FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH)
|
|
|
- Daniel White
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) What is pertussis? General Questions About Pertussis Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person sneezes or coughs and another individual breathes in the bacteria. Who gets pertussis? Pertussis can occur at any age. It may be very severe in infants and young children (especially those who have not had 3 doses of pertussis vaccine), resulting in hospitalization, seizures, long-term neurological problems, and even death. Pertussis can occur in immunized individuals, because the immunity gained from vaccination typically wanes over time, but milder illness is generally seen among vaccinated persons. Although widespread use of pertussis vaccines had reduced the number of pertussis cases, this disease has been increasing in recent years. What are the symptoms of pertussis? Symptoms usually appear between 7 to 10 days after exposure to the bacteria, but can develop 4 to 21 days after exposure. The disease starts with cold-type symptoms: low-grade fever, runny nose and mild cough. Within two weeks, the cough becomes more severe and is characterized by episodes of fits of coughing. Vomiting, breathlessness, a change in facial color, and/or whooping sound may follow the coughing fits. In between coughing fits, the individual may look and feel fine. These coughing fits may continue for several months, and are more frequent at night. In infants, the cough can be minimal or not present at all. Infants may have a symptom known as "apnea." Apnea is a pause in the child's breathing pattern. People who think they have pertussis should be evaluated by a physician. How is pertussis spread? Pertussis is spread through droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes or talks. The first symptoms usually appear 7 to 10 days after exposure. The greatest risk of spread is during the early stages of the illness through the first three weeks of coughing. Those treated with antibiotics are considered contagious until they have completed 5 days of an appropriate antibiotic. What are the complications of pertussis? In infants younger than 1 year of age who get pertussis, more than half must be hospitalized. The younger the infant, the more likely treatment in the hospital will be needed. Complications for infants with pertussis include: pneumonia (lung infection) convulsions (violent, uncontrolled shaking) apnea (slowed or stopped breathing) encephalopathy (disease of the brain) death Teens and adults can also get complications from pertussis, but they are usually less serious in this older age group, especially in those who have been vaccinated. The most common complications in teens and adults with pertussis are: Weight loss Loss of bladder control Passing out
2 Rib fractures from severe coughing Are some people at higher risk from pertussis? Yes. Infants < 12 months of age, people who have weakened immune systems or neuromuscular disease, and people with chronic respiratory conditions are most at risk of developing complications from pertussis. Persons who might expose someone else who is high risk include pregnant women (particularly in their third trimester), members of a household with infants or pregnant women, child care workers who take care of infants under one year old, childbirth educators, and health care workers who have face-to-face contact with infants under one year old or pregnant women. Getting vaccinated against pertussis is especially important for people who are considered high risk or who may expose someone who is high risk. How do I know if I have pertussis? Pertussis Diagnosis, Treatment, and Testing Pertussis (pertussis) can be diagnosed by a medical provider by taking into consideration if you have been exposed to pertussis, reviewing your symptoms, and doing a laboratory test which involves taking a sample of secretions (with a swab or syringe filled with saline) from the back of the throat through the nose. What is the treatment for pertussis? A health care provider may prescribe an appropriate antibiotic such as azithromycin (Zithromax, or Z-pack), clarithromycin, or erythromycin. There are other antibiotics that might also be used. These antibiotics will reduce the contagious period, but will not reduce the cough symptoms unless taken in the very early stage of the infection. Exposure to Pertussis What do I do if I was exposed to someone who has pertussis? See your health care provider as soon as possible. You may be given antibiotics that can stop the development of the disease. If you start to have symptoms of pertussis, try to isolate yourself at home and stay more than 3 feet away from other people (especially infants and pregnant women) until treated (or until another diagnosis for the cough proves it s not contagious). How should employers handle employees returning to work who have had pertussis? Employers should talk with their Human Resources Office to understand their company policies, procedures, and labor agreements. Employers should not share individual employee health information with others. Employers can also call their state or local health department for guidance. Are there special cleaning requirements for pertussis? No. Pertussis usually spreads by breathing in the pertussis bacteria. This germ comes out of the mouth and nose when an infected person coughs or sneezes. While the pertussis bacteria can live on a surface or object for several days, most people do not get pertussis by contact with that surface or object. The best protection is getting vaccinated. Also, try to stay away from people who are coughing and sneezing. If you are sick, try to stay away from people until your illness is treated; cover your mouth when you cough or sneeze; and wash your hands often.
3 How common is pertussis in Colorado? Petussis Epidemic in Colorado Even with the success of pertussis vaccines, the disease is still common in Colorado and in the rest of the United States. Cases of pertussis have been above epidemic levels since 2012, with several times the number of cases that occurred in previous years. What parts of Colorado have pertussis? The pertussis epidemic in Colorado is widespread throughout the state but Arapahoe, Boulder, Denver, and Jefferson counties have the highest number of cases. Why is there more pertussis in some years than others? Reported cases of pertussis vary from year to year and tend to peak every 3-5 years. Our last peak year in Colorado was 2005 when 1383 cases were reported. This pattern is not completely understood, but that s why it s important that everyone get vaccinated. If it weren t for vaccines, we d see many more cases of pertussis. What should I do if I live in an outbreak area? You can make sure you and your loved ones are up to date with recommended pertussis vaccines. There are two types of pertussis vaccines DTaP for infants and children and Tdap for adolescents and adults. Getting vaccinated with Tdap is especially important for family members and caregivers of new infants. Also, if caring for an infant, keep him or her away from anyone with cough or cold symptoms. Should I delay travel to an area that is having a pertussis outbreak? No, but those traveling to an area with a pertussis outbreak should make sure they are up to date on their vaccines including the pertussis vaccine. Pertussis Prevention and Vaccination Recommendations What can be done to prevent the spread of pertussis? The most effective measure is to maintain the highest level of pertussis immunization in our community. Immunization records of children, adolescents, and adults should be reviewed to ensure they are up-todate on their DTaP/Tdap shots. Persons not up to date with their pertussis shots should receive DTaP/Tdap vaccine as soon as possible. Persons with pertussis should avoid contact with others until they have taken 5 full days of an appropriate antibiotic. Close contacts of a case of pertussis should receive a course of an appropriate antibiotic to prevent pertussis. Is there a vaccine for pertussis? The vaccine for pertussis is given in combination with diphtheria and tetanus. Immunization authorities routinely recommend that five doses of DTaP (diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis) vaccine be given at two, four, six, 15 to 18 months of age, and between four and six years of age and a single dose of Tdap be administered at years of age. All adults aged 19 years and older who have not yet received a dose of Tdap should receive a single dose. Tdap should be administered regardless of interval since last tetanus or diphtheria toxoid-containing vaccine.
