Consolidated Financial Statements. Chapter 3. Consolidated Financial Statements. Consolidated Financial Statements. Consolidated Financial Statements
|
|
|
- Leona Harrison
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 3 The Reporting Entity and Consolidated Financial Statements Consolidated Financial Statements Many corporations are composed of numerous separate companies and, in turn, prepare consolidated financial statements. McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2005 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3-2 Consolidated Financial Statements Consolidated financial statements present the financial position and results of operations for a parent (controlling entity) and one or more subsidiaries (controlled entities) as if the individual entities actually were a single company or entity. Consolidated Financial Statements Consolidation is required when a corporation owns a majority of another corporation s outstanding common stock. The accounting principles applied in the preparation of the consolidated financial statements are the same accounting principles applied in preparing separate-company financial statements Consolidated Financial Statements Consolidated Financial Statements Two companies are considered to be related companies when one controls the other company. Consolidated financial statements are generally considered to be more useful than the separate financial statements of the individual companies when the companies are related. Whether the subsidiary is acquired or created, each individual company maintains its own accounting records, but consolidated financial statements are needed to present the companies together as a single economic entity for general-purpose financial reporting
2 Benefits Limitations Consolidated financial statements are presented primarily for the benefit of the shareholders, creditors, and other resource providers of the parent. Significantly, consolidated financial statements often represent the only means of obtaining a clear picture of the total resources of the combined entity that are under the control of the parent company. While consolidated financial statements are useful, their limitations also must be kept in mind. Some information is lost any time data sets are aggregated; this is particularly true when the information involves an aggregation across companies that have substantially different operating characteristics Subsidiary Financial Statements The Tradition View of Control Because subsidiaries are legally separate from their parents, the creditors and stockholders of a subsidiary generally have no claim on the parent, nor do the stockholders of the subsidiary share in the profits of the parent. Therefore, consolidated financial statements usually are of little use to those interested in obtaining information about the assets, capital, or income of individual subsidiaries. The professional guidance regarding consolidated financial statements is provided in ARB 51 and FASB 94. Under current standards, consolidated financial statements must be prepared if one corporation owns a majority of another corporation s outstanding common stock Less Than Majority Ownership Although majority ownership is the most common means of acquiring control, a company may be able to direct the operating and financing policies of another with less than majority ownership, such as when the remainder of the stock is widely held. FASB 94 does not preclude consolidation with less than majority ownership, but such consolidations have seldom been found in practice. Indirect Control The traditional view of control includes both direct and indirect control. Direct control typically occurs when one company owns a majority of another company s common stock. Indirect control (or pyramiding) occurs when a company s common stock is owned by one or more other companies that are all under common control
3 Ability to Exercise Control Under certain circumstances, the majority stockholders of a subsidiary may not be able to exercise control even though they hold more than 50 percent of its outstanding voting stock. Examples: Subsidiary is in legal reorganization or bankruptcy Foreign country restricts remittance of subsidiary profits to domestic parent company Parent is unable to control important aspects of the subsidiary s operations. Ability to Exercise Control When consolidation is not appropriate, the unconsolidated subsidiary is reported as an intercorporate investment Differences in Fiscal Periods A difference in the fiscal periods of a parent and subsidiary should not preclude consolidation of that subsidiary. Often the fiscal period of the subsidiary, if different from the parent s, is changed to coincide with that of the parent. Another alternative is to adjust the financial statement data of the subsidiary each period to place the data on a basis consistent with the fiscal period of the parent. Differences in Accounting Methods A difference in accounting methods between a parent and its subsidiary generally should have no effect on the decision to consolidate that subsidiary. In any event, adequate disclosure of the various accounting methods used must be given in the notes to the financial statements Reporting Entity-A Changing Concept The FASB is currently considering some of the difficult issues relating to control. Ultimately, the FASB is expected to move beyond the traditional concept of legal control based on majority ownership and also require consolidation of entities under the effective control of another entity, even though the other entity may not hold majority ownership. This broader view would contribute to the harmonization of accounting standards in the global economy Inadequate Standards Consolidation standards relating to partnerships or other types of entities (such as trusts) have been virtually nonexistent. Even corporate consolidation standards have not been adequate in situations where other relationships such as guarantees and operating agreements overshadow the lack of a significant ownership element
4 Inadequate Standards Although many companies have used special entities for legitimate purposes, companies such as Enron took advantage of the lack of standards to avoid reporting debt or losses by hiding them in special entities that were not consolidated. Only in the past few years have consolidation standards for these special entities started to provide some uniformity in the financial reporting for corporations having relationships with such entities. Special Purpose/Variable Interest Entities Special-purpose entities (SPEs) are corporations, trusts, or partnerships created for a single specified purpose. They have no substantive operations and are used only for financing purposes. Special-purpose entities have been used for several decades for asset securitization, risk sharing, and to take advantage of tax statutes Special-Purpose Entities Variable Interest Entities In general, FASB 140 states that SPEs be demonstrably distinct from the transferor, its activities be significantly limited, and it hold only certain types of financial assets. If the conditions of FASB 140 are met, this type of SPE is not consolidated by the transferor of assets to the SPE. A variable interest entity is a legal structure used for business purposes, usually a corporation, trust, or partnership, that either: Does not have equity investors that have voting rights and share in all profits and losses of the entity. Has equity investors that do not provide sufficient financial resources to support the entity s activities Variable Interest Entities In a variable interest entity, specific agreements may be limit the extent to which the equity investors, if any, share in the profits or losses (etc.) of the entity. FIN 46 (an interpretation of ARB 51) uses the term variable interest entity to encompass SPEs and other entities falling within its conditions. This pronouncement does not apply to entities that are considered SPEs under FASB 140. Overview of the Consolidation Process The consolidation process adds together the financial statements of two or more legally separate companies, creating a single set of financial statements. The specific procedures used to produce consolidated financial statements are discussed in considerable details in Chapters 4 to
5 Overview of the Consolidation Process Overview of the Consolidation Process The separate financial statements of the companies involved serve as the starting point each time consolidated statements are prepared. These separate statements are added together, after some adjustments and eliminations, to generate consolidated statements. After all the consolidation procedures have been applied, the preparer should review the resulting statements and ask: Do these statements appear as if the consolidated companies were actually a single company? Overview of the Consolidation Process Overview of the Consolidation Process Several items need to be given special attention to ensure that the consolidated financial statements appear as if they are the statements of a single company: Intercorporate stockholdings. Intercompany receivables and payables. Intercompany sales (i.e., unrealized profits) Stated otherwise: You can t own yourself. You can t owe yourself money. You can t make money selling to yourself Intercorporate Stockholdings The common stock of the parent is held by those outside the consolidated entity and is properly viewed as the common stock of the entire entity. In contrast, the common stock of the subsidiary is held entirely within the consolidated entity and is not stock outstanding from a consolidated viewpoint. Intercorporate Stockholdings Because a company cannot report (in its financial statements) an investment in itself, the investment, as well as the equity underlying that investment, is eliminated as follows: Common Stock-Subsidiary BV * Additional Paid-In Capital-Subsidiary BV Retained Earnings-Subsidiary BV Investment in Common Stock of Subsidiary BV * BV = Book Value
