Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 7. Consolidated Financial Statements
|
|
|
- Lewis Goodman
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 7 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 7 Consolidated Financial Statements 30 November 2004 Translated by Wei-heng Lin, Associate Professor (Chung Yuan Christian University) 31 December 1985 Translated by Liang-Feng Lin, Associate Professor (National Chengchi University) I Introduction (1) This Statement establishes the accounting standards for the preparation and presentation of consolidated financial statements. (2) This Statement does not deal with methods of accounting for business combinations and their effects on consolidation, including goodwill arising on a business combination. II Definitions (3) Terms used in this Statement are defined below: Financial Accounting Standards Committee 0 (a) (b) (c) (e) Consolidated financial statements: the financial statements of a group presented as those of a single economic entity; Control: the power to dominate and govern the financial, operating and personnel policies of an entity so as to obtain benefits from it s economic activities; A subsidiary: an entity that is controlled by another entity (known as the parent); A parent: an entity that has one or more subsidiaries; A group: a general term referring to a parent and all of its subsidiaries; 1
2 (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) Majority interests: the portion of the net income and net assets of a subsidiary attributable to equity interests that are owned, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, by the parent; Minority interests: the portion of the net income and net assets of a subsidiary attributable to equity interests that are not owned, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, by the parent; Intra-group gains or losses: the resultant gains or losses from transactions entered into between a parent and its subsidiaries or between the subsidiaries. Group net income: the net income arrived by aggregating the individual net income of a group of entities under the control of a parent and then eliminating all intra-group transactions and the resulting unrealized gains or losses; Parent s share of group net income: the portion of group net income attributable to equity interests that are owned, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, by the parent; Associate: an entity or a partnership over which the investor has significant influence and that is neither a subsidiary nor an interest in a joint venture; III Explanations entity. (5) The stockholders of a parent are concerned about the financial position, operating results and changes in financial position of a group rather than individual statements of the parent. (6) The financial information of a group can be presented by preparing consolidated financial statements as if they are a single economic entity regardless of each company s independent legal position. This reporting form can fairly present the financial position, operating results, and changes in financial position. (7) An investor may own share warrants, share call options, debt or equity instruments that are convertible into ordinary shares, or other similar instruments that have the potential, if exercised or converted, to give the holder additional voting power or reduce another party s voting power over the financial, operating and personnel policies of another entity (potential voting rights). The existence and effect of potential voting rights that are currently exercisable or convertible, including potential voting rights held by another entity, are considered when assessing whether an entity has the power to govern the financial, operating and personnel policies of another entity. Potential voting rights are not currently exercisable or convertible when, for example, they cannot be exercised or converted until a future date or until the occurrence of a future event. (8) A subsidiary is not excluded from consolidation simply because the investor is a venture capital organization, mutual fund, unit trust or similar entity. (4) Accounting information should focus on economic substance regardless of legal form. Considering legal, economic or other factors, a business sometimes may, through two or more legal entities (such as parent and subsidiaries), combine in order to operate. In such circumstances, it is impossible to understand the activities of the whole economic entity by merely reading a single entity s financial statements. Therefore, businesses should prepare consolidated financial statements to present the substance of the whole economic 2 (9) A subsidiary is not excluded from consolidation because its business activities are dissimilar from those of the other entities within the group. Relevant information is provided by consolidating such subsidiaries and disclosing additional information in the consolidated financial statements about the different nature of business activities of subsidiaries. For example, the disclosures required by the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 20 3
3 Operating Segments help to explain the significance of different nature of business activities within the group. (10) A parent loses control when it loses the power to govern the financial, operating and personnel policies of an investee so as to obtain benefit from its activities. The loss of control can occur with or without a change in absolute or relative ownership levels. It could occur, for example, when a subsidiary becomes subject to the control of a government, court, administrator or regulator. It could also occur as a result of a contractual agreement. (11) In preparing consolidated financial statements, an entity combines the financial statements of the parent and its subsidiaries line by line by adding together like items of assets, liabilities, equity, income and expenses. In order that the consolidated financial statements present financial information about the group as that of a single economic entity, the following steps are then taken: (a) the carrying amount of the parent s investment in each subsidiary and the parent s portion of equity of each subsidiary are eliminated (in accordance with the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 25 Business Combinations ); date of the combination. (12) When potential voting rights exist, the proportions of net income and changes in equity allocated to the parent and minority interests are determined on the basis of present ownership interests and do not reflect the possible exercise or conversion of potential voting rights. (13) Intra-group balances and transactions, including income, expenses and dividends, are eliminated in full. Gains or losses resulting from intra-group transactions that are recognized in assets, such as inventory and fixed assets, are eliminated in full. Intra-group losses may indicate an impairment that requires recognition in the consolidated financial statements. The Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 22 Income Taxes applies to temporary differences that arise from the elimination of profits and losses resulting from intra-group transactions. (14) Consolidated financial statements should include the following financial statements and footnotes: (a) Consolidated Balance Sheet, Consolidated Income statement, minority interests in the net income of consolidated subsidiaries for the reporting period are identified; and (c) Consolidated Changes of Owners (Stockholders ) Equity Statement, and (c) minority interests in the net assets of consolidated subsidiaries are identified separately from the parent s ownership interests in them. Minority interests in the net assets consist of: (i) (ii) the amount of those minority interests at the date of the original combination calculated in accordance with the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 25 Business Combinations ; and the minority s share of changes in equity since the 4 Consolidated Cash Flows Statement. (15) A parent or its subsidiary may be an investor in an associate or a venturer in a jointly controlled entity. In such cases, consolidated financial statements prepared and presented in accordance with this Statement are also prepared so as to comply with the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 5 Long-term Investments under Equity Method and the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 31 Interests in Joint Ventures. 5
4 IV Accounting standards Preparation and scope of consolidated financial statements Assessment of control (16) Control is presumed to exist when an investor owns, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, more than half of the voting power of an entity unless, in exceptional circumstances, it can be clearly demonstrated that such ownership does not constitute control. Control also exists when an investor owns half or less of the voting power of an entity when there is: (a) power over more than half of the voting rights by virtue of an agreement with other investors; arrangements whether considered individually or in combination) that affect potential voting rights, except the intention of management and the financial ability to exercise or convert such rights. A parent preparing consolidated financial statements (18) A parent shall present consolidated financial statements in which it consolidates its investments in subsidiaries in accordance with this Statement. However, a parent need not present consolidated financial statements if and only if: (a) the parent is itself a wholly-owned subsidiary, or is a partially-owned subsidiary of another entity and its other owners, including those not otherwise entitled to vote, have been informed about, and do not object to, the parent not presenting consolidated financial statements; power to govern the financial, operating and personnel policies of the entity under a statute or an agreement; the parent's debt or equity instruments are not traded in a public market; (c) (e) power to appoint or remove the majority of the members of the board of directors or equivalent governing body and control of the entity is by that board or body; power to cast the majority of votes at meetings of the board of directors or equivalent governing body and control of the entity is by that board or body; or other facts and circumstances that contribute to control. The fact that an investor has the power to control its investees establishes a parent-subsidiaries relationship. (17) In assessing whether potential voting rights contribute to control, the investor examines all facts and circumstances (including the terms of exercise of the potential voting rights and any other contractual 6 (c) the parent did not file, nor is it in the process of filing, its financial statements with a securities commission or other regulatory organisation for the purpose of issuing any class of instruments in a public market; and the ultimate or any intermediate parent of the parent produces consolidated financial statements available for public use that comply with this Statement. Subsidiaries incorporated into consolidated financial statements (19) Consolidated financial statements shall include all subsidiaries of the parent. Accounting for subsidiaries classified as held for sale 7
