Principles of Immunohistochemistry Queen s Laboratory For Molecular Pathology
|
|
|
- Dana Roberts
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Principles of Immunohistochemistry Queen s Laboratory For Molecular Pathology
2 Table of Contents POLYCLONAL VERSUS MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES...PAGE 3 DIRECT & INDIRECT ASSAYS.PAGE 4 LABELS..PAGE 5 DETECTION...PAGE 7 TISSUE PREP.PAGE 9 BLOCKING.PAGE 10 RINSING...PAGE 10 CONTROLS..PAGE 11 2
3 Principles of Immunohistochemistry This pamphlet provides a general overview of the basics of IHC, giving some insights into the operating principles of antigen-antibody interactions and IHC protocols that take advantage of these interactions. Immune cells, or B cells, produce antibodies against targeted proteins. These antibodies then can recognize, and bind to, those proteins, called antigens. More specifically, they have an affinity for certain sites on those antigens, called epitopes. Antibodies are also called immunoglobulins, abbreviated Ig. There are different classes, or isotypes, of Ig molecules, designated with a third letter, such as IgG, or IgA. Different isotypes of immunoglobulins perform different functions, in different places in the body. IgG provides the majority of antibody based immunity against invading pathogens. Polyclonal and Monoclonal antibodies When the immune system detects the presence of a foreign body, such as a virus, many B cells will produce antibodies against it. The different B cells will target different sites on the antigen, producing a mix of antibodies, all against that virus, but specifically against many different epitopes on that antigen. This produces a polyclonal antiserum where polyclonal denotes the mixed population of Ig molecules. In contrast, a monoclonal antibody preparation contains a single antibody with specificity to one epitope on the antigen molecule. This is achieved by fusing B cells from the spleen of an immunized animal with immortal myeloma cells, and growing clones from the single parent cells on microtitre wells. The most productive clone, or hybridoma will be selected for production and purification of a single epitope antibody. Typically monoclonal antibodies have been mouse antibodies, however advances have seen the production of many rabbit monoclonals lately.. 3
4 Monoclonals and polyclonals have their advantages and disadvantages. Polyclonals are cheaper, because they are cheaper to produce. They are typically more sensitive as they are directed against many sites on the antigen. This will increase the chance that some of the antibodies will survive adverse conditions and complete binding to the antigen. Because of this robust nature of the interaction, polyclonals in general can be used at higher dilutions, as detection of the epitope in sensitive assays is more assured. Monoclonals will be more expensive, and may be more vunerable to adverse conditions, due to their narrow specificity. But this specificity is very desirable for highly focused, low background immunostaining. MONOCLONAL PRODUCTION METHOD Direct and Indirect IHC Immunohistochemistry takes advantage of antigen-antibody affinity through its ability to identify and localize proteins of interest via detection with labelled conjugates. In the simplest example, a primary antibody (first in order of use, directed to the antigen epitope) which has had a label attached, is allowed to bind. The antibody, and thus the antigen on the tissue surface, is then detected through a series of treatments, which will visualize the label for analysis and quantification. This is called direct IHC. One other important characterization of an antibody that we must consider is the animal that the antibody was developed in. If an antibody against, say, vimentin has been produced in mouse, this is termed mouse anti vimentin. This distinction is important when considering another binding assay, called indirect IHC. Indirect IHC involves using an intermediary between the primary antibody and the detection system. 4
5 In this method, the primary antibody, without label, is bound to the antigen as in the direct method. But then a second antibody is applied. This antibody will have been developed against mouse antibodies in general, and so is termed anti-mouse. Because this second antibody (surprisingly called the secondary) is anti-mouse, it will bind to any mouse derived primary antibody. This secondary antibody will be labelled, which then can be detected as before. Because the primary antibody is being indirectly detected through the use of an intermediate Ig molecule, this is termed the indirect method. The direct method of IHC is simple and efficient, but the indirect holds some major advantages. With the direct method, you need specific labelled primary antibodies for every protein you want to investigate. But if you are using the indirect method, one labelled anti-mouse secondary will work with all mouse derived primaries. One antirabbit secondary will work with all rabbit derived primaries, and so on, thus reducing the number of labelled Ig molecules needed down to one for each type of antibody. A further advantage lies in the fact that each primary antibody will usually bind at least 2 labelled secondaries, thus doubling (at least) the signal of the assay. Generally the indirect method is seen as about 10 times more sensitive than the direct. Labels A variety of enzymatic and fluorescence type labels may be used. For our purposes here I will cover a few of the more commonly used ones. Enzymes such as horseradish peroxidase use chromogens that produce a precipitate visible with a normal light microscope. These are termed brightfield images. They are stable, permanent, and allow counterstaining so that the surrounding tissue can be viewed to give context to the antigenic site. Fluorescent labels produce a bright colour at a specific wavelength, allowing the antigen-antibody complex to be viewed in darkfield, on a fluorescence microscope. In a blacked-out field, only the label or labels used show up. 5
6 This can result in dramatic images of specific aspects of tissue morphology, including pronounced emphasis on antigen site to site comparisons. For example, below is an image in darkfield using 2 fluorescent labels. One label has targeted cellular membranes, the other being a nuclear stain. In combination, the two produce yellowgreen rings around blue nuclei. In this simple example, it may be that the protein being expressed in the membrane, and visualized with the yellow-green fluor, is not expressed in all cells. If this were the case, we could compare numbers of cells (blue nuclear stain) with and without membrane staining (yellow-green), giving us data on percent of cells expressing. Brightfield images are permanent, and allow counterstaining, but for quantification, they provide an image which digitally is mostly positive or negative. It is difficult to measure a range of signal strength as the chromogen tends to be opaque. There also are indications that during the reaction the chromogen precipitate can diffuse away from the epitope site, but for most purposes this does not pose a significant problem. Fluorescent labels are not permanent. They are subject to fade, and burn-out on the scope. A fluorescent stain should be digitized as soon as possible to permit long-term storage and potential analysis of the optimal image data. But to their advantage, they can be measured for their intensity, giving a more accurate and gradable range of signal strength. 6
7 Detection Earlier I summarized detection as a series of treatments. I can expand on these now. The first label I mentioned was an enzymatic label using horseradish peroxidase (HRP). We ve seen how the first steps in this process involve getting the labelled secondary conjugated to the primary antibody. The purpose for the next series of steps is to put a chromogen in place that will show up in brightfield. One of the most common methods is to use the HRP enzyme (label) to catalyze a DAB substrate, creating a reaction product precipitate at the site which is visible by microscopy. The signal of this interaction can be augmented by inserting steps in the chain which take advantage of the strong biotin-avidin affinity, or the biotin-streptavidin affinity. DAKO s LSAB kit utilizes streptavidin in this fashion. In this procedure, the secondary antibody is not labelled with HRP, but with biotin. The secondary is now a biotinylated antibody. This biotinylated molecule binds to the primary, and then is bound to several HRP labelled streptavidin molecules. This technique places many more HRP molecules into the conjugate, increasing the sensitivity of the assay many fold. Once the HRP molecules are bound, they can catalyze the DAB substrate-chromogen into a visible precipitate. AVIDIN-BIOTIN ASSAY HRP is the most widely used enzyme label, but others, such as alkaline phosphatase, or glucose oxidase, can be used. This provides a wider range of conditions available to choose from, and also allows the possibility of dual staining on one tissue section. 7
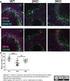
