Advanced Accounting-100 Introduction to Business Combinations Page 1
|
|
|
- Lambert Horton
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advanced Accounting-100 Introduction to Business Combinations Page 1 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS COMBINATIONS I. Key Concepts and Terms: A. Business Combinations 1. OBJECTIVES: a. Growth--increase economic strength; new markets; b. Diversification--decrease dependency on existing suppliers/markets c. Competitive Advantage--economies of scale; access to new data 4. Tax advantages-- tax free reorganization (as defined in the Internal Revenue Code (IRC) #368); Net operating loss (NOL) carry forward / carry back (IRC #172) 2. TYPES OF BUSINESS COMBINATIONS: (Defined by the courts through the Sherman and Clayton anti-trust acts) a. Horizontal--Firms in same market with similar products b. Vertical--Supplier/customer relationship c. Conglomerate--firms with various diversified products and markets Note: The IRC #368 recognizes three methods of combination; the 80% provision is an IRS requirement only; 50% is the requirement for GAAP 1. TYPE A: a. Statutory Merger-- (A + B = A); one survivor from combining firms; b. Statutory Consolidation-- (A + B = C); a new company is formed to acquire the net assets of the combining companies; -- the "statutory" reference refers to the statutes of the state where the Corporation is chartered -- a continuity of interest required -- debt and cash exchanged is limited by statute 2. TYPE B: a. Acquisition of Stock--(Independent A and Independent B combine to form parent A and subsidiary B) --generally no cash to change hands except to acquire a minority interest; --acquiring company must "control" at least 80% of the acquired company voting stock; 3. TYPE C: a. Acquisition of Assets--acquired directly from the company through direct negotiation; --to be tax free, at least 80% must be acquired for stock; 3. CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS: When one company obtains a controlling interest (generally an amount over 50 percent) of another parties stock in a purchase combination or at least 90% of another parties stock in a pooling combination, the acquiring company is able to exert "significant influence" over the acquired company. This influence means that transactions between the consolidated companies can no longer be considered independent (at arms-length), because one company could require the other to engage in transactions that would never be made between independent parties. The effects of these "intercompany transactions" must be eliminated prior to the presentation of the consolidated financial statements in order to avoid distortion of the economic reality underlying the transaction. This is accomplished by having the parent (in a purchase combination or "issuer" company in a pooling combination) prepare consolidated financial statements. The consolidated financial statements are the financial statements of the parent (issuer in a pooling) and the consolidated subsidiaries. The unique aspect of consolidated financial statements is that they eliminate the effects of all intercompany transactions between members of the consolidated group prior to the presentation of the financial statements. These elimination entries are working paper entries made by the parent (issuer company in a pooling) and are never recorded on the separate books of any member of the consolidated group. It is important to note that each entity continues to exist as a separate legal entity but is considered a single consolidated accounting entity for purposes of financial reporting. a. Example: To illustrate, consider that "P" company owns 100% of "S" company common stock. "S" purchases a machine tool for $100 in the open market from an independent party and then sells it to "P" for $500. Note that "P" could go into the open market and buy the exact same machine tool for $100. If "P" buys the machine tool from "S", the effect is to artificially overstate both the income of "S" and the assets on the books of "P". The following journal entries would have been made by "S" and "P" respectively:
2 Advanced Accounting-100 Introduction to Business Combinations Page 2 "S" Books "P" Books Record purchase of machine tool: Machine tool No entry Cash Record sale of machine tool to "P": Record purchase of machine tool: Cash Machine tool Machine tool Cash Gain on sale of machine tool Notice that "S" has recorded $400 gain, and "P" carries the machine tool at $500; both of these amounts are distortions resulting from an intercompany transaction. GAAP requires that "P" carry the asset at the lower cost to the consolidated group or market value. This means that the consolidated financial statements must carry the asset at $100 and "S" should not recognize any profit on the sale. This would be the same result that would have been obtained if "P" had made an "arm-length" purchase in the open market with an independent party. The following adjusting entries would be made by "P" on the consolidated working papers to eliminate the effects of the intercompany transaction and insure that the consolidated financial statements report only the fair market value of the asset (as established in the market) and eliminate the fictitious gain: Eliminate the effects of the intercompany sale: * Gain on sale of machine tool machine tool *This entry is made on the consolidated working papers prepared by the parent (issuer in a pooling) and are not recorded on the books of any member of the consolidated group. Note: We re getting a bit ahead of ourselves here, but notice that the machine tool is now carried at FMV ($100) and the gain on the sale is eliminated in the consolidation process we ll learn about this elimination process in detail in future examples. 4. MINORITY INTEREST: When the controlling interest in a business combination is less than 100% a minority interest exists; i.e. those subsidiary stockholders holding the shares that are not owned by the controlling interest are referred to as the minority interest; the minority interest may or may not be related to the consolidated group in other investments but are always treated as non- related in preparing consolidated financial statements. a. Example: "P" purchases 85% of the common stock of "S" in a purchase combination. The 15% not held by "P" (the controlling interest) are referred to as the minority interest. 5. METHODS OF BUSINESS COMBINATIONS: The GAAP underlying the procedures of recording business combinations is found in APB- 16 (Business Combinations), APB-18 (Equity Method) and SFAS-12 (Cost Method). APB-16 establishes 12 requirements that must be met by the combining firms in order for the combination to qualify as a pooling of interest; if any of those requirements are not met, the firms must record the combination as a purchase. Under purchase accounting, there are two alternative approaches, which may be elected: the equity method (as promulgated in APB-18) and the cost method (as promulgated in SFAS-12). This relationship is outlined below: APB-16 Business Combinations Establishes 12 requirements that must be met in order for the combining companies to qualify for a Pooling of Interest Requirements not met Requirements Met Follow Purchase Accounting Procedures i.e. SFAS 115 or APB 18 FMV ACCT Equity Method Follow Pooling Procedures* (Use of Pooling is allowed only if the consolidation was properly recorded as a Pooling prior to SFAS 141 in 2001(revised 2007)
3 Advanced Accounting-100 Introduction to Business Combinations Page 3 6. PURCHASE COMBINATIONS: In a purchase consolidation one company (the parent) gains control of another by purchasing a controlling interest (greater than 50%) of the assets or voting stock of another (subsidiary) company. Because a "purchase" has taken place, any excess of cost over the fair market value of the identifiable assets is allocated to goodwill. Remember that goodwill can only be created in a purchase combination. a. Summary of Procedures: 1. Record the investment at full cost: Full cost is defined as all costs normal and necessary to complete the purchase with the exception of SEC registration costs and stock issuance costs (which are expensed). 2. Analyzing the Investment in a Purchase Combination: Allocate the excess of cost over book value (or book value over cost) to the assets and liabilities of the subsidiary as follows: a. Subsidiary current assets, liabilities and investments in marketable equity securities will always be valued at their full market value. (These accounts can be referred to as the fair market value (FMV) accounts in that they must always be adjusted to full fair market value). b. Subsidiary non current assets will be allocated any excess of cost over book value remaining. c. Any excess of cost over book value remaining after bringing all other accounts to full fair market value is allocated to goodwill. Recall that goodwill can only be created in a purchase combination in which all identifiable assets and liabilities have been brought to full fair market value. 3. The application of these procedures is accomplished by through a procedure known as Analyzing the Investment. This procedure is illustrated below. 4. The effects of intercompany transactions must be eliminated. 5. Intercompany bonds must be treated as though retired. Purchase Combinations Summary Table Type of Account "P" Books "S" Books Consolidated Books FMV Accounts (CA, Liabilities, MES) All FMV accounts must be valued at full FMV BV + FMV Non-Current Assets (NCA) BV + Purchase Differential Available to NCA after writing FMV account to full FMV Note: the allocation of available excess to NCA is made so as to insure than NCA are carried in accordance with their relative FMV. BV + adjusted value CS PIC Retained Earnings SHE of "P" only 7. POOLING COMBINATIONS: The conceptual foundation underlying a pooling of interest is that two existing companies combine their existing interest and continue in a new form; a pooling is simply a change of accounting entity in which A + B = C or A + B = either A or B. No purchase takes place the ownership interest of the new entity consists of the pooled interest of the pre-existing companies. The company issuing the securities of the new entity is called the "issuer" company and the company or companies giving up their existing securities are called the "combiner" company. An important difference between pooling combinations and purchase combinations is that pooling combinations allow the "issuer" company to absorb the "combiners" retained earnings. This means that the issuer accrues the combiner s net income for the entire year even if the combination takes place on the last day of the accounting year. This is sometimes referred to as "instant earnings". a. Summary of procedures: 1. Record the investment at the book value of the assets less the book value of the liabilities, and expense all costs of the combination in the current period (recall that in a purchase all cost were capitalized except for SEC and stock registration costs). 2. The value of par issued to consummate the pooling is compared to the percentage of Combiner PIC obtained. No goodwill can ever be created in a pooling, but pre-existing goodwill is treated like any other asset. 3. If par issued is less than total combiner PIC obtained, the difference is credited to Issuer PIC. If par issued is greater than PIC obtained the difference is debited against I PIC to the extent available and then debited against C retained earnings.
