with Dr. Sarah Reid & Dr. Gina Neto
|
|
|
- Beverly Cain
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Is fever dangerous? Do we need to treat it? Episode 48 Pediatric Fever with Dr. Sarah Reid & Dr. Gina Neto prepared by Claire Heslop, edited by Anton Helman, July 2014 Pediatric Fever Fever in a child is a common emergency department presentation. About 20% will have fever without an identifiable source, and a small but significant number of these children will have an occult, serious bacterial infection (SBI) (1). UTIs are the most common occult SBI (2), especially in children <2 years of age, but other causes include pneumonia, early meningitis, and septisemia. What is a fever? Technically, an oral temperature >38 C, or rectal temperature >38 C. Take a rectal temperature in toddlers, infants and neonates; axillary and tympanic temperatures are less accurate for core temperature. Fever itself is the natural body s response to fighting infection, and does not in itself cause harm. However, fever causes dehydration; treat kids to help them feel better and stay hydrated. The precise height of the fever is not as important as the duration in predicting bacteremia. Children with infection as a cause for their fever almost never mount a fever high enough to be dangerous (>41.5 C); these very high temperatures are typically only seen in non-infectious causes of hyperthermia. The value of treating the fever in the emergency department besides patient comfort and minimizing dehydration, is so that the child can be re-examined when afebrile to help risk stratify for SBI and to counsel the parents. If the child s vital signs and clinical picture continue to be worrisome after their fever has been corrected, then SBI should be suspected. However, if, after normalizing the temperature, the child has normal vital signs and is clinically well, then SBI is less likely and the parents can be reassured that the fever itself is not dangerous. Temperature Corrected Heart Rate and Respiratory Rate: Heart Rate increases by approx 10 beats/min and Respiratory Rate by 5 breaths/min for every Celcius degree (1.8 degree of Fahrenheit) of fever >38 C. For example, if the temperature is 40 C and HR = 144 subtract 2x10 corrected HR = 124
2 If the child has tachycardia after being corrected for fever, consider other contributors (pain, crying, early compensated shock). Check perfusion, ask about urine output, and have a high degree of suspicion for dehydration and sepsis. Acetaminophen vs Ibuprophen for Fever Reduction Studies suggest that ibuprophen may be superior to acetominophen for treating pain and fever in children. Using both acetominophen and ibuprophen in combination in an alternating pattern may be more effective that either alone, however the complex dosing increases potential for errors. A dosing handout can help - prompt parents to record times and dosages given. Recommend no more than 3 doses of 10mg/kg of ibuprophen/24h and 4 doses of 15mg/kg of acetaminophen/24h, and emphasize keeping the child hydrated, to reduce risk of drug toxicity. Some experts suggest only giving antipyretics on a prn basis for fever, rather than on a schedule, so as to minimize potential complications with scheduled dosing (liver complications have been reported in children on q4h acetominophen, and renal complications have been reported in children on q6h ibuprophen). There is no good evidence that these medications prevent febrile seizure. history and physical assessment as the febrile child, even if they are afebrile in the ED. Particularly important, is whether antipyretics were given, and the duration of fever. If the child is <3 months of age and is afebrile in the ED, observe them for several hours to document normal feeding and a normal exam, repeating the rectal temperature to verify that it remains normal. Educate the parents how to do this at home, and to come back if a fever is measured after they leave. Pediatric Fever Without a Source Fever without a source: Child <3 years old who after an initial history and physical does not have an identified cause of their fever. Approx 5% are likely to have a bacterial infection (usually a UTI). As apposed to Fever of unknown origin: Fever for 2 to 3 weeks, without a known cause after initial investigations. These fevers may be caused by more unusual illnesses (rheumatologic, oncologic). However, the cause is still usually infection, most often viral. Is the Parent s Touch Accurate at Predicting Fever? The parent s touch has been shown to be fairly accurate for identifying fever, therefore a child without a measured fever at home but brought in for tactile fever should still receive the same Key questions to ask in the history in children with fever without an apparent source: Duration of fever Recent surgeries and underlying medical diseases
3 Previous infections Immunization status (especially the first two doses, i.e. at 2 and 4 months, of Hib and Pneumococcal vaccines. Physical examination for fever without a source: Watch behaviour and mental status; watch them walk (for septic arthritis/oteomyelitis); and examine the skin, joints, and abdomen very carefully. 5 Sources of Bacterial Infection to Look for in Fever Without A Source 1. Urine - UTI #1 2. Skin - cellulitis 3. Abdomen - appendicitis, abscess etc. 4. Joints - septic arthritis 5. Meningitis Pediatric Urinary Tract Infections What are the risk factors for UTI in children? History of previous UTI Temp >39 C, and without an apparent source, >24h Ill appearance Supra-pubic tenderness, (or dysuria/frequency/low-back pain or new-onset incontinence in children old enough) Females, uncircumcised boys and non-black race Who to test (see JAMA guideline article 3): < 3 months: check urine in all babies with fever without source 3-24 month: check all girls, and boys if >1 risk factor, or if circumcised and >2 risk factors >24 months: check all girls, all symptomatic uncircumcised boys, and circumcised boy who had several symptoms suggesting UTI Consider checking the urine even in children who have had another source for their illness identified; in children <60 days old with bronchiolitis, many will also have a UTI! (4) How to get the urine? <2 months: obtain a sample by catheterization (and send every sample for culture as the urinalysis may be normal in the presence of true infection) >2 months of age to toilet trained: bag urine okay to screen by microscopy, however if it is positive (>10-20 white cells), a sterile culture needs to be obtained by catheter Toilet-trained kids: obtain midstream urine. Which children with UTI require admission? Generally children <2 months should be admitted.
