 25 Century Blvd. Ste. 500
Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab will introduce to the student the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new. This introductory
Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab will introduce to the student the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new. This introductory
Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Learning Objectives Configure auto QoS to support IP phones Configure CoS override for data frames Configure the distribution layer to trust access
Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Learning Objectives Configure auto QoS to support IP phones Configure CoS override for data frames Configure the distribution layer to trust access
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers Document ID: 12738 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Step by Step Procedure
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers Document ID: 12738 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Step by Step Procedure
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections
 IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections Document ID: 100658 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections Document ID: 100658 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Table of Contents. Cisco Configuring a Basic MPLS VPN
 Table of Contents Configuring a Basic MPLS VPN...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...2 Related Products...2 Conventions...2 Configure...3 Network Diagram...3 Configuration
Table of Contents Configuring a Basic MPLS VPN...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...2 Related Products...2 Conventions...2 Configure...3 Network Diagram...3 Configuration
CCNA Exploration 4.0: (II) Routing Protocols and Concepts. Chapter 1: Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding
 Http://elmaestrodelared.blogspot.com CCNA Exploration 4.0: (II) Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1: Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding 1. If a router cannot find a valid configuration
Http://elmaestrodelared.blogspot.com CCNA Exploration 4.0: (II) Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1: Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding 1. If a router cannot find a valid configuration
IT-AD08: ADD ON DIPLOMA IN COMPUTER NETWORK DESIGN AND INSTALLATION
 IT-AD08: ADD ON DIPLOMA IN COMPUTER NETWORK DESIGN AND INSTALLATION Objective of the course: This course is designed to impart professional training to the students of computer Science, computer applications,
IT-AD08: ADD ON DIPLOMA IN COMPUTER NETWORK DESIGN AND INSTALLATION Objective of the course: This course is designed to impart professional training to the students of computer Science, computer applications,
IST 220 Honors Project. Subnets with Variable Length Subnet Masks
 IST 220 Honors Project Subnets with Variable Length Subnet Masks Project Objectives: In this project, you will subnet the IP address 193.170.10.0 according to needs of the organization. Overview a) Perform
IST 220 Honors Project Subnets with Variable Length Subnet Masks Project Objectives: In this project, you will subnet the IP address 193.170.10.0 according to needs of the organization. Overview a) Perform
Cisco Router Configuration Basics. Scalable Infrastructure Workshop
 Cisco Router Configuration Basics Scalable Infrastructure Workshop Router Components p RAM n Holds operating system, data structures, packet buffers, ARP cache, and routing tables n Reset on reload n Router
Cisco Router Configuration Basics Scalable Infrastructure Workshop Router Components p RAM n Holds operating system, data structures, packet buffers, ARP cache, and routing tables n Reset on reload n Router
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
CCNA Exploration 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual
 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
Effect of Windows XP Firewall on Network Simulation and Testing
 Issues in Informing Science and Information Technology Volume 4, 2007 Effect of Windows XP Firewall on Network Simulation and Testing Akram Al-Rawi College of CS & IT, King Faisal University, Al-Hassa,
Issues in Informing Science and Information Technology Volume 4, 2007 Effect of Windows XP Firewall on Network Simulation and Testing Akram Al-Rawi College of CS & IT, King Faisal University, Al-Hassa,
CHAPTER 3 STATIC ROUTING
 CHAPTER 3 STATIC ROUTING This chapter addresses the end-to-end delivery service of IP and explains how IP routers and hosts handle IP datagrams. The first section discusses how datagrams are forwarded
CHAPTER 3 STATIC ROUTING This chapter addresses the end-to-end delivery service of IP and explains how IP routers and hosts handle IP datagrams. The first section discusses how datagrams are forwarded
Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration
 Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration Learning Objectives Review of previously learned skills. Basic IOS Command Line Interface operation. Basic Router configuration. Verification and testing
Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration Learning Objectives Review of previously learned skills. Basic IOS Command Line Interface operation. Basic Router configuration. Verification and testing
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp
 Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
Lab Configuring Syslog and NTP (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands
 Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands Document ID: 16448 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions ip default gateway ip default network Flag a Default
Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands Document ID: 16448 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions ip default gateway ip default network Flag a Default
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
IOS NAT Load Balancing with Optimized Edge Routing for Two Internet Connections
 IOS NAT Load Balancing with Optimized Edge Routing for Two Internet Connections Document ID: 99427 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram
IOS NAT Load Balancing with Optimized Edge Routing for Two Internet Connections Document ID: 99427 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram
Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 Conceitos de protocolos de Encaminhamento Cap 2
 Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine
Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine
IP Networking. Overview. Networks Impact Daily Life. IP Networking - Part 1. How Networks Impact Daily Life. How Networks Impact Daily Life
 Overview Dipl.-Ing. Peter Schrotter Institute of Communication Networks and Satellite Communications Graz University of Technology, Austria Fundamentals of Communicating over the Network Application Layer
Overview Dipl.-Ing. Peter Schrotter Institute of Communication Networks and Satellite Communications Graz University of Technology, Austria Fundamentals of Communicating over the Network Application Layer
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2900 Series Integrated Services Router
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2900 Series Integrated Services Router Document ID: 112033 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2900 Series Integrated Services Router Document ID: 112033 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by
Router and Routing Basics
 Router and Routing Basics Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts CCNA2 Routing and packet forwarding Static routing Dynamic
Router and Routing Basics Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts CCNA2 Routing and packet forwarding Static routing Dynamic
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
JOB READY ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT COMPUTER NETWORKING FUNDAMENTALS - PILOT. Test Code: 4514 Version: 01
 JOB READY ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT COMPUTER NETWORKING FUNDAMENTALS - PILOT Test Code: 4514 Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: PC Principles Identify physical and equipment
JOB READY ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT COMPUTER NETWORKING FUNDAMENTALS - PILOT Test Code: 4514 Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: PC Principles Identify physical and equipment
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows
 Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
- Basic Router Security -
 1 Enable Passwords - Basic Router Security - The enable password protects a router s Privileged mode. This password can be set or changed from Global Configuration mode: Router(config)# enable password
1 Enable Passwords - Basic Router Security - The enable password protects a router s Privileged mode. This password can be set or changed from Global Configuration mode: Router(config)# enable password
Objectives. Background. Required Resources. CCNA Security
 Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram
 Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows
 Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Building a Network in GNS3
 Building a Network in GNS3 In this tutorial, you will create a network in GNS3 between two routers, and each router will have one host connected to it. The ultimate goal is to route data between network
Building a Network in GNS3 In this tutorial, you will create a network in GNS3 between two routers, and each router will have one host connected to it. The ultimate goal is to route data between network
s@lm@n CompTIA Exam N10-006 CompTIA Network+ certification Version: 5.1 [ Total Questions: 1146 ]
![s@lm@n CompTIA Exam N10-006 CompTIA Network+ certification Version: 5.1 [ Total Questions: 1146 ] s@lm@n CompTIA Exam N10-006 CompTIA Network+ certification Version: 5.1 [ Total Questions: 1146 ]](/thumbs/27/9611247.jpg) s@lm@n CompTIA Exam N10-006 CompTIA Network+ certification Version: 5.1 [ Total Questions: 1146 ] Topic break down Topic No. of Questions Topic 1: Network Architecture 183 Topic 2: Network Operations 149