4 Advanced Accounting-100 Introduction to Business Combinations Page 4 4. The application of these procedures is accomplished through a procedure known as analyzing the investment. Note that the analysis process in a pooling combination differs from the analysis procedure in a purchase combination. Analyzing the investment in a pooling combination: --Step 1: Analyze the pooling to determine the makeup of PIC received. Par issued (Par x number of shares issued)... Total PIC received: Common stock (Par x number of shares received)... If par issued < PIC received then allocated to issuer PIC (where x-y is negative number). gain**) $ xxx,xxx yyy,yyy Zzz, zzz (This is a Good Deal, equivalent to a If par issued > PIC received; excess of par issued over PIC received (w=x-y; w is positive) $ www,www (This is a Bad Deal, equivalent to a loss**) Therefore: 1. Reduce Issuer PIC (to extent available)... $ AA, AAA; if that is not sufficient to account for the deficit then 2. reduce Combiner RE as required to balance (w=a+b) bb,bbb ** Note: Remember there can never be a real gain or loss on transactions involving a companies own stock. When a credit is needed to balance, credit Paid in Capital in excess of Par (PIC); When a debit is called for, Debit the Combiner s (The surviving company) PIC to the extent it is available (you must check the account balances given in the problem) then reduce (debit) Combiner RE as required to balance. This is the same procedure followed in every transaction involving a companies own stock (including treasury stock transactions). --Step 2: Record the pooling Current assets... xx,xxx* Property, plant, and equipment... xxx,xxx* Other assets... xx,xxx* ** PIC-Issuer (if par issued > PIC received)... xx,xxx ** PIC-Issuer (par issued < PIC received)... xx,xxx Accumulated depreciation... xx,xxx* Accounts payable... xx,xxx* Common stock... xxx,xxx*** Retained earnings... xxx,xxx*** * Recorded at book value without adjustment ** Will not appear simultaneously *** Recorded at the adjusted value derived by the analysis of the pooling (see step #1 Above) -- Combinations by pooling of interest will NEVER result in goodwill because the combination is at book value. -- All expenses incurred in pooling are deducted from income of the combined corporation for the period in which the expenses are incurred. Recall that in a purchase combination only SEC registration costs and stock issuance cost were expense. -- Treasury stock issued by the acquiring company should be treated as though retired. -- The effects of intercompany transactions are eliminated. -- Intercompany bonds are treated as though retired
5 Advanced Accounting-100 Introduction to Business Combinations Page 5 Acquistion Terminology: A. Stock Acquisitions 1. Friendly: Stockholders of target company agree to sell shares based on the tender offer 2. Unfriendly: Management and/or a significant number of shareholders oppose the sale 3. Greenmail: The target company is willing to pay a premium price to purchase treasury shares in order to thwart to acquisition. 4. White Knight: Target company identifies another company to acquire it; often used when the initial acquisition is being made by a competitor in the same industry and the target companies management thinks it will be sacked after acquisition. 5. Poison Pill: If the acquiring company attempts to gain control by purchasing a minimal number of shares, the target company may offer to sell shares to its existing stockholders at an extremely discounted price. This has the effect of increasing the number of shares that that must be acquired to gain control which increases the cost of the acquisition. 6. Selling the Crown Jewels: Management of the target company may sell of those assets that the acquiring company is most interested in, thereby eliminating the purpose of the acquisition. 7. Leveraged Buyout: A technique often used by management of the target company to purchase controlling interest in their company through debt (bond) financing. The bonds issued to purchase the stock are often Junk Bonds (high interest with relatively little collateral value). i. An interesting and important tax consideration is that if the new management can raise the value of the company, that increase in value is taxed at capital gains rates as opposed to income tax rates This is how venture capitalist can convert what would normally be income into capital gains and reap the corresponding tax benefits (under current tax law) note:
COMPONENTS OF THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
 ILLUSTRATION 24-1 OPERATING, INVESTING, AND FINANCING ACTIVITIES COMPONENTS OF THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES + Sales and Service Revenue Received Cost of Sales Paid Selling
ILLUSTRATION 24-1 OPERATING, INVESTING, AND FINANCING ACTIVITIES COMPONENTS OF THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES + Sales and Service Revenue Received Cost of Sales Paid Selling
Dr. M. D. Chase Advanced Accounting Exam 1AA Page 1 of 9
 Advanced Accounting Exam 1AA Page 1 of 9 MARK THE LETTER OF THE BEST ANSWER ON YOUR SCANTRON FORM. 1. A business combination is accounted for appropriately as a pooling of interests. Costs of furnishing
Advanced Accounting Exam 1AA Page 1 of 9 MARK THE LETTER OF THE BEST ANSWER ON YOUR SCANTRON FORM. 1. A business combination is accounted for appropriately as a pooling of interests. Costs of furnishing
Outline: I. Background.
