Deep Neck Space Infections. Michael D. Puricelli, M.D. Jeffrey B. Jorgensen, M.D.
|
|
|
- Eustace Flowers
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Deep Neck Space Infections Michael D. Puricelli, M.D. Jeffrey B. Jorgensen, M.D.
2 Goals Review fascia and fascial spaces to facilitate understanding of how infections move through the neck. Provide current data on appropriate work-up and management of deep neck space infections. Review key complications of deep neck space infections.
3 Background Dividing the extracranial head and neck into different spaces dates back to the 1800s Arose to resolve the inexplicable extension of infections of the extracranial head and neck to other areas These studies led to detailed descriptions of the cervical fascia and the numerous soft tissue spaces that were contained within the fascial layers.
4 History Highly nuanced and complex "the cervical fascia appear in a new form under the pen of each author who attempts to describe them, French anatomist Malgaigne in Definition of fascia a band of connective tissue that surrounds structures (such as enveloping muscles), giving rise to potential tissue spaces and pathways that allow for infection to spread. Niel S. Norton. Netter s Head and Neck Anatomy for Dentistry. 2007
5 Deep Neck Space Infections
6 Deep Neck Space Infections
7 My Goal Mukherji SK, Castillo M. A simplified approach to the spaces of the suprahyoid neck. Radiol Clin North Am Sep;36(5):761-80, v. Review. PubMed PMID:
8 Overview Case Presentation Fascial Planes of the Head and Neck Deep Neck Spaces Microbiology Management Complications of Infections
9 Case ER consult 4 y/o female several days fever and neck stiffness What additional information would you like?
10 History HPI Inflammatory symptoms Pain, fever, swelling, and redness Onset and duration Localizing symptoms Dysphagia, odynophagia, drooling, hot potato voice, hoarseness, dyspnea, trismus, and ear pain Risk Factors (source) Peds - travel, pets, rodents, unpasturized milk, uncooked meat, tuberculosis exposure Adult - recent dental work, upper airway surgery or intubation, intravenous drug use, sinusitis, pharyngitis, otitis, or blunt or penetrating soft tissue trauma Lymphoma B-symptoms PMH Antibiotic allergies Recent antibiotic therapy Immunodeficiency HIV, hepatitis, diabetes, collagen vascular diseases, hematologic malignancy, and recent chemotherapy or steroid Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections
11 Case Onset 4 days ago Associated symptoms: purulent rhinorrhea, reduced oral intake, pain with swallowing. Denies hoarseness or voice changes. No trismus or ear pain. No skin erythema/crepitus. No recent choking episodes. No recent tonsillitis. No prior episodes. No recent dental work, intubation/upper airway procedures, penetrating trauma. No chest pain/dyspnea. No Rx to date. No immunodeficiency. What are the most important things to look for on exam?
12 Physical Examination Full examination, as in all patients. High points: Difficulty with mouth opening indicates inflammation spread Parapharyngeal, pterygoid, or masseteric spaces. Alveolar swelling and decayed, loose, tender, or broken teeth. Floor of the mouth Ludwig s angina. Stensen's and Wharton's ducts Upper dentition, paranasal sinuses, facial soft tissues Facial and ophthalmic venous drainage EOM and pupillary light reflex Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections
13 Case T: 38.9, respirations 24/min No stridor/stertor. CN 2-12 WNL. Normal dentition. No facial pain. Nasal crusting. Pain with palpation of the neck. Diffuse minimally enlarged lymphadenopathy. EOMI, vision normal What do you want to do next?
14 Case WBC 18.2, 88% neutrophils Mild prerenal azotemia
15 Case 2 cm
16 Case Management? Medical Surgical
17 Overview Case Presentation Fascial Planes of the Head and Neck Deep Neck Spaces Microbiology Management Complications of Infections
18 Fascia Planes of the Neck Superficial Cervical Fascia Deep Cervical Fascia Superficial layer Middle layer Deep layer Carotid Sheath Mukherji SK, Castillo M. A simplified approach to the spaces of the suprahyoid neck. Radiol Clin North Am Sep;36(5):761-80, v. Review. PubMed PMID:
19 Vieira F, Allen SM, Stocks RM, Thompson JW. Deep neck infection. Otolaryngol Clin North Am Jun;41(3):459-83, vii. doi: /j.otc Review. PubMed PMID:
20 Superficial Cervical Fascia Vieira F, Allen SM, Stocks RM, Thompson JW. Deep neck infection. Otolaryngol Clin North Am Jun;41(3):459-83, vii. doi: /j.otc Review. PubMed PMID:
21 Superficial Cervical Fascia Deep to the dermis Envelops Platysma and muscles of facial expression Incorporates musculoaponeurotic system Boundaries Superior: zygomatic process Inferior: clavicle, axillae, deltopectoral region Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections
22 Vieira F, Allen SM, Stocks RM, Thompson JW. Deep neck infection. Otolaryngol Clin North Am Jun;41(3):459-83, vii. doi: /j.otc Review. PubMed PMID:
23 Superficial Layer of Deep Cervical Fascia Vieira F, Allen SM, Stocks RM, Thompson JW. Deep neck infection. Otolaryngol Clin North Am Jun;41(3):459-83, vii. doi: /j.otc Review. PubMed PMID:
24 Deep Cervical Fascia Superficial layer Investing fascia Envelopes Trapezius, sternocleidomastoid, muscles of mastication (masseter, pterygoids, temporalis) Encloses parotid gland and covers the submandibular gland Forms stylomandibular ligament: separates the parotid from the submandibular gland Contributes to the lateral aspect of the carotid sheath Extent Superior Zygomatic arch and mandible Inferior Attaches to the clavicle, acromion, and spine of the scapula Deeply Extends along the temporal bone to the carotid canal Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections Anderson JC, Homan JA. Radiographic correlation with neck anatomy. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am Aug;20(3): doi: /j.coms Review. PubMed PMID:
25 Vieira F, Allen SM, Stocks RM, Thompson JW. Deep neck infection. Otolaryngol Clin North Am Jun;41(3):459-83, vii. doi: /j.otc Review. PubMed PMID:
26 Middle Layer of Deep Cervical Fascia muscular division Vieira F, Allen SM, Stocks RM, Thompson JW. Deep neck infection. Otolaryngol Clin North Am Jun;41(3):459-83, vii. doi: /j.otc Review. PubMed PMID:
27 Vieira F, Allen SM, Stocks RM, Thompson JW. Deep neck infection. Otolaryngol Clin North Am Jun;41(3):459-83, vii. doi: /j.otc Review. PubMed PMID:
28 Middle Layer of Deep Cervical Fascia visceral division Vieira F, Allen SM, Stocks RM, Thompson JW. Deep neck infection. Otolaryngol Clin North Am Jun;41(3):459-83, vii. doi: /j.otc Review. PubMed PMID:
29 Deep Cervical Fascia Middle layer Envelopes Muscular division Surrounds the strap muscles (sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid, omohyoid) Visceral division Surrounds the pharyngeal constrictor muscles, buccinator, larynx, trachea, esophagus, thyroid, and parathyroid glands Extent Superior Base of skull Inferior Mediastinum Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections Anderson JC, Homan JA. Radiographic correlation with neck anatomy. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am Aug;20(3): doi: /j.coms Review. PubMed PMID:
30 Vieira F, Allen SM, Stocks RM, Thompson JW. Deep neck infection. Otolaryngol Clin North Am Jun;41(3):459-83, vii. doi: /j.otc Review. PubMed PMID:
31 Deep Layer of Deep Cervical Fascia Vieira F, Allen SM, Stocks RM, Thompson JW. Deep neck infection. Otolaryngol Clin North Am Jun;41(3):459-83, vii. doi: /j.otc Review. PubMed PMID:
32 Deep Cervical Fascia Deep layer Prevertebral fascia Two layers: alar and pre-vertebral Envelopes Paraspinous muscles, cervical vertebrae Extent: Alar layer: skull base to mediastinum Pre-vertebral layer: skull base to the coccyx Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections Anderson JC, Homan JA. Radiographic correlation with neck anatomy. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am Aug;20(3): doi: /j.coms Review. PubMed PMID:
33 Vieira F, Allen SM, Stocks RM, Thompson JW. Deep neck infection. Otolaryngol Clin North Am Jun;41(3):459-83, vii. doi: /j.otc Review. PubMed PMID:
34 Carotid Sheath Vieira F, Allen SM, Stocks RM, Thompson JW. Deep neck infection. Otolaryngol Clin North Am Jun;41(3):459-83, vii. doi: /j.otc Review. PubMed PMID:
35 Overview Case Presentation Fascial Planes of the Head and Neck Deep Neck Spaces Microbiology Management Complications of Infections
36 Fascial Spaces Compartments regions of loose connective tissue that fill the areas between the fascial layers Interconnectedness of these areas is debated Some interconnect according to Cummings No universally accepted naming system Som, PM et. al Head and Neck Imaging 5 th Ed.