6 Intercorporate Stockholdings NOTE: The equity accounts of the parent represent the equity accounts disclosed on the financial statements of the consolidated entity. Difference between Cost and Book Value The elimination entry related to intercorporate stockholdings (in the previous slide) was prepared under the assumption that the parent purchased the subsidiary at book value. In reality, the purchase price of a subsidiary usually differs from the book value of the shares acquired. This differential is treated in the same way in preparing consolidated financial statements as for a merger, discussed in Chapter Difference between Cost and Book Value Intercompany Receivables and Payables Typical Situation: Generally speaking, if the parent paid more for the subsidiary than book value of the shares acquired (a net debit differential), the excess would be allocated (during the consolidation process) to specific assets and liabilities of the subsidiary, or to goodwill. Allocation of differentials is extensively discussed in Chapter A single company cannot owe itself money, that is, a company cannot report (in its financial statements) a receivable to itself and a payable to itself. Thus, with respect to the consolidated balance sheet, the following entry is made to eliminate intercompany receivables and payables between the parent and the subsidiary: Consolidated Accounts Payable BV * Consolidated Accounts Receivable BV * BV = Book Value 3-34 Intercompany Sales (Unrealized Profits) A single company may not recognize a profit and write up its inventory simply because the inventory is transferred from one department or division to another (since no arm s length transaction has occurred to justify recognition of the profit). This also applies to intercompany sales within a consolidated entity Intercompany Sales (Continued) Since unrealized profits (in ending inventory) overstate ending inventory and understate cost of goods sold, consolidated net income as well as consolidated retained earnings are overstated. With respect to the consolidated balance sheet, the following elimination entry is required with respect to unrealized profits in ending inventory (e.g., $2,000): Consolidated Retained Earnings $2,000 Consolidated Ending Inventory $2,
7 Single-Entity Viewpoint In understanding each of the adjustments needed in preparing consolidated statements, the focus should be on both: Identifying the treatment accorded a particular item by each of the separate companies. Identifying the amount that would appear in the financial statements with respect to that item if the consolidated entity were actually a single company. Mechanics of the Consolidation Process A worksheet is used to facilitate the process of combining and adjusting the account balances involved in a consolidation. While the parent company and the subsidiary each maintain their own books, there are no books for the consolidated entity. Instead, the balances of the accounts are taken at the end of each period from the books of the parent and the subsidiary and entered in the consolidation workpaper Mechanics of the Consolidation Process Where the simple adding of the amounts from the two companies leads to a consolidated figure different from the amount that would appear if the two companies were actually one, the combined amount must be adjusted to the desired figure. This is done through the preparation of eliminating entries. Consolidation workpapers and eliminating entries are discussed in more detail in Chapters 4 to Noncontrolling Interest For the parent to consolidate the subsidiary, only a controlling interest is needed not 100% interest. Those shareholders of the subsidiary other than the parent are referred to as noncontrolling or minority shareholders. The claim of these shareholders on the income and net assets of the subsidiary is referred to as the noncontrolling interest or the minority interest Noncontrolling Interest Noncontrolling Interest The FASB favors treating the noncontrolling interest as an ownership interest, with the noncontrolling interest s claim on subsidiary assets reported in consolidated stockholders equity and the claim on subsidiary net income reported as an allocation of consolidated net income. The noncontrolling shareholders claim on the net assets of the subsidiary is shown most commonly between liabilities and stockholders equity in the consolidated balance sheet. Some companies show the noncontrolling interest with liabilities although it clearly does not meet the legal or accounting definition of a liability
8 Noncontrolling Interest Combined Financial Statements The portion of the subsidiary net income assigned to the noncontrolling interest normally is deducted from earnings available to all shareholders to arrive at consolidated net income in the consolidated income statement. Although this assignment of income does not meet the definition of an expense, it normally is accorded this expense-type treatment. Financial statements sometimes are prepared for a group of companies when no one company in the group owns a majority of the common stock of any other company in the group. Financial statements that include a group of related companies without including the parent company or other owner are referred to as combined financial statements Different Approaches to Consolidation Different Approaches to Consolidation Several different theories exist that might serve as a basis for preparing consolidated financial statements. The choice of consolidation theory can have a significant impact on the consolidated financial statements in those cases where the parent company owns less than 100 percent of the subsidiary s common stock. The remaining slides focus on the following alternative theories of consolidation: Proprietary Parent company Entity Proprietary Theory The proprietary theory of accounting views the firm as an extension of its owners. The assets and liabilities of the firm are considered to be assets and liabilities of the owners themselves. Similarly, revenue of the firm is viewed as increasing the wealth of the owners, while expenses decrease the wealth of the owners. Proprietary Theory When applied to the preparation of consolidated financial statements, the proprietary concept results in a pro rata consolidation. The parent company consolidates only its proportionate share of the assets and liabilities of the subsidiary
9 Parent Company Theory The parent company theory is perhaps better suited to the modern corporation and the preparation of consolidated financial statements than is the proprietary approach. The parent company theory recognizes that although the parent does not have direct ownership of the assets or direct responsibility for the liabilities of the subsidiary, it has the ability to exercise effective control over all of the subsidiary s assets and liabilities, not simply a proportionate share. Parent Company Theory Under parent company theory, separate recognition is given in the consolidated balance sheet to the noncontrolling interest s claim on the net assets of the subsidiary and in the consolidated income statement to the earnings assigned to the noncontrolling shareholders Entity Theory As a general rule, the entity theory focuses on the firm as a separate economic entity, rather than on the ownership rights of the shareholders of the parent or subsidiary. Emphasis under the entity approach is on the consolidated entity itself, with the controlling and noncontrolling shareholders viewed as two separate groups, each having an equity in the consolidated entity. Neither of the two groups is emphasized over the other or over the consolidated entity Entity Theory Because the parent and subsidiary together are viewed as a single entity (under the entity approach), all the assets and liabilities of the subsidiary and any goodwill are reflected in the consolidated balance sheet at their full values on the date of combination regardless of the actual percentage of ownership acquired. Additionally, consolidated net income is a combined figure that is allocated between the controlling and noncontrolling ownership groups Current Practice The procedures used in practice represent a blending of the parent company and entity approaches. The amount of subsidiary net assets recognized in the consolidated balance sheet at acquisition is the same in practice as under the parent company approach. On the other hand, the determination of consolidated net income is a combination of the entity and parent company approaches Future Practice The FASB has proposed moving to an entity approach in practice. This would result in classifying the noncontrolling interest in the stockholders equity section of the consolidated balance sheet and labeling the total income of the consolidated entity as consolidated net income, with an allocation of consolidated net income between the controlling and noncontrolling interests in the income statement
10 You Will Survive This Chapter!!! Remember: You can t own yourself. You can t owe yourself money. You can t make money selling to yourself. NOTE: Elimination entries tend to reduce balances not increase them. EXCEPTION: Entries relating to the allocation of the difference between investment cost and book value, that is, the differential McGraw-Hill/Irwin Chapter 3 End of Chapter Copyright 2005 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 10
Consolidation-Date of Acquisition. Chapter 4. Consolidation-GAAP. Consolidation-Date of Acquisition. Roadmap Chapters 5 to 10.