s@lm@n CompTIA Exam N10-006 CompTIA Network+ certification Version: 5.1 [ Total Questions: 1146 ] Topic break down Topic No. of Questions Topic 1: Network Architecture 183 Topic 2: Network Operations 149
PT Activity 8.1.2: Network Discovery and Documentation Topology Diagram
 Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet
Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet
CCT vs. CCENT Skill Set Comparison
 Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Lab 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
(Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Brocade to Cisco Comparisons
 1 2 3 Console cables - The console cables are not interchangeable between Brocade and Cisco. Each vendor provides their console cable with each manageable unit it sells. Passwords - Neither Cisco or Brocade
1 2 3 Console cables - The console cables are not interchangeable between Brocade and Cisco. Each vendor provides their console cable with each manageable unit it sells. Passwords - Neither Cisco or Brocade
Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets
 Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 8 Device Interface
Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 8 Device Interface
APNIC Members Training Course Security workshop. 2-4 July, 2008. Port Vila Vanuatu. In conjunction with PACNOG 4
 APNIC Members Training Course Security workshop 2-4 July, 2008 Port Vila Vanuatu In conjunction with PACNOG 4 Router device security lab 1. APNIC s remote lab In these exercises you will be remotely accessing
APNIC Members Training Course Security workshop 2-4 July, 2008 Port Vila Vanuatu In conjunction with PACNOG 4 Router device security lab 1. APNIC s remote lab In these exercises you will be remotely accessing
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands
 Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Router Lab Reference Guide
 Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
1 Data information is sent onto the network cable using which of the following? A Communication protocol B Data packet
 Review questions 1 Data information is sent onto the network cable using which of the following? A Communication protocol B Data packet C Media access method D Packages 2 To which TCP/IP architecture layer
Review questions 1 Data information is sent onto the network cable using which of the following? A Communication protocol B Data packet C Media access method D Packages 2 To which TCP/IP architecture layer
640-607. QUESTION NO: 1 You can configure PPP on which of the following types of physical interfaces? (Choose two)
 640-607 Cisco Certified Network Associate 3.0 CCNA 3.0 Version 17.0 Important Note Please Read Carefully Study Tips This product will provide you questions and answers along with detailed explanations
640-607 Cisco Certified Network Associate 3.0 CCNA 3.0 Version 17.0 Important Note Please Read Carefully Study Tips This product will provide you questions and answers along with detailed explanations
Troubleshooting IP Routing
 C H A P T E R 7 Troubleshooting IP Routing This troubleshooting chapter has several goals. First, it explains several tools and functions not covered in Chapters 4 through 6 specifically, tools that can
C H A P T E R 7 Troubleshooting IP Routing This troubleshooting chapter has several goals. First, it explains several tools and functions not covered in Chapters 4 through 6 specifically, tools that can
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client
 Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Table of Contents. Cisco DSL Router Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
 Table of Contents...1 Types of Service...1 Step by Step Configuration of a PC Acting as a PPPoE Client...2 Step by Step Configuration...2 Connect the Cisco DSL Router and Your PC...2 Start and Set Up HyperTerminal...2
Table of Contents...1 Types of Service...1 Step by Step Configuration of a PC Acting as a PPPoE Client...2 Step by Step Configuration...2 Connect the Cisco DSL Router and Your PC...2 Start and Set Up HyperTerminal...2
http://computernetworkingnotes.com/ccna-study-guide/cisco-ios-naming-convention-explainedwith-examples.html
 IOS is the most critical part of any cisco device. We should always keep a backup copy of IOS to deal with any unwanted situation. In this article I will explain the backup and restore process of IOS in
IOS is the most critical part of any cisco device. We should always keep a backup copy of IOS to deal with any unwanted situation. In this article I will explain the backup and restore process of IOS in
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example
 Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Introduction. What is a Remote Console? What is the Server Service? A Remote Control Enabled (RCE) Console