5 (20) Investments in subsidiaries that are classified as held for sale (or included in a disposal group that is classified as held for sale) in accordance with paragraph 21 to paragraph 24 of the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 38 Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations shall be accounted for in accordance with that Statement. (21) Deleted Consolidation procedures (22) Intra-group balances, transactions, income and expenses shall be eliminated in full. (23) The financial statements of the parent and its subsidiaries used in the preparation of the consolidated financial statements shall be prepared as of the same date. When the end of the reporting period of the parent is different from that of a subsidiary, the subsidiary prepares, for consolidation purposes, additional financial statements as of the same date as the financial statements of the parent unless it is impracticable to do so. (24) When, in accordance with paragraph 23, the financial statements of a subsidiary used in the preparation of consolidated financial statements are prepared as of a date different from that of the parent s financial statements, adjustments shall be made for the effects of significant transactions or events that occur between that date and the date of the parent s financial statements. In any case, the difference between the end of the reporting period of the subsidiary and that of the parent shall be no more than three months. The length of the reporting periods and any difference between the ends of the reporting periods shall be the same from period to period. (25) Consolidated financial statements shall be prepared using uniform accounting policies for like transactions and other events in similar circumstances. Accounting for acquisition or loss of control 8 (26) The income and expenses of a subsidiary are included in the consolidated financial statements from the acquisition date. The income and expenses of a subsidiary are included in the consolidated financial statements until the date when the parent ceases to control the subsidiary. (27) The calculation of a subsidiary s income and expenses subsequent to acquisition date or prior to loss of control should be based on the audited (reviewed) interim financial statements of which the end of reporting period is the acquisition date or the date when the parent ceases to control the subsidiary. If such interim financial statements are not available, the calculation should be based on the income and expenses proportionate to the audited (reviewed) interim financial statements or those of annual financial statements if such interim financial statements are not available. The difference between the proceeds from the disposal of a subsidiary and its carrying amount as of the date of disposal, including the cumulative amount of any exchange differences that relate to the subsidiary recognized in other comprehensive income in accordance with the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 14 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates, is reclassified to the consolidated income statement as a reclassification adjustment as the gains or losses on the disposal of the subsidiary. Accounting for an investee company ceasing to be a subsidiary (28) An investment in an entity shall be accounted for in accordance with the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 34 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement from the date that it ceases to be a subsidiary, provided that it does not become an associate or a jointly controlled entity. (29) The carrying amount of the investment at the date that the investee ceases to be a subsidiary shall be regarded as the cost on initial measurement of a financial asset. 9
6 Accounting for the consolidated balance sheet Elimination of reciprocal accounts (30) The investments between the parent and subsidiaries and between the subsidiaries themselves should be eliminated with the investee s equity. Liabilities due to one group entity by another will be set off against the corresponding asset in the other group entity s financial statements. The allowance for consolidated doubtful accounts should be based on an amount after eliminating intra-group receivables and payables. Impairment of long-term equity investment (31) If the carrying amount of a parent s long-term equity investment in the subsidiary is impaired, the parent should apply the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 35 Impairment of Assets when preparing consolidated financial statements. equity section of the consolidated balance sheet and account for as the treatment of treasury stock. Accounting for reciprocally-held bonds (34) Any bonds that are reciprocally held by other group entities under the control of a parent should be treated as retirement of bonds when preparing consolidated financial statements. Accounting standards for consolidated income statement Elimination of gain or loss accounts (35) The gains or losses resulting from intra-group transactions must be eliminated from the consolidated financial statements. Accounting for unrealized intra-group gains or losses Preferred shares issued by subsidiaries (32) When a subsidiary issues both common and preferred stock, the preferred stock equity s carrying value should be determined by the attributes of the preferred stock. Common stock equity should be arrived by deducting preferred stock equity s carrying value from total stockholders equity. The common stock equity should be then used to eliminate the carrying amount of the parent s investment. The preferred stock equity held by the parent should be treated as retired preferred stock when preparing consolidated financial statements. A subsidiary holds its parent s common stock (33) When a subsidiary holds its parent s stock, the parent should deduct the subsidiary s equity interest in its parent from the stockholders 10 (36) The unrealized intra-group gains or losses on closing inventory, fixed assets and other assets resulting from intra-group transactions, must be eliminated until realization. The tax effect of the transaction should be accounted for in accordance with the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 22 Income Taxes. Net income calculation when a subsidiary issuing cumulative preferred shares (37) If a subsidiary has outstanding cumulative preference shares that are classified as equity and are held by minority interests, the parent computes its share of group net income and group net income applicable to minority interests after adjusting for the dividends on such shares, whether or not dividends have been declared. Accounting for losses exceeding the minority interest 11
7 (38) Losses applicable to the minority in a consolidated subsidiary may exceed the minority interest in the subsidiary's equity. The excess, and any further losses applicable to the minority, are allocated against the majority interest except to the extent that the minority has a binding obligation and is able to make an additional investment to cover the losses. If the subsidiary subsequently reports profits, such profits are allocated to the majority interest until the minority s share of losses previously absorbed by the majority has been recovered. Disclosure of a subsidiary s minority stock equity (42) Minority interests shall be presented in the total amount in owners equity section of the consolidated balance sheet, separately from the equity of the owners of the parent without the need to distinguish it from capital stock, paid-in capital and retained earnings (or cumulative deficit). Accounting for reciprocally-held bonds Calculation of group net income (39) When bonds are reciprocally held by other group entities under the control of a parent and are accounted for, as retirement of bonds in accordance with paragraph 34 of this Statement, the retirement gains or losses should be recognized when preparing the consolidated financial statements. Accounting for consolidated changes of owners equity statement (40) When a parent prepares Consolidated Changes in Owners Equity Statement, the ending balance of the consolidated owners equity less the minority interest should equal the parent s ending balance of owners equity. (43) Group net income on a consolidated income statement should be attributed to the parent s share of group net income and group net income allocated to the minority interests. Disclosure in consolidated financial statements (44) The notes to the consolidated financial statements should disclose the following items: (a) the name of each subsidiary, the nature of its operations, and the percentage of shareholders equity that is held by the parent; Accounting for consolidated cash flows statement (41) When a consolidated cash flows statement is prepared, cash flows from operating activities should include the parent s share of group net income and group net income allocated to minority. Cash flows from financing activities should include distributed cash dividends that are distributed by the parent and are distributed by a subsidiary to its minority stockholders. Presentation and disclosure of consolidated financial statements 12 (c) changes of subsidiaries that are included in the consolidated financial statements; the nature of the relationship between the parent and a subsidiary when the parent does not own, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, more than half of the voting power; the reasons why the ownership, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, of more than half of the voting or potential voting power of an investee does not constitute control; 13
8 (e) (f) (g) the name of each subsidiary not included in the consolidated financial statements, percentage of shareholder s equity that is held by the parent, and the reason for its exclusion from the consolidated financial statements; the arrangement made by a subsidiary in order to match the date of consolidated financial statements, the subsidiary s adjustments in its accounting period, reporting process and the reasons for differences; any specific operating risks incurred by a foreign subsidiary, such as changes in the exchange rate, etc.; (46) When an enterprise initially applies the first revision of this Statement, the financial statements need not to retroactively apply the first revision of this Statement. However, the amount of the cumulative effect of changes in accounting principles, if any, should be shown separately in the current income statement. (a) In the consolidated financial statements, an enterprise shall additionally disclose: the difference between the reporting entity of period initially applying this Statement and that of prior periods, and the reasons for the change in the reporting entity; (h) the nature and extent of any significant restrictions (e.g. resulting from borrowing arrangements or regulatory requirements) on the ability of subsidiaries to transfer funds to the parent in the form of cash dividends or to repay loans or advances; the subsidiaries underlying the previous difference of change in the reporting entity, and the enterprise (the parent) shall disclose the material transactions with these subsidiaries in prior periods and the items (a), (c), (g), (h), (i) and (j) of paragraph 44. (i) (j) details of the parent s stock that is held by it s subsidiaries; and the related information regarding a subsidiary s issuance of convertible bonds and new common stock. The provisions of this Statement need not be applied to immaterial items. V Notes (45) This Statement was issued on December, 31, 1985, with the first revision on December 9, 2004, and the second revision on November 30, The second revision of this Statement shall be effective for financial statements of fiscal years beginning on or after January 1, Earlier application is permitted. The financial statements prepared in accordance with the provisions of this Statement need not to retroactively apply the second revision of this Statement
International Accounting Standard 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements
 International Accounting Standard 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements Scope 1 This Standard shall be applied in the preparation and presentation of consolidated financial statements for a
International Accounting Standard 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements Scope 1 This Standard shall be applied in the preparation and presentation of consolidated financial statements for a
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-LKAS 27. Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements
 Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-LKAS 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements -675- Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-LKAS 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements Sri Lanka Accounting Standard
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-LKAS 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements -675- Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-LKAS 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements Sri Lanka Accounting Standard
Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements
 Compiled Accounting Standard AASB 127 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements This compiled Standard applies to annual reporting periods beginning on or after 1 July 2007. Early application is permitted.
Compiled Accounting Standard AASB 127 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements This compiled Standard applies to annual reporting periods beginning on or after 1 July 2007. Early application is permitted.
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard LKAS 28. Investments in Associates
 Sri Lanka Accounting Standard LKAS 28 Investments in Associates CONTENTS SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARD LKAS 28 INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES paragraphs SCOPE 1 DEFINITIONS 2 12 Significant influence 6 10 Equity
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard LKAS 28 Investments in Associates CONTENTS SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARD LKAS 28 INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES paragraphs SCOPE 1 DEFINITIONS 2 12 Significant influence 6 10 Equity
International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates
 International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates Scope 1 This Standard shall be applied in accounting for investments in associates. However, it does not apply to investments in associates
International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates Scope 1 This Standard shall be applied in accounting for investments in associates. However, it does not apply to investments in associates
2 This Standard shall be applied by all entities that are investors with joint control of, or significant influence over, an investee.
 International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures Objective 1 The objective of this Standard is to prescribe the accounting for investments in associates and to set out
International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures Objective 1 The objective of this Standard is to prescribe the accounting for investments in associates and to set out
Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures
 STATUTORY BOARD FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD SB-FRS 28 Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures This standard applies for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2013. Earlier application is
STATUTORY BOARD FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD SB-FRS 28 Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures This standard applies for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2013. Earlier application is
NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON INVESTMENT IN ASSOCIATES
 NAS 25 NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON INVESTMENT IN ASSOCIATES CONTENTS Paragraphs SCOPE 1-2 DEFINITIONS 3-13 Significant influence 7-11 Equity method 12-13 APPLICATION OF THE EQUITY METHOD 14-33 Impairment
NAS 25 NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON INVESTMENT IN ASSOCIATES CONTENTS Paragraphs SCOPE 1-2 DEFINITIONS 3-13 Significant influence 7-11 Equity method 12-13 APPLICATION OF THE EQUITY METHOD 14-33 Impairment
Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures
 International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures In April 2001 the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) adopted IAS 28 Accounting for Investments in Associates,
International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures In April 2001 the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) adopted IAS 28 Accounting for Investments in Associates,
Investments in Associates
 Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 28 Investments in Associates Investments in Associates Contents Paragraphs SCOPE 1 DEFINITIONS 2-12 Significant Influence 6-10 Equity Method 11-12 APPLICATION OF THE
Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 28 Investments in Associates Investments in Associates Contents Paragraphs SCOPE 1 DEFINITIONS 2-12 Significant Influence 6-10 Equity Method 11-12 APPLICATION OF THE
HKAS 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements 1
 HKAS 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements 1 Nelson Lam 1. Scope of HKAS 27 Hong Kong Accounting Standard (HKAS) 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements shall be applied in the preparation
HKAS 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements 1 Nelson Lam 1. Scope of HKAS 27 Hong Kong Accounting Standard (HKAS) 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements shall be applied in the preparation
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
 FACT SHEET September 2011 IAS 27 Consolidated and separate financial statements (This fact sheet is based on the standard as at 1 January 2011.) Important note: This fact sheet is based on the requirements
FACT SHEET September 2011 IAS 27 Consolidated and separate financial statements (This fact sheet is based on the standard as at 1 January 2011.) Important note: This fact sheet is based on the requirements
ACCOUNTING STANDARD 23 (AS - 23) Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements
 ACCOUNTING STANDARD 23 (AS - 23) Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements Commencement AS - 23 comes into effect from April 1,2002. Objective The standard explains
ACCOUNTING STANDARD 23 (AS - 23) Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements Commencement AS - 23 comes into effect from April 1,2002. Objective The standard explains
Investments in Associates
 HKAS 28 Revised June 2011July 2012 Effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2005* Hong Kong Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates *HKAS 28 is applicable for annual periods
HKAS 28 Revised June 2011July 2012 Effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2005* Hong Kong Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates *HKAS 28 is applicable for annual periods
IPSAS 7 INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES
 IPSAS 7 INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES Acknowledgment This International Public Sector Accounting Standard (IPSAS) is drawn primarily from International Accounting Standard (IAS) 28 (Revised 2003), Investments
IPSAS 7 INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES Acknowledgment This International Public Sector Accounting Standard (IPSAS) is drawn primarily from International Accounting Standard (IAS) 28 (Revised 2003), Investments
Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures
 IFAC Board Exposure Draft 50 October 2013 Comments due: February 28, 2014 Proposed International Public Sector Accounting Standard Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures This Exposure Draft 50, Investments
IFAC Board Exposure Draft 50 October 2013 Comments due: February 28, 2014 Proposed International Public Sector Accounting Standard Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures This Exposure Draft 50, Investments
Accounting Guideline GRAP 7. Investments in Associates
 Accounting Guideline GAP 7 Investments in Associates GAP 7 Investments in Associates Contents 1. INTODUCTION... 3 2. SCOPE... 4 3. THE BIG PICTUE... 5 4. IDENTIFICATION... 6 4.1 Identifying an associate...
Accounting Guideline GAP 7 Investments in Associates GAP 7 Investments in Associates Contents 1. INTODUCTION... 3 2. SCOPE... 4 3. THE BIG PICTUE... 5 4. IDENTIFICATION... 6 4.1 Identifying an associate...
International Accounting Standard 27 (IAS 27), Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements
 International Accounting Standard 27 (IAS 27), Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements By BRIAN FRIEDRICH, MEd, CGA, FCCA(UK), CertIFR and LAURA FRIEDRICH, MSc, CGA, FCCA(UK), CertIFR Updated By
International Accounting Standard 27 (IAS 27), Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements By BRIAN FRIEDRICH, MEd, CGA, FCCA(UK), CertIFR and LAURA FRIEDRICH, MSc, CGA, FCCA(UK), CertIFR Updated By
Consolidated Financial Statements and Investments in Subsidiaries
 LEMBAGA PIAWAIAN PERAKAUNAN MALAYSIA MALAYSIAN ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD MASB Standard 11 Consolidated Financial Statements and Investments in Subsidiaries Any correspondence regarding this Standard should
LEMBAGA PIAWAIAN PERAKAUNAN MALAYSIA MALAYSIAN ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD MASB Standard 11 Consolidated Financial Statements and Investments in Subsidiaries Any correspondence regarding this Standard should
Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements
 371 Accounting Standard (AS) 23 Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-2 DEFINITIONS 3-6 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS EQUITY METHOD
371 Accounting Standard (AS) 23 Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-2 DEFINITIONS 3-6 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS EQUITY METHOD
Consolidated Financial Statements
 408 Accounting Standard (AS) 21 (issued 2001) Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-4 DEFINITIONS 5-6 PRESENTATION OF CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 7-8 SCOPE OF CONSOLIDATED
408 Accounting Standard (AS) 21 (issued 2001) Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-4 DEFINITIONS 5-6 PRESENTATION OF CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 7-8 SCOPE OF CONSOLIDATED
IPSAS 7 INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES
 IPSAS 7 INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES Acknowledgment This International Public Sector Accounting Standard (IPSAS) is drawn primarily from International Accounting Standard (IAS) 28 (Revised 2003), Investments
IPSAS 7 INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES Acknowledgment This International Public Sector Accounting Standard (IPSAS) is drawn primarily from International Accounting Standard (IAS) 28 (Revised 2003), Investments
SSAP 32 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 32 CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN SUBSIDIARIES
 SSAP 32 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 32 CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN SUBSIDIARIES (Issued January 2001) The standards, which have been set in bold italic
SSAP 32 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 32 CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN SUBSIDIARIES (Issued January 2001) The standards, which have been set in bold italic
The following Accounting Standards Interpretations (ASIs) relate to AS 23:
 438 Accounting Standard (AS) 23 (issued 2001) Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-2 DEFINITIONS 3-6 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS
438 Accounting Standard (AS) 23 (issued 2001) Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-2 DEFINITIONS 3-6 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS
NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON BUSINESS COMBINATIONS
 NAS 21 NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON BUSINESS COMBINATIONS CONTENTS Paragraphs OBJECTIVE 1 SCOPE 2-14 Identifying a business combination 5-10 Business combinations involving entities under common control
NAS 21 NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON BUSINESS COMBINATIONS CONTENTS Paragraphs OBJECTIVE 1 SCOPE 2-14 Identifying a business combination 5-10 Business combinations involving entities under common control
Consolidated Financial Statements
 332 Accounting Standard (AS) 21 Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-4 DEFINITIONS 5-6 PRESENTATION OF CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 7-8 SCOPE OF CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
332 Accounting Standard (AS) 21 Consolidated Financial Statements Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-4 DEFINITIONS 5-6 PRESENTATION OF CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 7-8 SCOPE OF CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
AS 27 Financial Reporting of Interests in Joint Ventures
 CA. B. Ganesh AS 21 Consolidated Financial Statements AS 23 Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements AS 27 Financial Reporting of Interests in Joint Ventures Case studies
CA. B. Ganesh AS 21 Consolidated Financial Statements AS 23 Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements AS 27 Financial Reporting of Interests in Joint Ventures Case studies
SSAP 10 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 10 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES
 SSAP 10 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 10 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES (Issued January 1985; Revised July 1991, February 1999 and May 2001) The standards, which have been set in
SSAP 10 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 10 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES (Issued January 1985; Revised July 1991, February 1999 and May 2001) The standards, which have been set in
Investments in Associates
 International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates This version includes amendments resulting from IFRSs issued up to 31 December 2008. IAS 28 Accounting for Investments in Associates was issued
International Accounting Standard 28 Investments in Associates This version includes amendments resulting from IFRSs issued up to 31 December 2008. IAS 28 Accounting for Investments in Associates was issued
29 Accounting for investments in associates IAS 28
 29 Accounting for investments in associates IAS 28 A Key points An associate is a significant or material investment but it is not controlled by the investor. This Standard sets out how an investment in
29 Accounting for investments in associates IAS 28 A Key points An associate is a significant or material investment but it is not controlled by the investor. This Standard sets out how an investment in
Features. Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standards: HKAS 27. Subsidiary. Subsidiary. Subsidiary. Subsidiary. Subsidiary
 Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standards: HKS 27 (Relevant to TE aper 7 dvanced ccounting & E aper I Financial Reporting) Lindy W W Yau, F, FI, F and Morris Y M Kwok M, M, 25 HKS 27 onsolidated and Separate
Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standards: HKS 27 (Relevant to TE aper 7 dvanced ccounting & E aper I Financial Reporting) Lindy W W Yau, F, FI, F and Morris Y M Kwok M, M, 25 HKS 27 onsolidated and Separate
Issue 19: Joint Arrangements and Associates
 www.bdo.ca Assurance and accounting Comparison Series Issue 19: Joint Arrangements and Associates Both and are principle based frameworks, and from a conceptual standpoint many of the general principles
www.bdo.ca Assurance and accounting Comparison Series Issue 19: Joint Arrangements and Associates Both and are principle based frameworks, and from a conceptual standpoint many of the general principles
Consolidated financial statements
 Summary of significant accounting policies Basis of preparation DSM s consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) as adopted
Summary of significant accounting policies Basis of preparation DSM s consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) as adopted
HKFRS 3 Business Combinations 1 Nelson Lam
 HKFRS 3 Business Combinations 1 Nelson Lam 1. Objective of HKFRS 3 The objective of Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standard (HKFRS) 3 is to specify the financial reporting by an entity when it undertakes
HKFRS 3 Business Combinations 1 Nelson Lam 1. Objective of HKFRS 3 The objective of Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standard (HKFRS) 3 is to specify the financial reporting by an entity when it undertakes
Business Combinations
 Compiled Accounting Standard AASB 3 Business Combinations This compilation was prepared on 6 March 2006 taking into account amendments made up to and including 22 June 2005. Prepared by the staff of the
Compiled Accounting Standard AASB 3 Business Combinations This compilation was prepared on 6 March 2006 taking into account amendments made up to and including 22 June 2005. Prepared by the staff of the
International Accounting Standard 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
 International Accounting Standard 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates Objective 1 An entity may carry on foreign activities in two ways. It may have transactions in foreign currencies or
International Accounting Standard 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates Objective 1 An entity may carry on foreign activities in two ways. It may have transactions in foreign currencies or
IPSAS 7 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES
 IPSAS 7 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES Acknowledgment This International Public Sector Accounting Standard is drawn primarily from International Accounting Standard (IAS) 28, Accounting for Investments
IPSAS 7 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES Acknowledgment This International Public Sector Accounting Standard is drawn primarily from International Accounting Standard (IAS) 28, Accounting for Investments
Note 2 SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING
 Note 2 SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES BASIS FOR THE PREPARATION OF THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS The consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting
Note 2 SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES BASIS FOR THE PREPARATION OF THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS The consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting
KOREAN AIR LINES CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARIES. Consolidated Financial Statements
 Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2015 (With Independent Auditors Report Thereon) Contents Page Independent Auditors Report 1 Consolidated Statements of Financial Position 3 Consolidated Statements
Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2015 (With Independent Auditors Report Thereon) Contents Page Independent Auditors Report 1 Consolidated Statements of Financial Position 3 Consolidated Statements
Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 27. Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements
 Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements Contents Paragraphs Scope 1-3 Definitions 4-8 Presentation of Consolidated Financial 9-11 Statements Scope of Consolidated
Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements Contents Paragraphs Scope 1-3 Definitions 4-8 Presentation of Consolidated Financial 9-11 Statements Scope of Consolidated
IFrS. Disclosure checklist. July 2011. kpmg.com/ifrs
 IFrS Disclosure checklist July 2011 kpmg.com/ifrs Contents What s new? 1 1. General presentation 2 1.1 Presentation of financial statements 2 1.2 Changes in equity 12 1.3 Statement of cash flows 13 1.4
IFrS Disclosure checklist July 2011 kpmg.com/ifrs Contents What s new? 1 1. General presentation 2 1.1 Presentation of financial statements 2 1.2 Changes in equity 12 1.3 Statement of cash flows 13 1.4
ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD STANDARD OF GENERALLY RECOGNISED ACCOUNTING PRACTICE INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES GRAP 7
 ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD STANDARD OF GENERALLY RECOGNISED ACCOUNTING PRACTICE INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES GRAP 7 1 Acknowledgement This Standard of Generally Recognised Accounting Practice (GRAP) is drawn
ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD STANDARD OF GENERALLY RECOGNISED ACCOUNTING PRACTICE INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES GRAP 7 1 Acknowledgement This Standard of Generally Recognised Accounting Practice (GRAP) is drawn
ASPE at a Glance. Standards Included in Topic
 ASPE AT A GLANCE ASPE AT A GLANCE This publication has been compiled to assist users in gaining a high level overview of Accounting Standards for Private Enterprises (ASPE) included in Part II of the CPA
ASPE AT A GLANCE ASPE AT A GLANCE This publication has been compiled to assist users in gaining a high level overview of Accounting Standards for Private Enterprises (ASPE) included in Part II of the CPA
Consolidation Accounting
 Consolidation Accounting Indian GAAP Sailesh Patel (CA) Topics to be discussed: Why consolidation Consolidation Requirement Definition of subsidiary, associate, joint venture Exclusion from consolidation
Consolidation Accounting Indian GAAP Sailesh Patel (CA) Topics to be discussed: Why consolidation Consolidation Requirement Definition of subsidiary, associate, joint venture Exclusion from consolidation
Consolidated Balance Sheets March 31, 2001 and 2000
 Financial Statements SEIKAGAKU CORPORATION AND CONSOLIDATED SUBSIDIARIES Consolidated Balance Sheets March 31, 2001 and 2000 Assets Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents... Short-term investments (Note
Financial Statements SEIKAGAKU CORPORATION AND CONSOLIDATED SUBSIDIARIES Consolidated Balance Sheets March 31, 2001 and 2000 Assets Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents... Short-term investments (Note
Accounting for Investments
 133 Accounting Standard (AS) 13 Accounting for Investments Contents INTRODUCTION Paragraphs 1-3 Definitions 3 EXPLANATION 4-25 Forms of Investments 4-6 Classification of Investments 7-8 Cost of Investments
133 Accounting Standard (AS) 13 Accounting for Investments Contents INTRODUCTION Paragraphs 1-3 Definitions 3 EXPLANATION 4-25 Forms of Investments 4-6 Classification of Investments 7-8 Cost of Investments
SSAP 24 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 24 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN SECURITIES
 SSAP 24 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 24 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN SECURITIES (Issued April 1999) The standards, which have been set in bold italic type, should be read in the context of
SSAP 24 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 24 ACCOUNTING FOR INVESTMENTS IN SECURITIES (Issued April 1999) The standards, which have been set in bold italic type, should be read in the context of
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 25. Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No.25. Business Combinations
 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 25 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No.25 Business Combinations Revised on 30 November 2006 Translated by Ling-Tai Lynette Chou, Professor (National
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 25 Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No.25 Business Combinations Revised on 30 November 2006 Translated by Ling-Tai Lynette Chou, Professor (National
Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 7 Statement of Cash Flows
 Contents Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 7 Statement of Cash Flows Paragraphs OBJECTIVE SCOPE 1 3 BENEFITS OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION 4 5 DEFINITIONS 6 9 Cash and cash equivalents 7 9 PRESENTATION OF
Contents Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 7 Statement of Cash Flows Paragraphs OBJECTIVE SCOPE 1 3 BENEFITS OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION 4 5 DEFINITIONS 6 9 Cash and cash equivalents 7 9 PRESENTATION OF
Consolidated Financial Statements
 STATUTORY BOARD FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD SB-FRS 110 Consolidated Financial Statements This standard applies for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2013. Earlier application is permitted
STATUTORY BOARD FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD SB-FRS 110 Consolidated Financial Statements This standard applies for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2013. Earlier application is permitted
JGAAP-IFRS comparison. English version 3.0 [equivalent of Japanese version 4.0]
![JGAAP-IFRS comparison. English version 3.0 [equivalent of Japanese version 4.0] JGAAP-IFRS comparison. English version 3.0 [equivalent of Japanese version 4.0]](/thumbs/24/3831703.jpg) - comparison English version 3.0 [equivalent of Japanese version 4.0] Contents Contents... 2 Introduction... 3 Presentation of Financial Statements, Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates
- comparison English version 3.0 [equivalent of Japanese version 4.0] Contents Contents... 2 Introduction... 3 Presentation of Financial Statements, Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates
MASB Standard 12. Investments in Associates
 LEMBAGA PIAWAIAN PERAKAUNAN MALAYSIA MALAYSIAN ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD MASB Standard 12 Investments in Associates Any correspondence regarding this Standard should be addressed to: The Chairman Malaysian
LEMBAGA PIAWAIAN PERAKAUNAN MALAYSIA MALAYSIAN ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD MASB Standard 12 Investments in Associates Any correspondence regarding this Standard should be addressed to: The Chairman Malaysian
Interim Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
 Interim Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited) For the Six Months Ended, NTT FINANCE CORPORATION This document has been translated and reclassified from a part of the Japanese
Interim Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited) For the Six Months Ended, NTT FINANCE CORPORATION This document has been translated and reclassified from a part of the Japanese
International Accounting Standard 7 Statement of cash flows *
 International Accounting Standard 7 Statement of cash flows * Objective Information about the cash flows of an entity is useful in providing users of financial statements with a basis to assess the ability
International Accounting Standard 7 Statement of cash flows * Objective Information about the cash flows of an entity is useful in providing users of financial statements with a basis to assess the ability
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
 NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 1 SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (a) Statement of compliance These financial statements have been prepared in accordance with all applicable Hong Kong Financial Reporting
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 1 SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (a) Statement of compliance These financial statements have been prepared in accordance with all applicable Hong Kong Financial Reporting
The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
 Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates (This Indian Accounting Standard includes paragraphs set in bold type and plain type, which have equal authority.
Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates (This Indian Accounting Standard includes paragraphs set in bold type and plain type, which have equal authority.
Financial Accounting and Reporting in Malaysia
 Financial Accounting and Reporting in Malaysia Volume 2 Fourth Edition TAN LIONG TONG Dip. Agriculture, B.S. Agribusiness, MBA, CA, CPA xi TABLE OF CONTENTS About CCH...iii About the Author... iv Dedication...
Financial Accounting and Reporting in Malaysia Volume 2 Fourth Edition TAN LIONG TONG Dip. Agriculture, B.S. Agribusiness, MBA, CA, CPA xi TABLE OF CONTENTS About CCH...iii About the Author... iv Dedication...
The Kansai Electric Power Company, Incorporated and Subsidiaries
 The Kansai Electric Power Company, Incorporated and Subsidiaries Consolidated Financial Statements for the Years Ended March 31, 2003 and 2002 and for the Six Months Ended September 30, 2003 and 2002 The
The Kansai Electric Power Company, Incorporated and Subsidiaries Consolidated Financial Statements for the Years Ended March 31, 2003 and 2002 and for the Six Months Ended September 30, 2003 and 2002 The
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-LKAS 7. Statement of Cash Flows
 Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-LKAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows CONTENTS SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARD-LKAS 7 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS paragraphs OBJECTIVE SCOPE 1 3 BENEFITS OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION 4 5 DEFINITIONS
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-LKAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows CONTENTS SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARD-LKAS 7 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS paragraphs OBJECTIVE SCOPE 1 3 BENEFITS OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION 4 5 DEFINITIONS
Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
 Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates Contents Paragraph OBJECTIVE 1-2 SCOPE 3-7 DEFINITIONS 8-16 Elaboration on the definitions 9-16 Functional currency
Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates Contents Paragraph OBJECTIVE 1-2 SCOPE 3-7 DEFINITIONS 8-16 Elaboration on the definitions 9-16 Functional currency
16 BUSINESS ACCOUNTING STANDARD CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND INVESTMENTS IN SUBSIDIARIES I. GENERAL PROVISIONS
 APPROVED by Resolution No. 10 of 10 December 2003 of the Standards Board of the Public Establishment the Institute of Accounting of the Republic of Lithuania 16 BUSINESS ACCOUNTING STANDARD CONSOLIDATED
APPROVED by Resolution No. 10 of 10 December 2003 of the Standards Board of the Public Establishment the Institute of Accounting of the Republic of Lithuania 16 BUSINESS ACCOUNTING STANDARD CONSOLIDATED
Statement of Cash Flows
 STATUTORY BOARD FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD SB-FRS 7 Statement of Cash Flows This version of SB-FRS 7 does not include amendments that are effective for annual periods beginning after 1 January 2014.
STATUTORY BOARD FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD SB-FRS 7 Statement of Cash Flows This version of SB-FRS 7 does not include amendments that are effective for annual periods beginning after 1 January 2014.
ACER INCORPORATED AND SUBSIDIARIES. Consolidated Balance Sheets
 Consolidated Balance Sheets June 30, 2015, December 31, 2014, and (June 30, 2015 and 2014 are reviewed, not audited) Assets 2015.6.30 2014.12.31 2014.6.30 Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents $ 36,400,657
Consolidated Balance Sheets June 30, 2015, December 31, 2014, and (June 30, 2015 and 2014 are reviewed, not audited) Assets 2015.6.30 2014.12.31 2014.6.30 Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents $ 36,400,657
Consolidated Balance Sheets
 Consolidated Balance Sheets March 31 2015 2014 2015 Assets: Current assets Cash and cash equivalents 726,888 604,571 $ 6,057,400 Marketable securities 19,033 16,635 158,608 Notes and accounts receivable:
Consolidated Balance Sheets March 31 2015 2014 2015 Assets: Current assets Cash and cash equivalents 726,888 604,571 $ 6,057,400 Marketable securities 19,033 16,635 158,608 Notes and accounts receivable:
Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 33 - Consolidated financial statements Caikuai [2006] No.3
![Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 33 - Consolidated financial statements Caikuai [2006] No.3 Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 33 - Consolidated financial statements Caikuai [2006] No.3](/thumbs/40/20527296.jpg) Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 33 - Consolidated financial statements Caikuai [2006] No.3 Chapter I General Provisions Article 1: These Standards are formulated in accordance with the
Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 33 - Consolidated financial statements Caikuai [2006] No.3 Chapter I General Provisions Article 1: These Standards are formulated in accordance with the
Tax accounting services: Foreign currency tax accounting. October 2012
 Tax accounting services: Foreign currency tax accounting October 2012 The globalization of commerce and capital markets has resulted in business, investment and capital formation transactions increasingly
Tax accounting services: Foreign currency tax accounting October 2012 The globalization of commerce and capital markets has resulted in business, investment and capital formation transactions increasingly
24. Accounting for groups and the preparation of consolidated accounts
 24. Accounting for groups and the preparation of consolidated accounts Introduction 24.1. All charities preparing consolidated accounts, whether as a requirement of company or charity law or on a voluntary
24. Accounting for groups and the preparation of consolidated accounts Introduction 24.1. All charities preparing consolidated accounts, whether as a requirement of company or charity law or on a voluntary
CHAPTER NINE Group accounts
 CHAPTER NINE Group accounts 9.1 GROUP ACCOUNTS 9.1.1 Introduction 9.1.1.1 Authorities shall account for Group Accounts in accordance with IFRS 3 Business Combinations, IAS 27 Consolidated and Separate
CHAPTER NINE Group accounts 9.1 GROUP ACCOUNTS 9.1.1 Introduction 9.1.1.1 Authorities shall account for Group Accounts in accordance with IFRS 3 Business Combinations, IAS 27 Consolidated and Separate
Accounting for Equity Investments & Acquisitions
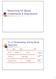 Accounting for Equity Investments & Acquisitions % of Outstanding Voting Stock Acquired 0% 20% 50% 100% Nominal Significant Control Level of Influence Fair Value Equity method Valuation Basis Investment
Accounting for Equity Investments & Acquisitions % of Outstanding Voting Stock Acquired 0% 20% 50% 100% Nominal Significant Control Level of Influence Fair Value Equity method Valuation Basis Investment
IFRS 10 Consolidated Financial Statements
 S U M M A R Y IFRS 10 Consolidated Financial Statements Overview IFRS 10 replaces the part of IAS 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements that addresses accounting for subsidiaries on consolidation.
S U M M A R Y IFRS 10 Consolidated Financial Statements Overview IFRS 10 replaces the part of IAS 27 Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements that addresses accounting for subsidiaries on consolidation.
Consolidated Financial Statements
 AASB Standard AASB 10 August 2011 Consolidated Financial Statements Obtaining a Copy of this Accounting Standard This Standard is available on the AASB website: www.aasb.gov.au. Alternatively, printed
AASB Standard AASB 10 August 2011 Consolidated Financial Statements Obtaining a Copy of this Accounting Standard This Standard is available on the AASB website: www.aasb.gov.au. Alternatively, printed
The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
 STATUTORY BOARD FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD SB-FRS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates SB-FRS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates was operative for Statutory Boards financial
STATUTORY BOARD FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD SB-FRS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates SB-FRS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates was operative for Statutory Boards financial
PART III. Consolidated Financial Statements of Hitachi, Ltd. and Subsidiaries: Independent Auditors Report 47
 PART III Item 17. Financial Statements Consolidated Financial Statements of Hitachi, Ltd. and Subsidiaries: Schedule: Page Number Independent Auditors Report 47 Consolidated Balance Sheets as of March
PART III Item 17. Financial Statements Consolidated Financial Statements of Hitachi, Ltd. and Subsidiaries: Schedule: Page Number Independent Auditors Report 47 Consolidated Balance Sheets as of March
Accounting for Investments in Associates
 Australian Accounting Standard AAS 14 May 1997 Accounting for Investments in Associates Prepared by the Public Sector Accounting Standards Board of the Australian Accounting Research Foundation and by
Australian Accounting Standard AAS 14 May 1997 Accounting for Investments in Associates Prepared by the Public Sector Accounting Standards Board of the Australian Accounting Research Foundation and by
Unaudited Interim Consolidated Financial Statements and Footnotes July 3, 2011
 Unaudited Interim Consolidated Financial Statements and Footnotes July 3, 2011 1 MEXICAN RESTAURANTS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS (unaudited) 7/3/2011 1/2/2011 ASSETS Current assets:
Unaudited Interim Consolidated Financial Statements and Footnotes July 3, 2011 1 MEXICAN RESTAURANTS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS (unaudited) 7/3/2011 1/2/2011 ASSETS Current assets:
Consolidation. CA Section 201 (3A) requires all Holding Co to present consolidated accounts. Section 5 (1) (a) define subsidiary as follows:
 Consolidation CA Section 201 (3A) requires all Holding Co to present consolidated accounts Section 5 (1) (a) define subsidiary as follows: Controls Board Control more than half of voting rights Holds more
Consolidation CA Section 201 (3A) requires all Holding Co to present consolidated accounts Section 5 (1) (a) define subsidiary as follows: Controls Board Control more than half of voting rights Holds more
Consolidated Financial Statements
 HKFRS 10 Revised October 2014January 2015 Effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2013 Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standard 10 Consolidated Financial Statements COPYRIGHT Copyright
HKFRS 10 Revised October 2014January 2015 Effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2013 Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standard 10 Consolidated Financial Statements COPYRIGHT Copyright
NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON CASH FLOW STATEMENTS
 NAS 03 NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON CASH FLOW STATEMENTS CONTENTS Paragraphs OBJECTIVE SCOPE 1-3 BENEFITS OF CASH FLOWS INFORMATION 4-5 DEFINITIONS 6-9 Cash and cash equivalents 7-9 PRESENTATION OF A
NAS 03 NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON CASH FLOW STATEMENTS CONTENTS Paragraphs OBJECTIVE SCOPE 1-3 BENEFITS OF CASH FLOWS INFORMATION 4-5 DEFINITIONS 6-9 Cash and cash equivalents 7-9 PRESENTATION OF A
SCORPEX INTERNATIONAL, INC.
 AUDIT REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM AND CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS C O N T E N T S Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.... 3 Consolidated Balance Sheets...
AUDIT REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM AND CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS C O N T E N T S Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.... 3 Consolidated Balance Sheets...
FUBON LIFE INSURANCE CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARIES. CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED INTERIM FINANCIAL STATEMENTS JUNE 30, 2013 and 2012
 FUBON LIFE INSURANCE CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARIES CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED INTERIM FINANCIAL STATEMENTS JUNE 30, 2013 and 2012 (with Independent Auditors Report Thereon) Address: 14F, No. 108, Sec. 1, Tun
FUBON LIFE INSURANCE CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARIES CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED INTERIM FINANCIAL STATEMENTS JUNE 30, 2013 and 2012 (with Independent Auditors Report Thereon) Address: 14F, No. 108, Sec. 1, Tun
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard LKAS 12. Income Taxes
 Sri Lanka Accounting Standard LKAS 12 Income Taxes CONTENTS paragraphs SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARD-LKAS 12 INCOME TAXES OBJECTIVE SCOPE 1 4 DEFINITIONS 5 11 Tax base 7 11 RECOGNITION OF CURRENT TAX LIABILITIES
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard LKAS 12 Income Taxes CONTENTS paragraphs SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARD-LKAS 12 INCOME TAXES OBJECTIVE SCOPE 1 4 DEFINITIONS 5 11 Tax base 7 11 RECOGNITION OF CURRENT TAX LIABILITIES
Statement of Cash Flows
 HKAS 7 Revised February November 2014 Hong Kong Accounting Standard 7 Statement of Cash Flows HKAS 7 COPYRIGHT Copyright 2014 Hong Kong Institute of Certified Public Accountants This Hong Kong Financial
HKAS 7 Revised February November 2014 Hong Kong Accounting Standard 7 Statement of Cash Flows HKAS 7 COPYRIGHT Copyright 2014 Hong Kong Institute of Certified Public Accountants This Hong Kong Financial
Consolidated Financial Statements
 IFAC Board Exposure Draft October 2013 Comments due: February 28, 2014 Proposed International Public Sector Accounting Standard Consolidated Financial Statements This Exposure Draft 49, Consolidated Financial
IFAC Board Exposure Draft October 2013 Comments due: February 28, 2014 Proposed International Public Sector Accounting Standard Consolidated Financial Statements This Exposure Draft 49, Consolidated Financial
Consolidated Interim Earnings Report
 Consolidated Interim Earnings Report For the Six Months Ended 30th September, 2003 23th Octorber, 2003 Hitachi Capital Corporation These financial statements were prepared for the interim earnings release
Consolidated Interim Earnings Report For the Six Months Ended 30th September, 2003 23th Octorber, 2003 Hitachi Capital Corporation These financial statements were prepared for the interim earnings release
International Accounting Standard 12 Income Taxes. Objective. Scope. Definitions IAS 12
 International Accounting Standard 12 Income Taxes Objective The objective of this Standard is to prescribe the accounting treatment for income taxes. The principal issue in accounting for income taxes
International Accounting Standard 12 Income Taxes Objective The objective of this Standard is to prescribe the accounting treatment for income taxes. The principal issue in accounting for income taxes
ZAMIL INDUSTRIAL INVESTMENT COMPANY (SAUDI JOINT STOCK COMPANY)
 ZAMIL INDUSTRIAL INVESTMENT COMPANY INTERIM CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND AUDITORS REPORT (LIMITED REVIEW) FOR THE THREE MONTHS AND NINE MONTHS PERIODS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, NOTES TO THE INTERIM
ZAMIL INDUSTRIAL INVESTMENT COMPANY INTERIM CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND AUDITORS REPORT (LIMITED REVIEW) FOR THE THREE MONTHS AND NINE MONTHS PERIODS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, NOTES TO THE INTERIM
FOREIGN CURRENCY TRANSACTIONS 8-16. Initial Recognition 8-10. Reporting at Subsequent Balance Sheet Dates 11-12
 108 Accounting Standard (AS) 11 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-6 DEFINITIONS 7 FOREIGN CURRENCY TRANSACTIONS 8-16 Initial Recognition 8-10 Reporting
108 Accounting Standard (AS) 11 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates Contents OBJECTIVE SCOPE Paragraphs 1-6 DEFINITIONS 7 FOREIGN CURRENCY TRANSACTIONS 8-16 Initial Recognition 8-10 Reporting
International Accounting Standard 12 Income Taxes
 EC staff consolidated version as of 21 June 2012, EN IAS 12 FOR INFORMATION PURPOSES ONLY International Accounting Standard 12 Income Taxes Objective The objective of this Standard is to prescribe the
EC staff consolidated version as of 21 June 2012, EN IAS 12 FOR INFORMATION PURPOSES ONLY International Accounting Standard 12 Income Taxes Objective The objective of this Standard is to prescribe the
Consolidated balance sheet
 83 Consolidated balance sheet December 31 Non-current assets Goodwill 14 675.1 978.4 Other intangible assets 14 317.4 303.8 Property, plant, and equipment 15 530.7 492.0 Investment in associates 16 2.5
83 Consolidated balance sheet December 31 Non-current assets Goodwill 14 675.1 978.4 Other intangible assets 14 317.4 303.8 Property, plant, and equipment 15 530.7 492.0 Investment in associates 16 2.5
NAS 09 NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON INCOME TAXES
 NAS 09 NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON INCOME TAXES CONTENTS Paragraphs OBJECTIVE SCOPE 1-4 DEFINITIONS 5-11 Tax Base 7-11 RECOGNITION OF CURRENT TAX LIABILITIES AND CURRENT TAX ASSETS 12-14 RECOGNITION
NAS 09 NEPAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ON INCOME TAXES CONTENTS Paragraphs OBJECTIVE SCOPE 1-4 DEFINITIONS 5-11 Tax Base 7-11 RECOGNITION OF CURRENT TAX LIABILITIES AND CURRENT TAX ASSETS 12-14 RECOGNITION
Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 12. Income Taxes
 Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 12 Contents Income Taxes Paragraphs Objective Scope 1 4 Definitions 5 11 Tax base 7 11 Recognition of current tax liabilities and current tax assets 12 14 Recognition
Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 12 Contents Income Taxes Paragraphs Objective Scope 1 4 Definitions 5 11 Tax base 7 11 Recognition of current tax liabilities and current tax assets 12 14 Recognition
IFRS. Disclosure checklist. August 2012. kpmg.com/ifrs
 IFRS Disclosure checklist August 2012 kpmg.com/ifrs Contents About this publication 1 What s new? 2 The Checklist 3 1. General presentation 3 1.1 Presentation of financial statements 3 1.2 Changes in equity
IFRS Disclosure checklist August 2012 kpmg.com/ifrs Contents About this publication 1 What s new? 2 The Checklist 3 1. General presentation 3 1.1 Presentation of financial statements 3 1.2 Changes in equity
Consolidated Financial Statements. FUJIFILM Holdings Corporation and Subsidiaries. March 31, 2015 with Report of Independent Auditors
 Consolidated Financial Statements FUJIFILM Holdings Corporation and Subsidiaries March 31, 2015 with Report of Independent Auditors Consolidated Financial Statements March 31, 2015 Contents Report of Independent
Consolidated Financial Statements FUJIFILM Holdings Corporation and Subsidiaries March 31, 2015 with Report of Independent Auditors Consolidated Financial Statements March 31, 2015 Contents Report of Independent
Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities
 IFAC Board Exposure Draft 52 October 2013 Comments due: February 28, 2014 Proposed International Public Sector Accounting Standard Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities This Exposure Draft 52, Disclosure
IFAC Board Exposure Draft 52 October 2013 Comments due: February 28, 2014 Proposed International Public Sector Accounting Standard Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities This Exposure Draft 52, Disclosure
136 ST ENGINEERING / ABOVE & BEYOND
 136 ST ENGINEERING / ABOVE & BEYOND Independent auditors report Members of the Company Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd Report on the financial STATEMENTS We have audited the accompanying financial
136 ST ENGINEERING / ABOVE & BEYOND Independent auditors report Members of the Company Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd Report on the financial STATEMENTS We have audited the accompanying financial
Jollibee Foods Corporation and Subsidiaries
 Jollibee Foods Corporation and Subsidiaries Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2013 and 2012 and Years Ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 and Independent Auditors Report SyCip Gorres Velayo
Jollibee Foods Corporation and Subsidiaries Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2013 and 2012 and Years Ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 and Independent Auditors Report SyCip Gorres Velayo
Accounting for Multiple Entities
 King Saud University College of Administrative Science Department of Accounting 2 nd Semester, 1426-1427 Accounting for Multiple Entities Chapter 15 Prepared By: Eman Al-Aqeel Professor : Dr: Amal Fouda
King Saud University College of Administrative Science Department of Accounting 2 nd Semester, 1426-1427 Accounting for Multiple Entities Chapter 15 Prepared By: Eman Al-Aqeel Professor : Dr: Amal Fouda
IFRS Illustrative Consolidated Financial Statements 2014
 IFRS Illustrative Consolidated Financial Statements 2014 1 PKF International Limited administers a network of legally independent member firms which carry on separate businesses under the PKF Name. PKF
IFRS Illustrative Consolidated Financial Statements 2014 1 PKF International Limited administers a network of legally independent member firms which carry on separate businesses under the PKF Name. PKF
