Single Gene and NextGen Panels
|
|
|
- Juniper Shawn Parker
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Molecular Testing for Hearing Loss: Single Gene and NextGen Panels Honey V Reddi, PhD, FACMG Clinical Molecular Geneticist Prevention Genetics, Marshfield, WI
2 Outline of Presentation Hearing Loss Terminology, Types, Causes Management Genetics of Hearing Loss Syndromic, Non-Syndromic Testing Algorithm for Hearing Loss at PreventionGenetics
3 Deafness & Hearing Loss
4 TERMINOLOGY: Hearing loss: Diminished sensitivity to sounds normally heard. Severity is categorized according to the increase in volume above the usual level necessary before the listener can detect it. Deafness: Inability to understand speech even in the presence of amplification. Profound deafness - even the loudest sounds may not be detected. Total deafness - no sounds are heard at all, regardless of amplification or method of production.
5 TERMINOLOGY: Speech perception: Involves the perceived clarity of a sound rather than its amplitude. These tests measure one's ability to understand speech, not to merely detect sound.
6 TYPES of HEARING LOSS Conductive Caused by diseases or obstructions in the outer or middle ear. Usually affects all frequencies of hearing evenly Does not result in severe loss. Hearing aid / surgical intervention helps.
7 TYPES of HEARING LOSS Sensorineural Results from damage to the delicate sensory hair cells of the inner ear or the nerves that supply it. Can range from mild to profound. Affect the person s ability to hear certain frequencies more than others. Use of Hearing aid is sometimes impossible.
8 TYPES of HEARING LOSS Mixed hearing loss: Combination of conductive and sensorineural loss Due to a problem in outer or middle & the inner ear. Central hearing loss: From damage or impairment to nerves or nuclei of the CNS, either in pathways to the brain or in brain itself. conversational speech is at approximately db HL (hearing level),
9 CAUSES of Hearing Loss Prelingual
10 CAUSES of Hearing Loss in Adults Age: Presbycusis Degenerative changes in the ear with aging, that make them less able to respond to sound waves. Prolonged Loud Noise Infection/Injury Measles, Meningitis, Mumps, Syphillis Neurological Disorders Multiple Sclerosis, Strokes Chemicals Drugs/medications Genetics Syndromic Non-syndromic
11 CAUSES of Prelingual Hearing Loss Incidence at birth: 127 per 100,000 Prevalence at 4 yrs: 270 per 100,000 Prematurity, infection during pregnancy, childhood infections Hereditary Hearing Loss
12 MANAGEMENT of Hereditary Hearing Loss Clinical Geneticist Otorynologist Opthamologist Neurologist Audiologist Pediatrician
13 MANAGEMENT of Hereditary Hearing Loss GENETIC COUNSELING SPEECH THERAPIST / EDUCATOR FOR HEARING LOSS TREATMENT [Hearing aids, cochlear implantation, otologic surgery GENETIC TESTING
14 Genetics of Hearing Loss
15 80 genes associated with prelingual hearing loss Volume 68, Issue 2, 21 October 2010, Pages
16 Genetics of Prelingual Hearing Loss
17 NON-SYNDROMIC Prelingual Hearing Loss Different gene loci are labeled DFN (for DeaFNess); based on mode of inheritance DFNA DFNX [GJB2/6] [36 genes] [26 genes] [3 genes]
18 NON-SYNDROMIC Hearing Loss MITOCHONDRIAL INHERITENCE
19 SYNDROMIC Hearing Loss (30%) Alport (COL4A5) Fabry (GLA) Nance (POU3F4) X-linked CMT (GJB1) 400 Syndromes associated with hearing loss.. Usher (10 genes exons) Waardenburg (5 genes 39 exons) Stickler (5 genes 258 exons) Perrault (4 genes 66 exons) Treacher Collins (3 genes) Branchiootorenal (3 genes) Jervell and Lange-Nielson (KCNQ1 and KCNE1) Alport (COL4A3, COL4A4 100 exons) Refsum Disease (PEX7 and PHYH) Wolfram (WFS1 and CISD2) Mohr-Tranebaerg (TIMM8A) Pendred (SLC26A4) with FOXI1 & KCNJ10 - Digenic Keratitis-Icthyosis-Deafness (GJB2) Neurofibromatosis Type2 (NF2) Bartter (BSND) Townes-Brooke (SALL1) Alstrom (ALMS1) Norrie (NDP) Muckle-Wells (NLRP3) Biotinidase deficiency (BTD)
20 SYNDROMIC Hearing Loss (30%) MITOCHONDRIAL INHERITENCE Progressive myoclonic epilepsy, ataxia & hearing impairment MTTS1:7512T->C Maternally inherited diabetes & Deafness (MIDD) MTTL1: 3243A->G MTTK: 8296A->G MTTE: 14709T->C