8 Fluorescent labels have the advantage of being easier and quicker to use, as they require fewer steps. Typical fluors are Texas red, FITC, DAPI, and a variety of Alexa fluors, such as Alexa 488, which, for example, fluoresces green with a maximum emission at excitation wavelength of 488. Once bound, detection simply involves observing the section on a fluorescent microscope at the correct wavelength. Dual and triple stain images can be produced by scanning the section at each required wavelength, producing multiple images that can be superimposed one on another, resulting in a multiple stain image. Below are 4 images of the same section. This section has been double labelled with Cy5 on mouse Bmi-1 (red), and Alexa 555 on rabbit CD20 (yellowgreen). A 3 rd fluor, DAPI, (blue) has been added in the cover slip medium. The panel of 3 images shows the individual fluors, the fourth image shows all the colours together. One section viewed at 3 separate wavelengths Composite Image 8
9 In cases where the primary antibody signal is weak, amplification can be achieved with a DAKO Envision system. This kit from DAKO utilizes a long chain polymer conjugated with an Ig fragment that will be anti mouse, or anti rabbit, allowing for binding to the primary. The polymer is HRP labelled, which then allows for the usual DAB detection. The advantage here is that the polymer will have about 14 HRP molecules on each chain, providing a substantial amplification of signal. It is important to note that a weak signal may not be due to a poorly performing primary antibody. Weak signal may result from low quantities of antigen on the tissue, or non-optimal assay conditions. The first response to boosting a weak signal may not necessarily be amplification. Tissue preparation The binding of the primary antibody to the antigen epitope requires the epitope to be in a condition that maximizes availability for reaction. Reduced accessibility of the primary antibody to the binding site will weaken or eliminate signal. Preparing the tissue to receive the primary antibody is an integral part of immunostaining, and is referred to as antigen retrieval, or A/R. Most tissue used in immunostaining has been formalin fixed and paraffin embedded. This treatment degrades the antigen to the point where, for many antibodies, the tissue requires one of several treatments. Heat induced epitope retrieval (HIER), is most commonly used. This involves an incubation period at or around 95 C. This can be achieved with steam bath (rice cooker), or microwave treatment, or pressure cooking. Buffers used here will be ph specific, as some antibodies require low ph (citrate, ~6) antigen treatment, and some require high ph (EDTA,~8). Certain companies, such as DAKO, provide these buffers. They are quite expensive, but can be used many times. Other antibodies perform optimally with protease treatment, such as Proteinase K. Frozen sections do not require such drastic A/R protocols, as the antigens are still viable. Section prep can be responsible for signal loss as well. High temp drying onto the glass slide must be monitored closely. 58 C to 60 C should be the operating range, for an incubation period of 2 hours. Sections should be as fresh as possible. Whenever possible the section should be stained within one or two days of mounting and drying. Some antibodies show reduced signal on sections that are only 3 or 4 days old. I should note here that some antibodies are more robust, and may provide a strong response on sections that are months or even years old. It is good policy to simply keep your sections as fresh as you possibly can, whichever antibody you are using. During the IHC assay, the tissue section goes through multiple buffer exchanges and rinses. It is important that these exchanges be performed in an orderly and timely fashion. If the section dries out for just a moment, the assay is ruined. Poor formalin fixation will also impact quality of signal. Most labs doing IHC will not have direct control over the fixation of tissues, but you should be aware that this can impact signal strength. An example of a poorly fixed piece of tissue would be where the formalin has not penetrated completely, producing a halo effect. This will result in strong signal around the edges of the section, with a weaker, faded response towards the interior. 9
10 Blocking IHC assay conditions are designed to optimize binding of the various specific components of the conjugates we are trying to assemble. Any other unintended binding is termed non-specific, and will obscure true binding, and suggest false positives. In order to install the correct blocking measures in your assay, you must be aware of the properties and actions of each component. When applying primary and secondary antibodies to the surface of the tissue, the antibodies will bind to non-specific sites by hydrophobic and electrostatic forces, generally with low affinity. This binding can be blocked in a variety of ways. A commonly used method is to wash the tissue, prior to application of the antibodies, with normal serum from the species of the secondary antibody. This will mask non-specific reactive sites while allowing specific binding to take place. Use of normal sera from the species the primary antibody was generated must not be used, as the secondary will bind all across the tissue in this case. Another approach, one used here in the QLMP lab, is to use 1% BSA (Fraction V) in solution. This is a universal block, binding to many sites on the tissue. When the primary antibody is applied, it has a stronger affinity for it s target epitope, and so out competes the buffer block for the site. As the primary has no greater affinity than the buffer block for the non-specific sites, it does not displace them, reducing non-specific staining. For optimal conditions the dilution buffer used for the antibodies should contain the same type of blocking buffer used in the assay. This acts as a stabilizer. The most common enzyme used in IHC assays is HRP. This peroxidase catalyzes the DAB substrate-chromogen to produce a visible precipitate. We want this to happen only on our targeted conjugate. However, tissues contain endogenous (naturally occurring) peroxidases that will also drive the reaction. This must be blocked. Typically a 3% H 2 O 2 solution is applied after A/R, and prior to incubation with the primary. Alternate enzymes will require different blockers. For example, if using alkaline phosphatase, endogenous activity should be blocked with levamisole. H 2 O 2 degrades to water over time, so be sure your solutions are fresh. This applies to your BSA blocks as well. As already outlined, many IHC assays utilize the affinity between biotin and avidin, or streptavidin. The biotin label on the secondary presents a binding site to a HRP labelled streptavidin molecule. The problem here is that some types of tissue, such as liver and kidney, have high levels of endogenous biotin. This endogenous biotin can be blocked with avidin/biotin washes, before the introduction of the conjugated streptavidin. As a footnote to blocking issues, there is debate today as to whether or not blocking against non-specific binding is even necessary anymore. With increased specificity of today s antibodies, and higher quality reagents overall, some researchers feel background noise in most typical assays is low enough to justify excluding the use of a blocking step. This is a decision probably best left up to the individual researcher, as every antibody comes with it s own set of requirements and characteristics needed for optimal performance. Certainly inclusion of appropriate blocking steps will do no harm. 10
11 Rinsing You might think variations in procedure here would be of little consequence, however there are some principles that should be observed. It is important to apply sufficient rinsing between each step, as excess remnants of the last incubation will interfere with the next component. As important as sufficient rinsing is, it is also important to be careful not to rinse too vigorously. It is possible to strip off previously applied components from the tissue, leaving the signal to appear blotchy or absent in random areas on the tissue. Follow a formal routine for rinsing, such as using a series of dips in rinse buffer combined with gentle washes from a transfer pipet. Avoid spraying rinse buffer directly at the tissue section. Flood the slide so the buffer washes over the section. Controls When assessing the outcome of your immunostain assay, experimental results are meaningless unless they are judged in the context of appropriate controls. When applied and interpreted correctly these controls assure us that reagents and protocols were correctly applied, and performed as expected. Many antibody producing companies will tell you which tissues act as positive controls for your antibody. Positive controls are tissues you run with the experimentals that have been proven to produce a signal if all is correct with the assay. If you run one experimental slide, and it is negative, it may be because the results are a true negative. But it may also be that the assay did not work properly, resulting in a failed stain. By including a positive control, you will know if your assay performed as expected. The internet site Human Protein Atlas is an excellent site for finding positive control tissue suggestions for many antibodies, and also for providing actual images showing how your antibody staining should look. A positive control should be included in every assay, as errors and omissions easily slip in to these many-step protocols. We are all human. Positive control sections should be comparable to the experimentals in every way that you have control over. Age of section, drying protocols, fixation, etc. In general, normal tissue should be used instead of cancer samples. As a rule of thumb, the positive control should operate in a range that produces a medium to weak signal on the tissue. In this way, if the assay starts to produce variable results (due to fading antibody viability, old buffers, etc) you will see it in this kind of signal. If you are using a positive control that produces a heavy, dark stain, and the signal fades by, say, 20%, you probably would not notice it. The next control you should include in your assay is the negative control. For this control, set aside one duplicate experimental slide. This slide will receive all reagents the other slides get, and go through exactly the same processes in all ways save one. Do not apply the primary antibody. Apply the buffer the antibody is usually applied in, just omit the primary. In this way the secondary has no target binding site, and this should result in no label on the slide, and thus no signal. If you still get signal, this tells you the secondary is finding non-specific binding sites, and some or all of your signal is false. Re-assessing your blocking strategies may be necessary. 11
