HUMAN MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS AS BASIC TOOLS FOR TISSUE ENGINEERING: ISOLATION AND CULTURE
|
|
|
- Coral Freeman
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HUMAN MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS AS BASIC TOOLS FOR TISSUE ENGINEERING: ISOLATION AND CULTURE MONICA NEAGU*, ERIKA SUCIU**, VALENTIN ORDODI**, VIRGIL PĂUNESCU** *Department of Biophysics and Medical Informatics, Victor Babeş University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timişoara, 2, P-Ńa E. Murgu, Timişoara, Romania **Department of Physiology and Immunology, Victor Babeş University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timişoara, 2, P-Ńa E. Murgu, Timişoara, Romania Abstract. Stem cells are immature cells capable of autoreplication, which are able to generate various mature cell types and have a remarkable viability and proliferative capacity. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), under proper conditions, can give rise to osteoblasts, adipocytes, chondrocytes, myocytes and even neurons. Several procedures applied in tissue engineering imply harvesting autologous MSC, expanding them in culture without loss of stemness, inducing differentiation, seeding them on suitable scaffolds in accordance with the targeted tissue type and implanting the construct into the patient s body. During this study, bone marrow has been extracted from 9 patients by aspiration from the upper posterior iliac crest and used in order to isolate the MSC by employing three different methods: (1) the Ficoll-Paque technique for the isolation of mononucleated cells followed by the separation of MSC by adherence to plastic, (2) Ficoll-Paque followed by the immuno-magnetic separation of MSC using a CliniMACS system and (3) a negative selection procedure of MSC using the RosetteSep technique followed by adherence to plastic. We have prepared and optimized our media, assuring control and reproducibility of the results. Finally, an immunophenotypic characterization of the cells by flowcytometry has been performed. On the 3 rd day after seeding the isolated mononucleated fraction in the optimally prepared culture medium, we observed elongated adherent cells which have undergone extensive proliferation between days 5 and 9, with colony forming around days 10 to 14. The cell population reached 70 80% confluence within 3 weeks in culture. Independent on the isolation procedure, the largest number of cell colonies has been obtained for a cell seeding density of 10 6 cells/cm 2. Key words: stem cells, differentiation, plasticity, flowcytometry. Received July 2005; in final form October INTRODUCTION In the case of tissue damage, transplant is one of the very few clinical solutions available today. Nevertheless, its feasibility is limited by donor organ shortage. In an effort to circumvent this problem, about two decades ago a new field of medical sciences emerged, which goes by the name of tissue engineering (TE) and aims to develop biologically based replacement tissues. Several problems must be solved before TE is used on large scales in clinical practice. These include ROMANIAN J. BIOPHYS., Vol. 15, Nos. 1 4, P , BUCHAREST, 2005
2 30 Monica Neagu, Erika Suciu, V. Ordodi, V. Păunescu questions regarding a suitable cell source, the identification of the appropriate scaffold for each tissue type of interest and the optimization of the culture conditions in order to ensure viability and physico-chemical properties comparable to the native organ. Stem cells (SC) are immature cells with two essential features: (1) they are capable of autoreplication and (2) they are able to give rise to various mature cell types of the organism. In culture, they have a remarkable viability and proliferative capacity [1, 2]. All these characteristics make them a favourite cell source for TE. The bone marrow is regarded as the most important non-hemopoietic, mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) source. MSCs have been identified in the periosteum, muscle, liver, blood and fetal bone marrow, whereas their occurrence in the umbilical cord blood is controversial. By supplementing the cell culture medium with specific growth and differentiation factors, MSC may be coaxed to give rise to osteoblasts, chondrocytes, myocytes, adipocytes, cardiomyocytes and neurons, too [7]. In order to use MSC in regenerative medicine, it is necessary to isolate and proliferate them without loss of stemness, i.e. preserving their pluripotentiality and proliferative capacity in undifferentiated state. Recent studies are focused on developing optimal culture conditions (including cell culture media, bioactive agents and biodegradable scaffolds) for each specific therapy [9]. MATERIALS AND METHODS PATIENTS Bone marrow from 9 patients (10 ml/patient) has been extracted from the upper posterior iliac crest using a heparinated syringe, under general anesthesia, in a sterile surgical room, in accordance with ethical regulations and having the acceptance of the patients. CELL SEPARATION We employed three methods of isolation of MSC from bone marrow: (1) the Ficoll-Paque technique for the isolation of mononucleated cells followed by the separation of MSC by adherence to plastic, (2) Ficoll-Paque followed by the immuno-magnetic separation of MSC and (3) a negative selection procedure of MSC using the RosetteSep technique, followed by adherence to plastic. 1. The Ficoll-Paque technique of density gradient centrifugation was employed by first diluting the bone marrow sample with cell culture medium supplemented with 2% PBS and 1 2 mm EDTA; the resulting solution was poured on the top of the separation medium (Ficoll-Paque solution of g/ml density), in a 50 ml centrifuge tube (Becton Dickinson, USA) and centrifuged at room
3 Isolation and culture of hmsc 31 temperature, at 445 g, for 35 minutes. The majority of the mononucleated cells accumulated on the Ficoll-plasma interface. The centrifugation was repeated for 10 minutes at 300 g. Finally, the cells were resuspended and counted using a hemocytometer. 2. RosetteSep combines the density gradient separation with antibodymediated specificity. The bone marrow was placed into a centrifuge tube (Becton Dickinson, USA) and, after adding the RosetteSep solution, the mixture was incubated at room temperature for 20 minutes and centrifuged for 25 minutes at 300 g. The result was a negative selection of MSC, which have not been targeted by antibodies and accumulated on the plasma-ficoll interface. The mononuclear cell suspension obtained by Ficoll or RosetteSep separation technique was plated on Petri dishes for selective isolation by adhesion. The cells were incubated at 37 o C, in 5% CO 2 and 95% minimal humidity at different seeding densities: 5, 10, 15, 50, 100 and 500 x 10 4 cells/cm 2. The non-adherent cells were eliminated on the 3 rd day after seeding by replaceing the culture medium. The adherent cells were cultured until 70 80% confluence was attained (14 21 days) with medium change every 4 th day. 3. Isolation using MACS Direct CD105 consists in magnetic sorting of CD105+ cells. To this end, we used a MidiMACS Separator (Miltenyi Biotec, Germany). The cells were immunomagnetically labeled using a cell-type specific reactive. The suspension obtained by the Ficoll technique was mixed with MACS CD105 superparamagnetic colloidal MicroBeads, (Miltenyi Biotec, Germany) coated with CD105 monoclonal antibodies: and incubated for 15 minutes at 6-12 C. The magnetically labeled separated cells were used in part for flowcytometric and viability analyses, the rest being cultured. CELL CULTURE We used Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium (DMEM) low glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, Germany), supplemented with 10% Fetal Calf Serum (FCS) (Promocell, Germany), 2 ng/ml FGFb (Sigma-Aldrich, Germany) and 1% antibiotic/antimycotic (penicillin u/ml; streptomycin 10 mg/ml; amfoterycin B 0,25 µg/ml) (Sigma-Aldrich, Germany). The cells were plated on T25 culture dishes (Becton Dickinson, USA) at 6 values of the seeding density, and incubated at 37 C in an atmosphere of 95% relative humidity and 5% CO 2. The first medium change was done 72 h after seeding, then medium was changed weekly. For passage, the medium was discarded, the system was washed with PBS, cells were detached using trypsin/edta 0,25%. After trypsin neutralization with DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, the cell suspension was centrifuged at room temperature for 10 minutes at 300 g, the supernatant was removed and the cells were resuspended, counted and distributed in culture dishes.
