Cisco Router Configuration Basics. Scalable Infrastructure Workshop
|
|
|
- Eustace Shelton
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cisco Router Configuration Basics Scalable Infrastructure Workshop
2 Router Components p RAM n Holds operating system, data structures, packet buffers, ARP cache, and routing tables n Reset on reload n Router s running-config is stored in RAM p Flash n Holds the IOS n Is not erased when the router is reloaded p NVRAM n Non-Volatile RAM - stores router s startup-config n Is not erased when router is reloaded
3 Router Components p Configuration Register n controls how router boots; n value can be seen with show version command; n is normally 0x2102, which tells the router to load the IOS from flash memory and the startup-config file from NVRAM n 0x2142, tells the router to ignore the NVRAM configuration when rebooting n Leading 0x means hexadecimal
4 Purpose of the Config Register p Reasons why you would want to modify the config-register: n Force the router into ROM Monitor Mode (recovery mode) n Select a boot source and default boot filename n Enable/Disable the Break function n Control broadcast addresses n Set console terminal baud rate n Load operating software from ROM
5 Configuration Overview p Router configuration controls the operation of the router s: n Interface IP address and netmask n Routing information (static, dynamic or default) n Boot and startup information n Security (passwords and authentication)
6 Where is the Configuration? p Router always has two configurations: n Running configuration p In RAM, determines how the router is currently operating p Is modified using the configure command p To see it: show running-config n Startup confguration p In NVRAM, determines how the router will operate after next reload p Is modified using the copy command p To see it: show startup-config
7 Where is the Configuration? p Can also be stored in more permanent places: n External hosts, using TFTP, FTP, SCP, etc n In flash memory in the router p Copy command is used to move it around copy run start copy run tftp copy start tftp copy tftp start copy flash start copy start flash
8 Router Access Modes p User mode limited access to router no configuration rights n Router> p Privileged EXEC mode detailed access and full configuration of the router, debugging, testing, file manipulation (router prompt changes to an octothorpe) n Router# p ROM Monitor useful for password recovery (amongst others) p Setup Mode entered when router has no startup-config file
9 External Configuration Sources p Console n Direct PC serial access p Auxiliary port n Modem access p Virtual terminals n Telnet/SSH access p TFTP Server n Copy configuration file into router RAM p Network Management Software n e.g., CiscoWorks
10 Changing the Configuration p Configuration statements can be entered interactively n changes are made (almost) immediately, to the running configuration p Can use direct serial connection to console port, or p Telnet/SSH to vty s ( virtual terminals ), or p Modem connection to aux port, or p Edited in a text file and uploaded to the router at a later time via tftp/ftp/scp n copy tftp start
11 Logging into the Router p Connect router to console port or telnet to router router> router>enable password router# router#? p Configuring the router n Terminal (entering the commands directly) router# configure terminal router(config)#
12 Connecting your FreeBSD Machine to the Router s Console Port p Connect your PC to the console port using the serial cable provided p Go to /etc/remote to see the device configured to be used with "tip. you will see at the end, a line begin with com1 bash$ tip com1 <enter> router> router>enable router#
13 Address Assignments G /28 SWITCH.7.8 H /28 F / I /28 E D C / / / / J /28 K /28 L /28 B / M /28 A / N /28
14 Configuring your Router (1) p Load configuration parameters into RAM n Router#configure terminal p Personalise router identification n Router#(config)hostname RouterA p Assign console & vty passwords n RouterA#(config)line console 0 n RouterA#(config-line)password afnog n RouterA#(config)line vty 0 4 n RouterA#(config-line)password afnog Spaces count, so don t add them at the end!!