12 If you cannot reduce this background noise to zero, you can at least compare the control with your experimental slides, to help identify true signal from false. Another negative control involves omitting all antibodies, along with the enzyme label. If signal results, something in the tissue is catalyzing the DAB (such as endogenous peroxidases), and needs to be blocked. This control is not often performed. One of the best controls will tell you if your primary antibody is truly specific for the antigen you are assaying. This involves absorbing the antibody, prior to application, with a purified solution of the reactive antigen, or peptide. In theory you will be applying an antibody that no longer has the ability to bind to the antigen epitope. Signal should be completely knocked out. When absorbing the primary, it may be possible that the peptide does not bind specifically, but still attaches in some way to interfere with binding when the antibody is applied. In this case you would get a false negative result. To control against this, you can absorb the antibody with a non-reactive peptide. You know this peptide will not be specific, so if staining is reduced or eliminated you are getting nonspecific interference from the peptides. The ideal results will be demonstrated by 3 outcomes: staining on the experimental, similar staining using the antibody absorbed with the non-reactive peptide, and no staining with the antibody absorbed with the reactive peptide. When you obtain these results you are assured your primary antibody is specific against the target antigen. When preparing to absorb the primary antibody with the peptide, the 2 should be mixed in a ratio that has the peptide at a strength many times higher than the antibody. The usual suggestion is to use the peptide at a concentration of at least 10 times that of the antibody, on a molar basis. QLMP, Jan Prepared by Lee Boudreau 12
Outline. 1. Experiment. 2. Sample analysis and storage. 3. Image analysis and presenting data. 4. Probemaker
 Tips and tricks Note: this is just an informative document with general recommendations. Please contact [email protected] should you have any queries. Document last reviewed 2011-11-17 Outline 1. Experiment
Tips and tricks Note: this is just an informative document with general recommendations. Please contact [email protected] should you have any queries. Document last reviewed 2011-11-17 Outline 1. Experiment
The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small
 The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small molecules that can elicit an immune response when linked
The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small molecules that can elicit an immune response when linked
Chapter 2 Antibodies. Contents. Introduction
 Chapter 2 Antibodies Keywords Immunohistochemistry Antibody labeling Fluorescence microscopy Fluorescent immunocytochemistry Fluorescent immunohistochemistry Indirect immunocytochemistry Immunostaining
Chapter 2 Antibodies Keywords Immunohistochemistry Antibody labeling Fluorescence microscopy Fluorescent immunocytochemistry Fluorescent immunohistochemistry Indirect immunocytochemistry Immunostaining
ab183294 TripleStain IHC Kit: M&M&R on rodent tissue (DAB, DAB/Ni & AP/Red)
 ab183294 TripleStain IHC Kit: M&M&R on rodent tissue (DAB, DAB/Ni & AP/Red) Instructions for Use For the detection of Rabbit and Mouse Primary antibodies on Rodent Tissue. This product is for research
ab183294 TripleStain IHC Kit: M&M&R on rodent tissue (DAB, DAB/Ni & AP/Red) Instructions for Use For the detection of Rabbit and Mouse Primary antibodies on Rodent Tissue. This product is for research
Hypoxyprobe -1 Plus Kit Kit contents:
 Updated 2015 1 PRODUCT INSERT Hypoxyprobe, Inc 121 Middlesex Turnpike Burlington, MA 01803 USA www.hypoxyprobe.com Hypoxyprobe -1 Plus Kit Kit contents: Solid pimonidazole HCl (Hypoxyprobe -1) FITC conjugated
Updated 2015 1 PRODUCT INSERT Hypoxyprobe, Inc 121 Middlesex Turnpike Burlington, MA 01803 USA www.hypoxyprobe.com Hypoxyprobe -1 Plus Kit Kit contents: Solid pimonidazole HCl (Hypoxyprobe -1) FITC conjugated
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology
 Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Chapter 3.2» Custom Monoclonal
 198 3 3.2 Custom Monoclonal 199 Mouse monoclonal antibody development Chapter 3.2» Custom Monoclonal 200 In vitro monoclonals expression service 201 Mouse monoclonal antibody additional services 202 Magnetic
198 3 3.2 Custom Monoclonal 199 Mouse monoclonal antibody development Chapter 3.2» Custom Monoclonal 200 In vitro monoclonals expression service 201 Mouse monoclonal antibody additional services 202 Magnetic
SCIENCE WHERE YOU ARE
 Newsletter. November 2013 SCIENCE WHERE YOU ARE Dealing with BioNordika includes a number of first class benefits: Next day delivery.... and some times even faster! Free delivery. Focus on your application.
Newsletter. November 2013 SCIENCE WHERE YOU ARE Dealing with BioNordika includes a number of first class benefits: Next day delivery.... and some times even faster! Free delivery. Focus on your application.
1.Gene Synthesis. 2.Peptide & Phospho-P. Assembly PCR. Design & Synthesis. Advantages. Specifications. Advantages
 1.Gene Synthesis Assembly PCR Looking for a cdna for your research but could not fish out the gene through traditional cloning methods or a supplier? Abnova provides a gene synthesis service via assembly
1.Gene Synthesis Assembly PCR Looking for a cdna for your research but could not fish out the gene through traditional cloning methods or a supplier? Abnova provides a gene synthesis service via assembly
The Use of Antibodies in Immunoassays
 TECHNICAL NOTE The Use of Antibodies in Immunoassays Introduction Structure of an IgG Antibody Immunological reagents are the backbone of every immunoassay system. Immunoassays can be utilized to quantitatively
TECHNICAL NOTE The Use of Antibodies in Immunoassays Introduction Structure of an IgG Antibody Immunological reagents are the backbone of every immunoassay system. Immunoassays can be utilized to quantitatively
KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service
 KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service 1. Polyclonal Antibody Development Service KMS offering a variety of Polyclonal Antibody Services to fit your research and production needs. we develop polyclonal
KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service 1. Polyclonal Antibody Development Service KMS offering a variety of Polyclonal Antibody Services to fit your research and production needs. we develop polyclonal
Your partner in immunology
 Your partner in immunology Expertise Expertise Reactivity Reactivity Quality Quality Advice Advice Who are we? Specialist of antibody engineering Covalab is a French biotechnology company, specialised
Your partner in immunology Expertise Expertise Reactivity Reactivity Quality Quality Advice Advice Who are we? Specialist of antibody engineering Covalab is a French biotechnology company, specialised
Clinical Histology Procedure histo13.01 Automated Immunohistochemical Staining Utilizing the Bond III Instrument
 Clinical Histology Procedure histo13.01 Automated Immunohistochemical Staining Utilizing the Bond III Instrument Final Approval: October 2010 Effective: October 2010 Next Review Date: February 2013 List
Clinical Histology Procedure histo13.01 Automated Immunohistochemical Staining Utilizing the Bond III Instrument Final Approval: October 2010 Effective: October 2010 Next Review Date: February 2013 List
Serology: Fluorescent antibody tests and other tests employing conjugated antibodies
 Serology: Fluorescent antibody tests and other tests employing conjugated antibodies Authors: Adapted by Prof M van Vuuren. Originally compiled by Dr RW Worthington. (Retired) Licensed under a Creative
Serology: Fluorescent antibody tests and other tests employing conjugated antibodies Authors: Adapted by Prof M van Vuuren. Originally compiled by Dr RW Worthington. (Retired) Licensed under a Creative
Chapter 6. Antigen-Antibody Properties 10/3/2012. Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Principles and Applications. Precipitin reactions
 Chapter 6 Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Principles and Applications Antigen-Antibody Properties You must remember antibody affinity (single) VS avidity (multiple) High affinity: bound tightly and longer!