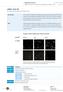
4 32 Monica Neagu, Erika Suciu, V. Ordodi, V. Păunescu FLOWCYTOMETRIC ANALYSIS The cells have been phenotypically characterized by using a flowcytometer (FACSCalibur, Beckton Dickinson). After trypsinization, cells were incubated with fluorescence-conjugated antibodies (marked with FITC fluorescein isothiocyanate and PE phycoerythrin fluorochromes, Beckton Dickinson) for 20 min in the dark. After 2 washing steps with PBS, cells were acquired in FACSCalibur (Becton Dickinson) flowcytometer using CellQuest software and analysed with Paint-A-Gate software. RESULTS We harvested human bone marrow from 9 patients, made a comparative study of three isolation techniques, cultivated and analysed the MSC and performed a morphological characterization together with a flowcytometric analysis of the cells. Fig. 1. Mesenchymal stem cells on day 14 (left, 200x magnification), and on day 21 after seeding, respectively (right, 40x magnification). On the 3 rd day after seeding we observed elongated adherent cells; these have undergone extensive proliferation between days 5 and 9, with colony formation around day 10 to 14. The cell population reached confluence within 3 weeks in culture. During long-term cultivation, cells were passed after 2 weeks from seeding, at 70 80% confluence, and were examined during 8 weeks. The initial flowcytometric analysis, performed on day 0 when cells were seeded, displayed a heterogeneous mixture of cells with different forward and sideward scattering profiles (data not shown). A major proportion of the cells expressed CD45 and Glycophorin A, while the specific MSC markers, CD105 and CD73 were not expressed. The immunophenotype of the cells resulted from passage 1 (day 21) showed low levels of CD14, Glycophorin A and CD45, probably due to contaminating cells (data not shown). The flowcytometric analysis revealed a significant increase of CD 73 expression at the second passage (day 42).
5 Isolation and culture of hmsc 33 The hemopoietic stem cell marker, CD34, was not expressed neither on day 0, nor after the two passages. The data have been displayed in the form of single-colour histograms, evidencing the CD34, CD45, CD90, CD105 and CD73 expression by the investigated cells (Fig. 2). Fig. 2. Immunophenotypic characterization of the cells by FACS analysis, on day 42 after seeding (passage 2). Each plot is a histogram depicting the number of cells vs. their fluorescence level. The numbers specify the percentage of cells expressing the specific markers (with fluorescence falling between the marker boundaries, marked by the horizontal segments). DISCUSSIONS During the past two decades MSC have been extensively investigated because of their far reaching therapeutic potential [10, 11]. From the point of view of cell and gene therapies, they display several exciting properties such as ease of isolation, good proliferative capacity and ease of transfection with exogeneous genes. Several procedures proposed for tissue repair imply harvesting autologous mesenchymal stem cells, expanding them in culture, inducing differentiation, seeding them on suitable scaffolds in accordance with the targeted tissue type and implanting the construct into the patient s body [4, 6, 8]. The composition of the cell culture medium turned out to be a decisive factor in preserving the stem cell features [5, 9]. Under certain conditions MSC may be passed times without observing signs of spontaneous differentiation. Yet other conditions coax MSC to engage towards one of several cell lineages; this property goes by the name of stem cell plasticity [3, 7].
6 34 Monica Neagu, Erika Suciu, V. Ordodi, V. Păunescu Human MSC isolated in our laboratories have expressed typical cell surface markers at levels in good agreement with recent results of similar studies. A typical MSC marker, CD105, displayed a slight regression from day 21 to day 42, presumably due to spontaneous differentiation of the cells, while the expression of CD90 and CD73 showed a significant increase. However, even after 42 days, 36,56% of the cells express CD105, 86,52% express CD73 and 66,32% express CD90 suggesting that their stemness has been preserved. By comparing the mean number of formed colonies, counted during all 21 performed experiments, no significant differences in colony formation between the three distinct MSC isolation methods have been observed (data not shown). This comparison allowed us to find the optimal cell seeding density (10 6 cells/cm 2 ) which assured a maximal number of colonies. These observations enable us to conclude that the cell culture media and conditions were suitable for MSC expansion. Future work will be focused on human MSC differentiation in vitro towards the osteogenic and chondrogenic lineages. Acknowledgements. This work was supported by Grant VIASAN nr. 313 / from the National Research, Development and Innovation Program (PNCDI). R E F E R E N C E S 1. BIANCO, P., M. RIMINUCCI, S. GRONTHOS, P.G. ROBEY, Bone marrow stromal stem cells: nature, biology, and potential applications. Stem Cells, 2001, 19, COMPSTON, J.E., Bone marrow and bone: a functional unit, Journal of Endocrinology, 2002, 173, CONGET, P.A., J.J. MINGUELL, Phenotypic and functional properties of human bone marrow mesenchymal progenitor cells, J. Cell Physiol., 1999, 181, DOMINICI, M., T.J. HOFMANN, E.M. HORWITZ, Bone marrow mesenchymal cells: biological properties and clinical applications, Journal of Biological regulators and Homeostatic Agents, 2002, 15, FRIEDENSTEIN, A.J., R.K. CHAILAKHYAN, U.V. GERASIMOV, Bone marrow osteogenic stem cells: in vitro cultivation and transplantation in diffusion chambers, Cell Tissue Kinet, 1987, 20, HUNG, S.-C., N.-J. CHEN, S.-L. SHIEH, H. LI, H.-L. MA, W.-H. LO, Isolation and Characterization of size-sieved stem cells from human bone marrow, Stem Cells, 2002, 20, KRAUSE, D.S., Plasticity of marrow-derived stem cells. Gene Therapy, 2002, 9, LANGER, R., J.P. VACANTI, Tissue engineering, Science, 1993, 260, MAJUMDAR, M.K., M.A. THIEDE, J.D. MOSCA, M. MOORMAN, S.L. GERSON, Phenotypic and functional comparison of cultures of marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and stromal cells, J. Cell Physiol., 1998, 176, PITTENGER, M.F., A.M. MACKAY, S.C. BECK, R.K. JAISWAL, R. DOUGLAS, J.D. MOSCA, M.A. MOORMAN, D.W. SIMONETTI, S. CRAIG, D.R. MARSHAK, Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells, Science, 1999, 284, ZIKUAN, G., Y. JINGQUING, L. XIAODAN, L. XIUSEN, H. CHUNMEI, T. PEI HSEIN, M. NING, Biological features of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow. Chin. Med. J., 2001, 114,
Basic Science in Medicine
 Medical Journal of th e Islamic Republic of Iran Volume 18 Number 3 Fall 1383 November 2004 Basic Science in Medicine ] EXPANSION OF HUMAN CORD BLOOD PRIMITIVE PROGENITORS IN SERUM-FREE MEDIA USING HUMAN
Medical Journal of th e Islamic Republic of Iran Volume 18 Number 3 Fall 1383 November 2004 Basic Science in Medicine ] EXPANSION OF HUMAN CORD BLOOD PRIMITIVE PROGENITORS IN SERUM-FREE MEDIA USING HUMAN
Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Mesenchymal Stem Cells Instruction Manual Product Size Catalog Number from Bone Marrow (hmsc-bm) from Umbilical Cord Matrix (hmsc-uc) from Adipose Tissue (hmsc-at) 500,000 cryopreserved cells 500,000 proliferating
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Instruction Manual Product Size Catalog Number from Bone Marrow (hmsc-bm) from Umbilical Cord Matrix (hmsc-uc) from Adipose Tissue (hmsc-at) 500,000 cryopreserved cells 500,000 proliferating
Human Umbilical Cord-derived Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (huc-msc) Handling Instructions
 Human Umbilical Cord-derived Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (huc-msc) Order No.: 19401-005, 19401-010 Handling Instructions For preclinical ex vivo use. Not intended for therapeutic use. Table of
Human Umbilical Cord-derived Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (huc-msc) Order No.: 19401-005, 19401-010 Handling Instructions For preclinical ex vivo use. Not intended for therapeutic use. Table of
Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34 + Progenitor Cell Care Manual
 Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34 + Progenitor Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0065.03 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34+ Progenitor Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human umbilical
Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34 + Progenitor Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0065.03 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34+ Progenitor Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human umbilical
Comparison of Mesenchymal Stem Cells derived from Amniotic Fluid and Umbilical Cord
 Academy of Sustainable Development and Technology. Comparison of Mesenchymal Stem Cells derived from Amniotic Fluid and Umbilical Cord Master of Science Thesis (30hp) Flemmingsberg, Sweden 2011 Åsa Ekblad
Academy of Sustainable Development and Technology. Comparison of Mesenchymal Stem Cells derived from Amniotic Fluid and Umbilical Cord Master of Science Thesis (30hp) Flemmingsberg, Sweden 2011 Åsa Ekblad
Minimal residual disease detection in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia on a Becton Dickinson flow cytometer
 Minimal residual disease detection in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia on a Becton Dickinson flow cytometer Purpose This procedure gives instruction on minimal residual disease (MRD) detection in patients with
Minimal residual disease detection in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia on a Becton Dickinson flow cytometer Purpose This procedure gives instruction on minimal residual disease (MRD) detection in patients with
Equine Stem Cells. Sources, Processing, Expansion, Storage and Shipping
 Equine Stem Cells Sources, Processing, Expansion, Storage and Shipping Sean Owens, DVM, Diplomate ACVP Medical Director, UC Davis Veterinary Regenerative Medicine Laboratory What is a Stem Cell and What
Equine Stem Cells Sources, Processing, Expansion, Storage and Shipping Sean Owens, DVM, Diplomate ACVP Medical Director, UC Davis Veterinary Regenerative Medicine Laboratory What is a Stem Cell and What
3D Cell Culture mimsys G
 3D Cell Culture mimsys G xeno-free & nutrient permeable hydrogel for 3D cell culture mimsys G is a xeno-free and non-immunogenic, easy to handle hydrogel for cell encapsulation in 3D experiments in vitro
3D Cell Culture mimsys G xeno-free & nutrient permeable hydrogel for 3D cell culture mimsys G is a xeno-free and non-immunogenic, easy to handle hydrogel for cell encapsulation in 3D experiments in vitro
PROTOCOL. Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry. Background. Materials and equipment required.
 PROTOCOL Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 Rev.0 Background The combination of single cell analysis using flow cytometry and the specificity of antibody-based
PROTOCOL Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 Rev.0 Background The combination of single cell analysis using flow cytometry and the specificity of antibody-based
Stem cells possess 2 main characteristics: Sources of pluripotent stem cells: -Long-term self renewal. -The inner cell mass of the blastocyst.
 Stem cells possess 2 main characteristics: -Long-term self renewal. - They give rise to all types of differentiate cells. Sources of pluripotent stem cells: -The inner cell mass of the blastocyst. - Fetal
Stem cells possess 2 main characteristics: -Long-term self renewal. - They give rise to all types of differentiate cells. Sources of pluripotent stem cells: -The inner cell mass of the blastocyst. - Fetal
Chondrogenical Differentiation of Umbilical Cord Lining. Stem Cells
 Chondrogenical Differentiation of Umbilical Cord Lining Stem Cells He Xi, Masilamani Jeyakumar, Phan Toan Thang Bioengineering, National University of Bioengineering Abstract Cartilage defects, such as
Chondrogenical Differentiation of Umbilical Cord Lining Stem Cells He Xi, Masilamani Jeyakumar, Phan Toan Thang Bioengineering, National University of Bioengineering Abstract Cartilage defects, such as
Transfection reagent for visualizing lipofection with DNA. For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.
 METAFECTENE FluoR Transfection reagent for visualizing lipofection with DNA For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
METAFECTENE FluoR Transfection reagent for visualizing lipofection with DNA For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
Processing & Utilization of Cord Blood for Transplant
 Processing & Utilization of Cord Blood for Transplant 2010-Jan Jan-15 Nicole L. Prokopishyn, PhD HPC Processing Laboratory Director Calgary Laboratory Services Overview Cord Blood Processing Pre-Freeze
Processing & Utilization of Cord Blood for Transplant 2010-Jan Jan-15 Nicole L. Prokopishyn, PhD HPC Processing Laboratory Director Calgary Laboratory Services Overview Cord Blood Processing Pre-Freeze
Human Adult Mesothelial Cell Manual
 Human Adult Mesothelial Cell Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0025.01 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Adult Mesothelial Cells Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier. All US and Canada orders are shipped
Human Adult Mesothelial Cell Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0025.01 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Adult Mesothelial Cells Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier. All US and Canada orders are shipped
PROTOCOL. Immunocytochemistry (ICC) MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
 PROTOCOL Immunocytochemistry (ICC) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 11-07 MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Materials: MitoSciences primary monoclonal antibody/antibodies Fluorophore-conjugated
PROTOCOL Immunocytochemistry (ICC) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 11-07 MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Materials: MitoSciences primary monoclonal antibody/antibodies Fluorophore-conjugated
MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit
 page 1 of 7 MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the mice they are isolated
page 1 of 7 MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the mice they are isolated
MEF Nucleofector Kit 1 and 2
 page 1 of 7 MEF Nucleofector Kit 1 and 2 for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the they are isolated
page 1 of 7 MEF Nucleofector Kit 1 and 2 for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the they are isolated
BioResearch. Hematopoietic and Immune Cell Products Essential Tools for Hematopoietic Research
 BioResearch Hematopoietic and Immune Cell Products Essential Tools for Hematopoietic Research BioResearch Hematopoietic and Immune Cell Products Essential Tools for Hematopoietic Research Working with
BioResearch Hematopoietic and Immune Cell Products Essential Tools for Hematopoietic Research BioResearch Hematopoietic and Immune Cell Products Essential Tools for Hematopoietic Research Working with
International Beryllium Conference, Montreal, Canada March 10, 2005
 Alternative Lymphocyte Proliferation Tests: BrdU and Flow Cytometry Based Tests International Beryllium Conference, Montreal, Canada March 10, 2005 Tim K. Takaro Department of Environmental and Occupational
Alternative Lymphocyte Proliferation Tests: BrdU and Flow Cytometry Based Tests International Beryllium Conference, Montreal, Canada March 10, 2005 Tim K. Takaro Department of Environmental and Occupational
Osteoblast Differentiation and Mineralization
 Osteoblast Differentiation and Mineralization Application Note Background Osteoblasts are specialized fibroblasts that secrete and mineralize the bone matrix. They develop from mesenchymal precursors.
Osteoblast Differentiation and Mineralization Application Note Background Osteoblasts are specialized fibroblasts that secrete and mineralize the bone matrix. They develop from mesenchymal precursors.
Evaporation-based Microfluidic Production of. Oil-free Cell-Containing Hydrogel Particles
 Supporting Information Evaporation-based Microfluidic Production of Oil-free Cell-Containing Hydrogel Particles Rong Fan, a Kubra Naqvi, b Krishna Patel, c Jun Sun d and Jiandi Wan *a a Microsystems Engineering
Supporting Information Evaporation-based Microfluidic Production of Oil-free Cell-Containing Hydrogel Particles Rong Fan, a Kubra Naqvi, b Krishna Patel, c Jun Sun d and Jiandi Wan *a a Microsystems Engineering
NCL Method ITA-14. Analysis of Nanoparticle Effects on Maturation of Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells In Vitro
 NCL Method ITA-14 Analysis of Nanoparticle Effects on Maturation of Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells In Vitro Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research
NCL Method ITA-14 Analysis of Nanoparticle Effects on Maturation of Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells In Vitro Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research
Instructions. Torpedo sirna. Material. Important Guidelines. Specifications. Quality Control
 is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
Application Note 10. Measurement of Cell Recovery. After Sorting with a Catcher-Tube-Based. Cell Sorter. Introduction
 Application Note 10 Measurement of Cell Recovery After Sorting with a Catcher-Tube-Based Cell Sorter Introduction In many experiments using sorted cells, it is important to be able to count the number
Application Note 10 Measurement of Cell Recovery After Sorting with a Catcher-Tube-Based Cell Sorter Introduction In many experiments using sorted cells, it is important to be able to count the number
Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual
 Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0067.02 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human CD4+T Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human CD4+T cells are shipped on dry ice and should be stored in liquid nitrogen
Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0067.02 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human CD4+T Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human CD4+T cells are shipped on dry ice and should be stored in liquid nitrogen
GASTRIC ORGANOID CULTURE PROTOCOL
 GASTRIC ORGANOID CULTURE PROTOCOL THIS PROTOCOL PROVIDES THE PROCEDURE FOR SUBCULTURING NORMAL HUMAN GASTRIC ORGANOIDS WHICH WAS DERIVED FROM THE SUBMERGED METHOD AS DESCRIBED IN BARKER N, ET AL. LGR5+VE
GASTRIC ORGANOID CULTURE PROTOCOL THIS PROTOCOL PROVIDES THE PROCEDURE FOR SUBCULTURING NORMAL HUMAN GASTRIC ORGANOIDS WHICH WAS DERIVED FROM THE SUBMERGED METHOD AS DESCRIBED IN BARKER N, ET AL. LGR5+VE
How To Expand Hematopoietic Stem Cells
 Purification and Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells Based on Proteins Expressed by a Novel Stromal Cell Population Our bodies are constantly killing old, nonfunctional, and unneeded cells and making
Purification and Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells Based on Proteins Expressed by a Novel Stromal Cell Population Our bodies are constantly killing old, nonfunctional, and unneeded cells and making
Poietics human mesenchymal stem cells Instructions for use
 Poietics human mesenchymal stem cells Instructions for use www.lonza.com U.S. Scientific Support: 800-521-0390 [email protected] EU/ROW Scientific Support: +49-221-99199-400 [email protected]
Poietics human mesenchymal stem cells Instructions for use www.lonza.com U.S. Scientific Support: 800-521-0390 [email protected] EU/ROW Scientific Support: +49-221-99199-400 [email protected]
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit
 CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Item No. 10009853 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Item No. 10009853 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
STEMCELL Quality Control Kits
 STEMCELL Quality Control Kits i Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction...1 2.0 Thawing Cells, Plating and Colony Enumeration...2 2.1 Supplies and reagents included in the QC kit...2 2.2 Additional reagents
STEMCELL Quality Control Kits i Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction...1 2.0 Thawing Cells, Plating and Colony Enumeration...2 2.1 Supplies and reagents included in the QC kit...2 2.2 Additional reagents
BD PuraMatrix Peptide Hydrogel
 BD PuraMatrix Peptide Hydrogel Catalog No. 354250 Guidelines for Use FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY NOT FOR CLINICAL, DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE SPC-354250-G rev 2.0 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Intended Use... 2 Materials
BD PuraMatrix Peptide Hydrogel Catalog No. 354250 Guidelines for Use FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY NOT FOR CLINICAL, DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE SPC-354250-G rev 2.0 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Intended Use... 2 Materials
NCL Method ITA-6. Leukocyte Proliferation Assay
 NCL Method ITA-6 Leukocyte Proliferation Assay Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory National Cancer Institute-Frederick SAIC-Frederick Frederick, MD 21702 (301) 846-6939 [email protected] December
NCL Method ITA-6 Leukocyte Proliferation Assay Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory National Cancer Institute-Frederick SAIC-Frederick Frederick, MD 21702 (301) 846-6939 [email protected] December
Cord Blood Re-imagined The use of cord blood stem cells for clinical applications and medical innovations
 GE Healthcare Proceedings of the Symposium Cord Blood Re-imagined The use of cord blood stem cells for clinical applications and medical innovations 12 th Annual Meeting of the International Society for
GE Healthcare Proceedings of the Symposium Cord Blood Re-imagined The use of cord blood stem cells for clinical applications and medical innovations 12 th Annual Meeting of the International Society for
HARVESTING AND CRYOPRESERVATION OF HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS (hescs)
 HARVESTING AND CRYOPRESERVATION OF HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS (hescs) OBJECTIVE: can be cryopreserved in a liquid nitrogen (LN 2 ) freezer for long-term storage. This Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
HARVESTING AND CRYOPRESERVATION OF HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS (hescs) OBJECTIVE: can be cryopreserved in a liquid nitrogen (LN 2 ) freezer for long-term storage. This Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
Follicle Dermal Papilla Cell
 Follicle Dermal Papilla Cell Instruction Manual Product Size Catalog Number Human Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells (HFDPC) 500,000 cryopreserved cells 500,000 proliferating cells C-12071 C-12072 Product Description
Follicle Dermal Papilla Cell Instruction Manual Product Size Catalog Number Human Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells (HFDPC) 500,000 cryopreserved cells 500,000 proliferating cells C-12071 C-12072 Product Description
Cellartis Protocol Culturing of hes Cells
 Cellartis Protocol Culturing of hes Cells This material was cultured and frozen using Cellartis protocols. WiCell recommends that stem cells should be thawed and established in the conditions in which
Cellartis Protocol Culturing of hes Cells This material was cultured and frozen using Cellartis protocols. WiCell recommends that stem cells should be thawed and established in the conditions in which
Optimized Protocol sirna Test Kit for Cell Lines and Adherent Primary Cells
 page 1 of 8 sirna Test Kit for Cell Lines and Adherent Primary Cells Kit principle Co-transfection of pmaxgfp, encoding the green fluorescent protein (GFP) from Pontellina p. with an sirna directed against
page 1 of 8 sirna Test Kit for Cell Lines and Adherent Primary Cells Kit principle Co-transfection of pmaxgfp, encoding the green fluorescent protein (GFP) from Pontellina p. with an sirna directed against
Role Of Mitochondria In Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Role Of Mitochondria In Mesenchymal Stem Cells Roman Eliseev, MD, PhD, Tamara Raymond, Regis O'Keefe, MD, PhD. University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, USA. Disclosures: R. Eliseev: None. T. Raymond: None.
Role Of Mitochondria In Mesenchymal Stem Cells Roman Eliseev, MD, PhD, Tamara Raymond, Regis O'Keefe, MD, PhD. University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, USA. Disclosures: R. Eliseev: None. T. Raymond: None.
CHARACTERISTIC FEATURES OF STEM CELLS. CLONING TECHNOLOGIES
 CHARACTERISTIC FEATURES OF STEM CELLS. CLONING TECHNOLOGIES 1 Science is discovering the unknown Stem cell field is still in its infancy Human embryonic stem cell research is a decade old, adult stem cell
CHARACTERISTIC FEATURES OF STEM CELLS. CLONING TECHNOLOGIES 1 Science is discovering the unknown Stem cell field is still in its infancy Human embryonic stem cell research is a decade old, adult stem cell
Ficoll-Paque PREMIUM Ficoll-Paque PREMIUM 1.084 Ficoll-Paque PREMIUM 1.073
 Instructions 28-4039-56 AE Cell Preparation Media Ficoll-Paque PREMIUM Ficoll-Paque PREMIUM 1.084 Ficoll-Paque PREMIUM 1.073 Intended use For in vitro isolation of mononuclear cells and/or granulocytes
Instructions 28-4039-56 AE Cell Preparation Media Ficoll-Paque PREMIUM Ficoll-Paque PREMIUM 1.084 Ficoll-Paque PREMIUM 1.073 Intended use For in vitro isolation of mononuclear cells and/or granulocytes
Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Manual
 Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0063.04 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human peripheral blood mononuclear
Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0063.04 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human peripheral blood mononuclear
Hoechst 33342 HSC Staining and Stem Cell Purification Protocol (see Goodell, M., et al. (1996) J Exp Med 183, 1797-806)
 Hoechst 33342 HSC Staining and Stem Cell Purification Protocol (see Goodell, M., et al. (1996) J Exp Med 183, 1797-86) The Hoechst purification was established for murine hematopoietic stem cells (HSC)
Hoechst 33342 HSC Staining and Stem Cell Purification Protocol (see Goodell, M., et al. (1996) J Exp Med 183, 1797-86) The Hoechst purification was established for murine hematopoietic stem cells (HSC)
Introduction to Flow Cytometry
 Introduction to Flow Cytometry presented by: Flow Cytometry y Core Facility Biomedical Instrumentation Center Uniformed Services University Topics Covered in this Lecture What is flow cytometry? Flow cytometer
Introduction to Flow Cytometry presented by: Flow Cytometry y Core Facility Biomedical Instrumentation Center Uniformed Services University Topics Covered in this Lecture What is flow cytometry? Flow cytometer
Islet Viability Assessment by Single Cell Flow Cytometry
 Islet Viability Assessment by Single Cell Flow Cytometry Page 1 of 8 Purpose: To comprehensively assess the viability of the islet cell preparation prior to transplantation. Tissue Samples: A sample containing
Islet Viability Assessment by Single Cell Flow Cytometry Page 1 of 8 Purpose: To comprehensively assess the viability of the islet cell preparation prior to transplantation. Tissue Samples: A sample containing
Fast, easy and effective transfection reagent for mammalian cells
 METAFECTENE EASY + Fast, easy and effective transfection reagent for mammalian cells For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
METAFECTENE EASY + Fast, easy and effective transfection reagent for mammalian cells For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
RPCI 004 v.002 Staining Procedure For all Directly Conjugated Reagents (Whole Blood Method)
 Immune Tolerance Network RPCI 004 v.002 Staining Procedure For all Directly Conjugated Reagents (Whole Blood Method) Author: Paul Wallace, Director, RPCI Laboratory of Flow Cytometry Approved by: Paul
Immune Tolerance Network RPCI 004 v.002 Staining Procedure For all Directly Conjugated Reagents (Whole Blood Method) Author: Paul Wallace, Director, RPCI Laboratory of Flow Cytometry Approved by: Paul
Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit
 Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit For T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice Evaluated for murine T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice This protocol is designed for murine lymphocytes or
Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit For T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice Evaluated for murine T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice This protocol is designed for murine lymphocytes or
Enumeration and Viability of Nucleated Cells from Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, and Mobilized Peripheral Blood
 Application Note Primary Cell Analysis Enumeration and Viability of Nucleated Cells from Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, and Mobilized Peripheral Blood Cell Viability Introduction: Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, Stem
Application Note Primary Cell Analysis Enumeration and Viability of Nucleated Cells from Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, and Mobilized Peripheral Blood Cell Viability Introduction: Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, Stem
The Prospect of Stem Cell Therapy in Multiple Sclerosis. Multiple sclerosis is a multifocal inflammatory disease of the central
 The Prospect of Stem Cell Therapy in Multiple Sclerosis Multiple sclerosis is a multifocal inflammatory disease of the central nervous system that generally affects young individuals, causing paralysis
The Prospect of Stem Cell Therapy in Multiple Sclerosis Multiple sclerosis is a multifocal inflammatory disease of the central nervous system that generally affects young individuals, causing paralysis
5 Frequently Asked Questions About Adult Stem Cell Research
 5 Frequently Asked Questions About Adult Stem Cell Research Stem cells are often referred to in the sociopolitical realm with some level of controversy and beyond that, some level of confusion. Many researchers
5 Frequently Asked Questions About Adult Stem Cell Research Stem cells are often referred to in the sociopolitical realm with some level of controversy and beyond that, some level of confusion. Many researchers
No-wash, no-lyse detection of leukocytes in human whole blood on the Attune NxT Flow Cytometer
 APPLICATION NOTE Attune NxT Flow Cytometer No-wash, no-lyse detection of leukocytes in human whole blood on the Attune NxT Flow Cytometer Introduction Standard methods for isolating and detecting leukocytes
APPLICATION NOTE Attune NxT Flow Cytometer No-wash, no-lyse detection of leukocytes in human whole blood on the Attune NxT Flow Cytometer Introduction Standard methods for isolating and detecting leukocytes
The Therapeutic Potential of Human Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation for Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury and Ischemic Stroke
 The Therapeutic Potential of Human Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation for Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury and Ischemic Stroke a,b* b,c a a b b b b a b a b c 430 Wang et al. Acta Med. Okayama Vol.
The Therapeutic Potential of Human Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation for Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury and Ischemic Stroke a,b* b,c a a b b b b a b a b c 430 Wang et al. Acta Med. Okayama Vol.
低 剂 量 辐 射 对 脐 血 T 淋 巴 细 胞 膜 分 子 表 达 的 影 响 EFFECT OF LOW DOSE IRRADIATION ON EXPRESSION OF MEMBRANE MOLECULES OF T LYMPHOCYTES IN CORD BLOOD
 CNIC-01513 PUTH-0001 低 剂 量 辐 射 对 脐 血 T 淋 巴 细 胞 膜 分 子 表 达 的 影 响 EFFECT OF LOW DOSE IRRADIATION ON EXPRESSION OF MEMBRANE MOLECULES OF T LYMPHOCYTES IN CORD BLOOD 中 国 核 情 报 中 心 China Nuclear Information
CNIC-01513 PUTH-0001 低 剂 量 辐 射 对 脐 血 T 淋 巴 细 胞 膜 分 子 表 达 的 影 响 EFFECT OF LOW DOSE IRRADIATION ON EXPRESSION OF MEMBRANE MOLECULES OF T LYMPHOCYTES IN CORD BLOOD 中 国 核 情 报 中 心 China Nuclear Information
Generation of EBV-immortalized B cell lines
 UCANU 0014 Version November 01, 2011 Page 1 van 6 Generation of EBVimmortalized B cell lines CMCI (Center for molecular and Cellular Intervention) University Medical Center Utrecht Written by Name Function
UCANU 0014 Version November 01, 2011 Page 1 van 6 Generation of EBVimmortalized B cell lines CMCI (Center for molecular and Cellular Intervention) University Medical Center Utrecht Written by Name Function
Amaxa 4D-Nucleofector Protocol for Mouse Embryonic Stem [ES] Cells For 4D-Nucleofector X Unit Transfection in suspension
![Amaxa 4D-Nucleofector Protocol for Mouse Embryonic Stem [ES] Cells For 4D-Nucleofector X Unit Transfection in suspension Amaxa 4D-Nucleofector Protocol for Mouse Embryonic Stem [ES] Cells For 4D-Nucleofector X Unit Transfection in suspension](/thumbs/30/14702458.jpg) For 4D-Nucleofector X Unit Transfection in suspension Cells derived from mouse blastocysts; round cells, growing in clumps s 1. This protocol is meant to provide an outline for the handling and the Nucleofection
For 4D-Nucleofector X Unit Transfection in suspension Cells derived from mouse blastocysts; round cells, growing in clumps s 1. This protocol is meant to provide an outline for the handling and the Nucleofection
Bio Deutschland CEO & CFO-Meeting 29. November 2012. Unternehmertum in den Life Sciences am Beispiel der Geschichte von Miltenyi Biotec
 Bio Deutschland CEO & CFO-Meeting 29. November 2012 Unternehmertum in den Life Sciences am Beispiel der Geschichte von Miltenyi Biotec Major locations Köln Our Passion SHARING OUR PASSION FOR CELLS We
Bio Deutschland CEO & CFO-Meeting 29. November 2012 Unternehmertum in den Life Sciences am Beispiel der Geschichte von Miltenyi Biotec Major locations Köln Our Passion SHARING OUR PASSION FOR CELLS We
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for the production and testing of embryonic stem cell lines in Taiwan Stem Cell Bank
 Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for the production and testing of embryonic stem cell lines in Taiwan Stem Cell Bank Bioresource Collection and Research Centre (BCRC) at Food Industry Research and
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for the production and testing of embryonic stem cell lines in Taiwan Stem Cell Bank Bioresource Collection and Research Centre (BCRC) at Food Industry Research and
STEM CELL FELLOWSHIP
 Module I: The Basic Principles of Stem Cells 1. Basics of Stem Cells a. Understanding the development of embryonic stem cells i. Embryonic stem cells ii. Embryonic germ cells iii. Differentiated stem cell
Module I: The Basic Principles of Stem Cells 1. Basics of Stem Cells a. Understanding the development of embryonic stem cells i. Embryonic stem cells ii. Embryonic germ cells iii. Differentiated stem cell
TERUMO Corporation Business Strategy Conference
 TERUMO Corporation Business Strategy Conference THERAPEUTIC SYSTEMS & CELL PROCESSING MARK FLOWER GLOBAL MARKETING December 5, 2011 Regenerative Medicine, Cell Therapy, & Cell Processing Regenerative Medicine
TERUMO Corporation Business Strategy Conference THERAPEUTIC SYSTEMS & CELL PROCESSING MARK FLOWER GLOBAL MARKETING December 5, 2011 Regenerative Medicine, Cell Therapy, & Cell Processing Regenerative Medicine
OriginalArticle. Critical Parameters for the Isolation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Umbilical Cord Blood
 OriginalArticle Critical Parameters for the Isolation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Umbilical Cord Blood KAREN BIEBACK, SUSANNE KERN, HARALD KLÜTER, HERMANN EICHLER Institute of Transfusion Medicine and
OriginalArticle Critical Parameters for the Isolation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Umbilical Cord Blood KAREN BIEBACK, SUSANNE KERN, HARALD KLÜTER, HERMANN EICHLER Institute of Transfusion Medicine and
protocol handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel
 handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel supporting real discovery handbook Index 01 Cell encapsulation in hydrogels 02 Cell viability by MTS assay 03 Live/Dead assay to assess cell viability 04 Fluorescent
handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel supporting real discovery handbook Index 01 Cell encapsulation in hydrogels 02 Cell viability by MTS assay 03 Live/Dead assay to assess cell viability 04 Fluorescent
EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS
 EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS FINAL REPORT OF THE STUDY GT050923 Study promoter: LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS ZA Les
EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS FINAL REPORT OF THE STUDY GT050923 Study promoter: LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS ZA Les
Stem Cell Research: Adult or Somatic Stem Cells
 Chiang 1 Stem Cell Research: Adult or Somatic Stem Cells Abstract Kelly Chiang Cluster 7 Dr. LeFebvre 07/26/10 Over the past few decades, stem cells have been a controversial topic in the scientific field.
Chiang 1 Stem Cell Research: Adult or Somatic Stem Cells Abstract Kelly Chiang Cluster 7 Dr. LeFebvre 07/26/10 Over the past few decades, stem cells have been a controversial topic in the scientific field.
STEM CELL FACTS. The ISSCR is an independent, nonproft organization providing a global forum for stem cell research and regenerative medicine.