 Chapter 4 Consolidation As Of The Date Of Acquisition Consolidation-Date of Acquisition Consolidated statements bring together the operating results and financial position of two or more separate legal
Chapter 4 Consolidation As Of The Date Of Acquisition Consolidation-Date of Acquisition Consolidated statements bring together the operating results and financial position of two or more separate legal
Consolidation Following Acquisition. Consolidation Following Acquisition. Consolidated Net Income. Computing Consolidated Net Income
 Chapter 5 Consolidation Following Acquisition The procedures used to prepare a consolidated balance sheet as of the date of acquisition were introduced in the preceding chapter, that is, Chapter 4. More
Chapter 5 Consolidation Following Acquisition The procedures used to prepare a consolidated balance sheet as of the date of acquisition were introduced in the preceding chapter, that is, Chapter 4. More
Intercompany Inventory Transactions. Chapter 7. Intercompany Inventory Transactions. Transfers at Cost. Transfers at Cost
 Chapter 7 Intercompany Inventory Transactions Intercompany Inventory Transactions Inventory transactions are the most common form of intercorporate exchange. Significantly, the consolidation procedures
Chapter 7 Intercompany Inventory Transactions Intercompany Inventory Transactions Inventory transactions are the most common form of intercorporate exchange. Significantly, the consolidation procedures
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 7. Consolidated Financial Statements
 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 7 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 7 Consolidated Financial Statements 30 November 2004 Translated by Wei-heng Lin, Associate Professor (Chung
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 7 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 7 Consolidated Financial Statements 30 November 2004 Translated by Wei-heng Lin, Associate Professor (Chung
Investments in Equity Securities. The Internet research exercise examines Cisco System s strategy of growth through acquisitions.
 CHAPTER 8 Investments in Equity Securities SYNOPSIS In this chapter, the author discusses investments in equity securities. The discussion is divided into equity securities classified as current and long-term
CHAPTER 8 Investments in Equity Securities SYNOPSIS In this chapter, the author discusses investments in equity securities. The discussion is divided into equity securities classified as current and long-term
Most economic transactions involve two unrelated entities, although
 139-210.ch04rev.qxd 12/2/03 2:57 PM Page 139 CHAPTER4 INTERCOMPANY TRANSACTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Understand the different types of intercompany transactions
139-210.ch04rev.qxd 12/2/03 2:57 PM Page 139 CHAPTER4 INTERCOMPANY TRANSACTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Understand the different types of intercompany transactions
Accounting for Multiple Entities
 King Saud University College of Administrative Science Department of Accounting 2 nd Semester, 1426-1427 Accounting for Multiple Entities Chapter 15 Prepared By: Eman Al-Aqeel Professor : Dr: Amal Fouda
King Saud University College of Administrative Science Department of Accounting 2 nd Semester, 1426-1427 Accounting for Multiple Entities Chapter 15 Prepared By: Eman Al-Aqeel Professor : Dr: Amal Fouda
RECOGNIZING A MINORITY INTEREST IN CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
 RECOGNIZING A MINORITY INTEREST IN CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS L E A R N I N G O B J E C T I V E Adapt the consolidation work sheet procedure to recognize a minority interest. Chapter 11 illustrates
RECOGNIZING A MINORITY INTEREST IN CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS L E A R N I N G O B J E C T I V E Adapt the consolidation work sheet procedure to recognize a minority interest. Chapter 11 illustrates
Intercompany Indebtedness. Chapter 8. Intercompany Indebtedness. Consolidation Overview. Consolidation Overview. Intercompany Indebtedness
 Chapter 8 Intercompany Indebtedness Intercompany Indebtedness One advantage of having control over other companies is that management has the ability to transfer resources from one legal entity to another
Chapter 8 Intercompany Indebtedness Intercompany Indebtedness One advantage of having control over other companies is that management has the ability to transfer resources from one legal entity to another
CHAPTER 4 CONSOLIDATION OF WHOLLY OWNED SUBSIDIARIES ACQUIRED AT MORE THAN BOOK VALUE
 CHAPTER 4 CONSOLIDATION OF WHOLLY OWNED SUBSIDIARIES ACQUIRED AT MORE THAN BOOK VALUE ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS Q4-1 The carrying value of the investment is reduced under equity method reporting when (a) a
CHAPTER 4 CONSOLIDATION OF WHOLLY OWNED SUBSIDIARIES ACQUIRED AT MORE THAN BOOK VALUE ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS Q4-1 The carrying value of the investment is reduced under equity method reporting when (a) a
Dr. M. D. Chase Advanced Accounting Exam 1AA Page 1 of 9
 Advanced Accounting Exam 1AA Page 1 of 9 MARK THE LETTER OF THE BEST ANSWER ON YOUR SCANTRON FORM. 1. A business combination is accounted for appropriately as a pooling of interests. Costs of furnishing
Advanced Accounting Exam 1AA Page 1 of 9 MARK THE LETTER OF THE BEST ANSWER ON YOUR SCANTRON FORM. 1. A business combination is accounted for appropriately as a pooling of interests. Costs of furnishing
AS 27 Financial Reporting of Interests in Joint Ventures
 CA. B. Ganesh AS 21 Consolidated Financial Statements AS 23 Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements AS 27 Financial Reporting of Interests in Joint Ventures Case studies
CA. B. Ganesh AS 21 Consolidated Financial Statements AS 23 Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements AS 27 Financial Reporting of Interests in Joint Ventures Case studies
Consolidated financial statements
 Financial 3 Becker Professional Education CPA Exam Review Consolidated financial statements I. CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS A. Control (over 50%) Consolidated financial statements are prepared when
Financial 3 Becker Professional Education CPA Exam Review Consolidated financial statements I. CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS A. Control (over 50%) Consolidated financial statements are prepared when
Accounting for Equity Investments & Acquisitions
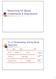 Accounting for Equity Investments & Acquisitions % of Outstanding Voting Stock Acquired 0% 20% 50% 100% Nominal Significant Control Level of Influence Fair Value Equity method Valuation Basis Investment
Accounting for Equity Investments & Acquisitions % of Outstanding Voting Stock Acquired 0% 20% 50% 100% Nominal Significant Control Level of Influence Fair Value Equity method Valuation Basis Investment
ACCOUNTING STANDARD 23 (AS - 23) Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements
 ACCOUNTING STANDARD 23 (AS - 23) Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements Commencement AS - 23 comes into effect from April 1,2002. Objective The standard explains
ACCOUNTING STANDARD 23 (AS - 23) Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements Commencement AS - 23 comes into effect from April 1,2002. Objective The standard explains
ASPE at a Glance. Standards Included in Topic
 ASPE AT A GLANCE ASPE AT A GLANCE This publication has been compiled to assist users in gaining a high level overview of Accounting Standards for Private Enterprises (ASPE) included in Part II of the CPA
ASPE AT A GLANCE ASPE AT A GLANCE This publication has been compiled to assist users in gaining a high level overview of Accounting Standards for Private Enterprises (ASPE) included in Part II of the CPA
CHAPTER 8 INTERCOMPANY INDEBTEDNESS
 CHAPTER 8 INTERCOMPANY INDEBTEDNESS ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS Q8-1 A gain or loss on bond retirement is reported by the consolidated entity whenever (a) one of the companies purchases its own bonds from a nonaffiliate
CHAPTER 8 INTERCOMPANY INDEBTEDNESS ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS Q8-1 A gain or loss on bond retirement is reported by the consolidated entity whenever (a) one of the companies purchases its own bonds from a nonaffiliate