 Sessions 11&12 Mergers & Acquisitions Damodaran: Chapter 24: 4,14,15 (read pages 661-665, empirical evidence on capital structure changes and dividend policy; pages 667-670, EVA) Damodaran Chapter 25:
Sessions 11&12 Mergers & Acquisitions Damodaran: Chapter 24: 4,14,15 (read pages 661-665, empirical evidence on capital structure changes and dividend policy; pages 667-670, EVA) Damodaran Chapter 25:
Most economic transactions involve two unrelated entities, although
 139-210.ch04rev.qxd 12/2/03 2:57 PM Page 139 CHAPTER4 INTERCOMPANY TRANSACTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Understand the different types of intercompany transactions
139-210.ch04rev.qxd 12/2/03 2:57 PM Page 139 CHAPTER4 INTERCOMPANY TRANSACTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Understand the different types of intercompany transactions
SCORPEX INTERNATIONAL, INC.
 AUDIT REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM AND CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS C O N T E N T S Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.... 3 Consolidated Balance Sheets...
AUDIT REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM AND CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS C O N T E N T S Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.... 3 Consolidated Balance Sheets...
Investments and advances... 313,669
 Consolidated Financial Statements of the Company The consolidated balance sheet, statement of income, and statement of equity of the Company are as follows. Please note the Company s consolidated financial
Consolidated Financial Statements of the Company The consolidated balance sheet, statement of income, and statement of equity of the Company are as follows. Please note the Company s consolidated financial
11. Corporate Restructuring. Corporate Control. Mergers & Acquisitions
 11. Corporate Restructuring. Corporate Control. Mergers & Acquisitions 1. Assets and Liabilities Engineering 1.1.1 Corporate Restructuring The term corporate restructuring pertains to a large range of
11. Corporate Restructuring. Corporate Control. Mergers & Acquisitions 1. Assets and Liabilities Engineering 1.1.1 Corporate Restructuring The term corporate restructuring pertains to a large range of
1. The primary forms of business organization are the proprietorship, the partnership, and the corporation.
 Chapter 15 Stockholders Equity: Contributed Capital LECTURE OUTLINE This material in this chapter is straight-forward and can be covered in one or two class sessions. Treasury stock transactions under
Chapter 15 Stockholders Equity: Contributed Capital LECTURE OUTLINE This material in this chapter is straight-forward and can be covered in one or two class sessions. Treasury stock transactions under
Consolidated Balance Sheets
 Consolidated Balance Sheets March 31 2015 2014 2015 Assets: Current assets Cash and cash equivalents 726,888 604,571 $ 6,057,400 Marketable securities 19,033 16,635 158,608 Notes and accounts receivable:
Consolidated Balance Sheets March 31 2015 2014 2015 Assets: Current assets Cash and cash equivalents 726,888 604,571 $ 6,057,400 Marketable securities 19,033 16,635 158,608 Notes and accounts receivable:
Consolidated Interim Earnings Report
 Consolidated Interim Earnings Report For the Six Months Ended 30th September, 2003 23th Octorber, 2003 Hitachi Capital Corporation These financial statements were prepared for the interim earnings release
Consolidated Interim Earnings Report For the Six Months Ended 30th September, 2003 23th Octorber, 2003 Hitachi Capital Corporation These financial statements were prepared for the interim earnings release
AAA PUBLIC ADJUSTING GROUP, INC. (EXACT NAME OF REGISTRANT AS SPECIFIED IN ITS CHARTER)
 UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549 FORM 10-Q [ X] QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OF 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 For the quarterly period ended
UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549 FORM 10-Q [ X] QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OF 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 For the quarterly period ended
07:58. Think about it STOCKHOLDERS EQUITY. Stockholders Equity Components. Chapter 15. Three Buckets:
 STOCKHOLDERS EQUITY Chapter 15 Think about it Who owns a Company? The Stockholders Who controls a Company? The Stockholders Who runs the Company? Executive Management (called C level, as in C EO, CFO,
STOCKHOLDERS EQUITY Chapter 15 Think about it Who owns a Company? The Stockholders Who controls a Company? The Stockholders Who runs the Company? Executive Management (called C level, as in C EO, CFO,
Consolidation Following Acquisition. Consolidation Following Acquisition. Consolidated Net Income. Computing Consolidated Net Income
 Chapter 5 Consolidation Following Acquisition The procedures used to prepare a consolidated balance sheet as of the date of acquisition were introduced in the preceding chapter, that is, Chapter 4. More
Chapter 5 Consolidation Following Acquisition The procedures used to prepare a consolidated balance sheet as of the date of acquisition were introduced in the preceding chapter, that is, Chapter 4. More
ACER INCORPORATED AND SUBSIDIARIES. Consolidated Balance Sheets
 Consolidated Balance Sheets June 30, 2015, December 31, 2014, and (June 30, 2015 and 2014 are reviewed, not audited) Assets 2015.6.30 2014.12.31 2014.6.30 Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents $ 36,400,657
Consolidated Balance Sheets June 30, 2015, December 31, 2014, and (June 30, 2015 and 2014 are reviewed, not audited) Assets 2015.6.30 2014.12.31 2014.6.30 Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents $ 36,400,657
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 25. Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No.25. Business Combinations
 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 25 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No.25 Business Combinations Revised on 30 November 2006 Translated by Ling-Tai Lynette Chou, Professor (National
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 25 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No.25 Business Combinations Revised on 30 November 2006 Translated by Ling-Tai Lynette Chou, Professor (National
Consolidated financial statements
 Financial 3 Becker Professional Education CPA Exam Review Consolidated financial statements I. CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS A. Control (over 50%) Consolidated financial statements are prepared when
Financial 3 Becker Professional Education CPA Exam Review Consolidated financial statements I. CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS A. Control (over 50%) Consolidated financial statements are prepared when
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 7. Consolidated Financial Statements
 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 7 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 7 Consolidated Financial Statements 30 November 2004 Translated by Wei-heng Lin, Associate Professor (Chung
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 7 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 7 Consolidated Financial Statements 30 November 2004 Translated by Wei-heng Lin, Associate Professor (Chung
2-8. Identify whether each of the following items increases or decreases cash flow:
 Problems 2-8. Identify whether each of the following items increases or decreases cash flow: Increase in accounts receivable Increase in notes payable Depreciation expense Increase in investments Decrease
Problems 2-8. Identify whether each of the following items increases or decreases cash flow: Increase in accounts receivable Increase in notes payable Depreciation expense Increase in investments Decrease
Consolidated Financial Statements. Chapter 3. Consolidated Financial Statements. Consolidated Financial Statements. Consolidated Financial Statements
 Chapter 3 The Reporting Entity and Consolidated Financial Statements Consolidated Financial Statements Many corporations are composed of numerous separate companies and, in turn, prepare consolidated financial
Chapter 3 The Reporting Entity and Consolidated Financial Statements Consolidated Financial Statements Many corporations are composed of numerous separate companies and, in turn, prepare consolidated financial
85.52 Investments. 85.52.10 July 1, 2003. About investments. Short-term investments. 85.52.20 June 1, 2003 85.52.10
 85.52.10 85.52 Investments 85.52.10 July 1, 2003 About investments Investments are made as authorized by law and/or contractual agreement. Investment purchase and sale transactions are to be reported for
85.52.10 85.52 Investments 85.52.10 July 1, 2003 About investments Investments are made as authorized by law and/or contractual agreement. Investment purchase and sale transactions are to be reported for
Investments and advances... 344,499
 Consolidated Financial Statements of the Company The consolidated balance sheet, statement of income, and statement of equity of the Company are as follows. Please note the Company s consolidated financial
Consolidated Financial Statements of the Company The consolidated balance sheet, statement of income, and statement of equity of the Company are as follows. Please note the Company s consolidated financial
Accounting for Multiple Entities
 King Saud University College of Administrative Science Department of Accounting 2 nd Semester, 1426-1427 Accounting for Multiple Entities Chapter 15 Prepared By: Eman Al-Aqeel Professor : Dr: Amal Fouda
King Saud University College of Administrative Science Department of Accounting 2 nd Semester, 1426-1427 Accounting for Multiple Entities Chapter 15 Prepared By: Eman Al-Aqeel Professor : Dr: Amal Fouda
6. Depreciation is a process of a. asset devaluation. b. cost accumulation. c. cost allocation. d. asset valuation.
 1. A company purchased land for $72,000 cash. Real estate brokers' commission was $5,000 and $7,000 was spent for demolishing an old building on the land before construction of a new building could start.