 STEM CELL FACTS The ISSCR is an independent, nonproft organization providing a global forum for stem cell research and regenerative medicine. WHAT ARE STEM CELLS? Stem cells are the foundation cells for
STEM CELL FACTS The ISSCR is an independent, nonproft organization providing a global forum for stem cell research and regenerative medicine. WHAT ARE STEM CELLS? Stem cells are the foundation cells for
HyStem. Hydrogels CELLULAR MATRICES FOR TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH. esibio.com
 HyStem Hydrogels CELLULAR MATRICES FOR TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH HyStem Hydrogel Extracellular Matrices Chemically-defined For use in 2D and 3D formats in vitro and in vivo applications Customizable for many
HyStem Hydrogels CELLULAR MATRICES FOR TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH HyStem Hydrogel Extracellular Matrices Chemically-defined For use in 2D and 3D formats in vitro and in vivo applications Customizable for many
Human Hepatic Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell Manual
 Human Hepatic Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL SHIPPING CONDITIONS ZBM0093.00 Human Hepatic Sinusoidal Cells. Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier. All US and Canada orders
Human Hepatic Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL SHIPPING CONDITIONS ZBM0093.00 Human Hepatic Sinusoidal Cells. Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier. All US and Canada orders
Lab 2. Isolation of mononuclear cells from peripheral blood and separation into subpopulations
 Lab 2 Isolation of mononuclear cells from peripheral blood and separation into subpopulations Supervisors: Sissela Broos [email protected] tel: 222 96 78 Niclas Olsson [email protected]
Lab 2 Isolation of mononuclear cells from peripheral blood and separation into subpopulations Supervisors: Sissela Broos [email protected] tel: 222 96 78 Niclas Olsson [email protected]
Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics
 Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells are the starting point from which the rest of the body grows. The adult human body is made up of hundreds of millions of different
Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells are the starting point from which the rest of the body grows. The adult human body is made up of hundreds of millions of different
RITMIR024 - STEM CELL RESEARCH IN CARDIOLOGY
 1. SCOPE AND METHODOLOGY 2. REPORT SYNOPSIS 2.1 General Definitions Myoblasts Pluripotent Cells Multipotent Cells Progenitor Cells Role of Stem Cells in Repairing the Heart Stem Cell Therapy Stem Cells
1. SCOPE AND METHODOLOGY 2. REPORT SYNOPSIS 2.1 General Definitions Myoblasts Pluripotent Cells Multipotent Cells Progenitor Cells Role of Stem Cells in Repairing the Heart Stem Cell Therapy Stem Cells
WHOLE BLOOD LYSING SOLUTION FOR FLOW CYTOMETRIC APPLICATIONS
 FOR IN-VITRO DIAGNOSTIC USE INVITROGEN CAL-LYSE TM Lysing Solution WHOLE BLOOD LYSING SOLUTION FOR FLOW CYTOMETRIC APPLICATIONS CAL-LYSE TM CATALOG No. GAS-010 250 tests 25 ml CATALOG No. GAS-010S-100
FOR IN-VITRO DIAGNOSTIC USE INVITROGEN CAL-LYSE TM Lysing Solution WHOLE BLOOD LYSING SOLUTION FOR FLOW CYTOMETRIC APPLICATIONS CAL-LYSE TM CATALOG No. GAS-010 250 tests 25 ml CATALOG No. GAS-010S-100
S YN T H E T I C C A N C E L LO U S B O N E
 S YN T H E T I C C A N C E L LO U S B O N E CELLPLEX TCP Graft is a synthetic cancellous scaffold that provides an optimum environment for cellular infiltration. Composed of tricalcium phosphate, the scaffold
S YN T H E T I C C A N C E L LO U S B O N E CELLPLEX TCP Graft is a synthetic cancellous scaffold that provides an optimum environment for cellular infiltration. Composed of tricalcium phosphate, the scaffold
Biotechnology. Srivatsan Kidambi, Ph.D.
 Stem Stem Cell Cell Engineering-What, Biology and it Application Why, How?? to Biotechnology Srivatsan Kidambi, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering University of
Stem Stem Cell Cell Engineering-What, Biology and it Application Why, How?? to Biotechnology Srivatsan Kidambi, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering University of
Especially developed for the transfection of mammalian cells with sirna or mirna
 METAFECTENE SI Especially developed for the transfection of mammalian cells with sirna or mirna For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No.
METAFECTENE SI Especially developed for the transfection of mammalian cells with sirna or mirna For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No.
Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay (Laminin Coated)
 Product Manual Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay (Laminin Coated) Catalog Number CBA-125-LN 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cell migration is a highly
Product Manual Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay (Laminin Coated) Catalog Number CBA-125-LN 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cell migration is a highly
CytoSelect 48-Well Cell Adhesion Assay (ECM Array, Fluorometric Format)
 Product Manual CytoSelect 48-Well Cell Adhesion Assay (ECM Array, Fluorometric Format) Catalog Number CBA-071 CBA-071-5 48 assays 5 x 48 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Product Manual CytoSelect 48-Well Cell Adhesion Assay (ECM Array, Fluorometric Format) Catalog Number CBA-071 CBA-071-5 48 assays 5 x 48 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures
San Diego Stem Cell Treatment Center Frequently Asked Questions
 San Diego Stem Cell Treatment Center Frequently Asked Questions What is a Stem Cell? A stem cell is basically any cell that can replicate and differentiate. This means the cell can not only multiply, but
San Diego Stem Cell Treatment Center Frequently Asked Questions What is a Stem Cell? A stem cell is basically any cell that can replicate and differentiate. This means the cell can not only multiply, but
EdU Flow Cytometry Kit. User Manual
 User Manual Ordering information: (for detailed kit content see Table 2) EdU Flow Cytometry Kits for 50 assays: Product number EdU Used fluorescent dye BCK-FC488-50 10 mg 6-FAM Azide BCK-FC555-50 10 mg
User Manual Ordering information: (for detailed kit content see Table 2) EdU Flow Cytometry Kits for 50 assays: Product number EdU Used fluorescent dye BCK-FC488-50 10 mg 6-FAM Azide BCK-FC555-50 10 mg
Cultivation and Cryopreservation of Cord Tissue MSCs with Cord Blood AB Plasma
 Cultivation and Cryopreservation of Cord Tissue MSCs with Cord Blood AB Plasma Manasi Talwadekar, Darshana Kadekar, Sonal Rangole, Nikhat Firdaus Khan, Vaijayanti Kale and Lalita Limaye* Stem Cell Laboratory,
Cultivation and Cryopreservation of Cord Tissue MSCs with Cord Blood AB Plasma Manasi Talwadekar, Darshana Kadekar, Sonal Rangole, Nikhat Firdaus Khan, Vaijayanti Kale and Lalita Limaye* Stem Cell Laboratory,
CD34+ CD45- Cells Isolated from Human Blood Have Molecular and Functional Characteristics of Vascular Endothelial Progenitors
 CD34+ CD45- Cells Isolated from Human Blood Have Molecular and Functional Characteristics of Vascular Endothelial Progenitors Yajuan Jiang 1, Alexander M. Tsankov 2, Alexander Meissner 2 and David W. O
CD34+ CD45- Cells Isolated from Human Blood Have Molecular and Functional Characteristics of Vascular Endothelial Progenitors Yajuan Jiang 1, Alexander M. Tsankov 2, Alexander Meissner 2 and David W. O
guides BIOLOGY OF AGING STEM CELLS An introduction to aging science brought to you by the American Federation for Aging Research
 infoaging guides BIOLOGY OF AGING STEM CELLS An introduction to aging science brought to you by the American Federation for Aging Research WHAT ARE STEM CELLS? Stem cells are cells that, in cell cultures
infoaging guides BIOLOGY OF AGING STEM CELLS An introduction to aging science brought to you by the American Federation for Aging Research WHAT ARE STEM CELLS? Stem cells are cells that, in cell cultures
STEM CELLS FROM THE UMBLICAL CORD BLOOD AND UMBLICAL CORD TISSUE
 STEM CELLS FROM THE UMBLICAL CORD BLOOD AND UMBLICAL CORD TISSUE What are Stem Cells? Stem cells are the basic building blocks of all the cells, tissues and organs in the human body. The role of the stem
STEM CELLS FROM THE UMBLICAL CORD BLOOD AND UMBLICAL CORD TISSUE What are Stem Cells? Stem cells are the basic building blocks of all the cells, tissues and organs in the human body. The role of the stem
Chapter 16 Reproductive Technology, Gene Therapy, and Stem Cells (modified)
 Chapter 16 Reproductive Technology, Gene Therapy, and Stem Cells (modified) Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) Artificial insemination (AI) In vitro fertilization (IVF) Gamete intrafallopian transfer
Chapter 16 Reproductive Technology, Gene Therapy, and Stem Cells (modified) Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) Artificial insemination (AI) In vitro fertilization (IVF) Gamete intrafallopian transfer
Stem Cells. Part 1: What is a Stem Cell?