37 Osborn TM, Assael LA, Bell RB. Deep space neck infection: principles of surgical management. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am Aug;20(3): doi: /j.coms Review. PubMed PMID:
38 Osborn TM, Assael LA, Bell RB. Deep space neck infection: principles of surgical management. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am Aug;20(3): doi: /j.coms Review. PubMed PMID:
39 Masticator Retropharyngeal Prevertebral Parapharyngeal Parotid Carotid STATDX.COM
40 Deep Neck Spaces Anatomical Suprahyoid Infrahyoid Transhyoid Pathophysiologic Sources Sequential spread Key Spaces Parapharyngeal Submandibular/sublingual Retropharyngeal, danger, prevertebral, carotid
41 Parapharyngeal Space Skull base Hyoid Stambuk, HE. Patel, SG. Imaging of the Parapharyngeal Space. Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America. Vol 41. Iss
42 Parapharyngeal Space Anterior: pterygomandibular raphe and medial pterygoid muscle Lateral: parotid gland, mandible, and lateral pterygoid muscle Medial: superior constrictor, tensor, and levator veli palatini muscles STATDX.COM Posterior: prevertebral
43 Parapharyngeal space Central connection for the suprahyoid spaces Medially peritonsillar space Inferiorly submandibular space Laterally masticator space Carotid sheath courses through this space Posteromedially retropharyngeal space
44 Hartmann, RW. Ludwig s Angina in Children. Am Fam Physician 1999 July 1;60(1) Superior: Oral mucosa Sublingual Space Posterior: Digastric and stylomandibular ligament Inferior: Mylohyoid
45 Superior: Mylohyoid Submandibular Space Posterior: Digastric and stylomandibular ligament Anterior: Digastric Inferior: Hyoid Hartmann, RW. Ludwig s Angina in Children. Am Fam Physician 1999 July 1;60(1) Lateral: Platysma and mandible
46 Hartmann, RW. Ludwig s Angina in Children. Am Fam Physician 1999 July 1;60(1) Submandibular and Sublingual Spaces Functionally comprise a single space Clinical significance: The mylohyoid line Tooth apices anterior to second molar: sublingual space Second and third molars: submandibular Ludwig described indurated edema of the submandibular and sublingual areas with minimal throat inflammation but without lymph node involvement or suppuration. At that time, the condition was almost always fatal. Hartmann
47 Google images: mylohyoid line
48 Submandibular and Sublingual Spaces Hartmann, RW. Ludwig s Angina in Children. Am Fam Physician 1999 July 1;60(1)
49 Retropharyngeal Space Boundaries: Superior: skull base Inferior: mediastinum (fusion of middle cervical fascia with alar fascia, near T4) Anterior: Buccopharyngeal fascia Posterior: Alar fascia Lateral: Carotid sheath Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections
50
51 Retropharyngeal Space Clinical Significance Direct spread from the parapharyngeal space Lymphatic spread from the paranasal sinuses/nasopharyngeal region
52 Danger Space Boundaries: Superior: skull base Inferior: diaphragm Anterior: alar fascial layer of deep cervical fascia Posterior: prevertebral fascial layer of deep cervical fascia Lateral: Transverse processes of vertebral Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections
53
54 Danger Space Clinical significance: Potential for rapid inferior spread Loose areolar tissue Infectious infiltration from the retropharyngeal, parapharyngeal, or prevertebral spaces are the primary routes to the danger space
55 Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections Osborn TM, Assael LA, Bell RB. Deep space neck infection: principles of surgical management. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am Aug;20(3): doi: /j.coms Review. PubMed PMID: Prevertebral Space Boundaries: Anterior: prevertebral fascia Superior: Clivus Inferior: Coccyx
56 Prevertebral Space Clinical significance: Dense areolar tissue Mechanisms of spread Infection of the vertebral bodies Penetrating injuries.
57 Masticator Space Enclosed by superficial layer of deep cervical fascia Boundaries: Anterior buccal fat pad Medial: Fascia medial to pterygoid muscles Lateral: Fascia lateral to masseter Superior temporal fossa Subspaces: Mandible Temporalis muscle Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections STATDX.COM
58 Masticator Space Clinical significance: Anterolateral to parapharyngeal space Most commonly from the third mandibular molars May involve temporal space with maxillary molar infection STATDX.COM Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections
59 Peritonsillar Space Boundaries: Medial: capsule of the palatine tonsil Lateral: superior constrictor muscle. Anterior/posterior: anterior and posterior tonsillar pillars Inferior: posterior tongue Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections
60 Wikipedia: Peritonsillar abscess Peritonsillar Space Clinical significance Loose connective tissue Readily spread to the parapharyngeal space.
61 Parotid Space Boundaries: Lateral: superficial layer of deep cervical fascia Medial: fascia, which does not enclose the superomedial aspect of the gland Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections STATDX.COM
62 Parotid Space Clinical significance Parotid space is lateral to the parapharyngeal space. Incomplete superomedial border permits communication with the prestyloid compartment of the parapharyngeal space.