1. Debt securities are instruments representing a creditor relationship with an enterprise.
 Chapter 18 Investments LECTURE OUTLINE The material in this chapter can be covered in three class periods. Students will have some difficulty with the classifications of debt securities into trading, available-for-sale,
Chapter 18 Investments LECTURE OUTLINE The material in this chapter can be covered in three class periods. Students will have some difficulty with the classifications of debt securities into trading, available-for-sale,
Financial Accounting Series
 Financial Accounting Series NO. 299-B DECEMBER 2007 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 160 Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements an amendment of ARB No. 51 Financial
Financial Accounting Series NO. 299-B DECEMBER 2007 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 160 Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements an amendment of ARB No. 51 Financial
Corporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and Dividends
 C H A P T E R 13 Corporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and Dividends Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Advantages and Disadvantages of the Corporate Form
C H A P T E R 13 Corporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and Dividends Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Advantages and Disadvantages of the Corporate Form
Consolidated Financial Statements and Investments in Subsidiaries
 LEMBAGA PIAWAIAN PERAKAUNAN MALAYSIA MALAYSIAN ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD MASB Standard 11 Consolidated Financial Statements and Investments in Subsidiaries Any correspondence regarding this Standard should
LEMBAGA PIAWAIAN PERAKAUNAN MALAYSIA MALAYSIAN ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD MASB Standard 11 Consolidated Financial Statements and Investments in Subsidiaries Any correspondence regarding this Standard should
International Accounting Standard 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements
 International Accounting Standard 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements Scope 1 This Standard shall be applied in the preparation and presentation of consolidated financial statements for a
International Accounting Standard 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements Scope 1 This Standard shall be applied in the preparation and presentation of consolidated financial statements for a
Consolidated Balance Sheets
 Consolidated Balance Sheets March 31 2015 2014 2015 Assets: Current assets Cash and cash equivalents 726,888 604,571 $ 6,057,400 Marketable securities 19,033 16,635 158,608 Notes and accounts receivable:
Consolidated Balance Sheets March 31 2015 2014 2015 Assets: Current assets Cash and cash equivalents 726,888 604,571 $ 6,057,400 Marketable securities 19,033 16,635 158,608 Notes and accounts receivable:
2 This Standard shall be applied by all entities that are investors with joint control of, or significant influence over, an investee.
 International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures Objective 1 The objective of this Standard is to prescribe the accounting for investments in associates and to set out
International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures Objective 1 The objective of this Standard is to prescribe the accounting for investments in associates and to set out
FREEDOM INVESTMENTS, INC. STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AS OF JUNE 30, 2015 (UNAUDITED)
 FREEDOM INVESTMENTS, INC. STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AS OF JUNE 30, 2015 (UNAUDITED) ****** Index Page(s) Statement of Financial Condition. 2 Notes to Statement of Financial Condition. 3-5 Statement
FREEDOM INVESTMENTS, INC. STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AS OF JUNE 30, 2015 (UNAUDITED) ****** Index Page(s) Statement of Financial Condition. 2 Notes to Statement of Financial Condition. 3-5 Statement
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-LKAS 27. Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements
 Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-LKAS 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements -675- Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-LKAS 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements Sri Lanka Accounting Standard
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-LKAS 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements -675- Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-LKAS 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements Sri Lanka Accounting Standard
Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures
 STATUTORY BOARD FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD SB-FRS 28 Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures This standard applies for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2013. Earlier application is
STATUTORY BOARD FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD SB-FRS 28 Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures This standard applies for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2013. Earlier application is
Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements
 371 Accounting Standard (AS) 23 Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-2 DEFINITIONS 3-6 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS EQUITY METHOD
371 Accounting Standard (AS) 23 Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-2 DEFINITIONS 3-6 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS EQUITY METHOD
SSAP 32 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 32 CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN SUBSIDIARIES
 SSAP 32 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 32 CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN SUBSIDIARIES (Issued January 2001) The standards, which have been set in bold italic
SSAP 32 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 32 CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN SUBSIDIARIES (Issued January 2001) The standards, which have been set in bold italic
Consolidated Balance Sheets March 31, 2001 and 2000
 Financial Statements SEIKAGAKU CORPORATION AND CONSOLIDATED SUBSIDIARIES Consolidated Balance Sheets March 31, 2001 and 2000 Assets Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents... Short-term investments (Note
Financial Statements SEIKAGAKU CORPORATION AND CONSOLIDATED SUBSIDIARIES Consolidated Balance Sheets March 31, 2001 and 2000 Assets Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents... Short-term investments (Note
New Accounting for Business Combinations and Minority Interests
 New Accounting for Business Combinations and Minority Interests John Scott Senior Manager, Enterprise Group Travis Wolff January 19, 2010 Agenda Overview and background of the new standards- ASC 805 (FAS
New Accounting for Business Combinations and Minority Interests John Scott Senior Manager, Enterprise Group Travis Wolff January 19, 2010 Agenda Overview and background of the new standards- ASC 805 (FAS
SCORPEX INTERNATIONAL, INC.