4 If I had pertussis, should I still get vaccinated? Yes. When someone gets pertussis, their body develops a natural immunity. However, it is unknown how long that immunity lasts for each person, so routine vaccination against pertussis is recommended. How long are you protected if you get pertussis? It s unclear how long immunity lasts but immunity does decline over time whether the immunity came from getting the disease or from the vaccine. That s why experts recommend that all children and adults get vaccinated, even if they ve had pertussis. Should I get vaccinated again if I had a Tdap shot a few years ago? The current recommendation is that all adults aged 19 years and older should get one dose of Tdap. Tdap is also recommended for pregnant women during the third trimester or late second trimester (after 20 weeks of gestation) during every pregnancy. In addition, Tdap is recommended in the immediate postpartum period for new mothers who were not previously vaccinated or whose vaccination status is unknown. Will vaccination recommendations change? It s possible that the recommendations might change. Information from current epidemics in the United States will help the CDC to develop and adjust recommendations. Do the vaccines really work? Questions about Vaccine Efficacy Yes. The pertussis vaccine is very effective at protecting us from severe and deadly disease. How long does the DTaP vaccine for younger kids last? Recent studies show that the DTaP vaccine that young kids now get doesn t last as long as expected, and protection wears off over time. In the 1990s, the United States switched to a new pertussis vaccine for kids. This vaccine (DTaP) causes fewer side effects than the previous vaccine (DTP) but doesn t last as long. This may explain why there are more pertussis cases in older children. Children and teens years old today are the first group of kids to get only the newer DTaP vaccine as babies; they didn t get any doses of the previous vaccine. How long does the Tdap vaccine last? Vaccine experts aren t sure about that yet. There are more reported pertussis cases among year olds a changing trend across the country that indicates a shorter duration for Tdap vaccine protection against pertussis. The CDC is studying how long the Tdap vaccine lasts and how well it protects people. The study will also look for any differences between kids who got the original DTP (whole cell) vs. the more recent DTaP (acellular) vaccines. If the vaccine doesn t last very long, why should I be vaccinated? The vaccine we use now (DTaP) works very well for the first couple of years. Even after five years, people still have 70 percent protection from pertussis. People who are vaccinated and still get sick have a milder, shorter illnesses, and are less likely to spread the disease to others; this is especially important for babies. Infants who are too young to get vaccinated usually get pertussis from a family member or caregiver. Infants are at the most risk for getting very sick and potentially dying from pertussis.
5 If I got vaccinated, can I still get pertussis? It s possible, however, vaccinated people who get pertussis have milder symptoms, a shorter illness, and are less likely to spread the disease to other people. How many vaccinated people are getting sick? There have been many pertussis cases reported among people who ve been vaccinated. That s not a surprise it s known that the vaccine protection declines over time. However, according to CDC, data from California s epidemic in 2010 showed that unvaccinated children are almost nine times more likely to get pertussis than fully vaccinated children. Are there side effects from the vaccine? Vaccine Safety Like any medication, vaccines may cause side effects. Most are mild: Pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site. Mild fever. Headache. Tiredness. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or stomach ache. Chills, body aches, sore joints, rash, or swollen glands (uncommon). I m unsure if I ve had the Tdap vaccine; is it harmful to get it again? No. For most people, the benefits of protection against pertussis outweigh the risk of any side effects. Check with your health care provider if you have specific concerns. Is the pertussis vaccine safe for pregnant women? Yes. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) has determined that there is no elevated risk of adverse events among pregnant women who have received Tdap vaccine, or in their newborns. Both tetanus and diphtheria toxoids (Td) and tetanus toxoid (TT) vaccines have been used extensively in pregnant women worldwide since the 1960s to prevent tetanus in newborns. Td and TT vaccines administered during pregnancy have not been shown to harm either the mother or baby/fetus. Women should see their health care provider to get Tdap. Tdap is now recommended for pregnant women during the third trimester or late second trimester (after 20 weeks of gestation) during every pregnancy. Tdap is recommended in the immediate postpartum period for new mothers who were not previously vaccinated or whose vaccination status is unknown. Is the pertussis vaccine safe for women who are breastfeeding? Yes. Women who are breastfeeding can receive the vaccine. Tdap vaccine can and should be given to anyone, including breastfeeding women, who are frequent close contact with infants. Preventing pertussis in mothers and other caregivers can reduce the chance that the infant will get pertussis. Also, by breastfeeding, mothers can pass antibodies they ve made in response to the Tdap shot on to their infants, which may reduce an infant s chances of getting sick with pertussis. This is especially important for infants younger than 6 months of age, who have no other way of receiving enough pertussis antibodies, since they are not fully protected until their third dose of DTaP vaccine at 6 months of age.
6 Where can I get the pertussis vaccine? There are many places that offer pertussis vaccine: Your health care provider. Most pharmacies. Your local health department. Does Medicare cover the vaccine? How to Get and/or Pay for Pertussis Vaccination Yes. Medicare Part D covers the cost of the adult vaccine (called Tdap) for adults aged 65 and older. Since it is a prescription drug benefit, coverage depends on the use of that benefit so far during the year. Call with questions about Medicare. Health care workers with questions should contact their patients Part D plan for Part D vaccine information. Does Medicaid cover the vaccine? Yes. Medicaid covers the pertussis vaccine per the recommended immunization schedule. Submit questions about your coverage online. How can I pay for the vaccine if I m uninsured? There may be programs that can help you. Call your local health department to find out if free vaccination clinics are planned in your community. Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment Communicable Disease Epidemiology Program (303) November 2013
Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis)
 Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis) About whooping cough What is whooping cough? Whooping cough is a highly contagious illness caused by bacteria. It mainly affects the respiratory
Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis) About whooping cough What is whooping cough? Whooping cough is a highly contagious illness caused by bacteria. It mainly affects the respiratory
Remove this cover sheet before redistributing and replace it with your own. Please ensure that DPHHS is included on your HAN distribution list.