4 Well appearing children >2 months can usually be discharged home on antibioitcs with good follow up, unless they are dehydrated or parents are unreliable. Treatment of UTI: Antibiotic options depend on local antibiotic resistance patterns, however, in our experts catchment area, In hospital: IV ampicillin and gentamicin Oral: cephalexin for most, or cefixime for infants 2-6 months old, or those you are worried have a complicated UTI or urinary tract abnormalities. Which children need further investigations for Fever Without a Source? Indications for CXR in Pediatric Fever Without a Source? Fever >5 days, or cough >10 days, if the temperature is persistently high (>40), or if a white count >20 with no other explanation Remember: Examine patients carefully for quiet tachnypnea beyond what is expected for the height of fever. Do all children with a first-time UTI need a renal ultrasound and voiding cystourethrography (VCUG)? All need an ultrasound, and then only VCUG if there is hydronephrosis found on the ultrassound. Indications for Bloodwork and Blood Cultures in Pediatric Fever Without a Source? A well-appearing, immunized child with a fever typically does not need blood work or cultures (6). CRP and Pro-calcitonin might be helpful in risk-stratifying patients with fever without a source, it hasn t become standard of practice or available in most centres. Guidelines by age for fever and the septic workup: Our experts recommend using chronological age (how many days since the child s birth, rather than adjusted gestational age) to help guide decision making for septic workup. *However premature
5 infants with a complex hospital course are already high-risk patients, so these babies usually require more thorough investigations. A full septic workup including LP is recommended for babies under 28 days, because they have the highest risk of SBI. This includes routine blood work and culture, urinalysis and culture, and lumbar puncture (cell count, protein, glucose, culture, gram stain and culture, and viral studies). Which infants should receive acyclovir for meningitis? If you suspect meningitis based on physical, or LP results (especially in <14 days), start acyclovir. HSV also causes pneumonitis and hepatitis, so also check for these if you are suspicious of HSV meningitis. For infants 29 days to 90 days, use the low-risk criteria (see below for American Academy of Pediatrics Fever Without a Source Guidelines). If they are well appearing, with no obvious source of infection, no complex past medical history, normal laboratory criteria (WBC count, normal urinalysis, and normal stool white count if diarrhea is present), they can usually be sent home if they have reliable parents and good availability for follow up in 24h. These infants have a chance of SBI of about 1.5%, usually UTI, so make sure urine is sent also for culture. References: 1) Baraff, L. Management of Infants and Young Children with Fever without Source. Pediatr Ann. 2008;37: PDF 2) Subcommittee on Urinary Tract Infection, Steering Committee on Quality Improvement and Management Pediatrics. 2011;128: ) Shaikh, N. Does This Child Have a Urinary Tract Infection? JAMA. 2007;298: PDF 4) Levine, D. Risk of Serious Bacterial Inection in Young Febrile Infants with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections. Pediatrics. 2004;113;1728. Full Text 5) Urinary Tract Infection: Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of the Initial UTI in Febrile Infants and Children 2 to 24 Months. Pediatrics. 2011;128; PDF 6) Wilkinson, M. et al. Prevalence of occult bacteremia in children aged 3 to 36 months presenting to the emergency department with fever in the postpneumococcal conjugate vaccine era. Acad Emerg Med. 2009;16: PDF 7) Sur, DK and Bukont EL.Evaluating Fever of Unidentifiable Source in Young Children Am Fam Physician Jun 15;75: PDF
Recognizing and Treating Fevers in Children with Complex Medical Issues by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Recognizing and Treating Fevers in Children with Complex Medical Issues by Susan Agrawal Fevers can be some of the scariest symptoms we see in our children, but they are also some
www.complexchild.com Recognizing and Treating Fevers in Children with Complex Medical Issues by Susan Agrawal Fevers can be some of the scariest symptoms we see in our children, but they are also some
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
Streptococcal Infections
 Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail?
 Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
The American Academy of Pediatrics
 Revised AAP Guideline on UTI in Febrile Infants and Young Children KENNETH B. ROBERTS, MD, University of rth Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, rth Carolina In 2011, the American Academy of Pediatrics
Revised AAP Guideline on UTI in Febrile Infants and Young Children KENNETH B. ROBERTS, MD, University of rth Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, rth Carolina In 2011, the American Academy of Pediatrics
2 P age. Babies from Birth to Age 2
 Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
Musculoskeletal Infection Care Process Model
 Musculoskeletal Infection Care Process Model Musculoskeletal infections are serious and potentially life-threatening. Musculoskeletal infections include necrotizing fasciitis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis,
Musculoskeletal Infection Care Process Model Musculoskeletal infections are serious and potentially life-threatening. Musculoskeletal infections include necrotizing fasciitis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis,
FAILURE TO THRIVE What Is Failure to Thrive?
 FAILURE TO THRIVE The first few years of life are a time when most children gain weight and grow much more rapidly than they will later on. Sometimes, however, babies and children don't meet expected standards
FAILURE TO THRIVE The first few years of life are a time when most children gain weight and grow much more rapidly than they will later on. Sometimes, however, babies and children don't meet expected standards
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page
 A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Headache: Differential diagnosis and Evaluation. Raymond Rios PGY-1 Pediatrics
 Headache: Differential diagnosis and Evaluation Raymond Rios PGY-1 Pediatrics You are evaluating a 9 year old male patient at the ED brought by his mother, who says that her son has had a fever, cough,
Headache: Differential diagnosis and Evaluation Raymond Rios PGY-1 Pediatrics You are evaluating a 9 year old male patient at the ED brought by his mother, who says that her son has had a fever, cough,
What You Need to know about Your Pet s Upcoming Dentistry and Periodontal Treatment
 What You Need to know about Your Pet s Upcoming Dentistry and Periodontal Treatment We are sending this packet of information in anticipation of your pet s upcoming dental procedure. Many people have questions
What You Need to know about Your Pet s Upcoming Dentistry and Periodontal Treatment We are sending this packet of information in anticipation of your pet s upcoming dental procedure. Many people have questions
Defining Normal Cerebrospinal Fluid White Blood Cell Counts in Neonates and Young Infants: A Scholarly Pursuit
 Defining Normal Cerebrospinal Fluid White Blood Cell Counts in Neonates and Young Infants: A Scholarly Pursuit Lori A. Kestenbaum, Jessica L. Ebberson, Joseph J. Zorc, Caitlin LaRussa, Richard L. Hodinka
Defining Normal Cerebrospinal Fluid White Blood Cell Counts in Neonates and Young Infants: A Scholarly Pursuit Lori A. Kestenbaum, Jessica L. Ebberson, Joseph J. Zorc, Caitlin LaRussa, Richard L. Hodinka
Substance Use Guideline 4B PERINATAL OPIOID EXPOSURE, CARE OF THE NEWBORN
 British Columbia Reproductive Care Program Substance Use Guideline 4B PERINATAL OPIOID EXPOSURE, CARE OF THE NEWBORN INTRODUCTION During the antenatal period, the opportunity exists for the primary care
British Columbia Reproductive Care Program Substance Use Guideline 4B PERINATAL OPIOID EXPOSURE, CARE OF THE NEWBORN INTRODUCTION During the antenatal period, the opportunity exists for the primary care
Protecting your baby against meningitis and septicaemia
 Protecting your baby against meningitis and septicaemia caused by meningococcal B bacteria MenB vaccine now available! Information about the MenB vaccine and recommended paracetamol use mmunisation The
Protecting your baby against meningitis and septicaemia caused by meningococcal B bacteria MenB vaccine now available! Information about the MenB vaccine and recommended paracetamol use mmunisation The
Childhood Urinary Tract Infections
 Childhood Urinary Tract Infections What is a UTI? Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections in childhood. It can cause distress to the child, concerns to the parents, and may
Childhood Urinary Tract Infections What is a UTI? Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections in childhood. It can cause distress to the child, concerns to the parents, and may
CPT Pediatric Coding Updates 2009. The 2009 Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes are effective as of January 1, 2009.