 AUDIT REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM AND CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS C O N T E N T S Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.... 3 Consolidated Balance Sheets...
AUDIT REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM AND CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS C O N T E N T S Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.... 3 Consolidated Balance Sheets...
International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates
 International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates Scope 1 This Standard shall be applied in accounting for investments in associates. However, it does not apply to investments in associates
International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates Scope 1 This Standard shall be applied in accounting for investments in associates. However, it does not apply to investments in associates
Consolidated and other financial statements
 Financial reporting developments A comprehensive guide Consolidated and other financial statements Noncontrolling interests, combined financial statements, and parent company financial statements Revised
Financial reporting developments A comprehensive guide Consolidated and other financial statements Noncontrolling interests, combined financial statements, and parent company financial statements Revised
Financial Accounting Series
 Financial Accounting Series NO. 299-A DECEMBER 2007 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 141 (revised 2007) Business Combinations Financial Accounting Standards Board of the Financial Accounting
Financial Accounting Series NO. 299-A DECEMBER 2007 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 141 (revised 2007) Business Combinations Financial Accounting Standards Board of the Financial Accounting
ZAMIL INDUSTRIAL INVESTMENT COMPANY (SAUDI JOINT STOCK COMPANY)
 ZAMIL INDUSTRIAL INVESTMENT COMPANY INTERIM CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND AUDITORS REPORT (LIMITED REVIEW) FOR THE THREE MONTHS AND NINE MONTHS PERIODS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, NOTES TO THE INTERIM
ZAMIL INDUSTRIAL INVESTMENT COMPANY INTERIM CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND AUDITORS REPORT (LIMITED REVIEW) FOR THE THREE MONTHS AND NINE MONTHS PERIODS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, NOTES TO THE INTERIM
Consolidation Accounting
 Consolidation Accounting Indian GAAP Sailesh Patel (CA) Topics to be discussed: Why consolidation Consolidation Requirement Definition of subsidiary, associate, joint venture Exclusion from consolidation
Consolidation Accounting Indian GAAP Sailesh Patel (CA) Topics to be discussed: Why consolidation Consolidation Requirement Definition of subsidiary, associate, joint venture Exclusion from consolidation
SSAP 10 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 10 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES
 SSAP 10 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 10 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES (Issued January 1985; Revised July 1991, February 1999 and May 2001) The standards, which have been set in
SSAP 10 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 10 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES (Issued January 1985; Revised July 1991, February 1999 and May 2001) The standards, which have been set in
Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures
 International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures In April 2001 the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) adopted IAS 28 Accounting for Investments in Associates,
International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures In April 2001 the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) adopted IAS 28 Accounting for Investments in Associates,
Consolidated Interim Earnings Report
 Consolidated Interim Earnings Report For the Six Months Ended 30th September, 2003 23th Octorber, 2003 Hitachi Capital Corporation These financial statements were prepared for the interim earnings release
Consolidated Interim Earnings Report For the Six Months Ended 30th September, 2003 23th Octorber, 2003 Hitachi Capital Corporation These financial statements were prepared for the interim earnings release
Investments and advances... 313,669
 Consolidated Financial Statements of the Company The consolidated balance sheet, statement of income, and statement of equity of the Company are as follows. Please note the Company s consolidated financial
Consolidated Financial Statements of the Company The consolidated balance sheet, statement of income, and statement of equity of the Company are as follows. Please note the Company s consolidated financial
Summary of Significant Differences between Japanese GAAP and U.S. GAAP
 Summary of Significant Differences between Japanese GAAP and U.S. GAAP The consolidated financial statements of SMFG and its subsidiaries presented in this annual report conform with generally accepted
Summary of Significant Differences between Japanese GAAP and U.S. GAAP The consolidated financial statements of SMFG and its subsidiaries presented in this annual report conform with generally accepted
NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON INVESTMENT IN ASSOCIATES
 NAS 25 NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON INVESTMENT IN ASSOCIATES CONTENTS Paragraphs SCOPE 1-2 DEFINITIONS 3-13 Significant influence 7-11 Equity method 12-13 APPLICATION OF THE EQUITY METHOD 14-33 Impairment
NAS 25 NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON INVESTMENT IN ASSOCIATES CONTENTS Paragraphs SCOPE 1-2 DEFINITIONS 3-13 Significant influence 7-11 Equity method 12-13 APPLICATION OF THE EQUITY METHOD 14-33 Impairment
Tax accounting services: Foreign currency tax accounting. October 2012
 Tax accounting services: Foreign currency tax accounting October 2012 The globalization of commerce and capital markets has resulted in business, investment and capital formation transactions increasingly
Tax accounting services: Foreign currency tax accounting October 2012 The globalization of commerce and capital markets has resulted in business, investment and capital formation transactions increasingly
Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements
 Compiled Accounting Standard AASB 127 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements This compiled Standard applies to annual reporting periods beginning on or after 1 July 2007. Early application is permitted.
Compiled Accounting Standard AASB 127 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements This compiled Standard applies to annual reporting periods beginning on or after 1 July 2007. Early application is permitted.