 State of Montana Health Alert Network DPHHS HAN ADVISORY Cover Sheet DATE: May 15, 2012 SUBJECT: Pertussis INSTRUCTIONS: DISTRIBUTE to your local HAN contacts. This HAN is intended for general sharing
State of Montana Health Alert Network DPHHS HAN ADVISORY Cover Sheet DATE: May 15, 2012 SUBJECT: Pertussis INSTRUCTIONS: DISTRIBUTE to your local HAN contacts. This HAN is intended for general sharing
I am reaching out to you with some preventative information that you might be interested in sharing with your school community.
 Reported cases of pertussis (whooping cough) are on the rise in Colorado and El Paso County. As of October 23, more than 1,000 cases of pertussis have been reported across the state. El Paso County cases
Reported cases of pertussis (whooping cough) are on the rise in Colorado and El Paso County. As of October 23, more than 1,000 cases of pertussis have been reported across the state. El Paso County cases
What is whooping cough. (pertussis)? Information and Prevention. Ocument dn
 What is whooping cough Ocument dn (pertussis)? Information and Prevention IMPORTANT Pertussis (or whooping cough) is a highly contagious infection that can cause uncontrollable, violent coughing. If you
What is whooping cough Ocument dn (pertussis)? Information and Prevention IMPORTANT Pertussis (or whooping cough) is a highly contagious infection that can cause uncontrollable, violent coughing. If you
2 P age. Babies from Birth to Age 2
 Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
The Reality Pertussis can be a serious illness, part icularly for babies and young children.
 Sounds of Pertussis Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a poten tially deadly infection that can strike at any age, but is particularly dangerous for babies. The sounds of pertussis are like no
Sounds of Pertussis Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a poten tially deadly infection that can strike at any age, but is particularly dangerous for babies. The sounds of pertussis are like no
Whooping Cough. The Lungs Whooping cough is an infection of the lungs and breathing tubes, both of which are parts of the respiratory system.
 Whooping Cough Introduction Whooping cough is a serious bacterial infection of the lungs and breathing tubes. It is also called pertussis. About 16 million cases of whooping cough happen worldwide each
Whooping Cough Introduction Whooping cough is a serious bacterial infection of the lungs and breathing tubes. It is also called pertussis. About 16 million cases of whooping cough happen worldwide each
New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Pertussis FAQs. Date: January 10, 2013
 New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Pertussis FAQs Date: January 10, 2013 KEY MESSAGES: 1. Pertussis is a very contagious vaccine-preventable disease that can cause serious
New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Pertussis FAQs Date: January 10, 2013 KEY MESSAGES: 1. Pertussis is a very contagious vaccine-preventable disease that can cause serious
Information on Measles and Whooping Cough: Vaccination and Disease
 Information on Measles and Whooping Cough: Vaccination and Disease Vaccine s Mechanism of Action Vaccines expose the recipient to a small amount of an weakened organism. Through this exposure, the body
Information on Measles and Whooping Cough: Vaccination and Disease Vaccine s Mechanism of Action Vaccines expose the recipient to a small amount of an weakened organism. Through this exposure, the body
Why Pertussis matters..
 Why Pertussis matters.. Pertussis (Whooping cough) outbreaks continue to impact children & adults, both locally and across the US. Cases have been on the rise since the 1980 s. However, recent data on
Why Pertussis matters.. Pertussis (Whooping cough) outbreaks continue to impact children & adults, both locally and across the US. Cases have been on the rise since the 1980 s. However, recent data on
safest place for your baby is in your arms...
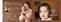 Help protect your baby by helping to protect yourself. Photo: John Bentham Imagine a cough barreling through your infant s body at up to 100 mph. Help protect yourself and your family by getting an adult
Help protect your baby by helping to protect yourself. Photo: John Bentham Imagine a cough barreling through your infant s body at up to 100 mph. Help protect yourself and your family by getting an adult
Adult Vaccination Frequently Asked Questions: The Basics
 The Basics Why should I get vaccinated? Vaccination is the best way to protect against infections that can make you sick and be passed on to those around you. 1 What kinds of side effects will I get from
The Basics Why should I get vaccinated? Vaccination is the best way to protect against infections that can make you sick and be passed on to those around you. 1 What kinds of side effects will I get from
Pertussis (Whooping Cough) http://www.cdc.gov/pertussis/index.html. Causes and Transmission. Causes. Transmission
 Pertussis (Whooping Cough) http://www.cdc.gov/pertussis/index.html Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a highly contagious respiratory disease. It is caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis.
Pertussis (Whooping Cough) http://www.cdc.gov/pertussis/index.html Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a highly contagious respiratory disease. It is caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis.
Know the Symptoms. Call Your Doctor, Treat Whooping Gough Early. Whooping Cough Signs and Symptoms. Whooping Cough Shots Prevent the Disease
 What ls Whooping Cough? Whooping cough disease (also called pertussis) causes coughing fits that make it hard to breathe. It spreads easily when someone with the disease coughs or sneezes. It can kill
What ls Whooping Cough? Whooping cough disease (also called pertussis) causes coughing fits that make it hard to breathe. It spreads easily when someone with the disease coughs or sneezes. It can kill
Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) - the replacement of Repevax with Boostrix -IPV an update for registered healthcare practitioners
 Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) - the replacement of Repevax with Boostrix -IPV an update for registered healthcare practitioners Questions and Answers May 2014 Health Protection Scotland
Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) - the replacement of Repevax with Boostrix -IPV an update for registered healthcare practitioners Questions and Answers May 2014 Health Protection Scotland
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Release #2014-04
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Release #2014-04 CONTACT for this Release: Krista Dommer Office Phone: (209) 468-3571 Email: [email protected] Alvaro Garza, MD, MPH. Public Health Officer MEASLES OUTBREAKS PROMPT
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Release #2014-04 CONTACT for this Release: Krista Dommer Office Phone: (209) 468-3571 Email: [email protected] Alvaro Garza, MD, MPH. Public Health Officer MEASLES OUTBREAKS PROMPT
Whooping Cough Vaccine for Pregnant Women
 Whooping Cough Vaccine for Pregnant Women What is whooping cough (pertussis)? Whooping cough (also known as pertussis) is a highly contagious illness that can be life threatening. The disease is most serious
Whooping Cough Vaccine for Pregnant Women What is whooping cough (pertussis)? Whooping cough (also known as pertussis) is a highly contagious illness that can be life threatening. The disease is most serious
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine
 Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Factsheet September 2012. Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women. Introduction
 Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis.
Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis.
Why you and your Family Should Get the Flu Shot
 Why you and your Family Should Get the Flu Shot Why Get VaCCinated against influenza? Influenza (flu) is a virus that can lead to serious complications, hospitalization, or even death. Even healthy children
Why you and your Family Should Get the Flu Shot Why Get VaCCinated against influenza? Influenza (flu) is a virus that can lead to serious complications, hospitalization, or even death. Even healthy children
Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.
 Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.org/ Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) is a common, mild, childhood
Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.org/ Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) is a common, mild, childhood
Is your family at risk for pertussis?
 Is your family at risk for pertussis? Help protect your family against a serious disease and talk to your health-care professional about adult and adolescent immunization with Adacel vaccine. Please click
Is your family at risk for pertussis? Help protect your family against a serious disease and talk to your health-care professional about adult and adolescent immunization with Adacel vaccine. Please click
Pertussis Toolkit for Schools
 Pertussis Toolkit for Schools Cerro Gordo County experienced a significant pertussis outbreak in 2012. To lessen the effects of future outbreaks, several community partners worked together to improve our
Pertussis Toolkit for Schools Cerro Gordo County experienced a significant pertussis outbreak in 2012. To lessen the effects of future outbreaks, several community partners worked together to improve our
Laboratory confirmation requires isolation of Bordetella pertussis or detection of B. pertussis nucleic acid, preferably from a nasopharyngeal swab.
 Pertussis Epidemiology in New Zealand New Zealand has continued to experience outbreaks of pertussis in recent decades. This is in part due to historically low immunisation rates and in part because immunity
Pertussis Epidemiology in New Zealand New Zealand has continued to experience outbreaks of pertussis in recent decades. This is in part due to historically low immunisation rates and in part because immunity
Parents and Grandparents
 Parents and Grandparents Vaccination for parents and grandparents is vital to help protect newborn babies against whooping cough. Protect your baby by being immunised too. To find out more about Boostrix
Parents and Grandparents Vaccination for parents and grandparents is vital to help protect newborn babies against whooping cough. Protect your baby by being immunised too. To find out more about Boostrix
BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE.
 DON T GET OR GIVE THE FLU THIS YEAR THANK YOU Vaccination is the only protection. www.immunisation.ie BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE. FLU VACCINE 2013-2014 Healthcare workers prevent the spread of flu and
DON T GET OR GIVE THE FLU THIS YEAR THANK YOU Vaccination is the only protection. www.immunisation.ie BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE. FLU VACCINE 2013-2014 Healthcare workers prevent the spread of flu and
INFLUENZA (FLU) Flu and You
 Influenza (Flu) What is the flu? The flu is an illness caused by flu viruses. The flu may make people cough and have a sore throat and fever. They may also have a runny or stuffy nose, feel tired, have
Influenza (Flu) What is the flu? The flu is an illness caused by flu viruses. The flu may make people cough and have a sore throat and fever. They may also have a runny or stuffy nose, feel tired, have
Pertussis (whooping cough) immunisation for pregnant women the safest way to protect yourself and your baby
 Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis (whooping cough) immunisation for pregnant women the safest way to protect yourself and your baby The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective
Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis (whooping cough) immunisation for pregnant women the safest way to protect yourself and your baby The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective
CATHOLIC CHARITIES MAINE FAMILY CHILD CARE
 CATHOLIC CHARITIES MAINE FAMILY CHILD CARE October 2012 In accordance with Federal law and U.S. Department of Agriculture policy, this institution is prohibited from discriminating on the basis of race,
CATHOLIC CHARITIES MAINE FAMILY CHILD CARE October 2012 In accordance with Federal law and U.S. Department of Agriculture policy, this institution is prohibited from discriminating on the basis of race,
Pertussis or Whooping Cough
 The Emily Center Diagnosis/Disease/Illness Este folleto se encuentra traducido al español. Solicitelo al enfermero o médico. #1336 Name of Child: Date: What is pertussis? Pertussis, also called whooping
The Emily Center Diagnosis/Disease/Illness Este folleto se encuentra traducido al español. Solicitelo al enfermero o médico. #1336 Name of Child: Date: What is pertussis? Pertussis, also called whooping
Vaccines for a Healthy Pregnancy
 Vaccines for a Healthy Pregnancy Vaccines for a Healthy Pregnancy G ALLERY I.1 Healthy Mother and Baby I II Introduction to Tutorial About Flu and Whooping Cough III Getting Vaccinated During Pregnancy:
Vaccines for a Healthy Pregnancy Vaccines for a Healthy Pregnancy G ALLERY I.1 Healthy Mother and Baby I II Introduction to Tutorial About Flu and Whooping Cough III Getting Vaccinated During Pregnancy:
Whooping cough (Pertussis) Information for you
 Whooping cough (Pertussis) Information for you Visit our website: www.nhsaaa.net All our publications are available in other formats ...Information for you...information for you...information for you.
Whooping cough (Pertussis) Information for you Visit our website: www.nhsaaa.net All our publications are available in other formats ...Information for you...information for you...information for you.
