Patient Care Radiology
|
|
|
- Moses Norman
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Patient Care Radiology Cardiac Imaging Modalities Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Donna Lesniak, RN, CCRC Cardiovascular Imaging Laboratory Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) Stress Echocardiography Nurse/Coordinator Responsibilities TEAMWORK-TEAMWORK-TEAMWORK Patient care Safety issues Licensed BLS and ACLS Regulations for Research Good Clinical Practices (GCP) Budget IND applications IRB knowledge, writing consent forms, conducting annual reviews. Organizations (ACRP and SOCRA)-examination available after 2 years experience Nurse/Coordinator Responsibilities Technical Computer skills-microsoft word, Power Point and Excel Database development and maintenance Purchasing and maintaining supplies for the lab Protocol review and writing protocol worksheets Calibrating devices, stocking crash cart and synchronizing all clocks(scanner, monitoring device, EKG) Billing codes Screening Chart review Contraindications for imaging and/or drugs Inclusion/Exclusion Phone interview Consent process Imaging safety checklist Medical history Scheduling Nurses/Coordinators Good communication with scheduling center Know correct billing codes for scan Balance time slots between physicians Cancel time slot if not needed Keep an organized calendar for different cases Call patient the day prior to confirm appointment Patients/Participants Detailed instructions on preparation of the imaging being scheduled Directions to Imaging Center Contact information if the patient has any questions
2 CTA Research Experience Total: 255 (64 slice) participants enrolled in a PI initiated CTA pilot 26 participants enrolled in a phase II sponsored CTA 46 participants enrolled in a PI initiated CTA and PET 56 participants enrolled in a PI initiated CTA vs. Echo (dual source) participants enrolled in a PI initiated CTA and heart failure CTA Safety Radiation exposure Administration of (IV) contrast media Administration of ß-blocker and nitroglycerine CT Safety-Radiation Exposure ALARA Physician familiar with various technical parameters of the exam that affect radiation dosage milliampere-seconds (mas) peak voltage settings (kvp) scan pitch Automated x-ray dose shaping algorithms and x-ray tube pulsing applied to minimize exposure (while allowing diagnostic image quality) CT Safety-Contrast media Contrast reactions occurring in approximately 2% of patients are considered mild reactions skin hives/rash minimal throat tightening Prior contrast reactions-oral steroids given beforehand (some institutions give steroids and benadryl) Contrast reaction treatment-observe for a period of time (approx. 30 min.) If no improvement or severe Admin. Benadryl 50mg. CT Safety-Contrast media Contrast induced bronchospasm Mild: Treatment includes oxygen 10-12L by face mask, close observation, and/or 2 puffs of an albuterol or metaproterenol inhaler. Moderate: without hypotension: Treatment is as above, with 1:1000, ml given subcutaneously, repeated every min. as needed until 1 ml is administered. Severe: Administer epinephrine 1:10,000 1 ml slow IV injection over approximately 5 min., repeated every 5-10 min. as needed. Contrast induced bronchospasm Mild to moderate: Treatment includes oxygen L by face mask and epinephrine 1: ml given subcutaneously, repeated every minutes as needed until 1 ml is administered. CT Safety-Contrast media Contrast induced nephropathy Creatinine 1.5mg/dL usually excluded Encourage hydration Diabetics-Patients taking Glucophage, Glucovance or metformin should hold the medication the day of imaging and for 48hrs. following the procedure. Contrast Extravasation A physician should evaluate all extravasations Observe in radiology dept. for 2-4 hrs. Elevate affected arm above the heart Cool dry packs applied to the site
3 CT Safety- ß-blocker and nitrate administration Administration Physician or nurse trained in administration of cardiac medications Side effects Hypotension, dizziness, lightheaded, nausea and/or headache Contraindications History of Asthma or COPD (ß-blocker) Current use of Viagra, Cialis or Levitra patient needs to hold these medications, 24-72hrs. (Nitrate) SBP is <100mmHg (both) CTA Contraindications (64 slice) Potential artifacts Elevated calcium score Irregular heart rate Tachycardia Poor IV access BMI >35 Patient safety contraindications Elevated creatinine ( 1.5mg/dL) IV contrast allergy Iodine/shellfish allergies Pregnancy or breast feeding CTA Patient Preparation Consent process and safety checklist Check creatinine Check HR and BP and monitor during scan Start gauge IV in the right antecubital vein Administer ß-blocker for HR >62 bpm Prep skin and attach leads for CTA below clavicle with the arms in the up position Remind patient that they will be getting Nitroglycerine during their CTA and the feeling they may experience during the contrast injection CTA Patient Monitoring Several monitoring devices are available for CTA monitoring. NIBP O 2 saturation EKG HR Temperature Clock CTA (64 slice) Lopressor Protocol HR >62bpm and SBP >100mmHg Lopressor 5mg. slow IV push every 5 min. until target HR met Max dose 35mg. Practice breathholds HR may drop during breathholds, but may increase upon the administration of IV contrast ß-blockers do not have same effect on diabetics CTA-Nitroglycerine Protocol Immediately prior to performing CTA, sublingual nitroglycerine 0.4mg. is given to enhance visualization of coronary arteries HR and BP will be continuously measured prior to and throughout the scan.
4 MRI Research Experience Total = 454 ( ) 166 Stress MRI s 239 Participants enrolled in various research MRI s as part of an MRI course (121 no contrast, 74 contrast and 44 contrast and Adenosine) 55 Participants enrolled in a Phase II sponsored MRI 17 Participants enrolled in a PI initiated MRI perfusion with Adenosine 24 Participants enrolled in a MRI and attenuation 14 Participants enrolled in a PI initiated MRI and LAAT 89 Participants enrolled in 3 PI initiated rest and stress with Dobutamine MRI and PET studies 5 Participants enrolled in an ongoing PI initiated MRI vs. SPECT using regadenoson 11 Participants received a perfusion MRI with adenosine in a clinical setting MRI Safety Magnetic memory of credit cards and badges, as well as magnetic devices such as watches, phones, beepers and tapes can be damaged by MRI magnets. Patients and non MRI personnel need to be informed each and every time to leave them outside the magnet room. MRI Scanner Safety This incident happened at our facility when a janitorial worker thought the magnet was off since the lights were out for the evening. THE MAGNET IS NEVER OFF The magnet had to be shut down for the removal of the waxer. MRI Patient and Scanner Safety Unfortunately, the IV pole in the middle was my mistake. Even after years of experience around the magnet. I walked a patient into the magnet with an IV pole. Currently we have added to our equipment an MRI compatible IV pole and pump by Medrad. MRI Safety with Contrast NSF/NFD what is it? NSF- Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis NFD- Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy Systemic disorder - most prominent and visible effects in the skin Occurs only in patients with kidney disease No cases identified prior to 1997 No convincing evidence that NSF is caused by Medication Microorganism Dialysis MRI - FDA Report on GBCA FDA ALERT [6/2006, updated 12/2006 and 5/23/2007]: This updated Alert highlights FDA s request for addition of a boxed warning and new warnings about risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) to the full prescribing information for all gadoliniumbased contrast agents (GBCAs) (Magnevist, MultiHance, Omniscan, OptiMARK, ProHance). This new labeling highlights and describes the risk for NSF following exposure to a GBCA in patients with acute or chronic severe renal insufficiency (a glomerular filtration rate <30 ml/min/1.73m 2 ) and patients with acute renal insufficiency of any severity due to the hepato-renal syndrome or in the peri-operative liver transplantation period. In these patients, avoid the use of a GBCA unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating systemic fibrosis. A GFR calculator can be found on the National Kidney Foundation website. Current updates can be found on the ISMRM website.
5 MRI Contraindications Pacemakers, shrapnel, brain aneurysm clips or other implanted devices Claustophobia Excessive abdominal girth Pregnancy (1 st trimester) Hemodynamic instability or critical illness MRI Contraindications with Contrast History of contrast allergy History of renal insufficiency (GFR <30 ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) Pregnancy/Breastfeeding Current updates can be found on the MRI safety website. MRI Patient Preparation Consent process and safety checklist Patient removes jewelry and changes into a gown/scrubs Check creatinine (unless pt. had it checked within 30 days) Check HR and BP Start 18-20ga. IV in an antecubital vein (for perfusion studies start a second IV) Have patient use the restroom prior to going into the scanner Prep skin and attach leads to patient (Currently, we re using fiberoptics and wireless for gating, depending on the scanner.) MRI Monitoring Several monitoring devices are available for MRI monitoring. NIBP O 2 saturation EKG HR Temperature Clock MRI compatibility is most important MRI: Pharmacological Stress Testing The stress chemical agents usually used in the cardiac MRI setting are dobutamine, adenosine and regadenoson. Adenosine and regadenoson are vasodilators that are extremely short acting and easier to use. Dobutamine is an inotropic vasopressor that requires incremental increases in doses, therefore taking a longer time to stress the heart. Cardiac MR perfusion exams as of Jan have their own CPT code which is reimbursed by CMS for appropriate indications. Adenosine/Regadenoson Hemodynamics They produce negative chronotropic, dromotropic and inotropic (rate, velocity, force) effect on the cardiac muscle fibers and nerves. Net effect is a mild to moderate decrease in systolic, diastolic and mean arterial blood pressure associated with a reflex increase in heart rate. Rarely significant hypotension or tachycardia have been observed. Adenosine Phamacokinetics Rapidly cleared from the circulation by cellular uptake. It is degraded by the cell. Half life of <10sec. makes this a great drug in the clinical setting. Requires no hepatic or renal function for activation. Renal or hepatic failure does not alter its effectiveness or tolerability.
6 Perfusion Stress Indications Alternative to exercise stress testing for: Patients with Angina Pectoris Risk stratification Surgical clearance Post MI and coronary revascularization procedures Patients with risk factors for CAD or atypical chest pain When exercise stress is not possible or desirable: Patients unable to perform treadmill exercise Patients with LBBB Paced rhythm Concomitant treatment with meds that blunt the heart rate response (beta blockers and calcium channel blockers) Perfusion Stress Contraindications Second or third degree atrial ventricular node block Sinus node disease, such as sick sinus syndrome or symptomatic bradycardia Known or suspected bronchoconstrictive or bronchospastic lung disease (COPD per se is not a contraindication) Known sensitivity to adenosine Systolic BP<90mm Hg. Severe sinus bradycardia (<40/min) is a relative contraindication Adenosine Adverse Reactions >1% Flushing 44% Chest discomfort 40% Dyspnea or urge to breath deeply 28% Headache 18% Throat, neck or jaw discomfort 15% Gastrointestinal discomfort 13% Lightheadedness Adenosine Adverse Reactions <1% Back discomfort, lower extremity discomfort, weakness, drowsiness, emotional instability, tremors Non-fatal MI, life threatening ventricular arrhythmias, third degree AV block bradycardia, palpitations, sinus exit block, sinus pause, T-wave changes, hypertension (systolic BP >200) Genital urinary urgency Cough, blurred vision, dry mouth, ear discomfort, metallic taste, nasal congestion, tongue discomfort, scotomas Adenosine Dosage and Administration Adenosine should be administered through a peripheral vein by continuous infusion over 4 minutes in a separate line from the contrast. The dose for adults is 140ug/kg/min. Infusion rate = 0.140(mg/kg/min) x body wt.(kg) (ml/min) Adenosine concentration (3mg/ml) Adenoscan* available in 20 or 30ml vials, 3mg/ml Lexiscan (regadenoson) is given as a single bolus dose of 0.4mg/5mL Stress Perfusion Patient Preparation 1 Restriction of Xanthine containing products hours before test. (Tea, coffee, Uniphyl, Theo-Dur, Slo-Bid, Theophylline etc.) Theophylline is the antidote for Adenosine. Nothing to eat or drink at least 6, however best if 8 hrs. before test No caffeine or chocolate at least 6, however best if 24 hrs. before test. No smoking, use of pipe or snuff for 4 hrs. before test Any prior studies with results should be available and reviewed by clinician. Cardiac enzymes (CK, CKmb, Troponin) reviewed only in case of angina symptoms. Prior 12 lead EKG available and reviewed. Order checked
7 Adenosine Stress Patient Preparation 2 Test should be explained and informed consent given by patient. Chest preparation, EKG electrode placement IV access should be obtained with a large bore catheter no small than a #18gauge. Adenosine Infusion Monitoring Patient is remotely monitored for NIBP, O 2 saturation, HR, EKG and adverse reactions. Stop infusion if wheezing starts to develop. Half-life of adenosine is <10 seconds. Baseline EKG, BP, HR and pulse oximetry IV sedation prn. (Versed 1mg. IVP) With IV sedation -O 2 via nasal cannula at 2L/min. Most episodes of AV block are asymptomatic, transient, and do not require intervention; less than 7% require termination of adenosine infusion, which is done if the patient becomes symptomatic from AV block. Adenosine Infusion EKG Changes Tachycardia/bradycardia ST depression. Stop infusion if severe chest pain is associated with 2mm ST depression. ST depression alone does not require stopping infusion. Heart block-1, 2, 3 Stop infusion of adenosine, if patient develops symptomatic persistent second degree or complete heart block. If asymptomatic, infusion can continue. PVC s T wave inversion Sinus pause (rare) Methods for Administration of Adenosine and Dobutamine in the MRI Suite Historically, the patient would either be removed from the medication, remain connected to a non-mr compatible infusion pump outside the scanner room with up to 30 feet of tubing, or be disqualified from MR imaging altogether. The newer systems help to enable scanning of patients who could most benefit from MR imaging regardless of their need for infusion therapy. MRI compatible infusion pumps: Continuum MR Compatible Infusion System by Medrad, Inc. MRidium(TM) MRI Infusion Pump by Iradimed, Inc. marketed by Covidien What is Dobutamine? Dobutamine is a synthetic chemical with primarily beta 1 adrenergic activity (rocket fuel for the heart). Here it is used as an agent to increase heart rate. Dobutamine is supplied as Dobutamine HCl a synthetic inotropic agent related structurally to dopamine. It occurs as white, to off-white, crystalline powder with a pka of 9.4. Dobutamine is sparingly soluble in water and alcohol Dobutamine Pharmacology It is an inotropic vasopressor. It increases myocardial contractility, blood pressure, cardiac index and output, blood flow, oxygen delivery and oxygen consumption. It is metabolized in the liver to an inactive compound. The onset of action is 1-2 minutes after IV administration with the peak effect occuring in 10 minutes. The half-life of its drug effect is two minutes.
8 Dobutamine Hemodynamics Blood pressure and cardiac rate generally are unaltered or slightly increased because of increased cardiac output. Increased myocardial contractility may increase myocardial oxygen demand and coronary blood flow. Dobutamine Indications Alternative to exercise stress testing for: Patients with asthma Patients with angina pectoris Risk stratification Surgical clearance Post MI and coronary revascularization procedures Patients with risk factors for CAD and atypical chest pain When exercise stress not possible or desirable: Patients unable to perform treadmill exercise Patients with LBBB Dobutamine Contraindications Known hypersensitivity to the drug Patients with a history of ventricular ectopy, and poor LV function should be considered for a adenosine Patients with atrial fibrillation or other dysrhythmia should have a well controlled ventricular rate CV medications, especially beta blockers should be restricted if possible Unstable angina Uncontrolled hypertension ( 200/115mmHg) Valvular heart disease (critical aortic stenosis, IHSS, MR) are absolute Hemodynamically significant LV outflow tract obstruction Dobutamine Dosage and Administration Dobutamine should be administered through a peripheral vein by continuous infusion. Start infusing at a rate of 10ug/kg/min, increasing the dose by 10ug/kg increments every 3min. until 40ug/kg/min or 85% of AAMHR is achieved. Close monitoring of patient is critical since Dobutamine will produce myocardial ischemia at higher doses. Cine imaging will be acquired at the end of each 3 min. interval. After stress, measure BP and monitor EKG until HR and BP are within normal limits. Dobutamine Stress End Points Secondary end points include severe angina, prolonged run of non sustained VT, VF, SVT with rapid ventricular rate, severe side effects leading to patient refusal to continue. Usually side effects resolve with discontinuation of infusion, however, if they don t a bolus of a short acting beta blocker(metoprolol from 1-5mg) may be administered. Dobutamine Stress Patient Preparation Beta blocker should be held for 24hrs before the test. Preparation is very similar to adenosine stress except that patients may have xanthine (caffeine).
9 Dobutamine Adverse Reactions Severe ventricular arrhythmias Minor side effects include: Flushing Facial tingling Dyspnea Headache Chest pain Arrhythmias occur 15% of the time and generally resolve spontaneously. Dobutamine Infusion Monitoring Patient is remotely monitored for NIBP, O 2 saturation, HR, EKG and adverse reactions. Management of most minor side effects includes discontinuation of infusion. Severe ischemia can be managed with NTG and beta blockers. Dobutamine Treatment for Signs and Symptoms Often stopping the dobutamine infusion is all that is necessary. Severe side effects may require IV administration of a short acting betablocker. IV metoprolol, 1-5mg used to reverse the effects of dobutamine if these did not revert quickly. Donna Lesniak, RN, CCRC Cardiovascular Imaging Laboratory [email protected]
Pharmacologic Stress Agents
 Pharmacologic Stress Agents Donna Lesniak, RN, CCRC Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine Saint Louis, Missouri Disclosure Neither I nor my immediate family members
Pharmacologic Stress Agents Donna Lesniak, RN, CCRC Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine Saint Louis, Missouri Disclosure Neither I nor my immediate family members
Pharmacologic Stress Agents: Protocol and Safety
 Pharmacologic Stress Agents: Protocol and Safety Donna Lesniak, RN, CCRC Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine Saint Louis, Missouri Disclosure Neither I nor my immediate
Pharmacologic Stress Agents: Protocol and Safety Donna Lesniak, RN, CCRC Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine Saint Louis, Missouri Disclosure Neither I nor my immediate
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY. Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol
 ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines
 ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
Crash Cart Drugs Drugs used in CPR. Dr. Layla Borham Professor of Clinical Pharmacology Umm Al Qura University
 Crash Cart Drugs Drugs used in CPR Dr. Layla Borham Professor of Clinical Pharmacology Umm Al Qura University Introduction A list of the drugs kept in the crash carts. This list has been approved by the
Crash Cart Drugs Drugs used in CPR Dr. Layla Borham Professor of Clinical Pharmacology Umm Al Qura University Introduction A list of the drugs kept in the crash carts. This list has been approved by the
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI)
 Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
ACLS PRE-TEST ANNOTATED ANSWER KEY
 ACLS PRE-TEST ANNOTATED ANSWER KEY June, 2011 Question 1: Question 2: There is no pulse with this rhythm. Question 3: Question 4: Question 5: Question 6: Question 7: Question 8: Question 9: Question 10:
ACLS PRE-TEST ANNOTATED ANSWER KEY June, 2011 Question 1: Question 2: There is no pulse with this rhythm. Question 3: Question 4: Question 5: Question 6: Question 7: Question 8: Question 9: Question 10:
Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain
 Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain Vikranth Gongidi, DO FACC FACOI Indian River Medical Center Vero Beach, FL No Disclosures Outline Background Chest pain pathway Indications for stress test Stress test
Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain Vikranth Gongidi, DO FACC FACOI Indian River Medical Center Vero Beach, FL No Disclosures Outline Background Chest pain pathway Indications for stress test Stress test
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients
 Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication. Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South
 Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
123 Main St NY, New York 12345 ph: (202) 555 5555 fax: (202) 555 5555
 Patient Name: DOE, JOHN D. Gender: M Date of Study: 4/2/2013 Date of birth: 6/28/1962 Age: 50 Medical Record #: 45869725 Ordering Physician: JANE INTERNIST, MD History: Atypical Angina, Abn ECG, High Cholesterol,
Patient Name: DOE, JOHN D. Gender: M Date of Study: 4/2/2013 Date of birth: 6/28/1962 Age: 50 Medical Record #: 45869725 Ordering Physician: JANE INTERNIST, MD History: Atypical Angina, Abn ECG, High Cholesterol,
Section 8: Clinical Exercise Testing. a maximal GXT?
 Section 8: Clinical Exercise Testing Maximal GXT ACSM Guidelines: Chapter 5 ACSM Manual: Chapter 8 HPHE 4450 Dr. Cheatham Outline What is the purpose of a maximal GXT? Who should have a maximal GXT (and
Section 8: Clinical Exercise Testing Maximal GXT ACSM Guidelines: Chapter 5 ACSM Manual: Chapter 8 HPHE 4450 Dr. Cheatham Outline What is the purpose of a maximal GXT? Who should have a maximal GXT (and
NAME OF THE HOSPITAL: 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3
 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation
 Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation Caroline McKillop Advisor: Dr. Tam Psenka 10-3-2007 Importance of Cardiac Guidelines -Used multiple times every day -Patient Safety -Part of Surgical Care Improvement Project
Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation Caroline McKillop Advisor: Dr. Tam Psenka 10-3-2007 Importance of Cardiac Guidelines -Used multiple times every day -Patient Safety -Part of Surgical Care Improvement Project
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL
 Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness
 Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
Procedure for Inotrope Administration in the home
 Procedure for Inotrope Administration in the home Purpose This purpose of this procedure is to define the care used when administering inotropic agents intravenously in the home This includes: A. Practice
Procedure for Inotrope Administration in the home Purpose This purpose of this procedure is to define the care used when administering inotropic agents intravenously in the home This includes: A. Practice
If you do not wish to print the entire pre-test you may print Page 2 only to write your answers, score your test, and turn in to your instructor.
 This is a SAMPLE of the pretest you can access with your AHA PALS Course Manual at Heart.org/Eccstudent using your personal code that comes with your PALS Course Manual The American Heart Association strongly
This is a SAMPLE of the pretest you can access with your AHA PALS Course Manual at Heart.org/Eccstudent using your personal code that comes with your PALS Course Manual The American Heart Association strongly
ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767
 ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767 Copyright 2010 American Heart Association ACLS Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767
ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767 Copyright 2010 American Heart Association ACLS Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767
Official Online ACLS Exam
 \ Official Online ACLS Exam Please fill out this form before you take the exam. Name : Email : Phone : 1. Hypovolemia initially produces which arrhythmia? A. PEA B. Sinus tachycardia C. Symptomatic bradyarrhythmia
\ Official Online ACLS Exam Please fill out this form before you take the exam. Name : Email : Phone : 1. Hypovolemia initially produces which arrhythmia? A. PEA B. Sinus tachycardia C. Symptomatic bradyarrhythmia
2015 Reimbursement Guide
 Reimbursement Guide - Cardiology 2015 Reimbursement Guide for Myocardial Perfusion Imaging including radiopharmaceuticals and related product information 2015 Reimbursement Guide for Myocardial Perfusion
Reimbursement Guide - Cardiology 2015 Reimbursement Guide for Myocardial Perfusion Imaging including radiopharmaceuticals and related product information 2015 Reimbursement Guide for Myocardial Perfusion
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias
 Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. ADRENALINE (TARTRATE) STEROP 1 mg/1 ml Solution for injection. Adrenaline (Levorenine, Epinephrine)
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER ADRENALINE (TARTRATE) STEROP 1 mg/1 ml Solution for injection Adrenaline (Levorenine, Epinephrine) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER ADRENALINE (TARTRATE) STEROP 1 mg/1 ml Solution for injection Adrenaline (Levorenine, Epinephrine) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this
UC San Diego Health System Intravenous Contrast Media Guidelines Adult Approved by P&T Committee 6/18/2014
 UC San Diego Health System Intravenous Contrast Media Guidelines Adult Approved by P&T Committee 6/18/2014 Policy Statement To establish guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of contrast
UC San Diego Health System Intravenous Contrast Media Guidelines Adult Approved by P&T Committee 6/18/2014 Policy Statement To establish guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of contrast
---------------------------DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS---------------- For Injection: 3 mg/ml in single-dose vials (3)
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ADENOSCAN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ADENOSCAN. ADENOSCAN (adenosine)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ADENOSCAN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ADENOSCAN. ADENOSCAN (adenosine)
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
Adult Drug Reference. Dopamine Drip Chart. Pediatric Drug Reference. Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES
 Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Quiz 4 Arrhythmias summary statistics and question answers
 1 Quiz 4 Arrhythmias summary statistics and question answers The correct answers to questions are indicated by *. All students were awarded 2 points for question #2 due to no appropriate responses for
1 Quiz 4 Arrhythmias summary statistics and question answers The correct answers to questions are indicated by *. All students were awarded 2 points for question #2 due to no appropriate responses for
PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP 10 mg/ml Sandoz Canada Inc. Date of Preparation: September 1992 145 Jules-Léger Date of Revision : January 13, 2011 Boucherville, QC, Canada
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP 10 mg/ml Sandoz Canada Inc. Date of Preparation: September 1992 145 Jules-Léger Date of Revision : January 13, 2011 Boucherville, QC, Canada
Upstate University Health System Medication Exam - Version A
 Upstate University Health System Medication Exam - Version A Name: ID Number: Date: Unit: Directions: Please read each question below. Choose the best response for each of the Multiple Choice and Medication
Upstate University Health System Medication Exam - Version A Name: ID Number: Date: Unit: Directions: Please read each question below. Choose the best response for each of the Multiple Choice and Medication
Heart Attack: What You Need to Know
 A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
Team Leader. Ensures high-quality CPR at all times Assigns team member roles Ensures that team members perform well. Bradycardia Management
 ACLS Megacode Case 1: Sinus Bradycardia (Bradycardia VF/Pulseless VT Asystole Out-of-Hospital Scenario You are a paramedic and arrive on the scene to find a 57-year-old woman complaining of indigestion.
ACLS Megacode Case 1: Sinus Bradycardia (Bradycardia VF/Pulseless VT Asystole Out-of-Hospital Scenario You are a paramedic and arrive on the scene to find a 57-year-old woman complaining of indigestion.
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM
 CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM Preparation for the Cardiac Rehabilitation Program After your heart problem is stable, your physician or cardiologist will refer you to the Cardiac Rehabilitation program.
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM Preparation for the Cardiac Rehabilitation Program After your heart problem is stable, your physician or cardiologist will refer you to the Cardiac Rehabilitation program.
Emergency Scenario. Chest Pain
 Emergency Scenario Chest Pain This emergency scenario reviews chest pain in a primary care patient, and is set up for roleplay and case review with your staff. 1) The person facilitating scenarios can
Emergency Scenario Chest Pain This emergency scenario reviews chest pain in a primary care patient, and is set up for roleplay and case review with your staff. 1) The person facilitating scenarios can
SMO: Anaphylaxis and Allergic Reactions
 REGION I EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic SMO: Anaphylaxis and Allergic Reactions Overview: Allergic reactions can vary in severity from a mild reaction consisting of hives
REGION I EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic SMO: Anaphylaxis and Allergic Reactions Overview: Allergic reactions can vary in severity from a mild reaction consisting of hives
Is it really so? : Varying Presentations for ACS among Elderly, Women and Diabetics. Yen Tibayan, M.D. Division of Cardiovascular Medicine
 Is it really so? : Varying Presentations for ACS among Elderly, Women and Diabetics Yen Tibayan, M.D. Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Case Presentation 69 y.o. woman calls 911 with the complaint of
Is it really so? : Varying Presentations for ACS among Elderly, Women and Diabetics Yen Tibayan, M.D. Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Case Presentation 69 y.o. woman calls 911 with the complaint of
Septic Shock: Pharmacologic Agents for Hemodynamic Support. Nathan E Cope, PharmD PGY2 Critical Care Pharmacy Resident
 Septic Shock: Pharmacologic Agents for Hemodynamic Support Nathan E Cope, PharmD PGY2 Critical Care Pharmacy Resident Objectives Define septic shock and briefly review pathophysiology Outline receptor
Septic Shock: Pharmacologic Agents for Hemodynamic Support Nathan E Cope, PharmD PGY2 Critical Care Pharmacy Resident Objectives Define septic shock and briefly review pathophysiology Outline receptor
Name: Age: Resting BP: Wt. kg: Est. HR max : 85%HR max : Resting HR:
 Bruce Protocol - Submaximal GXT Name: Age: Resting BP: Wt. kg: Est. HR max : 85%HR max : Resting HR: Stage Min. % Grade MPH METs 2min HR 3min HR BP RPE 1 0-3 10 1.7 4.7 2 3-6 12 2.5 7.0 3 6-9 14 3.4 10.1
Bruce Protocol - Submaximal GXT Name: Age: Resting BP: Wt. kg: Est. HR max : 85%HR max : Resting HR: Stage Min. % Grade MPH METs 2min HR 3min HR BP RPE 1 0-3 10 1.7 4.7 2 3-6 12 2.5 7.0 3 6-9 14 3.4 10.1
American Heart Association ACLS Pre-Course Self Assessment Dec., 2006. ECG Analysis. Name the following rhythms from the list below:
 American Heart Association ACLS Pre-Course Self Assessment Dec., 2006 ECG Analysis This pre-test is exactly the same as the pretest on the ACLS Provider manual CD. This paper version can be completed in
American Heart Association ACLS Pre-Course Self Assessment Dec., 2006 ECG Analysis This pre-test is exactly the same as the pretest on the ACLS Provider manual CD. This paper version can be completed in
Medical Direction and Practices Board WHITE PAPER
 Medical Direction and Practices Board WHITE PAPER Use of Pressors in Pre-Hospital Medicine: Proper Indication and State of the Science Regarding Proper Choice of Pressor BACKGROUND Shock is caused by a
Medical Direction and Practices Board WHITE PAPER Use of Pressors in Pre-Hospital Medicine: Proper Indication and State of the Science Regarding Proper Choice of Pressor BACKGROUND Shock is caused by a
Cardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station Checklist
 Cardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station Checklist VF/VT 00 American Heart Association Adult Cardiac Arrest Shout for Help/Activate Emergency Response Epinephrine every - min Amiodarone Start CPR
Cardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station Checklist VF/VT 00 American Heart Association Adult Cardiac Arrest Shout for Help/Activate Emergency Response Epinephrine every - min Amiodarone Start CPR
E C C. American Heart Association. Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support. Written Precourse Self-Assessment. May 2011. 2011 American Heart Association
 E C C American Heart Association Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Written Precourse Self-Assessment May 2011 2011 American Heart Association 2011 ACLS Written Precourse Self-Assessment 1. Ten minutes
E C C American Heart Association Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Written Precourse Self-Assessment May 2011 2011 American Heart Association 2011 ACLS Written Precourse Self-Assessment 1. Ten minutes
Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations.
 INTRODUCTION Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations. Although decrease in cardiovascular mortality still major cause of morbidity & burden of disease.
INTRODUCTION Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations. Although decrease in cardiovascular mortality still major cause of morbidity & burden of disease.
Ischemic Heart Disease: Angina Pectoris
 Ischemic Heart Disease: Angina Pectoris Robert J. Straka, Pharm.D. FCCP Associate Professor University of Minnesota College of Pharmacy Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA [email protected] Learning Objectives
Ischemic Heart Disease: Angina Pectoris Robert J. Straka, Pharm.D. FCCP Associate Professor University of Minnesota College of Pharmacy Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA [email protected] Learning Objectives
Pharmacologic Stress Test: Adenosine
 Pharmacologic Stress Test: Adenosine OVERVIEW The purpose of this document is to specifically identify the critical components involved in performing a pharmacologic stress test with adenosine. This information
Pharmacologic Stress Test: Adenosine OVERVIEW The purpose of this document is to specifically identify the critical components involved in performing a pharmacologic stress test with adenosine. This information
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation DISCLOSURES. Heart Beat Anatomy. I have no financial conflicts to disclose
 Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PhD course in Medical Imaging. Anne Günther Department of Radiology OUS Rikshospitalet
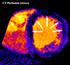 MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PhD course in Medical Imaging Anne Günther Department of Radiology OUS Rikshospitalet CORONARY CT ANGIOGRAPHY (CTA) Accurate method in the assessment of possible
MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PhD course in Medical Imaging Anne Günther Department of Radiology OUS Rikshospitalet CORONARY CT ANGIOGRAPHY (CTA) Accurate method in the assessment of possible
The science of medicine. The compassion to heal.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
!!! BOLUS DOSE IV. Use 5-10 mcg IV boluses STD ADRENALINE INFUSION. Use IM adrenaline in advance of IV dosing!
 ADRENALINE IVI BOLUS IV Open a vial of 1:1000 ADRENALINE 1 mg /ml Add 1 ml to 9 ml N/Saline = 1mg adrenaline in 10 ml (or 100 mcg/ml) Add 1 ml 1:10,000 to 9 ml N/Saline = 100 mcg adrenaline in 10 ml (or
ADRENALINE IVI BOLUS IV Open a vial of 1:1000 ADRENALINE 1 mg /ml Add 1 ml to 9 ml N/Saline = 1mg adrenaline in 10 ml (or 100 mcg/ml) Add 1 ml 1:10,000 to 9 ml N/Saline = 100 mcg adrenaline in 10 ml (or
Inotropes/Vasoactive Agents Hina N. Patel, Pharm.D., BCPS Cathy Lawson, Pharm.D., BCPS
 Inotropes/Vasoactive Agents Hina N. Patel, Pharm.D., BCPS Cathy Lawson, Pharm.D., BCPS 1. Definition -an agent that affects the contractility of the heart -may be positive (increases contractility) or
Inotropes/Vasoactive Agents Hina N. Patel, Pharm.D., BCPS Cathy Lawson, Pharm.D., BCPS 1. Definition -an agent that affects the contractility of the heart -may be positive (increases contractility) or
table of contents drug reference
 table of contents drug reference ADULT DRUG REFERENCE...155 161 PEDIATRIC DRUG REFERENCE...162 164 PEDIATRIC WEIGHT-BASED DOSING CHARTS...165 180 Adenosine...165 Amiodarone...166 Atropine...167 Defibrillation...168
table of contents drug reference ADULT DRUG REFERENCE...155 161 PEDIATRIC DRUG REFERENCE...162 164 PEDIATRIC WEIGHT-BASED DOSING CHARTS...165 180 Adenosine...165 Amiodarone...166 Atropine...167 Defibrillation...168
The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010.
 ACLS Study Guide The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010. Please read the below information carefully This letter is to confirm your
ACLS Study Guide The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010. Please read the below information carefully This letter is to confirm your
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations. CardioCase presentation. Ethel s Case. Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC
 Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Anaphylaxis: Treatment in the Community
 : Treatment in the Community is likely if a patient who, within minutes of exposure to a trigger (allergen), develops a sudden illness with rapidly progressing skin changes and life-threatening airway
: Treatment in the Community is likely if a patient who, within minutes of exposure to a trigger (allergen), develops a sudden illness with rapidly progressing skin changes and life-threatening airway
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL)
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
UBISTESIN 1:200,000 and UBISTESIN FORTE 1:100,000
 UBISTESIN 1:200,000 and UBISTESIN FORTE 1:100,000 Articaine hydrochloride and adrenaline hydrochloride Consumer Medicine Information WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET Please read this leaflet carefully before you
UBISTESIN 1:200,000 and UBISTESIN FORTE 1:100,000 Articaine hydrochloride and adrenaline hydrochloride Consumer Medicine Information WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET Please read this leaflet carefully before you
Pre-Screening and Risk Stratification
 Pre-Screening and Risk Stratification Chapter 1, 2 and 3 ACSM What is involved in the prescreening process? The Basic Goal To determine if it is safe for an individual to start an exercise program, what
Pre-Screening and Risk Stratification Chapter 1, 2 and 3 ACSM What is involved in the prescreening process? The Basic Goal To determine if it is safe for an individual to start an exercise program, what
It is recommended that the reader review each medical directive presented in this presentation along with the actual PCP Core medical directive.
 It is recommended that the reader review each medical directive presented in this presentation along with the actual PCP Core medical directive. This presentation will highlight the changes and any new
It is recommended that the reader review each medical directive presented in this presentation along with the actual PCP Core medical directive. This presentation will highlight the changes and any new
Quiz 5 Heart Failure scores (n=163)
 Quiz 5 Heart Failure summary statistics The correct answers to questions are indicated by *. Students were awarded 2 points for question #3 for either selecting spironolactone or eplerenone. However, the
Quiz 5 Heart Failure summary statistics The correct answers to questions are indicated by *. Students were awarded 2 points for question #3 for either selecting spironolactone or eplerenone. However, the
The patient s response to therapy within the first hour in the Emergency Room is one of the most reliable ways to predict need for hospitalization.
 Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm The Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm is to be used for any patient seen in the Emergency Room with the diagnosis of asthma. (The initial history should
Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm The Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm is to be used for any patient seen in the Emergency Room with the diagnosis of asthma. (The initial history should
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Case Scenarios
 Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Case Scenarios ACLS Respiratory Arrest Case Out-of-Hospital Scenario You are a paramedic and respond to the scene of a possible cardiac arrest. A young man lies motionless
Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Case Scenarios ACLS Respiratory Arrest Case Out-of-Hospital Scenario You are a paramedic and respond to the scene of a possible cardiac arrest. A young man lies motionless
Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier
 Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier Most common dysrhythmia seen in ED, and incidence increasing with ageing population Presentation Common presentations: younger patients often
Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier Most common dysrhythmia seen in ED, and incidence increasing with ageing population Presentation Common presentations: younger patients often
New England Pain Management Consultants At New England Baptist Hospital
 New England Pain Management Consultants At New England Baptist Hospital Pain Management Center Health Assessment Dear New Pain Management Patient, Welcome to the New England Pain Management Consultants
New England Pain Management Consultants At New England Baptist Hospital Pain Management Center Health Assessment Dear New Pain Management Patient, Welcome to the New England Pain Management Consultants
RATE VERSUS RHYTHM CONTROL OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: SPECIAL CONSIDERATION IN ELDERLY. Charles Jazra
 RATE VERSUS RHYTHM CONTROL OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: SPECIAL CONSIDERATION IN ELDERLY Charles Jazra NO CONFLICT OF INTEREST TO DECLARE Relationship Between Atrial Fibrillation and Age Prevalence, percent
RATE VERSUS RHYTHM CONTROL OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: SPECIAL CONSIDERATION IN ELDERLY Charles Jazra NO CONFLICT OF INTEREST TO DECLARE Relationship Between Atrial Fibrillation and Age Prevalence, percent
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona
 Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona Areas to be covered Historical, current, and future treatments for various cardiovascular disease: Atherosclerosis (Coronary
Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona Areas to be covered Historical, current, and future treatments for various cardiovascular disease: Atherosclerosis (Coronary
Management of the Patient with Aortic Stenosis undergoing Non-cardiac Surgery
 Management of the Patient with Aortic Stenosis undergoing Non-cardiac Surgery Srinivasan Rajagopal M.D. Assistant Professor Division of Cardiothoracic Anesthesia Objectives Describe the pathophysiology
Management of the Patient with Aortic Stenosis undergoing Non-cardiac Surgery Srinivasan Rajagopal M.D. Assistant Professor Division of Cardiothoracic Anesthesia Objectives Describe the pathophysiology
Heart Diseases and their Complications
 Heart Diseases and their Complications Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-252-01-021914-E
Heart Diseases and their Complications Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-252-01-021914-E
Case Presentation: Mr. E.M. Dr. Braun
 Case Presentation: Mr. E.M. Dr. Braun Case Presentation: Mr. E.M. 66 years old; PMHx CAD with stent 2010; carotid artery disease with stent 1999; aortic stenosis; CVA 1998; type 2 DM; colon cancer with
Case Presentation: Mr. E.M. Dr. Braun Case Presentation: Mr. E.M. 66 years old; PMHx CAD with stent 2010; carotid artery disease with stent 1999; aortic stenosis; CVA 1998; type 2 DM; colon cancer with
HYPERTENSION ASSOCIATED WITH RENAL DISEASES
 RENAL DISEASE v Patients with renal insufficiency should be encouraged to reduce dietary salt and protein intake. v Target blood pressure is less than 135-130/85 mmhg. If patients have urinary protein
RENAL DISEASE v Patients with renal insufficiency should be encouraged to reduce dietary salt and protein intake. v Target blood pressure is less than 135-130/85 mmhg. If patients have urinary protein
4/7/2015. Cardiac Rehabilitation: From the other side of the glass door. Chicago, circa 1999. Objectives. No disclosures, no conflicts
 Cardiac Rehabilitation: From the other side of the glass door No disclosures, no conflicts Charles X. Kim, MD, FACC, ABVM Objectives 1. Illustrate common CV benefits of CV rehab in real world practice.
Cardiac Rehabilitation: From the other side of the glass door No disclosures, no conflicts Charles X. Kim, MD, FACC, ABVM Objectives 1. Illustrate common CV benefits of CV rehab in real world practice.
Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life
 Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life Luis R. Castellanos MD, MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California San Diego School of Medicine Sulpizio Family Cardiovascular
Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life Luis R. Castellanos MD, MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California San Diego School of Medicine Sulpizio Family Cardiovascular
New 7/1/2015 MCFRS 1
 New 7/1/2015 MCFRS 1 The providers will summarize the need for this change from an epinephrine auto injector The provider will define the proper dosage of epinephrine for the adult and pediatric patient
New 7/1/2015 MCFRS 1 The providers will summarize the need for this change from an epinephrine auto injector The provider will define the proper dosage of epinephrine for the adult and pediatric patient
38 year old female with mild obesity. She is planning an exercise program to loose weight. She has no other known risk factors for CAD.
 Stress Testing: Wael A. Jaber, MD,FACC 38 year old female with mild obesity She is planning an exercise program to loose weight. She has no other known risk factors for CAD. You recommend: A. Exercise
Stress Testing: Wael A. Jaber, MD,FACC 38 year old female with mild obesity She is planning an exercise program to loose weight. She has no other known risk factors for CAD. You recommend: A. Exercise
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. ADRENALINE (HCl) STEROP 0,8mg/1ml. Solution for injection. Adrenaline (Levorenine, Epinephrine)
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER ADRENALINE (HCl) STEROP 0,4mg/1ml ADRENALINE (HCl) STEROP 0,8mg/1ml Solution for injection Adrenaline (Levorenine, Epinephrine) Read all of this leaflet carefully
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER ADRENALINE (HCl) STEROP 0,4mg/1ml ADRENALINE (HCl) STEROP 0,8mg/1ml Solution for injection Adrenaline (Levorenine, Epinephrine) Read all of this leaflet carefully
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
Universitätsklinik für Kardiologie. Test. Thomas M. Suter Akute Herzinsuffizienz Diagnostik und Therapie [email protected] 1
 Test Thomas M. Suter Akute Herzinsuffizienz Diagnostik und Therapie [email protected] 1 Heart Failure - Definition European Heart Journal (2008) 29, 2388 2442 Akute Herzinsuffizienz Diagnostik und
Test Thomas M. Suter Akute Herzinsuffizienz Diagnostik und Therapie [email protected] 1 Heart Failure - Definition European Heart Journal (2008) 29, 2388 2442 Akute Herzinsuffizienz Diagnostik und
Oxygen Therapy. Oxygen therapy quick guide V3 July 2012.
 PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in a compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in a liquid form. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the patient by means of plastic tubing
PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in a compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in a liquid form. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the patient by means of plastic tubing
Hypertension and Heart Failure Medications. Dr William Dooley
 Hypertension and Heart Failure Medications Dr William Dooley Plan Heart Failure Acute vs. chronic Mx Hypertension Common drugs used Method of action Choice of medications Heart Failure Aims; Short term:
Hypertension and Heart Failure Medications Dr William Dooley Plan Heart Failure Acute vs. chronic Mx Hypertension Common drugs used Method of action Choice of medications Heart Failure Aims; Short term:
Jeopardy Topics: THE CLOT STOPS HERE (anticoagulants) SUGAR, SUGAR, HOW D YOU GET SO HIGH (insulins)
 Jeopardy Topics: THE CLOT STOPS HERE (anticoagulants) SUGAR, SUGAR, HOW D YOU GET SO HIGH (insulins) I HEAR YA KNOCKING BUT YOU CAN T COME IN (electrolytes) TAKE MY BREATH AWAY (Opiates-morphine) OUT WITH
Jeopardy Topics: THE CLOT STOPS HERE (anticoagulants) SUGAR, SUGAR, HOW D YOU GET SO HIGH (insulins) I HEAR YA KNOCKING BUT YOU CAN T COME IN (electrolytes) TAKE MY BREATH AWAY (Opiates-morphine) OUT WITH
Stowe School Medications Policy
 INTRODUCTION Most pupils will need medication at some stage of their school life. Although this will mainly be for short periods there are a few pupils with chronic conditions who may require regular medication
INTRODUCTION Most pupils will need medication at some stage of their school life. Although this will mainly be for short periods there are a few pupils with chronic conditions who may require regular medication
8. Strategies in Patients at Risk for Allergic Reactions to IV Contrast for CT
 Updated 7/14/09 UAB Department of Radiology Guidelines for Administering Gadolinium-based and Iodine-based Intravenous Contrast Agents in Patients with Renal Dysfunction or at Risk for Adverse Reactions
Updated 7/14/09 UAB Department of Radiology Guidelines for Administering Gadolinium-based and Iodine-based Intravenous Contrast Agents in Patients with Renal Dysfunction or at Risk for Adverse Reactions
All patients presenting to the Emergency Department with symptoms suggestive of
 APPENDIX: Online Data Supplements Clinical Trial Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria All patients presenting to the Emergency Department with symptoms suggestive of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) were screened
APPENDIX: Online Data Supplements Clinical Trial Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria All patients presenting to the Emergency Department with symptoms suggestive of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) were screened
Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology
 Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology Chapter 4: Endocrine, Nutritional, and Metabolic Diseases (E00-E89) The diabetes mellitus codes are combination codes
Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology Chapter 4: Endocrine, Nutritional, and Metabolic Diseases (E00-E89) The diabetes mellitus codes are combination codes
Adrenergic, Adrenergic Blockers, Cholinergic and Cholinergic Blockers
 Adrenergic, Adrenergic Blockers, Cholinergic and Cholinergic Blockers Objective 1: Explain the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic
Adrenergic, Adrenergic Blockers, Cholinergic and Cholinergic Blockers Objective 1: Explain the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008
 Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
INTRODUCTION TO EECP THERAPY
 INTRODUCTION TO EECP THERAPY is an FDA cleared, Medicare approved, non-invasive medical therapy for the treatment of stable and unstable angina, congestive heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and
INTRODUCTION TO EECP THERAPY is an FDA cleared, Medicare approved, non-invasive medical therapy for the treatment of stable and unstable angina, congestive heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and
Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results
 Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results Paul K. Whelton, MB, MD, MSc Chair, SPRINT Steering Committee Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, and
Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results Paul K. Whelton, MB, MD, MSc Chair, SPRINT Steering Committee Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, and
Atrial Fibrillation: Do We Have A Cure? Raymond Kawasaki, MD AMG Electrophysiology February 21, 2015
 Atrial Fibrillation: Do We Have A Cure? Raymond Kawasaki, MD AMG Electrophysiology February 21, 2015 Disclaimer I have no relationships to disclose Do we have a cure for Atrial Fibrillation? The short
Atrial Fibrillation: Do We Have A Cure? Raymond Kawasaki, MD AMG Electrophysiology February 21, 2015 Disclaimer I have no relationships to disclose Do we have a cure for Atrial Fibrillation? The short
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease.
 Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
Allergy Emergency Treatment Protocol
 Allergy Emergency Treatment Protocol I. Initial evaluation of possible allergic reaction a. Cease administration of allergenic extracts b. Notify physician c. Record vital signs: blood pressure, pulse,
Allergy Emergency Treatment Protocol I. Initial evaluation of possible allergic reaction a. Cease administration of allergenic extracts b. Notify physician c. Record vital signs: blood pressure, pulse,
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
PRO-CPR. 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview. (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material)
 PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