63 Carotid Space Borders: Carotid sheath Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections
64 Wikipedia: Lincoln highway Carotid Space Clinical significance: Infection from the surrounding parapharyngeal space, penetrating trauma, or intravenous drug use may potentiate spread into this space. Lincoln highway of the neck Coined by Harris B. Mosher in 1929
65 Anterior Visceral Space Boundaries: The visceral division of the middle layer of deep cervical fascia encloses the anterior visceral space, or pretracheal space Superior: thyroid cartilage Inferior: mediastinum Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections
66 Anterior Visceral Space Clinical significance Perforation of the anterior esophageal wall by endoscopic instrumentation, foreign bodies, or trauma may introduce infection to this space. Direct spread from submandibular space
67 Matching Mechanism Acute tonsillitis Rhinosinusitis Dental infection (upper) Dental infection (lower) 2 nd /3 rd molar Dental infection (lower) anterior Esophagoscopy Space Retropharyngeal/ Parapharyngeal Sublingual Submandibular Masticator space Retropharyngeal Peritonsillar space
68 Matching Mechanism Acute tonsillitis Rhinosinusitis Dental infection (upper) Dental infection (lower) 2 nd /3 rd molar Dental infection (lower) anterior Esophagoscopy Space Retropharyngeal/ Parapharyngeal Sublingual Submandibular Masticator space Retropharyngeal Peritonsillar space
69 Overview Case Presentation Fascial Planes of the Head and Neck Deep Neck Spaces Microbiology Management Complications of Infections
70 Microbiology Usually mixed aerobic and anaerobic organisms, predominance of oral flora. Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal species, alpha-hemolytic streptococcal species, Staphylococcus aureus, Fusobacterium nucleatum, Bacteroides melaninogenicus, Bacteroides oralis, and Spirochaeta, Peptostreptococcus, and Neisseria species Pseudomonas species, Escherichia coli, and Haemophilus influenzae are occasionally encountered. Increasing documentation of MRSA, especially within pediatric patient populations Higher gram negative incidence in diabetics Thomason TS, Brenski A, McClay J, Ehmer D. The rising incidence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in pediatric neck abscesses. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg Sep;137(3): PubMed PMID: Murray, AD et. Al. Deep Neck infections. Emedicine. Mar 12, 2012
71 Overview Case Presentation Fascial Planes of the Head and Neck Deep Neck Spaces Microbiology Management Complications of Infections
72 Vieira, F. Allen, SM. Etal. Deep Neck Infection. Otolaryngol Clini N Am. 41 (2008) Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections Imaging CT scan is indicated in cases of a suspected deep neck space infection It has been suggested that size (>2 cm) is more predictive of a deep neck abscess than the presence of a ring-enhancing lesion. Lateral neck radiographs are less sensitive that CT and are not recommended Presence of an air-fluid level or greater than 5 mm of thickening in a child or greater than 7 mm of thickening in an adult of the prevertebral tissue at C2 indicate retropharyngeal infection until proven otherwise Ultrasound is more accurate than CECT in differentiating a drainable abscess from cellulitis May not visualize deeper lesions Does not provide anatomic information necessary for planning surgery
73 5 year retrospective review of suspected deep neck space infections 89 patients identified, 13 excluded Of 76, all had CT scans. fluid collection was present in 65 people. 57 taken to surgery, rest treated with antibiotics Negative if no pus or responded to antibiotics All false positives were all less than 3.5 cm Negative predictive value of CT 100% Freling N, Roele E, Schaefer-Prokop C, Fokkens W. Prediction of deep neck abscesses by contrast-enhanced computerized tomography in 76 clinically suspect consecutive patients. Laryngoscope Sep;119(9): doi: /lary PubMed PMID:
74 Medical Management Airway, Airway, Airway Loss of airway is a major source of mortality from deep neck infection Aggressive management Dyspnea, stridor, retractions Impending airway compromise Consider tracheostomy over intubation Shorter overall hospital stay (4.8 vs 5.9 days) did not reach significance Reduced cost by 60% Fewer lost airways Antibiotics Steroids Advocated by some Felt to worsen hyperglycemia etc. by others Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections Potter JK, Herford AS, Ellis E 3rd. Tracheotomy versus endotracheal intubation for airway management in deep neck space infections. J Oral Maxillofac Surg Apr;60(4):349-54; discussion Review. PubMed PMID:
75 Recommended Antibiotics Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections
76 Surgical Management Indicated (1) air-fluid level in the neck or evidence of gas-producing organisms; (2) abscess visualized in the fascial spaces of the head and neck; (3) threatened airway compromise from abscess or phlegmon; (4) failure to respond to 48 to 72 hours of empiric intravenous antibiotic therapy. Needle Aspiration Transoral Incision and Drainage Transcervical Incision and Drainage The guiding principle of surgery for deep neck infection is obtaining adequate access and drainage of the infected space while minimizing risk to normal structures. Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections
77 Cheng J, Elden L. Children with deep space neck infections: our experience with 178 children. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg Jun;148(6): doi: / Epub 2013 Mar 21. PubMed PMID:
78 Overview Case Presentation Fascial Planes of the Head and Neck Deep Neck Spaces Microbiology Management Complications of Infections
79 Complications Lemierre's Syndrome Carotid Artery Pseudoaneurysm or Rupture Mediastinitis Necrotizing Fasciitis Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections
80 Vieira, F. Allen, SM. Etal. Deep Neck Infection. Otolaryngol Clini N Am. 41 (2008) Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections Lemierre's Syndrome Definition Thrombophlebitis of the internal jugular vein Origin Carotid space infection Microbiology Gram-negative bacillus Fusobacterium necrophorum Endotoxin induces platelet aggregation and septic thrombus formation. Symptoms Swelling and tenderness at the angle of the jaw and along the SCM, along with signs of sepsis with pulmonary emboli Imaging Filling defect in the internal jugular system. Treatment Prolonged antimicrobial treatment +/- anticoagulation Surgery limited to worsening clinical course despite appropriate medical therapy
81 Vieira, F. Allen, SM. Etal. Deep Neck Infection. Otolaryngol Clini N Am. 41 (2008) Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections Carotid Artery Pseudoaneurysm or Rupture Origin Retropharyngeal or parapharyngeal spaces Symptoms Sentinel hemorrhages Hemodynamic compromise Protracted course Hematoma Other: pulsating neck mass, Horner's syndrome, palsies of cranial nerves IX through XII Treatment Proximal control and ligation of the carotid artery.?role for interventional radiology
82 Corsten, MJ, Shamji, FM etal. Optimal treatment of descending necrotising mediastinitis. Thorax. 1997; 52: Vieira, F. Allen, SM. Etal. Deep Neck Infection. Otolaryngol Clini N Am. 41 (2008) Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections Mediastinitis Origin Retropharyngeal, danger and prevertebral spaces Anterior visceral space Symptoms Dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, tachycardia, pleural effusion, mediastinal widening/air Management Broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotics Drainage Surgical Drainage Optimal approach is somewhat debated Bilateral cervical approach advocated by some with infection limited to the anterior-superior mediastinum Thoracotomy in cases that extend beyond the upper mediastinum or that involve more than one mediastinal compartment Corsten: analysis ofpatients with mediastinitis from cervical abscess showing mortality rate was 19% among patients who underwent both cervical and thoracic drainage and 47% among those who underwent cervical drainage alone
83 Necrotizing Fasciitis Definition Infection that spreads along fascial planes and causes necrosis of connective tissue Microbiology Mixed including S pyogenes, Clostridium perfringens, others MRSA Symptoms Fevers, skin changes (tender, edematous, erythematous), soft tissue crepitation Later developing pale, anesthetic, dusky and blistering skin Management IV antibiotics Aggressive and frequent debridement of necrotic tissue Hyperbaric oxygen Flanagan et al show that hyperbaric oxygen may decrease hospital stay 10 patient (9 received 1 did not due to hemodynamic instability). Multiple studies in other specialties literature showing no difference in amputation rate or mortality Mortality 20% to 30% in treated patients Vieira, F. Allen, SM. Etal. Deep Neck Infection. Otolaryngol Clini N Am. 41 (2008) Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections Wolf, H, R M. Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Head and Neck. Head and Neck. December 2010 Flanagan, CE. Daramola, OO. Surgical debridement and adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen in cervical necrotizing fasciitis. Otolaryngology Heada dn Neck Surgery : 730.