Chapter 6 Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Principles and Applications Antigen-Antibody Properties You must remember antibody affinity (single) VS avidity (multiple) High affinity: bound tightly and longer!
Dot Blot Analysis. Teacher s Guidebook. (Cat. # BE 502) think proteins! think G-Biosciences www.gbiosciences.com
 PR110 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 [email protected] A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Dot Blot Analysis Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 502) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
PR110 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 [email protected] A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Dot Blot Analysis Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 502) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
Protein Analysis. -Detection and quantification. Toby M Holmes
 Protein Analysis -Detection and quantification Toby M Holmes Clinical Research Unit UCD school of Medicine and Medical Sciences Mater Misericordiae University Hospital Dublin Protein structure General
Protein Analysis -Detection and quantification Toby M Holmes Clinical Research Unit UCD school of Medicine and Medical Sciences Mater Misericordiae University Hospital Dublin Protein structure General
IHC-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL (IHC-P)
 IHC-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL (IHC-P) Immunohistochemistry (or IHC) is a method for demonstrating the presence and location of proteins in tissue sections. Though less sensitive quantitatively than immunoassays
IHC-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL (IHC-P) Immunohistochemistry (or IHC) is a method for demonstrating the presence and location of proteins in tissue sections. Though less sensitive quantitatively than immunoassays
Chapter 6: Antigen-Antibody Interactions
 Chapter 6: Antigen-Antibody Interactions I. Strength of Ag-Ab interactions A. Antibody Affinity - strength of total noncovalent interactions between single Ag-binding site on an Ab and a single epitope
Chapter 6: Antigen-Antibody Interactions I. Strength of Ag-Ab interactions A. Antibody Affinity - strength of total noncovalent interactions between single Ag-binding site on an Ab and a single epitope
DISCOVERY. through color. A Guide to Multiple Antigen Labeling VECTOR LABORATORIES
 DISCOVERY through color. A Guide to Multiple Antigen Labeling VECTOR LABORATORIES Vector Laboratories has been at the forefront of developing novel, innovative labeling and detection reagents for over
DISCOVERY through color. A Guide to Multiple Antigen Labeling VECTOR LABORATORIES Vector Laboratories has been at the forefront of developing novel, innovative labeling and detection reagents for over
INSTRUCTION Probemaker
 INSTRUCTION Probemaker Instructions for Duolink In Situ Probemaker PLUS (Art. no. 92009-0020) and Duolink In Situ Probemaker MINUS (Art. no. 92010-0020) Table of content 1. Introduction 4 2. Applications
INSTRUCTION Probemaker Instructions for Duolink In Situ Probemaker PLUS (Art. no. 92009-0020) and Duolink In Situ Probemaker MINUS (Art. no. 92010-0020) Table of content 1. Introduction 4 2. Applications
STANDING Tall CUSTOM PRODUCTS AND SERVICES
 STANDING Tall CUSTOM PRODUCTS AND SERVICES COME GROW WITH US! Contact KPL and let us know how we can support your OEM needs. Quality antibodies, substrates, and immunoassay support reagents Large scale
STANDING Tall CUSTOM PRODUCTS AND SERVICES COME GROW WITH US! Contact KPL and let us know how we can support your OEM needs. Quality antibodies, substrates, and immunoassay support reagents Large scale
WHO Prequalification of Diagnostics Programme PUBLIC REPORT. Product: Genscreen ULTRA HIV Ag-Ab Number: PQDx 0096-031-00. Abstract
 WHO Prequalification of Diagnostics Programme PUBLIC REPORT Product: Genscreen ULTRA HIV Ag-Ab Number: PQDx 0096-031-00 Abstract Genscreen ULTRA HIV Ag-Ab with product codes 72386 and 72388, manufactured
WHO Prequalification of Diagnostics Programme PUBLIC REPORT Product: Genscreen ULTRA HIV Ag-Ab Number: PQDx 0096-031-00 Abstract Genscreen ULTRA HIV Ag-Ab with product codes 72386 and 72388, manufactured
PROTOCOL. Immunocytochemistry (ICC) MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
 PROTOCOL Immunocytochemistry (ICC) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 11-07 MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Materials: MitoSciences primary monoclonal antibody/antibodies Fluorophore-conjugated
PROTOCOL Immunocytochemistry (ICC) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 11-07 MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Materials: MitoSciences primary monoclonal antibody/antibodies Fluorophore-conjugated
WESTERN BLOTTING TIPS AND TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
 WESTERN BLOTTING TIPS AND TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE TIPS FOR SUCCESSFUL WESTERB BLOTS TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE 1. Suboptimal protein transfer. This is the most common complaint with western blotting and could
WESTERN BLOTTING TIPS AND TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE TIPS FOR SUCCESSFUL WESTERB BLOTS TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE 1. Suboptimal protein transfer. This is the most common complaint with western blotting and could
Guide to Purification of Polyclonal Antibodies
 Guide to Purification of Polyclonal Antibodies When choosing a polyclonal antibody, either as a primary or secondary antibody in an immunoassay, researchers are often inundated with an array of antibody
Guide to Purification of Polyclonal Antibodies When choosing a polyclonal antibody, either as a primary or secondary antibody in an immunoassay, researchers are often inundated with an array of antibody
THE His Tag Antibody, mab, Mouse
 THE His Tag Antibody, mab, Mouse Cat. No. A00186 Technical Manual No. TM0243 Update date 01052011 I Description.... 1 II Key Features. 2 III Storage 2 IV Applications.... 2 V Examples - ELISA..... 2 VI
THE His Tag Antibody, mab, Mouse Cat. No. A00186 Technical Manual No. TM0243 Update date 01052011 I Description.... 1 II Key Features. 2 III Storage 2 IV Applications.... 2 V Examples - ELISA..... 2 VI
Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a
 Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a Ryan S. Stowers, 1 Jacqueline A. Callihan, 2 James D. Bryers 2 1 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson,
Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a Ryan S. Stowers, 1 Jacqueline A. Callihan, 2 James D. Bryers 2 1 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson,
Aviva Systems Biology
 Aviva Custom Antibody Service and Price Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Service Package Number Description Package Contents Time Price Customer provides antigen protein $6,174 Monoclonal package1 (From protein
Aviva Custom Antibody Service and Price Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Service Package Number Description Package Contents Time Price Customer provides antigen protein $6,174 Monoclonal package1 (From protein
Western BLoT Immuno Booster
 Cat. # T7111A For Research Use Western BLoT Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 3 IV. Materials Required but Not Provided... 3 V. Precautions... 3 VI.
Cat. # T7111A For Research Use Western BLoT Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 3 IV. Materials Required but Not Provided... 3 V. Precautions... 3 VI.
WESTERN BLOT DETECTION KIT Buffers and detection reagents for up to ten 10 x 10 cm 2 blots. Fluorescent detection via: Goat anti-mouse SureLight P3
 WESTERN BLOT DETECTION KIT Buffers and detection reagents for up to ten 10 x 10 cm 2 blots Fluorescent detection via: Goat anti-mouse SureLight P3 Cat. #: WK-P112 6440 Dobbin Road, Suite D Phone (443)
WESTERN BLOT DETECTION KIT Buffers and detection reagents for up to ten 10 x 10 cm 2 blots Fluorescent detection via: Goat anti-mouse SureLight P3 Cat. #: WK-P112 6440 Dobbin Road, Suite D Phone (443)
Clinical Histology Procedure Histo03.01 Automated Immunohistochemical Staining Utilizing the Ventana Benchmark Instrument
 Clinical Histology Procedure Histo03.01 Automated Immunohistochemical Staining Utilizing the Ventana Benchmark Instrument Final Approval: May 2010 Effective: May 2010 Next Review Date: May 2012 List all
Clinical Histology Procedure Histo03.01 Automated Immunohistochemical Staining Utilizing the Ventana Benchmark Instrument Final Approval: May 2010 Effective: May 2010 Next Review Date: May 2012 List all
ECL Western Blotting Substrate INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF PRODUCTS W1001 AND W1015.