 Contents Introduction... 3 What is a Remote Console?... 3 What is the Server Service?... 3 A Remote Control Enabled (RCE) Console... 3 Differences Between the Server Service and an RCE Console... 4 Configuring
Contents Introduction... 3 What is a Remote Console?... 3 What is the Server Service?... 3 A Remote Control Enabled (RCE) Console... 3 Differences Between the Server Service and an RCE Console... 4 Configuring
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations
 PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
Laboratorio 3 Comunicación sincrónica Vía Satélite
 Laboratorio 3 Comunicación sincrónica Vía Satélite Esquema de la Red WAN 192.168.0.0 /30 192.168.0.1 Router 1 Router 2 10.0.1.1 192.168.0.1 10.0.2.1 Ethernet Ethernet 10.0.1.20 LAN 1 10.0.1.0 /24 LAN 2
Laboratorio 3 Comunicación sincrónica Vía Satélite Esquema de la Red WAN 192.168.0.0 /30 192.168.0.1 Router 1 Router 2 10.0.1.1 192.168.0.1 10.0.2.1 Ethernet Ethernet 10.0.1.20 LAN 1 10.0.1.0 /24 LAN 2
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1
 Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
SSVVP SIP School VVoIP Professional Certification
 SSVVP SIP School VVoIP Professional Certification Exam Objectives The SSVVP exam is designed to test your skills and knowledge on the basics of Networking, Voice over IP and Video over IP. Everything that
SSVVP SIP School VVoIP Professional Certification Exam Objectives The SSVVP exam is designed to test your skills and knowledge on the basics of Networking, Voice over IP and Video over IP. Everything that
Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router
 CHAPTER 2 Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router This chapter describes how to boot and configure the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router. It discusses the following subjects: Cisco
CHAPTER 2 Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router This chapter describes how to boot and configure the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router. It discusses the following subjects: Cisco
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Deploying Windows Streaming Media Servers NLB Cluster and metasan
 Deploying Windows Streaming Media Servers NLB Cluster and metasan Introduction...................................................... 2 Objectives.......................................................
Deploying Windows Streaming Media Servers NLB Cluster and metasan Introduction...................................................... 2 Objectives.......................................................
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Guideline for setting up a functional VPN
 Guideline for setting up a functional VPN Why do I want a VPN? VPN by definition creates a private, trusted network across an untrusted medium. It allows you to connect offices and people from around the
Guideline for setting up a functional VPN Why do I want a VPN? VPN by definition creates a private, trusted network across an untrusted medium. It allows you to connect offices and people from around the
Network Simulator Lab Study Plan
 The CCNA 640-802 Network Simulator has 300 lab exercises, organized both by type (Skill Builder, Configuration Scenario, Troubleshooting Scenario, and Subnetting Exercise) and by major topic within each
The CCNA 640-802 Network Simulator has 300 lab exercises, organized both by type (Skill Builder, Configuration Scenario, Troubleshooting Scenario, and Subnetting Exercise) and by major topic within each
Configuring a Cisco 2509-RJ Terminal Router
 created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
Configuring IP Load Sharing in AOS Quick Configuration Guide
 Configuring IP Load Sharing in AOS Quick Configuration Guide ADTRAN Operating System (AOS) includes IP Load Sharing for balancing outbound IP traffic across multiple interfaces. This feature can be used
Configuring IP Load Sharing in AOS Quick Configuration Guide ADTRAN Operating System (AOS) includes IP Load Sharing for balancing outbound IP traffic across multiple interfaces. This feature can be used
OSPF Configuring Multi-Area OSPF
 OSPF Configuring Multi-Area OSPF Objective In this lab configure a multiarea OSPF operation, interarea summarization, external route summarization, and default routing. Scenario International Travel Agency
OSPF Configuring Multi-Area OSPF Objective In this lab configure a multiarea OSPF operation, interarea summarization, external route summarization, and default routing. Scenario International Travel Agency
How To Learn Cisco Cisco Ios And Cisco Vlan
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated Course CCNAX v2.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX) v2.0 is a 60-hour instructor-led
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated Course CCNAX v2.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX) v2.0 is a 60-hour instructor-led
CCNA Discovery 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual
 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