 CPT Pediatric Coding Updates 2009 The 2009 Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes are effective as of January 1, 2009. NEW CODES Evaluation and Management Services Normal Newborn Care Codes 99431-99440
CPT Pediatric Coding Updates 2009 The 2009 Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes are effective as of January 1, 2009. NEW CODES Evaluation and Management Services Normal Newborn Care Codes 99431-99440
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN CHILDREN. Yap Hui Kim, Belinda Murugasu
 URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN CHILDREN Yap Hui Kim, Belinda Murugasu Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common problem in childhood and the primary health care practitioner is usually the frontline in diagnosis
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN CHILDREN Yap Hui Kim, Belinda Murugasu Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common problem in childhood and the primary health care practitioner is usually the frontline in diagnosis
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
 A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
Other Causes of Fever
 T e c h n i c a l S e m i n a r s Other Causes of Fever Febrile Illness Causes Fever After Seven Days Referral Relapsing Fever - Borreliosis Overview JHR Adaptation Sore Throat Overview Prevention Management
T e c h n i c a l S e m i n a r s Other Causes of Fever Febrile Illness Causes Fever After Seven Days Referral Relapsing Fever - Borreliosis Overview JHR Adaptation Sore Throat Overview Prevention Management
Ear Infections Fever fever
 Ear Infections Fever fever Fever is when the temperature of the body rises above normal, generally above 38 degrees (38ºC) when the temperature is taken under the arm or in the mouth. Fever usually occurs
Ear Infections Fever fever Fever is when the temperature of the body rises above normal, generally above 38 degrees (38ºC) when the temperature is taken under the arm or in the mouth. Fever usually occurs
Sepsis Awareness Month
 Aon Kenya Insurance Brokers Ltd Aon Hewitt Healthcare Division Sepsis Awareness Month Issue 11 September 2015 In this Issue 2 Getting to understand Sepsis 3 Stages in Sepsis Advancement 4 Diagnosis & Treatment
Aon Kenya Insurance Brokers Ltd Aon Hewitt Healthcare Division Sepsis Awareness Month Issue 11 September 2015 In this Issue 2 Getting to understand Sepsis 3 Stages in Sepsis Advancement 4 Diagnosis & Treatment
Preventive health guidelines As of May 2015
 Preventive health guidelines As of May 2015 What is your plan for better health? Make this year your best year for wellness. Your health plan may help pay for tests to find disease early and routine wellness
Preventive health guidelines As of May 2015 What is your plan for better health? Make this year your best year for wellness. Your health plan may help pay for tests to find disease early and routine wellness
LEARNING OUTCOMES. Identify children at risk of developing TB disease. Correctly manage and refer children suspected of TB. Manage child contacts
 TB in Children 1a TB IN CHILDREN 2 LEARNING OUTCOMES Identify children at risk of developing TB disease Correctly manage and refer children suspected of TB Manage child contacts 3 TB Infection and Disease
TB in Children 1a TB IN CHILDREN 2 LEARNING OUTCOMES Identify children at risk of developing TB disease Correctly manage and refer children suspected of TB Manage child contacts 3 TB Infection and Disease
Vaccinations and Spina Bifida and Hydrocephalus
 shinecharity.org.uk [email protected] 42 Park Road Peterborough PE1 2UQ 01733 555988 Vaccinations and Spina Bifida and Hydrocephalus Vaccines are made from parts of bacteria or viruses that cause
shinecharity.org.uk [email protected] 42 Park Road Peterborough PE1 2UQ 01733 555988 Vaccinations and Spina Bifida and Hydrocephalus Vaccines are made from parts of bacteria or viruses that cause
Remove this cover sheet before redistributing and replace it with your own. Please ensure that DPHHS is included on your HAN distribution list.
 State of Montana Health Alert Network DPHHS HAN ADVISORY Cover Sheet DATE: May 15, 2012 SUBJECT: Pertussis INSTRUCTIONS: DISTRIBUTE to your local HAN contacts. This HAN is intended for general sharing
State of Montana Health Alert Network DPHHS HAN ADVISORY Cover Sheet DATE: May 15, 2012 SUBJECT: Pertussis INSTRUCTIONS: DISTRIBUTE to your local HAN contacts. This HAN is intended for general sharing
Policy Clinical Guideline Management of Fever without Focus in Children (excluding neonates) Clinical Guideline
 Policy Clinical Guideline Management of Fever without Focus in Children (excluding neonates) Clinical Guideline Policy developed by: SA Child Health Clinical Network Approved SA Health Safety & Quality
Policy Clinical Guideline Management of Fever without Focus in Children (excluding neonates) Clinical Guideline Policy developed by: SA Child Health Clinical Network Approved SA Health Safety & Quality
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of. Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care
 A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
ASTHMA IN INFANTS AND YOUNG CHILDREN
 ASTHMA IN INFANTS AND YOUNG CHILDREN What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. Symptoms of asthma are variable. That means that they can be mild to severe, intermittent to
ASTHMA IN INFANTS AND YOUNG CHILDREN What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. Symptoms of asthma are variable. That means that they can be mild to severe, intermittent to
How can herpes simplex spread to an infant?
 CHAPTER 3 HERPES AND PREGNANCY As an expectant parent eagerly awaiting the birth of your new baby, you are probably taking a number of steps to ensure your baby s health. One step many experts recommend
CHAPTER 3 HERPES AND PREGNANCY As an expectant parent eagerly awaiting the birth of your new baby, you are probably taking a number of steps to ensure your baby s health. One step many experts recommend
35-40% of GBS disease occurs in the elderly or in adults with chronic medical conditions.