15 Configuring your Router (2) p Set the enable (secret) password: n router(config)# enable secret afnog p This MD5 encrypts the password n The old method was to use the enable password command. But this is not secure (weak encryption) and is ABSOLUTELY NOT RECOMMENDED. DO NOT USE! p Ensure that all passwords stored on router are (weakly) encrypted rather than clear text: n router(config)# service password-encryption
16 Configuring your Router (3) p Configure interfaces n RouterA#(config)interface fastethernet 0/0 n RouterA#(config-if)ip address n.n.n.n m.m.m.m n RouterA#(config-if)no shutdown p Configure routing/routed protocols n RouterA#(config)router bgp 100 n RouterA#(config-router) p Save configuration parameters to NVRAM n RouterA#copy running-config startup-config n (or write memory)
17 Configuring your Router (4) p IP Specific Configuration n no ip source-route disable source routing n ip domain-name domain-name n ip nameserver n.n.n.n set name server p Static Route Creation ip route n.n.n.n m.m.m.m g.g.g.g n.n.n.n = network block m.m.m.m = network mask denoting block size g.g.g.g = next hop gateway destination packets are sent to
18 Router Prompts How to tell where you are on the router p You can tell in which area of the router s configuration you are by looking at the router prompts - some examples: Router> USER prompt mode Router# PRIVILEGED EXEC prompt mode Router(config) terminal configuration prompt Router(config-if) interface configuration prompt Router(config-subif) sub-interface configuration prompt rommon 1> ROM Monitor mode
19 The NO Command p Used to reverse or disable commands e.g ip domain-lookup no ip domain-lookup router ospf 1 no router ospf 1 ip address no ip address
20 Interface Configuration p Interfaces are named by slot/type; e.g.: n ethernet0, ethernet5/1, serial0/0/0, serial2 p And can be abbreviated: n ethernet0 or eth0 or e0 n Serial0/0 or ser0/0 or s0/0 p Interfaces are shutdown by default n router(config-if)#no shutdown wake up interface p Description n router(config-if)#description Link to Admin Building router
21 Global Configuration Commands p Cisco global config should always include: ip classless ip subnet-zero n (These are default as from IOS 12.2 release) p Cisco interface config should usually include: no shutdown no ip proxy-arp no ip redirects no ip directed-broadcast p Industry recommendations are at
22 Looking at the Configuration p Use show running-configuration to see the current configuration p Use show startup-configuration to see the configuration in NVRAM, that will be loaded the next time the router is rebooted or reloaded n (or show conf)
23 Storing the Configuration on a Remote System p Requires: tftpd on a unix host; destination file must exist before the file is written and must be world writable... rtra#copy run tftp Remote host []? n.n.n.n Name of configuration file to write [rtra-confg]? Write file rtra-confg on Host n.n.n.n? [confirm] Building configuration... Writing rtra-confg!![ok] router#
24 Restoring the Configuration from a Remote System p Use tftp to pull file from UNIX host, copying to runningconfig (added to existing running configuration) or startupconfig (stored in configuration NVRAM and used on next reboot) rtra#copy tftp start Address of remote host [ ]? n.n.n.n Name of configuration file [rtra-confg]? Configure using rtra-confg from n.n.n.n? [confirm] Loading rtra-confg from n.n.n.n (via Ethernet0/0):! [OK / bytes] rtra# reload
25 Getting Command Help p IOS has a command help facility; n use? to get a list of possible configuration options p? after the prompt lists all possible commands: router#? p <command>? lists all possible subcommands router#show? router#show ip? p <partial command>? lists all possible command completions: router#con? configure connect
26 Getting Lazy Command Help p TAB character will complete a partial word hostel-rtr(config)#int<tab> hostel-rtr(config)#interface et<tab> hostel-rtr(config)#interface ethernet 0 hostel-rtr(config-if)#ip add<tab> hostel-rtr(config-if)#ip address n.n.n.n m.m.m.m p Not really necessary to complete command keywords; partial commands can be used: router#conf t router(config)#int e0/0 router(config-if)#ip addr n.n.n.n
27 Editing p Command history n IOS maintains a list of previously typed commands n up-arrow or ^p recalls previous command n down-arrow or ^n recalls next command p Line editing n left-arrow, right-arrow moves cursor inside command n ^d or backspace will delete character in front of cursor n Ctrl-a takes you to start of line n Ctrl-e takes you to end of line n Ctrl-u deletes an entire line Many other unix-like tricks