Financial Accounting Series
 Financial Accounting Series NO. 310 JUNE 2009 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 166 Accounting for Transfers of Financial Assets an amendment of FASB Statement No. 140 Financial Accounting
Financial Accounting Series NO. 310 JUNE 2009 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 166 Accounting for Transfers of Financial Assets an amendment of FASB Statement No. 140 Financial Accounting
Financial Statement Analysis: An Introduction
 Financial Statement Analysis: An Introduction 2014 Level I Financial Reporting and Analysis IFT Notes for the CFA exam Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Scope of Financial Statement Analysis... 3 3. Major
Financial Statement Analysis: An Introduction 2014 Level I Financial Reporting and Analysis IFT Notes for the CFA exam Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Scope of Financial Statement Analysis... 3 3. Major
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard LKAS 28. Investments in Associates
 Sri Lanka Accounting Standard LKAS 28 Investments in Associates CONTENTS SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARD LKAS 28 INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES paragraphs SCOPE 1 DEFINITIONS 2 12 Significant influence 6 10 Equity
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard LKAS 28 Investments in Associates CONTENTS SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARD LKAS 28 INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES paragraphs SCOPE 1 DEFINITIONS 2 12 Significant influence 6 10 Equity
Chapter 9, Problem 7 Closing inventory profits Before Tax After tax 40% tax
 Chapter 9, Problem 7 Cost of 70% of Simon 900,000 Book value of Simon Common stock 550,000 Retained earnings Jan. 1 400,000 Net income to April 1 (¼ 200,000) 50,000 1,000,000 70% 700,000 Purchase discrepancy
Chapter 9, Problem 7 Cost of 70% of Simon 900,000 Book value of Simon Common stock 550,000 Retained earnings Jan. 1 400,000 Net income to April 1 (¼ 200,000) 50,000 1,000,000 70% 700,000 Purchase discrepancy
CHAPTER 17. Investments. 1. Debt securities. 1, 2, 3, 15 1 7 (a) Held-to-maturity. 4, 5, 7, 8, 15, 1, 3 2, 3, 5 1, 7 4
 CHAPTER 17 Investments ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE Topics Questions Brief Exercises Exercises Problems Cases 1. Debt securities. 1, 2, 3, 15 1 7 (a) Held-to-maturity. 4, 5, 7, 8, 15, 1, 3 2, 3, 5 1,
CHAPTER 17 Investments ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE Topics Questions Brief Exercises Exercises Problems Cases 1. Debt securities. 1, 2, 3, 15 1 7 (a) Held-to-maturity. 4, 5, 7, 8, 15, 1, 3 2, 3, 5 1,
The following Accounting Standards Interpretations (ASIs) relate to AS 23:
 438 Accounting Standard (AS) 23 (issued 2001) Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-2 DEFINITIONS 3-6 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS
438 Accounting Standard (AS) 23 (issued 2001) Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-2 DEFINITIONS 3-6 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS
CHAPTER 11 Reporting and Analyzing Stockholders Equity
 CHAPTER 11 Reporting and Analyzing Stockholders Equity Major Characteristics of a Corporation Ownership A publicly held corporation is regularly traded on a national securities market and may have thousands
CHAPTER 11 Reporting and Analyzing Stockholders Equity Major Characteristics of a Corporation Ownership A publicly held corporation is regularly traded on a national securities market and may have thousands
CHAPTER 25 ACCOUNTING FOR INTRAGROUP TRANSACTIONS
 CHAPTER 25 ACCOUNTING FOR INTRAGROUP TRANSACTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon completing this chapter readers should be able to: LO1 explain the nature of intragroup transactions; LO2 describe how and why
CHAPTER 25 ACCOUNTING FOR INTRAGROUP TRANSACTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon completing this chapter readers should be able to: LO1 explain the nature of intragroup transactions; LO2 describe how and why
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
 FACT SHEET June 2010 IFRS 3 Business Combinations (This fact sheet is based on the standard as at 1 January 2010.) Important note: This fact sheet is based on the requirements of the International Financial
FACT SHEET June 2010 IFRS 3 Business Combinations (This fact sheet is based on the standard as at 1 January 2010.) Important note: This fact sheet is based on the requirements of the International Financial
Securitization Accounting
 !@ # Securitization Accounting David N. Thrope (212) 773-0930 david.thrope@ey.com Agenda Securitization Basics Sale Criteria Consolidation Gain on Sale Sample Transaction 2 Securitization Basics 3 What
!@ # Securitization Accounting David N. Thrope (212) 773-0930 david.thrope@ey.com Agenda Securitization Basics Sale Criteria Consolidation Gain on Sale Sample Transaction 2 Securitization Basics 3 What
Investments and advances... 344,499
 Consolidated Financial Statements of the Company The consolidated balance sheet, statement of income, and statement of equity of the Company are as follows. Please note the Company s consolidated financial
Consolidated Financial Statements of the Company The consolidated balance sheet, statement of income, and statement of equity of the Company are as follows. Please note the Company s consolidated financial
Cathay Life Insurance Co., Ltd. Financial Statements As of December 31, 2006 and 2007 With Independent Auditors Report
 Financial Statements With Independent Auditors Report The reader is advised that these financial statements have been prepared originally in Chinese. These financial statements do not include additional
Financial Statements With Independent Auditors Report The reader is advised that these financial statements have been prepared originally in Chinese. These financial statements do not include additional
CHAPTER 15. Stockholders Equity ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE (BY TOPIC) Concepts for Analysis. Brief Exercises Exercises Problems
 CHAPTER 15 Stockholders Equity ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE (BY TOPIC) Topics Questions Brief Exercises Exercises Problems Concepts for Analysis *1. Stockholders rights; corporate form. 1, 2, 3, 4,
CHAPTER 15 Stockholders Equity ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE (BY TOPIC) Topics Questions Brief Exercises Exercises Problems Concepts for Analysis *1. Stockholders rights; corporate form. 1, 2, 3, 4,
CHAPTER 3 THE REPORTING ENTITY AND CONSOLIDATION OF LESS-THAN-WHOLLY-OWNED SUBSIDIARIES WITH NO DIFFERENTIAL
 CHAPTER 3 THE REPORTING ENTITY AND CONSOLIDATION OF LESS-THAN-WHOLLY-OWNED SUBSIDIARIES WITH NO DIFFERENTIAL ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS Q3-1 The basic idea underlying the preparation of consolidated financial
CHAPTER 3 THE REPORTING ENTITY AND CONSOLIDATION OF LESS-THAN-WHOLLY-OWNED SUBSIDIARIES WITH NO DIFFERENTIAL ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS Q3-1 The basic idea underlying the preparation of consolidated financial
Consolidation (Topic 810)
 No. 2015-02 February 2015 Consolidation (Topic 810) Amendments to the Consolidation Analysis An Amendment of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification The FASB Accounting Standards Codification is the
No. 2015-02 February 2015 Consolidation (Topic 810) Amendments to the Consolidation Analysis An Amendment of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification The FASB Accounting Standards Codification is the
27 Business combinations IFRS 3
 27 Business combinations IFRS 3 A Key points When businesses are taken over or merged there are many possible ways of accounting. Mergers are banned it is considered there will always be a dominant acquirer.
27 Business combinations IFRS 3 A Key points When businesses are taken over or merged there are many possible ways of accounting. Mergers are banned it is considered there will always be a dominant acquirer.
Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures
 IFAC Board Exposure Draft 50 October 2013 Comments due: February 28, 2014 Proposed International Public Sector Accounting Standard Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures This Exposure Draft 50, Investments
IFAC Board Exposure Draft 50 October 2013 Comments due: February 28, 2014 Proposed International Public Sector Accounting Standard Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures This Exposure Draft 50, Investments
Corporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and Dividends
 C H A P T E R 11 Corporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and Dividends Corporate Financial Accounting 13e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Characteristics of a Corporation (slide
C H A P T E R 11 Corporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and Dividends Corporate Financial Accounting 13e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Characteristics of a Corporation (slide
Unit 6 Receivables. Receivables - Claims resulting from credit sales to customers and others goods or services for money,.