21 GENETIC TESTING FOR HEARING LOSS AT PREVENTION GENETICS
22 10 years and 1000 genes later - Who We Are.. Comprehensive genetic testing (>1000 genes) Unsurpassed Quality Exceptional Customer Service (16 geneticists, 2 GCs, 3 Tech Reps) Lowest Prices and Quick TATs (40-50% lower, <20-40days)
23 Comprehensive Provider Largest Sanger Sequencing menu in the US Over 1000 genes and growing every week Next-Gen Sequencing Panels 60 panels covering 530 genes Deletion/Duplication analysis via arraycgh 833 genes Affordable DNA Banking $98 (one-time fee) for a min. of 20 years storage
24 Exceptional Customer Service Exceptional Customer Service Comes From The People Team of 16 highly experienced PhD level geneticists Assigned specific gene portfolio to build expertise 2 Certified Genetic Counselors Clinical counseling experience 3 Technical Product Representatives Experienced in laboratory testing and development
25 Distinguishing Features Clear and Comprehensive Test Reports reviewed by two PhD geneticists Free Family Studies for up to 2 family members for VUS [variant of uncertain significance] identified Quick Turn around times Customized testing single gene/panels
26 Genetic Testing Algorithm for Hearing Loss at PreventionGenetics Treatment Dx EVALUATION Family history, Physical examination, Audiologic Workup No Dx Apparent syndromic phenotype GENETIC TESTING No apparent phenotype SYNDROMIC TESTING Single/Multi Gene TESTING FOR NONSYNDROMIC HEARING LOSS
27 Genetic Testing for Hearing Loss at PreventionGenetics Apparent syndromic phenotype GENETIC TESTING SYNDROMIC TESTING Single/Multi Gene
28 WAARDENBURG SYNDROME Auditory-Pigmentary Disorder Congenital SNHL Hair Abnormalities [white forelock] Eye Abnormalities [heterochromia] Pingault et al Human Mutation 31:
29 WAARDENBURG SYNDROME WS I: Auditory-pigmentory abnormalites + dystopia canthorum (lateral displacement of the inner canthi) Caused by mutations in PAX3 WS II: Auditory-pigmentory abnormalites without dystopia canthorum Mutations in MITF, SNAI2 and SOX10 WS III: Type I with musculo-skeletal abnormalities of the upper limb (Klein- Waardenburg syndrome) Caused by mutations in PAX3 WS IV: Type II with Hirschsprung disease (Waardenburg-Shah syndrome) Mutations in EDNRB, EDN3 and SOX10 Ghosh etal IJDVL. 76:550 Pingault et al Human Mutation 31:
30 WAARDENBURG SYNDROME - Subtypes WS I WS IIA WS IID WS IIE WS III WS IVA WS IVB WS IVC Autosomal Dominant, PAX3 Autosomal Dominant, MITF Autosomal Recessive, SNAI2 Autosomal Dominant, SOX10 Dominant or Recessive, PAX3 Autosomal Dominant, EDNRB Autosomal Recessive, EDN3 Autosomal Dominant, SOX10
31 Genetic Testing for Hearing Loss at PreventionGenetics Apparent syndromic phenotype GENETIC TESTING No apparent phenotype SYNDROMIC TESTING Single/Multi Gene TESTING FOR NONSYNDROMIC HEARING LOSS 24 Syndromes.. 61 genes exons.. Tier 1: Sanger Panel GJB2, GJB3, GJB6 7 exons Tier 2: NextGen Panel Non-Syndromic Panel (50 genes) GENETIC COUNSELING
32 Genetic Testing for Hearing Loss at PreventionGenetics
33 Contact Information Website: Clinical Phone: Fax: Address: PreventionGenetics 3800 S. Business Park Ave. Marshfield, WI 54449
34
Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida
 Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida 60% of childhood hearing loss is genetic Syndromic Nonsyndromic 40% of childhood hearing
Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida 60% of childhood hearing loss is genetic Syndromic Nonsyndromic 40% of childhood hearing
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation. 5 y.o. boy with severe SNHL
 Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
About The Causes of Hearing Loss
 About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
DURATION OF HEARING LOSS
 When your child is diagnosed with a hearing loss, it may be very overwhelming. This may be a difficult time for you and your family. However, gaining a greater knowledge in this area is crucial in helping