28 Connecting your FreeBSD machine to the Router s Console port p Look at your running configuration p Configure an IP address for fastethernet0/1 depending on your table n use n.n.n.n for table A etc p Look at your running configuration and your startup configuration p Check what difference there is, if any
29 Deleting your Router s Configuration p To delete your router s configuration Router#erase startup-config OR Router#write erase Router#reload n Router will start up again, but in setup mode, since startup-config file does not exists
30 Password Recovery Working around a forgotten or lost password
31 Disaster Recovery ROM Monitor p ROM Monitor is very helpful in recovering from emergency failures such as: n Password recovery n Upload new IOS into router with NO IOS installed n Selecting a boot source and default boot filename n Set console terminal baud rate to upload new IOS quicker n Load operating software from ROM n Enable booting from a TFTP server
32 Getting to the ROM Monitor p Windows using HyperTerminal for the console session n Ctrl-Break p FreeBSD/UNIX using Tip for the console session n <Enter>, then ~# OR n Ctrl-], then Break or Ctrl-C p Linux using Minicom for the console session n Ctrl-A F p MacOS using Zterm for the console session n Apple B
33 Disaster Recovery: How to Recover a Lost Password p Connect your PC s serial port to the router s console port p Configure your PC s serial port: n n n n n 9600 baud rate No parity 8 data bits 1 stop bit No flow control
34 Disaster Recovery: How to Recover a Lost Password p Your configuration register should be 0x2102; use show version command to check p Reboot the router and apply the Breaksequence within 60 seconds of powering the router, to put it into ROMMON mode Rommon 1>confreg 0x2142 Rommon 2>reset n Router reboots, bypassing startup-config file
35 Disaster Recovery: How to Recover a Lost Password Type Ctrl-C to exit Setup mode Router>enable Router#copy start run (only!!!) Router#show running Router#conf t Router(config)enable secret forgotten Router(config)int e0/0 Router(config-if)no shut Router(config)config-register 0x2102 Router(config)Ctrl-Z or end Router#copy run start Router#reload
36 Basic IPv6 Configuration
37 IPv6 Configuration p IPv6 is not enabled by default in IOS p Enabling IPv6: Router(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing p Disable Source Routing Router(config)# no ipv6 source route p Activating IPv6 CEF Router(config)# ipv6 cef
38 IPv6 Configuration - Interfaces p Configuring a global or unique local IPv6 address: n Router(config-if)# ipv6 address X:X..X:X/prefix p Configuring an EUI-64 based IPv6 address (not such a good idea on a router): n Router(config-if)# ipv6 address X:X::/prefix eui-64
39 IPv6 Configuration p Note that by configuring any IPv6 address on an interface, you will see a global or unique-local IPv6 address and a link-local IPv6 address on the interface n Link-local IPv6 address format is FE80::interface-id p The local-link IPv6 address is constructed automatically by concatenating FE80 with Interface ID as soon as IPv6 is enabled on the interface: n Router(config-if)# ipv6 enable
40 IOS IPv6 Interface Status Link Local br01#sh ipv6 interface fast 0/1.220 FastEthernet0/1.220 is up, line protocol is up IPv6 is enabled, link-local address is FE80::225:45FF:FE6A:5B39 No global unicast address is configured Joined group address(es): FF02::1 FF02::2 FF02::1:FF6A:5B39 MTU is 1500 bytes ICMP error messages limited to one every 100 milliseconds ICMP redirects are enabled
41 IOS IPv6 Interface Status br01#sh ipv6 interface fast 0/1.223 FastEthernet0/1.223 is up, line protocol is up IPv6 is enabled, link-local address is FE80::225:45FF:FE6A:5B39 Description: backbone Global unicast address(es): 2001:4348:0:223:196:200:223:254, subnet is 2001:4348:0:223::/64 Joined group address(es): FF02::1 FF02::2 FF02::1:FF23:254 FF02::1:FF6A:5B39 MTU is 1500 bytes ICMP error messages limited to one every 100 milliseconds ICMP redirects are enabled
42 IPv6 Configuration Miscellaneous p Disable IPv6 redirects on interfaces interface fastethernet 0/0 no ipv6 redirects p Nameserver, syslog etc can be IPv6 accessible ip nameserver 2001:db8:2:1::2 ip nameserver
43 Static Routing IOS p Syntax is: ipv6 route ipv6-prefix/prefix-length {ipv6- address interface-type interface-number} [admin-distance] p Static Route ipv6 route 2001:db8::/ :db8:0:CC00::1 n Routes packets for network 2001:db8::/64 to a networking device at 2001:db8:0:CC00::1
