Instrumented in situ posterolateral fusion for low-grade lytic spondylolisthesis in adults
|
|
|
- Clarence Thompson
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, ORIGINAL STUDY Instrumented in situ posterolateral fusion for low-grade lytic spondylolisthesis in adults Mohamed A. EL MASRY, Walaa I. EL ASSUITY, Youssry K. EL HAWARY, Christopher R. WEATHERLEY From Royal Devon & Exeter Hospital, Exeter, United Kingdom and Nasser Institute, Cairo, Egypt. Lytic olisthesis is an accepted cause of low back pain and may also be associated with leg pain. When conservative treatment fails, operative management with fusion and if necessary decompression is considered. Most reports regarding surgical management in the literature relate to children or adolescents. This paper reviews 75 adult cases treated by in situ pedicular fixation and posterolateral fusion with simultaneous decompression in 55 cases. The mean follow-up was 72 months. Ninety-six percent of the cases had a satisfactory clinical outcome, and this correlates closely with a solid fusion. This approach therefore appears to be safe and successful in the treatment of symptomatic low-grade lytic spondylolisthesis in adults. INTRODUCTION Lytic olisthesis is a common condition, which occurs most frequently in the lower lumbar spine. It is an accepted cause of back pain and it may also be associated with leg pain. If the symptoms justify it, the accepted management is fusion across the level of the olisthesis. Much has been written about the surgical management in children and adolescents but much less in relation to adult cases. This may be due to the fact that the picture is complicated in adults in whom degenerative changes may also be present at contiguous levels and the pain source is less clear. The extent of the slip (olisthesis) is usually graded using the Meyerding classification (8) in which the displacement of one vertebral body on another is divided into four equal parts. Grades I and II, which represent up to a 25% and 50% displacement and which cover the majority of cases, are referred to as low-grade slips. The initial management of the condition is conservative. When this is deemed to have failed, surgery is considered. On the assumption that the back pain relates to the level of the olisthesis, it is our practice to do a fusion across this level. Where, however, an MRI scan demonstrates degenerative changes in discs at contiguous levels and these levels cannot be excluded as a coincidental pain source or as a possible pain source post-fusion, these levels are also included in the fusion. Mohamed A. El Masry, MSc (Orth), MD, MRCS, Spine Fellow. Christopher R. Weatherley, MD, FRCS, FRCS Ed, FRCS Ed (Orth), Consultant Spinal Surgeon. Royal Devon & Exeter Hospital, Exeter, United Kingdom. Walaa I. El Assuity, MSc (Orth), MD. Spine Fellow. Youssry K. El Hawary, MSc (Orth), MD, Consultant Spinal Surgeon. Nasser Institute, Cairo, Egypt. Correspondence : Mohamed A. El Masry, 175 Warren House, Beckford Close, London W14 8TR, United Kingdom. [email protected]. 2005, Acta Orthopædica Belgica.
2 84 M. A. EL MASRY, W. I. EL ASSUITY, Y. K. EL HAWARY, C. R. WEATHERLEY Leg pain when present in these cases is either radicular or referred. If it is radicular, it will usually extend below the knee on the basis that the commonest sites for olisthesis in the lumbar spine is at the lowest two levels, L4 and L5. Nerve compression in these cases usually occurs subjacent to the lysis and pseudarthosis and will thus involve either the L4 or L5 nerve roots. Surgical management in these cases involves simultaneous decompression of the involved root. By contrast, referred pain does not extend into the lower leg and resolves with stabilisation of the failed motion segment or segments. If there is any doubt, however, about whether the leg pain is radicular or referred, decompression is performed. Irrespective of whether the leg pain is unilateral or bilateral we always do a bilateral nerve root decompression and use a procedure that preserves the mid-line structures (12). There are many ways to carry out a spinal fusion, but simpler methods carry the least complications. It is received wisdom that simultaneous instrumentation carries a greater chance of achieving fusion, and pedicular fixation is the technique most commonly used. On this basis, our operative approach involves a bilateral posterolateral fusion with pedicular fixation. The posterior approach to the spine also allows for simultaneous nerve root decompression when necessary. The purpose of this study was to review the outcome of adopting the above rationale of surgical management. PATIENTS AND METHODS Between 1993 and 1998, 25 consecutive adult patients presenting with back and leg pain were treated operatively for a low-grade lytic spondylolisthesis on the basis of the philosophy outlined above. Once we had assessed the outcome in these patients, a further 50 were evaluated and operated on between 1998 and 2000 using the same surgical rationale. This study, which comes from two centers, is therefore part retrospective (n = 25) and part prospective (n = 50). All patients were assessed with a full history and detailed clinical evaluation and had plain radiographs of the lumbar spine. Each patient also had an MRI of the Table I. Level of spondylolisthesis Level Number of Patients Single level L3/4 4 L4/5 24 L5/S1 45 Two-level L4/5 and L5/S1 2 lumbar spine to clarify the questions of disc degeneration and, where relevant, nerve compression. Every patient had a history of low back pain with or without leg pain and had had persistent symptoms for at least six months despite conservative treatment. All were judged to have a significant reduction in their quality of life. All patients included in the study were diagnosed with low-grade lytic spondylolisthesis. Patients were excluded from the study if they had had previous lumbar spine surgery, were involved in medico-legal claims or had other spine or hip pathology which might have contributed to their symptoms. There were 31 females and 44 males. The average age at surgery was 41 years (range : 21 to 63) and the average duration of symptoms prior to surgery was 23 months (range : 6 to 60). Seventy three patients had a single-level olisthesis and two patients had a two-level olisthesis (table I). The degree of slip was assessed using Meyerding s classification (8) : 58 patients were diagnosed with grade 1 and 17 with grade 2 slip. All patients underwent in situ fusion using autogenous iliac graft and pedicular fixation of the level of the olisthesis. We did not attempt to reduce the slip in any case, thereby avoiding possible intra-operative neurological damage that can be secondary to this procedure. The fusion was also extended to include any contiguous level shown to be degenerative on MRI. In practice, of the 73 patients who had a one-level olisthesis, 60 (82%) had a one-level fusion, 12 (17%) a twolevel fusion and one patient had a three-level fusion. Of the two cases who had a two-level olisthesis, one had a two-level fusion and one a three-level fusion. A simultaneous bilateral nerve root decompression was carried out in the 55 patients (73%) who presented with suspected or probable radicular symptoms and signs. All patients were followed up clinically and assessed using the criteria reported in 1995 by Ricciardi et al (10). This involves an assessment of the presence or absence of symptoms, use of analgesics, patients level of function and radiological evidence of fusion. On this basis,