 Unit 6 Receivables 7-1 Receivables - Claims resulting from credit sales to customers and others goods or services for money,. Oral promises of the purchaser to pay for goods and services sold (credit sale;
Unit 6 Receivables 7-1 Receivables - Claims resulting from credit sales to customers and others goods or services for money,. Oral promises of the purchaser to pay for goods and services sold (credit sale;
an amendment of ARB No. 51, with related amendments of APB Opinion No. 18 and ARB No. 43, Chapter 12 CONTENTS Paragraph Numbers
 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 94 FAS94 Status Page FAS94 Summary Consolidation of All Majority-Owned Subsidiaries (an amendment of ARB No. 51, with related amendments of APB Opinion No.
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 94 FAS94 Status Page FAS94 Summary Consolidation of All Majority-Owned Subsidiaries (an amendment of ARB No. 51, with related amendments of APB Opinion No.
NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON BUSINESS COMBINATIONS
 NAS 21 NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON BUSINESS COMBINATIONS CONTENTS Paragraphs OBJECTIVE 1 SCOPE 2-14 Identifying a business combination 5-10 Business combinations involving entities under common control
NAS 21 NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON BUSINESS COMBINATIONS CONTENTS Paragraphs OBJECTIVE 1 SCOPE 2-14 Identifying a business combination 5-10 Business combinations involving entities under common control
CIMA Managerial Level Paper F2 FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT (REVISION SUMMARIES)
 CIMA Managerial Level Paper F2 FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT (REVISION SUMMARIES) Chapter Title Page number 1 The regulatory framework 3 2 What is a group 9 3 Group accounts the statement of financial position
CIMA Managerial Level Paper F2 FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT (REVISION SUMMARIES) Chapter Title Page number 1 The regulatory framework 3 2 What is a group 9 3 Group accounts the statement of financial position
Similarities and differences*
 Investment Management & Real Estate Similarities and differences* Global Reporting Revolution June 2007 *connectedthinking Contents How to use this publication 01 Summary of Similarities and Difference
Investment Management & Real Estate Similarities and differences* Global Reporting Revolution June 2007 *connectedthinking Contents How to use this publication 01 Summary of Similarities and Difference
STUDY UNIT FIFTEEN BUSINESS COMBINATIONS AND CONSOLIDATION
 STUDY UNIT FIFTEEN BUSINESS COMBINATIONS AND CONSOLIDATION 545 (20 pages of outline) 15.1 Business Combinations... 545 15.2 Consolidation... 555 15.3 Combined Financial Statements... 564 15.4 Practice
STUDY UNIT FIFTEEN BUSINESS COMBINATIONS AND CONSOLIDATION 545 (20 pages of outline) 15.1 Business Combinations... 545 15.2 Consolidation... 555 15.3 Combined Financial Statements... 564 15.4 Practice
ONLINE LEARNING PROBLEMS
 ONLINE LEARNING PROBLEMS Thomas H. Beechy Schulich School of Business Advanced Financial Accounting Fifth Edition Thomas H. Beechy Schulich School of Business Elizabeth Farrell Schulich School of Business
ONLINE LEARNING PROBLEMS Thomas H. Beechy Schulich School of Business Advanced Financial Accounting Fifth Edition Thomas H. Beechy Schulich School of Business Elizabeth Farrell Schulich School of Business
Equity Financing. Overview
 13 Equity Financing Overview After discussing debt financing in Chapter 12, we now turn to the other kind of financing available to businesses equity financing. Like debt financing, equity financing, once
13 Equity Financing Overview After discussing debt financing in Chapter 12, we now turn to the other kind of financing available to businesses equity financing. Like debt financing, equity financing, once
Advanced Accounting-100 Introduction to Business Combinations Page 1
 Advanced Accounting-100 Introduction to Business Combinations Page 1 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS COMBINATIONS I. Key Concepts and Terms: A. Business Combinations 1. OBJECTIVES: a. Growth--increase economic
Advanced Accounting-100 Introduction to Business Combinations Page 1 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS COMBINATIONS I. Key Concepts and Terms: A. Business Combinations 1. OBJECTIVES: a. Growth--increase economic
Investments in Associates
 Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 28 Investments in Associates Investments in Associates Contents Paragraphs SCOPE 1 DEFINITIONS 2-12 Significant Influence 6-10 Equity Method 11-12 APPLICATION OF THE
Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 28 Investments in Associates Investments in Associates Contents Paragraphs SCOPE 1 DEFINITIONS 2-12 Significant Influence 6-10 Equity Method 11-12 APPLICATION OF THE
3,000 3,000 2,910 2,910 3,000 3,000 2,940 2,940
 1. David Company uses the gross method to record its credit purchases, and it uses the periodic inventory system. On July 21, 20D, the company purchased goods that had an invoice price of $ with terms
1. David Company uses the gross method to record its credit purchases, and it uses the periodic inventory system. On July 21, 20D, the company purchased goods that had an invoice price of $ with terms
Consolidated Financial Statements
 332 Accounting Standard (AS) 21 Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-4 DEFINITIONS 5-6 PRESENTATION OF CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 7-8 SCOPE OF CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
332 Accounting Standard (AS) 21 Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-4 DEFINITIONS 5-6 PRESENTATION OF CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 7-8 SCOPE OF CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
CHAPTER 6 INTERCOMPANY INVENTORY TRANSACTIONS
 CHAPTER 6 INTERCOMPANY INVENTORY TRANSACTIONS ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS Q6-1 All inventory transfers between related companies must be eliminated to avoid an overstatement of revenue and cost of goods sold
CHAPTER 6 INTERCOMPANY INVENTORY TRANSACTIONS ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS Q6-1 All inventory transfers between related companies must be eliminated to avoid an overstatement of revenue and cost of goods sold
Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 33 - Consolidated financial statements Caikuai [2006] No.3
![Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 33 - Consolidated financial statements Caikuai [2006] No.3 Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 33 - Consolidated financial statements Caikuai [2006] No.3](/thumbs/40/20527296.jpg) Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 33 - Consolidated financial statements Caikuai [2006] No.3 Chapter I General Provisions Article 1: These Standards are formulated in accordance with the
Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 33 - Consolidated financial statements Caikuai [2006] No.3 Chapter I General Provisions Article 1: These Standards are formulated in accordance with the
Consolidation theories and push-down accounting: achieving global convergence
 ABSTRACT Consolidation theories and push-down accounting: achieving global convergence Catherine Baluch Gartner, Inc. Dee Burgess Florida Gulf Coast University Reuben Cohen Sothern Wine and Spirits Edmond
ABSTRACT Consolidation theories and push-down accounting: achieving global convergence Catherine Baluch Gartner, Inc. Dee Burgess Florida Gulf Coast University Reuben Cohen Sothern Wine and Spirits Edmond
New Accounting for Business Combinations and Non-controlling Interests
 IFRS ADVISORY SERVICES New Accounting for Business Combinations and Non-controlling Interests August 2008 KPMG LLP The proposed new accounting standards for business combinations and non-controlling interests