44 Cisco Router Configuration Basics Questions?
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration
 3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
Applicazioni Telematiche
 Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Configuring a Router
 CHAPTER 3 Configuring a Router This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring a router, specifically: Names Passwords Interfaces MOTD banners IP host tables
CHAPTER 3 Configuring a Router This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring a router, specifically: Names Passwords Interfaces MOTD banners IP host tables
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP. Objective. Background / Preparation. General Configuration Tips
 Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
- Advanced IOS Functions -
 1 The Configuration Register - Advanced IOS Functions - The configuration register (config-register) is a hexadecimal value that controls various aspects of how a router boots, including: Baud Rate Boot
1 The Configuration Register - Advanced IOS Functions - The configuration register (config-register) is a hexadecimal value that controls various aspects of how a router boots, including: Baud Rate Boot
Introduction to Cisco router configuration
 Introduction to Cisco router configuration AFNOG 2001 Workshop 07 to 11 May 2001 Accra - GHANA By: Adiel AKPLOGAN CAFE Informatique S. A. - TOGO E-mail: [email protected] - Web: http://www.akplogan.net
Introduction to Cisco router configuration AFNOG 2001 Workshop 07 to 11 May 2001 Accra - GHANA By: Adiel AKPLOGAN CAFE Informatique S. A. - TOGO E-mail: [email protected] - Web: http://www.akplogan.net
Configuring a Cisco 2509-RJ Terminal Router
 created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices)
 Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
- Basic Router Security -
 1 Enable Passwords - Basic Router Security - The enable password protects a router s Privileged mode. This password can be set or changed from Global Configuration mode: Router(config)# enable password
1 Enable Passwords - Basic Router Security - The enable password protects a router s Privileged mode. This password can be set or changed from Global Configuration mode: Router(config)# enable password
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers Document ID: 22189 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by Step Procedure
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers Document ID: 22189 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by Step Procedure
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers Document ID: 12065 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers Document ID: 12065 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP
 Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Angelos Stavrou. OF COURSE there is no Magic so lets see show things work in practice...
 Cisco Inter-network Operating System (IOS) A short guide for the NetAdmin Angelos Stavrou Let's start out at the very beginning with the question: "What is a Command?" The most important thing to understand
Cisco Inter-network Operating System (IOS) A short guide for the NetAdmin Angelos Stavrou Let's start out at the very beginning with the question: "What is a Command?" The most important thing to understand
Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router
 CHAPTER 2 Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router This chapter describes how to boot and configure the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router. It discusses the following subjects: Cisco
CHAPTER 2 Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router This chapter describes how to boot and configure the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router. It discusses the following subjects: Cisco
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers Document ID: 12738 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Step by Step Procedure
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers Document ID: 12738 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Step by Step Procedure
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network
 LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
How to Configure Cisco 2600 Routers
 Helsinki University of Technology Department of Communications and Networking How to Configure Cisco 2600 Routers Juha Järvinen 10.6.2004 [email protected] Modified by Zhong Yunqiu 7.8.2008 Table
Helsinki University of Technology Department of Communications and Networking How to Configure Cisco 2600 Routers Juha Järvinen 10.6.2004 [email protected] Modified by Zhong Yunqiu 7.8.2008 Table
Objectives Understand Cisco IOS system architecture components. Work with the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface (CLI) and common commands.
 Objectives Understand Cisco IOS system architecture components. Work with the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface (CLI) and common commands. Learn about Cisco IOS troubleshooting techniques. Understand upgrading
Objectives Understand Cisco IOS system architecture components. Work with the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface (CLI) and common commands. Learn about Cisco IOS troubleshooting techniques. Understand upgrading
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2900 Series Integrated Services Router
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2900 Series Integrated Services Router Document ID: 112033 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2900 Series Integrated Services Router Document ID: 112033 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA
 ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network
 Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network CMPE 150 Fall 2005 Introduction Today you are going to be thrown into using Cisco s Internetwork Operating System (IOS) to configure
Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network CMPE 150 Fall 2005 Introduction Today you are going to be thrown into using Cisco s Internetwork Operating System (IOS) to configure
Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration
 CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
ROM Monitor. Entering the ROM Monitor APPENDIX
 APPENDIX B This appendix describes the Cisco router ROM monitor (also called the bootstrap program). The ROM monitor firmware runs when the router is powered up or reset. The firmware helps to initialize
APPENDIX B This appendix describes the Cisco router ROM monitor (also called the bootstrap program). The ROM monitor firmware runs when the router is powered up or reset. The firmware helps to initialize
LAB Configuring NAT. Objective. Background/Preparation
 LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial
 Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial Cisco Inter-network Operating System: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation The Cisco IOS software provides access to several different command modes. Each command mode provides
Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial Cisco Inter-network Operating System: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation The Cisco IOS software provides access to several different command modes. Each command mode provides
Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab will introduce to the student the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new. This introductory
Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab will introduce to the student the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new. This introductory
Objectives. Router as a Computer. Router components and their functions. Router components and their functions
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. Part 1: Router & Switch
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
Lab: Basic Router Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Router Lab Reference Guide
 Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
ICND1 Lab Guide. 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version 2.0. Labs powered by
 ICND1 Lab Guide 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version 2.0 ii Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 100-101 Lab Guide LM20130929/BV2.01 iii 25 Century Blvd. Ste. 500
ICND1 Lab Guide 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version 2.0 ii Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 100-101 Lab Guide LM20130929/BV2.01 iii 25 Century Blvd. Ste. 500
IPv6 for Cisco IOS Software, File 2 of 3: Configuring
 IPv6 for Cisco IOS Software, File 2 of 3: Configuring This document provides configuration tasks for the Cisco implementation of IP version 6 (IPv6) in the Cisco IOS software and includes the following
IPv6 for Cisco IOS Software, File 2 of 3: Configuring This document provides configuration tasks for the Cisco implementation of IP version 6 (IPv6) in the Cisco IOS software and includes the following
Using Cisco IOS Software
 Using Cisco IOS Software This chapter provides helpful tips for understanding and configuring Cisco IOS software using the command-line interface (CLI). It contains the following sections: Understanding
Using Cisco IOS Software This chapter provides helpful tips for understanding and configuring Cisco IOS software using the command-line interface (CLI). It contains the following sections: Understanding
Connect the Host to attach to Fast Ethernet switch port Fa0/2. Configure the host as shown in the topology diagram above.
 Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface
 Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface This document describes how to use the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) to perform a basic software configuration for your
Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface This document describes how to use the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) to perform a basic software configuration for your
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
 APPENDIXC Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI) setup procedure for a standalone switch. To set up the switch by using Express Setup, see
APPENDIXC Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI) setup procedure for a standalone switch. To set up the switch by using Express Setup, see
Configuring System Message Logging
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter describes how to configure system message logging on the Cisco 4700 Series Application Control Engine (ACE) appliance. Each ACE contains a number of log files that retain records
CHAPTER 1 This chapter describes how to configure system message logging on the Cisco 4700 Series Application Control Engine (ACE) appliance. Each ACE contains a number of log files that retain records
How To Configure A Cisco Router With A Cio Router
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
http://computernetworkingnotes.com/ccna-study-guide/cisco-ios-naming-convention-explainedwith-examples.html
 IOS is the most critical part of any cisco device. We should always keep a backup copy of IOS to deal with any unwanted situation. In this article I will explain the backup and restore process of IOS in
IOS is the most critical part of any cisco device. We should always keep a backup copy of IOS to deal with any unwanted situation. In this article I will explain the backup and restore process of IOS in
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
CISCO CATALYST 3550 Series Switches
 CISCO CATALYST 3550 Series Switches The switches that belong to this series are stackable and are multilayer switches that provide QoS, high availability and security that are responsible for enhancing
CISCO CATALYST 3550 Series Switches The switches that belong to this series are stackable and are multilayer switches that provide QoS, high availability and security that are responsible for enhancing
Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program
 APPENDIX D Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI)-based setup procedure for a standalone switch. For product overview information,
APPENDIX D Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI)-based setup procedure for a standalone switch. For product overview information,
CCNA 2 Chapter 5. Managing Cisco IOS Software
 1 CCNA 2 Chapter 5 Managing Cisco IOS Software The default source for Cisco IOS Software depends on the hardware platform; most commonly, though, the router looks to the configuration commands that are
1 CCNA 2 Chapter 5 Managing Cisco IOS Software The default source for Cisco IOS Software depends on the hardware platform; most commonly, though, the router looks to the configuration commands that are
LAB II: Securing The Data Path and Routing Infrastructure
 LAB II: Securing The Data Path and Routing Infrastructure 8. Create Packet Filters a. Create a packet filter which will deny packets that have obviously bogus IP source addresses but permit everything
LAB II: Securing The Data Path and Routing Infrastructure 8. Create Packet Filters a. Create a packet filter which will deny packets that have obviously bogus IP source addresses but permit everything
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Document ID: 45741. Introduction
 Products & Services 6bone Connection Using 6to4 Tunnels for IPv6 Document ID: 45741 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions How 6to4 Tunnels Work Limitations of 6to4
Products & Services 6bone Connection Using 6to4 Tunnels for IPv6 Document ID: 45741 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions How 6to4 Tunnels Work Limitations of 6to4
GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
 GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) protects data traffic from a failed router or circuit, like Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy
GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) protects data traffic from a failed router or circuit, like Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1
 Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Comware versus Cisco IOS Command Guide
 Technical Marketing Engineering Routing and Switching Technology Routing and Switching Comware versus Cisco IOS Command Guide Technical Marketing Brief Revision v5 March 23, 2009 http://www.3com.com 3Com
Technical Marketing Engineering Routing and Switching Technology Routing and Switching Comware versus Cisco IOS Command Guide Technical Marketing Brief Revision v5 March 23, 2009 http://www.3com.com 3Com
NetFlow Subinterface Support
 NetFlow Subinterface Support Feature History Release Modification 12.2(14)S This feature was introduced. 12.2(15)T This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T. This document describes the
NetFlow Subinterface Support Feature History Release Modification 12.2(14)S This feature was introduced. 12.2(15)T This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T. This document describes the
CHAPTER 3 STATIC ROUTING
 CHAPTER 3 STATIC ROUTING This chapter addresses the end-to-end delivery service of IP and explains how IP routers and hosts handle IP datagrams. The first section discusses how datagrams are forwarded