1. A company purchased land for $72,000 cash. Real estate brokers' commission was $5,000 and $7,000 was spent for demolishing an old building on the land before construction of a new building could start.
EMERSON AND SUBSIDIARIES CONSOLIDATED OPERATING RESULTS (AMOUNTS IN MILLIONS EXCEPT PER SHARE, UNAUDITED)
 CONSOLIDATED OPERATING RESULTS (AMOUNTS IN MILLIONS EXCEPT PER SHARE, UNAUDITED) TABLE 1 Quarter Ended March 31, Percent Change Net Sales $ 5,854 $ 5,919 1% Costs and expenses: Cost of sales 3,548 3,583
CONSOLIDATED OPERATING RESULTS (AMOUNTS IN MILLIONS EXCEPT PER SHARE, UNAUDITED) TABLE 1 Quarter Ended March 31, Percent Change Net Sales $ 5,854 $ 5,919 1% Costs and expenses: Cost of sales 3,548 3,583
Consolidation-Date of Acquisition. Chapter 4. Consolidation-GAAP. Consolidation-Date of Acquisition. Roadmap Chapters 5 to 10.
 Chapter 4 Consolidation As Of The Date Of Acquisition Consolidation-Date of Acquisition Consolidated statements bring together the operating results and financial position of two or more separate legal
Chapter 4 Consolidation As Of The Date Of Acquisition Consolidation-Date of Acquisition Consolidated statements bring together the operating results and financial position of two or more separate legal
STATE OF FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF BUSINESS AND PROFESSIONAL REGULATION. BALANCE SHEET As of
 STATE OF FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF BUSINESS AND PROFESSIONAL REGULATION BALANCE SHEET As of ASSETS CURRENT ASSETS Cash and Cash Equivalents Cash - Restricted Accounts Receivable - Trade Accounts Receivable
STATE OF FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF BUSINESS AND PROFESSIONAL REGULATION BALANCE SHEET As of ASSETS CURRENT ASSETS Cash and Cash Equivalents Cash - Restricted Accounts Receivable - Trade Accounts Receivable
Property and equipment, net 1,043 167 Goodwill, net 59,169 - Other intangibles, net 3,005 - Other assets 892 744
 U.S. SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549 ------------------------------- FORM 10-QSB Quarterly Report under Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 For the quarterly
U.S. SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549 ------------------------------- FORM 10-QSB Quarterly Report under Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 For the quarterly
Investments and Acquisitions
 Investments and Acquisitions Understand that the accounting method used for investments depends on the extent to which the investor exerts influence over the investee. Understand the effects of dividends
Investments and Acquisitions Understand that the accounting method used for investments depends on the extent to which the investor exerts influence over the investee. Understand the effects of dividends
Chapter 8: account receivable
 Chapter 8: account receivable Three accounting issues associated with accounts receivable are: 1. Recognizing accounts receivable 2. Valuing accounts receivable 3. Disposing of accounts receivable Recognizing
Chapter 8: account receivable Three accounting issues associated with accounts receivable are: 1. Recognizing accounts receivable 2. Valuing accounts receivable 3. Disposing of accounts receivable Recognizing
CHAPTER 15. Stockholders Equity ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE (BY TOPIC) Concepts for Analysis. Brief Exercises Exercises Problems
 CHAPTER 15 Stockholders Equity ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE (BY TOPIC) Topics Questions Brief Exercises Exercises Problems Concepts for Analysis *1. Stockholders rights; corporate form. 1, 2, 3, 4,
CHAPTER 15 Stockholders Equity ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE (BY TOPIC) Topics Questions Brief Exercises Exercises Problems Concepts for Analysis *1. Stockholders rights; corporate form. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Vizrt Group AS Reports Q1 2015 Results
 Vizrt Group AS Quarterly report March 31, 2015 Vizrt Group AS Reports Q1 2015 Results Business Overview On March 19, 2015, Vizrt Group AS (formerly Aksjeselskapet av 17. Oktober 2014 AS ) ( the Company
Vizrt Group AS Quarterly report March 31, 2015 Vizrt Group AS Reports Q1 2015 Results Business Overview On March 19, 2015, Vizrt Group AS (formerly Aksjeselskapet av 17. Oktober 2014 AS ) ( the Company
CIMA Managerial Level Paper F2 FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT (REVISION SUMMARIES)
 CIMA Managerial Level Paper F2 FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT (REVISION SUMMARIES) Chapter Title Page number 1 The regulatory framework 3 2 What is a group 9 3 Group accounts the statement of financial position
CIMA Managerial Level Paper F2 FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT (REVISION SUMMARIES) Chapter Title Page number 1 The regulatory framework 3 2 What is a group 9 3 Group accounts the statement of financial position
RECOGNIZING A MINORITY INTEREST IN CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
 RECOGNIZING A MINORITY INTEREST IN CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS L E A R N I N G O B J E C T I V E Adapt the consolidation work sheet procedure to recognize a minority interest. Chapter 11 illustrates
RECOGNIZING A MINORITY INTEREST IN CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS L E A R N I N G O B J E C T I V E Adapt the consolidation work sheet procedure to recognize a minority interest. Chapter 11 illustrates
CHAPTER 23. Statement of Cash Flows 1, 2, 7, 8, 12 3, 4, 5, 6, 16, 17, 19 9, 20 4, 5, 9, 10, 11 10, 13, 15, 16. 7. Worksheet adjustments.
 CHAPTER 23 Statement of Cash Flows ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE (BY TOPIC) Topics Questions Brief Exercises Exercises Problems Concepts for Analysis 1. Format, objectives purpose, and source of statement.
CHAPTER 23 Statement of Cash Flows ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE (BY TOPIC) Topics Questions Brief Exercises Exercises Problems Concepts for Analysis 1. Format, objectives purpose, and source of statement.
Assignment Problems For Chapter 3
 Page 4 Assignment Problems For Chapter 3 (The solutions for these problems are only available in the solutions manual that has been provided to your instructor.) Assignment Problem Three - 1 (Purchase
Page 4 Assignment Problems For Chapter 3 (The solutions for these problems are only available in the solutions manual that has been provided to your instructor.) Assignment Problem Three - 1 (Purchase
ACCOUNTING SOLUTIONS SCO: 209, First Floor, Sector-36/D. Chandigarh (M): 0172-5017149, 9876149390,9915169925 HOLDING COMPANIES
 : ACCOUNTING SOLUTIONS HOLDING COMPANIES When a company acquires majority of shares in the ownership or is in a position to control the management of the other company, the company is called a holding
: ACCOUNTING SOLUTIONS HOLDING COMPANIES When a company acquires majority of shares in the ownership or is in a position to control the management of the other company, the company is called a holding
Intercompany Indebtedness. Chapter 8. Intercompany Indebtedness. Consolidation Overview. Consolidation Overview. Intercompany Indebtedness
 Chapter 8 Intercompany Indebtedness Intercompany Indebtedness One advantage of having control over other companies is that management has the ability to transfer resources from one legal entity to another
Chapter 8 Intercompany Indebtedness Intercompany Indebtedness One advantage of having control over other companies is that management has the ability to transfer resources from one legal entity to another
Consolidated Balance Sheets March 31, 2001 and 2000
 Financial Statements SEIKAGAKU CORPORATION AND CONSOLIDATED SUBSIDIARIES Consolidated Balance Sheets March 31, 2001 and 2000 Assets Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents... Short-term investments (Note
Financial Statements SEIKAGAKU CORPORATION AND CONSOLIDATED SUBSIDIARIES Consolidated Balance Sheets March 31, 2001 and 2000 Assets Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents... Short-term investments (Note
The Statement of Cash Flows
 CHAPTER The Statement of Cash Flows OBJECTIVES After careful study of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Define operating, investing, and financing activities. 2. Know the categories of inflows and
CHAPTER The Statement of Cash Flows OBJECTIVES After careful study of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Define operating, investing, and financing activities. 2. Know the categories of inflows and
Corporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and Dividends
 C H A P T E R 13 Corporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and Dividends Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Advantages and Disadvantages of the Corporate Form
C H A P T E R 13 Corporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and Dividends Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Advantages and Disadvantages of the Corporate Form
Pursuit Management, Inc. dba: MobileSpike Technologies, Inc. Financial Statements and Independent Accountants Review Report December 31, 2015 and
 Financial Statements and Independent Accountants Review Report December 31, 2015 and 2014 Financial Statements Contents INDEPENDENT ACCOUNTANTS REVIEW REPORT 1 Page FINANCIAL STATEMENTS: Balance sheets
Financial Statements and Independent Accountants Review Report December 31, 2015 and 2014 Financial Statements Contents INDEPENDENT ACCOUNTANTS REVIEW REPORT 1 Page FINANCIAL STATEMENTS: Balance sheets
Accounting for Equity Investments & Acquisitions
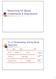 Accounting for Equity Investments & Acquisitions % of Outstanding Voting Stock Acquired 0% 20% 50% 100% Nominal Significant Control Level of Influence Fair Value Equity method Valuation Basis Investment
Accounting for Equity Investments & Acquisitions % of Outstanding Voting Stock Acquired 0% 20% 50% 100% Nominal Significant Control Level of Influence Fair Value Equity method Valuation Basis Investment
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS. Balance Sheets as of June 30, 2015 and December 31, 2014 (Unaudited) F-2
 INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS Page Financial Statements Balance Sheets as of and December 31, 2014 (Unaudited) F-2 Statements of Operations for the three months ended and 2014 (Unaudited) F-3 Statements
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS Page Financial Statements Balance Sheets as of and December 31, 2014 (Unaudited) F-2 Statements of Operations for the three months ended and 2014 (Unaudited) F-3 Statements
Chapter 1 Buying Assets
 1 Chapter 1 2 Chapter 1 Buying Assets Introduction (What we already know from Intro Acct Class) 3 Intro Acct Class When Buying Bundle of Assets E.g. Purch of Shopping Center Buying Land & Building Allocate
1 Chapter 1 2 Chapter 1 Buying Assets Introduction (What we already know from Intro Acct Class) 3 Intro Acct Class When Buying Bundle of Assets E.g. Purch of Shopping Center Buying Land & Building Allocate
Business Combinations
 59 CHAP TER 3 Business Combinations A Note On Relevant Accounting Standards 3-0. During the period until 2011 when IFRSs are incorporated into Canadian GAAP, the CICA Handbook contains two different Sections
59 CHAP TER 3 Business Combinations A Note On Relevant Accounting Standards 3-0. During the period until 2011 when IFRSs are incorporated into Canadian GAAP, the CICA Handbook contains two different Sections
Chapter 8 Accounting for Receivable
 Chapter 8 Accounting for Receivable Type of receivable: Receivable refers to amounts due from individuals and companies. o Account receivable: Amount customer owe on account, result from sales of goods
Chapter 8 Accounting for Receivable Type of receivable: Receivable refers to amounts due from individuals and companies. o Account receivable: Amount customer owe on account, result from sales of goods
PART III. Consolidated Financial Statements of Hitachi, Ltd. and Subsidiaries: Independent Auditors Report 47
 PART III Item 17. Financial Statements Consolidated Financial Statements of Hitachi, Ltd. and Subsidiaries: Schedule: Page Number Independent Auditors Report 47 Consolidated Balance Sheets as of March
PART III Item 17. Financial Statements Consolidated Financial Statements of Hitachi, Ltd. and Subsidiaries: Schedule: Page Number Independent Auditors Report 47 Consolidated Balance Sheets as of March
Corporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and Dividends
 C H A P T E R 11 Corporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and Dividends Corporate Financial Accounting 13e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Characteristics of a Corporation (slide
C H A P T E R 11 Corporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and Dividends Corporate Financial Accounting 13e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Characteristics of a Corporation (slide
SOLUTIONS. Learning Goal 30
 S1 Learning Goal 30 Multiple Choice 1. c A corporation wants to reissue treasury stock at a higher price than it paid. In this way, a greater amount of capital can be obtained than was returned to the
S1 Learning Goal 30 Multiple Choice 1. c A corporation wants to reissue treasury stock at a higher price than it paid. In this way, a greater amount of capital can be obtained than was returned to the
What is an ESOP? ESOPs are defined contribution pension plans that invest primarily in the stock of the plan sponsor