Pertussis (whooping cough) immunisation for pregnant women
 Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis (whooping cough) immunisation for pregnant women Immunisation DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH Rheynn Slaynt The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective
Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis (whooping cough) immunisation for pregnant women Immunisation DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH Rheynn Slaynt The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective
Parent s Guide to CHILDHOOD IMMUNIZATIONS
 Part One Vaccine-Preventable Part Three More Diseases About Vaccines and Childhood Vaccines 30 Parent s Guide to CHILDHOOD IMMUNIZATIONS Part 3: More About Vaccines How do vaccines work? To understand
Part One Vaccine-Preventable Part Three More Diseases About Vaccines and Childhood Vaccines 30 Parent s Guide to CHILDHOOD IMMUNIZATIONS Part 3: More About Vaccines How do vaccines work? To understand
PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH 2015 PAHAN 307 04-02-ADV Pertussis in Centre County
 PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH 2015 PAHAN 307 04-02-ADV Pertussis in Centre County DATE: 04/02/2015 TO: Health Alert Network FROM: Karen M. Murphy, PhD, RN, Acting Secretary of Health SUBJECT: DISTRIBUTION:
PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH 2015 PAHAN 307 04-02-ADV Pertussis in Centre County DATE: 04/02/2015 TO: Health Alert Network FROM: Karen M. Murphy, PhD, RN, Acting Secretary of Health SUBJECT: DISTRIBUTION:
FAQs on Influenza A (H1N1-2009) Vaccine
 FAQs on Influenza A (H1N1-2009) Vaccine 1) What is Influenza A (H1N1-2009) (swine flu) 1? Influenza A (H1N1-2009), previously known as "swine flu", is a new strain of influenza virus that spreads from
FAQs on Influenza A (H1N1-2009) Vaccine 1) What is Influenza A (H1N1-2009) (swine flu) 1? Influenza A (H1N1-2009), previously known as "swine flu", is a new strain of influenza virus that spreads from
Influenza Vaccine Frequently Asked Questions. Influenza Control Program
 Influenza Vaccine Frequently Asked Questions Influenza Control Program Influenza or the flu can be a serious contagious disease, which is spread by droplet transmission through close contact with an infected
Influenza Vaccine Frequently Asked Questions Influenza Control Program Influenza or the flu can be a serious contagious disease, which is spread by droplet transmission through close contact with an infected
Updated Recommendations for Use of Tdap in Pregnant Women
 From the Texas Department of State Health Services Immunization Branch The goal of the Vaccine Advisory is to disseminate, in a timely manner, practical information related to vaccines, vaccine-preventable
From the Texas Department of State Health Services Immunization Branch The goal of the Vaccine Advisory is to disseminate, in a timely manner, practical information related to vaccines, vaccine-preventable
Health Professionals Advice: Azithromycin now fully funded 3 December 2012
 Health Professionals Advice: Azithromycin now fully funded 3 December 2012 SITUATION UPDATE The Pertussis epidemic has continued all year, and is expected to continue throughout 2013. Between 1 January
Health Professionals Advice: Azithromycin now fully funded 3 December 2012 SITUATION UPDATE The Pertussis epidemic has continued all year, and is expected to continue throughout 2013. Between 1 January
Prevention of Pertussis Among Pregnant & Post Partum Women and Their Infants. Marilyn Michels RN MSN CIC Kathleen Curtis MS RN
 Prevention of Pertussis Among Pregnant & Post Partum Women and Their Infants Marilyn Michels RN MSN CIC Kathleen Curtis MS RN Pertussis and Adults Pertussis (whooping cough) a poorly controlled vaccine-preventable
Prevention of Pertussis Among Pregnant & Post Partum Women and Their Infants Marilyn Michels RN MSN CIC Kathleen Curtis MS RN Pertussis and Adults Pertussis (whooping cough) a poorly controlled vaccine-preventable
4/30/2013 HPV VACCINE AND NORTH DAKOTA HPV IMMUNIZATION RATES HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS (HPV) HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS HPV CONTINUED
 HPV VACCINE AND NORTH DAKOTA HPV IMMUNIZATION RATES HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS (HPV) HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS What is human papillomavirus (HPV)? HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection. There are
HPV VACCINE AND NORTH DAKOTA HPV IMMUNIZATION RATES HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS (HPV) HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS What is human papillomavirus (HPV)? HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection. There are
Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults
 Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults What is chickenpox? Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a very contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is spread easily through the
Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults What is chickenpox? Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a very contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is spread easily through the
DID YOU KNOW? A SORE THROAT CAN KILL YOUR STUDENT
 DID YOU KNOW? A SORE THROAT CAN KILL YOUR STUDENT Each year, more than 60 Fijians die of Rheumatic Heart Disease and it all starts with an untreated sore throat. TEACHING PROGRAM FOR SCHOOLS ACROSS FIJI
DID YOU KNOW? A SORE THROAT CAN KILL YOUR STUDENT Each year, more than 60 Fijians die of Rheumatic Heart Disease and it all starts with an untreated sore throat. TEACHING PROGRAM FOR SCHOOLS ACROSS FIJI
Quick Reference H1N1 Flu (swine flu)
 Quick Reference H1N1 Flu (swine flu) The United States declared a public health emergency in response to the recent reports of swine flu. UMR wants to help you understand some important facts about H1N1
Quick Reference H1N1 Flu (swine flu) The United States declared a public health emergency in response to the recent reports of swine flu. UMR wants to help you understand some important facts about H1N1
Community Health Administration
 Community Health Administration 300 North San Antonio Road Santa Barbara, CA 93110-1332 805/681-5439 FAX 805/681-5200 Takashi M. Wada, MD, MPH Director/Health Officer Anne M. Fearon Deputy Director Suzanne
Community Health Administration 300 North San Antonio Road Santa Barbara, CA 93110-1332 805/681-5439 FAX 805/681-5200 Takashi M. Wada, MD, MPH Director/Health Officer Anne M. Fearon Deputy Director Suzanne
Influenza Education Presentation Prepared by Peel Public Health 2014
 Influenza Education Presentation Prepared by Peel Public Health 2014 Disclaimer We are pleased to be able to offer you the use of our Influenza PowerPoint presentation for your use. Peel Public Health
Influenza Education Presentation Prepared by Peel Public Health 2014 Disclaimer We are pleased to be able to offer you the use of our Influenza PowerPoint presentation for your use. Peel Public Health
Plan early - get your vaccinations in time for full protection. To prepare for your trip, schedule an appointment: (910) 347-2154, option #2.
 The Onslow County Health Department Travel Clinic offers a complete line of immunizations and prescriptions to protect you while traveling abroad. The most appropriate immunizations and travel medications
The Onslow County Health Department Travel Clinic offers a complete line of immunizations and prescriptions to protect you while traveling abroad. The most appropriate immunizations and travel medications
READ THIS LEAFLET VERY CAREFULLY, AND KEEP IT IN A SAFE PLACE. FLU IS SPREADING IN IRELAND, AND THIS INFORMATION IS IMPORTANT FOR YOU AND YOUR FAMILY.
 READ THIS LEAFLET VERY CAREFULLY, AND KEEP IT IN A SAFE PLACE. FLU IS SPREADING IN IRELAND, AND THIS INFORMATION IS IMPORTANT FOR YOU AND YOUR FAMILY. Information and medical advice for the public on Pandemic
READ THIS LEAFLET VERY CAREFULLY, AND KEEP IT IN A SAFE PLACE. FLU IS SPREADING IN IRELAND, AND THIS INFORMATION IS IMPORTANT FOR YOU AND YOUR FAMILY. Information and medical advice for the public on Pandemic
Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management. March 2010
 Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management March 2010 Infectious Agent Bordetella pertussis (a bacterium) Clinical Features Infants and Young
Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management March 2010 Infectious Agent Bordetella pertussis (a bacterium) Clinical Features Infants and Young
The flu vaccination WINTER 2016/17. Who should have it and why. Flu mmunisation 2016/17
 The flu vaccination WINTER 2016/17 Who should have it and why Flu mmunisation 2016/17 The flu vaccination 1 Winter 2016/17 Helping to protect everyone, every winter This leaflet explains how you can help
The flu vaccination WINTER 2016/17 Who should have it and why Flu mmunisation 2016/17 The flu vaccination 1 Winter 2016/17 Helping to protect everyone, every winter This leaflet explains how you can help
MUMPS PUBLIC FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program MUMPS PUBLIC FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Date: April 17, 2014 DESCRIPTION OF MUMPS What is mumps? Mumps is a disease that is caused by
New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program MUMPS PUBLIC FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Date: April 17, 2014 DESCRIPTION OF MUMPS What is mumps? Mumps is a disease that is caused by
swine flu vaccination:
 swine flu vaccination: what you need to know Flu. Protect yourself and others. Contents What is swine flu?............... 3 About the swine flu vaccine....... 4 What else do I need to know?...... 8 What
swine flu vaccination: what you need to know Flu. Protect yourself and others. Contents What is swine flu?............... 3 About the swine flu vaccine....... 4 What else do I need to know?...... 8 What
PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL
 PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate the public, particularly parents of infants, about the dangers of whooping cough and the advantages of initiating immunization
PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate the public, particularly parents of infants, about the dangers of whooping cough and the advantages of initiating immunization
The Immunization Office, located in the Student Health Center, is open year round to administer needed immunizations at a nominal fee.
 Student Health Services 2815 Cates Avenue Raleigh, NC 27695-7304 919-515-2563 healthcenter.ncsu.edu The Immunization Record Form is designed to collect information about your current immunization status.
Student Health Services 2815 Cates Avenue Raleigh, NC 27695-7304 919-515-2563 healthcenter.ncsu.edu The Immunization Record Form is designed to collect information about your current immunization status.
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
 Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) What is? is a common virus that infects the linings of the airways - the nose, throat, windpipe, bronchi and bronchioles (the air passages of the lungs). RSV is found
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) What is? is a common virus that infects the linings of the airways - the nose, throat, windpipe, bronchi and bronchioles (the air passages of the lungs). RSV is found
TEMPORARY PROGRAMME PERTUSSIS VACCINATION FOR PREGNANT WOMEN
 TEMPORARY PROGRAMME PERTUSSIS VACCINATION FOR PREGNANT WOMEN Richard Smithson Neil Irvine Maureen McCartney Consultant Health Protection October 2012 Pertussis/whooping cough The disease Whooping Cough
TEMPORARY PROGRAMME PERTUSSIS VACCINATION FOR PREGNANT WOMEN Richard Smithson Neil Irvine Maureen McCartney Consultant Health Protection October 2012 Pertussis/whooping cough The disease Whooping Cough
This article is a CME/CE certified activity. To earn credit for this activity visit: http://www.medscape.org/viewarticle/750546
 1 of 6 10/10/2011 7:17 PM This article is a CME/CE certified activity. To earn credit for this activity visit: http://www.medscape.org/viewarticle/750546 CME/CE Information CME/CE Released: 09/28/2011;
1 of 6 10/10/2011 7:17 PM This article is a CME/CE certified activity. To earn credit for this activity visit: http://www.medscape.org/viewarticle/750546 CME/CE Information CME/CE Released: 09/28/2011;
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)]
![Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)] Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)]](/thumbs/27/12172665.jpg) EMA/14365/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)] Overview of disease epidemiology Diphtheria
EMA/14365/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)] Overview of disease epidemiology Diphtheria
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines August 2011
 August 2011 Pertussis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 December 2005 Case Definition
August 2011 Pertussis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 December 2005 Case Definition
FOR INFORMATION CONTACT:
 NEWS RELEASE FOR INFORMATION CONTACT: Caroline Calderone Baisley Deborah C. Travers Director of Health Director of Family Health Tel [203] 622-7836 Tel [203] 622-7854 September 10, 2014 For Immediate Release
NEWS RELEASE FOR INFORMATION CONTACT: Caroline Calderone Baisley Deborah C. Travers Director of Health Director of Family Health Tel [203] 622-7836 Tel [203] 622-7854 September 10, 2014 For Immediate Release
Tdap and MenC booster vaccines. Information for parents of children in First Year of second level school
 Tdap and MenC booster vaccines Information for parents of children in First Year of second level school Tdap and MenC booster vaccines Information for parents of children in First Year of second level
Tdap and MenC booster vaccines Information for parents of children in First Year of second level school Tdap and MenC booster vaccines Information for parents of children in First Year of second level
protect your child IMMUNIZE ON TIME, EVERY TIME. Haemophilus Influenzae Type B (Hib) Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Influenza (Flu) Disease Disease
 protect your child IMMUNIZE ON TIME, EVERY TIME. Diphtheria Haemophilus Influenzae Type B (Hib) Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Human Papillomavirus Influenza (Flu) Measles Meningococcal Disease Mumps Pertussis
protect your child IMMUNIZE ON TIME, EVERY TIME. Diphtheria Haemophilus Influenzae Type B (Hib) Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Human Papillomavirus Influenza (Flu) Measles Meningococcal Disease Mumps Pertussis
Swine Flu and Common Infections to Prepare For. Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf October 15, 2009
 Swine Flu and Common Infections to Prepare For Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf October 15, 2009 Supporters Deaf Health Community Committee Members Julia Aggas Cathie Armstrong Michael McKee Mistie
Swine Flu and Common Infections to Prepare For Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf October 15, 2009 Supporters Deaf Health Community Committee Members Julia Aggas Cathie Armstrong Michael McKee Mistie
TdaP-Booster (tee-dee-ay-pee boo-ster)