84 Acknowledgement I would like to thank Dr. Sindhwani of the Department of Radiology for assistance in obtaining some of the images used in this presentation The images obtained from STATDX.COM are meant for educational purposes only.
85 References Anderson JC, Homan JA. Radiographic correlation with neck anatomy. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am Aug;20(3): doi: /j.coms Review. PubMed PMID: Biron VL, Kurien G, Dziegielewski P, Barber B, Seikaly H. Surgical vs ultrasound-guided drainage of deep neck space abscesses: a randomized controlled trial: surgical vs ultrasound drainage. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg Feb 26;42(1):18. doi: / PubMed PMID: ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC Cheng J, Elden L. Children with deep space neck infections: our experience with 178 children. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg Jun;148(6): doi: / Epub 2013 Mar 21. PubMed PMID: Corsten, MJ, Shamji, FM etal. Optimal treatment of descending necrotising mediastinitis. Thorax. 1997; 52: Cummings otolaryngology 5 th Ed. Chapter 14 deep neck space infections Flanagan, CE. Daramola, OO. Surgical debridement and adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen in cervical necrotizing fasciitis. Otolaryngology Heada dn Neck Surgery : 730 Freling N, Roele E, Schaefer-Prokop C, Fokkens W. Prediction of deep neck abscesses by contrast-enhanced computerized tomography in 76 clinically suspect consecutive patients. Laryngoscope Sep;119(9): doi: /lary PubMed PMID: Hartmann, RW. Ludwig s Angina in Children. Am Fam Physician 1999 July 1;60(1) Miller WD, Furst IM, Sàndor GK, Keller MA. A prospective, blinded comparison of clinical examination and computed tomography in deep neck infections. Laryngoscope Nov;109(11): PubMed PMID: Mukherji SK, Castillo M. A simplified approach to the spaces of the suprahyoid neck. Radiol Clin North Am Sep;36(5):761-80, v. Review. PubMed PMID: Murray, AD et. Al. Deep Neck infections. Emedicine. Mar 12, 2012 Osborn TM, Assael LA, Bell RB. Deep space neck infection: principles of surgical management. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am Aug;20(3): doi: /j.coms Review. PubMed PMID: Potter JK, Herford AS, Ellis E 3rd. Tracheotomy versus endotracheal intubation for airway management in deep neck space infections. J Oral Maxillofac Surg Apr;60(4):349-54; discussion Review. PubMed PMID: Som, PM et. al Head and Neck Imaging 5 th Ed. Stambuk, HE. Patel, SG. Imaging of the Parapharyngeal Space. Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America. Vol 41. Iss STATDX.COM Thomason TS, Brenski A, McClay J, Ehmer D. The rising incidence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in pediatric neck abscesses. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg Sep;137(3): PubMed PMID: Vieira F, Allen SM, Stocks RM, Thompson JW. Deep neck infection. Otolaryngol Clin North Am Jun;41(3):459-83, vii. doi: /j.otc Review. PubMed PMID: Wolf, H, R M. Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Head and Neck. Head and Neck. December 2010
Deep Neck Spaces and Infections
 Deep Neck Spaces and Infections Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Faculty Advisor: Byron J. Bailey, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation April 17, 2002
Deep Neck Spaces and Infections Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Faculty Advisor: Byron J. Bailey, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation April 17, 2002
Key Points. Eric R. Oliver M. Boyd Gillespie
 Eric R. Oliver M. Boyd Gillespie Key Points Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is an increasingly common cause of deep neck space infections. Ultrasound will likely be applied more frequently
Eric R. Oliver M. Boyd Gillespie Key Points Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is an increasingly common cause of deep neck space infections. Ultrasound will likely be applied more frequently
Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy
 Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy Kris Cummings, M.D. Axial CT Unlabeled Labeled Deep s/lymph Node Chains s/lymph Nodes Temporalis Muscle Occipitalis Muscle s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph
Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy Kris Cummings, M.D. Axial CT Unlabeled Labeled Deep s/lymph Node Chains s/lymph Nodes Temporalis Muscle Occipitalis Muscle s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph
Infection of the neck is a common clinical. Deep Neck Spaces radiology and review of deep neck infections at King Abdulaziz University Hospital
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Deep Neck Spaces radiology and review of deep neck infections at King Abdulaziz University Hospital Khaled Al-Noury a, Alsaid Lotfy b Otolaryngology Department a, King Abdulaziz University,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Deep Neck Spaces radiology and review of deep neck infections at King Abdulaziz University Hospital Khaled Al-Noury a, Alsaid Lotfy b Otolaryngology Department a, King Abdulaziz University,
IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Level IA: Submental Group
 IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Fig. 1 The level system is used for describing the location of lymph nodes in the neck: Level I, submental and submandibular group; Level II, upper jugular
IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Fig. 1 The level system is used for describing the location of lymph nodes in the neck: Level I, submental and submandibular group; Level II, upper jugular
Deeper: geniohyoid, cricothyroid
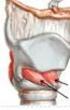 VitalStim Therapy ELECTRODE PLACEMENT WITH NECK MUSCLES Electrode Placements Placement 1 - All electrodes aligned vertically along midline - First electrode is placed well above hyoid bone - Second electrode
VitalStim Therapy ELECTRODE PLACEMENT WITH NECK MUSCLES Electrode Placements Placement 1 - All electrodes aligned vertically along midline - First electrode is placed well above hyoid bone - Second electrode
Oct 17:Deep Neck Space Infections (updated 08/06) Oct 17: Deep Neck Space Infections (updated 08/06) Vacation: none! ; Preceptor
 Oct 17: Deep Neck Space Infections (updated 08/06) Vacation: none! ; Preceptor 1. (Deya) Describe the anatomy of the cervical fascia. 2. (Deya) Name the deep neck spaces. Be prepared to draw pictures to
Oct 17: Deep Neck Space Infections (updated 08/06) Vacation: none! ; Preceptor 1. (Deya) Describe the anatomy of the cervical fascia. 2. (Deya) Name the deep neck spaces. Be prepared to draw pictures to
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Contents
 Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
Spread of Dental Infection
 Spread of Dental Infection The healthy body usually lives in balance with a number of resident normal flora. However, pathogens can invade and initiate an infectious process. 1 Dental infections involving
Spread of Dental Infection The healthy body usually lives in balance with a number of resident normal flora. However, pathogens can invade and initiate an infectious process. 1 Dental infections involving
Case Report Facial and cervical emphysema after oral surgery: a rare case
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2013;6(9):840-844 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1307016 Case Report Facial and cervical emphysema after oral surgery: a rare case Sergio Olate 1,2, Adriano Assis 3, Simei Freire
Int J Clin Exp Med 2013;6(9):840-844 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1307016 Case Report Facial and cervical emphysema after oral surgery: a rare case Sergio Olate 1,2, Adriano Assis 3, Simei Freire
by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin
 by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin body mechanics palpation of the anterior neck ESOUCES For more information go to www.medlineplus.gov and search under anterior neck. The anterior
by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin body mechanics palpation of the anterior neck ESOUCES For more information go to www.medlineplus.gov and search under anterior neck. The anterior
Cranial Nerve I Name: Foramen: Fiber Type: Function: Branches: Embryo:
 Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections
 Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections Format: 1. Case 2. Topic Summary 3. Questions 4. References Case: A 3-year-old boy presents with 2 days of increasing redness, swelling, and pain
Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections Format: 1. Case 2. Topic Summary 3. Questions 4. References Case: A 3-year-old boy presents with 2 days of increasing redness, swelling, and pain
Recurrent & Persistent Papillary Thyroid Cancer Central Nodal Dissection vs. Node-Picking Patterns of Nodal Metastases Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve,
 Recurrent & Persistent Papillary Thyroid Cancer Central Nodal Dissection vs. Node-Picking Patterns of Nodal Metastases Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve, Larynx, Trachea, & Esophageal Management Robert C. Wang,
Recurrent & Persistent Papillary Thyroid Cancer Central Nodal Dissection vs. Node-Picking Patterns of Nodal Metastases Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve, Larynx, Trachea, & Esophageal Management Robert C. Wang,
Diagnosis and Management of Deeper Neck Infections - A Review
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 5 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 36-41 Diagnosis and Management of Deeper Neck Infections - A Review
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 5 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 36-41 Diagnosis and Management of Deeper Neck Infections - A Review
CMEArticle Infections of the deep neck spaces
 Singapore Med J 2012; 53(5) : 305 CMEArticle Infections of the deep neck spaces Amogh Hegde 1, MD, FRCR, Suyash Mohan 2, MD, PDCC, Winston Eng Hoe Lim 3, FRCR ABSTRACT Deep neck infections (DNI) have a
Singapore Med J 2012; 53(5) : 305 CMEArticle Infections of the deep neck spaces Amogh Hegde 1, MD, FRCR, Suyash Mohan 2, MD, PDCC, Winston Eng Hoe Lim 3, FRCR ABSTRACT Deep neck infections (DNI) have a
Deep neck space abscesses in children and Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) as an emerging pathogen A clinical study
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 6 (2015) pp. 1087-1097 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Deep neck space abscesses in children
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 6 (2015) pp. 1087-1097 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Deep neck space abscesses in children
Deep neck abscesses: the Singapore experience
 DOI 10.1007/s00405-010-1387-8 HEAD AND NECK Deep neck abscesses: the Singapore experience Yan Qing Lee Jeevendra Kanagalingam Received: 25 July 2010 / Accepted: 6 September 2010 Ó Springer-Verlag 2010
DOI 10.1007/s00405-010-1387-8 HEAD AND NECK Deep neck abscesses: the Singapore experience Yan Qing Lee Jeevendra Kanagalingam Received: 25 July 2010 / Accepted: 6 September 2010 Ó Springer-Verlag 2010
A case of concurrent deep venous thrombosis, pseudoaneurysm, and extremity abscess in an intravenous methamphetamine abuser
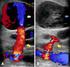 A case of concurrent deep venous thrombosis, pseudoaneurysm, and extremity abscess in an intravenous methamphetamine abuser BY MATTHEW L HARRISON Abstract Introduction. Intravenous drug abuse is a global
A case of concurrent deep venous thrombosis, pseudoaneurysm, and extremity abscess in an intravenous methamphetamine abuser BY MATTHEW L HARRISON Abstract Introduction. Intravenous drug abuse is a global
ENT Emergencies. Injuries of the Neck. Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital
 ENT Emergencies Injuries of the Neck Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital Neck Injuries Blunt and Penetrating Trauma Blunt Injuries Blunt trauma direct/indirect Trauma to larynx
ENT Emergencies Injuries of the Neck Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital Neck Injuries Blunt and Penetrating Trauma Blunt Injuries Blunt trauma direct/indirect Trauma to larynx
ORAL MAXILLO FACIAL SURGERY REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS
 ORAL MAXILLO FACIAL SURGERY REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines General problems include: Soft tissue conditions of the face and oral cavity
ORAL MAXILLO FACIAL SURGERY REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines General problems include: Soft tissue conditions of the face and oral cavity
Visit ER at 09:14. ER & infection conference. Present illness. Past history. Physical examination
 Visit ER at 09:14 ER & infection conference A 50 y/o female, Sereve left neck and chest pain for 3 weeks Chief complaint: left neck and chest pain for 3 weeks Triage: III T/P/R:36.2/79/20, BP=130/78, SpO2=99%
Visit ER at 09:14 ER & infection conference A 50 y/o female, Sereve left neck and chest pain for 3 weeks Chief complaint: left neck and chest pain for 3 weeks Triage: III T/P/R:36.2/79/20, BP=130/78, SpO2=99%
Developmental Cysts. Non-odontogenic Cysts. Nasopalatine duct cyst. Palatal and gingival cysts of newborns
 Non-odontogenic Cysts Dr. Ioannis G. Koutlas Division of Oral Pathology Developmental Cysts a.k.a. fissural cysts Exact pathogenesis of some of them uncertain Generally, slow increase May be identified
Non-odontogenic Cysts Dr. Ioannis G. Koutlas Division of Oral Pathology Developmental Cysts a.k.a. fissural cysts Exact pathogenesis of some of them uncertain Generally, slow increase May be identified
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck. Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW
 Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Suprahyoid Neck Lesions. C. Douglas Phillips, MD FACR Professor of Radiology Weill Cornell Medical College NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital
 Suprahyoid Neck Lesions C. Douglas Phillips, MD FACR Professor of Radiology Weill Cornell Medical College NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital Objectives To introduce spatial concept of neck anatomy with imaging
Suprahyoid Neck Lesions C. Douglas Phillips, MD FACR Professor of Radiology Weill Cornell Medical College NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital Objectives To introduce spatial concept of neck anatomy with imaging
Tonsillitis. complications
 and its complications By Paolo Campisi MSc, MD, FRCSC; and Ted L. Tewfik MD, FRCSC Peritonsillar cellulitis and abscess are the most common deep infections of the head and neck in children. Inadequate
and its complications By Paolo Campisi MSc, MD, FRCSC; and Ted L. Tewfik MD, FRCSC Peritonsillar cellulitis and abscess are the most common deep infections of the head and neck in children. Inadequate
Image. 3.11.3 SW Review the anatomy of the EAC and how this plays a role in the spread of tumors.
 Neoplasms of the Ear and Lateral Skull Base Image 3.11.1 SW What are the three most common neoplasms of the auricle? 3.11.2 SW What are the four most common neoplasms of the external auditory canal (EAC)
Neoplasms of the Ear and Lateral Skull Base Image 3.11.1 SW What are the three most common neoplasms of the auricle? 3.11.2 SW What are the four most common neoplasms of the external auditory canal (EAC)
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
 A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
Anterior Approach Burn s Space Esophagus
 Cervical Complications Complications after Cervical Spine Surgery Dr. Rock Patel University of Michigan, Ann Arbor APPROACH RELATED Anterior Posterior PROCEDURE RELATED ACDF Disc Arthroplasty Laminectomy/Fusion
Cervical Complications Complications after Cervical Spine Surgery Dr. Rock Patel University of Michigan, Ann Arbor APPROACH RELATED Anterior Posterior PROCEDURE RELATED ACDF Disc Arthroplasty Laminectomy/Fusion
Diffuse Neck Swelling after Car Accident
 中 華 放 射 醫 誌 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 283-287 283 Diffuse Neck Swelling after Car Accident HUAN-WU CHEN SHENG-CHAU HUANG HUAN-WEN CHEN 2 KOU-MOU HUANG Departments of Medical Imaging, National Taiwan University
中 華 放 射 醫 誌 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 283-287 283 Diffuse Neck Swelling after Car Accident HUAN-WU CHEN SHENG-CHAU HUANG HUAN-WEN CHEN 2 KOU-MOU HUANG Departments of Medical Imaging, National Taiwan University
MOLLOY COLLEGE DIVISION OF NURSING NURSE PRACTITIONER PROGRAMS. Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam
 DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
GUIDELINE Sinusitis. David M. Poetker MD, MA Associate Professor. Division of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery
 GUIDELINE Sinusitis David M. Poetker MD, MA Associate Professor Division of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Guideline Fokkens et al. The European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012. Rhinology.
GUIDELINE Sinusitis David M. Poetker MD, MA Associate Professor Division of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Guideline Fokkens et al. The European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012. Rhinology.
TNM Staging of Head and Neck Cancer and Neck Dissection Classification
 QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE TO TNM Staging of Head and Neck Cancer and Neck Dissection Classification Fourth Edition 2014 All materials in this ebook are copyrighted by the American Academy of Otolaryngology
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE TO TNM Staging of Head and Neck Cancer and Neck Dissection Classification Fourth Edition 2014 All materials in this ebook are copyrighted by the American Academy of Otolaryngology
Interventional Radiology
 Nationwide Children s Hospital Department of Radiology is recognized as a pioneering center for research and innovation, and a renowned leader in diagnostic and interventional pediatric radiology. Our
Nationwide Children s Hospital Department of Radiology is recognized as a pioneering center for research and innovation, and a renowned leader in diagnostic and interventional pediatric radiology. Our
Sore Throat. Definition. Causes. (Pharyngitis; Tonsillopharyngitis; Throat Infection) Pronounced: Fare-en-JY-tis /TAHN-sill-oh-fare-en-JY-tis
 Sore Throat (Pharyngitis; Tonsillopharyngitis; Throat Infection) Pronounced: Fare-en-JY-tis /TAHN-sill-oh-fare-en-JY-tis by Jennifer Lewy, MSW En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A sore throat is the
Sore Throat (Pharyngitis; Tonsillopharyngitis; Throat Infection) Pronounced: Fare-en-JY-tis /TAHN-sill-oh-fare-en-JY-tis by Jennifer Lewy, MSW En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A sore throat is the
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
ANTERIOR CERVICAL DISCECTOMY AND FUSION. Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Anterior Cervical Spine
 Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
Examine the neck. Lumps in the neck. - thyroglossal cyst - pharyngeal pouch
 Lumps in the neck Midline - goitre - thyroglossal cyst - pharyngeal pouch Examine the neck Lateral - lymph node - sebaceous cyst / lipoma - cystic hygroma/ branchial cyst - vascular: aneurysm, tumour -
Lumps in the neck Midline - goitre - thyroglossal cyst - pharyngeal pouch Examine the neck Lateral - lymph node - sebaceous cyst / lipoma - cystic hygroma/ branchial cyst - vascular: aneurysm, tumour -
Respiratory System. Chapter 21
 Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
Head and Neck Exam. Charlie Goldberg, M.D. [email protected]
 Head and Neck Exam Charlie Goldberg, M.D. [email protected] Hammer & Nails icon indicates A Slide Describing Skills You Should Perform In Lab Observation and Palpation Note right sided neck/jaw area
Head and Neck Exam Charlie Goldberg, M.D. [email protected] Hammer & Nails icon indicates A Slide Describing Skills You Should Perform In Lab Observation and Palpation Note right sided neck/jaw area
Streptococcal Infections
 Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
Dentistry Students (2014/2015 entry) Session 2015-2016, Term 2
 Number of Units Dentistry Students (2014/2015 entry) Session 2015-2016, Term 2 Course Name 2.0 Anatomical Sciences II (theory) 1.0 Anatomical Sciences II (practical) 1.0 Parasitology 2.0 Psychology 1.5
Number of Units Dentistry Students (2014/2015 entry) Session 2015-2016, Term 2 Course Name 2.0 Anatomical Sciences II (theory) 1.0 Anatomical Sciences II (practical) 1.0 Parasitology 2.0 Psychology 1.5
Perianal Abscess and Fistula-in-ano. Background
 Perianal Abscess and Fistula-in-ano Background Anorectal abscesses are some of the more common anorectal conditions encountered, and they are potentially debilitating conditions. The current theory as
Perianal Abscess and Fistula-in-ano Background Anorectal abscesses are some of the more common anorectal conditions encountered, and they are potentially debilitating conditions. The current theory as
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT
 This assessment is effective as of October 2014. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, e-mail [email protected] EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT
This assessment is effective as of October 2014. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, e-mail [email protected] EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT
Canine Lymphoma Frequently Asked Questions by Pet Owners
 Canine Lymphoma Frequently Asked Questions by Pet Owners What is lymphoma? The term lymphoma describes a diverse group of cancers in dogs that are derived from white blood cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes
Canine Lymphoma Frequently Asked Questions by Pet Owners What is lymphoma? The term lymphoma describes a diverse group of cancers in dogs that are derived from white blood cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes
Thyroid Eye Disease. Anatomy: There are 6 muscles that move your eye.
 Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Airway assessment. Bran Retnasingham Andy McKechnie
 Airway assessment Bran Retnasingham Andy McKechnie The average Camberwell patient? Airway assessment There is one skill above all else that an anaesthetist is expected to exhibit and that is to
Airway assessment Bran Retnasingham Andy McKechnie The average Camberwell patient? Airway assessment There is one skill above all else that an anaesthetist is expected to exhibit and that is to
Objectives. Mylene T. Truong, MD. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Background
 Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON. 1. Frontal Bone. 2. Parietal Bones. 3. Temporal Bones. CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired)
 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Normal CT scan of the chest
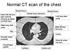 Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Headaches + Facial pain
 Headaches + Facial pain Introduction: Each of us experienced sporadically/ chronically headache 40% worldwide population suffers with severe, disabling headache at least annually Common ailment Presenting
Headaches + Facial pain Introduction: Each of us experienced sporadically/ chronically headache 40% worldwide population suffers with severe, disabling headache at least annually Common ailment Presenting
Early Colonoscopy in Patients with Acute Diverticulitis Simon Bar-Meir, M.D.
 Early Colonoscopy in Patients with Acute Diverticulitis Simon Bar-Meir, M.D. Professor of Medicine Germanis Kaufman Chair of Gastroenterology Director, Dept. of Gastroenterology Chaim Sheba Medical Center,
Early Colonoscopy in Patients with Acute Diverticulitis Simon Bar-Meir, M.D. Professor of Medicine Germanis Kaufman Chair of Gastroenterology Director, Dept. of Gastroenterology Chaim Sheba Medical Center,
HOMEOPATHY AS AN ALTERNATIVE TO ANTIBIOTICS
 HOMEOPATHY AS AN ALTERNATIVE TO ANTIBIOTICS Professor Dr. Michael FRASS Medical University of Vienna, Department Medicine I Doctor s Asscociation for Classical Homeopathy www.aekh.at President, Umbrella
HOMEOPATHY AS AN ALTERNATIVE TO ANTIBIOTICS Professor Dr. Michael FRASS Medical University of Vienna, Department Medicine I Doctor s Asscociation for Classical Homeopathy www.aekh.at President, Umbrella
Clinical Reasoning Handout: URI Symptoms Sore Throat. 1) Pearls
 Clinical Reasoning Handout: URI Symptoms Sore Throat 1) Pearls Background: Sore throat is one the most common symptoms evaluated in primary care Almost 5% of patient report sore throat as the primary reason
Clinical Reasoning Handout: URI Symptoms Sore Throat 1) Pearls Background: Sore throat is one the most common symptoms evaluated in primary care Almost 5% of patient report sore throat as the primary reason
Local Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
 Local Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Sean M. Healy, D.D.S. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Francis B. Quinn, M.D., FACS Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery The University of Texas
Local Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Sean M. Healy, D.D.S. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Francis B. Quinn, M.D., FACS Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery The University of Texas
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis. A radiologic tour of a patient encounter
 Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Sore Throats That Kill
 Disclosures Sore Throats That Kill No relevant financial interests in any product discussed today H. Gene Hern, MD, MS, FACEP, FAAEM Assoc. Clinical Professor, UCSF Residency Director Alameda County -
Disclosures Sore Throats That Kill No relevant financial interests in any product discussed today H. Gene Hern, MD, MS, FACEP, FAAEM Assoc. Clinical Professor, UCSF Residency Director Alameda County -
Claims submission simplified for emergency dental procedure codes
 January 2002 No. 2002-02 PHC 1844 To: Dentists HMOs and Other Managed Care Programs Claims submission simplified for emergency dental procedure codes Effective immediately, both electronic and paper claims
January 2002 No. 2002-02 PHC 1844 To: Dentists HMOs and Other Managed Care Programs Claims submission simplified for emergency dental procedure codes Effective immediately, both electronic and paper claims
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE
 INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Basic modules: List of individual modules Basic Module 1 Basic principles of general and dental medicine
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Basic modules: List of individual modules Basic Module 1 Basic principles of general and dental medicine
Who are these patients? Neck Pain in Voice Disorders. Etiologies of Cervicalgia. Role of Physical Therapy in Treatment of Voice Disorders
 Role of Physical Therapy in Treatment of Voice Disorders DAVID O. FRANCIS, MD MS VANDERBILT VOICE CENTER NOVEMBER 5, 2011 Singers Who are these patients? Performers Athletes Exercise with weights Heavy
Role of Physical Therapy in Treatment of Voice Disorders DAVID O. FRANCIS, MD MS VANDERBILT VOICE CENTER NOVEMBER 5, 2011 Singers Who are these patients? Performers Athletes Exercise with weights Heavy
Childhood ENT disorders. When to refer to specialists. Claire Harris
 Childhood ENT disorders When to refer to specialists Claire Harris Background. Ear, nose and throat (ENT) are among the commonest reasons for attendance in general practice. Acute problems are managed
Childhood ENT disorders When to refer to specialists Claire Harris Background. Ear, nose and throat (ENT) are among the commonest reasons for attendance in general practice. Acute problems are managed
SPONTANEOUS PNEUMOTHORAX AS A COMPLICATION OF SEPTIC PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN AN INTRAVENOUS DRUG USER: A CASE REPORT
 Spontaneous pneumothorax in an IV drug user SPONTANEOUS PNEUMOTHORAX AS A COMPLICATION OF SEPTIC PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN AN INTRAVENOUS DRUG USER: A CASE REPORT Chau-Chyun Sheu, Jhi-Jhu Hwang, Jong-Rung
Spontaneous pneumothorax in an IV drug user SPONTANEOUS PNEUMOTHORAX AS A COMPLICATION OF SEPTIC PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN AN INTRAVENOUS DRUG USER: A CASE REPORT Chau-Chyun Sheu, Jhi-Jhu Hwang, Jong-Rung
Horizon Blue Cross Blue Shield of NJ Radiology Rules Bank
 Horizon Blue Cross Blue Shield of NJ Radiology Rules Bank * Rule added 05/30/13 Code Pay Code Do Not Pay Source 70010 Myelography, posterior fossa, radiological supervision and 76000 Fluoroscopy, up to
Horizon Blue Cross Blue Shield of NJ Radiology Rules Bank * Rule added 05/30/13 Code Pay Code Do Not Pay Source 70010 Myelography, posterior fossa, radiological supervision and 76000 Fluoroscopy, up to
UNMH Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinical Privileges
 All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees effective: 09/26/2014 INSTRUCTIONS Applicant: Check off the "Requested" box for each privilege requested.
All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees effective: 09/26/2014 INSTRUCTIONS Applicant: Check off the "Requested" box for each privilege requested.
Ultrasound Billing CPT Codes Summary and Notes
 Ultrasound Billing CPT Codes Summary and Notes CPT codes for ultrasound examinations are considered to be complete studies unless specified as limited studies in their code definitions. A limited study
Ultrasound Billing CPT Codes Summary and Notes CPT codes for ultrasound examinations are considered to be complete studies unless specified as limited studies in their code definitions. A limited study
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
GENERAL OTOLARYNGOLOGY HEAD and NECK SURGICAL ONCOLOGY. MEE General ORL/Head and Neck Rotation - PGY 2,3,4,5 Longwood Rotation - PGY 2,3,4,5
 GENERAL OTOLARYNGOLOGY HEAD and NECK SURGICAL ONCOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION Training in general otolaryngology, upper aerodigestive tract endoscopy and head and neck oncologic surgery begins and continues
GENERAL OTOLARYNGOLOGY HEAD and NECK SURGICAL ONCOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION Training in general otolaryngology, upper aerodigestive tract endoscopy and head and neck oncologic surgery begins and continues
Ludwig s Angina: Diagnosis and Treatment
 Clinical Review Article Ludwig s Angina: Diagnosis and Treatment David M. Lemonick, MD Arare disorder, Ludwig s angina is a serious, potentially life-threatening infection of the neck and the floor of
Clinical Review Article Ludwig s Angina: Diagnosis and Treatment David M. Lemonick, MD Arare disorder, Ludwig s angina is a serious, potentially life-threatening infection of the neck and the floor of
Hemodialysis catheter infection
 Hemodialysis catheter infection Scary facts In 2006, 82% of patients in the United States initiated dialysis via a catheter The overall likelihood of Tunneled cuffed catheters use was 35% greater in 2005
Hemodialysis catheter infection Scary facts In 2006, 82% of patients in the United States initiated dialysis via a catheter The overall likelihood of Tunneled cuffed catheters use was 35% greater in 2005
Acute Dental Problems in the School Setting
 Acute Dental Problems in the School Setting Keri Discepolo, D.D.S., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, Yale Pediatric Dentistry Residency Program Associate, Yale School of Medicine Objectives Brief Description of
Acute Dental Problems in the School Setting Keri Discepolo, D.D.S., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, Yale Pediatric Dentistry Residency Program Associate, Yale School of Medicine Objectives Brief Description of
Approach to Masses of the Head and Neck
 Approach to Masses of the Head and Neck Kristi Chang, MD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Objectives Recognize when practitioners
Approach to Masses of the Head and Neck Kristi Chang, MD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Objectives Recognize when practitioners
Sinus Headache vs. Migraine
 Sinus Headache vs. Migraine John M. DelGaudio, MD, FACS Professor and Vice Chair Chief of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Department of Otolaryngology Emory University School of Medicine 1 Sinus Headache Problems
Sinus Headache vs. Migraine John M. DelGaudio, MD, FACS Professor and Vice Chair Chief of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Department of Otolaryngology Emory University School of Medicine 1 Sinus Headache Problems
Cardiac Masses and Tumors
 Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
Cervical lymphadenopathy
 Cervical lymphadenopathy Introduction There are various classifications of lymphadenopathy, but a simple and clinically useful system is to classify lymphadenopathy as "generalized" if lymph nodes are
Cervical lymphadenopathy Introduction There are various classifications of lymphadenopathy, but a simple and clinically useful system is to classify lymphadenopathy as "generalized" if lymph nodes are
SCAPULAR FRACTURES. Jai Relwani, Shoulder Fellow, Reading Shoulder Unit, Reading.