 Stem Cells Part 1: What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells differ from other kinds of cells in the body. When a stem cell divides by mitosis, each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell or become
Stem Cells Part 1: What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells differ from other kinds of cells in the body. When a stem cell divides by mitosis, each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell or become
Animal Cell Culture. Third Edition. A Practical Approach OXJORD VNIVVRSITY 1'RVSS
 Animal Cell Culture Third Edition A Practical Approach Edited by John R. W. Masters 3rd Floor Research Laboratories, University College London OXJORD VNIVVRSITY 1'RVSS Contents List of protocols page xiii
Animal Cell Culture Third Edition A Practical Approach Edited by John R. W. Masters 3rd Floor Research Laboratories, University College London OXJORD VNIVVRSITY 1'RVSS Contents List of protocols page xiii
Below is a list of things you should be aware of before you schedule your sort.
 Sorting at the Flow Cytometry Facility At the present time, the assistance of a trained cell sorter operator is needed for all sorting applications. As such, if you are planning a first time sort you will
Sorting at the Flow Cytometry Facility At the present time, the assistance of a trained cell sorter operator is needed for all sorting applications. As such, if you are planning a first time sort you will
Expression of CD163 on Bovine Alveolar Macrophages and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
 Expression of CD163 on Bovine Alveolar Macrophages and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Mary E. Kopechek Honor s Research Thesis May 17, 2007 Research Advisor: Dr. Jeff Lakritz, DVM, PhD The Ohio State
Expression of CD163 on Bovine Alveolar Macrophages and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Mary E. Kopechek Honor s Research Thesis May 17, 2007 Research Advisor: Dr. Jeff Lakritz, DVM, PhD The Ohio State
Measuring Cell Viability/Cytotoxicity: Cell Counting Kit-F
 Introduction The Cell Counting Kit-F is a fluorometic assay for the determination of viable cell numbers. Calcein-AM in this kit passes through the cell membrane and is hydrolized by the esterase in the
Introduction The Cell Counting Kit-F is a fluorometic assay for the determination of viable cell numbers. Calcein-AM in this kit passes through the cell membrane and is hydrolized by the esterase in the
14.0 Stem Cell Laboratory Services
 Laboratory Services Contact Information: To inquire about assisting with surgical harvesting of bone marrow, cellular therapy (CT) product processing, cryopreservation, storage, or any other lab services,
Laboratory Services Contact Information: To inquire about assisting with surgical harvesting of bone marrow, cellular therapy (CT) product processing, cryopreservation, storage, or any other lab services,
APPLICATION INFORMATION
 DRAFT: Rev. D A-2045A APPLICATION INFORMATION Flow Cytometry 3-COLOR COMPENSATION Raquel Cabana,* Mark Cheetham, Jay Enten, Yong Song, Michael Thomas,* and Brendan S. Yee Beckman Coulter, Inc., Miami FL
DRAFT: Rev. D A-2045A APPLICATION INFORMATION Flow Cytometry 3-COLOR COMPENSATION Raquel Cabana,* Mark Cheetham, Jay Enten, Yong Song, Michael Thomas,* and Brendan S. Yee Beckman Coulter, Inc., Miami FL
Analyzing Samples for CD34 Enumeration Using the BD Stem Cell Enumeration Kit
 2 Analyzing Samples for CD34 Enumeration Using the BD Stem Cell Enumeration Kit Presented by Ellen Meinelt, MS MLS(ASCP) CM, Technical Applications Specialist and Calin Yuan, Product Course Developer,
2 Analyzing Samples for CD34 Enumeration Using the BD Stem Cell Enumeration Kit Presented by Ellen Meinelt, MS MLS(ASCP) CM, Technical Applications Specialist and Calin Yuan, Product Course Developer,
The Types of stem cells: Totipotent Pluripotent Multipotent
 Stem Cells is the main material for building and regeneration of the body Stem cells are not differentiated and can transform to any cell of organism Stem cells are capable of indefinite renewal through
Stem Cells is the main material for building and regeneration of the body Stem cells are not differentiated and can transform to any cell of organism Stem cells are capable of indefinite renewal through
Utility of flow cytometric κ and λ light chain analysis of peripheral blood
 JBUON 2015; 20(5): 1322-1326 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: [email protected] ORIGINAL ARTICLE Utility of flow cytometric κ and λ light chain analysis of peripheral
JBUON 2015; 20(5): 1322-1326 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: [email protected] ORIGINAL ARTICLE Utility of flow cytometric κ and λ light chain analysis of peripheral
Enhance Sensitivity of FISH Analysis with Highly Purified Multiple Myeloma Cells Using RoboSep, the Fully Automated Cell Separator
 Enhance Sensitivity of FISH Analysis with Highly Purified Multiple Myeloma Cells Using RoboSep, the Fully Automated Cell Separator Benoit Guilbault, PhD Field Applications Scientist t STEMCELL Technologies,
Enhance Sensitivity of FISH Analysis with Highly Purified Multiple Myeloma Cells Using RoboSep, the Fully Automated Cell Separator Benoit Guilbault, PhD Field Applications Scientist t STEMCELL Technologies,