 New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information TdaP-Booster (tee-dee-ay-pee boo-ster) Tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis (acellular mono-component) vaccine (adsorbed, reduced antigen content) CONSUMER MEDICINE
New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information TdaP-Booster (tee-dee-ay-pee boo-ster) Tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis (acellular mono-component) vaccine (adsorbed, reduced antigen content) CONSUMER MEDICINE
Streptococcal Infections
 Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
Immunization Healthcare Branch. Meningococcal Vaccination Program Questions and Answers. Prepared by
 Immunization Healthcare Branch Meningococcal Vaccination Program Questions and Answers Prepared by Immunization Healthcare Branch (IHB), Defense Health Agency Last Updated: 27 Mar 06 www.vaccines.mil 877-GET-VACC
Immunization Healthcare Branch Meningococcal Vaccination Program Questions and Answers Prepared by Immunization Healthcare Branch (IHB), Defense Health Agency Last Updated: 27 Mar 06 www.vaccines.mil 877-GET-VACC
2 months Diptheria; Tetanus; Whooping Cough; Hib & Polio 1st dose Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination
 IMMUNISATIONS You may want to know if your child should have routine immunisations and whether there could be an increased risk of complications because of the heart condition. We have sought the opinions
IMMUNISATIONS You may want to know if your child should have routine immunisations and whether there could be an increased risk of complications because of the heart condition. We have sought the opinions
Whooping cough and pregnancy
 Your guide to Vaccinations Whooping cough and pregnancy What you need to know and do to help protect your baby There is a lot of whooping cough around at the moment and babies who are too young to start
Your guide to Vaccinations Whooping cough and pregnancy What you need to know and do to help protect your baby There is a lot of whooping cough around at the moment and babies who are too young to start
Tuberculosis: FAQs. What is the difference between latent TB infection and TB disease?
 Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
APIC Practice Guidance Committee: Implementation Insights Prevention & Control of Pertussis
 1275 K Street, NW, Suite 1000 Washington, DC 20005-4006 Phone: 202/789-1890 Fax: 202/789-1899 [email protected] www.apic.org APIC Practice Guidance Committee: Implementation Insights Prevention & Control
1275 K Street, NW, Suite 1000 Washington, DC 20005-4006 Phone: 202/789-1890 Fax: 202/789-1899 [email protected] www.apic.org APIC Practice Guidance Committee: Implementation Insights Prevention & Control
A Guide to Your Baby s Care The First Year
 A Guide to Your Baby s Care The First Year A Guide to Your Baby s Care The First Year What s Inside Congratulations! Your baby is finally here. Having a baby is a special gift. You ll want to take good
A Guide to Your Baby s Care The First Year A Guide to Your Baby s Care The First Year What s Inside Congratulations! Your baby is finally here. Having a baby is a special gift. You ll want to take good
Tdap booster vaccine for Health Care Workers Frequently Asked Questions for Health Professionals
 Tdap booster vaccine for Health Care Workers Frequently Asked Questions for Health Professionals NEW items in 2013 Immunisation Guidelines for Ireland are in RED What is Tdap booster vaccine? Tdap is a
Tdap booster vaccine for Health Care Workers Frequently Asked Questions for Health Professionals NEW items in 2013 Immunisation Guidelines for Ireland are in RED What is Tdap booster vaccine? Tdap is a
Explanation of Immunization Requirements
 Explanation of Immunization Requirements CONTENTS Hepatitis A... 2 Hepatitis B... 3 Influenza... 4 Measles (Rubella), Mumps, and Rubella (MMR)... 5 Pertussis (Tdap)... 6 Tuberculosis (TB) Test... 7 Varicella/Chicken
Explanation of Immunization Requirements CONTENTS Hepatitis A... 2 Hepatitis B... 3 Influenza... 4 Measles (Rubella), Mumps, and Rubella (MMR)... 5 Pertussis (Tdap)... 6 Tuberculosis (TB) Test... 7 Varicella/Chicken
IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ
 PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION combined hepatitis A (inactivated) and hepatitis B (recombinant) vaccine This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when was approved for sale
PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION combined hepatitis A (inactivated) and hepatitis B (recombinant) vaccine This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when was approved for sale
Pertussis. Chapter 15 Pertussis. August 2015. Pertussis. Vaccine introduced in 1952/53 (DTP) and 1996 (DTaP) NOTIFIABLE
 Chapter 15 15 Vaccine introduced in 1952/53 (DTP) and 1996 (DTaP) NOTIFIABLE In some circumstances, advice in these guidelines may differ from that in the Summary of Product Characteristics of the vaccines.
Chapter 15 15 Vaccine introduced in 1952/53 (DTP) and 1996 (DTaP) NOTIFIABLE In some circumstances, advice in these guidelines may differ from that in the Summary of Product Characteristics of the vaccines.
H1N1 Flu Vaccine Available to All Virginia Beach City Public Schools Students
 V i r g i n i a B e a c h C i t y P u b l i c S c h o o l s apple-a-day F o r O u r F a m i l y o f I n t e r e s t e d C i t i z e n s Special Edition H1N1 Flu Vaccine Available to All Virginia Beach
V i r g i n i a B e a c h C i t y P u b l i c S c h o o l s apple-a-day F o r O u r F a m i l y o f I n t e r e s t e d C i t i z e n s Special Edition H1N1 Flu Vaccine Available to All Virginia Beach
Vaccinations and Spina Bifida and Hydrocephalus
 shinecharity.org.uk [email protected] 42 Park Road Peterborough PE1 2UQ 01733 555988 Vaccinations and Spina Bifida and Hydrocephalus Vaccines are made from parts of bacteria or viruses that cause
shinecharity.org.uk [email protected] 42 Park Road Peterborough PE1 2UQ 01733 555988 Vaccinations and Spina Bifida and Hydrocephalus Vaccines are made from parts of bacteria or viruses that cause
Whooping cough and pregnancy
 Whooping cough and pregnancy Your questions answered on how to help protect your baby the safest way to protect yourself and your baby There is a lot of whooping cough around at the moment and babies who
Whooping cough and pregnancy Your questions answered on how to help protect your baby the safest way to protect yourself and your baby There is a lot of whooping cough around at the moment and babies who
Immunization FAQs Required Vaccines for 2014-15 School Year
 Immunization Schedules and Documentation Immunization FAQs Required Vaccines for 2014-15 School Year 1. Question: What is the difference between the recommended immunization schedule and the Colorado School
Immunization Schedules and Documentation Immunization FAQs Required Vaccines for 2014-15 School Year 1. Question: What is the difference between the recommended immunization schedule and the Colorado School
BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC
 BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC HIV What are HIV and AIDS? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV is
BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC HIV What are HIV and AIDS? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV is
What Is. Norovirus? Learning how to control the spread of norovirus. Web Sites
 Web Sites Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) http://www.cdc.gov/norovirus/index.html Your Local Health Department http://www.azdhs.gov/diro/lhliaison/countymap.htm What Is Ocument dn Norovirus?
Web Sites Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) http://www.cdc.gov/norovirus/index.html Your Local Health Department http://www.azdhs.gov/diro/lhliaison/countymap.htm What Is Ocument dn Norovirus?
PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CLOSE CONTACTS OF PERTUSSIS INFECTION
 PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CLOSE CONTACTS OF PERTUSSIS INFECTION Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL PROTOCOL NO. 1.03 Policy Group Infection Control Committee
PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CLOSE CONTACTS OF PERTUSSIS INFECTION Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL PROTOCOL NO. 1.03 Policy Group Infection Control Committee
MEDICATION GUIDE STELARA
 MEDICATION GUIDE STELARA (stel ar a) (ustekinumab) Injection What is the most important information I should know about STELARA? STELARA is a medicine that affects your immune system. STELARA can increase
MEDICATION GUIDE STELARA (stel ar a) (ustekinumab) Injection What is the most important information I should know about STELARA? STELARA is a medicine that affects your immune system. STELARA can increase
MINISTRY OF HEALTH PANDEMIC INFLUENZA A / H1N1 2009 VACCINE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 Government of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago MINISTRY OF HEALTH PANDEMIC INFLUENZA A / H1N1 2009 VACCINE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Influenza vaccines are one of the most effective ways to protect
Government of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago MINISTRY OF HEALTH PANDEMIC INFLUENZA A / H1N1 2009 VACCINE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Influenza vaccines are one of the most effective ways to protect
Useful contacts. Call 0800 1 513 513 to hear the latest information on swine flu. England: www.nhs.uk www.direct.gov.uk/swineflu
 Useful contacts Call 0800 1 513 513 to hear the latest information on swine flu. England: www.nhs.uk www.direct.gov.uk/swineflu Scotland: www.nhs24.com Wales: www.nhsdirect.wales.nhs.uk www.wales.gov.uk/health
Useful contacts Call 0800 1 513 513 to hear the latest information on swine flu. England: www.nhs.uk www.direct.gov.uk/swineflu Scotland: www.nhs24.com Wales: www.nhsdirect.wales.nhs.uk www.wales.gov.uk/health
MEDICATION GUIDE. PROCRIT (PRO KRIT) (epoetin alfa)
 MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
GENERAL INFORMATION. Hepatitis B Foundation - Korean Chapter Pg. 3 www.hepb.org
 GENERAL INFORMATION What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is the world's most common liver infection that can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which attacks and
GENERAL INFORMATION What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is the world's most common liver infection that can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which attacks and
Staying on Track with TUBERCULOSIS. Medicine
 Staying on Track with TB TUBERCULOSIS Medicine What s Inside: Read this brochure to learn about TB and what you can do to get healthy. Put it in a familiar place to pull out and read when you have questions.
Staying on Track with TB TUBERCULOSIS Medicine What s Inside: Read this brochure to learn about TB and what you can do to get healthy. Put it in a familiar place to pull out and read when you have questions.
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Vaccination against pertussis (Whooping cough) for pregnant women- 2014. Information for healthcare professionals
 Vaccination against pertussis (Whooping cough) for pregnant women- 2014 Information for healthcare professionals About Public Health England Public Health England s mission is to protect and improve the
Vaccination against pertussis (Whooping cough) for pregnant women- 2014 Information for healthcare professionals About Public Health England Public Health England s mission is to protect and improve the
RSV infection. Information about RSV and how you can reduce the risk of your infant developing a severe infection.
 RSV infection Information about RSV and how you can reduce the risk of your infant developing a severe infection. What is RSV? RSV is one of the most common respiratory viruses and is spread easily. By
RSV infection Information about RSV and how you can reduce the risk of your infant developing a severe infection. What is RSV? RSV is one of the most common respiratory viruses and is spread easily. By
Planning for 2009 H1N1 Influenza. A Preparedness Guide for Small Business
 09 Planning for 2009 H1N1 Influenza A Preparedness Guide for Small Business Table of Contents 02 Foreword 03 Introduction 04 How to Write Your Plan 05 Keeping Healthy: 10 Tips for Businesses 06 Keeping
09 Planning for 2009 H1N1 Influenza A Preparedness Guide for Small Business Table of Contents 02 Foreword 03 Introduction 04 How to Write Your Plan 05 Keeping Healthy: 10 Tips for Businesses 06 Keeping
Neiko Rust, RN Northern Indiana Immunization Task Force St. Joseph County Health Department - Mishawaka
 Neiko Rust, RN Northern Indiana Immunization Task Force St. Joseph County Health Department - Mishawaka Purpose Statement: Address barriers related to immunizations, reporting of immunizations, provide
Neiko Rust, RN Northern Indiana Immunization Task Force St. Joseph County Health Department - Mishawaka Purpose Statement: Address barriers related to immunizations, reporting of immunizations, provide
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
Anthrax vaccine side-effects
 Anthrax vaccine side-effects What are the risks from anthrax vaccine? Like any medicine, a vaccine could cause a serious problem, such as a severe allergic reaction. Anthrax is a very serious disease,
Anthrax vaccine side-effects What are the risks from anthrax vaccine? Like any medicine, a vaccine could cause a serious problem, such as a severe allergic reaction. Anthrax is a very serious disease,