 What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter
 Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package. Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula
 Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Preventive health guidelines As of May 2014
 To learn more about your plan, please see anthem.com/ca. To learn more about vaccines, please see the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website: cdc.gov. Preventive health guidelines As
To learn more about your plan, please see anthem.com/ca. To learn more about vaccines, please see the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website: cdc.gov. Preventive health guidelines As
Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD
 Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD Hand, foot, and mouth disease, or HFMD, is a contagious illness caused by different viruses. Infants and children younger than 5 years are more likely to
Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD Hand, foot, and mouth disease, or HFMD, is a contagious illness caused by different viruses. Infants and children younger than 5 years are more likely to
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection
 Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
2 months Diptheria; Tetanus; Whooping Cough; Hib & Polio 1st dose Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination
 IMMUNISATIONS You may want to know if your child should have routine immunisations and whether there could be an increased risk of complications because of the heart condition. We have sought the opinions
IMMUNISATIONS You may want to know if your child should have routine immunisations and whether there could be an increased risk of complications because of the heart condition. We have sought the opinions
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Definitions and Reporting
 AHRQ Safety Program for Long-term Care: HAIs/CAUTI Learning Objectives Upon completion of the webinar, core team members will be able to: Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Definitions
AHRQ Safety Program for Long-term Care: HAIs/CAUTI Learning Objectives Upon completion of the webinar, core team members will be able to: Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Definitions
Preventive Health Guidelines
 Preventive Health Guidelines As of April 2010 What is your plan for better health? Make this year your best year for overall wellness. Your health benefits plan may cover early detection screenings and
Preventive Health Guidelines As of April 2010 What is your plan for better health? Make this year your best year for overall wellness. Your health benefits plan may cover early detection screenings and
VOCATIONAL NURSE PROGRAM EXPECTED CLINICAL ROTATION PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES
 VN: Objective 01 EXPECTED CLINICAL ROTATION PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Clinical rotation expected performances are reflected in the clinical objectives. Clinical objectives are posted by instructor at each
VN: Objective 01 EXPECTED CLINICAL ROTATION PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Clinical rotation expected performances are reflected in the clinical objectives. Clinical objectives are posted by instructor at each
Keeping Track of Your Health
 Your Health Journal Keeping Track of Your Health Your Health Journal THE BASICS Name: Height: Weight: Date of birth: Primary doctor: Specialist: Specialist: Specialist: Specialist: Pharmacy: Health insurance:
Your Health Journal Keeping Track of Your Health Your Health Journal THE BASICS Name: Height: Weight: Date of birth: Primary doctor: Specialist: Specialist: Specialist: Specialist: Pharmacy: Health insurance:
& WHEN SHOULD I WORRY?
 WHEN SHOULD I WORRY? - Your guide to Coughs, Colds, Earache & Sore Throats Information For:- Who is this booklet for? Having an ill child can be a very scary experience for parents. If you understand more
WHEN SHOULD I WORRY? - Your guide to Coughs, Colds, Earache & Sore Throats Information For:- Who is this booklet for? Having an ill child can be a very scary experience for parents. If you understand more
Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC. OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract
 Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Preventive Care Recommendations THE BASIC FACTS
 Preventive Care Recommendations THE BASIC FACTS MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Carlos Healey, diagnosed in 2001 The Three Most Common Eye Disorders in Multiple Sclerosis Blood Pressure & Pulse Height & Weight Complete
Preventive Care Recommendations THE BASIC FACTS MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Carlos Healey, diagnosed in 2001 The Three Most Common Eye Disorders in Multiple Sclerosis Blood Pressure & Pulse Height & Weight Complete
Prevents future health problems. You receive these services without having any specific symptoms.
 Preventive Care To help you live the healthiest life possible, we offer free preventive services for most Network Health members. Please refer to your member materials, which you received when you enrolled
Preventive Care To help you live the healthiest life possible, we offer free preventive services for most Network Health members. Please refer to your member materials, which you received when you enrolled
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention. Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013
 Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
Supporting Breastfeeding and Lactation: The Primary Care Pediatrician s Guide to Getting Paid
 Supporting Breastfeeding and Lactation: The Primary Care Pediatrician s Guide to Getting Paid Breastfeeding support can often be quite time-intensive initially but pays off in a healthier patient population.
Supporting Breastfeeding and Lactation: The Primary Care Pediatrician s Guide to Getting Paid Breastfeeding support can often be quite time-intensive initially but pays off in a healthier patient population.