 Technical Manual ECL Western Blotting Substrate INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF PRODUCTS W1001 AND W1015. PRINTED IN USA. 6/09 ECL Western Blotting Substrate All technical literature is available on the Internet
Technical Manual ECL Western Blotting Substrate INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF PRODUCTS W1001 AND W1015. PRINTED IN USA. 6/09 ECL Western Blotting Substrate All technical literature is available on the Internet
Antibody Production Price List
 Antibody Production Price List Presenting Insight Biotechnology s price list for custom polyclonal and monoclonal antibody production services. We are happy to tailor individual packages towards the specific
Antibody Production Price List Presenting Insight Biotechnology s price list for custom polyclonal and monoclonal antibody production services. We are happy to tailor individual packages towards the specific
ab176915 StayBlue/AP Plus Stain Kit Instructions for Use An immunohistochemical chromogen substrate for staining tissue sections
 ab176915 StayBlue/AP Plus Stain Kit Instructions for Use An immunohistochemical chromogen substrate for staining tissue sections This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab176915 StayBlue/AP Plus Stain Kit Instructions for Use An immunohistochemical chromogen substrate for staining tissue sections This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Custom Antibodies Services. GeneCust Europe. GeneCust Europe
 GeneCust Europe Laboratoire de Biotechnologie du Luxembourg S.A. 6 rue Dominique Lang L-3505 Dudelange Luxembourg Tél. : +352 27620411 Fax : +352 27620412 Email : [email protected] Web : www.genecust.com
GeneCust Europe Laboratoire de Biotechnologie du Luxembourg S.A. 6 rue Dominique Lang L-3505 Dudelange Luxembourg Tél. : +352 27620411 Fax : +352 27620412 Email : [email protected] Web : www.genecust.com
ELISA: a solid-phase immune assay
 Theoretical course: Basic biochemical methods and ischemic heart models ELISA: a solid-phase immune assay Margit Keresztes MD PhD University of Szeged Medical Faculty Dept. Biochemistry Supported by: HURO/0901/069/2.3.1
Theoretical course: Basic biochemical methods and ischemic heart models ELISA: a solid-phase immune assay Margit Keresztes MD PhD University of Szeged Medical Faculty Dept. Biochemistry Supported by: HURO/0901/069/2.3.1
3 months 1.5 months 1.5 months. 1 month
 Rabbit monoclonal antibody (Mab) is secreted by the plasma B-cell of the rabbit. Traditional generation of rabbit Mab relies on a rabbit myeloma for B- cell fusion (
Rabbit monoclonal antibody (Mab) is secreted by the plasma B-cell of the rabbit. Traditional generation of rabbit Mab relies on a rabbit myeloma for B- cell fusion (
竞 争 性 分 析 Epitope Mapping 实 验 方 法
 竞 争 性 分 析 Epitope Mapping 实 验 方 法 ABSTRACT The simplest way to determine whether two monoclonal antibodies bind to distinct sites on a protein antigen is to carry out a competition assay. The assay can
竞 争 性 分 析 Epitope Mapping 实 验 方 法 ABSTRACT The simplest way to determine whether two monoclonal antibodies bind to distinct sites on a protein antigen is to carry out a competition assay. The assay can
Mouse Typer Sub-Isotyping Kit Instruction Manual
 Mouse Typer Sub-Isotyping Kit Instruction Manual Protocol for Mouse Typer Sub-Isotyping Kit (Catalog Number 172-2051) and Mouse Typer Sub Isotyping Panel (Catalog Number 172-2055) For Technical Service
Mouse Typer Sub-Isotyping Kit Instruction Manual Protocol for Mouse Typer Sub-Isotyping Kit (Catalog Number 172-2051) and Mouse Typer Sub Isotyping Panel (Catalog Number 172-2055) For Technical Service
CUSTOM ANTIBODIES. Fully customised services: rat and murine monoclonals, rat and rabbit polyclonals, antibody characterisation, antigen preparation
 CUSTOM ANTIBODIES Highly competitive pricing without compromising quality. Rat monoclonal antibodies for the study of gene expression and proteomics in mice and in mouse models of human diseases available.
CUSTOM ANTIBODIES Highly competitive pricing without compromising quality. Rat monoclonal antibodies for the study of gene expression and proteomics in mice and in mouse models of human diseases available.
Geniron. Custom Antibody Services. Serum services Antibody Monoclonal. Purification Antibody Mono Y Genetic Immunization Genbody Polyclonal Antibody
 Geniron Custom Antibody Services Serum services Antibody Monoclonal Purification Antibody Mono Y Genetic Immunization Genbody Polyclonal Antibody Geniron Poly Y WE PROVIDE OUR SERVICES TO With Expertise
Geniron Custom Antibody Services Serum services Antibody Monoclonal Purification Antibody Mono Y Genetic Immunization Genbody Polyclonal Antibody Geniron Poly Y WE PROVIDE OUR SERVICES TO With Expertise
Non Specific Binding (NSB) in Antigen-Antibody Assays
 Non Specific Binding (NSB) in Antigen-Antibody Assays Chem 395 Spring 2007 Instructor : Dr. James Rusling Presenter : Bhaskara V. Chikkaveeraiah OUTLINE Immunoassays Introduction Factors contributing to
Non Specific Binding (NSB) in Antigen-Antibody Assays Chem 395 Spring 2007 Instructor : Dr. James Rusling Presenter : Bhaskara V. Chikkaveeraiah OUTLINE Immunoassays Introduction Factors contributing to
How To Use Calretinin
 Product Code: MP-092-CR01 (0.1ml concentrate) MP-092-CR05 (0.5ml concentrate) MP-092-CR1 (1ml concentrate) MP-092-PR6 (6ml RTU) Product Description: Calretinin Concentrated and Prediluted Polyclonal Antibody
Product Code: MP-092-CR01 (0.1ml concentrate) MP-092-CR05 (0.5ml concentrate) MP-092-CR1 (1ml concentrate) MP-092-PR6 (6ml RTU) Product Description: Calretinin Concentrated and Prediluted Polyclonal Antibody
Human Free Testosterone(F-TESTO) ELISA Kit
 Human Free Testosterone(F-TESTO) ELISA Kit Catalog Number. MBS700040 For the quantitative determination of human free testosterone(f-testo) concentrations in serum, plasma. This package insert must be
Human Free Testosterone(F-TESTO) ELISA Kit Catalog Number. MBS700040 For the quantitative determination of human free testosterone(f-testo) concentrations in serum, plasma. This package insert must be
Antibody Purification and Labeling
 5 Antibody Purification and Labeling 5.1 Antibody Purification 65 Magne Protein A Beads and Magne Protein G Beads 67 5.2 Antibody Labeling 69 phab Amine and Thiol Reactive Dyes 71 63 Discover Reliable
5 Antibody Purification and Labeling 5.1 Antibody Purification 65 Magne Protein A Beads and Magne Protein G Beads 67 5.2 Antibody Labeling 69 phab Amine and Thiol Reactive Dyes 71 63 Discover Reliable
MAB Solut. MABSolys Génopole Campus 1 5 rue Henri Desbruères 91030 Evry Cedex. www.mabsolut.com. is involved at each stage of your project
 Mabsolus-2015-UK:Mise en page 1 03/07/15 14:13 Page1 Services provider Department of MABSolys from conception to validation MAB Solut is involved at each stage of your project Creation of antibodies Production
Mabsolus-2015-UK:Mise en page 1 03/07/15 14:13 Page1 Services provider Department of MABSolys from conception to validation MAB Solut is involved at each stage of your project Creation of antibodies Production
TFE3 (MRQ-37) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody PRODUCT AVAILABILITY SYMBOL DEFINITIONS INTENDED USE PRINCIPLES AND PROCEDURES SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION
 Rev. 0.0 TFE3 (MRQ-37) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody PRODUCT AVAILABILITY Cat. No. Description 354R-14 0.1 ml, concentrate 354R-15 0.5 ml, concentrate 354R-16 1.0 ml, concentrate 354R-17 1.0 ml, predilute
Rev. 0.0 TFE3 (MRQ-37) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody PRODUCT AVAILABILITY Cat. No. Description 354R-14 0.1 ml, concentrate 354R-15 0.5 ml, concentrate 354R-16 1.0 ml, concentrate 354R-17 1.0 ml, predilute
Blood-Based Cancer Diagnostics
 The Biotechnology Education Company Blood-Based Cancer Diagnostics EDVO-Kit 141 Store entire experiment at room temperature. EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE: The objective of this experiment is to learn and understand
The Biotechnology Education Company Blood-Based Cancer Diagnostics EDVO-Kit 141 Store entire experiment at room temperature. EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE: The objective of this experiment is to learn and understand
Custom Antibody Services
 prosci-inc.com Custom Antibody Services High Performance Antibodies and More Broad Antibody Catalog Extensive Antibody Services CUSTOM ANTIBODY SERVICES Established in 1998, ProSci Incorporated is a leading
prosci-inc.com Custom Antibody Services High Performance Antibodies and More Broad Antibody Catalog Extensive Antibody Services CUSTOM ANTIBODY SERVICES Established in 1998, ProSci Incorporated is a leading
How to Biotinylate with Reproducible Results
 How to Biotinylate with Reproducible Results Introduction The Biotin Streptavidin system continues to be used in many protein based biological research applications including; ELISAs, immunoprecipitation,
How to Biotinylate with Reproducible Results Introduction The Biotin Streptavidin system continues to be used in many protein based biological research applications including; ELISAs, immunoprecipitation,
Designing Assays for the TaqMan Protein Assay
 Designing Assays for the TaqMan Protein Assay Antibody Selection...2 Assay Design...2 Antibody Search...3 Biotinylated Antibodies...3 Working with pre-biotinylated antibodies...4 Working with non-biotinylated
Designing Assays for the TaqMan Protein Assay Antibody Selection...2 Assay Design...2 Antibody Search...3 Biotinylated Antibodies...3 Working with pre-biotinylated antibodies...4 Working with non-biotinylated
High Resolution Epitope Mapping of Human Autoimmune Sera against Antigens CENPA and KDM6B. PEPperPRINT GmbH Heidelberg, 06/2014
 High Resolution Epitope Mapping of Human Autoimmune Sera against Antigens CENPA and KDM6B PEPperPRINT GmbH Heidelberg, 06/2014 Introduction This report describes the epitope mapping of autoimmune sera
High Resolution Epitope Mapping of Human Autoimmune Sera against Antigens CENPA and KDM6B PEPperPRINT GmbH Heidelberg, 06/2014 Introduction This report describes the epitope mapping of autoimmune sera
Chapter 2 Antibody Labeling and the Choice of the Label
 Chapter 2 Antibody Labeling and the Choice of the Label In order for the antigen antibody immunoreaction to be seen in the microscope, the antibody must take a label enzyme, fluorophore, colloidal gold
Chapter 2 Antibody Labeling and the Choice of the Label In order for the antigen antibody immunoreaction to be seen in the microscope, the antibody must take a label enzyme, fluorophore, colloidal gold
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies
 HuCAL Custom Monoclonal HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific, Recombinant Antibodies in 8 Weeks Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in Just 8 Weeks HuCAL PLATINUM (Human Combinatorial Antibody
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific, Recombinant Antibodies in 8 Weeks Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in Just 8 Weeks HuCAL PLATINUM (Human Combinatorial Antibody
Immunoblotting (Western blotting)
 Immunoblotting (Western blotting) HIV Transfer to NC membrane membrane gel support buffer Dissociate in SDS Incubate with 1ary antiserum Separate by SDS-PAG Incubate w/ labeled 2nd ab Immunoblotting :
Immunoblotting (Western blotting) HIV Transfer to NC membrane membrane gel support buffer Dissociate in SDS Incubate with 1ary antiserum Separate by SDS-PAG Incubate w/ labeled 2nd ab Immunoblotting :
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. FluoroTag FITC Conjugation Kit. Product Number FITC1 Storage Temperature 2 8 C
 FluoroTag FITC Conjugation Kit Product Number FITC1 Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The FluoroTag FITC Conjugation Kit is suitable for the conjugation of polyclonal and
FluoroTag FITC Conjugation Kit Product Number FITC1 Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The FluoroTag FITC Conjugation Kit is suitable for the conjugation of polyclonal and
DELFIA assays bring convenience in monoclonal antibody development
 DELFIA DELFIA assays bring convenience in monoclonal development INTRODUCTION The DELFIA system provides a method of discovering specific, high-affinity monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) even in low concentrations
DELFIA DELFIA assays bring convenience in monoclonal development INTRODUCTION The DELFIA system provides a method of discovering specific, high-affinity monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) even in low concentrations
Antigens & Antibodies II. Polyclonal antibodies vs Monoclonal antibodies
 A Brief Review of Antibody Structure A Brief Review of Antibody Structure The basic antibody is a dimer of dimer (2 heavy chain-light chain pairs) composed of repeats of a single structural unit known
A Brief Review of Antibody Structure A Brief Review of Antibody Structure The basic antibody is a dimer of dimer (2 heavy chain-light chain pairs) composed of repeats of a single structural unit known
The Value of Thyroid Transcription Factor-1 in Cytologic Preparations as a Marker for Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of Lung Origin
 Anatomic Pathology / TTF-1 IN CYTOLOGY OF BODY FLUIDS The Value of Thyroid Transcription Factor-1 in Cytologic Preparations as a Marker for Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of Lung Origin Jonathan L. Hecht, MD,
Anatomic Pathology / TTF-1 IN CYTOLOGY OF BODY FLUIDS The Value of Thyroid Transcription Factor-1 in Cytologic Preparations as a Marker for Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of Lung Origin Jonathan L. Hecht, MD,
Topic: Serological reactions: the purpose and a principle of reactions. Agglutination test. Precipitation test. CFT, IFT, ELISA, RIA.
 Topic: Serological reactions: the purpose and a principle of reactions. Agglutination test. Precipitation test. CFT, IFT, ELISA, RIA. Serology is the study and use of immunological tests to diagnose and
Topic: Serological reactions: the purpose and a principle of reactions. Agglutination test. Precipitation test. CFT, IFT, ELISA, RIA. Serology is the study and use of immunological tests to diagnose and
Introduction to flow cytometry
 Introduction to flow cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology. Discover more with our introduction to flow cytometry. Flow cytometry is now a widely used method for analyzing the expression
Introduction to flow cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology. Discover more with our introduction to flow cytometry. Flow cytometry is now a widely used method for analyzing the expression
IHC/ICC Protocol Guide
 IHC/ICC Protocol Guide 2014 R&D Systems Trademark and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. This guide provides an introduction to the techniques, protocols, and troubleshooting
IHC/ICC Protocol Guide 2014 R&D Systems Trademark and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. This guide provides an introduction to the techniques, protocols, and troubleshooting
VECTOR L A B O R A T O R I E S
 VECTOR L A B O R A T O R I E S s t a t e o f t h e a r t l a b e l i n g & d E t e c t i o n s y s t e m s Since 1976 Vector Laboratories has provided innovative labeling and detection solutions to the
VECTOR L A B O R A T O R I E S s t a t e o f t h e a r t l a b e l i n g & d E t e c t i o n s y s t e m s Since 1976 Vector Laboratories has provided innovative labeling and detection solutions to the
ChIP TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS
 ChIP TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS Creative Diagnostics Abstract ChIP dissects the spatial and temporal dynamics of the interactions between chromatin and its associated factors CD Creative Diagnostics info@creative-
ChIP TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS Creative Diagnostics Abstract ChIP dissects the spatial and temporal dynamics of the interactions between chromatin and its associated factors CD Creative Diagnostics info@creative-
CHAPTER 6 ANTIBODY GENETICS: ISOTYPES, ALLOTYPES, IDIOTYPES
 CHAPTER 6 ANTIBODY GENETICS: ISOTYPES, ALLOTYPES, IDIOTYPES See APPENDIX: (3) OUCHTERLONY; (4) AFFINITY CHROMATOGRAPHY Human immunoglobulins are made up of LIGHT and HEAVY chains encoded by a total of
CHAPTER 6 ANTIBODY GENETICS: ISOTYPES, ALLOTYPES, IDIOTYPES See APPENDIX: (3) OUCHTERLONY; (4) AFFINITY CHROMATOGRAPHY Human immunoglobulins are made up of LIGHT and HEAVY chains encoded by a total of
ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit
 ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit Catalog no. A1346 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Composition Storage Stability ArC reactive beads (Component A) ArC negative beads (Component
ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit Catalog no. A1346 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Composition Storage Stability ArC reactive beads (Component A) ArC negative beads (Component
ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit
 ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit Instructions for Use For the measuring in vivo protein sumoylation in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit Instructions for Use For the measuring in vivo protein sumoylation in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Biotinylated Secondary Antibodies
 Biotinylated Secondary Antibodies Anti-Goat ABB-02-01 Biotin Labeled Rabbit Anti-Goat IgG (H+L) Antibody $44.00 Affinity purified polyclonal antibody to Goat IgG, heavy and light chains (whole IgG) made
Biotinylated Secondary Antibodies Anti-Goat ABB-02-01 Biotin Labeled Rabbit Anti-Goat IgG (H+L) Antibody $44.00 Affinity purified polyclonal antibody to Goat IgG, heavy and light chains (whole IgG) made
Western Blot Analysis
 Odyssey Infrared Imaging System Western Blot Analysis Published January 2003. Revised July, 2007. The most recent version of this protocol is posted at http://biosupport.licor.com/support Doc# 988-09288
Odyssey Infrared Imaging System Western Blot Analysis Published January 2003. Revised July, 2007. The most recent version of this protocol is posted at http://biosupport.licor.com/support Doc# 988-09288
Custom Antibody Services
 Custom Antibody Services Custom service offerings DNA sequence Plasmid Peptide Structure Protein Peptide Small molecule Cells Spleen Lymphocytes Antigen Preparation Immunization Fusion & Subcloning Expansion
Custom Antibody Services Custom service offerings DNA sequence Plasmid Peptide Structure Protein Peptide Small molecule Cells Spleen Lymphocytes Antigen Preparation Immunization Fusion & Subcloning Expansion
Ep-CAM/Epithelial Specific Antigen (MOC-31)
 Ep-CAM/Epithelial Specific Antigen (MOC- Product Identification Cat. No. Description 44588 EP-CAM 0,1 M (MOC- 44589 EP-CAM 1 M (MOC- 44283 EP-CAM RTU M (MOC- Symbol Definitions P C A E S DIL DOC# DIS ready-to-use
Ep-CAM/Epithelial Specific Antigen (MOC- Product Identification Cat. No. Description 44588 EP-CAM 0,1 M (MOC- 44589 EP-CAM 1 M (MOC- 44283 EP-CAM RTU M (MOC- Symbol Definitions P C A E S DIL DOC# DIS ready-to-use
Aviva Systems Biology
 Aviva Custom Antibody Services and Prices Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody Service Package Number Description Package Contents Time Price Polyclonal package 1 (From protein to antiserum) Polyclonal package 2
Aviva Custom Antibody Services and Prices Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody Service Package Number Description Package Contents Time Price Polyclonal package 1 (From protein to antiserum) Polyclonal package 2
Compromise Elsewhere Protocols. Western Blotting Methods. 800-656-ROCK www.rockland-inc.com [email protected] 1 of 11
 Compromise Elsewhere Protocols Western Blotting Methods [email protected] 1 of 11 Odyssey Western Blotting Protocols Odyssey reagents: Additional reagents needed: IR-labeled secondary antibodies Odyssey
Compromise Elsewhere Protocols Western Blotting Methods [email protected] 1 of 11 Odyssey Western Blotting Protocols Odyssey reagents: Additional reagents needed: IR-labeled secondary antibodies Odyssey
Interim Progress Report R&D Project 348. Development of a Field Test Kit for Detection of Blue-Green Algal Toxins
 Interim Progress Report R&D Project 348 Development of a Field Test Kit for Detection of Blue-Green Algal Toxins Biocode Limited November 1992 R&D 348/04/A ENVIRONMENT AGENCY 135357 CONTENTS SUMMARY KEYWORDS
Interim Progress Report R&D Project 348 Development of a Field Test Kit for Detection of Blue-Green Algal Toxins Biocode Limited November 1992 R&D 348/04/A ENVIRONMENT AGENCY 135357 CONTENTS SUMMARY KEYWORDS
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies
 HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in just 8 Weeks PROVEN, HIGHLY SPECIFIC, HIGH AFFINITY ANTIBODIES IN 8 WEEKS WITHOUT HuCAL PLATINUM IMMUNIZATION (Human Combinatorial
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in just 8 Weeks PROVEN, HIGHLY SPECIFIC, HIGH AFFINITY ANTIBODIES IN 8 WEEKS WITHOUT HuCAL PLATINUM IMMUNIZATION (Human Combinatorial
Canine creatine kinase MB isoenzyme (CK-MB)ELISA Kit
 Canine creatine kinase MB isoenzyme (CK-MB)ELISA Kit Catalog No. CSB-E15852c (96T) This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of canine CK-MB concentrations in serum and plasma.
Canine creatine kinase MB isoenzyme (CK-MB)ELISA Kit Catalog No. CSB-E15852c (96T) This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of canine CK-MB concentrations in serum and plasma.
APPLICATION FOCUS. Application Solutions for Western Blotting
 APPLICATION FOCUS Application Solutions for Western Blotting WESTERN BLOTTING Companion Products Solutions for consistently better blotting. Companion products from Cell Signaling Technology (CST) are
APPLICATION FOCUS Application Solutions for Western Blotting WESTERN BLOTTING Companion Products Solutions for consistently better blotting. Companion products from Cell Signaling Technology (CST) are
LAB 14 ENZYME LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY (ELISA)
 STUDENT GUIDE LAB 14 ENZYME LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY (ELISA) GOAL The goal of this laboratory lesson is to explain the concepts and technique of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). OBJECTIVES
STUDENT GUIDE LAB 14 ENZYME LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY (ELISA) GOAL The goal of this laboratory lesson is to explain the concepts and technique of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). OBJECTIVES
Basics of Immunology
 Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
A Novel Bioconjugation Technology
 A Novel Bioconjugation Technology for Assay Development and More! Presentation overview Who we are Solutions we provide for our customers Solulink s technology Linking system The Solulink advantage Applications
A Novel Bioconjugation Technology for Assay Development and More! Presentation overview Who we are Solutions we provide for our customers Solulink s technology Linking system The Solulink advantage Applications
protocol handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel
 handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel supporting real discovery handbook Index 01 Cell encapsulation in hydrogels 02 Cell viability by MTS assay 03 Live/Dead assay to assess cell viability 04 Fluorescent
handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel supporting real discovery handbook Index 01 Cell encapsulation in hydrogels 02 Cell viability by MTS assay 03 Live/Dead assay to assess cell viability 04 Fluorescent
Chapter 15 Multi-Staining Immunohistochemistry
 Chapter 15 Multi-Staining Immunohistochemistry Nanna K. Christensen PhD and Lars Winther PhD Immunohistochemistry (IHC) has become an established tool for both research and diagnostic purposes. However,
Chapter 15 Multi-Staining Immunohistochemistry Nanna K. Christensen PhD and Lars Winther PhD Immunohistochemistry (IHC) has become an established tool for both research and diagnostic purposes. However,
Mouse Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme (CKMB) ELISA
 KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Mouse Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme (CKMB) ELISA For the quantitative determination of mouse CKMB in serum, plasma, cell culture fluid and other biological fluids Cat. No. KT-57681
KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Mouse Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme (CKMB) ELISA For the quantitative determination of mouse CKMB in serum, plasma, cell culture fluid and other biological fluids Cat. No. KT-57681
Advanced BioDesign Outlines Solutions. Antibody Overview. by Advanced BioDesign. Project Start. Immunogenicity. Selecting Your Antigen
 Advanced BioDesign Outlines Solutions by Advanced BioDesign Antibody Overview Launching an immunisation programme is an important experimental step that needs care. With Advanced BioDesign, you may develop
Advanced BioDesign Outlines Solutions by Advanced BioDesign Antibody Overview Launching an immunisation programme is an important experimental step that needs care. With Advanced BioDesign, you may develop
Immunohistochemistry Application Guide
 Immunohistochemistry Application Guide 1 Common abbreviations ABC: AEC: AP: BCIP: BSA: DAB: FISH: FITC: FFPE: HIER: HRP: H 2 O 2 : ICC: IHC: IP: ISH: LSAB: KO: NBF: NBT: PBS: PFA: PIER: RabMAb: TMA: TMB:
Immunohistochemistry Application Guide 1 Common abbreviations ABC: AEC: AP: BCIP: BSA: DAB: FISH: FITC: FFPE: HIER: HRP: H 2 O 2 : ICC: IHC: IP: ISH: LSAB: KO: NBF: NBT: PBS: PFA: PIER: RabMAb: TMA: TMB:
LANCE Eu-labeled antibodies for serine/threonine kinase assays
 AD0078P-1 (en) 1 LANCE Eu-labeled antibodies for serine/threonine kinase assays For Research Use Only These instructions for use apply to the following reagents: AD0094 LANCE Eu-W1024 phospho-threonine
AD0078P-1 (en) 1 LANCE Eu-labeled antibodies for serine/threonine kinase assays For Research Use Only These instructions for use apply to the following reagents: AD0094 LANCE Eu-W1024 phospho-threonine
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE Title: Evaluation using Western Blot SOP#: M-103 Version #: 1 Author: R. Saul Date Approved: Feb. 5, 2009 Date Modified: 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this document is to describe
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE Title: Evaluation using Western Blot SOP#: M-103 Version #: 1 Author: R. Saul Date Approved: Feb. 5, 2009 Date Modified: 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this document is to describe
Proteomics Research with BIOCHAIN
 Proteomics Research with IOCHIN Protein Extraction CNMCS Compartmental Protein Extraction Kit Cytoplasmic, Nuclear, Membrane, and Cytoskeleton Protein One kit isolates four different proteins sequentially
Proteomics Research with IOCHIN Protein Extraction CNMCS Compartmental Protein Extraction Kit Cytoplasmic, Nuclear, Membrane, and Cytoskeleton Protein One kit isolates four different proteins sequentially
Pure-IP Western Blot Detection Kit
 Product Manual Pure-IP Western Blot Detection Kit Catalog Number PRB-5002 20 blots FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The technique of immunoprecipitation (IP) is used
Product Manual Pure-IP Western Blot Detection Kit Catalog Number PRB-5002 20 blots FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The technique of immunoprecipitation (IP) is used
www.gbo.com/bioscience Tissue Culture 1 Cell/ Microplates 2 HTS- 3 Immunology/ HLA 4 Microbiology/ Bacteriology Purpose Beakers 5 Tubes/Multi-
 11 Cryo 5 Tubes/Multi 2 HTS 3 Immunology / Immunology Technical Information 3 I 2 96 Well ELISA 3 I 4 96 Well ELISA Strip Plates 3 I 6 8 Well Strip Plates 3 I 7 12 Well Strip Plates 3 I 8 16 Well Strip
11 Cryo 5 Tubes/Multi 2 HTS 3 Immunology / Immunology Technical Information 3 I 2 96 Well ELISA 3 I 4 96 Well ELISA Strip Plates 3 I 6 8 Well Strip Plates 3 I 7 12 Well Strip Plates 3 I 8 16 Well Strip
Application Guide... 2
 Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
Practical Cell Analysis
 Practical Cell Analysis Dimitri Pappas Dept of Chemistry & Biochemistry, Texas Tech University, USA WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd, Publication Contents Preface Acknowledgments xiii xix 1 Getting Started
Practical Cell Analysis Dimitri Pappas Dept of Chemistry & Biochemistry, Texas Tech University, USA WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd, Publication Contents Preface Acknowledgments xiii xix 1 Getting Started
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1. Immunity and Disease
 ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
Some Immunological Test. Presented by Alaa Faeiz Ashwaaq Dyaa Aseel Abd AL-Razaq Supervised by D.Feras
 Some Immunological Test Presented by Alaa Faeiz Ashwaaq Dyaa Aseel Abd AL-Razaq Supervised by D.Feras Alaa Faeiz Antigen -Antibody Reactions. Antigen antibody reactions are performed to determine the presence
Some Immunological Test Presented by Alaa Faeiz Ashwaaq Dyaa Aseel Abd AL-Razaq Supervised by D.Feras Alaa Faeiz Antigen -Antibody Reactions. Antigen antibody reactions are performed to determine the presence
Biology 309 Lab Notebook
 Name: Biology 309 Lab Notebook This is a guided lab notebook for you to keep well-organized notes about procedures and record experimental data for experiments as they are performed. It is guided because,
Name: Biology 309 Lab Notebook This is a guided lab notebook for you to keep well-organized notes about procedures and record experimental data for experiments as they are performed. It is guided because,
Methods for Protein Analysis
 Methods for Protein Analysis 1. Protein Separation Methods The following is a quick review of some common methods used for protein separation: SDS-PAGE (SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) separates
Methods for Protein Analysis 1. Protein Separation Methods The following is a quick review of some common methods used for protein separation: SDS-PAGE (SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) separates
Secondary Antibodies and Conjugates
 biodescriptor biomolecules Full image -- Remove color from text box when placing image Secondary Antibodies and Conjugates Initiative Descriptor Primary Cover Header Popular Reagents for Quality Secondary
biodescriptor biomolecules Full image -- Remove color from text box when placing image Secondary Antibodies and Conjugates Initiative Descriptor Primary Cover Header Popular Reagents for Quality Secondary
Mouse Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin antibody(igm) ELISA Kit
 Mouse Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin antibody(igm) ELISA Kit Catalog No. MBS702810 (96 tests) This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro semi-quantitative determination of mouse KLH(IgM)antibody concentrations
Mouse Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin antibody(igm) ELISA Kit Catalog No. MBS702810 (96 tests) This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro semi-quantitative determination of mouse KLH(IgM)antibody concentrations