When your child is diagnosed with a hearing loss, it may be very overwhelming. This may be a difficult time for you and your family. However, gaining a greater knowledge in this area is crucial in helping
Patient Information. for Childhood
 Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
The Genetics of Hearing Loss. Heidi L. Rehm, Ph.D. Harvard Medical School Boston, MA
 The Genetics of Hearing Loss Heidi L. Rehm, Ph.D. Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Faculty Disclosure Information In the past 12 months, I have not had a significant financial interest or other relationship
The Genetics of Hearing Loss Heidi L. Rehm, Ph.D. Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Faculty Disclosure Information In the past 12 months, I have not had a significant financial interest or other relationship
So, how do we hear? outer middle ear inner ear
 The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
1/26/2011. 50% of deafness and hearing impairment is avoidable through prevention, early diagnosis, and management.
 Hearing Impairment Roseann Mulligan, DDS, MS Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry of the University of Southern California 1 JAMA, July 4, 2007 Vol 298, No. 1 2 278 million - moderate to profound bilateral
Hearing Impairment Roseann Mulligan, DDS, MS Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry of the University of Southern California 1 JAMA, July 4, 2007 Vol 298, No. 1 2 278 million - moderate to profound bilateral
Why does my child have a hearing loss?
 Introduction This factsheet will tell you about the range of tests that can be carried out to try to find the cause of your child s hearing loss. The process to find out why a child is deaf is sometimes
Introduction This factsheet will tell you about the range of tests that can be carried out to try to find the cause of your child s hearing loss. The process to find out why a child is deaf is sometimes
Usher Syndrome Genetics
 Usher Syndrome Genetics October 2012 Page 1 of 20 Introduction Usher syndrome is a genetic or inherited condition that affects hearing, vision and balance The sight loss is caused by an eye condition known
Usher Syndrome Genetics October 2012 Page 1 of 20 Introduction Usher syndrome is a genetic or inherited condition that affects hearing, vision and balance The sight loss is caused by an eye condition known
Deafness and Hereditary Hearing Loss Overview
 Page 1 of 25 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. Pagon RA, Bird TD, Dolan CR, et al., editors. GeneReviews [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University
Page 1 of 25 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. Pagon RA, Bird TD, Dolan CR, et al., editors. GeneReviews [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University
Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan
 Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan Definition Deaf A deaf person is one whose hearing disability precludes successful processing of linguistic information
Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan Definition Deaf A deaf person is one whose hearing disability precludes successful processing of linguistic information
Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics
 Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
Section 4. Hearing loss and hearing tests
 Section 4 Hearing loss and hearing tests How we hear Outer Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear 4. 7. 8. 1. 3. 6. 2. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Ear canal Ear drum Middle ear cavity Middle ear bones the malleus, incus,
Section 4 Hearing loss and hearing tests How we hear Outer Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear 4. 7. 8. 1. 3. 6. 2. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Ear canal Ear drum Middle ear cavity Middle ear bones the malleus, incus,
Facts and figures on hearing loss, deafness and tinnitus
 FACTSHEET Facts and figures on hearing loss, deafness and tinnitus This factsheet gives you information about the latest available figures on hearing loss, deafness and tinnitus among adults in the UK.
FACTSHEET Facts and figures on hearing loss, deafness and tinnitus This factsheet gives you information about the latest available figures on hearing loss, deafness and tinnitus among adults in the UK.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
 Sensorineural Hearing Loss 1. Review the patterns of hearing loss in hereditary hearing impairment. AL First, we must understand that genetic hearing loss seems to breach all categories of hearing loss,
Sensorineural Hearing Loss 1. Review the patterns of hearing loss in hereditary hearing impairment. AL First, we must understand that genetic hearing loss seems to breach all categories of hearing loss,
Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884. www.childrensent.com
 Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com You just found out your child has a hearing loss. You know what the Audiologist explained to you, but it is hard to keep track of all the new
Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com You just found out your child has a hearing loss. You know what the Audiologist explained to you, but it is hard to keep track of all the new
Hearing, Hearing Testing, Hearing Aids, Hearing Conservation And Services
 Hearing, Hearing Testing, Hearing Aids, Hearing Conservation And Services is retained in all printings. 1 is retained in all printings. 2 Table of Contents Terminology... 4 How We Hear... 5 Causes of Hearing
Hearing, Hearing Testing, Hearing Aids, Hearing Conservation And Services is retained in all printings. 1 is retained in all printings. 2 Table of Contents Terminology... 4 How We Hear... 5 Causes of Hearing
Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video. IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
 Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video (Notes are also available for Video segments: Common Mistakes and FAQs) IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video (Notes are also available for Video segments: Common Mistakes and FAQs) IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS
 CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
Getting Started Kei Te Timata
 Getting Started Kei Te Timata AN INTRODUCTION FOR THE FAMILIES AND WHANAU OF CHILDREN DIAGNOSED WITH A HEARING LOSS. THIS IS A JOINT PROJECT BY DEAF EDUCATION AOTEAROA NEW ZEALAND AND THE NATIONAL AUDIOLOGY
Getting Started Kei Te Timata AN INTRODUCTION FOR THE FAMILIES AND WHANAU OF CHILDREN DIAGNOSED WITH A HEARING LOSS. THIS IS A JOINT PROJECT BY DEAF EDUCATION AOTEAROA NEW ZEALAND AND THE NATIONAL AUDIOLOGY
Presbycusis. What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis?
 Presbycusis What is presbycusis? Presbycusis is the loss of hearing that gradually occurs in most individuals as they grow older. Hearing loss is a common disorder associated with aging. About 30-35 percent
Presbycusis What is presbycusis? Presbycusis is the loss of hearing that gradually occurs in most individuals as they grow older. Hearing loss is a common disorder associated with aging. About 30-35 percent
Infant hearing screening will not hurt your baby, and will only take between 5 and 20 minutes. Ideally it is done whilst baby is asleep or settled.
 Early diagnosis of hearing loss will make a difference to your baby s life. Significant hearing loss is the most common condition present at birth. In the private sector, 3 in every 1000 babies are born
Early diagnosis of hearing loss will make a difference to your baby s life. Significant hearing loss is the most common condition present at birth. In the private sector, 3 in every 1000 babies are born
Cochlear implants for children and adults with severe to profound deafness
 Issue date: January 2009 Review date: February 2011 Cochlear implants for children and adults with severe to profound deafness National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Page 1 of 41 Final appraisal
Issue date: January 2009 Review date: February 2011 Cochlear implants for children and adults with severe to profound deafness National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Page 1 of 41 Final appraisal
Audiology Services. Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS
 Audiology Services Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS What are we going to cover today? General overview of the ear Hearing loss Hearing assessments, results Hearing aids Paediatric
Audiology Services Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS What are we going to cover today? General overview of the ear Hearing loss Hearing assessments, results Hearing aids Paediatric
Questions and Answers for Parents
 Questions and Answers for Parents There are simple, inexpensive tests available to detect hearing impairment in infants during the first days of life. In the past, most hearing deficits in children were
Questions and Answers for Parents There are simple, inexpensive tests available to detect hearing impairment in infants during the first days of life. In the past, most hearing deficits in children were
Synopsis of Causation. Sensorineural Hearing Loss
 Ministry of Defence Synopsis of Causation Sensorineural Hearing Loss Author: Validator: Dr Adrian Roberts, Medical Author, Medical Text, Edinburgh Mr Kevin Gibbin, University Hospital, Queen s Medical
Ministry of Defence Synopsis of Causation Sensorineural Hearing Loss Author: Validator: Dr Adrian Roberts, Medical Author, Medical Text, Edinburgh Mr Kevin Gibbin, University Hospital, Queen s Medical
Hearing Tests for Children with Multiple or Developmental Disabilities by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Hearing Tests for Children with Multiple or Developmental Disabilities by Susan Agrawal Hearing impairment is a common problem in children with developmental disabilities or who have
www.complexchild.com Hearing Tests for Children with Multiple or Developmental Disabilities by Susan Agrawal Hearing impairment is a common problem in children with developmental disabilities or who have
What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who has a hearing loss? How does hearing work?
 This e-book will answer the following questions: What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis? What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who
This e-book will answer the following questions: What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis? What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who
Hearing Tests And Your Child
 HOW EARLY CAN A CHILD S HEARING BE TESTED? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
HOW EARLY CAN A CHILD S HEARING BE TESTED? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
Unilateral (Hearing Loss in One Ear) Hearing Loss Guidance
 Unilateral (Hearing Loss in One Ear) Hearing Loss Guidance Indiana s Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Program Before universal newborn hearing screening, most children with unilateral hearing loss
Unilateral (Hearing Loss in One Ear) Hearing Loss Guidance Indiana s Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Program Before universal newborn hearing screening, most children with unilateral hearing loss
Guide for families of infants and children with hearing loss
 With early detection, Early Intervention can begin! Guide for families of infants and children with hearing loss Birth to 3 2008 Cover photograph Geneva Marie Durgin was born January 20, 2007. She lives
With early detection, Early Intervention can begin! Guide for families of infants and children with hearing loss Birth to 3 2008 Cover photograph Geneva Marie Durgin was born January 20, 2007. She lives
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives
 What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
The Work-Up of Childhood Sensorineural Hearing Loss Jonathan M. Sherman, Eliot Shearer, Richard J.H. Smith, and Dana Suskind
 2 The Work-Up of Childhood Sensorineural Hearing Loss Jonathan M. Sherman, Eliot Shearer, Richard J.H. Smith, and Dana Suskind The Problem Hearing loss in children is common in the United States with an
2 The Work-Up of Childhood Sensorineural Hearing Loss Jonathan M. Sherman, Eliot Shearer, Richard J.H. Smith, and Dana Suskind The Problem Hearing loss in children is common in the United States with an
Prevalence of otological disorders in diabetic patients with hearing loss
 Prevalence of otological disorders in diabetic patients with hearing loss Manche Santoshi Kumari *, Jangala Madhavi *, Koralla Raja Meganadh *, Akka Jyothy Institute of Genetics and Hospital for Genetic
Prevalence of otological disorders in diabetic patients with hearing loss Manche Santoshi Kumari *, Jangala Madhavi *, Koralla Raja Meganadh *, Akka Jyothy Institute of Genetics and Hospital for Genetic
GONCA SENNAROĞLU PhD LEVENT SENNAROĞLU MD. Department of Otolaryngology Hacettepe University ANKARA, TURKEY
 GONCA SENNAROĞLU PhD LEVENT SENNAROĞLU MD Department of Otolaryngology Hacettepe University ANKARA, TURKEY To present the audiological findings and rehabilitative outcomes of CI in children with cochlear
GONCA SENNAROĞLU PhD LEVENT SENNAROĞLU MD Department of Otolaryngology Hacettepe University ANKARA, TURKEY To present the audiological findings and rehabilitative outcomes of CI in children with cochlear
Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine
 Physiological Basis of Hearing Tests By Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Introduction Def: Hearing is the ability to perceive certain pressure vibrations in the
Physiological Basis of Hearing Tests By Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Introduction Def: Hearing is the ability to perceive certain pressure vibrations in the
Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians
 Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received for such services is a
Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received for such services is a
Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD)
 Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD) The term muscular dystrophy is used to cover a wide range of conditions which have in common progressive muscle weakness due to an inherited genetic defect (mutation).
Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD) The term muscular dystrophy is used to cover a wide range of conditions which have in common progressive muscle weakness due to an inherited genetic defect (mutation).
Hearing Aids. What Is a Hearing Aid? How Common Is Hearing Loss and What Causes It? How Do We Hear?
 Hearing Aids What Is a Hearing Aid? A hearing aid is an electronic, battery-operated device that amplifies and changes sound to allow for improved communication. Hearing aids receive sound through a microphone,
Hearing Aids What Is a Hearing Aid? A hearing aid is an electronic, battery-operated device that amplifies and changes sound to allow for improved communication. Hearing aids receive sound through a microphone,
HEARING SCREENING (May 2006)
 HEARING SCREENING (May 2006) Definition Procedures for Hearing Screening Student with hearing loss School Nurse Role Referral Criteria Resources Definition: Hearing is the perception of sound. The normal
HEARING SCREENING (May 2006) Definition Procedures for Hearing Screening Student with hearing loss School Nurse Role Referral Criteria Resources Definition: Hearing is the perception of sound. The normal
Patient Information. Ordering Physician Information. Indication for Testing (REQUIRED)
 EPILEPSY EXOME CLINICAL CHECKLIST REQUIRED Please check all clinical features that apply, and use the additional space provided at the bottom of the form if needed Patient Information Name: Last First
EPILEPSY EXOME CLINICAL CHECKLIST REQUIRED Please check all clinical features that apply, and use the additional space provided at the bottom of the form if needed Patient Information Name: Last First
REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING
 REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING Please provide the following information. We cannot perform your test without ALL of this information. PLEASE PRINT ALL ANSWERS PATIENT INFORMATION* FIRST NAME MI LAST
REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING Please provide the following information. We cannot perform your test without ALL of this information. PLEASE PRINT ALL ANSWERS PATIENT INFORMATION* FIRST NAME MI LAST
More information >>> HERE <<<
 More information >>> HERE http://urlzz.org/hearloss/pdx/dcli864/ Tags: ## best way to get cheapest natural methods to
More information >>> HERE http://urlzz.org/hearloss/pdx/dcli864/ Tags: ## best way to get cheapest natural methods to
SEMI-IMPLANTABLE AND FULLY IMPLANTABLE MIDDLE EAR HEARING AIDS
 Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be read in its
Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be read in its
Documentation Requirements ADHD
 Documentation Requirements ADHD Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is considered a neurobiological disability that interferes with a person s ability to sustain attention, focus on a task
Documentation Requirements ADHD Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is considered a neurobiological disability that interferes with a person s ability to sustain attention, focus on a task
COCHLEAR NERVE APLASIA : THE AUDIOLOGIC PERSPECTIVE A CASE REPORT. Eva Orzan, MD Pediatric Audiology University Hospital of Padova, Italy
 COCHLEAR NERVE APLASIA : THE AUDIOLOGIC PERSPECTIVE A CASE REPORT Eva Orzan, MD Pediatric Audiology University Hospital of Padova, Italy Congenital absence or underdevelopment of the cochlear nerve has
COCHLEAR NERVE APLASIA : THE AUDIOLOGIC PERSPECTIVE A CASE REPORT Eva Orzan, MD Pediatric Audiology University Hospital of Padova, Italy Congenital absence or underdevelopment of the cochlear nerve has
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger
 The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 3 Heredity and Environment PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 3 Heredity and Environment PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
Hearing Tests And Your Child
 How Early Can A Child s Hearing Be Tested? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
How Early Can A Child s Hearing Be Tested? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs)
 Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice
 AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF JOINT COMMITTEE ON INFANT HEARING YEAR 2007 POSITION STATEMENT. Intervention Programs
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF JOINT COMMITTEE ON INFANT HEARING YEAR 2007 POSITION STATEMENT Principles and Guidelines for Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Programs The Joint Committee on Infant Hearing
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF JOINT COMMITTEE ON INFANT HEARING YEAR 2007 POSITION STATEMENT Principles and Guidelines for Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Programs The Joint Committee on Infant Hearing
Genetic Bases of Hearing Loss: Future Treatment Implications
 Genetic Bases of Hearing Loss: Future Treatment Implications Luis F. Escobar, MD Medical Director Medical Genetics & Neurodevelopmental Pediatrics of Indiana Peyton Manning Children s Hospital St. Vincent
Genetic Bases of Hearing Loss: Future Treatment Implications Luis F. Escobar, MD Medical Director Medical Genetics & Neurodevelopmental Pediatrics of Indiana Peyton Manning Children s Hospital St. Vincent
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects:
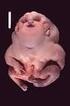 Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES
 DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES Extracts from a review article by KN North and KJ Jones: Recent advances in diagnosis of the childhood muscular dystrophies Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES Extracts from a review article by KN North and KJ Jones: Recent advances in diagnosis of the childhood muscular dystrophies Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
Neurofibromatosis Type 2: Information for Patients & Families by Mia MacCollin, M.D., Catherine Bove, R.N. Ed. & M. Priscilla Short, M.D.