 Employee Stock Ownership Plans May 2013 http://aicpa.org/ebpaqc [email protected] Topix Primer Series The AICPA Employee Benefit Plan Audit Quality Center (EBPAQC) has developed this primer to provide Center
Employee Stock Ownership Plans May 2013 http://aicpa.org/ebpaqc [email protected] Topix Primer Series The AICPA Employee Benefit Plan Audit Quality Center (EBPAQC) has developed this primer to provide Center
Tower International Reports Solid Third Quarter And Raises Full Year Outlook
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Tower International Reports Solid Third Quarter And Raises Full Year Outlook LIVONIA, Mich., November 3, 2011 Tower International, Inc. [NYSE: TOWR], a leading integrated global manufacturer
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Tower International Reports Solid Third Quarter And Raises Full Year Outlook LIVONIA, Mich., November 3, 2011 Tower International, Inc. [NYSE: TOWR], a leading integrated global manufacturer
STUDY UNIT FIFTEEN BUSINESS COMBINATIONS AND CONSOLIDATION
 STUDY UNIT FIFTEEN BUSINESS COMBINATIONS AND CONSOLIDATION 545 (20 pages of outline) 15.1 Business Combinations... 545 15.2 Consolidation... 555 15.3 Combined Financial Statements... 564 15.4 Practice
STUDY UNIT FIFTEEN BUSINESS COMBINATIONS AND CONSOLIDATION 545 (20 pages of outline) 15.1 Business Combinations... 545 15.2 Consolidation... 555 15.3 Combined Financial Statements... 564 15.4 Practice
AMAZON.COM, INC. CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS (in millions)
 CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF PERIOD $ 8,084 $ 5,269 $ 3,777 OPERATING ACTIVITIES: Net income (loss) 274 (39) 631 Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF PERIOD $ 8,084 $ 5,269 $ 3,777 OPERATING ACTIVITIES: Net income (loss) 274 (39) 631 Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss)
Delaware 20-3708500 -------- ----------
 U.S. SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION Washington, D.C. 20549 FORM 10-QSB [X] QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 For the quarterly period ended November
U.S. SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION Washington, D.C. 20549 FORM 10-QSB [X] QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 For the quarterly period ended November
Corporate Taxation Chapter Eight: Taxable Acquisitions
 Presentation: Corporate Taxation Chapter Eight: Taxable Acquisitions Professors Wells March 18, 2013 Chapter 8 Taxable Corporate Acquisitions/Dispositions Corporate ownership disposition options: 1) Sale
Presentation: Corporate Taxation Chapter Eight: Taxable Acquisitions Professors Wells March 18, 2013 Chapter 8 Taxable Corporate Acquisitions/Dispositions Corporate ownership disposition options: 1) Sale
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE. Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations:
 TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
Employee Stock Ownership Plans ESOPs 101
 Employee Stock Ownership Plans ESOPs 101 BTA INC 2013 Complete Turn Key Services Full Service ESOP Implementation Services Preliminary Analysis Feasibility Studies Valuation Consulting Plan and Transaction
Employee Stock Ownership Plans ESOPs 101 BTA INC 2013 Complete Turn Key Services Full Service ESOP Implementation Services Preliminary Analysis Feasibility Studies Valuation Consulting Plan and Transaction
Session 19 -Taxable acquisitions
 -Taxable acquisitions Acquire stock or assets? Assume that Buyer Corporation wants to acquire the business of Target Corporation Target's assets have appreciated and are worth more than their tax basis
-Taxable acquisitions Acquire stock or assets? Assume that Buyer Corporation wants to acquire the business of Target Corporation Target's assets have appreciated and are worth more than their tax basis
Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 33 - Consolidated financial statements Caikuai [2006] No.3
![Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 33 - Consolidated financial statements Caikuai [2006] No.3 Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 33 - Consolidated financial statements Caikuai [2006] No.3](/thumbs/40/20527296.jpg) Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 33 - Consolidated financial statements Caikuai [2006] No.3 Chapter I General Provisions Article 1: These Standards are formulated in accordance with the
Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 33 - Consolidated financial statements Caikuai [2006] No.3 Chapter I General Provisions Article 1: These Standards are formulated in accordance with the
SECURITIES & EXCHANGE COMMISSION EDGAR FILING. NaturalShrimp Inc. Form: 8-K/A. Date Filed: 2015-08-27
 SECURITIES & EXCHANGE COMMISSION EDGAR FILING NaturalShrimp Inc Form: 8-K/A Date Filed: 2015-08-27 Corporate Issuer CIK: 1465470 Copyright 2016, Issuer Direct Corporation. All Right Reserved. Distribution
SECURITIES & EXCHANGE COMMISSION EDGAR FILING NaturalShrimp Inc Form: 8-K/A Date Filed: 2015-08-27 Corporate Issuer CIK: 1465470 Copyright 2016, Issuer Direct Corporation. All Right Reserved. Distribution
1 CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (1) Consolidated Balance Sheets
 1 CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (1) Consolidated Balance Sheets As of March 31,2014 As of March 31,2015 Assets Cash and due from banks 478,425 339,266 Call loans and bills bought 23,088 58,740 Monetary
1 CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (1) Consolidated Balance Sheets As of March 31,2014 As of March 31,2015 Assets Cash and due from banks 478,425 339,266 Call loans and bills bought 23,088 58,740 Monetary
JOHNSON GRADUATE SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT Cornell University
 JOHNSON GRADUATE SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT Cornell University Sample Accounting Exemption Exam Questions 1. On July 1, 20D, Allen Company signed a $50,000, one-year, 10 percent note payable. At due date, June
JOHNSON GRADUATE SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT Cornell University Sample Accounting Exemption Exam Questions 1. On July 1, 20D, Allen Company signed a $50,000, one-year, 10 percent note payable. At due date, June
Statement of Cash Flow
 Management Accounting 337 Statement of Cash Flow Cash is obviously an important asset to all, both individually and in business. A shortage or lack of cash may mean an inability to purchase needed inventory
Management Accounting 337 Statement of Cash Flow Cash is obviously an important asset to all, both individually and in business. A shortage or lack of cash may mean an inability to purchase needed inventory
EQUINIX, INC. CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS - GAAP PRESENTATION (in thousands, except per share data) (unaudited)
 CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS - GAAP PRESENTATION (in thousands, except per share data) Recurring revenues $ 314,727 $ 282,117 $ 216,517 $ 834,080 $ 610,384 Non-recurring revenues 15,620
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS - GAAP PRESENTATION (in thousands, except per share data) Recurring revenues $ 314,727 $ 282,117 $ 216,517 $ 834,080 $ 610,384 Non-recurring revenues 15,620
How To Calculate Cash Flow From Operating Activities
 Lawson Software, Inc. 10 Q Quarterly report pursuant to sections 13 or 15(d) Filed on 10/8/2009 Filed Period 8/31/2009 UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION Washington, D.C. 20549 FORM 10 Q
Lawson Software, Inc. 10 Q Quarterly report pursuant to sections 13 or 15(d) Filed on 10/8/2009 Filed Period 8/31/2009 UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION Washington, D.C. 20549 FORM 10 Q