CHAPTER 3 STATIC ROUTING This chapter addresses the end-to-end delivery service of IP and explains how IP routers and hosts handle IP datagrams. The first section discusses how datagrams are forwarded
The Purpose and Use of the Configuration Register on All Cisco Routers
 The Purpose and Use of the Configuration Register on All Cisco Routers Document ID: 50421 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions The Purpose of the Configuration Register
The Purpose and Use of the Configuration Register on All Cisco Routers Document ID: 50421 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions The Purpose of the Configuration Register
[HOW TO RECOVER AN INFINITI/EVOLUTION MODEM IDX3.0.0.0] 1
![[HOW TO RECOVER AN INFINITI/EVOLUTION MODEM IDX3.0.0.0] 1 [HOW TO RECOVER AN INFINITI/EVOLUTION MODEM IDX3.0.0.0] 1](/thumbs/24/2694327.jpg) [HOW TO RECOVER AN INFINITI/EVOLUTION MODEM IDX3.0.0.0] 1 How to Recover an infiniti/evolution Modem Software Reference idx 3.0.0.0 (12.0.0.0) Updated: November 17 th 2011 Overview Recovery Procedures
[HOW TO RECOVER AN INFINITI/EVOLUTION MODEM IDX3.0.0.0] 1 How to Recover an infiniti/evolution Modem Software Reference idx 3.0.0.0 (12.0.0.0) Updated: November 17 th 2011 Overview Recovery Procedures
Configuring the MNLB Forwarding Agent
 CHAPTER 3 Configuring the MNLB Forwarding Agent This chapter describes how to configure a Cisco router as an MNLB Forwarding Agent to operate in conjunction with a Cisco LocalDirector serving as Services
CHAPTER 3 Configuring the MNLB Forwarding Agent This chapter describes how to configure a Cisco router as an MNLB Forwarding Agent to operate in conjunction with a Cisco LocalDirector serving as Services
CCNA Exploration 4.0: (II) Routing Protocols and Concepts. Chapter 1: Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding
 Http://elmaestrodelared.blogspot.com CCNA Exploration 4.0: (II) Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1: Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding 1. If a router cannot find a valid configuration
Http://elmaestrodelared.blogspot.com CCNA Exploration 4.0: (II) Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1: Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding 1. If a router cannot find a valid configuration
CCNA Exploration 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual
 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands
 Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
APNIC Members Training Course Security workshop. 2-4 July, 2008. Port Vila Vanuatu. In conjunction with PACNOG 4
 APNIC Members Training Course Security workshop 2-4 July, 2008 Port Vila Vanuatu In conjunction with PACNOG 4 Router device security lab 1. APNIC s remote lab In these exercises you will be remotely accessing
APNIC Members Training Course Security workshop 2-4 July, 2008 Port Vila Vanuatu In conjunction with PACNOG 4 Router device security lab 1. APNIC s remote lab In these exercises you will be remotely accessing
Chapter 3 Configuring Basic IPv6 Connectivity
 Chapter 3 Configuring Basic IPv6 Connectivity This chapter explains how to get a ProCurve Routing Switch that supports IPv6 up and running. To configure basic IPv6 connectivity, you must do the following:
Chapter 3 Configuring Basic IPv6 Connectivity This chapter explains how to get a ProCurve Routing Switch that supports IPv6 up and running. To configure basic IPv6 connectivity, you must do the following:
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client
 Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Telnet, Console and AUX Port Passwords on Cisco Routers Configuration Example
 Telnet, Console and AUX Port Passwords on Cisco Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 45843 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Passwords
Telnet, Console and AUX Port Passwords on Cisco Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 45843 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Passwords
Table of Contents. Cisco How to Download a Software Image to a Cisco 2600 via TFTP Using the tftpdnld ROMmon Command
 load a Software Image to a Cisco 2600 via TFTP Using the tftpd nd Table of Contents How to Download a Software Image to a Cisco 2600 via TFTP Using the tftpdnld ROMmon Command...1 Introduction...1 Before
load a Software Image to a Cisco 2600 via TFTP Using the tftpd nd Table of Contents How to Download a Software Image to a Cisco 2600 via TFTP Using the tftpdnld ROMmon Command...1 Introduction...1 Before
Table of Contents. Cisco How to Download a Software Image to a Cisco 2600 through TFTP Using the tftpdnld ROMmon Command
 mand Table of Contents How to Download a Software Image to a Cisco 2600 through TFTP Using the tftpdnld ROMmon Command...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...1
mand Table of Contents How to Download a Software Image to a Cisco 2600 through TFTP Using the tftpdnld ROMmon Command...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...1
Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH
 Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH Objectives Use SDM to configure a router to accept SSH connections. Configure SSH client software on a PC. Establish a connection to a Cisco ISR using SSH
Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH Objectives Use SDM to configure a router to accept SSH connections. Configure SSH client software on a PC. Establish a connection to a Cisco ISR using SSH
Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration
 Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration Learning Objectives Review of previously learned skills. Basic IOS Command Line Interface operation. Basic Router configuration. Verification and testing
Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration Learning Objectives Review of previously learned skills. Basic IOS Command Line Interface operation. Basic Router configuration. Verification and testing
Central America Workshop - Guatemala City Guatemala 30 January - 1 February 07. IPv6 Router s Configuration
 Central America Workshop - Guatemala City Guatemala 30 January - 1 February 07 IPv6 Router s Configuration Pedro Lorga ([email protected]) Simon Muyal ([email protected]) Piers O'Hanlon ([email protected])
Central America Workshop - Guatemala City Guatemala 30 January - 1 February 07 IPv6 Router s Configuration Pedro Lorga ([email protected]) Simon Muyal ([email protected]) Piers O'Hanlon ([email protected])
Terminal Server Configuration and Reference Errata
 Doc. No. 78-0944-06A0 June 14, 1993 Terminal Server Configuration and Reference Errata This document supplies corrections and additional informaiton for the 9.0 version of the Cisco publication Terminal
Doc. No. 78-0944-06A0 June 14, 1993 Terminal Server Configuration and Reference Errata This document supplies corrections and additional informaiton for the 9.0 version of the Cisco publication Terminal
Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide
 Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide April 29, 2011 This document explains how to start using Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) and Cisco Configuration Professional
Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide April 29, 2011 This document explains how to start using Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) and Cisco Configuration Professional
Backing Up and Restoring Data
 Backing Up and Restoring Data Cisco Unity Express backup and restore functions use an FTP server to store and retrieve data. The backup function copies the files from the Cisco Unity Express application
Backing Up and Restoring Data Cisco Unity Express backup and restore functions use an FTP server to store and retrieve data. The backup function copies the files from the Cisco Unity Express application
Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and Managing the Configuration
 CHAPTER 3 Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Connecting
CHAPTER 3 Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Connecting
How To Install Cisco Asr 9000 Series Router Software On A Mini Mini Mini (Cisco Ios) Router
 This chapter describes the router recovery methods in ROM Monitor (ROMMON) mode of the router. Table 1: Feature History for Router Recovery with the ROM Monitor Release Modification Release 4.2.0 A new
This chapter describes the router recovery methods in ROM Monitor (ROMMON) mode of the router. Table 1: Feature History for Router Recovery with the ROM Monitor Release Modification Release 4.2.0 A new
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Configuring Basic Settings
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on your ASA that are typically required for a functioning configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Configuring the
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on your ASA that are typically required for a functioning configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Configuring the
Backup and Recovery Procedures
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter provides Content Distribution Manager database backup and ACNS software recovery procedures. This chapter contains the following sections: Performing Backup and Restore Operations
CHAPTER 10 This chapter provides Content Distribution Manager database backup and ACNS software recovery procedures. This chapter contains the following sections: Performing Backup and Restore Operations
Brocade to Cisco Comparisons
 1 2 3 Console cables - The console cables are not interchangeable between Brocade and Cisco. Each vendor provides their console cable with each manageable unit it sells. Passwords - Neither Cisco or Brocade
1 2 3 Console cables - The console cables are not interchangeable between Brocade and Cisco. Each vendor provides their console cable with each manageable unit it sells. Passwords - Neither Cisco or Brocade
Chapter 2 Using the Command Line Interface
 Chapter 2 Using the Command Line Interface The CLI is a text-based interface for configuring and monitoring HP ProCurve switches and routing switches. You can access the CLI can through either a direct
Chapter 2 Using the Command Line Interface The CLI is a text-based interface for configuring and monitoring HP ProCurve switches and routing switches. You can access the CLI can through either a direct
Lab Configuring Syslog and NTP (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Administering the Network Analysis Module. Cisco IOS Software. Logging In to the NAM with Cisco IOS Software CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 4 How you administer the NAM on your Catalyst 6500 series switch or Cisco 7600 series router depends on whether you are using the Cisco IOS software or the Catalyst operating system software. Several
CHAPTER 4 How you administer the NAM on your Catalyst 6500 series switch or Cisco 7600 series router depends on whether you are using the Cisco IOS software or the Catalyst operating system software. Several
How Do I Upgrade Firmware and Save Configurations on PowerConnect Switches?
 PowerConnect Application Note #12 February 2004 How Do I Upgrade Firmware and Save Configurations on PowerConnect Switches? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell PowerConnect products: PowerConnect
PowerConnect Application Note #12 February 2004 How Do I Upgrade Firmware and Save Configurations on PowerConnect Switches? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell PowerConnect products: PowerConnect
File Transfers. Contents
 A File Transfers Contents Overview..................................................... A-2................................... A-2 General Switch Software Download Rules..................... A-3 Using
A File Transfers Contents Overview..................................................... A-2................................... A-2 General Switch Software Download Rules..................... A-3 Using
USB Disable for Cisco ISRs Feature Module
 USB Disable for Cisco ISRs Feature Module First Published: March 28, 2011 Part Number: This guide describes the USB Disable feature in the following major sections: Feature Introduction, page 1 Restrictions,
USB Disable for Cisco ISRs Feature Module First Published: March 28, 2011 Part Number: This guide describes the USB Disable feature in the following major sections: Feature Introduction, page 1 Restrictions,
Using the Command Line Interface (CLI)
 4 Using the Command Line Interface (CLI) Contents Overview...................................................... 4-2 Accessing the CLI............................................... 4-2...................................................
4 Using the Command Line Interface (CLI) Contents Overview...................................................... 4-2 Accessing the CLI............................................... 4-2...................................................
How To Set Up A Netvanta For A Pc Or Ipad (Netvanta) With A Network Card (Netvina) With An Ipa (Net Vanta) And A Ppl (Netvi) (Netva)
 VPN WAN LAN PWR STAT TD RD TD RD TD RD VPN WAN LAN PWR STAT TD RD TD RD TD RD NetVanta 3200 NetVanta 3200 NetVanta Series (with T1/FT1 or T1/FT1 + DSX-1 Network Interface Module) Quick Configuration Guide
VPN WAN LAN PWR STAT TD RD TD RD TD RD VPN WAN LAN PWR STAT TD RD TD RD TD RD NetVanta 3200 NetVanta 3200 NetVanta Series (with T1/FT1 or T1/FT1 + DSX-1 Network Interface Module) Quick Configuration Guide
Configuring Basic Settings
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on your ASASM that are typically required for a functioning configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Configuring the
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on your ASASM that are typically required for a functioning configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Configuring the
Objectives. Background. Required Resources. CCNA Security
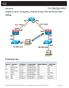 Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
The Cisco IOS Firewall feature set is supported on the following platforms: Cisco 2600 series Cisco 3600 series
 Cisco IOS Firewall Feature Set Feature Summary The Cisco IOS Firewall feature set is available in Cisco IOS Release 12.0. This document includes information that is new in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T, including
Cisco IOS Firewall Feature Set Feature Summary The Cisco IOS Firewall feature set is available in Cisco IOS Release 12.0. This document includes information that is new in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T, including
Lab Exercise Configure the PIX Firewall and a Cisco Router
 Lab Exercise Configure the PIX Firewall and a Cisco Router Scenario Having worked at Isis Network Consulting for two years now as an entry-level analyst, it has been your hope to move up the corporate
Lab Exercise Configure the PIX Firewall and a Cisco Router Scenario Having worked at Isis Network Consulting for two years now as an entry-level analyst, it has been your hope to move up the corporate
Debugging Network Communications. 1 Check the Network Cabling
 Debugging Network Communications Situation: you have a computer and your NetBurner device on a network, but you cannot communicate between the two. This application note provides a set of debugging steps
Debugging Network Communications Situation: you have a computer and your NetBurner device on a network, but you cannot communicate between the two. This application note provides a set of debugging steps
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses.
 Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