 Neurofibromatosis Type 2: Information for Patients & Families by Mia MacCollin, M.D., Catherine Bove, R.N. Ed. & M. Priscilla Short, M.D. Neurofibromatosis Type 2 is a rare genetic disease, which causes
Neurofibromatosis Type 2: Information for Patients & Families by Mia MacCollin, M.D., Catherine Bove, R.N. Ed. & M. Priscilla Short, M.D. Neurofibromatosis Type 2 is a rare genetic disease, which causes
Noice induced hearing loss, Ototoxic drugs, Meniers disease, Rotataory vertigo, Sensorineural hearing loss, Tinnitis, Infections, Acoustic neuroma,
 Disorders of hearing and balance LEARNING OBJECTIVE At the end of lecture student must be able to know, Hearing disorders, Types of hearing disorders, Functional classification, Causes, Middle ear disorders,
Disorders of hearing and balance LEARNING OBJECTIVE At the end of lecture student must be able to know, Hearing disorders, Types of hearing disorders, Functional classification, Causes, Middle ear disorders,
3-1 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 C A S E S T U D Y 3 : T o d d l e r Adapted from Thomson Delmar Learning s Case Study Series: Pediatrics, by Bonita E. Broyles, RN, BSN, MA, PhD. Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning, Clifton Park, NY.
C A S E S T U D Y 3 : T o d d l e r Adapted from Thomson Delmar Learning s Case Study Series: Pediatrics, by Bonita E. Broyles, RN, BSN, MA, PhD. Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning, Clifton Park, NY.
This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive.
 11111 This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive. In summary Genes contain the instructions for
11111 This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive. In summary Genes contain the instructions for
Education Adjustment Program (EAP) Handbook
 Education Adjustment Program (EAP) Handbook Current as at September 2015 The State of Queensland (2015) This document is licensed under CC-BY 4.0, with the exception of the government coat of arms, logos
Education Adjustment Program (EAP) Handbook Current as at September 2015 The State of Queensland (2015) This document is licensed under CC-BY 4.0, with the exception of the government coat of arms, logos
The Genomics of Hearing Loss
 The Genomics of Hearing Loss Ian Krantz, M.D. The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Objectives 1. Understand the clinical and genetic
The Genomics of Hearing Loss Ian Krantz, M.D. The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Objectives 1. Understand the clinical and genetic
ICD-10 Codes Utilized by Audiologists
 ICD-10 Codes Utilized by Audiologists Introduction Beginning with the first claim filed to all payers on or after October 1, 2015, the ICD-10 codes must be utilized in box 21 A-L on the CMS 1500 claim
ICD-10 Codes Utilized by Audiologists Introduction Beginning with the first claim filed to all payers on or after October 1, 2015, the ICD-10 codes must be utilized in box 21 A-L on the CMS 1500 claim
Occupational Noise Induced Hearing Loss
 Occupational Noise Induced Hearing Loss M Baxter FRACS SISA Adelaide June 2014 ENT in Personal Injury Claims EAR Hearing Loss -main, Dizziness Nose Injuries ->cosmesis,breathing: Loss of sense of smell:
Occupational Noise Induced Hearing Loss M Baxter FRACS SISA Adelaide June 2014 ENT in Personal Injury Claims EAR Hearing Loss -main, Dizziness Nose Injuries ->cosmesis,breathing: Loss of sense of smell:
HEARING & HEARING LOSS. Dr I Butler 2015
 HEARING & HEARING LOSS Dr I Butler 2015 DISCLOSURE Sponsorship to attend local and international workshops Cochlear (Southern ENT) Med el TOPICS Anatomy Classification of hearing loss Congenital hearing
HEARING & HEARING LOSS Dr I Butler 2015 DISCLOSURE Sponsorship to attend local and international workshops Cochlear (Southern ENT) Med el TOPICS Anatomy Classification of hearing loss Congenital hearing
Hearing Loss in Geriatric Primary Care Mary Ann Forciea MD Josh Uy MD
 Hearing Loss in Geriatric Primary Care Mary Ann Forciea MD Josh Uy MD Q: In my office practice, I screen for hearing loss with A Level of difficulty in office conversation Questionnaire Hand held hldaudiometer
Hearing Loss in Geriatric Primary Care Mary Ann Forciea MD Josh Uy MD Q: In my office practice, I screen for hearing loss with A Level of difficulty in office conversation Questionnaire Hand held hldaudiometer
Position Paper on Cochlear Implants in Children
 Position Paper on Cochlear Implants in Children Position: The Canadian Association of Speech-Language Pathologists and Audiologists (CASLPA) supports cochlear implantation in children where appropriate
Position Paper on Cochlear Implants in Children Position: The Canadian Association of Speech-Language Pathologists and Audiologists (CASLPA) supports cochlear implantation in children where appropriate
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia deep vein thrombosis DVT pulmonary embolism PE inherited thrombophilia
 INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
POLICY NUMBER: POL-09
 Chapter: CLAIMS Subject: HEARING LOSS Effective Date: April 28, 1994 Last Updated: November 28, 2013 REFERENCE: Occupational Health And Safety Act R.S.P.E.I. 1988, Cap. 0-1.1, General Regulations, Section
Chapter: CLAIMS Subject: HEARING LOSS Effective Date: April 28, 1994 Last Updated: November 28, 2013 REFERENCE: Occupational Health And Safety Act R.S.P.E.I. 1988, Cap. 0-1.1, General Regulations, Section
Audiology (0340) Test at a Glance. About this test. Test Guide Available. See Inside Back Cover. Test Code 0340
 Audiology (0340) Test Guide Available See Inside Back Cover Test at a Glance Test Name Audiology Test Code 0340 Time 2 hours Number of Questions 150 Format Multiple-choice questions Approximate Approximate
Audiology (0340) Test Guide Available See Inside Back Cover Test at a Glance Test Name Audiology Test Code 0340 Time 2 hours Number of Questions 150 Format Multiple-choice questions Approximate Approximate
DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS
 DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS 1. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 is a civil rights law, which makes it unlawful to discriminate on the basis of disability. It covers employment in the
DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS 1. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 is a civil rights law, which makes it unlawful to discriminate on the basis of disability. It covers employment in the
Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit
 Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit 2013 The Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit is available on the Enhanced Option only. Overview This document tells you about the Allied,
Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit 2013 The Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit is available on the Enhanced Option only. Overview This document tells you about the Allied,
Background Paper 6.21 Hearing Loss
 Priority Medicines for Europe and the World "A Public Health Approach to Innovation" Update on 2004 Background Paper Background Paper 6.21 Hearing Loss By Béatrice Duthey, Ph.D 20 February 2013 Table of
Priority Medicines for Europe and the World "A Public Health Approach to Innovation" Update on 2004 Background Paper Background Paper 6.21 Hearing Loss By Béatrice Duthey, Ph.D 20 February 2013 Table of
Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians
 1/1/2015 Hearing Testing Coding Fact Sheet Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received
1/1/2015 Hearing Testing Coding Fact Sheet Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received