The debt-to-equity conversion is a part of the Debt Restructuring Plan. The principles of a debt-to-equity conversion are as follows:
 "! 1. Policy and Procedures of the Debt-to-Equity Conversion Scheme, Rationale, Advantages and Disadvantages, and Benefits which the Company will obtain from the Debt-to-Equity Conversion Scheme 1.1 Policy
"! 1. Policy and Procedures of the Debt-to-Equity Conversion Scheme, Rationale, Advantages and Disadvantages, and Benefits which the Company will obtain from the Debt-to-Equity Conversion Scheme 1.1 Policy
TIME WARNER CABLE INC. CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET (Unaudited)
 CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET June 30, December 31, 2011 2010 (in millions) ASSETS Current assets: Cash and equivalents...$ 3,510 $ 3,047 Receivables, less allowances of $86 million and $74 million as of
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET June 30, December 31, 2011 2010 (in millions) ASSETS Current assets: Cash and equivalents...$ 3,510 $ 3,047 Receivables, less allowances of $86 million and $74 million as of
Cathay Life Insurance Co., Ltd. Financial Statements As of December 31, 2006 and 2007 With Independent Auditors Report
 Financial Statements With Independent Auditors Report The reader is advised that these financial statements have been prepared originally in Chinese. These financial statements do not include additional
Financial Statements With Independent Auditors Report The reader is advised that these financial statements have been prepared originally in Chinese. These financial statements do not include additional
Investments and International Operations
 A Look at This Appendix This appendix focuses on investments in securities. We explain how to identify, account for, and report investments in both debt and equity securities. We also explain accounting
A Look at This Appendix This appendix focuses on investments in securities. We explain how to identify, account for, and report investments in both debt and equity securities. We also explain accounting
Consolidated Financial Statements. Nippon Unipac Holding and Consolidated Subsidiaries
 Consolidated Financial Statements Nippon Unipac Holding and Consolidated Subsidiaries Period from March 30, 2001 (date inception) to September 30, 2001 Nippon Unipac Holding and Consolidated Subsidiaries
Consolidated Financial Statements Nippon Unipac Holding and Consolidated Subsidiaries Period from March 30, 2001 (date inception) to September 30, 2001 Nippon Unipac Holding and Consolidated Subsidiaries
DRAFT. Quarterly Savings and Loan Holding Company Report FR 2320. General Instructions Who Must Report. When to Submit the Report
 JOBNAME: No Job Name PAGE: 1 SESS: 378 OUTPUT: Mon Nov 21 10:08:25 2011 /frb/bsr/instructs/fr2320/4_dec11_2320-gen_v3 INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARATION OF Quarterly Savings and Loan Holding Company Report General
JOBNAME: No Job Name PAGE: 1 SESS: 378 OUTPUT: Mon Nov 21 10:08:25 2011 /frb/bsr/instructs/fr2320/4_dec11_2320-gen_v3 INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARATION OF Quarterly Savings and Loan Holding Company Report General
MITSUI SUMITOMO INSURANCE COMPANY, LIMITED AND SUBSIDIARIES. CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS March 31, 2005 and 2006
 CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS March 31, 2005 and 2006 2005 2006 ASSETS Investments - other than investments in affiliates: Securities available for sale: Fixed maturities, at fair value 3,043,851 3,193,503
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS March 31, 2005 and 2006 2005 2006 ASSETS Investments - other than investments in affiliates: Securities available for sale: Fixed maturities, at fair value 3,043,851 3,193,503
Chapter 11 Intercorporate Investments and Consolidations 567
 CHAPTER 11 11-1 Marketable securities may be either short-term or long-term investments. Short-term refers to intention, not to salability. 11-2 Trading securities are debt or equity securities that a
CHAPTER 11 11-1 Marketable securities may be either short-term or long-term investments. Short-term refers to intention, not to salability. 11-2 Trading securities are debt or equity securities that a
PINK OTC MARKETS. DALRADA FINANCIAL CORPORATION (A Delaware Company)
 PINK OTC MARKETS DALRADA FINANCIAL CORPORATION (A Delaware Company) QUARTERLY REPORT: For the Three and Nine Months ended March 31, 2012 and 2011 Contents: Section (I) Dalrada Financial Corporation Quarterly
PINK OTC MARKETS DALRADA FINANCIAL CORPORATION (A Delaware Company) QUARTERLY REPORT: For the Three and Nine Months ended March 31, 2012 and 2011 Contents: Section (I) Dalrada Financial Corporation Quarterly
SunGard Capital Corp. SunGard Capital Corp. II SunGard Data Systems Inc.
 United States Securities and Exchange Commission Washington, D.C. 20549 FORM 10-Q (Mark One) Quarterly report pursuant to section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 For the quarterly period
United States Securities and Exchange Commission Washington, D.C. 20549 FORM 10-Q (Mark One) Quarterly report pursuant to section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 For the quarterly period
N otes to Consolidated Financial Statements
 N otes to Consolidated Financial Statements Brother Industries, Ltd. and Consolidated Subsidiaries For the Years ended March 31, 2011 and 2010 1. Basis of Presenting Consolidated Financial Statements The
N otes to Consolidated Financial Statements Brother Industries, Ltd. and Consolidated Subsidiaries For the Years ended March 31, 2011 and 2010 1. Basis of Presenting Consolidated Financial Statements The
EQUINIX, INC. (Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
 Table of Contents UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION Washington, D.C. 20549 FORM 10-Q x QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 For the quarterly
Table of Contents UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION Washington, D.C. 20549 FORM 10-Q x QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 For the quarterly
The Ultimate Accountants' Reference, 3 rd Edition
 The Ultimate Accountants' Reference, 3 rd Edition INCLUDING GAAP, IRS AND SEC REGULATIONS, LEASES, AND MORE STEVEN M. BRAGG WILEY JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. vi 4.8 4.9 4.10 4.11 4.12 4.13 4.14 4.15 4.16 4.17
The Ultimate Accountants' Reference, 3 rd Edition INCLUDING GAAP, IRS AND SEC REGULATIONS, LEASES, AND MORE STEVEN M. BRAGG WILEY JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. vi 4.8 4.9 4.10 4.11 4.12 4.13 4.14 4.15 4.16 4.17
Consolidated Financial Results for Fiscal Year 2013 (April 1, 2013 March 31, 2014)
 Consolidated Financial Results for Fiscal Year 2013 (April 1, 2013 March 31, 2014) 28/4/2014 Name of registrant: ShinMaywa Industries, Ltd. Stock Exchange Listed: Tokyo Code number: 7224 (URL: http://www.shinmaywa.co.jp
Consolidated Financial Results for Fiscal Year 2013 (April 1, 2013 March 31, 2014) 28/4/2014 Name of registrant: ShinMaywa Industries, Ltd. Stock Exchange Listed: Tokyo Code number: 7224 (URL: http://www.shinmaywa.co.jp
Financial Statements
 Financial Statements Years ended March 31,2002 and 2003 Contents Consolidated Financial Statements...1 Report of Independent Auditors on Consolidated Financial Statements...2 Consolidated Balance Sheets...3