Treatment of Fever and Infection in Children with Transfusion Dependent Thalassaemia
 Treatment of Fever and Infection in Children with Transfusion Dependent Thalassaemia Document Information Version: 2 Date: June 2014 Authors (incl. job title): Professor David Rees, Sue Height (consultant
Treatment of Fever and Infection in Children with Transfusion Dependent Thalassaemia Document Information Version: 2 Date: June 2014 Authors (incl. job title): Professor David Rees, Sue Height (consultant
Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis)
 Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis) About whooping cough What is whooping cough? Whooping cough is a highly contagious illness caused by bacteria. It mainly affects the respiratory
Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis) About whooping cough What is whooping cough? Whooping cough is a highly contagious illness caused by bacteria. It mainly affects the respiratory
Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.
 Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.org/ Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) is a common, mild, childhood
Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.org/ Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) is a common, mild, childhood
LOUISIANA STATE UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER - SHREVEPORT MEDICAL RECORDS CONTENT/DOCUMENTATION
 LOUISIANA STATE UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER - SHREVEPORT MEDICAL RECORDS CONTENT/DOCUMENTATION Hospital Policy Manual Purpose: To define the components of the paper and electronic medical record
LOUISIANA STATE UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER - SHREVEPORT MEDICAL RECORDS CONTENT/DOCUMENTATION Hospital Policy Manual Purpose: To define the components of the paper and electronic medical record
Preventive health guidelines
 Preventive health guidelines As of May 2015 What is your plan for better health? Make this year your best year for wellness. Your health plan may help pay for tests to find disease early and routine wellness
Preventive health guidelines As of May 2015 What is your plan for better health? Make this year your best year for wellness. Your health plan may help pay for tests to find disease early and routine wellness
HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES
 HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES INTRODUCTION Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in the United States, and diabetes is a disease that affects the way the body handles blood sugar. Approximately
HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES INTRODUCTION Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in the United States, and diabetes is a disease that affects the way the body handles blood sugar. Approximately
Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy. Chapter 7
 Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy Chapter 7 An unborn baby makes no IgG (antibody) and only slowly starts producing it after birth. However, starting at about the sixth month of pregnancy, the
Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy Chapter 7 An unborn baby makes no IgG (antibody) and only slowly starts producing it after birth. However, starting at about the sixth month of pregnancy, the
Feverish illness in children Assessment and initial management in children younger than 5 years
 Feverish illness in children Assessment and initial management in children younger than 5 years NICE guideline Draft for consultation, November 2012 If you wish to comment on this version of the guideline,
Feverish illness in children Assessment and initial management in children younger than 5 years NICE guideline Draft for consultation, November 2012 If you wish to comment on this version of the guideline,
Implementing the Long-Term Care UTI Toolkit Wisconsin Coalition on HealthCare Association Infection in Long Term Care
 Implementing the Long-Term Care UTI Toolkit Wisconsin Coalition on HealthCare Association Infection in Long Term Care MetaStar Health Care Quality Symposium: The Value of Better Health Paula Kock RN [email protected]
Implementing the Long-Term Care UTI Toolkit Wisconsin Coalition on HealthCare Association Infection in Long Term Care MetaStar Health Care Quality Symposium: The Value of Better Health Paula Kock RN [email protected]
Clinical Policy for Children Younger Than Three Years Presenting to the Emergency Department With Fever
 PEDIATRICS/CLINICAL POLICY Clinical Policy for Children Younger Than Three Years Presenting to the Emergency Department With Fever Policy statements and clinical policies are the official policies of the
PEDIATRICS/CLINICAL POLICY Clinical Policy for Children Younger Than Three Years Presenting to the Emergency Department With Fever Policy statements and clinical policies are the official policies of the
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
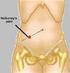 Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)]
![Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)] Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)]](/thumbs/27/12172665.jpg) EMA/14365/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)] Overview of disease epidemiology Diphtheria
EMA/14365/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)] Overview of disease epidemiology Diphtheria
Parent s Guide to CHILDHOOD IMMUNIZATIONS
 Part One Vaccine-Preventable Part Three More Diseases About Vaccines and Childhood Vaccines 30 Parent s Guide to CHILDHOOD IMMUNIZATIONS Part 3: More About Vaccines How do vaccines work? To understand
Part One Vaccine-Preventable Part Three More Diseases About Vaccines and Childhood Vaccines 30 Parent s Guide to CHILDHOOD IMMUNIZATIONS Part 3: More About Vaccines How do vaccines work? To understand