IFRS ADVISORY SERVICES New Accounting for Business Combinations and Non-controlling Interests August 2008 KPMG LLP The proposed new accounting standards for business combinations and non-controlling interests
Accounting Harmonization and Market Conditions Under Impact of a European Company
 Katarína Máziková Michal Hrapko Accounting Harmonization and Market Conditions Under Impact of a European Company Article Info:, Vol. 3 (2008), No. 2, pp. 003-009 Received 12 Jun 2008 Accepted 24 October
Katarína Máziková Michal Hrapko Accounting Harmonization and Market Conditions Under Impact of a European Company Article Info:, Vol. 3 (2008), No. 2, pp. 003-009 Received 12 Jun 2008 Accepted 24 October
Financial Statements Tutorial
 Financial Statement Review: Financial Statements Tutorial There are four major financial statements used to communicate information to external users (creditors, investors, suppliers, etc.) - 1. Balance
Financial Statement Review: Financial Statements Tutorial There are four major financial statements used to communicate information to external users (creditors, investors, suppliers, etc.) - 1. Balance
How To Account For An Amalgamation
 144 Accounting Standard (AS) 14 Accounting for Amalgamations Contents INTRODUCTION Paragraphs 1-3 Definitions 3 EXPLANATION 4-27 Types of Amalgamations 4-6 Methods of Accounting for Amalgamations 7-13
144 Accounting Standard (AS) 14 Accounting for Amalgamations Contents INTRODUCTION Paragraphs 1-3 Definitions 3 EXPLANATION 4-27 Types of Amalgamations 4-6 Methods of Accounting for Amalgamations 7-13
DRAFT. Quarterly Savings and Loan Holding Company Report FR 2320. General Instructions Who Must Report. When to Submit the Report
 JOBNAME: No Job Name PAGE: 1 SESS: 378 OUTPUT: Mon Nov 21 10:08:25 2011 /frb/bsr/instructs/fr2320/4_dec11_2320-gen_v3 INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARATION OF Quarterly Savings and Loan Holding Company Report General
JOBNAME: No Job Name PAGE: 1 SESS: 378 OUTPUT: Mon Nov 21 10:08:25 2011 /frb/bsr/instructs/fr2320/4_dec11_2320-gen_v3 INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARATION OF Quarterly Savings and Loan Holding Company Report General
AMAZON.COM, INC. CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS (in millions)
 CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF PERIOD $ 8,084 $ 5,269 $ 3,777 OPERATING ACTIVITIES: Net income (loss) 274 (39) 631 Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF PERIOD $ 8,084 $ 5,269 $ 3,777 OPERATING ACTIVITIES: Net income (loss) 274 (39) 631 Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss)
CHAPTER 22. Accounting Changes and Error Analysis 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 12, 13, 15
 CHAPTER 22 Accounting Changes and Error Analysis ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE (BY TOPIC) Topics 1. Differences between change in principle, change in estimate, change in entity, errors. Questions 4,
CHAPTER 22 Accounting Changes and Error Analysis ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE (BY TOPIC) Topics 1. Differences between change in principle, change in estimate, change in entity, errors. Questions 4,
Chapter 11 Intercorporate Investments and Consolidations 567
 CHAPTER 11 11-1 Marketable securities may be either short-term or long-term investments. Short-term refers to intention, not to salability. 11-2 Trading securities are debt or equity securities that a
CHAPTER 11 11-1 Marketable securities may be either short-term or long-term investments. Short-term refers to intention, not to salability. 11-2 Trading securities are debt or equity securities that a
HKFRS 3 Business Combinations 1 Nelson Lam
 HKFRS 3 Business Combinations 1 Nelson Lam 1. Objective of HKFRS 3 The objective of Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standard (HKFRS) 3 is to specify the financial reporting by an entity when it undertakes
HKFRS 3 Business Combinations 1 Nelson Lam 1. Objective of HKFRS 3 The objective of Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standard (HKFRS) 3 is to specify the financial reporting by an entity when it undertakes
29 Accounting for investments in associates IAS 28
 29 Accounting for investments in associates IAS 28 A Key points An associate is a significant or material investment but it is not controlled by the investor. This Standard sets out how an investment in
29 Accounting for investments in associates IAS 28 A Key points An associate is a significant or material investment but it is not controlled by the investor. This Standard sets out how an investment in
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 25. Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No.25. Business Combinations
 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 25 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No.25 Business Combinations Revised on 30 November 2006 Translated by Ling-Tai Lynette Chou, Professor (National
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 25 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No.25 Business Combinations Revised on 30 November 2006 Translated by Ling-Tai Lynette Chou, Professor (National
Term Sheet for Potential Investment by Strategic Investor
 Form: Term Sheet for Potential Investment by Strategic Investor Description: This is a very detailed term sheet for a prospective Preferred Stock investment in a private company, coupled with a strategic
Form: Term Sheet for Potential Investment by Strategic Investor Description: This is a very detailed term sheet for a prospective Preferred Stock investment in a private company, coupled with a strategic
Statement of Cash Flows
 PREPARING THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS: THE INDIRECT METHOD OF REPORTING CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES The work sheet method described in the text book is not the recommended approach. We will provide
PREPARING THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS: THE INDIRECT METHOD OF REPORTING CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES The work sheet method described in the text book is not the recommended approach. We will provide
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Forming a Florida Limited Liability Company (LLC) Versus a Florida Corporation. by Karen J.
 The Advantages and Disadvantages of Forming a Florida Limited Liability Company (LLC) Versus a Florida Corporation by Karen J. Orlin This Note outlines advantages and disadvantages of forming a new business
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Forming a Florida Limited Liability Company (LLC) Versus a Florida Corporation by Karen J. Orlin This Note outlines advantages and disadvantages of forming a new business
Consolidated Financial Statements
 408 Accounting Standard (AS) 21 (issued 2001) Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-4 DEFINITIONS 5-6 PRESENTATION OF CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 7-8 SCOPE OF CONSOLIDATED
408 Accounting Standard (AS) 21 (issued 2001) Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-4 DEFINITIONS 5-6 PRESENTATION OF CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 7-8 SCOPE OF CONSOLIDATED
24. Accounting for groups and the preparation of consolidated accounts
 24. Accounting for groups and the preparation of consolidated accounts Introduction 24.1. All charities preparing consolidated accounts, whether as a requirement of company or charity law or on a voluntary
24. Accounting for groups and the preparation of consolidated accounts Introduction 24.1. All charities preparing consolidated accounts, whether as a requirement of company or charity law or on a voluntary