Financial Statements Years ended March 31,2002 and 2003 Contents Consolidated Financial Statements...1 Report of Independent Auditors on Consolidated Financial Statements...2 Consolidated Balance Sheets...3
3. CONSOLIDATED QUARTERLY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
 3. CONSOLIDATED QUARTERLY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (1) Consolidated Quarterly Balance Sheets September 30, 2014 and March 31, 2014 Supplementary Information 2Q FY March 2015 March 31, 2014 September 30, 2014
3. CONSOLIDATED QUARTERLY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (1) Consolidated Quarterly Balance Sheets September 30, 2014 and March 31, 2014 Supplementary Information 2Q FY March 2015 March 31, 2014 September 30, 2014
Items Disclosed via the Internet Concerning the Notice of. Convocation of the 117th Annual General Meeting of Shareholders
 To our shareholders: Items Disclosed via the Internet Concerning the Notice of Convocation of the 117th Annual General Meeting of Shareholders Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements Notes to Non-consolidated
To our shareholders: Items Disclosed via the Internet Concerning the Notice of Convocation of the 117th Annual General Meeting of Shareholders Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements Notes to Non-consolidated
3,000 3,000 2,910 2,910 3,000 3,000 2,940 2,940
 1. David Company uses the gross method to record its credit purchases, and it uses the periodic inventory system. On July 21, 20D, the company purchased goods that had an invoice price of $ with terms
1. David Company uses the gross method to record its credit purchases, and it uses the periodic inventory system. On July 21, 20D, the company purchased goods that had an invoice price of $ with terms
Chapter 21 The Statement of Cash Flows Revisited
 Chapter 21 The Statement of Cash Flows Revisited AACSB assurance of learning standards in accounting and business education require documentation of outcomes assessment. Although schools, departments,
Chapter 21 The Statement of Cash Flows Revisited AACSB assurance of learning standards in accounting and business education require documentation of outcomes assessment. Although schools, departments,
Tax accounting services: Foreign currency tax accounting. October 2012
 Tax accounting services: Foreign currency tax accounting October 2012 The globalization of commerce and capital markets has resulted in business, investment and capital formation transactions increasingly
Tax accounting services: Foreign currency tax accounting October 2012 The globalization of commerce and capital markets has resulted in business, investment and capital formation transactions increasingly
Business Valuation and Exit Planning. Aaron J. Pryor, CFA, ASA
 Business Valuation and Exit Planning Aaron J. Pryor, CFA, ASA Phases of a Business Valuation Assignment Define the valuation assignment What exactly is the subject of the valuation What is the purpose
Business Valuation and Exit Planning Aaron J. Pryor, CFA, ASA Phases of a Business Valuation Assignment Define the valuation assignment What exactly is the subject of the valuation What is the purpose
Accounting for Bonds and Long-Term Notes
 Accounting for Bonds and Long-Term Notes Bond Premiums and Discounts Effective interest method Bond issuance Interest expense Types of Debt Instruments Zero-Coupon Bonds Convertible Bonds Detachable Warrants
Accounting for Bonds and Long-Term Notes Bond Premiums and Discounts Effective interest method Bond issuance Interest expense Types of Debt Instruments Zero-Coupon Bonds Convertible Bonds Detachable Warrants
中 原 大 學 95 學 年 度 轉 學 考 招 生 入 學 考 試
 中 原 大 學 95 學 年 度 轉 學 考 招 生 入 學 考 試 7 月 12 日 14:00~15:30 商 學 群 組 二 年 級 科 目 : 會 計 學 ( 共 七 頁 第 一 頁 ) 可 使 用 計 算 機, 惟 僅 限 不 具 可 程 式 及 多 重 記 憶 者 一 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: (50%) 誠 實 是 我 們 珍 視 的 美 德, 我 們 喜
中 原 大 學 95 學 年 度 轉 學 考 招 生 入 學 考 試 7 月 12 日 14:00~15:30 商 學 群 組 二 年 級 科 目 : 會 計 學 ( 共 七 頁 第 一 頁 ) 可 使 用 計 算 機, 惟 僅 限 不 具 可 程 式 及 多 重 記 憶 者 一 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: (50%) 誠 實 是 我 們 珍 視 的 美 德, 我 們 喜
CHAPTER 29 Mergers and Acquisitions
 CHAPTER 29 Mergers and Acquisitions Multiple Choice Questions: I. DEFINITIONS MERGER a 1. The complete absorption of one company by another, wherein the acquiring firm retains its identity and the acquired
CHAPTER 29 Mergers and Acquisitions Multiple Choice Questions: I. DEFINITIONS MERGER a 1. The complete absorption of one company by another, wherein the acquiring firm retains its identity and the acquired
Fuqua School of Business, Duke University ACCOUNTG 510: Foundations of Financial Accounting
 Fuqua School of Business, Duke University ACCOUNTG 510: Foundations of Financial Accounting Lecture Note: Financial Statement Basics, Transaction Recording, and Terminology I. The Financial Reporting Package
Fuqua School of Business, Duke University ACCOUNTG 510: Foundations of Financial Accounting Lecture Note: Financial Statement Basics, Transaction Recording, and Terminology I. The Financial Reporting Package
(A) Comprehensive Revaluation of Assets and Liabilities. (B) Bankruptcy and Receivership CHAPTER 14 CHAPTER OUTLINE LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 CHAPTER 14 (A) Comprehensive Revaluation of Assets and Liabilities (B) Bankruptcy and Receivership CHAPTER OUTLINE (A) Comprehensive Revaluation of Assets and Liabilities Push-down Accounting Application
CHAPTER 14 (A) Comprehensive Revaluation of Assets and Liabilities (B) Bankruptcy and Receivership CHAPTER OUTLINE (A) Comprehensive Revaluation of Assets and Liabilities Push-down Accounting Application
a. $ 65,000. b. $ 80,000. c. $130,000. d. $145,000.
 注 意 1. 本 試 題 卷 共 50 題, 總 分 100 分 第 01-15 題, 每 題 1.75 分, 合 計 26.25 分 ; 第 16-35 題, 每 題 2 分, 合 計 40 分 ; 第 36-50 題, 每 題 2.25 分, 合 計 33.75 答 錯 不 倒 扣 2. 請 將 答 案 按 試 題 題 號, 依 序 填 入 答 案 卡 1.FastForward had cash
注 意 1. 本 試 題 卷 共 50 題, 總 分 100 分 第 01-15 題, 每 題 1.75 分, 合 計 26.25 分 ; 第 16-35 題, 每 題 2 分, 合 計 40 分 ; 第 36-50 題, 每 題 2.25 分, 合 計 33.75 答 錯 不 倒 扣 2. 請 將 答 案 按 試 題 題 號, 依 序 填 入 答 案 卡 1.FastForward had cash
B Exercises 4-1. (d) Intangible assets. (i) Paid-in capital in excess of par.
 B Exercises E4-1B (Balance Sheet Classifications) Presented below are a number of balance sheet accounts of Castillo Inc. (a) Trading Securities. (h) Warehouse in Process of Construction. (b) Work in Process.
B Exercises E4-1B (Balance Sheet Classifications) Presented below are a number of balance sheet accounts of Castillo Inc. (a) Trading Securities. (h) Warehouse in Process of Construction. (b) Work in Process.
Anadolu Hayat Emeklilik Anonim Şirketi Consolidated Balance Sheet As At 31 December 2015 (Currency: Turkish Lira (TRY))
 Consolidated Balance Sheet As At ASSETS I- Current Assets A- Cash and Cash Equivalents 14 302,999,458 216,428,429 1- Cash 14 3,385 27,952 2- Cheques Received 3- Banks 14 145,598,543 87,301,020 4- Cheques
Consolidated Balance Sheet As At ASSETS I- Current Assets A- Cash and Cash Equivalents 14 302,999,458 216,428,429 1- Cash 14 3,385 27,952 2- Cheques Received 3- Banks 14 145,598,543 87,301,020 4- Cheques
General Cable Corporation (Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
 UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549 FORM 8-K/A CURRENT REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 Date of Report (Date of earliest
UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549 FORM 8-K/A CURRENT REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 Date of Report (Date of earliest

 Shareholder=s Equity Objectives
Shareholder=s Equity Objectives