1333 Plaza Blvd, Suite E, Central Point, OR 97502 * www.mountainviewvet.net
 1333 Plaza Blvd, Suite E, Central Point, OR 97502 * www.mountainviewvet.net Diabetes Mellitus (in cats) Diabetes, sugar Affected Animals: Most diabetic cats are older than 10 years of age when they are
1333 Plaza Blvd, Suite E, Central Point, OR 97502 * www.mountainviewvet.net Diabetes Mellitus (in cats) Diabetes, sugar Affected Animals: Most diabetic cats are older than 10 years of age when they are
STROKE CARE PLAN: BLADDER & BOWEL CONTINENCE
 Urinary incontinence related to loss of ability to identify and respond to need to urinate; involuntary bladder contractions, increased nightly urine production, difficulty communication need to urinate
Urinary incontinence related to loss of ability to identify and respond to need to urinate; involuntary bladder contractions, increased nightly urine production, difficulty communication need to urinate
Cystic Fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis affects various systems in children and young adults, including the following:
 Cystic Fibrosis What is cystic fibrosis? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disease characterized by an abnormality in the glands that produce sweat and mucus. It is chronic, progressive, and is usually
Cystic Fibrosis What is cystic fibrosis? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disease characterized by an abnormality in the glands that produce sweat and mucus. It is chronic, progressive, and is usually
Sepsis: Identification and Treatment
 Sepsis: Identification and Treatment Daniel Z. Uslan, MD Associate Clinical Professor Division of Infectious Diseases Medical Director, UCLA Sepsis Task Force Severe Sepsis: A Significant Healthcare Challenge
Sepsis: Identification and Treatment Daniel Z. Uslan, MD Associate Clinical Professor Division of Infectious Diseases Medical Director, UCLA Sepsis Task Force Severe Sepsis: A Significant Healthcare Challenge
What is whooping cough. (pertussis)? Information and Prevention. Ocument dn
 What is whooping cough Ocument dn (pertussis)? Information and Prevention IMPORTANT Pertussis (or whooping cough) is a highly contagious infection that can cause uncontrollable, violent coughing. If you
What is whooping cough Ocument dn (pertussis)? Information and Prevention IMPORTANT Pertussis (or whooping cough) is a highly contagious infection that can cause uncontrollable, violent coughing. If you
Section H Bladder and Bowel
 Section Bladder and Bowel Intent To gather information on the use of bowel and bladder appliances, the use of and response to urinary toileting programs, urinary and bowel continence, bowel training programs,
Section Bladder and Bowel Intent To gather information on the use of bowel and bladder appliances, the use of and response to urinary toileting programs, urinary and bowel continence, bowel training programs,
2011 NTP Paediatric guidelines update- final draft
 Childhood TB Investigation and management of children suspected to have tuberculosis (TB) or who are close contacts of a TB case (sputum smear positive or negative) Key facts Children who are close contacts
Childhood TB Investigation and management of children suspected to have tuberculosis (TB) or who are close contacts of a TB case (sputum smear positive or negative) Key facts Children who are close contacts
Gastroschisis and My Baby
 Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
UTI in children. Quick reference guide. Issue date: August 2007. Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management
 Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased.
 Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
1584 Wesleyan Drive FORM A Norfolk, VA 23504 Phone: (757) 455-3108 Health History immunization & Physical Form
 Mail completed form to: Marlin Health Services 1584 Wesleyan Drive FORM A Norfolk, VA 23504 Phone: (757) 455-3108 Health History immunization & Physical Form Virginia State law (code 23-7.5) requires all
Mail completed form to: Marlin Health Services 1584 Wesleyan Drive FORM A Norfolk, VA 23504 Phone: (757) 455-3108 Health History immunization & Physical Form Virginia State law (code 23-7.5) requires all
95% of childhood kidney cancer cases are Wilms tumours. Childhood kidney cancer is extremely rare, with only 90 cases a year in
 James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
PATIENT INFORMATION FILL OUT ALL ITEMS
 PATIENT INFORMATION FILL OUT ALL ITEMS FAILURE TO COMPLETELY FILL OUT THIS FORM MAY RESULT IN YOU BEING BILLED IN FULL Patient Last Name: First: MI:. Address:. Date of Birth: Gender: M or F Marital Status:
PATIENT INFORMATION FILL OUT ALL ITEMS FAILURE TO COMPLETELY FILL OUT THIS FORM MAY RESULT IN YOU BEING BILLED IN FULL Patient Last Name: First: MI:. Address:. Date of Birth: Gender: M or F Marital Status:
Human Capital Development & Education Program Proposal
 Human Capital Development & Education Program Proposal Cardiology & Cardiovascular Surgery Emergency Medicine Respiratory Medicine Infection Control HMIS 1 (15 Courses) Module 1/2 1/15 Course Title : Management
Human Capital Development & Education Program Proposal Cardiology & Cardiovascular Surgery Emergency Medicine Respiratory Medicine Infection Control HMIS 1 (15 Courses) Module 1/2 1/15 Course Title : Management
VUMC Guidelines for Management of Indwelling Urinary Catheters. UC Access/ Maintenance
 VUMC Guidelines for Management of Indwelling Urinary Catheters UC Insertion Preparation & Procedure Indications for insertion and continued use of indwelling urinary catheters include: Urinary retention
VUMC Guidelines for Management of Indwelling Urinary Catheters UC Insertion Preparation & Procedure Indications for insertion and continued use of indwelling urinary catheters include: Urinary retention
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD)
 Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) VETERINARY GUIDE 2 What is FLUTD? FLUTD describes a collection of common conditions that affect the bladder and/or urethra the narrow tube that carries urine
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) VETERINARY GUIDE 2 What is FLUTD? FLUTD describes a collection of common conditions that affect the bladder and/or urethra the narrow tube that carries urine
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines August 2011
 August 2011 Pertussis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 December 2005 Case Definition
August 2011 Pertussis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 December 2005 Case Definition
PHYSICIAN ASSISTANT STUDIES UTMB ESSENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND TECHNICAL STANDARDS Updated 04/10/13
 PHYSICIAN ASSISTANT STUDIES UTMB ESSENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND TECHNICAL STANDARDS Updated 04/10/13 This description defines the capabilities that are necessary for an individual to successfully complete the
PHYSICIAN ASSISTANT STUDIES UTMB ESSENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND TECHNICAL STANDARDS Updated 04/10/13 This description defines the capabilities that are necessary for an individual to successfully complete the
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH)
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) What is pertussis? General Questions About Pertussis Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) What is pertussis? General Questions About Pertussis Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
Lupus in Children and Teenagers. Arielle Hay, MD Pediatric Rheumatologist Nicklaus Children s Hospital
 Lupus in Children and Teenagers Arielle Hay, MD Pediatric Rheumatologist Nicklaus Children s Hospital Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Chronic Illness What is lupus? Autoimmune Multisystem Antinuclear
Lupus in Children and Teenagers Arielle Hay, MD Pediatric Rheumatologist Nicklaus Children s Hospital Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Chronic Illness What is lupus? Autoimmune Multisystem Antinuclear
Headaches in Children
 Children s s Hospital Headaches in Children Manikum Moodley, MD, FRCP Section of Pediatric Neurology The Cleveland Clinic Foundation Introduction Headaches are common in children Most headaches are benign
Children s s Hospital Headaches in Children Manikum Moodley, MD, FRCP Section of Pediatric Neurology The Cleveland Clinic Foundation Introduction Headaches are common in children Most headaches are benign
GENERAL INFORMATION. Hepatitis B Foundation - Korean Chapter Pg. 3 www.hepb.org
 GENERAL INFORMATION What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is the world's most common liver infection that can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which attacks and
GENERAL INFORMATION What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is the world's most common liver infection that can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which attacks and
Clinical Quality Measure Crosswalk: HEDIS, Meaningful Use, PQRS, PCMH, Beacon, 10 SOW
 Clinical Crosswalk: HEDIS, Meaningful Use, PQRS, PCMH, Beacon, 10 SOW NQF 0105 PQRS 9 NQF 0002 PQRS 66 Antidepressant Medication Management Appropriate Testing for Children with Pharyngitis (2-18 years)
Clinical Crosswalk: HEDIS, Meaningful Use, PQRS, PCMH, Beacon, 10 SOW NQF 0105 PQRS 9 NQF 0002 PQRS 66 Antidepressant Medication Management Appropriate Testing for Children with Pharyngitis (2-18 years)
TB CARE EARLY DETECTION AND PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS (TB) IN CHILDREN. Risk factors in children acquiring TB:
 EARLY DETECTION AND PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS (TB) IN CHILDREN Risk factors in children acquiring TB: Children living in the same household as a lung TB patient (especially children under 5) Children
EARLY DETECTION AND PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS (TB) IN CHILDREN Risk factors in children acquiring TB: Children living in the same household as a lung TB patient (especially children under 5) Children
The Liver and Alpha-1. Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION
 The Liver and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION What Is Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency? Alpha-1 is a condition that may result in serious lung disease in adults and/or liver
The Liver and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION What Is Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency? Alpha-1 is a condition that may result in serious lung disease in adults and/or liver
Pentavalent Vaccine. Guide for Health Workers. with Answers to Frequently Asked Questions
 Pentavalent Vaccine Guide for Health Workers with Answers to Frequently Asked Questions Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Government of India 2012 Immunization is one of the most well-known and effective
Pentavalent Vaccine Guide for Health Workers with Answers to Frequently Asked Questions Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Government of India 2012 Immunization is one of the most well-known and effective
A Child s guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization. Boys
 A Child s guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization Boys Introduction Probably you have just heard that you have to learn to catheterize your bladder. Most children are worried, frightened or scared
A Child s guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization Boys Introduction Probably you have just heard that you have to learn to catheterize your bladder. Most children are worried, frightened or scared
More details >>> HERE <<<
 More details >>> HERE http://urlzz.org/conitp/pdx/cc8648/ Tags:
More details >>> HERE http://urlzz.org/conitp/pdx/cc8648/ Tags:
