C. starting positive displacement pumps with the discharge valve closed.
|
|
|
- Christian Phelps
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 KNOWLEDGE: K1.04 [3.4/3.6] P78 The possibility of water hammer in a liquid system is minimized by... A. maintaining temperature above the saturation temperature. B. starting centrifugal pumps with the casing vent valve fully open. C. starting positive displacement pumps with the discharge valve closed. D. venting systems prior to starting centrifugal pumps. ANSWER: D. KNOWLEDGE: K1.04 [3.4/3.6] P278 Which one of the following methods will increase the possibility and/or severity of water hammer? A. Opening and closing system valves slowly. B. Venting fluid systems prior to starting a pump. C. Starting a centrifugal pump with the discharge valve fully open. D. Starting a centrifugal pump with the discharge valve fully closed. ANSWER: C. -1-
2 KNOWLEDGE: K1.04 [3.4/3.6] P679 (B279) A sudden stop of fluid flow in a piping system, due to rapid closure of an isolation valve, will most likely result in... A. check valve slamming. B. pump runout. C. water hammer. D. pressurized thermal shock. ANSWER: C. KNOWLEDGE: K1.04 [3.4/3.6] P879 One reason for keeping condensate out of the steam lines is to... A. minimize corrosion buildup. B. reduce heat losses. C. eliminate steam traps. D. prevent water/steam hammer. ANSWER: D. -2-
3 KNOWLEDGE: K1.04 [3.4/3.6] P1079 The possibility of water hammer will be increased by... A. maintaining the discharge line filled with liquid on an automatically starting pump. B. condensation in a steam line just prior to initiating flow. C. warming steam lines prior to initiating steam flow. D. slowly closing the discharge valve on an operating pump. KNOWLEDGE: K1.04 [3.4/3.6] P1279 To minimize the possibility of water hammer when initiating flow in a system, the operator should... A. vent the system prior to initiating flow. B. vent the system only after flow has been initiated. C. fully open the pump discharge valve prior to starting a pump. D. rapidly open the pump discharge valve after a pump is running. ANSWER: A. -3-
4 KNOWLEDGE: K1.04 [3.4/3.6] P1879 (B2779) Which one of the following describes why large steam lines are gradually warmed instead of suddenly admitting full steam flow? A. To minimize the possibility of stress corrosion cracking of the steam lines. B. To minimize the total thermal expansion of the steam lines. C. To minimize the potential for water hammer in the steam lines. D. To minimize the heat loss from the steam lines. ANSWER: C. KNOWLEDGE: K1.04 [3.4/3.6] P2079 (B2081) Which one of the following will minimize the possibility of water hammer? A. Draining the discharge line of a centrifugal pump after shutdown. B. Draining condensate out of steam lines before and after initiating flow. C. Starting a centrifugal pump with its discharge valve fully open. D. Starting a positive displacement pump with its discharge valve partially closed. -4-
5 KNOWLEDGE: K1.04 [3.4/3.6] P2279 (B2679) Which one of the following operating practices minimizes the possibility of water hammer? A. Change valve positions as rapidly as possible. B. Start centrifugal pumps with the discharge valve throttled. C. Start positive displacement pumps with the discharge valve closed. D. Vent systems only after initiating system flow. -5-
6 KNOWLEDGE: K1.04 [3.4/3.6] P4042 (B4041) Refer to the drawing of two lengths of 6-inch diameter pipe, each containing an identical automatic isolation valve. The actual pipe lengths are proportional to their symbols in the drawing Water at 65 F is flowing at 1,000 gpm through each pipe. If the isolation valves instantly close, valve A piping will experience a pressure increase that is the pressure increase experienced by valve B piping; and the pressure spike will dissipate quicker in the length of pipe. A. equal to; shorter B. equal to; longer C. less than; shorter D. less than; longer ANSWER: A. -6-
7 KNOWLEDGE: K1.04 [3.4/3.6] P6242 (B6241) Refer to the drawing of two lengths of 16-inch diameter pipe, each containing an identical automatic isolation valve. The actual pipe lengths are proportional to their symbols in the drawing. Water is flowing at 10,000 gpm through each pipe when both isolation valves instantly close. Consider two cases: Case 1: The water temperature upstream of both valves is 65 F. Case 2: The water temperature is 65 F upstream of valve A, and 85 F upstream of valve B. For which case(s), if any, will valve A experience a pressure spike that is greater than the pressure spike at valve B? A. Case 1 only B. Case 2 only C. Both cases D. Neither case -7-
8 KNOWLEDGE: K1.04 [3.4/3.6] P6742 (B6741) Refer to the drawing of two lengths of 16-inch diameter pipe, each containing an identical automatic isolation valve. The actual pipe lengths are proportional to their symbols in the drawing. Water is flowing at 10,000 gpm through each pipe when both isolation valves instantly close. Consider two cases: Case 1: The water temperature upstream of both valves is 65 F. Case 2: The water temperature is 85 F upstream of valve A, and 65 F upstream of valve B. For which case(s), if any, will valve A experience a pressure spike that is greater than the pressure spike at valve B? A. Case 1 only B. Case 2 only C. Both cases D. Neither case ANSWER: D. -8-
9 KNOWLEDGE: K1.04 [3.4/3.6] P7620 (B7620) Which one of the following will result in a higher probability and/or severity of water hammer in a flowing water system? A. Gradual pipe bends rather than sharp pipe bends. B. Shorter pipe lengths rather than longer pipe lengths. C. Lower initial flow rates rather than higher initial flow rates. D. Shorter valve stroke times rather than longer valve stroke times. ANSWER: D. KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P380 (B383) An 85 gpm leak to atmosphere has developed from a cooling water system that is operating at 100 psig. Which one of the following will be the approximate leak rate when system pressure has decreased to 50 psig? A. 33 gpm B. 41 gpm C. 52 gpm D. 60 gpm ANSWER: D. -9-
10 KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P579 Mass flow rate equals volumetric flow rate times... A. specific volume. B. density. C. specific gravity. D. velocity. KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P680 (B681) A 55 gpm leak to atmosphere has developed from a cooling water system that is operating at 100 psig. Which one of the following will be the approximate leak rate when system pressure has decreased to 50 psig? A. 28 gpm B. 32 gpm C. 39 gpm D. 45 gpm ANSWER: C. -10-
11 KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P1382 A 75 gpm leak to atmosphere has developed from a cooling water system that is operating at 80 psig. Which one of the following will be the approximate leak rate when system pressure has decreased to 40 psig? A. 38 gpm B. 44 gpm C. 53 gpm D. 59 gpm ANSWER: C. KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P1580 (B1979) A 60 gpm leak to atmosphere has developed from a cooling water system that is operating at 150 psig. Which one of the following will be the approximate leak rate when system pressure has decreased to 75 psig? A. 15 gpm B. 30 gpm C. 42 gpm D. 53 gpm ANSWER: C. -11-
12 KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P1679 (B2981) A 100 gpm leak to atmosphere has developed from a cooling water system that is operating at 60 psig. Which one of the following will be the approximate leak rate when system pressure has decreased to 20 psig? A. 33 gpm B. 53 gpm C. 58 gpm D. 71 gpm ANSWER: C. KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P1779 (B1783) A 100 gpm leak to atmosphere has developed from a cooling water system that is operating at 45 psig. Which one of the following will be the approximate leak rate when system pressure has decreased to 30 psig? A. 25 gpm B. 50 gpm C. 67 gpm D. 82 gpm ANSWER: D. -12-
13 KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P1986 A 47 gpm leak to atmosphere has developed from a cooling water system that is operating at 150 psig. Which one of the following will be the approximate leak rate when system pressure has decreased to 75 psig? A. 24 gpm B. 33 gpm C. 39 gpm D. 46 gpm KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P2080 (B2080) An 80 gpm leak to atmosphere has developed from a cooling water system that is operating at 100 psig. Which one of the following will be the approximate leak rate when system pressure has decreased to 75 psig? A. 69 gpm B. 60 gpm C. 51 gpm D. 40 gpm ANSWER: A. -13-
14 KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P2379 (B2381) A 60 gpm leak to atmosphere has developed from a cooling water system that is operating at 150 psig. Which one of the following will be the approximate leak rate when system pressure has decreased to 100 psig? A. 27 gpm B. 35 gpm C. 40 gpm D. 49 gpm ANSWER: D. KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P2779 (B2781) An 80 gpm leak to atmosphere has developed from a cooling water system that is operating at 150 psig. Which one of the following will be the approximate leak rate when system pressure has decreased to 75 psig? A. 20 gpm B. 40 gpm C. 49 gpm D. 57 gpm ANSWER: D. -14-
15 KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P2980 An 80 gpm leak to atmosphere has developed from a cooling water system that is operating at 150 psig. Which one of the following will be the approximate leak rate when system pressure has decreased to 100 psig? A. 36 gpm B. 53 gpm C. 56 gpm D. 65 gpm ANSWER: D. KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P3080 (B3181) A 75 gpm leak to atmosphere has developed from a cooling water system that is operating at 100 psig. Which one of the following will be the approximate leak rate when system pressure has decreased to 80 psig? A. 26 gpm B. 39 gpm C. 56 gpm D. 67 gpm ANSWER: D. -15-
16 KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P3780 Which one of the following describes the relationship between the main steam mass flow rate leaving a steam generator and the main feedwater mass flow rate entering the same steam generator at steady-state power operation? (Assume no other addition/removal of steam generator inventory.) A. The mass flow rates will be the same only if downcomer level is constant. B. The mass flow rates will be the same only if the reactor is operating near rated power. C. The main steam mass flow rate is smaller than the main feedwater mass flow rate by the amount of moisture removed by the steam generator moisture separators. D. The main steam mass flow rate is greater than the main feedwater mass flow rate by the amount of moisture removed by the steam generator moisture separators. ANSWER: A. -16-