3 LOW GRADE LYTIC SPONDYLOLISTHESIS IN ADULTS 85 the postoperative results were graded as poor, fair, good or excellent. The radiological results were also assessed separately using the criteria reported by Lenke et al (7) for posterolateral fusion. Four grades designated A, B, C and D are described in which, depending on the radiological appearance, A and B equate to a solid fusion. Grade C represents a questionable fusion and D a pseudarthosis. Patients were seen routinely at three, six, nine, twelve months and then yearly following their surgery. The minimum postoperative follow-up was three years, apart from two patients who were lost to follow-up one year post-surgery. The mean follow-up was 72 months (range : 3 to 9 years). RESULTS The mean operating time was 2.5 hours (range : 2 to 4) and the mean external blood loss was 850 ml (range : 300 to 2,300). The mean hospital stay was 8 days (range : 5 to 16). There were no intra-operative problems and no neurological complications. Two patients developed postoperative superficial wound infections, which resolved with antibiotics alone, and one had a deep wound infection which resolved after treatment with antibiotics and debridement of the wound. Using the Ricciardi criteria for clinical outcome (10), 51 cases were graded as excellent, 21 as good, one patient as fair and two as poor. Considering excellent and good results to be satisfactory, 72 of the cases (96%) were adjudged to have a satisfactory clinical outcome. Assessing the fusion using the criteria reported by Lenke et al (7), 71 of the 75 cases (95%) were assessed to be Grade A or B, in other words consistent with a solid fusion. The remaining four cases were assessed as Grade D, that is to say they had a pseudarthrosis. Case Study A 21-year-old electrician presented with a twoyear history of worsening low back pain, without leg pain, unresponsive to conservative treatment. Plain radiographs revealed a Grade I lytic olisthesis of L5 (fig 1). An MRI scan of his lumbar spine showed disc degeneration at the L5/S1 level only Fig. 1. Pre-operative radiograph shows a Grade I lytic olisthesis of L5. (fig 2). He had an in situ bilateral posterolateral (alar transverse) fusion with pedicular fixation. At last follow-up, he was judged to have an excellent clinical outcome which correlated with a solid fusion (fig 3 a, b). DISCUSSION We have shown in this series that 82% of cases involved fusion of only the level of the olisthesis, and all but one of the others had a two-level fusion. These figures add credence to the notion that the principal pain source in these cases relates to the level of the olisthesis. Regardless of the problems of dealing with coincidental degenerative levels, the decision in the majority of cases about the level of fusion is straightforward. Other reports have made the case for fusion in low back pain (2) and for fusion in the management of a lytic olisthesis (9).
4 86 M. A. EL MASRY, W. I. EL ASSUITY, Y. K. EL HAWARY, C. R. WEATHERLEY a Fig. 2. An MRI scan shows disc degeneration at the L5/S1 level only. In cases of spondylolisthesis presenting also with radiculopathy, a simultaneous nerve root decompression is advocated (1, 3, 4). The incidence of a simultaneous decompression in 73% of our cases is probably of a high order. This relates to the inclusion of cases in which root irritation/compression could not be excluded and it was deemed prudent to add a decompression at the time of operation rather than regret its exclusion at subsequent follow-up. As the decompression was not associated in any case with neurological problems, there would seem to be no contra-indication to this approach even if its adoption was unnecessary in some cases. Another surgical option which includes a supplemental posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) has been used in the treatment of patients diagnosed with lytic spondylolisthesis. The b Fig. 3. a and b) Postoperative radiographs (2.5 years postsurgery) show a solid bilateral alar transverse fusion.
5 LOW GRADE LYTIC SPONDYLOLISTHESIS IN ADULTS 87 advantages of adopting this procedure are believed to be related to the support provided to the anterior column by the interbody graft, which may then improve the fusion rate and endurance of the construct. In a recent comparative study the clinical, functional, and radiographic outcomes of thirtyfive consecutive patients diagnosed with lytic spondylolisthesis were assessed following either a posterolateral instrumented fusion (18 patients) or posterior lumbar interbody fusion (17 patients). No statistical differences were demonstrated in terms of neurological improvement, or functional outcome, or in terms of fusion rate (6). A posterior lumbar interbody fusion is, however, a more demanding procedure and increases costs and risks of the intervention. The comparison of the clinical outcome scores with the assessment of a radiological fusion is of interest. Of the 75 cases, 72 were judged to have a satisfactory outcome (excellent or good results) and three an unsatisfactory outcome (one fair and two poor). Radiologically there were non-unions in four patients. All three cases with an unsatisfactory clinical outcome had a non-union. This finally shows a nice correlation of clinical outcome with a solid fusion. Of the four cases of non-union, two subsequently had revision posterior surgery with re-instrumentation and fusion and both proceeded to fusion with a good clinical outcome. One of the non-union cases had a good clinical outcome and therefore had no further surgery. The fourth case with an unsatisfactory clinical outcome elected to live with his remaining symptoms. We believe that the results reported here compare very favourably with the best reported in the literature (5, 10, 11). On this basis we would advocate the approach laid out here as a satisfactory and safe way of dealing with a symptomatic, low-grade adult lytic spondylolisthesis. REFERENCES 1. Carragee EJ. Single level posterolateral arthrodesis with or without posterior decompression for the treatment of isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults. A prospective randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg 1997 ; 79-A : Fritzel P, Hagg O, Wessbert P et al. Lumbar fusion versus non surgical treatment for chronic low back pain. Spine 2001 ; 26 : Hanley EN, Levy JA. Surgical treatment of isthmic lumbosacral spondylolisthesis. Analysis of variables influencing results. Spine 1989 ; 14 : Johnson LP, Naska RJ, Dunham WK. Surgical management of isthmic spondylolisthesis Spine 1988 ; 13 : Kim NH, Lee JW, Graziano GP. Anterior interbody fusion versus posterolateral fusion with transpedicular fixation for isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults. A comparison of clinical results. Spine 1999 ; 24 : La Rosa G, Conti A, Cacciola F et al. Pedicle screw fixation for isthmic spondylolisthesis : does posterior lumbar interbody fusion improve outcome over posterolateral fusion? J Neurosurg 2003 ; 99 (Suppl 2) : Lenke LG, Bridwell KH. Adult spondylolisthesis with lysis. In : Bridwell KH and DeWald RL (eds) : Textbook of Spinal Surgery 2 nd Edition, Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia pp Meyerding HW. Spondylolisthesis : Surgical treatment and results. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1932 ; 54 : Moller H, Helund R. Surgery versus conservative management in adult isthmic spondylolisthesis. A prospective randomized study : Part 1. Spine 2000 ; 25 : Ricciardi JE, Pflueger PC, Isaza JE, Whitecloud TS III. Transpedicular fixation for the treatment of isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults. Spine 1995 ; 20 : Stambough JL. Lumbosacral instrumented fusion : Analysis of 124 consecutive cases. J Spinal Disord 1999 ; 12 : Weatherley CR, Farrington WJ, Lin Sin Chow G et al. Segmental spinal decompression, a mid-line preserving operation for lumbar spinal stenosis operative technique and results. J Bone Joint Surg 2004 ; 86-B (Suppl 2) : 114.
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients
 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients Lukas P. Zebala, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopaedic and Neurological Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients Lukas P. Zebala, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopaedic and Neurological Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of
Spinal Surgery 2. Teaching Aims. Common Spinal Pathologies. Disc Degeneration. Disc Degeneration. Causes of LBP 8/2/13. Common Spinal Conditions
 Teaching Aims Spinal Surgery 2 Mr Mushtaque A. Ishaque BSc(Hons) BChir(Cantab) DM FRCS FRCS(Ed) FRCS(Orth) Hunterian Professor at The Royal College of Surgeons of England Consultant Orthopaedic Spinal
Teaching Aims Spinal Surgery 2 Mr Mushtaque A. Ishaque BSc(Hons) BChir(Cantab) DM FRCS FRCS(Ed) FRCS(Orth) Hunterian Professor at The Royal College of Surgeons of England Consultant Orthopaedic Spinal
visualized. The correct level is then identified again. With the use of a microscope and
 SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
Low Back Pain (LBP) Prevalence. Low Back Pain (LBP) Prevalence. Lumbar Fusion: Where is the Evidence?
 15 th Annual Cleveland Clinic Pain Management Symposium Sarasota, Florida Lumbar Fusion: Where is the Evidence? Gordon R. Bell, M.D. Director, Cleveland Clinic Low Back Pain (LBP) Prevalence Lifetime prevalence:
15 th Annual Cleveland Clinic Pain Management Symposium Sarasota, Florida Lumbar Fusion: Where is the Evidence? Gordon R. Bell, M.D. Director, Cleveland Clinic Low Back Pain (LBP) Prevalence Lifetime prevalence:
Surgical Guideline for Lumbar Fusion (Arthrodesis)
 I. Introduction Surgical Guideline for Lumbar Fusion (Arthrodesis) The purpose of this guideline is: A. To provide utilization review staff with the information necessary to make recommendations about
I. Introduction Surgical Guideline for Lumbar Fusion (Arthrodesis) The purpose of this guideline is: A. To provide utilization review staff with the information necessary to make recommendations about
Subject: BlueCross BlueShield of North Carolina Lumbar Spine Fusion Surgery Notification
 , 2010 Don W. Bradley, M.D. Senior Vice President, Healthcare & Chief Medical Officer Blue Cross and Blue Shield of North Carolina 5901 Chapel Hill Road Durham, NC 27707 Subject: BlueCross BlueShield of
, 2010 Don W. Bradley, M.D. Senior Vice President, Healthcare & Chief Medical Officer Blue Cross and Blue Shield of North Carolina 5901 Chapel Hill Road Durham, NC 27707 Subject: BlueCross BlueShield of
The outcome of Microscopic Selective Decompression of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.28, No.4, December 2006 The outcome of Microscopic Selective Decompression of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis A.Aziz Mohammed, CABS, FRCS (Ortho, Tr)* Tariq El Kalifa,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.28, No.4, December 2006 The outcome of Microscopic Selective Decompression of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis A.Aziz Mohammed, CABS, FRCS (Ortho, Tr)* Tariq El Kalifa,
Nonoperative Management of Herniated Cervical Intervertebral Disc With Radiculopathy. Spine Volume 21(16) August 15, 1996, pp 1877-1883
 Nonoperative Management of Herniated Cervical Intervertebral Disc With Radiculopathy 1 Spine Volume 21(16) August 15, 1996, pp 1877-1883 Saal, Joel S. MD; Saal, Jeffrey A. MD; Yurth, Elizabeth F. MD FROM
Nonoperative Management of Herniated Cervical Intervertebral Disc With Radiculopathy 1 Spine Volume 21(16) August 15, 1996, pp 1877-1883 Saal, Joel S. MD; Saal, Jeffrey A. MD; Yurth, Elizabeth F. MD FROM
1 REVISOR 5223.0070. (4) Pain associated with rigidity (loss of motion or postural abnormality) or
 1 REVISOR 5223.0070 5223.0070 MUSCULOSKELETAL SCHEDULE; BACK. Subpart 1. Lumbar spine. The spine rating is inclusive of leg symptoms except for gross motor weakness, bladder or bowel dysfunction, or sexual
1 REVISOR 5223.0070 5223.0070 MUSCULOSKELETAL SCHEDULE; BACK. Subpart 1. Lumbar spine. The spine rating is inclusive of leg symptoms except for gross motor weakness, bladder or bowel dysfunction, or sexual
ISPI Newsletter Archive Lumbar Spine Surgery
 ISPI Newsletter Archive Lumbar Spine Surgery January 2005 Effects of Charite Artificial Disc on the Implanted and Adjacent Spinal Segments Mechanics Using a Hybrid Testing Protocol Spine. 30(24):2755-2764,
ISPI Newsletter Archive Lumbar Spine Surgery January 2005 Effects of Charite Artificial Disc on the Implanted and Adjacent Spinal Segments Mechanics Using a Hybrid Testing Protocol Spine. 30(24):2755-2764,
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS?
 SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
Spinal Surgery Functional Status and Quality of Life Outcome Specifications 2015 (01/01/2013 to 12/31/2013 Dates of Procedure) September 2014
 Description Methodology For patients ages 18 years and older who undergo a lumbar discectomy/laminotomy or lumbar spinal fusion procedure during the measurement year, the following measures will be calculated:
Description Methodology For patients ages 18 years and older who undergo a lumbar discectomy/laminotomy or lumbar spinal fusion procedure during the measurement year, the following measures will be calculated:
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: lumbar_spine_fusion_surgery 9/2010 5/2015 5/2016 5/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Low back pain
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: lumbar_spine_fusion_surgery 9/2010 5/2015 5/2016 5/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Low back pain
DUKE ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY GOALS AND OBJECTIVES SPINE SERVICE
 GOALS AND OBJECTIVES PATIENT CARE Able to perform a complete musculoskeletal and neurologic examination on the patient including cervical spine, thoracic spine, and lumbar spine. The neurologic examination
GOALS AND OBJECTIVES PATIENT CARE Able to perform a complete musculoskeletal and neurologic examination on the patient including cervical spine, thoracic spine, and lumbar spine. The neurologic examination
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression
 X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 5: 567-571, 2013
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 5: 567-571, 2013 Treatment of multilevel degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis with spondylolisthesis using a combination of microendoscopic discectomy and minimally
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 5: 567-571, 2013 Treatment of multilevel degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis with spondylolisthesis using a combination of microendoscopic discectomy and minimally
Value Analysis Brief MIS Lateral Approach to Interbody Fusion
 Value Analysis Brief MIS Lateral Approach to Interbody Fusion Methods This value analysis brief presents information on the clinical and economic benefits of the minimally invasive lateral approach to
Value Analysis Brief MIS Lateral Approach to Interbody Fusion Methods This value analysis brief presents information on the clinical and economic benefits of the minimally invasive lateral approach to
Advances In Spine Care. James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery
 Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Direct Lateral Interbody Fusion A Minimally Invasive Approach to Spinal Stabilization
 APPROVED IRN10389-1.1-04 Direct Lateral Interbody Fusion A Minimally Invasive Approach to Spinal Stabilization Because it involves accessing the spine through the patient s side, the Direct Lateral approach
APPROVED IRN10389-1.1-04 Direct Lateral Interbody Fusion A Minimally Invasive Approach to Spinal Stabilization Because it involves accessing the spine through the patient s side, the Direct Lateral approach
Information for the Patient About Surgical
 Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS OBSERVATIONS, EVIDENCE, AND TRENDS FULILLING THE UNMET CLINICAL NEED WRITTEN BY: HALLETT MATHEWS, MD, MBA
 LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS OBSERVATIONS, EVIDENCE, AND TRENDS FULILLING THE UNMET CLINICAL NEED WRITTEN BY: HALLETT MATHEWS, MD, MBA Overview of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Spine stabilization, which has equated
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS OBSERVATIONS, EVIDENCE, AND TRENDS FULILLING THE UNMET CLINICAL NEED WRITTEN BY: HALLETT MATHEWS, MD, MBA Overview of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Spine stabilization, which has equated
White Paper: Reducing Utilization Concerns Regarding Spinal Fusion and Artificial Disc Implants
 White Paper: Reducing Utilization Concerns Regarding Spinal Fusion and Artificial Disc Implants For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Back pain is one of the most
White Paper: Reducing Utilization Concerns Regarding Spinal Fusion and Artificial Disc Implants For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Back pain is one of the most
Title: Interspinous Process Decompression with the X-Stop Device for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Retrospective Review. Authors: Jennifer R.
 Title: Interspinous Process Decompression with the X-Stop Device for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Retrospective Review. Authors: Jennifer R. Madonia-Barr, MS, PA-C and David L. Kramer, MD Institution: Connecticut
Title: Interspinous Process Decompression with the X-Stop Device for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Retrospective Review. Authors: Jennifer R. Madonia-Barr, MS, PA-C and David L. Kramer, MD Institution: Connecticut
SPINE SERVICE ROTATION ROTATION SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES (RSO) DEPT. OF ORTHOPEDICS AND PHYSICAL REHABILITATION UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS
 SPINE SERVICE ROTATION ROTATION SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES (RSO) DEPT. OF ORTHOPEDICS AND PHYSICAL REHABILITATION UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS The purpose of this RSO is to outline and clarify the objectives of
SPINE SERVICE ROTATION ROTATION SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES (RSO) DEPT. OF ORTHOPEDICS AND PHYSICAL REHABILITATION UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS The purpose of this RSO is to outline and clarify the objectives of
Single-Level Lumbar Spine Fusion: A Comparison of Anterior and Posterior Approaches
 Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques Vol. 15, No. 5, pp. 355 361 2002 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Single-Level Lumbar Spine Fusion: A Comparison of Anterior and Posterior Approaches
Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques Vol. 15, No. 5, pp. 355 361 2002 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Single-Level Lumbar Spine Fusion: A Comparison of Anterior and Posterior Approaches
Motion Preservation. Hansen Yuan, MD President, Spine Arthroplasty Society
 Motion Preservation Procedure Codes Hansen Yuan, MD President, Spine Arthroplasty Society Who are we? The Spine Arthroplasty Society (SAS) is a group of medical and associated specialists devoted to the
Motion Preservation Procedure Codes Hansen Yuan, MD President, Spine Arthroplasty Society Who are we? The Spine Arthroplasty Society (SAS) is a group of medical and associated specialists devoted to the
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery. David H Strothman, M.D.
 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery David H Strothman, M.D. The Lumbar Spine Lumbar Disc Annulus Fibrosus High collagen content Concentric layers of intertwined annular bands Nucleus Pulposus Hydrated Proteoglycans
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery David H Strothman, M.D. The Lumbar Spine Lumbar Disc Annulus Fibrosus High collagen content Concentric layers of intertwined annular bands Nucleus Pulposus Hydrated Proteoglycans
Hybrid Technique for Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Combination of Open Decompression and Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation
 135 2013 Chinese Orthopaedic Association and Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Hybrid Technique for Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Combination of Open Decompression and Percutaneous
135 2013 Chinese Orthopaedic Association and Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Hybrid Technique for Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Combination of Open Decompression and Percutaneous
Employees Compensation Appeals Board
 U. S. DEPARTMENT OF LABOR Employees Compensation Appeals Board In the Matter of DEBORAH R. EVANS and U.S. POSTAL SERVICE, POST OFFICE, Orlando, FL Docket No. 02-1888; Submitted on the Record; Issued December
U. S. DEPARTMENT OF LABOR Employees Compensation Appeals Board In the Matter of DEBORAH R. EVANS and U.S. POSTAL SERVICE, POST OFFICE, Orlando, FL Docket No. 02-1888; Submitted on the Record; Issued December
How To Understand The Anatomy Of A Lumbar Spine
 Sciatica: Low back and Leg Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Options Presented by Devesh Ramnath, MD Orthopaedic Associates Of Dallas Baylor Spine Center Sciatica Compression of the spinal nerves in the back
Sciatica: Low back and Leg Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Options Presented by Devesh Ramnath, MD Orthopaedic Associates Of Dallas Baylor Spine Center Sciatica Compression of the spinal nerves in the back
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery What is it and how will it benefit patients?
 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery What is it and how will it benefit patients? Dr Raoul Pope MBChB, FRACS, Neurosurgeon and Minimally Invasive Spine Surgeon Concord Hospital and Mater Private Hospital Sydney
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery What is it and how will it benefit patients? Dr Raoul Pope MBChB, FRACS, Neurosurgeon and Minimally Invasive Spine Surgeon Concord Hospital and Mater Private Hospital Sydney
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Introduction Lumbar spinal stenosis is defined as reduction in the diameter of the spinal canal, lateral nerve canals or neural foramina. The stenosis may involve multiple level
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Introduction Lumbar spinal stenosis is defined as reduction in the diameter of the spinal canal, lateral nerve canals or neural foramina. The stenosis may involve multiple level
Lumbar Decompression and Stabilisation for Degenerative Spondylolisthesis
 Lumbar Decompression and Stabilisation for Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 5: August 2014 Review date: July 2017 Following your recent investigations and consultation
Lumbar Decompression and Stabilisation for Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 5: August 2014 Review date: July 2017 Following your recent investigations and consultation
Patient Information. Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression. Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust
 Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Reference Number: TO 05 004 004 (version date: June 2015) Introduction
Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Reference Number: TO 05 004 004 (version date: June 2015) Introduction
Complications in Adult Deformity Surgery
 Complications in Adult Deformity Surgery Proximal Junctional Kyphosis: Thoracolumbar and Cervicothoracic Sigurd Berven, MD Professor in Residence UC San Francisco Disclosures Research/Institutional Support:
Complications in Adult Deformity Surgery Proximal Junctional Kyphosis: Thoracolumbar and Cervicothoracic Sigurd Berven, MD Professor in Residence UC San Francisco Disclosures Research/Institutional Support:
Update to the Treatment of Degenerative Cervical Disc Disease
 Update to the Treatment of Degenerative Cervical Disc Disease Michael Lynn, MD Neurosurgeon, Southeastern Neurosurgical & Spine Institute Adjunct Assistant Clinical Professor of Bioengineering, Clemson
Update to the Treatment of Degenerative Cervical Disc Disease Michael Lynn, MD Neurosurgeon, Southeastern Neurosurgical & Spine Institute Adjunct Assistant Clinical Professor of Bioengineering, Clemson
Marc A. Cohen, MD, FAAOS, FACS Diplomate American Board of Spinal Surgery Fellow American College of Spinal Surgery
 Marc A. Cohen, MD, FAAOS, FACS Diplomate American Board of Spinal Surgery Fellow American College of Spinal Surgery 221 Madison Ave Morristown, New Jersey 07960 (973) 538 4444 Fax (973) 538 0420 Patient
Marc A. Cohen, MD, FAAOS, FACS Diplomate American Board of Spinal Surgery Fellow American College of Spinal Surgery 221 Madison Ave Morristown, New Jersey 07960 (973) 538 4444 Fax (973) 538 0420 Patient
Dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine Robert W. Molinari
 Dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine Robert W. Molinari Purpose of review This is a review of the recent literature involving dynamic posterior stabilization in the lumbar spine. Recent findings As
Dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine Robert W. Molinari Purpose of review This is a review of the recent literature involving dynamic posterior stabilization in the lumbar spine. Recent findings As
White Paper: Cervical Disc Replacement: When is the Mobi-C Cervical Disc Medically Necessary?
 White Paper: Cervical Disc Replacement: When is the Mobi-C Cervical Disc Medically Necessary? For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Cervical Disc Disease: An Overview The cervical
White Paper: Cervical Disc Replacement: When is the Mobi-C Cervical Disc Medically Necessary? For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Cervical Disc Disease: An Overview The cervical
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion
 Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion Biomechanical Evaluation (1) coflex-f screw Biomechanical Evaluation (1) coflex-f intact Primary Stability intact Primary Stability Extension Neutral Position Flexion Coflex
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion Biomechanical Evaluation (1) coflex-f screw Biomechanical Evaluation (1) coflex-f intact Primary Stability intact Primary Stability Extension Neutral Position Flexion Coflex
REVIEW DECISION. Review Reference #: R0103014 Board Decision under Review: March 3, 2009
 REVIEW DECISION Re: Review Reference #: R0103014 Board Decision under Review: March 3, 2009 Date: Review Officer: Lyall Zucko The worker requests a review of the decision of WorkSafeBC (the Board) dated
REVIEW DECISION Re: Review Reference #: R0103014 Board Decision under Review: March 3, 2009 Date: Review Officer: Lyall Zucko The worker requests a review of the decision of WorkSafeBC (the Board) dated
Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) Augmentation Of A Cannulated And Fenestrated Pedicle
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 5 Ver. III. (May. 2014), PP 77-81 Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) Augmentation Of A Cannulated
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 5 Ver. III. (May. 2014), PP 77-81 Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) Augmentation Of A Cannulated
Sample Treatment Protocol
 Sample Treatment Protocol 1 Adults with acute episode of LBP Definition: Acute episode Back pain lasting
Sample Treatment Protocol 1 Adults with acute episode of LBP Definition: Acute episode Back pain lasting
Outcome of the L5-S1 Segment after Posterior Instrumented Spinal Surgery in Degenerative Lumbar Diseases
 Original Article 81 Outcome of the L5-S1 Segment after Posterior Instrumented Spinal Surgery in Degenerative Lumbar Diseases Jen-Chung Liao, MD; Wen-Jer Chen, MD; Lih-Huei Chen, MD; Chi-Chien Niu, MD Results:
Original Article 81 Outcome of the L5-S1 Segment after Posterior Instrumented Spinal Surgery in Degenerative Lumbar Diseases Jen-Chung Liao, MD; Wen-Jer Chen, MD; Lih-Huei Chen, MD; Chi-Chien Niu, MD Results:
Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Spine Clinic Neurospine Specialists, Orthopaedics and Neurosurgery
 Spine Clinic Neurospine Specialists, Orthopaedics and Neurosurgery REVISION SPINE SURGERY Revision surgery is a very complex field which requires experience, training and evaluation in a very individual
Spine Clinic Neurospine Specialists, Orthopaedics and Neurosurgery REVISION SPINE SURGERY Revision surgery is a very complex field which requires experience, training and evaluation in a very individual
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Interspinous Fixation (Fusion) Devices Page 1 of 6 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: See Also: Interspinous Fixation (Fusion) Devices Lumbar Spine
Interspinous Fixation (Fusion) Devices Page 1 of 6 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: See Also: Interspinous Fixation (Fusion) Devices Lumbar Spine
CURRICULUM VITAE. D. ALWYN JONES Consultant Orthopaedic Spinal Surgeon. Spire Cardiff Hospital Croescadarn Road Pentwyn Cardiff CF23 8XL
 CURRICULUM VITAE D. ALWYN JONES Consultant Orthopaedic Spinal Surgeon Spire Cardiff Hospital Croescadarn Road Pentwyn Cardiff CF23 8XL Name Mr David Alwyn Jones FRCS Address for Medico-Legal Correspondence
CURRICULUM VITAE D. ALWYN JONES Consultant Orthopaedic Spinal Surgeon Spire Cardiff Hospital Croescadarn Road Pentwyn Cardiff CF23 8XL Name Mr David Alwyn Jones FRCS Address for Medico-Legal Correspondence
Spine Trauma: When to Transfer. Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU
 Spine Trauma: When to Transfer Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU Disclosures Depuy Spine Consultant (teaching and courses) Department education and research funds Atlas Spine
Spine Trauma: When to Transfer Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU Disclosures Depuy Spine Consultant (teaching and courses) Department education and research funds Atlas Spine
LOW BACK PAIN; MECHANICAL
 1 ORTHO 16 LOW BACK PAIN; MECHANICAL Background This case definition was developed by the Armed Forces Health Surveillance Center (AFHSC) for the purpose of epidemiological surveillance of a condition
1 ORTHO 16 LOW BACK PAIN; MECHANICAL Background This case definition was developed by the Armed Forces Health Surveillance Center (AFHSC) for the purpose of epidemiological surveillance of a condition
Patient Information for Lumbar Spinal Fusion. What is a lumbar spinal fusion? Page 1 of 5
 Patient Information for Lumbar Spinal Fusion What is a lumbar spinal fusion? You have been offered surgery to the lumbar region of your spine, your lower back. The operation is called a lumbar spinal fusion.
Patient Information for Lumbar Spinal Fusion What is a lumbar spinal fusion? You have been offered surgery to the lumbar region of your spine, your lower back. The operation is called a lumbar spinal fusion.
Khaled s Radiology report
 Khaled s Radiology report Patient Name: Khaled Adli Moustafa Date 06/15/2014 The patient is not present. And the following report is based upon what was in the MRI of the cervical and lumbar spine report
Khaled s Radiology report Patient Name: Khaled Adli Moustafa Date 06/15/2014 The patient is not present. And the following report is based upon what was in the MRI of the cervical and lumbar spine report
Research Article Partial Facetectomy for Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis
 Advances in Orthopedics, Article ID 534658, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/534658 Research Article Partial Facetectomy for Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis Kevin Kang, 1 Juan Carlos Rodriguez-Olaverri,
Advances in Orthopedics, Article ID 534658, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/534658 Research Article Partial Facetectomy for Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis Kevin Kang, 1 Juan Carlos Rodriguez-Olaverri,
https://www.laserspineinstitute.com/back_problems/foraminal_stenosis/e...
 Questions? Call toll free 1-866-249-1627 Contact us today. We're here for you seven days a week. MRI Review Consultation Live help Call 1-866-249-1627 Chat Live Home Laser Spine Institute Laser Spine Institute's
Questions? Call toll free 1-866-249-1627 Contact us today. We're here for you seven days a week. MRI Review Consultation Live help Call 1-866-249-1627 Chat Live Home Laser Spine Institute Laser Spine Institute's
Surgical Procedures of the Spine
 Surgical Procedures of the Spine Jaideep Chunduri, M.D. Orthopaedic Spine Surgeon Beacon Orthopaedics and Sports Medicine Beacon Spine Center Objectives Discuss the 4 most common procedures performed in
Surgical Procedures of the Spine Jaideep Chunduri, M.D. Orthopaedic Spine Surgeon Beacon Orthopaedics and Sports Medicine Beacon Spine Center Objectives Discuss the 4 most common procedures performed in
IMPAIRMENT RATING 5 TH EDITION MODULE II
 IMPAIRMENT RATING 5 TH EDITION MODULE II THE SPINE AND ALTERATION OF MOTION SEGMENT INTEGRITY (AOMSI) PRESENTED BY: RONALD J. WELLIKOFF, D.C., FACC, FICC In conjuction with: The chapter on the spine includes
IMPAIRMENT RATING 5 TH EDITION MODULE II THE SPINE AND ALTERATION OF MOTION SEGMENT INTEGRITY (AOMSI) PRESENTED BY: RONALD J. WELLIKOFF, D.C., FACC, FICC In conjuction with: The chapter on the spine includes
SPINAL FUSION. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 SPINAL FUSION North American Spine Society Public Education Series WHAT IS SPINAL FUSION? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
SPINAL FUSION North American Spine Society Public Education Series WHAT IS SPINAL FUSION? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
Presented by Zoran Maric, M.D. Orthopaedic Spine Surgeon May 22, 2010
 Presented by Zoran Maric, M.D. Orthopaedic Spine Surgeon May 22, 2010 1 cervical area thoracic area lumbar area sacrum coccyx Mayfield Clinic 2 3 4 5 Zoran Maric, MD Spine Surgery Procedures How to Document
Presented by Zoran Maric, M.D. Orthopaedic Spine Surgeon May 22, 2010 1 cervical area thoracic area lumbar area sacrum coccyx Mayfield Clinic 2 3 4 5 Zoran Maric, MD Spine Surgery Procedures How to Document
Spinal Surgery Clinical Coverage Policy No: 1A-30 Revised Date: DRAFT Table of Contents
 Clinical Coverage Policy No: 1A-30 Table of Contents 1.0 Description of the Procedure, Product, or Service... 1 1.1 Definitions... 1 2.0 Eligible Recipients... 2 2.1 General Provisions... 2 2.2 EPSDT Special
Clinical Coverage Policy No: 1A-30 Table of Contents 1.0 Description of the Procedure, Product, or Service... 1 1.1 Definitions... 1 2.0 Eligible Recipients... 2 2.1 General Provisions... 2 2.2 EPSDT Special
Patient Guide to Lower Back Surgery
 The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Open Lumbar Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Lower Back Surgery Open Lumbar Fusion Dynesys The Dynesys Dynamic Stabilization
The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Open Lumbar Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Lower Back Surgery Open Lumbar Fusion Dynesys The Dynesys Dynamic Stabilization
Case Study: Reduction and Stabilization of Grade III L5-S1 Dysplastic Spondylolisthesis in 15-Year-Old Female Using Posterior Approach
 Case Study: Reduction and Stabilization of Grade III L5-S1 Dysplastic Spondylolisthesis in 15-Year-Old Female Using Posterior Approach Terrence L. Piper, MD Piper Spine Care Background Context: A female
Case Study: Reduction and Stabilization of Grade III L5-S1 Dysplastic Spondylolisthesis in 15-Year-Old Female Using Posterior Approach Terrence L. Piper, MD Piper Spine Care Background Context: A female
GUIDELINES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPINAL STABILITY THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE. CP57 Version: V3
 GUIDELINES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPINAL STABILITY THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE Procedure Reference: Document Owner: CP57 Version: V3 Dr V. Misra Accountable Committee: Acute Oncology Group Network
GUIDELINES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPINAL STABILITY THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE Procedure Reference: Document Owner: CP57 Version: V3 Dr V. Misra Accountable Committee: Acute Oncology Group Network
Department of Spine Surgery, Third Hospital of HeBei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China. * Equal contributors.
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):3579-3584 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0005603 Original Article Unilateral posterior vertebral column resection for severe thoracolumbar kyphotic deformity caused by
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):3579-3584 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0005603 Original Article Unilateral posterior vertebral column resection for severe thoracolumbar kyphotic deformity caused by
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time.
 If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
Adult Spinal Deformity: Contemporary Treatment and Patient Outcomes
 Adult Spinal Deformity: Contemporary Treatment and Patient Outcomes ALAN H. DANIELS, MD; J. MASON DEPASSE, MD; CRAIG P. EBERSON, MD; PHILIP R. LUCAS, MD; MARK A PALUMBO, MD ABSTRACT The incidence of symptomatic
Adult Spinal Deformity: Contemporary Treatment and Patient Outcomes ALAN H. DANIELS, MD; J. MASON DEPASSE, MD; CRAIG P. EBERSON, MD; PHILIP R. LUCAS, MD; MARK A PALUMBO, MD ABSTRACT The incidence of symptomatic
ICD 10 CM IMPLEMENTATION DATE OCT 1, 2015
 Presented by: Teri Romano, RN, MBA, CPC, CMDP ICD 10 CM IMPLEMENTATION DATE OCT 1, 2015 Source: http://journal.ahima.org/2015/02/04/us house committee to hold hearing on icd 10 implementation/ 2 2015 Web_Non
Presented by: Teri Romano, RN, MBA, CPC, CMDP ICD 10 CM IMPLEMENTATION DATE OCT 1, 2015 Source: http://journal.ahima.org/2015/02/04/us house committee to hold hearing on icd 10 implementation/ 2 2015 Web_Non
Patient Information. Posterior Cervical Surgery. Here to help. Respond Deliver & Enable
 Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
ICD-10-PCS Documentation and Coding for Spinal Procedures October 22, 2015
 Questions and Answers 1. We have a question regarding a spinal surgical procedure. The diagnosis was bilateral lateral recess stenosis and central stenosis from L2-L5. The procedure was an open lumbar
Questions and Answers 1. We have a question regarding a spinal surgical procedure. The diagnosis was bilateral lateral recess stenosis and central stenosis from L2-L5. The procedure was an open lumbar
Surgical Procedures and Clinical Results of Endoscopic Decompression for Lumbar Canal Stenosis
 Surgical Procedures and Clinical Results of Endoscopic Decompression for Lumbar Canal Stenosis Munehito Yoshida, Akitaka Ueyoshi, Kazuhiro Maio, Masaki Kawai, and Yukihiro Nakagawa Summary. The purpose
Surgical Procedures and Clinical Results of Endoscopic Decompression for Lumbar Canal Stenosis Munehito Yoshida, Akitaka Ueyoshi, Kazuhiro Maio, Masaki Kawai, and Yukihiro Nakagawa Summary. The purpose
NON SURGICAL SPINAL DECOMPRESSION. Dr. Douglas A. VanderPloeg
 NON SURGICAL SPINAL DECOMPRESSION Dr. Douglas A. VanderPloeg CONTENTS I. Incidence of L.B.P. II. Anatomy Review III. IV. Disc Degeneration, Bulge, and Herniation Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression 1. History
NON SURGICAL SPINAL DECOMPRESSION Dr. Douglas A. VanderPloeg CONTENTS I. Incidence of L.B.P. II. Anatomy Review III. IV. Disc Degeneration, Bulge, and Herniation Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression 1. History
CURRICULUM VITAE TIMOTHY J. BIRNEY, M.D. University of Pittsburgh, School of Medicine M.D. Degree, Cum Laude 1983
 CURRICULUM VITAE TIMOTHY J. BIRNEY, M.D. EDUCATION: Undergraduate: Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH B.A. Degree, Cum Laude 1979 Medical: University of Pittsburgh, School of Medicine M.D. Degree, Cum Laude
CURRICULUM VITAE TIMOTHY J. BIRNEY, M.D. EDUCATION: Undergraduate: Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH B.A. Degree, Cum Laude 1979 Medical: University of Pittsburgh, School of Medicine M.D. Degree, Cum Laude
4052 Slimplicity Tech final_layout 1 6/29/15 3:29 PM Page 2 Surgical Technique
 Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS Slimplicity Anterior Cervical Plate System Overview 2 Indications 2 Implants 3 Instruments 4 Surgical Technique 6 1. Patient Positioning and Approach 6 2. Plate Selection
Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS Slimplicity Anterior Cervical Plate System Overview 2 Indications 2 Implants 3 Instruments 4 Surgical Technique 6 1. Patient Positioning and Approach 6 2. Plate Selection
Orthopaedic Approach to Back Pain. Seth Cheatham, MD
 Orthopaedic Approach to Back Pain Seth Cheatham, MD 262 Seth A. Cheatham, MD VCU Sports Medicine I have no financial disclosures. Focus on clinical situations where a referral to an orthopaedic surgeon
Orthopaedic Approach to Back Pain Seth Cheatham, MD 262 Seth A. Cheatham, MD VCU Sports Medicine I have no financial disclosures. Focus on clinical situations where a referral to an orthopaedic surgeon
OUTLINE. Anatomy Approach to LBP Discogenic LBP. Treatment. Herniated Nucleus Pulposus Annular Tear. Non-Surgical Surgical
 DISCOGENIC PAIN OUTLINE Anatomy Approach to LBP Discogenic LBP Herniated Nucleus Pulposus Annular Tear Treatment Non-Surgical Surgical Facet Joints: bear 20% of weight Discs bear 80% of weight Neural Foramen
DISCOGENIC PAIN OUTLINE Anatomy Approach to LBP Discogenic LBP Herniated Nucleus Pulposus Annular Tear Treatment Non-Surgical Surgical Facet Joints: bear 20% of weight Discs bear 80% of weight Neural Foramen
Treating Bulging Discs & Sciatica. Alexander Ching, MD
 Treating Bulging Discs & Sciatica Alexander Ching, MD Disclosures Depuy Spine Teaching and courses K2 Spine Complex Spine Study Group Disclosures Take 2 I am a spine surgeon I like spine surgery I believe
Treating Bulging Discs & Sciatica Alexander Ching, MD Disclosures Depuy Spine Teaching and courses K2 Spine Complex Spine Study Group Disclosures Take 2 I am a spine surgeon I like spine surgery I believe
RENOWN REGIONAL MEDICAL CENTER DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPAEDICS DELINEATION OF PRIVILEGES
 RENOWN REGIONAL MEDICAL CENTER DEPARTMENT OF THOPAEDICS DELINEATION OF PRIVILEGES BASIC EDUCATION: M.D. or D.O. MINIMAL FMAL TRAINING: ABMS Board certification or eligibility, or be able to document equivalent
RENOWN REGIONAL MEDICAL CENTER DEPARTMENT OF THOPAEDICS DELINEATION OF PRIVILEGES BASIC EDUCATION: M.D. or D.O. MINIMAL FMAL TRAINING: ABMS Board certification or eligibility, or be able to document equivalent
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Lumbar Spinal Stenosis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? The vertebrae are the bones that make up the lumbar spine (low back). The spinal canal runs through
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? The vertebrae are the bones that make up the lumbar spine (low back). The spinal canal runs through
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
The Surgical Spine. Sergio Rivero M.D.
 The Surgical Spine Sergio Rivero M.D. Goals: Review Current literature in spinal surgery. To utilize evidence based medicine to treat spinal pathology. It is much more important to know what sort of a
The Surgical Spine Sergio Rivero M.D. Goals: Review Current literature in spinal surgery. To utilize evidence based medicine to treat spinal pathology. It is much more important to know what sort of a
ARTIFICIAL DISC REPLACEMENT FOR DEGENERATIVE DISC DISEASE OF THE LUMBAR SPINE. A Technology Assessment
 ARTIFICIAL DISC REPLACEMENT FOR DEGENERATIVE DISC DISEASE OF THE LUMBAR SPINE A Technology Assessment INTRODUCTION The California Technology Assessment Forum has been asked to update its review of the
ARTIFICIAL DISC REPLACEMENT FOR DEGENERATIVE DISC DISEASE OF THE LUMBAR SPINE A Technology Assessment INTRODUCTION The California Technology Assessment Forum has been asked to update its review of the
Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF).
 Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra, allows
Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra, allows
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Spinal Surgery: Laminectomy and Fusion
 Spinal Surgery: Laminectomy and Fusion Page 1 of 42 Clinical Policy Bulletin: Spinal Surgery: Laminectomy and Fusion Revised April 2014 Number: 0743 Policy I. Aetna considers cervical laminectomy (and/or
Spinal Surgery: Laminectomy and Fusion Page 1 of 42 Clinical Policy Bulletin: Spinal Surgery: Laminectomy and Fusion Revised April 2014 Number: 0743 Policy I. Aetna considers cervical laminectomy (and/or
Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery
 Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery Dr. Connie D Astolfo, DC, PhD (candidate) In past articles I have stressed that the causes of back pain can be very complex. This
Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery Dr. Connie D Astolfo, DC, PhD (candidate) In past articles I have stressed that the causes of back pain can be very complex. This
CERVICAL PROCEDURES PHYSICIAN CODING
 CERVICAL PROCEDURES PHYSICIAN CODING Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Interbody Fusion (ACDF) Anterior interbody fusion, with discectomy and decompression; cervical below C2 22551 first interspace 22552
CERVICAL PROCEDURES PHYSICIAN CODING Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Interbody Fusion (ACDF) Anterior interbody fusion, with discectomy and decompression; cervical below C2 22551 first interspace 22552
Patient Guide to Neck Surgery
 The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Anterior Cervical Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Neck Surgery Anterior Cervical Fusion Trinica Select With the Trinica and
The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Anterior Cervical Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Neck Surgery Anterior Cervical Fusion Trinica Select With the Trinica and
Cervical Spine Surgery. Orthopaedic Nursing Seminar. Dr Michelle Atkinson. Friday October 21 st 2011. Cervical Disc Herniation
 Cervical Spine Surgery Dr Michelle Atkinson The Sydney and Dalcross Adventist Hospitals Orthopaedic Nursing Seminar Friday October 21 st 2011 Cervical disc herniation The most frequently treated surgical
Cervical Spine Surgery Dr Michelle Atkinson The Sydney and Dalcross Adventist Hospitals Orthopaedic Nursing Seminar Friday October 21 st 2011 Cervical disc herniation The most frequently treated surgical
ANTERIOR LUMBAR INTERBODY FUSION (ALIF) Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Anterior Lumbar Spine
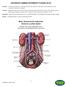 (ALIF) Anterior In human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or the position of one structure relative to another Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between
(ALIF) Anterior In human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or the position of one structure relative to another Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between
Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances?
 Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances? Do you experience weakness, tingling, numbness, stiffness, or cramping in your legs, buttocks or
Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances? Do you experience weakness, tingling, numbness, stiffness, or cramping in your legs, buttocks or
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study
 Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine
Clinical Guideline. Low Back Pain Orthopaedics. Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department. 1 Purpose. 2 Background
 Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department Clinical Guideline Orthopaedics Review Officer: Katherine Isoardi Version no: 1 Approval date: 18/03/2015 Review date: 18/03/2017 Approving Officer Dr James
Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department Clinical Guideline Orthopaedics Review Officer: Katherine Isoardi Version no: 1 Approval date: 18/03/2015 Review date: 18/03/2017 Approving Officer Dr James
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
A review of spinal problems
 Dr Ulrich R Hähnle MD, FCS Orthopaedic Surgeon, Wits Facharzt für Orthopädie, Berlin Phone: +27 11 485 3236 Fax: +27 11 485 2446 Suite 102, Medical Centre, Linksfield Park Clinic P.O. Box 949, Johannesburg
Dr Ulrich R Hähnle MD, FCS Orthopaedic Surgeon, Wits Facharzt für Orthopädie, Berlin Phone: +27 11 485 3236 Fax: +27 11 485 2446 Suite 102, Medical Centre, Linksfield Park Clinic P.O. Box 949, Johannesburg