 SCAPULAR FRACTURES Jai Relwani, Shoulder Fellow, Reading Shoulder Unit, Reading. Aims Anatomy Incidence/Importance Mechanism Classification Principles of treatment Specific variations Conclusion Anatomy
SCAPULAR FRACTURES Jai Relwani, Shoulder Fellow, Reading Shoulder Unit, Reading. Aims Anatomy Incidence/Importance Mechanism Classification Principles of treatment Specific variations Conclusion Anatomy
Musculoskeletal Infection Care Process Model
 Musculoskeletal Infection Care Process Model Musculoskeletal infections are serious and potentially life-threatening. Musculoskeletal infections include necrotizing fasciitis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis,
Musculoskeletal Infection Care Process Model Musculoskeletal infections are serious and potentially life-threatening. Musculoskeletal infections include necrotizing fasciitis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis,
8_Neck Trauma STN E-Library 2012 1
 1 The evaluation and management of neck trauma has evolved over the past few decades. However, the challenges remain the same in that injuries to structures in the neck may cause life threatening situations
1 The evaluation and management of neck trauma has evolved over the past few decades. However, the challenges remain the same in that injuries to structures in the neck may cause life threatening situations
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Small cell lung cancer
 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
TRACHEOSTOMY TUBE PARTS
 Page1 NR 33 TRACHEOSTOMY CARE AND SUCTIONING Review ATI Basic skills videos: Tracheostomy care and Endotracheal suction using a closed suction set. TRACHEOSTOMY TUBE PARTS Match the numbers on the diagram
Page1 NR 33 TRACHEOSTOMY CARE AND SUCTIONING Review ATI Basic skills videos: Tracheostomy care and Endotracheal suction using a closed suction set. TRACHEOSTOMY TUBE PARTS Match the numbers on the diagram
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Spinal Cord Injury*
 ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Spinal Cord Injury* indicates intervening codes have been left out of this list. OTHER DISORDERS OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (340-349) 344 Other paralytic syndromes
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Spinal Cord Injury* indicates intervening codes have been left out of this list. OTHER DISORDERS OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (340-349) 344 Other paralytic syndromes
Pediatric Oncology for Otolaryngologists
 Pediatric Oncology for Otolaryngologists Frederick S. Huang, M.D. Division of Hematology/Oncology Department of Pediatrics The University of Texas Medical Branch Grand Rounds Presentation to Department
Pediatric Oncology for Otolaryngologists Frederick S. Huang, M.D. Division of Hematology/Oncology Department of Pediatrics The University of Texas Medical Branch Grand Rounds Presentation to Department
General Thoracic Surgery ICD9 to ICD10 Crosswalks. C34.11 Malignant neoplasm of upper lobe, right bronchus or lung
 ICD-9 Code ICD-9 Description ICD-10 Code ICD-10 Description 150.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus 150.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle
ICD-9 Code ICD-9 Description ICD-10 Code ICD-10 Description 150.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus 150.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle
How To Harvest Fat From The Infratemporal Fossila
 Techniques in Cosmetic Surgery Harvesting Fat from the Infratemporal Fossa Bahman Guyuron, M.D., and Kevin Rose, M.D. Cleveland, Ohio As part of forehead rejuvenation and surgical treatment of migraine
Techniques in Cosmetic Surgery Harvesting Fat from the Infratemporal Fossa Bahman Guyuron, M.D., and Kevin Rose, M.D. Cleveland, Ohio As part of forehead rejuvenation and surgical treatment of migraine
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS
 BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS Course Title: DMS 213 - Abdominal Sonography 2 2 lec. 3 lab. 3 credits (5 hours) Required
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS Course Title: DMS 213 - Abdominal Sonography 2 2 lec. 3 lab. 3 credits (5 hours) Required
Diagnostic Radiology is a branch of medical practice concerned with the use of imaging techniques in the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease.
 Objectives of Training in the Specialty of Diagnostic Radiology This document applies to those who begin training on or after July 1 st, 2014. 2014 VERSION 1.0 DEFINITION Diagnostic Radiology is a branch
Objectives of Training in the Specialty of Diagnostic Radiology This document applies to those who begin training on or after July 1 st, 2014. 2014 VERSION 1.0 DEFINITION Diagnostic Radiology is a branch
Difficult Vascular Access Alternative Approaches & Troubleshooting Tips
 Difficult Vascular Access Alternative Approaches & Troubleshooting Tips Michelle Lin, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Emergency Medicine UC San Francisco - San Francisco General Hospital [email protected]
Difficult Vascular Access Alternative Approaches & Troubleshooting Tips Michelle Lin, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Emergency Medicine UC San Francisco - San Francisco General Hospital [email protected]
9. Discuss guidelines for follow-up post-thyroidectomy for cancer (labs/tests) HH
 9. Discuss guidelines for follow-up post-thyroidectomy for cancer (labs/tests) HH Differentiated thyroid cancer expresses the TSH receptor on the cell membrane and responds to TSH stimulation by increasing
9. Discuss guidelines for follow-up post-thyroidectomy for cancer (labs/tests) HH Differentiated thyroid cancer expresses the TSH receptor on the cell membrane and responds to TSH stimulation by increasing
Instability concept. Symposium- Cervical Spine. Barcelona, February 2014
 Instability concept Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd AOSpine Principles Symposium- Cervical Spine Orthopaedic Depatment. Spine Unit. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor UAB Barcelona, February 2014
Instability concept Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd AOSpine Principles Symposium- Cervical Spine Orthopaedic Depatment. Spine Unit. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor UAB Barcelona, February 2014
Wound Classification Name That Wound Sheridan, WY June 8 th 2013
 Initial Wound Care Consult Sheridan, WY June 8 th, 2013 History Physical Examination Detailed examination of the wound Photographs Cultures Procedures TCOM ABI Debridement Management Decisions A Detailed
Initial Wound Care Consult Sheridan, WY June 8 th, 2013 History Physical Examination Detailed examination of the wound Photographs Cultures Procedures TCOM ABI Debridement Management Decisions A Detailed
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time.
 If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