17 KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P5342 (B5342) A heat exchanger has the following initial cooling water inlet temperature and differential pressure (ΔP) parameters: Inlet Temperature = 70 F Heat Exchanger ΔP = 10 psi Six hours later, the current heat exchanger cooling water parameters are: Inlet Temperature = 85 F Heat Exchanger ΔP = 10 psi In comparison to the initial cooling water mass flow rate, the current mass flow rate is... A. lower, because the density of the cooling water has decreased. B. higher, because the velocity of the cooling water has increased. C. the same, because the changes in cooling water velocity and density offset. D. the same, because the heat exchanger cooling water ΔP is the same. ANSWER: A. KNOWLEDGE: K1.05 [2.9/3.0] P7342 (B7342) An 80 gpm leak to atmosphere has developed from a cooling water system that is operating at 150 psig. Which one of the following will be the approximate leak rate when system pressure has decreased to 100 psig? A. 70 gpm B. 65 gpm C. 53 gpm D. 47 gpm -17-
18 KNOWLEDGE: K1.06 [2.8/2.9] P580 Reactor coolant system (RCS) hot leg temperature is constant at 568 F while RCS pressure is decreasing due to a small reactor coolant leak. Which one of the following RCS pressure ranges includes the pressure at which two-phase flow will first occur in the hot leg? A. 1,250 to 1,201 psig B. 1,200 to 1,151 psig C. 1,150 to 1,101 psig D. 1,100 to 1,051 psig KNOWLEDGE: K1.06 [2.8/2.9] P1180 Reactor coolant system (RCS) hot leg temperature is constant at 538 F while RCS pressure is decreasing due to a small reactor coolant leak. Which one of the following RCS pressure ranges includes the pressure at which two-phase flow will first occur in the hot leg? A. 1,100 to 1,151 psig B. 1,050 to 1,001 psig C. 1,000 to 951 psig D. 950 to 901 psig ANSWER: D. -18-
19 KNOWLEDGE: K1.06 [2.8/2.9] P1480 Reactor coolant system (RCS) hot leg temperature is constant at 520 F while RCS pressure is decreasing due to a small reactor coolant leak. Which one of the following pressure ranges includes the pressure at which two-phase flow will first occur in the hot leg? A. 950 to 901 psig B. 900 to 851 psig C. 850 to 801 psig D. 800 to 751 psig ANSWER: D. KNOWLEDGE: K1.06 [2.8/2.9] P2581 Reactor coolant system (RCS) hot leg temperature is constant at 552 F while RCS pressure is decreasing due to a small reactor coolant leak. Which one of the following pressure ranges includes the pressure at which two-phase flow will first occur in the hot leg? A. 1,100 to 1,051 psig B. 1,050 to 1,001 psig C. 1,000 to 951 psig D. 950 to 901 psig -19-
20 KNOWLEDGE: K1.06 [2.8/2.9] P7649 (B7649) If the quality of a flowing steam-water mixture is known, what additional information, if any, is needed to determine the percent moisture content of the steam-water mixture? A. The mass flow rate of the mixture. B. The specific volume of the mixture. C. The pressure and/or temperature of the mixture. D. No additional information is needed. ANSWER: D. KNOWLEDGE: K1.06 [2.8/2.9] P7689 A nuclear power plant is initially operating at steady-state 100 percent power. If an unplanned load rejection causes the main generator load to rapidly decrease to 90 percent, the voids in the two-phase flow in the steam generator tube bundle region will initially ; which causes indicated steam generator water level (measured in the downcomer) to initially. A. shrink; decrease B. shrink; increase C. expand; decrease D. expand; increase ANSWER: A. -20-
21 KNOWLEDGE: K1.07 [2.7/2.7] P581 A nuclear power plant is recovering from a loss of offsite power that caused all reactor coolant pumps (RCPs) to stop. Pressurizer level indication is off-scale high. Which one of the following is most likely to occur if the steam generator (SG) temperatures are 50 F higher than their associated reactor coolant system (RCS) loop temperatures when an RCP is restarted? A. Localized water hammer in the RCS. B. Pressurized thermal shock to the SGs. C. A large pressure spike throughout the RCS. D. Inadvertent lifting of a SG atmospheric relief valve. ANSWER: C. KNOWLEDGE: K1.08 [2.8/1.8] P279 (B143) A centrifugal water pump was returned to service after maintenance. However, the operator failed to vent the pump. Compared to normal pump operating conditions, after the pump is started the operator will see a flow rate and a discharge head. A. higher; lower B. higher; higher C. lower; lower D. lower; higher ANSWER: C. -21-
22 KNOWLEDGE: K1.08 [2.8/2.8] P3481 Refer to the drawing of a cooling water system (see figure below). Centrifugal pump A is circulating water at 100 F. Which one of the following will cause the centrifugal pump to operate closer to a condition in which gas/vapor binding can occur? A. Surge tank level is raised by 5 percent. B. Service water flow rate is decreased by 5 percent. C. The pump discharge valve is repositioned to decrease cooling water system flow rate by 5 percent. D. Makeup water containing a high concentration of total dissolved solids is added to the cooling water system. -22-
23 KNOWLEDGE: K1.10 [3.3/3.4] P80 (B79) If a valve closure suddenly stops fluid flow, the resulting piping system pressure transient is referred to as... A. cavitation. B. shutoff head. C. water hammer. D. valve chatter. ANSWER: C. KNOWLEDGE: K1.10 [3.3/3.4] P381 (B380) The major concern with starting a main feedwater pump with downstream fluid in a saturated condition is... A. cavitation. B. water hammer. C. thermal shock. D. positive reactivity addition. -23-
24 KNOWLEDGE: K1.10 [3.3/3.4] P2480 (B1180) Which one of the following will increase the possibility of water hammer? A. Opening and closing system valves very slowly. B. Venting liquid systems only after initiating system flow. C. Starting centrifugal pumps with the discharge valve closed. D. Starting positive displacement pumps with the discharge valve open. KNOWLEDGE: K1.10 [3.3/3.4] P2880 The primary reason for slowly opening the discharge valve of a large motor-driven centrifugal cooling water pump after starting the pump is to minimize the... A. net positive suction head requirements. B. potential for a water hammer. C. motor running current requirements. D. potential for pump cavitation. -24-
25 KNOWLEDGE: K1.11 [3.1/3.3] P79 Cavitation in an operating pump can be caused by... A. lowering the pump suction temperature. B. throttling the pump suction valve. C. increasing the pump backpressure. D. increasing the pump suction pressure. KNOWLEDGE: K1.11 [3.1/3.3] P149 Cavitation of a centrifugal pump in an open system is indicated by discharge pressure and flow rate. A. low; low B. high; high C. low; high D. high; low ANSWER: A. -25-
26 KNOWLEDGE: K1.11 [3.1/3.3] P382 (B80) Which one of the following is most likely to cause cavitation in an operating centrifugal pump? A. Lowering the suction temperature. B. Throttling the pump suction valve. C. Throttling the pump discharge valve. D. Decreasing the pump speed. KNOWLEDGE: K1.11 [3.1/3.3] P481 While on surveillance rounds, an operator notices that a centrifugal pump is making a great deal of noise (like marbles rattling inside the pump casing) and the pump discharge pressure is fluctuating. This set of conditions indicates that the pump is experiencing... A. runout. B. cavitation. C. bearing deterioration. D. packing deterioration. -26-
27 KNOWLEDGE: K1.11 [3.1/3.3] P1181 Indications of pump cavitation include abnormally pump discharge pressure and abnormally pump flow rate. A. low; low B. low; high C. high; low D. high; high ANSWER: A. KNOWLEDGE: K1.11 [3.1/3.3] P1381 Cavitation is the formation of vapor bubbles in the of a pump with the subsequent collapse of these bubbles in the pump. A. impeller; casing B. impeller; discharge piping C. volute; casing D. volute; discharge piping ANSWER: A. -27-
28 KNOWLEDGE: K1.11 [3.1/3.3] P2680 (B280) Cavitation is the formation of vapor bubbles in the pressure area of a pump followed by the of these bubbles within the pump casing. A. low; expansion B. low; collapse C. high; expansion D. high; collapse KNOWLEDGE: K1.11 [3.1/3.3] P2981 (B1880) Pump cavitation occurs when vapor bubbles are formed at the eye of a pump impeller... A. because the localized flow velocity exceeds sonic velocity for the existing fluid temperature. B. because the localized pressure exceeds the vapor pressure for the existing fluid temperature. C. and enter a high pressure region of the pump where they collapse causing damaging pressure pulsations. D. and are discharged from the pump where they expand into larger bubbles causing damaging pressure pulsations. ANSWER: C. -28-
29 KNOWLEDGE: K1.12 [2.5/2.6] P81 In an operating cooling water system with a constant water velocity, if water temperature decreases, system volumetric flow rate (gpm) will... A. remain the same, because the density of the water has not changed. B. increase, because the density of the water has increased. C. remain the same, because the water velocity has not changed. D. increase, because the viscosity of the water has increased. ANSWER: C. KNOWLEDGE: K1.12 [2.5/2.6] P281 Flow instruments that measure the mass flow rate of steam often have a density compensation feature because, for a steam pressure increase at a constant volumetric flow rate, steam density will and the actual mass flow rate will. A. decrease; increase B. increase; decrease C. increase; increase D. decrease; decrease ANSWER: C. -29-
30 KNOWLEDGE: K1.12 [2.5/2.6] P982 A density-compensated flow instrument is being used to measure mass flow rate in a steam system. If the pressure of the steam decreases, indicated mass flow rate will: (Assume volumetric flow rate is constant.) A. increase for all steam conditions. B. decrease for all steam conditions. C. increase, but only if the steam is saturated (not superheated). D. decrease, but only if the steam is saturated (not superheated). KNOWLEDGE: K1.12 [2.5/2.6] P1083 A steam generator transient causes main steam pressure to decrease although the actual steam mass flow rate to the main turbine remains constant. If the main steam flow instrument is not density compensated, indicated steam mass flow rate will... A. increase, due to the increased velocity of the steam. B. increase, due to the increased density of the steam. C. decrease, due to the decreased velocity of the steam. D. decrease, due to the decreased density of the steam. ANSWER: A. -30-
31 KNOWLEDGE: K1.12 [2.5/2.6] P1182 A cooling water system is supplying 1.0 x 10 6 lbm/hour of flow at 100 F. Assuming volumetric flow rate does not change, which one of the following will be the mass flow rate in the system if cooling water temperature increases to 140 F? A. 7.5 x 10 5 lbm/hr B. 8.3 x 10 5 lbm/hr C. 9.0 x 10 5 lbm/hr D. 9.9 x 10 5 lbm/hr ANSWER: D. KNOWLEDGE: K1.12 [2.5/2.6] P1780 A reactor coolant system is supplying 1.0 x 10 8 lbm/hour of coolant flow at a temperature of 100 F. Assuming volumetric flow rate does not change, which one of the following is the approximate mass flow rate that will be supplied by the system if cooling water temperature increases to 400 F? A. 1.2 x 10 8 lbm/hr B. 1.1 x 10 8 lbm/hr C. 9.2 x 10 7 lbm/hr D. 8.7 x 10 7 lbm/hr ANSWER: D. -31-
32 KNOWLEDGE: K1.12 [2.5/2.6] P2182 A reactor coolant system is supplying 1.0 x 10 8 lbm/hr of coolant flow at a temperature of 100 F. Assuming volumetric flow rate does not change, which one of the following is the approximate mass flow rate that will be supplied by the system if coolant temperature increases to 500 F? A. 1.2 x 10 8 lbm/hr B. 1.1 x 10 8 lbm/hr C. 8.7 x 10 7 lbm/hr D. 7.9 x 10 7 lbm/hr ANSWER: D. KNOWLEDGE: K1.12 [2.5/2.6] P2681 A cooling water system is supplying 2,000 lbm/min coolant flow at a temperature of 100 F. Assuming volumetric flow rate does not change, which one of the following is the approximate mass flow rate that will be supplied by the system if cooling water temperature increases to 140 F? A. 1,964 lbm/min B. 1,980 lbm/min C. 2,020 lbm/min D. 2,036 lbm/min -32-
33 KNOWLEDGE: K1.12 [2.5/2.6] P2882 A steam generator transient causes main steam pressure to increase although the actual mass flow rate of steam remains constant. If the main steam flow instrument is not density compensated, the increased main steam pressure will cause indicated steam mass flow rate to... A. increase, due to a higher steam velocity. B. increase, due to a greater steam density. C. decrease, due to a lower steam velocity. D. decrease, due to a reduced steam density. ANSWER: C. KNOWLEDGE: K1.12 [2.5/2.6] P3081 (B3032) The volumetric flow rate of cooling water entering a heat exchanger is 500 gpm. Given the following: Cooling water pressure entering and leaving the heat exchanger is 10 psig. Cooling water inlet temperature is 90 F. Cooling water outlet temperature is 160 F. Heat exchanger inlet and outlet piping have the same diameter. What is the approximate volumetric flow rate of the cooling water exiting the heat exchanger? A. 496 gpm B. 500 gpm C. 504 gpm D. 509 gpm ANSWER: D. -33-
34 KNOWLEDGE: K1.12 [2.5/2.6] P3783 (B3733) A condensate pump is taking suction on a main condenser hotwell, containing water at 100 F, and discharging the water at a volumetric flow rate of 100,000 gpm to the main feedwater system. The main feedwater system heats the water to 400 F before it enters the steam generators. Assume there is no leakage, and no bypass or recirculation flow paths are in use. What is the approximate volumetric flow rate of the feedwater entering the steam generators? A. 100,000 gpm B. 105,000 gpm C. 109,000 gpm D. 115,000 gpm ANSWER: D. P147 Operating two pumps in parallel instead of operating a single pump will result in a... A. large increase in pump head and a small increase in pump flow rate. B. small increase in pump head and a small increase in pump flow rate. C. small increase in pump head and a large increase in pump flow rate. D. large increase in pump head and a large increase in pump flow rate. ANSWER: C. -34-
35 P280 The major effect of starting a second centrifugal pump in parallel with an operating centrifugal pump in an open system is increased... A. system pressure. B. system flow rate. C. pump discharge pressure. D. pump flow rate. P282 To decrease the flow rate through an operating positive displacement pump, an operator should... A. throttle the pump discharge valve partially closed. B. throttle the pump suction valve partially closed. C. decrease the pump s available net positive suction head. D. decrease the pump s speed. ANSWER: D. -35-
36 P981 Which one of the following will decrease the head loss occurring in an operating cooling water system? A. Starting a second pump in parallel with the operating pump. B. Shifting two heat exchangers from parallel to series operation. C. Replacing a 10 foot section of 10-inch diameter pipe with a 20 foot section of 10-inch diameter pipe. D. Replacing a 20 foot section of 10-inch diameter pipe with a 20 foot section of 12-inch diameter pipe. ANSWER: D. P1282 Two centrifugal pumps and two positive displacement pumps are able to be cross-connected to provide makeup water flow to a system. Each pump will produce 100 gpm at a system pressure of 1,000 psig. If system pressure is 1,200 psig, which one of the following combinations will produce the greatest flow rate to the system? A. Two positive displacement pumps in series B. Two positive displacement pumps in parallel C. Two centrifugal pumps in series D. Two centrifugal pumps in parallel -36-
37 P1683 Two centrifugal pumps and two positive displacement pumps are able to be cross-connected to provide makeup water flow to a system. Each pump will produce 100 gpm at a system pressure of 1,000 psig backpressure. If system pressure is 800 psig, which one of the following combinations will produce the greatest flow rate to the system? A. Two centrifugal pumps in parallel. B. Two centrifugal pumps in series. C. Two positive displacement pumps in parallel. D. Two positive displacement pumps in series. ANSWER: A. -37-
38 P1784 (B1725) Two identical centrifugal pumps (CPs) and two identical positive displacement pumps (PDPs) are able to take suction on a vented water storage tank and provide makeup water flow to a cooling water system. The pumps are capable of being cross-connected to provide multiple configurations. In single pump alignment, each pump will supply 100 gpm at a system pressure of 1,000 psig. Given the following information: Centrifugal Pumps Shutoff head = 1,500 psig Maximum design pressure = 2,000 psig Flow rate with no backpressure = 180 gpm Positive Displacement Pumps Maximum design pressure = 2,000 psig Which one of the following pump configurations will supply the lowest makeup water flow rate to the system if system pressure is 1,700 psig? A. Two CPs in series B. Two CPs in parallel C. One PDP and one CP in series (CP supplying PDP) D. One PDP and one CP in parallel -38-
39 P1979 Two identical centrifugal pumps (CPs) and two identical positive displacement pumps (PDPs) are able to take suction on a vented water storage tank and provide makeup water flow to a cooling water system. The pumps are capable of being cross-connected to provide multiple configurations. In single pump alignment, each pump will supply 100 gpm at a system pressure of 1,000 psig. Given the following information: Centrifugal Pumps Shutoff head = 1,500 psig Maximum design pressure = 2,000 psig Flow rate with no backpressure = 180 gpm Positive Displacement Pumps Maximum design pressure = 2,000 psig Which one of the following pump configurations will supply the highest makeup flow rate to the system if system pressure is 800 psig? A. One PDP and one CP in series (CP supplying PDP) B. One PDP and one CP in parallel C. Two CPs in series D. Two CPs in parallel ANSWER: D. -39-
40 P2282 (B2281) Water at 90 F and 50 psig is flowing through a 10-inch diameter pipe at 100 lbm/sec. The pipe then splits into two pipes, a 4-inch diameter pipe and an 8-inch diameter pipe. Disregarding any flow restrictions other than pipe size, which one of the following lists the approximate flow rates through the 4-inch and 8-inch diameter pipes? (Assume that water velocity is the same in each pipe.) 4-inch Pipe (lbm/sec) 8-inch Pipe (lbm/sec) A B C D ANSWER: A. -40-
41 P2383 (B2324) Two identical centrifugal pumps (CPs) and two identical positive displacement pumps (PDPs) are able to take suction on a vented water storage tank and provide makeup water flow to a cooling water system. The pumps are capable of being cross-connected to provide multiple configurations. In single pump alignment, each pump will supply 100 gpm at a system pressure of 1,200 psig. Given the following information: Centrifugal Pumps Shutoff head = 1,500 psig Maximum design pressure = 2,000 psig Flow rate with no backpressure = 180 gpm Positive Displacement Pumps Maximum design pressure = 2,000 psig Which one of the following pump configurations will supply the highest makeup flow rate to the system if system pressure is 500 psig? A. Two CPs in series B. Two CPs in parallel C. Two PDPs in parallel D. One CP and one PDP in series (CP supplying PDP) -41-
42 P2481 (B2479) Water at 90 F and 50 psig is flowing through a 10-inch diameter pipe at 100 lbm/sec. The pipe then splits into two pipes, a 3-inch diameter pipe and a 6-inch diameter pipe. Disregarding any flow restrictions other than pipe size, which one of the following lists the approximate flow rates through the 3-inch and 6-inch diameter pipes. (Assume that water velocity is the same in each pipe.) 3-inch Pipe (lbm/sec) 6-inch Pipe (lbm/sec) A B C D
43 P2582 (B2581) Water at 90 F and 50 psig is flowing through a 10-inch diameter pipe at 100 lbm/sec. The pipe then splits into two pipes, a 6-inch diameter pipe and an 8-inch diameter pipe. Disregarding any flow restrictions other than pipe size, which one of the following lists the approximate flow rates through the 6-inch and 8-inch diameter pipes? (Assume that water velocity is the same in each pipe.) 6-inch Pipe (lbm/sec) 8-inch Pipe (lbm/sec) A B C D ANSWER: C. -43-
44 P2783 (B2723) Two identical centrifugal pumps (CPs) and two identical positive displacement pumps (PDPs) are able to take suction on a vented water storage tank and provide makeup water flow to a cooling water system. The pumps are capable of being cross-connected to provide multiple configurations. In single pump alignment, each pump will supply 100 gpm at a system pressure of 1,200 psig. Given the following information: Centrifugal Pumps Shutoff head = 1,500 psig Maximum design pressure = 2,000 psig Flow rate with no backpressure = 180 gpm Positive Displacement Pumps Maximum design pressure = 2,000 psig Which one of the following pump configurations will supply the highest makeup flow rate to the cooling water system if system pressure is 1,700 psig? A. Two CPs in series B. Two CPs in parallel C. Two PDPs in parallel D. One CP and one PDP in series (CP supplying PDP) ANSWER: C. -44-
45 P3183 A four-loop PWR nuclear power plant uses four identical reactor coolant pumps (RCPs) to supply reactor coolant flow through the reactor vessel. The plant is currently operating at 20 percent power with all RCPs in operation. Which one of the following describes the stable RCS flow rate through the reactor vessel following the trip of one RCP? (Assume that no operator actions are taken and the reactor does not trip.) A. Less than 75 percent of the original flow rate. B. Exactly 75 percent of the original flow rate. C. Greater than 75 percent of the original flow rate. D. Unpredictable without pump curves for the RCPs. ANSWER: C. -45-
46 P3582 A reactor shutdown has been performed because of leakage from the reactor coolant system (RCS) to a steam generator (SG) via a tube leak. Given the following current conditions: SG pressure is 1,000 psia. RCS pressure is 2,200 psia. RCS average temperature is 500 F. Leak rate from the RCS to the SG is 100 gpm. If RCS pressure is decreased to 1,600 psia, with no other changes in plant parameters, what will be the approximate leak rate from the RCS to the SG? A. 50 gpm B. 71 gpm C. 79 gpm D. 85 gpm -46-
47 P3683 (B3681) Two identical single-speed centrifugal pumps (CPs) and two identical single-speed positive displacement pumps (PDPs) are able to take suction on a vented water storage tank and provide makeup water flow to a cooling water system. The pumps are capable of being cross-connected to provide multiple configurations. In single pump alignment, each pump will supply 100 gpm at a system pressure of 1,200 psig. Given the following information: Centrifugal Pumps Discharge pressure at shutoff head = 1,500 psig Maximum design pressure = 2,000 psig Flow rate with no backpressure = 180 gpm Positive Displacement Pumps Maximum design pressure = 2,000 psig Which one of the following pump configurations will supply the highest initial flow rate to a cooling water system that is drained and depressurized? A. Two CPs in series B. Two CPs in parallel C. Two PDPs in parallel D. One CP and one PDP in series (CP supplying PDP) -47-
48 P4243 (B4242) Refer to the drawing of a venturi in a main steam line (see figure below). The venturi inlet and outlet pipe diameters are equal. A main steam line break downstream of the venturi causes the main steam mass flow rate through the venturi to increase. Soon, the steam reaches sonic velocity in the throat of the venturi. How will the main steam mass flow rate through the venturi be affected as the steam pressure downstream of the venturi continues to decrease? A. It will continue to increase at a rate that is dependent on the steam velocity in the throat of the venturi. B. It will continue to increase at a rate that is dependent on the differential pressure (P1 - P2) across the venturi. C. It will not continue to increase because the steam velocity cannot increase above sonic velocity in the throat of the venturi. D. It will not continue to increase because the differential pressure (P1 - P2) across the venturi cannot increase further once the steam reaches sonic velocity in the throat of the venturi. ANSWER: C. -48-
49 P4343 (B4342) Two identical single-speed centrifugal pumps (CPs) and two identical single-speed positive displacement pumps (PDPs) are able to take suction on a vented water storage tank and provide makeup water flow to a cooling water system. The pumps are capable of being cross-connected to provide multiple configurations. In single pump alignment, each pump will supply 100 gpm at a system pressure of 1,200 psig. Given the following information: Centrifugal Pumps Discharge pressure at shutoff head = 1,500 psig Maximum design pressure = 2,000 psig Flow rate with no backpressure = 180 gpm Positive Displacement Pumps Maximum design pressure = 2,000 psig Which one of the following pump configurations will supply the lowest initial flow rate of makeup water to a cooling water system that is drained and depressurized? A. Two CPs in series B. Two CPs in parallel C. Two PDPs in parallel D. One CP and one PDP in series (CP supplying PDP) ANSWER: D. -49-
50 P4543 (B4542) Refer to the drawing of a main water header that splits into two parallel headers (see figure below). Header A has a 2-inch diameter and header B has a 3-inch diameter. The velocity of the water in both headers is the same. If the main water header has a flow rate of 500 gpm, what is the approximate flow rate in each of the parallel headers? Header A (gpm) Header B (gpm) A B C D
51 P4643 (B4642) A length of pipe in a cooling water system uses a reducer fitting to decrease the pipe diameter from 6 inches to 4 inches. The flow rate in the 6-inch diameter section of pipe is 200 gpm. What is the flow rate in the 4-inch diameter section of pipe? A. 133 gpm B. 200 gpm C. 300 gpm D. 450 gpm P4743 A four-loop PWR nuclear power plant uses four identical single-speed reactor coolant pumps (RCPs) to supply reactor coolant flow through the reactor vessel. The plant is currently shut down with one RCP in operation. Which one of the following describes the stable reactor coolant flow rate through the reactor vessel following the start of a second RCP? A. Less than twice the original flow rate. B. Exactly twice the original flow rate. C. More than twice the original flow rate. D. Cannot be determined without additional information. ANSWER: A. -51-
52 P5543 (B5542) A vented water storage tank contains 60 feet of water at 70 F. A cracked weld at the bottom of the tank results in a leak rate of 12 gpm. If makeup water flow rate is 5 gpm, at what water level will the tank stabilize? A feet B feet C feet D. 0.0 feet ANSWER: C. P5943 (B5942) A vented water storage tank contains 64 feet of water at 70 F. A cracked weld at the bottom of the tank results in a leak rate of 12 gpm. At what water level will the leak rate be 3 gpm? A. 48 feet B. 32 feet C. 16 feet D. 4 feet ANSWER: D. -52-
53 P6143 (B6142) A plant shutdown will be performed because of leakage from the main condenser cooling water system into the main condenser via a tube leak. Given the following initial conditions: $ Main condenser pressure is 1.7 psia. $ Atmospheric pressure is 14.7 psia $ Main condenser cooling water pressure at the location of the tube leak is 18 psig. $ Cooling water leak rate into the main condenser is 80 gpm. If the main condenser is brought to atmospheric pressure, with no changes to the main condenser cooling water system parameters, what will be the approximate rate of cooling water leakage into the main condenser? A. 36 gpm B. 52 gpm C. 61 gpm D. 72 gpm ANSWER: C. -53-
54 P6543 (B6542) An ideal positive displacement pump is operating in an open system with the following initial parameters: Suction pressure = 10 psig Discharge pressure = 25 psig Flow rate = 100 gpm If the pump discharge pressure increases to 40 psig, the pump flow rate will... A. remain constant. B. decrease in direct proportion to the change in pump differential pressure. C. decrease in direct proportion to the square of the change in pump differential pressure. D. decrease in direct proportion to the square root of the change in pump differential pressure. ANSWER: A. -54-
55 P6743 (B6742) A centrifugal pump is operating at a constant speed in a closed system with the following initial parameters: Suction pressure = 10 psig Discharge pressure = 25 psig Pump flow rate = 500 gpm If the pump discharge flow control valve is throttled such that the pump discharge pressure increases to 40 psig, the change in pump flow rate will be... A. directly proportional to the square of the change in pump differential pressure. B. directly proportional to the square root of the change in pump differential pressure. C. inversely proportional to the square root of the change in pump differential pressure. D. impossible to determine from the provided information. ANSWER: D. -55-
56 P6843 (B6842) Refer to the drawing of a venturi in a steam line (see figure below). The venturi inlet and outlet pipe diameters at P1 and P2 are equal. Currently, steam is flowing through the venturi, reaching sonic velocity in the throat of the venturi. If the steam inlet pressure (P1) remains constant while the downstream pressure (P2) decreases, the mass flow rate of the steam will ; and the velocity of the steam at the venturi outlet will. A. increase; increase B. increase; remain the same C. remain the same; increase D. remain the same; remain the same ANSWER: C. -56-
57 P7143 The following are current parameter values for an operating PWR nuclear power plant: Steam generator (SG) pressure = 1,000 psia Main feed pump (MFP) discharge pressure = 1,220 psia If SG pressure does not change, what MFP discharge pressure will increase main feedwater mass flow rate by 10 percent? (Assume MFP inlet temperature remains the same. Also, assume all valves/components that contribute to head loss downstream of the MFP remain in their current configuration.) A. 1,242 psia B. 1,266 psia C. 1,293 psia D. 1,342 psia P7543 (B7542) Which one of the following will increase the head loss occurring in an operating cooling water system? A. Shifting two heat exchangers from parallel to series operation. B. Increasing the flow rate in the system by throttling open a flow control valve. C. Replacing a 20 foot section of 10-inch diameter pipe with a 10 foot section of 10-inch diameter pipe. D. Replacing a 20 foot section of 10-inch diameter pipe with a 20 foot section of 12-inch diameter pipe. ANSWER: A. -57-
58 P7660 (B7660) Which one of the following will decrease the head loss occurring in an operating cooling water system? A. Shifting two heat exchangers from parallel to series operation. B. Increasing the flow rate in the system by positioning a flow control valve more open. C. Replacing a 10 foot length of 10-inch diameter pipe with a 20 foot length of 10-inch diameter pipe. D. Replacing a 20 foot length of 12-inch diameter pipe with a 20 foot length of 10-inch diameter pipe. -58-
59 P7669 (B7669) Refer to the drawing of a main water header that splits into two parallel headers (see figure below). Header A has a 2-inch diameter and header B has a 4-inch diameter. The velocity of the water in both headers is the same. If the main water header has a flow rate of 500 gpm, what is the approximate flow rate in each of the parallel headers? Header A (gpm) Header B (gpm) A B C D ANSWER: A. -59-
TOPIC: 191004 KNOWLEDGE: K1.01 [3.3/3.5] Which one of the following contains indications of cavitation in an operating centrifugal pump?
![TOPIC: 191004 KNOWLEDGE: K1.01 [3.3/3.5] Which one of the following contains indications of cavitation in an operating centrifugal pump? TOPIC: 191004 KNOWLEDGE: K1.01 [3.3/3.5] Which one of the following contains indications of cavitation in an operating centrifugal pump?](/thumbs/17/105210.jpg) KNOWLEDGE: K1.01 [3.3/3.5] P21 Which one of the following contains indications of cavitation in an operating centrifugal pump? A. Low flow rate with low discharge pressure. B. Low flow rate with high discharge
KNOWLEDGE: K1.01 [3.3/3.5] P21 Which one of the following contains indications of cavitation in an operating centrifugal pump? A. Low flow rate with low discharge pressure. B. Low flow rate with high discharge
How To Clean Up A Reactor Water Cleanup
 General Electric Systems Technology Manual Chapter 2.8 Reactor Water Cleanup System TABLE OF CONTENTS 2.8 REACTOR CLEANUP SYSTEM... 1 2.8.1 Introduction... 2 2.8.2 System Description... 2 2.8.3 Component
General Electric Systems Technology Manual Chapter 2.8 Reactor Water Cleanup System TABLE OF CONTENTS 2.8 REACTOR CLEANUP SYSTEM... 1 2.8.1 Introduction... 2 2.8.2 System Description... 2 2.8.3 Component
Boiling Water Reactor Systems
 Boiling Water (BWR) s This chapter will discuss the purposes of some of the major systems and components associated with a boiling water reactor (BWR) in the generation of electrical power. USNRC Technical
Boiling Water (BWR) s This chapter will discuss the purposes of some of the major systems and components associated with a boiling water reactor (BWR) in the generation of electrical power. USNRC Technical
Pressurized Water Reactor B&W Technology Crosstraining Course Manual. Chapter 9.0. Integrated Control System
 Pressurized Water Reactor B&W Technology Crosstraining Course Manual Chapter 9.0 Integrated Control System TABLE OF CONTENTS 9.0 INTEGRATED CONTROL SYSTEM... 1 9.1 Introduction... 1 9.2 General Description...
Pressurized Water Reactor B&W Technology Crosstraining Course Manual Chapter 9.0 Integrated Control System TABLE OF CONTENTS 9.0 INTEGRATED CONTROL SYSTEM... 1 9.1 Introduction... 1 9.2 General Description...
Steam System Best Practices Condensate System Piping
 Steam System Best Practices Condensate System Piping Summary The best method for improving steam system energy efficiency, reducing chemical costs, and reducing make-up water costs is to return the maximum
Steam System Best Practices Condensate System Piping Summary The best method for improving steam system energy efficiency, reducing chemical costs, and reducing make-up water costs is to return the maximum
HS-901(A) BASIC STEAM HEATING SYSTEMS
 HS-901(A) BASIC HEATING SYSTEMS One-Pipe Two-Pipe Basic Steam Heating Systems One-pipe steam heating system EQUALIZER SAFETY FACTOR STATIC HEAD PRESSURE DROP 2" HEATING UNIT 15" DRIP CONNECTION In a one-pipe,
HS-901(A) BASIC HEATING SYSTEMS One-Pipe Two-Pipe Basic Steam Heating Systems One-pipe steam heating system EQUALIZER SAFETY FACTOR STATIC HEAD PRESSURE DROP 2" HEATING UNIT 15" DRIP CONNECTION In a one-pipe,
DIRECT STEAM INJECTION HOT WATER SYSTEMS FOR JACKETED HEATING
 By Philip Sutter Pick Heaters, Inc. DIRECT STEAM INJECTION HOT WATER SYSTEMS FOR JACKETED HEATING INTRODUCTION Many process plants currently use steam or hot water to heat jacketed devices such as tanks,
By Philip Sutter Pick Heaters, Inc. DIRECT STEAM INJECTION HOT WATER SYSTEMS FOR JACKETED HEATING INTRODUCTION Many process plants currently use steam or hot water to heat jacketed devices such as tanks,
Theory, Application, and Sizing of Air Valves
 Theory, Application, and Sizing of Air Valves VAL-MATIC VALVE AND MANUFACTURING CORP. 905 RIVERSIDE DRIVE, ELMHURST, IL 60126 TEL. (630) 941-7600 FAX. (630) 941-8042 www.valmatic.com 1 THEORY, APPLICATION,
Theory, Application, and Sizing of Air Valves VAL-MATIC VALVE AND MANUFACTURING CORP. 905 RIVERSIDE DRIVE, ELMHURST, IL 60126 TEL. (630) 941-7600 FAX. (630) 941-8042 www.valmatic.com 1 THEORY, APPLICATION,
Pressurized Water Reactor Systems
 Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) Systems For a nuclear power plant to perform the function of generating electricity, many different systems must perform their functions. These functions may range from
Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) Systems For a nuclear power plant to perform the function of generating electricity, many different systems must perform their functions. These functions may range from
Heating Water by Direct Steam Injection
 Heating Water by Direct Steam Injection Producing hot water by direct steam injection provides a solution where large volumes of hot water at precise temperatures are required, and where energy and space
Heating Water by Direct Steam Injection Producing hot water by direct steam injection provides a solution where large volumes of hot water at precise temperatures are required, and where energy and space
Pressure Locking & Thermal Binding In Wedge Gate & Parallel Slide Gate Valves
 Pressure Locking & Thermal Binding In Wedge Gate & Parallel Slide Gate Valves CRANE Energy Flow Solutions TM Donald H. Johnson Crane Energy Flow Solutions 1 Crane Co. Resolution Made By Richard Teller
Pressure Locking & Thermal Binding In Wedge Gate & Parallel Slide Gate Valves CRANE Energy Flow Solutions TM Donald H. Johnson Crane Energy Flow Solutions 1 Crane Co. Resolution Made By Richard Teller
The Piping System Model a New Life Cycle Document. Elements of the Piping System Model
 Piping System Model as a Life Cycle Document White Paper Introduction When designing piping systems, a variety of documents are created providing the details necessary to design, purchase, build, and test
Piping System Model as a Life Cycle Document White Paper Introduction When designing piping systems, a variety of documents are created providing the details necessary to design, purchase, build, and test
SOLVING REACTOR WATER CLEAN-UP SYSTEM ANOMALIES USING RELAP5 MOD3.3
 11 th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering Tokyo, JAPAN, April 20-23, 2003 ICONE11-36149 SOLVING REACTOR WATER CLEAN-UP SYSTEM ANOMALIES USING RELAP5 MOD3.3 Joseph S. Miller EDA, Inc 6397 True
11 th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering Tokyo, JAPAN, April 20-23, 2003 ICONE11-36149 SOLVING REACTOR WATER CLEAN-UP SYSTEM ANOMALIES USING RELAP5 MOD3.3 Joseph S. Miller EDA, Inc 6397 True
Flashing and Cavitation
 As seen in the Summer 2015 issue of MAGAZINE BACK TO BASICS A high-power boiler burner in a co-generation plant Flashing and Cavitation Some of the following questions may seem unrelated, but they all
As seen in the Summer 2015 issue of MAGAZINE BACK TO BASICS A high-power boiler burner in a co-generation plant Flashing and Cavitation Some of the following questions may seem unrelated, but they all
Chokes. Types Reasons Basics of Operations Application
 Chokes Types Reasons Basics of Operations Application Most Common Chokes Positive: Fixed orifice Disassemble to change bean Adjustable Provides variable orifice size through external adjustment Schematic
Chokes Types Reasons Basics of Operations Application Most Common Chokes Positive: Fixed orifice Disassemble to change bean Adjustable Provides variable orifice size through external adjustment Schematic
CENTRIFUGAL PUMP OVERVIEW Presented by Matt Prosoli Of Pumps Plus Inc.
 CENTRIFUGAL PUMP OVERVIEW Presented by Matt Prosoli Of Pumps Plus Inc. 1 Centrifugal Pump- Definition Centrifugal Pump can be defined as a mechanical device used to transfer liquid of various types. As
CENTRIFUGAL PUMP OVERVIEW Presented by Matt Prosoli Of Pumps Plus Inc. 1 Centrifugal Pump- Definition Centrifugal Pump can be defined as a mechanical device used to transfer liquid of various types. As
Minor losses include head losses through/past hydrants, couplers, valves,
 Lecture 10 Minor Losses & Pressure Requirements I. Minor Losses Minor (or fitting, or local ) hydraulic losses along pipes can often be estimated as a function of the velocity head of the water within
Lecture 10 Minor Losses & Pressure Requirements I. Minor Losses Minor (or fitting, or local ) hydraulic losses along pipes can often be estimated as a function of the velocity head of the water within
UNITED STATES NUCLEAR REGULATORY COMMISSION OFFICE OF NUCLEAR REACTOR REGULATION WASHINGTON, DC 20555-0001. June 16, 2011
 UNITED STATES NUCLEAR REGULATORY COMMISSION OFFICE OF NUCLEAR REACTOR REGULATION WASHINGTON, DC 20555-0001 June 16, 2011 NRC INFORMATION NOTICE 2011-12: REACTOR TRIPS RESULTING FROM WATER INTRUSION INTO
UNITED STATES NUCLEAR REGULATORY COMMISSION OFFICE OF NUCLEAR REACTOR REGULATION WASHINGTON, DC 20555-0001 June 16, 2011 NRC INFORMATION NOTICE 2011-12: REACTOR TRIPS RESULTING FROM WATER INTRUSION INTO
Evaluation Of Hybrid Air- Cooled Flash/Binary Power Cycle
 INL/CON-05-00740 PREPRINT Evaluation Of Hybrid Air- Cooled Flash/Binary Power Cycle Geothermal Resources Council Annual Meeting Greg Mines October 2005 This is a preprint of a paper intended for publication
INL/CON-05-00740 PREPRINT Evaluation Of Hybrid Air- Cooled Flash/Binary Power Cycle Geothermal Resources Council Annual Meeting Greg Mines October 2005 This is a preprint of a paper intended for publication
In-Line Air Separators
 Air Elimination & Control In-Line Air Separators The AC models of air separators deliver all the quality and performance you expect from Taco products. They are built to last with shell, heads and ANSI
Air Elimination & Control In-Line Air Separators The AC models of air separators deliver all the quality and performance you expect from Taco products. They are built to last with shell, heads and ANSI
Steam System Efficiency. Bill Lumsden Leidos Engineering
 Steam System Efficiency Bill Lumsden Leidos Engineering Steam System Efficiency Steam System Efficiency Key Take-aways: Review of the properties of ice, water, and steam Learn the basics of steam trap
Steam System Efficiency Bill Lumsden Leidos Engineering Steam System Efficiency Steam System Efficiency Key Take-aways: Review of the properties of ice, water, and steam Learn the basics of steam trap
Pump ED 101. Positive Displacement Pumps. Part I Reciprocating Pumps
 Pump ED 101 Positive Displacement Pumps Part I Reciprocating Pumps Joe Evans, Ph.D http://www.pumped101.com There are many pump designs that fall into the positive displacement category but, for the most
Pump ED 101 Positive Displacement Pumps Part I Reciprocating Pumps Joe Evans, Ph.D http://www.pumped101.com There are many pump designs that fall into the positive displacement category but, for the most
Water hammering in fire fighting installation
 Water hammering in fire fighting installation Forward One of major problems raised in the fire fighting network installed at Pioneer company for pharmaceutical industry /Sulaymania was the high water hammering
Water hammering in fire fighting installation Forward One of major problems raised in the fire fighting network installed at Pioneer company for pharmaceutical industry /Sulaymania was the high water hammering
Mechanical Seal Piping Plans
 Mechanical Seal Piping Plans Single Seals plans 01, 02, 03, 11, 13, 14, 21, 23, 31, 32, 41 Dual Seals plans 52, 53A, 53B, 53C, 54, 55 Quench Seals plans 62, 65A, 65B, 66A, 66B Gas Seals plans 72, 74, 75,
Mechanical Seal Piping Plans Single Seals plans 01, 02, 03, 11, 13, 14, 21, 23, 31, 32, 41 Dual Seals plans 52, 53A, 53B, 53C, 54, 55 Quench Seals plans 62, 65A, 65B, 66A, 66B Gas Seals plans 72, 74, 75,
How To Clean Water From An Ammonia Refrigeration System
 Water Contamination and Water Removal in Industrial Ammonia Refrigeration Systems By Ray Ficker, PE Effects of Water Contamination Water contamination in an industrial ammonia refrigeration system can
Water Contamination and Water Removal in Industrial Ammonia Refrigeration Systems By Ray Ficker, PE Effects of Water Contamination Water contamination in an industrial ammonia refrigeration system can
PUMPS TYPE OF PUMP PRESSURE/FLOW RATING CHARACTERISTICS. Centrifugal Low Pressure/High Flow Flow changes when
 PUMPS Pumps provide the means for moving water through the system at usable working pressures. The operation and maintenance of these pumps are some of the most important duties for many water utility
PUMPS Pumps provide the means for moving water through the system at usable working pressures. The operation and maintenance of these pumps are some of the most important duties for many water utility
Dynamic Behavior of BWR
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering 22.06 Engineering of Nuclear Systems Dynamic Behavior of BWR 1 The control system of the BWR controls the reactor pressure,
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering 22.06 Engineering of Nuclear Systems Dynamic Behavior of BWR 1 The control system of the BWR controls the reactor pressure,
Pump Maintenance - Repair
 Pump Maintenance - Repair Brian Trombly Mo Droppers Cummins Bridgeway, Gaylord, Mi The basic centrifugal pump consists of two main elements: 1. The rotating element which includes an impeller and a shaft.
Pump Maintenance - Repair Brian Trombly Mo Droppers Cummins Bridgeway, Gaylord, Mi The basic centrifugal pump consists of two main elements: 1. The rotating element which includes an impeller and a shaft.
CHAPTER II. This chapter contains a simplified description of the pipeline safety requirements. The complete text can be found in 49 CFR Part 192.
 CHAPTER II REGULATOR AND RELIEF DEVICES This chapter contains a simplified description of the pipeline safety requirements. The complete text can be found in 49 CFR Part 192. BASIC CONCEPT In understanding
CHAPTER II REGULATOR AND RELIEF DEVICES This chapter contains a simplified description of the pipeline safety requirements. The complete text can be found in 49 CFR Part 192. BASIC CONCEPT In understanding
FLASH TANK ECONOMIZER PRODUCT GUIDE
 FLASH TANK ECONOMIZER PRODUCT GUIDE Overview A flash tank is used to recover blowdown energy in the form of flash steam and blowdown. This can only be used with a deaerator or some other pressurized device.
FLASH TANK ECONOMIZER PRODUCT GUIDE Overview A flash tank is used to recover blowdown energy in the form of flash steam and blowdown. This can only be used with a deaerator or some other pressurized device.
Pumps: Convert mechanical energy (often developed from electrical source) into hydraulic energy (position, pressure and kinetic energy).
 HYDRAULIC MACHINES Used to convert between hydraulic and mechanical energies. Pumps: Convert mechanical energy (often developed from electrical source) into hydraulic energy (position, pressure and kinetic
HYDRAULIC MACHINES Used to convert between hydraulic and mechanical energies. Pumps: Convert mechanical energy (often developed from electrical source) into hydraulic energy (position, pressure and kinetic
Specific Volume of Liquid (Column 7). The volume per unit of mass in cubic feet per pound.
 Steam Tables What They Are How to Use Them The heat quantities and temperature/ pressure relationships referred to in this Handbook are taken from the Properties of Saturated Steam table. Definitions of
Steam Tables What They Are How to Use Them The heat quantities and temperature/ pressure relationships referred to in this Handbook are taken from the Properties of Saturated Steam table. Definitions of
DEVELOPMENT OF A TWIN SCREW EXPRESSOR AS A THROTTLE VALVE REPLACEMENT FOR WATER-COOLED CHILLERS
 DEVELOPMENT OF A TWIN SCREW EXPRESSOR AS A THROTTLE VALVE REPLACEMENT FOR WATER-COOLED CHILLERS J J Brasz, Carrier Corporation, Syracuse, NY, 13221, USA [email protected] I K Smith and N Stosic
DEVELOPMENT OF A TWIN SCREW EXPRESSOR AS A THROTTLE VALVE REPLACEMENT FOR WATER-COOLED CHILLERS J J Brasz, Carrier Corporation, Syracuse, NY, 13221, USA [email protected] I K Smith and N Stosic
CENTRIFUGAL PUMP SELECTION, SIZING, AND INTERPRETATION OF PERFORMANCE CURVES
 CENTRIFUGAL PUMP SELECTION, SIZING, AND INTERPRETATION OF PERFORMANCE CURVES 4.0 PUMP CLASSES Pumps may be classified in two general types, dynamic and positive displacement. Positive displacement pumps
CENTRIFUGAL PUMP SELECTION, SIZING, AND INTERPRETATION OF PERFORMANCE CURVES 4.0 PUMP CLASSES Pumps may be classified in two general types, dynamic and positive displacement. Positive displacement pumps
Hot Water Boilers and Controls Why Condensing Boilers are Different. Presented Oct. 14, 2008 Long Island Chapter, ASHRAE
 Hot Water Boilers and Controls Why Condensing Boilers are Different Presented Oct. 14, 2008 Long Island Chapter, ASHRAE H.W. Boilers and Controls Major types of boilers Advantages and disadvantages Resistance
Hot Water Boilers and Controls Why Condensing Boilers are Different Presented Oct. 14, 2008 Long Island Chapter, ASHRAE H.W. Boilers and Controls Major types of boilers Advantages and disadvantages Resistance
OPTIMIZING CONDENSER WATER FLOW RATES. W. A. Liegois, P.E. Stanley Consultants, Inc. Muscatine, Iowa
 OPTIMIZING CONDENSER WATER FLOW RATES W. A. Liegois, P.E. Stanley Consultants, Inc. Muscatine, Iowa T.A. Brown, P.E. Thermal Energy Corporation Houston, Texas ABSTRACT Most chillers are designed for a
OPTIMIZING CONDENSER WATER FLOW RATES W. A. Liegois, P.E. Stanley Consultants, Inc. Muscatine, Iowa T.A. Brown, P.E. Thermal Energy Corporation Houston, Texas ABSTRACT Most chillers are designed for a
VAL-MATIC VALVE AND MANUFACTURING CORP. 905 RIVERSIDE DRIVE, ELMHURST, IL 60126 TEL. (630) 941-7600 FAX.
 Cavitation in Valves VAL-MATIC VALVE AND MANUFACTURING CORP. 905 RIVERSIDE DRIVE, ELMHURST, IL 60126 TEL. (630) 941-7600 FAX. (630) 941-8042 www.valmatic.com CAVITATION IN VALVES INTRODUCTION Cavitation
Cavitation in Valves VAL-MATIC VALVE AND MANUFACTURING CORP. 905 RIVERSIDE DRIVE, ELMHURST, IL 60126 TEL. (630) 941-7600 FAX. (630) 941-8042 www.valmatic.com CAVITATION IN VALVES INTRODUCTION Cavitation
Why and How we Use Capacity Control
 Why and How we Use Capacity Control On refrigeration and air conditioning applications where the load may vary over a wide range, due to lighting, occupancy, product loading, ambient weather variations,
Why and How we Use Capacity Control On refrigeration and air conditioning applications where the load may vary over a wide range, due to lighting, occupancy, product loading, ambient weather variations,
Equivalents & Conversion Factors 406 Capacity Formulas for Steam Loads 407 Formulas for Control Valve Sizing 408-409
 Engineering Data Table of Contents Page No. I II Formulas, Conversions & Guidelines Equivalents & Conversion Factors 406 Capacity Formulas for Steam Loads 407 Formulas for Control Sizing 408-409 Steam
Engineering Data Table of Contents Page No. I II Formulas, Conversions & Guidelines Equivalents & Conversion Factors 406 Capacity Formulas for Steam Loads 407 Formulas for Control Sizing 408-409 Steam
VAD. Variable Area Desuperheaters
 Desuperheater overview Steam used in process plants can be superheated, that is, heated to a temperature above saturation. The excess of temperature above its saturation is called 'superheat'. Desuperheated
Desuperheater overview Steam used in process plants can be superheated, that is, heated to a temperature above saturation. The excess of temperature above its saturation is called 'superheat'. Desuperheated
SAMPLE CHAPTERS UNESCO EOLSS
 STEAM TURBINE OPERATIONAL ASPECTS R.A. Chaplin Department of Chemical Engineering, University of New Brunswick, Canada Keywords: Steam Turbines, Operation, Supersaturation, Moisture, Back Pressure, Governing
STEAM TURBINE OPERATIONAL ASPECTS R.A. Chaplin Department of Chemical Engineering, University of New Brunswick, Canada Keywords: Steam Turbines, Operation, Supersaturation, Moisture, Back Pressure, Governing
Oil and Coolant Circulating Heating System. Model - OCSM
 Oil and Coolant Circulating Heating System Model - OCSM Installation & Operation Manual 216280-000 REV 2 Identifying Your System The HOTSTART heating system is designed to heat fluids for use in marine
Oil and Coolant Circulating Heating System Model - OCSM Installation & Operation Manual 216280-000 REV 2 Identifying Your System The HOTSTART heating system is designed to heat fluids for use in marine
STEAM HEATING SYSTEM TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
 Page 1 of 9 PURPOSE Steam is the most commonly used heating medium for maintaining process temperatures. Compared to other heating media, steam contains a significant amount of heat energy, and this heat
Page 1 of 9 PURPOSE Steam is the most commonly used heating medium for maintaining process temperatures. Compared to other heating media, steam contains a significant amount of heat energy, and this heat
Practice Problems on Pumps. Answer(s): Q 2 = 1850 gpm H 2 = 41.7 ft W = 24.1 hp. C. Wassgren, Purdue University Page 1 of 16 Last Updated: 2010 Oct 29
 _02 A centrifugal with a 12 in. diameter impeller requires a power input of 60 hp when the flowrate is 3200 gpm against a 60 ft head. The impeller is changed to one with a 10 in. diameter. Determine the
_02 A centrifugal with a 12 in. diameter impeller requires a power input of 60 hp when the flowrate is 3200 gpm against a 60 ft head. The impeller is changed to one with a 10 in. diameter. Determine the
Example. Fluid Power. Circuits
 Example Fluid Power Circuits To Enhance Symbol Reading Skills To Work On Circuit Reading Skills With Answers HI LO Pump Circuit 18 A1 B1 17 16 15 13 Set 14 2,000 PSI PG2 Set 500 PSI 12 11 7 8 10 PG1 9
Example Fluid Power Circuits To Enhance Symbol Reading Skills To Work On Circuit Reading Skills With Answers HI LO Pump Circuit 18 A1 B1 17 16 15 13 Set 14 2,000 PSI PG2 Set 500 PSI 12 11 7 8 10 PG1 9
VACUUM REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS
 VACUUM REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS CHILL VACTOR The Croll-Reynolds CHILL-VACTOR is a chiller that uses a vapor flashing process. Water has a pressure-temperature relationship which is its boiling point. If its
VACUUM REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS CHILL VACTOR The Croll-Reynolds CHILL-VACTOR is a chiller that uses a vapor flashing process. Water has a pressure-temperature relationship which is its boiling point. If its
A basic introduction to steam
 A basic introduction to steam FOR HOT, COLD, MOIST AND DRY, FOUR CHAMPIONS FIERCE. STRIVE HERE FOR MASTERY Milton 1666 Steam Wonderful Steam Very high heat content Recyclable Clean, non toxic Biodegradable
A basic introduction to steam FOR HOT, COLD, MOIST AND DRY, FOUR CHAMPIONS FIERCE. STRIVE HERE FOR MASTERY Milton 1666 Steam Wonderful Steam Very high heat content Recyclable Clean, non toxic Biodegradable
Centrifugal Fans and Pumps are sized to meet the maximum
 Fans and Pumps are sized to meet the maximum flow rate required by the system. System conditions frequently require reducing the flow rate. Throttling and bypass devices dampers and valves are installed
Fans and Pumps are sized to meet the maximum flow rate required by the system. System conditions frequently require reducing the flow rate. Throttling and bypass devices dampers and valves are installed
2. System Based Design Descriptions and ITAAC AP1000 Design Control Document
 2.3.2 Chemical and Volume Control System Design Description The chemical and volume control system (CVS) provides reactor coolant system (RCS) purification, RCS inventory control and makeup, chemical shim
2.3.2 Chemical and Volume Control System Design Description The chemical and volume control system (CVS) provides reactor coolant system (RCS) purification, RCS inventory control and makeup, chemical shim
HIGH TEMPERATURE TWIN SCREW PUMPS. By: David B. Parker Two Screw Product Engineer IMO Pump Warren Warren, Massachusetts
 HIGH TEMPERATURE TWIN SCREW PUMPS By: David B. Parker Two Screw Product Engineer IMO Pump Warren Warren, Massachusetts David B. Parker is the Two Screw Product Engineer for IMO Pump - Warren, in Warren,
HIGH TEMPERATURE TWIN SCREW PUMPS By: David B. Parker Two Screw Product Engineer IMO Pump Warren Warren, Massachusetts David B. Parker is the Two Screw Product Engineer for IMO Pump - Warren, in Warren,
Operational Reactor Safety 22.091/22.903
 Operational Reactor Safety 22.091/22.903 Professor Andrew C. Kadak Professor of the Practice Lecture 19 Three Mile Island Accident Primary system Pilot operated relief valve Secondary System Emergency
Operational Reactor Safety 22.091/22.903 Professor Andrew C. Kadak Professor of the Practice Lecture 19 Three Mile Island Accident Primary system Pilot operated relief valve Secondary System Emergency
LECTURE 28 to 29 ACCUMULATORS FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 LECTURE 28 to 29 ACCUMULATORS FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1. Define an accumulator and explain its function A hydraulic accumulator is a device that stores the potential energy of an incompressible fluid
LECTURE 28 to 29 ACCUMULATORS FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1. Define an accumulator and explain its function A hydraulic accumulator is a device that stores the potential energy of an incompressible fluid
OUR PRODUCTS TRH-TRS-TRM-TRV. LIQUID RING VACUUM PUMPS AND COMPRESSORS Capacity up to 2100 ACFM Vacuum to 29 Hg. Our Other Products.
 Our Other Products OUR PRODUCTS Liquid Ring & Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps and Systems Liquid Ring Vacuum Pumps: 3 CFM to,000 CFM Liquid Ring Compressors up to 1 psig Heat Transfer Pumps for hot thermal oils
Our Other Products OUR PRODUCTS Liquid Ring & Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps and Systems Liquid Ring Vacuum Pumps: 3 CFM to,000 CFM Liquid Ring Compressors up to 1 psig Heat Transfer Pumps for hot thermal oils
No. Name Description Main input Data Main Output Data. cooling duty, process in/out temperature, inlet air temperature
 1 AIRCOOLER Air cooler preliminary sizing cooling duty, process in/out temperature, inlet air temperature No of fans, Air cooler Dimension, bare area, no of rows, Fan Diameter, fan power 2 BLOW DOWN FACILITATOR
1 AIRCOOLER Air cooler preliminary sizing cooling duty, process in/out temperature, inlet air temperature No of fans, Air cooler Dimension, bare area, no of rows, Fan Diameter, fan power 2 BLOW DOWN FACILITATOR
Select the Right Relief Valve - Part 1 Saeid Rahimi
 Select the Right Relief Valve - Part 1 Saeid Rahimi 8-Apr-01 Introduction Selecting a proper type of relief valve is an essential part of an overpressure protection system design. The selection process
Select the Right Relief Valve - Part 1 Saeid Rahimi 8-Apr-01 Introduction Selecting a proper type of relief valve is an essential part of an overpressure protection system design. The selection process
CPX/HT Series. REFRIGERATED AND HIGH TEMPERATURE DRYER 12 to 2400 CFM. High-performance products. Designed for you!
 CPX/HT Series REFRIGERATED AND HIGH TEMPERATURE DRYER 12 to 2400 CFM High-performance products. Designed for you! COMPRESSED AIR WATER CONTAMINATION Atmospheric air contains water in vapor form in different
CPX/HT Series REFRIGERATED AND HIGH TEMPERATURE DRYER 12 to 2400 CFM High-performance products. Designed for you! COMPRESSED AIR WATER CONTAMINATION Atmospheric air contains water in vapor form in different
REGULATING VALVE APPLICATIONS
 REGULATING APPLICATIONS GENERAL REGULAR APPLICATION & INSTALLATION NOTES Regulator Application & Installation Notes The following are considerations for all steam regulator installations, as system operation
REGULATING APPLICATIONS GENERAL REGULAR APPLICATION & INSTALLATION NOTES Regulator Application & Installation Notes The following are considerations for all steam regulator installations, as system operation
Chapter 19 Purging Air from Piping and Vessels in Hydrocarbon Service
 BP Lower 48 Onshore Operations Safety Manual Page 4.19 1 Chapter 19 Purging Air from Piping and Vessels in Hydrocarbon Service I. General Requirements A. After motor vehicle accidents and underground excavation
BP Lower 48 Onshore Operations Safety Manual Page 4.19 1 Chapter 19 Purging Air from Piping and Vessels in Hydrocarbon Service I. General Requirements A. After motor vehicle accidents and underground excavation
Turbo Tech 101 ( Basic )
 Turbo Tech 101 ( Basic ) How a Turbo System Works Engine power is proportional to the amount of air and fuel that can get into the cylinders. All things being equal, larger engines flow more air and as
Turbo Tech 101 ( Basic ) How a Turbo System Works Engine power is proportional to the amount of air and fuel that can get into the cylinders. All things being equal, larger engines flow more air and as
HOW TO SELECT A LOW VOLUME (L.V ) BOILER
 HOW TO SELECT A LOW VOLUME (L.V ) BOILER FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS OR COMMENTS ON BOILERS Dear Potential Customer: Low Volume Operator Exempt boilers have been marketed in Ontario to eliminate the requirement
HOW TO SELECT A LOW VOLUME (L.V ) BOILER FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS OR COMMENTS ON BOILERS Dear Potential Customer: Low Volume Operator Exempt boilers have been marketed in Ontario to eliminate the requirement
Air Eliminators and Combination Air Eliminators Strainers
 Description Air Eliminators and Combination Air Eliminator Strainers are designed to provide separation, elimination and prevention of air in piping systems for a variety of installations and conditions.
Description Air Eliminators and Combination Air Eliminator Strainers are designed to provide separation, elimination and prevention of air in piping systems for a variety of installations and conditions.
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE
 IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE To: Our Valued Customers User safety is a major focus in the design of our products. Following the precautions outlined in this manual will minimize your risk of injury. ITT Goulds
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE To: Our Valued Customers User safety is a major focus in the design of our products. Following the precautions outlined in this manual will minimize your risk of injury. ITT Goulds
Table V. Troubleshooting Checklist for Refrigeration Systems. Air or non-condensable gas in system. Inlet water warm.
 Table V Troubleshooting Checklist for Refrigeration Systems TROUBLE POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTIVE MEASURE High condensing pressure. Low condensing pressure. Air or non-condensable gas in system. Inlet water
Table V Troubleshooting Checklist for Refrigeration Systems TROUBLE POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTIVE MEASURE High condensing pressure. Low condensing pressure. Air or non-condensable gas in system. Inlet water
Overview. Introduction Cooling Tower Basics Principles of Operation Types of Cooling Towers Common Applications Design Considerations
 Stephen Lowe ASHRAE Hampton Roads Chapter Past President AECOM Design Mechanical Engineering Discipline Manager, Virginia Beach Division Professional Engineer Commonwealth of Virginia, NCEES BSME University
Stephen Lowe ASHRAE Hampton Roads Chapter Past President AECOM Design Mechanical Engineering Discipline Manager, Virginia Beach Division Professional Engineer Commonwealth of Virginia, NCEES BSME University
Industrial Process Pump Safety Manual IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE
 Industrial Process Pump Safety Manual IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE To: Our Valued Customers User safety is a major focus in the design of our products. Following the precautions outlined in this manual will
Industrial Process Pump Safety Manual IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE To: Our Valued Customers User safety is a major focus in the design of our products. Following the precautions outlined in this manual will
www.klmtechgroup.com TABLE OF CONTENT
 Page : 1 of 38 Project Engineering Standard www.klmtechgroup.com KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru Malaysia CAUSTIC AND CHEMICAL TABLE OF CONTENT
Page : 1 of 38 Project Engineering Standard www.klmtechgroup.com KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru Malaysia CAUSTIC AND CHEMICAL TABLE OF CONTENT
COUNTERBALANCE VALVES
 COUNTERBALANCE VALVES Introduction They are modulating valves which allow free flow into the actuator and then block the reverse flow until they feel a pilot pressure inversely proportional to the load
COUNTERBALANCE VALVES Introduction They are modulating valves which allow free flow into the actuator and then block the reverse flow until they feel a pilot pressure inversely proportional to the load
Desuperheater Online Program Sizing Guidance
 Local regulations may restrict the use of this product to below the conditions quoted. In the interests of development and improvement of the product, we reserve the right to change the specification without
Local regulations may restrict the use of this product to below the conditions quoted. In the interests of development and improvement of the product, we reserve the right to change the specification without
Michael Montgomery Marketing Product Manager Rosemount Inc. Russ Evans Manager of Engineering and Design Rosemount Inc.
 ASGMT / Averaging Pitot Tube Flow Measurement Michael Montgomery Marketing Product Manager Rosemount Inc. Russ Evans Manager of Engineering and Design Rosemount Inc. Averaging Pitot Tube Meters Introduction
ASGMT / Averaging Pitot Tube Flow Measurement Michael Montgomery Marketing Product Manager Rosemount Inc. Russ Evans Manager of Engineering and Design Rosemount Inc. Averaging Pitot Tube Meters Introduction
Improved Modern Control Station for High Pressure Bypass System in Thermal Power Plant
 Improved Modern Control Station for High Pressure Bypass System in Thermal Power Plant P.Karthikeyan 1, A.Nagarajan 2, A.Vinothkumar 3 UG Student, Department of EEE, S.A. Engineering College, Chennai,
Improved Modern Control Station for High Pressure Bypass System in Thermal Power Plant P.Karthikeyan 1, A.Nagarajan 2, A.Vinothkumar 3 UG Student, Department of EEE, S.A. Engineering College, Chennai,
Open Cycle Refrigeration System
 Chapter 9 Open Cycle Refrigeration System Copy Right By: Thomas T.S. Wan 温 到 祥 著 Sept. 3, 2008 All rights reserved An open cycle refrigeration system is that the system is without a traditional evaporator.
Chapter 9 Open Cycle Refrigeration System Copy Right By: Thomas T.S. Wan 温 到 祥 著 Sept. 3, 2008 All rights reserved An open cycle refrigeration system is that the system is without a traditional evaporator.
Steam-jet vacuum systems combine ejectors, condensers
 DESIGNING STEAM JET VACUUM SYSTEMS For cost-effective vacuum pumping, the proper placement of condensers and pipe supports are critical DAVID B. BIRGENHEIER AND THOMAS L. BUTZBACH, Graham Manufacturing
DESIGNING STEAM JET VACUUM SYSTEMS For cost-effective vacuum pumping, the proper placement of condensers and pipe supports are critical DAVID B. BIRGENHEIER AND THOMAS L. BUTZBACH, Graham Manufacturing
Float and Thermostatic Traps Series H, C and X
 Hoffman Specialty Installation & Maintenance Instructions HS-(E) and Thermostatic Traps Series H, C and X Series C & NPT Series C NPT Series X NPT Series C NPT Series H Ratings Maximum Max. Operating NPT
Hoffman Specialty Installation & Maintenance Instructions HS-(E) and Thermostatic Traps Series H, C and X Series C & NPT Series C NPT Series X NPT Series C NPT Series H Ratings Maximum Max. Operating NPT
Anti-Cavitation Trim. Eliminates cavitation damage Reduces noise Preserves valve and surrounding pipe systems. singervalve.com
 Anti-Cavitation Trim Eliminates cavitation damage Reduces noise Preserves valve and surrounding pipe systems Say Goodbye to Cavitation Damage! Cavitation, a common problem in pumps and control valves,
Anti-Cavitation Trim Eliminates cavitation damage Reduces noise Preserves valve and surrounding pipe systems Say Goodbye to Cavitation Damage! Cavitation, a common problem in pumps and control valves,
Vogt Valves The Connection Bulletin for Forged Steel Flow Control Valves CB 15
 The Connection Bulletin for Forged Steel Flow Control Valves CB 15 Flow Control Division Forged Steel Flow Control Valves GRADUATED DIAL AND INDICATOR FULLY GUIDED V-PORT THROTTLING DISC AND INTEGRAL HARD
The Connection Bulletin for Forged Steel Flow Control Valves CB 15 Flow Control Division Forged Steel Flow Control Valves GRADUATED DIAL AND INDICATOR FULLY GUIDED V-PORT THROTTLING DISC AND INTEGRAL HARD
The Fundamentals of Gas Flow Calibration
 The Fundamentals of Gas Flow Calibration Application Note Introduction Understanding the fundamentals of gas flow calibration is essential for evaluating calibration systems, estimating the magnitude of
The Fundamentals of Gas Flow Calibration Application Note Introduction Understanding the fundamentals of gas flow calibration is essential for evaluating calibration systems, estimating the magnitude of
I. STEAM GENERATION, BOILER TYPES
 I. STEAM GENERATION, BOILER TYPES and BOILER PLANT SYSTEMS 1 Steam Generation Water s Unique Properties: High Thermal Capacity (Specific Heat) High Critical Temperature Ideal Medium for Heat Delivery High
I. STEAM GENERATION, BOILER TYPES and BOILER PLANT SYSTEMS 1 Steam Generation Water s Unique Properties: High Thermal Capacity (Specific Heat) High Critical Temperature Ideal Medium for Heat Delivery High
BOWIE PUMPS OPERATION - MAINTENANCE
 BOWIE PUMPS OPERATION - MAINTENANCE PUMPING PRINCIPLE: The meshing owieeof the gears cause a slight depression, with the resulting enmeshing of the gears causing a vacuum drawing the fluid being pumped
BOWIE PUMPS OPERATION - MAINTENANCE PUMPING PRINCIPLE: The meshing owieeof the gears cause a slight depression, with the resulting enmeshing of the gears causing a vacuum drawing the fluid being pumped
Constantemp Double Wall Low pressure steam-water Heater F-340LDW,F-640LDW, F-940LDW and F-1240LDW
 Installation, Operating and Maintenance Instructions 90/4.5.5 Rev. 0 Constantemp Double Wall Low pressure steam-water Heater F-340LDW,F-640LDW, F-940LDW and F-1240LDW Table of Contents SECTION I... 2 INSTALLATION...
Installation, Operating and Maintenance Instructions 90/4.5.5 Rev. 0 Constantemp Double Wall Low pressure steam-water Heater F-340LDW,F-640LDW, F-940LDW and F-1240LDW Table of Contents SECTION I... 2 INSTALLATION...
Turbocharger System Optimization
 This Turbo Tech Section is intended to cover many of the auxiliary systems in a more complete and in-depth manner than what is originally covered in Turbo Tech 101, Turbo Tech 102, Turbo Tech 103 and Diesel
This Turbo Tech Section is intended to cover many of the auxiliary systems in a more complete and in-depth manner than what is originally covered in Turbo Tech 101, Turbo Tech 102, Turbo Tech 103 and Diesel
CONTAMINANT REMOVAL FROM CENTRIFUGAL SYSTEMS
 CONTAMINANT REMOVAL FROM CENTRIFUGAL SYSTEMS BULLETIN 240-10-3 June 2004 Supersedes June 1983 Many centrifugal systems get little maintenance. As a result they operate with the refrigerant highly contaminated
CONTAMINANT REMOVAL FROM CENTRIFUGAL SYSTEMS BULLETIN 240-10-3 June 2004 Supersedes June 1983 Many centrifugal systems get little maintenance. As a result they operate with the refrigerant highly contaminated
Overview of Heat Recovery Boiler Systems and Operating Costs Factors Effecting Blowdown Blowdown Heat Recovery The Energy Tank
 Overview of Heat Recovery Boiler Systems and Operating Costs Factors Effecting Blowdown Blowdown Heat Recovery The Energy Tank Unbiased, Third-Party, Water & Energy Management Consulting Firm: - Not affiliated
Overview of Heat Recovery Boiler Systems and Operating Costs Factors Effecting Blowdown Blowdown Heat Recovery The Energy Tank Unbiased, Third-Party, Water & Energy Management Consulting Firm: - Not affiliated
1. Conductivity < 15 micro ohms/cm 2. ph of 6.0 to 9.0 3. Nonvolatile TOC content < 1.0 ppm
 PART 1: GENERAL 1.01 Purpose: A. This standard is intended to provide useful information to the Professional Service Provider (PSP) to establish a basis of design. The responsibility of the engineer is
PART 1: GENERAL 1.01 Purpose: A. This standard is intended to provide useful information to the Professional Service Provider (PSP) to establish a basis of design. The responsibility of the engineer is
Quiz On Information Learned From Chapter 1
 Quiz On Information Learned From Chapter 1 1. Most hydraulic circuits are designed by: A. mechanical engineers. B. fluid power engineers. C. fluid power distributor salesmen. 2. Atmospheric pressure at
Quiz On Information Learned From Chapter 1 1. Most hydraulic circuits are designed by: A. mechanical engineers. B. fluid power engineers. C. fluid power distributor salesmen. 2. Atmospheric pressure at
A Guide to Trouble-Free Cooling Towers
 A Guide to Trouble-Free Cooling Towers A basic understanding of cooling tower operation and maintenance will help keep a cooling water system running in top condition, year after year By David M. Suptic
A Guide to Trouble-Free Cooling Towers A basic understanding of cooling tower operation and maintenance will help keep a cooling water system running in top condition, year after year By David M. Suptic
ELECTRIC/DIESEL FIRE PUMP CHECK LIST
 BUILDING NAME: DESIGNER: SCO REPRESENTATIVE: PUMP MANUF.: LOCATION: INSTALLER: DATE: OWNER NAME: INSTALLATION Certificate for flushing and hydrostatic test furnished Piping been hydrostatically tested
BUILDING NAME: DESIGNER: SCO REPRESENTATIVE: PUMP MANUF.: LOCATION: INSTALLER: DATE: OWNER NAME: INSTALLATION Certificate for flushing and hydrostatic test furnished Piping been hydrostatically tested
SECTION 5 COMMERCIAL REFRIGERATION UNIT 22 CONDENSERS
 SECTION 5 COMMERCIAL REFRIGERATION UNIT 22 CONDENSERS UNIT OBJECTIVES After studying this unit, the reader should be able to explain the purpose of the condenser in a refrigeration system. describe differences
SECTION 5 COMMERCIAL REFRIGERATION UNIT 22 CONDENSERS UNIT OBJECTIVES After studying this unit, the reader should be able to explain the purpose of the condenser in a refrigeration system. describe differences
FIXED DISPLACEMENT HYDRAULIC VANE PUMPS BQ SERIES
 BQ FIXED DISPLACEMENT HYDRAULIC VANE PUMPS BQ SERIES Versatility, power, compactness and low running costs are the main characteristics of B&C vane pumps. All the components subject to wear are contained
BQ FIXED DISPLACEMENT HYDRAULIC VANE PUMPS BQ SERIES Versatility, power, compactness and low running costs are the main characteristics of B&C vane pumps. All the components subject to wear are contained
FIXED DISPLACEMENT HYDRAULIC VANE PUMPS BQ SERIES
 BQ FIXED DISPLACEMENT HYDRAULIC VANE PUMPS BQ SERIES Versatility, power, compactness and low running costs are the main characteristics of B&C vane pumps. All the components subject to wear are contained
BQ FIXED DISPLACEMENT HYDRAULIC VANE PUMPS BQ SERIES Versatility, power, compactness and low running costs are the main characteristics of B&C vane pumps. All the components subject to wear are contained
PEERLESS PUMP COMPANY SYSTEM ANALYSIS FOR PUMPING EQUIPMENT SELECTION
 PEERLESS PUMP COMPANY SYSTEM ANALYSIS FOR PUMPING EQUIPMENT SELECTION Peerless Pump Company 005 Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. Street P.O. Box 706 Indianapolis, Indiana 4607-706 Phone: (317) 95-9661 Fax: (317)
PEERLESS PUMP COMPANY SYSTEM ANALYSIS FOR PUMPING EQUIPMENT SELECTION Peerless Pump Company 005 Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. Street P.O. Box 706 Indianapolis, Indiana 4607-706 Phone: (317) 95-9661 Fax: (317)
The Versatile Differential Pressure Transmitter. By David Gunn Honeywell Process Solutions
 The Versatile Differential Pressure Transmitter By David Gunn Honeywell Process Solutions The Versatile Differential Pressure Transmitter 2 Table of Contents Abstract... 3 Pressure Fundamentals... 3 Applications...
The Versatile Differential Pressure Transmitter By David Gunn Honeywell Process Solutions The Versatile Differential Pressure Transmitter 2 Table of Contents Abstract... 3 Pressure Fundamentals... 3 Applications...
Vacuum Control. Vacuum Applications. Vacuum Regulators. Vacuum Breakers (Relief Valves) Vacuum Control Devices. Vacuum Terminology
 Vacuum Applications Vacuum regulators and breakers are widely used in process plants. Conventional regulators and relief valves might be suitable for service if applied correctly. This section provides
Vacuum Applications Vacuum regulators and breakers are widely used in process plants. Conventional regulators and relief valves might be suitable for service if applied correctly. This section provides
A BRIEF INTRODUCTION TO CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS
 A BRIEF INTRODUCTION TO CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS figure below is a cross section of a centrifugal pump and shows the two basic parts. Joe Evans, Ph.D IMPELLER This publication is based upon an introductory, half
A BRIEF INTRODUCTION TO CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS figure below is a cross section of a centrifugal pump and shows the two basic parts. Joe Evans, Ph.D IMPELLER This publication is based upon an introductory, half
Module 9: Basics of Pumps and Hydraulics Instructor Guide
 Module 9: Basics of Pumps and Hydraulics Instructor Guide Activities for Unit 1 Basic Hydraulics Activity 1.1: Convert 45 psi to feet of head. 45 psis x 1 ft. = 103.8 ft 0.433 psi Activity 1.2: Determine
Module 9: Basics of Pumps and Hydraulics Instructor Guide Activities for Unit 1 Basic Hydraulics Activity 1.1: Convert 45 psi to feet of head. 45 psis x 1 ft. = 103.8 ft 0.433 psi Activity 1.2: Determine
Pump Selection and Sizing (ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINE)
 Guidelines for Processing Plant Page : 1 of 51 Rev 01 Feb 2007 Rev 02 Feb 2009 Rev 03 KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru. (ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINE)
Guidelines for Processing Plant Page : 1 of 51 Rev 01 Feb 2007 Rev 02 Feb 2009 Rev 03 KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru. (ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINE)
FIXED DISPLACEMENT HYDRAULIC VANE PUMPS BQ SERIES
 BQ FIXED DISPLACEMENT HYDRAULIC VANE PUMPS BQ SERIES Versatility, power, compactness and low running costs are the main characteristics of B&C vane pumps. All the components subject to wear are contained
BQ FIXED DISPLACEMENT HYDRAULIC VANE PUMPS BQ SERIES Versatility, power, compactness and low running costs are the main characteristics of B&C vane pumps. All the components subject to wear are contained
APPENDIX A CONTROL VALVE TESTING PROCEDURES AND EQUATIONS FOR LIQUID FLOWS
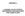 APPENDIX A CONTROL VALVE TESTING PROCEDURES AND EQUATIONS FOR LIQUID FLOWS Section A.1. Flow Coefficients Definition The flow coefficient or pressure loss coefficient is used to relate the pressure loss
APPENDIX A CONTROL VALVE TESTING PROCEDURES AND EQUATIONS FOR LIQUID FLOWS Section A.1. Flow Coefficients Definition The flow coefficient or pressure loss coefficient is used to relate the pressure loss
Characteristics of Evaporators
 Characteristics of Evaporators Roger D. Holder, CM, MSME 10-28-2003 Heat or Energy In this paper, we will discuss the characteristics of an evaporator coil. The variance of the operational condenses of
Characteristics of Evaporators Roger D. Holder, CM, MSME 10-28-2003 Heat or Energy In this paper, we will discuss the characteristics of an evaporator coil. The variance of the operational condenses of
Course available 24/7 for up to six months from the date of purchase or until completion
 SPED ONLINE COURSE TRAINING Piper BootCamp and Process Plant Layout BOTH Piper BootCamp and Process Plant Layout online courses contain: Approximately 25 hours of online videos Printable notes Links to
SPED ONLINE COURSE TRAINING Piper BootCamp and Process Plant Layout BOTH Piper BootCamp and Process Plant Layout online courses contain: Approximately 25 hours of online videos Printable notes Links to
Refrigeration and Airconditioning Prof. M. Ramgopal Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Refrigeration and Airconditioning Prof. M. Ramgopal Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 22 Refrigeration System Components: Compressor (Continued)
Refrigeration and Airconditioning Prof. M. Ramgopal Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 22 Refrigeration System Components: Compressor (Continued)
